[Michael Hoyer]. Vita B. Ioannis Chisii a Maciaretto, ord. ermit. s. p. Augustini. — Antverpiæ, Apud Henricum Aertssens, Anno MDCXLI [1641].
Pagination: [2] *3+recto unpag. *4+recto unpag., [10], 5-135 [3].
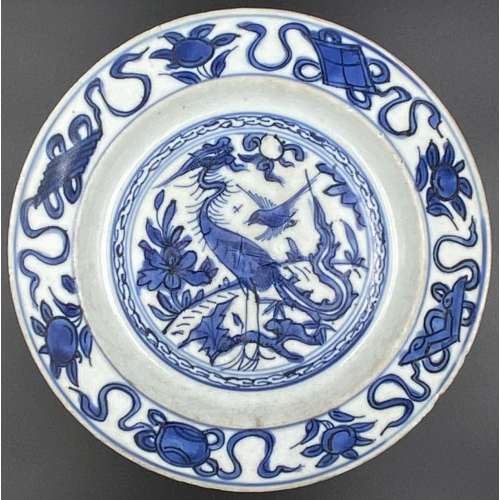
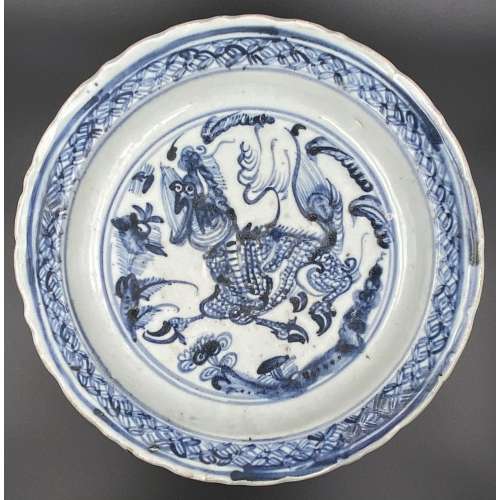
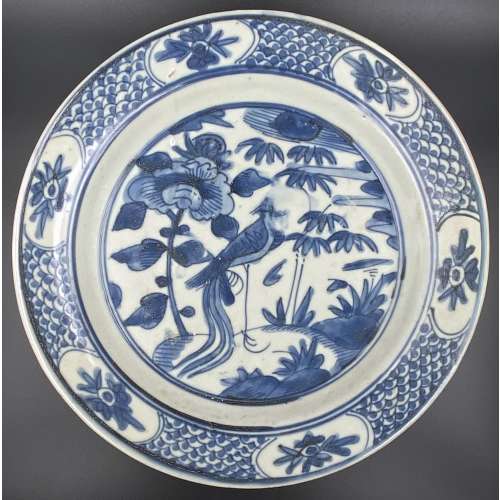
Illustrations: Frontispiece missing, 4 copperplate engravings (pp. 22, 64, 90, and 120) by
Pieter de Jode the Younger (1606–1674, Flemish printmaker, draughtsman, painter and art dealer) after
Erasmus Quellinus the Younger (1607–1678, Flemish painter, engraver, draughtsman and tapestry designer).
Size: Pott 8vo (15.5 x 10 cm), vellum binding.
Expanded title: Vita Beati Ioannis Chisii, a Maciaretto, Ordinis Eremitarum Sancti Patris Augustini. [Translation: Life of Blessed Giovanni Chigi from Maciaretto,
Order of Hermits of St. Augustine].
Blessed Giovanni Chigi (1300 - 1363) [1] was a lay brother of the
Order of Hermits of St. Augustine. The Chigi family is a Roman princely family of Sienese extraction descended from the counts of Ardenghesca. The earliest authentic mention of them is in the 13th century, with one Alemanno, counsellor of the Republic of Siena. The Wikipedia article does not mention Giovanni Chigi, however, it states that one of the Chigi, Cardinal Fabio Chigi, was elected pope as Alexander VII at the Conclave of 1655. The book was published in 1641 with a dedication to the said Cardinal Fabio Chigi before he was elected pope.
The town, Maciaretto, where Giovanni Chigi was from, is unclear because there is no such place in modern Italy, and there are two places called Macereto: (1) Macereto Alta/Basso in Perugia province and (2) Macereto in the municipality of Visso, in the province of Macerata, region Marche. I assume that our Giovanni Chigi was from the one that is closer to Siena, i.e. Macereto in Perugia province.
Regarding the author. There is no author's name in the book. However, in various sources, the book is mentioned as written by
Michel Hoyer, who was born in Hesdin, Flanders in 1593 and died in 1650. He
pursued an ecclesiastical career and professed rhetoric at the College of Saint Pierre in Lille. He later joined the Order of Saint Augustine, in the convent of Ypres, and settled in various schools in the Netherlands. His reputation attracted many students, among them Albert Rubens (1614–1657), the eldest son of Peter Paul Rubens and Isabella Brant. Michel Hoyer wrote several books, the most known is Flammulae amoris, S.P. Augustini versibus et iconibus exornatae:

Surprisingly, there is only limited information about
Michel Hoyer in Spanish Wikipedia; other language versions of his biography do not exist. Another author mentioned in the book is some anonymous Augustinian from Cologne.
Regarding the illustrations. In our copy, the frontispiece is missing. It was probably ripped off by some unscrupulous seller of antique prints.
The image on the missing frontispiece is this:

The names of the artists engraved in the bottom of the stone:
E. Quellinus, delin. to the left and
P. de Jode, fecit. to the right. We can infer that the other illustrations in that book are produced by the same duo. The image represents three cherubs: one with Athena's serpent in his left hand and a cardinal's hat in his right hand; another in Athen's helmet on his head and her owl beside his feet, with the staff of Mercurius (
serpent-twined staff adorned with a winged hat) in his left hand, and the House of Chigi - Della Rovere coat of arms in his right hand; the third cherub depicted with the Hercules attributes - lion pelt and a club.
Regarding the publisher. Henricum Aertssens or Hendrik Aertssen, 1586-1658. Besides the other books, he published
PIA DESIDERIA by Herman Hugo in 1636 [1621 french edition by Jean Cnobbartin in Antwerp in his collection LIB-1657.2018]. According to Nina Lamal [2], nothing is known about career of this publisher, besides what's said in Adresboek van zeventiende-eeuwse drukkers, uitgevers en boekverkopers in Vlaanderen / Directory of seventeenth-century Printers, Publishers and Booksellers in Flanders / Vlieger-De Wilde, Koen De (editor). The list of his publications can be seen here.
Other artists who turned to the figure of Blessed Giovanni Chigi were
Abraham van Diepenbeeck (painter) and
Conrad Lauwers (engraver). The
print is in
Rijksmuseum, in Amsterdam.

Here we see a more complex composition but with a clear reference to the work of Quellinus and de Jode: The cherub in Athena's helmet takes away the old coat of arms of the Chigi, and the other cherub points out to the new one, with papal symbols of St. Peter's keys, another cherub carries the
papal tiara. Rijksmuseum dates the image as 1642 - 1685; most probably it is ca. 1655, when Fabio Chigi became Pope Alexander VII, and propaganda was focused on promoting his outstanding ancestor Giovanni, who died 300 years before. Giovanni Chigi is depicted here resurrected, accompanied by the archangel, and receiving the blessing from Jesus on the cross.
1 -
Michael J. Walsh. A New Dictionary of Saints: East and West, p. 308.
2 - Nina Lamal. Publishing military books in the Low Countries and in Italy in the early seventeenth century in 'Specialist Markets in the Early Modern Book World', ed. Richard Kirwan, Sophia Mullins, Leiden: Koninklijke Brill, 2015, pp. 232-233.




















 See also tsuba
See also tsuba 

































 Surprisingly, there is only limited information about
Surprisingly, there is only limited information about  The names of the artists engraved in the bottom of the stone: E. Quellinus, delin. to the left and P. de Jode, fecit. to the right. We can infer that the other illustrations in that book are produced by the same duo. The image represents three cherubs: one with Athena's serpent in his left hand and a cardinal's hat in his right hand; another in Athen's helmet on his head and her owl beside his feet, with the staff of Mercurius (
The names of the artists engraved in the bottom of the stone: E. Quellinus, delin. to the left and P. de Jode, fecit. to the right. We can infer that the other illustrations in that book are produced by the same duo. The image represents three cherubs: one with Athena's serpent in his left hand and a cardinal's hat in his right hand; another in Athen's helmet on his head and her owl beside his feet, with the staff of Mercurius ( Here we see a more complex composition but with a clear reference to the work of Quellinus and de Jode: The cherub in Athena's helmet takes away the old coat of arms of the Chigi, and the other cherub points out to the new one, with papal symbols of St. Peter's keys, another cherub carries the
Here we see a more complex composition but with a clear reference to the work of Quellinus and de Jode: The cherub in Athena's helmet takes away the old coat of arms of the Chigi, and the other cherub points out to the new one, with papal symbols of St. Peter's keys, another cherub carries the 









