-
 Title: THE | WORKS | OF THE FAMOUS | Nicholas Machiavel, | CITIZEN and SECRETARY | OF | FLORENCE. |—| WRITTEN | Originally in ITALIAN, and from thence newly | and faithfully Tranſlated into ENGLISH. |—|[ornament]|—| LONDON, | Printed for John Starkey, Charles Harper, and John | Amery, at the Miter, the Flower-de-Luce, and the | Peacock, in Fleetstreet. 1680. Content: (1) The history of Florence; (2) The Prince; (3) The Original of the Guelf and Ghibilin Factions; (4) The Life of Castruccio Castracani; (5) The Murther of Vitelli, etc. by Duke Valentino; (6) The State of France; (7) The State of Germany; (8) The Discourses on Titus Livius; (9) The Art of War; (10) The Marriage of Belphegor, a Novel; (11) Nicholas Machiavel's Letter in Vindication of Himself and His Writings. Pagination: ffl, 24 unnumbered pages before the first numbered: [2] – tp / license], [2] – contents / blank], [2] ftp “Florence” / blank, [3] – epistle to Clement VII, [3] – introduction, [12] – table; Misnumbering (X instead of Y format – X/Y): History of Florence: 1- 28/24, 19/91, 198/98, 180/108, 190/109, 174/164, 175/ 165, 179/169, 180/170, 185/175, 186/176, 188/178, 189/179, [190/180 blank]; The Prince, Lucca, State of France: [4] 199-262; State of Germany: 256/263, 266/264, 267/265 [268/266]; Discourses: [4] 267-314, 317-431 [432]; Art of War: [4] 433-528; [4] – publisher, [12] –Machiavelli’s letter, bfl. Collation: π3 Aa3 b-d2 B-Z4 Aa-Bb2 Cc-Zz4 Aaa-Yyy4 (*)-(**)4 Binding: Original mottled leather boards with embossing, later leather spine with 5 raised bands, crimson label with gilt lettering. Size: 32.4 x 21.0 x 4.0 cm Provenance: Bradford H. Gray This is the second edition; despite misnumbering, the collation is correct and all pages present. The first edition of this book was published in 1675 by Robert Bolter (British, fl. 1666 – 1683).
Title: THE | WORKS | OF THE FAMOUS | Nicholas Machiavel, | CITIZEN and SECRETARY | OF | FLORENCE. |—| WRITTEN | Originally in ITALIAN, and from thence newly | and faithfully Tranſlated into ENGLISH. |—|[ornament]|—| LONDON, | Printed for John Starkey, Charles Harper, and John | Amery, at the Miter, the Flower-de-Luce, and the | Peacock, in Fleetstreet. 1680. Content: (1) The history of Florence; (2) The Prince; (3) The Original of the Guelf and Ghibilin Factions; (4) The Life of Castruccio Castracani; (5) The Murther of Vitelli, etc. by Duke Valentino; (6) The State of France; (7) The State of Germany; (8) The Discourses on Titus Livius; (9) The Art of War; (10) The Marriage of Belphegor, a Novel; (11) Nicholas Machiavel's Letter in Vindication of Himself and His Writings. Pagination: ffl, 24 unnumbered pages before the first numbered: [2] – tp / license], [2] – contents / blank], [2] ftp “Florence” / blank, [3] – epistle to Clement VII, [3] – introduction, [12] – table; Misnumbering (X instead of Y format – X/Y): History of Florence: 1- 28/24, 19/91, 198/98, 180/108, 190/109, 174/164, 175/ 165, 179/169, 180/170, 185/175, 186/176, 188/178, 189/179, [190/180 blank]; The Prince, Lucca, State of France: [4] 199-262; State of Germany: 256/263, 266/264, 267/265 [268/266]; Discourses: [4] 267-314, 317-431 [432]; Art of War: [4] 433-528; [4] – publisher, [12] –Machiavelli’s letter, bfl. Collation: π3 Aa3 b-d2 B-Z4 Aa-Bb2 Cc-Zz4 Aaa-Yyy4 (*)-(**)4 Binding: Original mottled leather boards with embossing, later leather spine with 5 raised bands, crimson label with gilt lettering. Size: 32.4 x 21.0 x 4.0 cm Provenance: Bradford H. Gray This is the second edition; despite misnumbering, the collation is correct and all pages present. The first edition of this book was published in 1675 by Robert Bolter (British, fl. 1666 – 1683). -
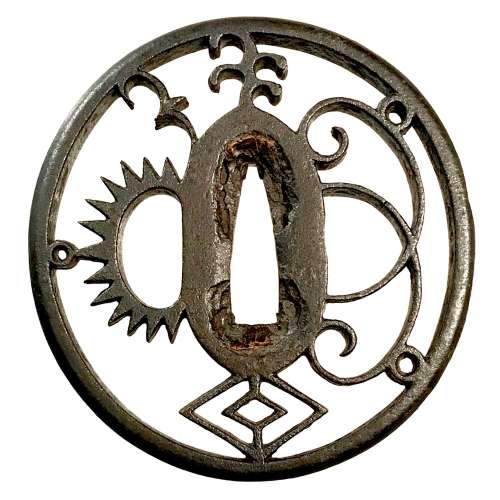 Iron tsuba of round form with a dense combination of symbols: slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol), also often described as "tokei" or "clock gear", wild goose in flight, bracken, and lozenges in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Edo period.
Iron tsuba of round form with a dense combination of symbols: slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol), also often described as "tokei" or "clock gear", wild goose in flight, bracken, and lozenges in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Edo period.Size: 76.0 x 72.6 x 6.2 mm
Unsigned.
For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91.
-
 THE | POETICAL | WORKS | OF | Mr. John Milton. | Paradise Lost, Paradise Regained, | Sampson Agonistes, and his Poems | on several Occasions. | TOGETHER WITH | Explanatory NOTES on each Book of the | PARADISE LOST, and a TABLE | never before Printed. | LONDON: | Printed for Jacob Tonson, at Judges-Head near Inner-Temple-| Gate in Fleet – street , M DC XC V. || Pagination: [6] 1-343 [5] 1-66 [4] 1-57 [5] 1-60 [2] 321 [1], frontispiece and 12 plates, one before each book of Paradise Lost. Collation: 4to, folio; blank leaf, π3 B2, C-Z4, Aa-Yy4, A-H4 I2, [A]-D2 †D2 E-Q2 [A]1 B-Z2 Aa-Zz2 Aaa-Zzz2 Aaaa-Mmmm2 [N]1, 2 blank leaves, + frontis. portrait and 12 plates extraneous to collation. Plates: Portrait of John Milton (British, 1608 – 1674) engraved by Robert White (British, 1645 – 1703) after William Faithorne (British, 1616 – 1691) 11 plates engraved by Michael Burghers (Dutch, c. 1640 – c. 1723) after John Baptiste de Medina (Flemish, 1659 –1710); 1 plate (for Book IV) engraved by Peter-Paul Bouché (Dutch, 1646 – c. 1697) after Bernard Lens (British, 1659 – 1725). Binding: Folio, bound in full contemporary English panelled and speckled calf, tooled in blind, re-backed, corners repaired, the lines in Paradise Lost numbered; title pages of Paradise Regain'd and Samson Agonistes dated 1695; without a list of subscribers after the general title; with the Table for Paradise Lost; printed on laid paper, with tall "s", margins sprayed red. Provenance: near-contemporary ex libris of Sarah Bugg inside front board; along with that of Sam Bontham, 1726; later owned by forger Osborne Charles Vyse Aldis (1843 – 1916), with his signature on general title, with a nine-line note in his hand and initialled on page 343. Catalogue raisonné: Gordon N. Ray, Illustrated book in England (1976): p. 3. Ref: National Gallery of Art Contributors: Bouché, Peter-Paul (Dutch, 1646 – c. 1697) Burghers, Michael (Dutch, c. 1640 – c. 1723) Faithorne, William (British, 1616 – 1691) Lens, Bernard (British, 1659 – 1725) Medina, John Baptiste de (Flemish, 1659 – 1710) Milton, John (British, 1608 – 1674) Tonson, Jacob, the Elder (British, 1655 – 1736) White, Robert (British, 1645 – 1703)
THE | POETICAL | WORKS | OF | Mr. John Milton. | Paradise Lost, Paradise Regained, | Sampson Agonistes, and his Poems | on several Occasions. | TOGETHER WITH | Explanatory NOTES on each Book of the | PARADISE LOST, and a TABLE | never before Printed. | LONDON: | Printed for Jacob Tonson, at Judges-Head near Inner-Temple-| Gate in Fleet – street , M DC XC V. || Pagination: [6] 1-343 [5] 1-66 [4] 1-57 [5] 1-60 [2] 321 [1], frontispiece and 12 plates, one before each book of Paradise Lost. Collation: 4to, folio; blank leaf, π3 B2, C-Z4, Aa-Yy4, A-H4 I2, [A]-D2 †D2 E-Q2 [A]1 B-Z2 Aa-Zz2 Aaa-Zzz2 Aaaa-Mmmm2 [N]1, 2 blank leaves, + frontis. portrait and 12 plates extraneous to collation. Plates: Portrait of John Milton (British, 1608 – 1674) engraved by Robert White (British, 1645 – 1703) after William Faithorne (British, 1616 – 1691) 11 plates engraved by Michael Burghers (Dutch, c. 1640 – c. 1723) after John Baptiste de Medina (Flemish, 1659 –1710); 1 plate (for Book IV) engraved by Peter-Paul Bouché (Dutch, 1646 – c. 1697) after Bernard Lens (British, 1659 – 1725). Binding: Folio, bound in full contemporary English panelled and speckled calf, tooled in blind, re-backed, corners repaired, the lines in Paradise Lost numbered; title pages of Paradise Regain'd and Samson Agonistes dated 1695; without a list of subscribers after the general title; with the Table for Paradise Lost; printed on laid paper, with tall "s", margins sprayed red. Provenance: near-contemporary ex libris of Sarah Bugg inside front board; along with that of Sam Bontham, 1726; later owned by forger Osborne Charles Vyse Aldis (1843 – 1916), with his signature on general title, with a nine-line note in his hand and initialled on page 343. Catalogue raisonné: Gordon N. Ray, Illustrated book in England (1976): p. 3. Ref: National Gallery of Art Contributors: Bouché, Peter-Paul (Dutch, 1646 – c. 1697) Burghers, Michael (Dutch, c. 1640 – c. 1723) Faithorne, William (British, 1616 – 1691) Lens, Bernard (British, 1659 – 1725) Medina, John Baptiste de (Flemish, 1659 – 1710) Milton, John (British, 1608 – 1674) Tonson, Jacob, the Elder (British, 1655 – 1736) White, Robert (British, 1645 – 1703) -
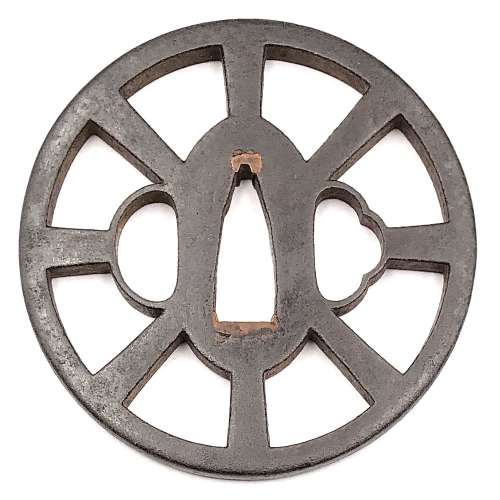 Iron tsuba of round form with design of wheel (kuruma) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Yagyu school. Signed of the face: Fukui Tsuguzaemon. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun/Enppo era). Height: 76.7 mm. Width: 76.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.2 mm. Center thickness: 5.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 203: "This design of spoke wheel relates to the 'circular principle' found in the Yagyu philosophy. Although it is very faint, Fukui Tsuguzaemon's signature is visible. Without a signature and based on appearance alone, it would undoubtable attributed to a later period".
Iron tsuba of round form with design of wheel (kuruma) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Yagyu school. Signed of the face: Fukui Tsuguzaemon. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun/Enppo era). Height: 76.7 mm. Width: 76.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.2 mm. Center thickness: 5.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 203: "This design of spoke wheel relates to the 'circular principle' found in the Yagyu philosophy. Although it is very faint, Fukui Tsuguzaemon's signature is visible. Without a signature and based on appearance alone, it would undoubtable attributed to a later period".Merrily Baird in her book "Symbols of Japan" [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001] provides the following explanation of the Wheel-of-the-Law symbol: "The Wheel-of-the-Law or Golden Wheel (rimbo, kinrin) has its origins in India, where it is known as chakra. [...] In Buddhist practice, it has been represented with eight spokes, reflecting the eight-fold path to overcoming worldly desire, and it signifies that all illusions will be crushed by the faith's enlightenment. [...] The Wheel-of-the-Law is an attribute of such deities as Senju Kannon, the Thousand-Armed Kannon, and Dainichi Nyorai, the all-illuminating solar figure who is the principal deity for Shingon Buddhism. From the Edo period on, the wheel also has been used in a secular manner", e.g. on family crests.
-
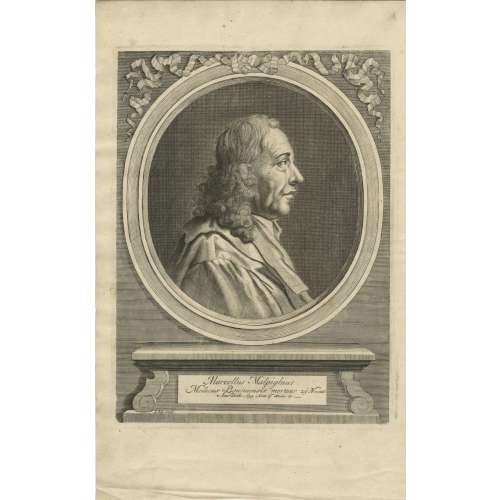

A portrait of Marcello Malpighi from his book Opera posthuma: figuris aeneis illustrata, quibus praefixa est ejusdem vita a seipso scripta, Londini:Churchill, 1697. Inscription: Marcellus Malpighius | Medicus Bononiensis mortuus 29 Novemb. Anno Dom. 1694. Anno aetatis 67. I. Kip. sculp.
Marcello Malpighi (10 March 1628 – 29 November 1694) was an Italian biologist and physician, who is referred to as the "Father of microscopical anatomy, histology, physiology and embryology" [Wikipedia].
From European Journal of Anatomy 22(5):433-439 · September 2018, an article by Sanjib Ghosh and Ashutosh Kumar 'Marcello Malpighi (1628-1694): Pioneer of microscopic anatomy and exponent of the scientific revolution of the 17th Century': Italian anatomist and an eminent scientist who significantly contributed to the advancement of the anatomical sciences in the 17th century. Malpighi was one of the first to use the compound microscope (an instrument designed by Galileo in 1609) and made the most important discovery of his life in 1661 when he identified capillaries as connecting vessels between small arteries and veins in the lungs. Malpighi thus provided the missing link in William Harvey's theory of blood circulation. He made significant contributions in the field of embryology based on his observations on chick embryo, and his efforts provided deep insights into the development of the heart and the nervous system. His communications based on microscopic studies scripted valuable details on the structural organization of organs like the liver, kidney and spleen. He identified the hepatic lobule as the fundamental unit of the liver and noted that bile was being secreted by these lobules and not from the gall bladder (the popular belief then). In the kidney, he discovered the glomerulus (Malpighian Corpuscle) and was the first to observe the convoluted tubules in the renal cortex. He was the first to describe the presence of lymphatic bodies (Malpighi's Corpuscle) in the spleen. Although he was exceedingly successful in his scientific activities, his life was fraught with unfortunate events and savage criticism from detractors arising out of professional jealousy and personal feuds. Nevertheless, his exploits were instrumental in understanding the human microscopic anatomy (histology) and his accomplishments have etched his name in the pages of medical science forever.
The portrait was engraved by Johannes "Jan" Kip (1652/53, Amsterdam – 1722, Westminster) - a Dutch draftsman, engraver and print dealer.
-
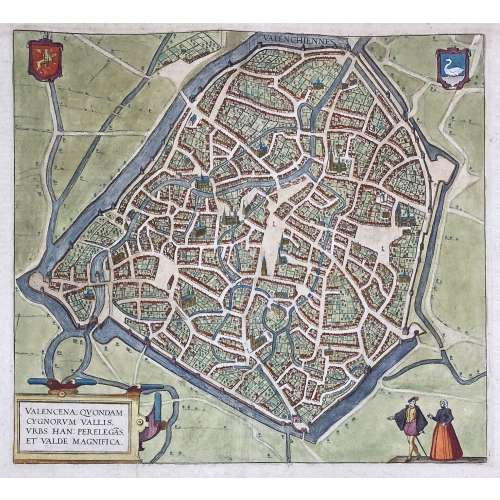 VALENCENA, QUONDAM | CYGNORUM VALLIS | URBS HAN: PERELEGÃS | ET VALDE MAGNIFICA. ||
VALENCENA, QUONDAM | CYGNORUM VALLIS | URBS HAN: PERELEGÃS | ET VALDE MAGNIFICA. ||Engraved and hand-coloured map of Valenciennes first produced for Braun & Hogenberg's 6-volume Civitates orbis terrarum edition in 1570.
English translation of the text printed on verso: "The Loire, an exceedingly well-known river in France, flows directly past the city and is very beneficial for trade. The fields surrounding the city are very fertile, and for this reason, the city is also called the granary throughout France, just as in earlier times Sicily was the granary of Rome. A famous wine also grows in this soil, which is exported from here not only throughout France but to all the countries in Europe. [...] The French spoken here is pure and uncorrupted, which is also the reason why so many foreigners settle here. For some are here for trade, others for study and others again to acquire the language, but also many without doubt for both these last two reasons, [...] and Germans, in particular, send their children here." [by Barry Lawrence Ruderman Antique Maps Inc.]
Dimensions: Sheet: 39.8 x 53.5 cm; Image: 35.2 x 38.5 cm.
Probably published in Cologne is 1612-18 by Petrum à Brachel: [Coloniae Agrippinae: apud Petrum à Brachel, sumptibus auctorum, 1612-1618]. Ref: LOC.Georg Braun [Brunus; Bruin] (German, 1541 – 1622).
Frans Hogenberg (Flemish-German, 1535 – 1590).
Abraham Ortelius [Ortels; Orthellius; Wortels] (Dutch, 1527 – 1598).


