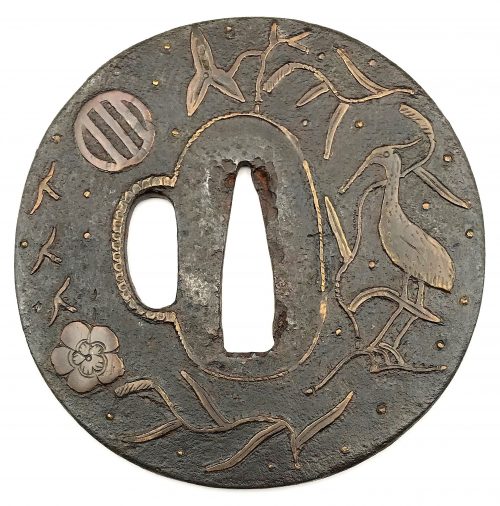
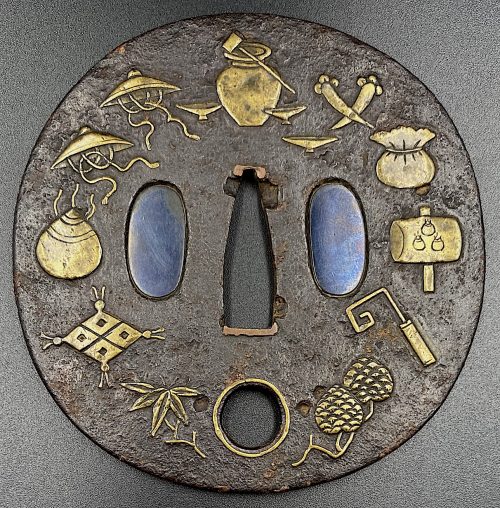
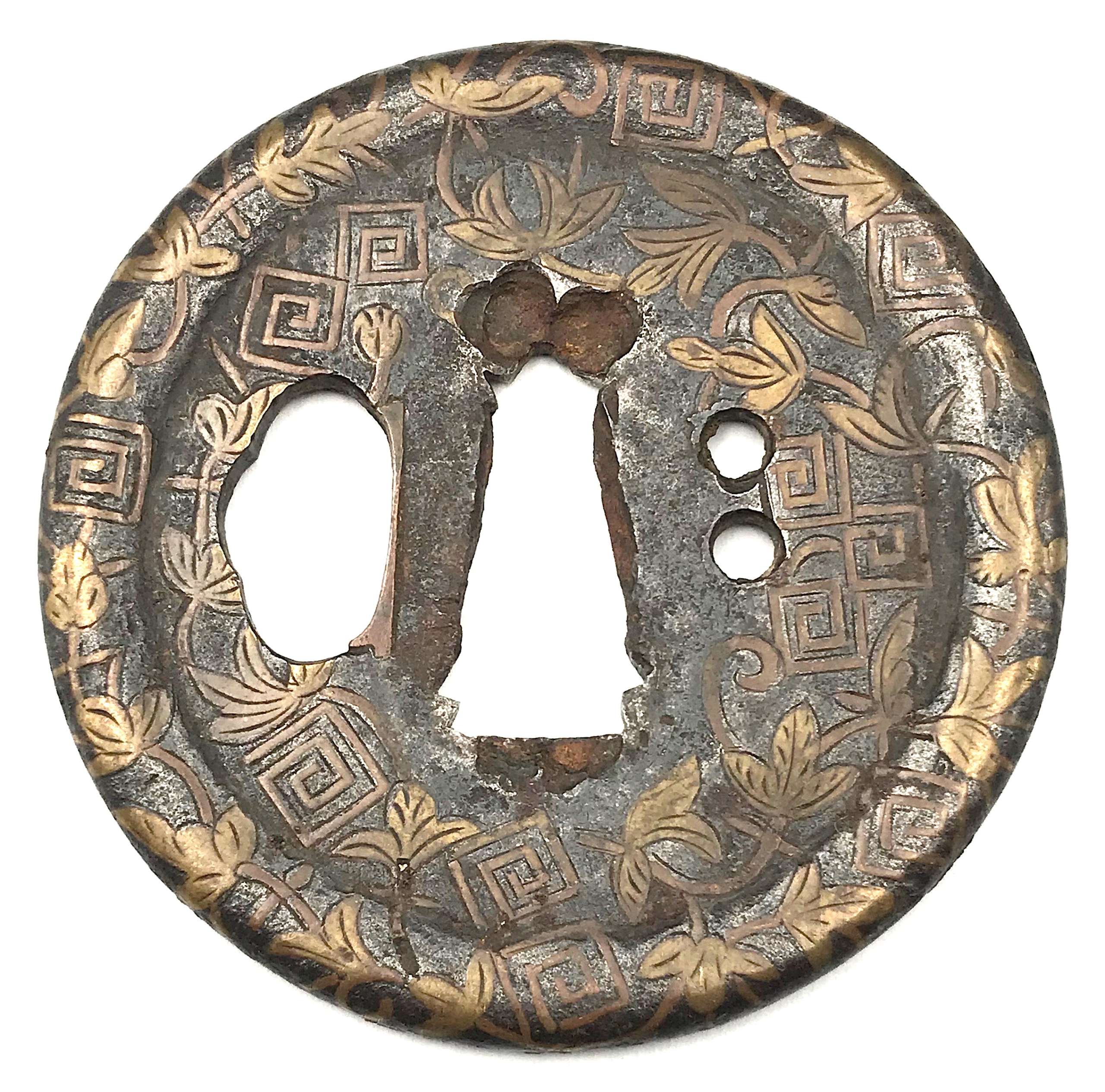
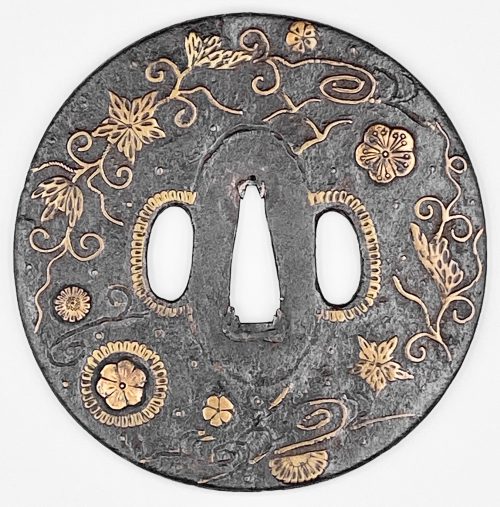
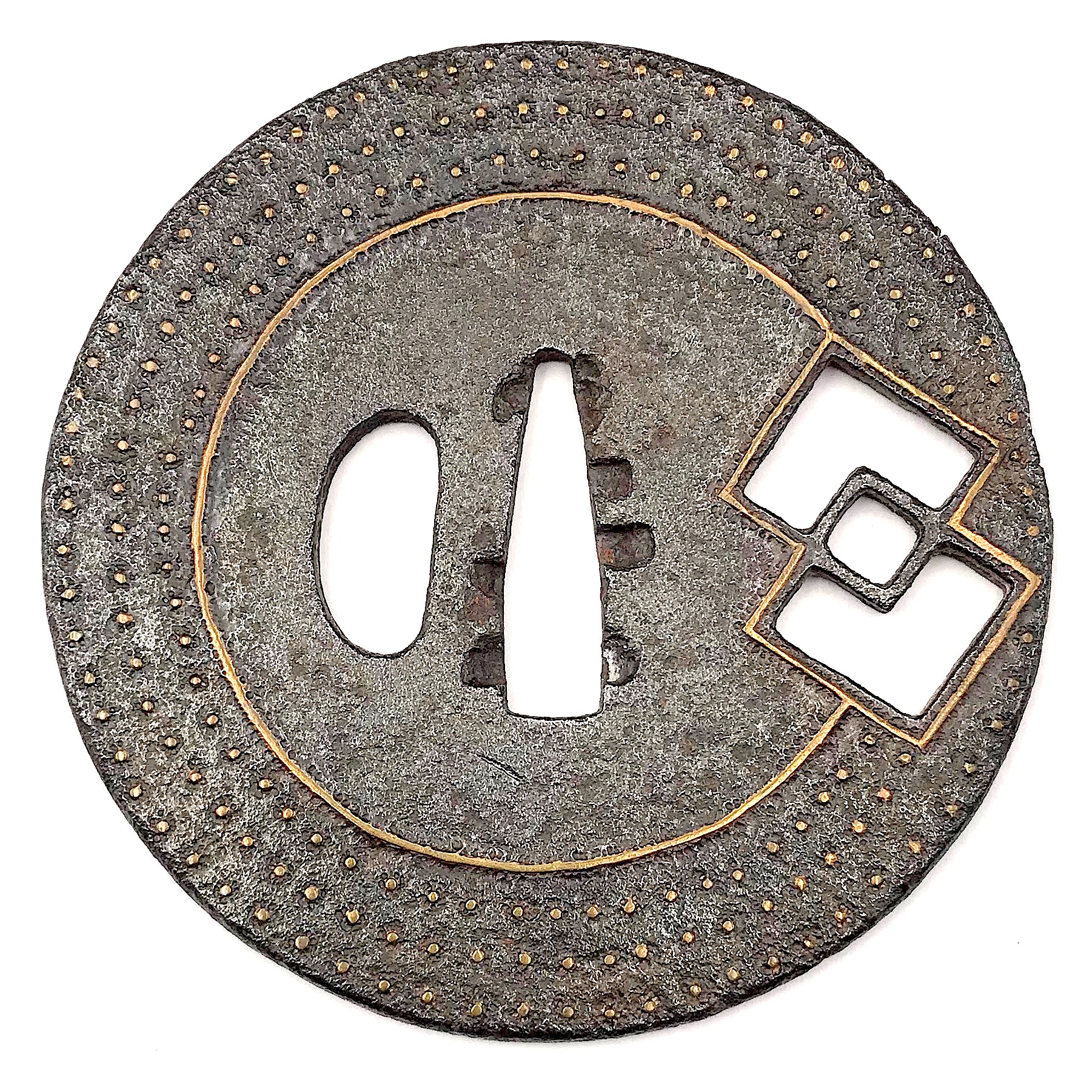
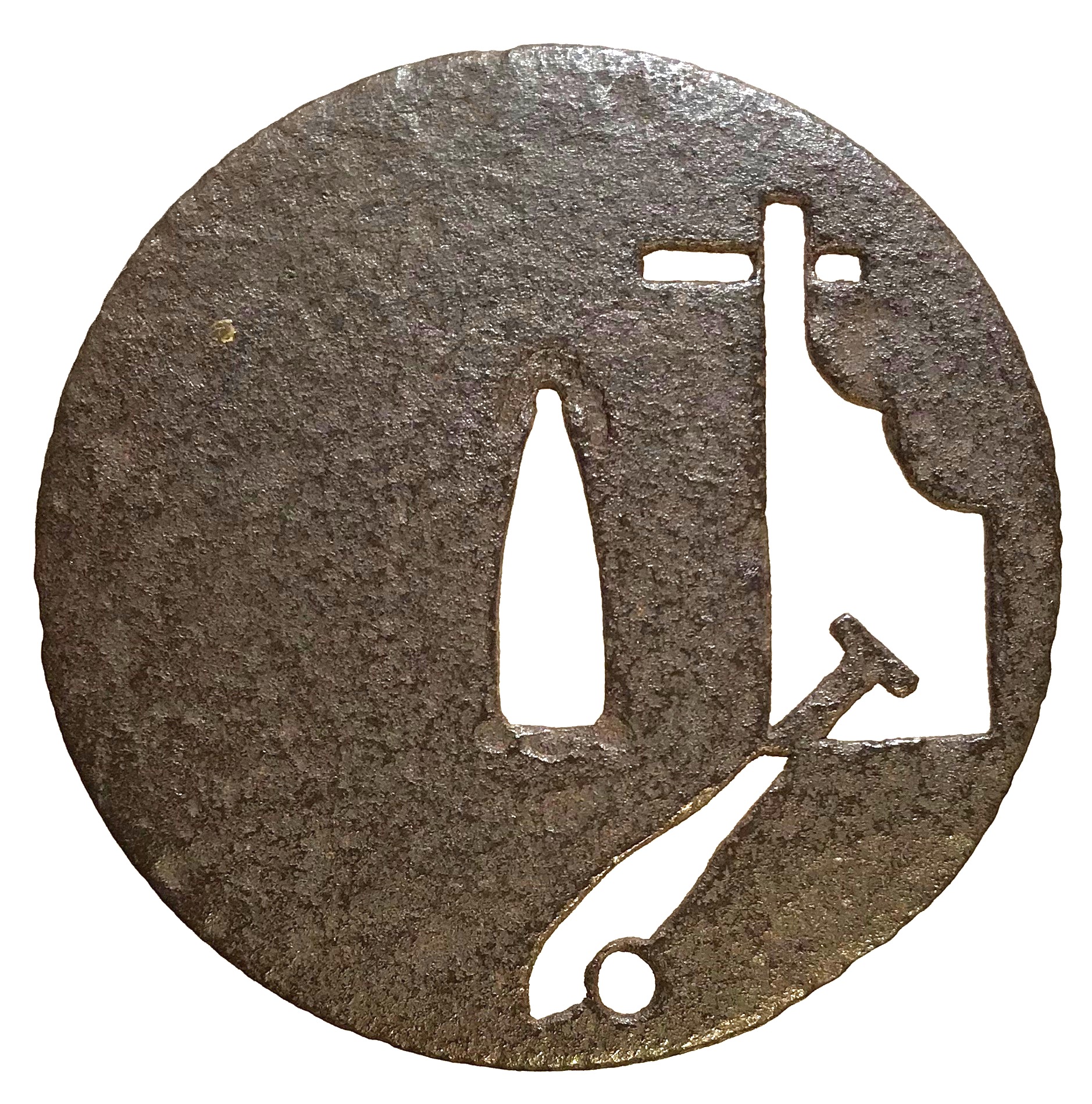
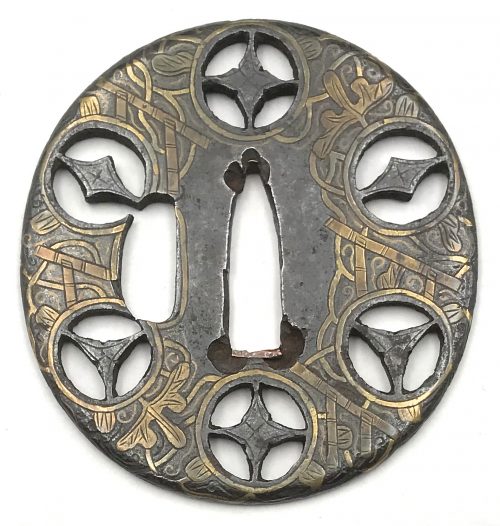
Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (
sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [
takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (
suemon-zōgan);
hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with
shakudo,
nakaga-ana fitted with copper
sekigane. According to Merrily Baird
*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):
- Sake set [shuki, 酒器], namely flask, ladle, and cups
- Cloves [choji, 丁子]
- Purse of inexhaustible reaches [kinchaku, 巾着]
- Magic mallet [kozuchi, 小槌]
- Key to the storehouse of the Gods [kagi, 鍵]
Then, Pine, Moon, and Bamboo (see below);
- Rhombus, or Lozenge (hosho, 方勝), with the second ideograph meaning victory.
- Sacred (or wish-granting) gem, or jewel [hōju, 宝珠]
- Hats of invisibility [kakuregasa, 隠れ笠]
The Myriad Treasures is carried by the
Seven Gods of Good Luck (a.k.a. the Seven Lucky Gods or Seven Gods of Fortune [
shichifukujin, 七福神], who are transported by the
Treasure Ship [
takarabune, 宝船] during the first three days of the New Year.
Pine, Moon, and Bamboo: bamboo [
take, 竹] and pinecones [
matsukasa, 松笠], or pine [
matsu, 松] – two of the Three Friends of Winter [
shōchikubai, 松竹梅] – symbolize fidelity, fortitude, steadfastness, perseverance, and resilience. The third ‘friend’ – plum, [
ume, 梅] – in this case replaced by the Moon [
tsuki, 月] – large (11 mm) circular opening at 6 o’clock; the three small carved dots represent the dewdrops.
The other side is decorated with an arabesque (
karakusa) of cloves and vines, with carved dots (dewdrops) along the rim.
The overall New Year / Winter connotation of the tsuba is clear. The prominence of the Moon conveys purity, coldness (sadness/loneliness), and slenderness – the inherent qualities of a samurai.
H: 93 mm x W: 90 mm, thickness 4.2 mm at the centre, slightly tapered towards the rim.
*) Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan: Thematic motifs in art and design. — NY: Rizzoli international publications, 2001.
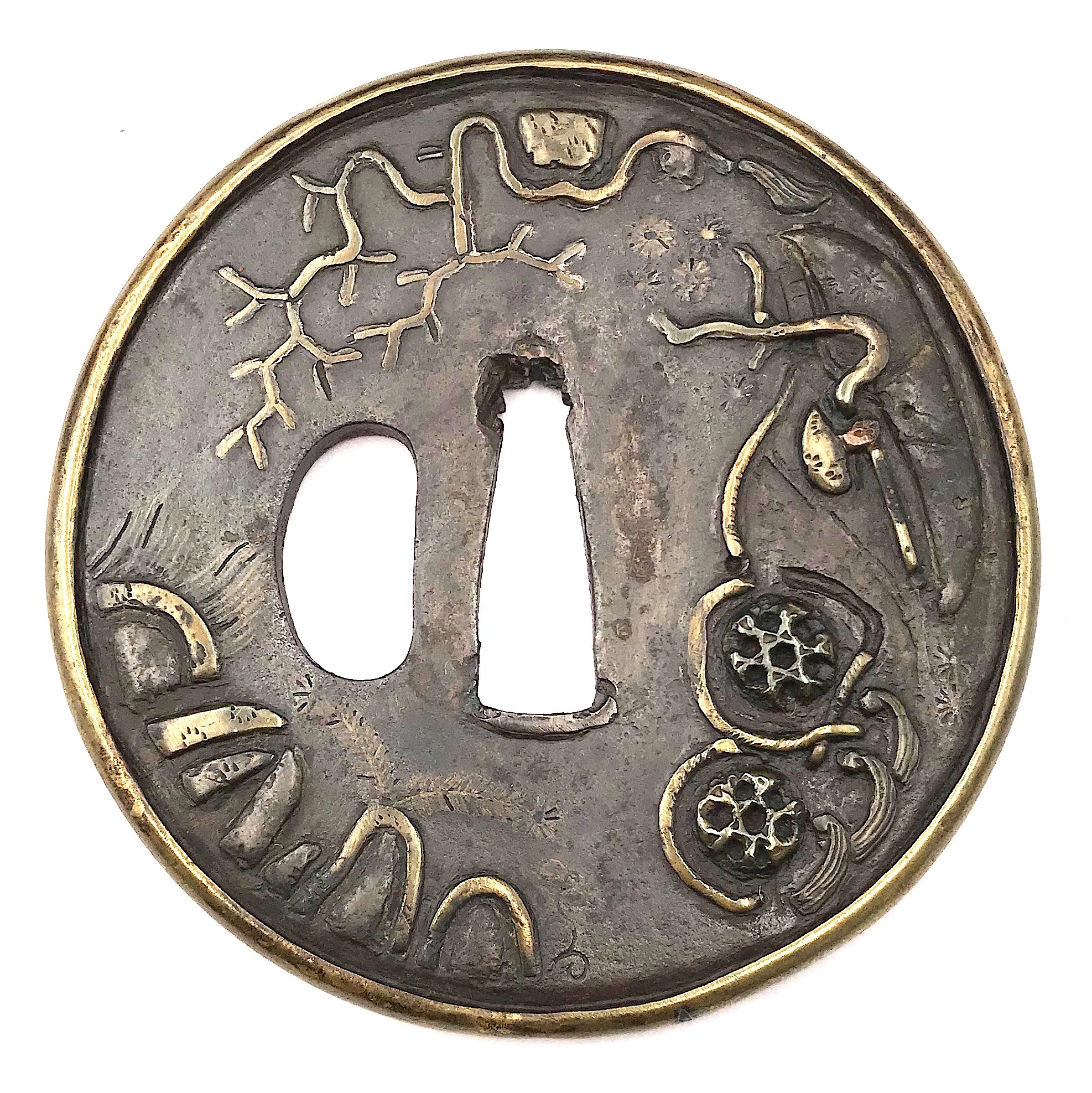
Seller’s description: École Heianjo - Début Époque EDO (1603 - 1868). Nagamaru gata en fer à décor incrusté en hira-zogan de laiton de tama, choji, jarre à saké et des attributs de Daikoku (maillet, chapeau d'invisibilité et sac de richesse) et de branches de choji de l'autre côté et ajourée en kage-sukashi d'un cercle. H. 9,2 cm
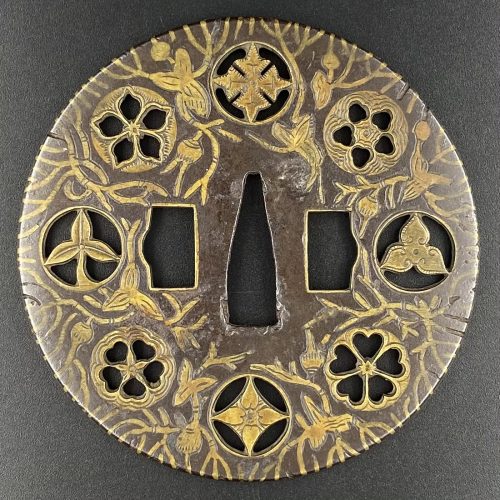
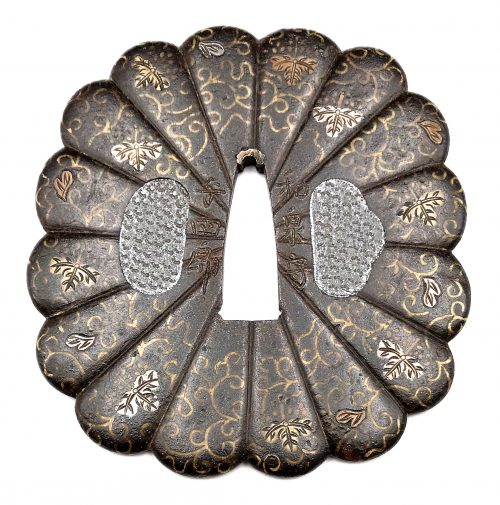
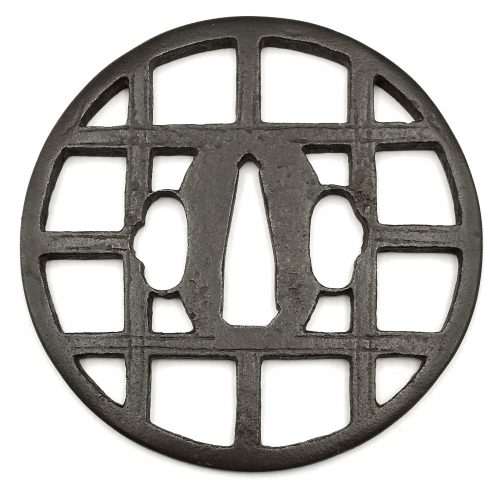







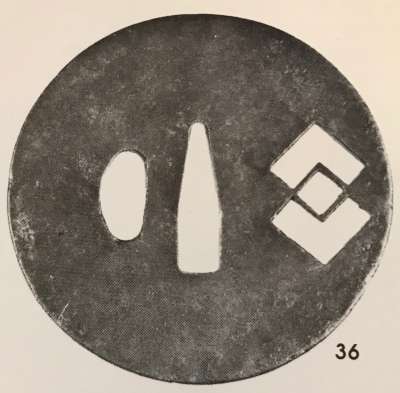



















 English translation of the book indicated above Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1 by Harry Afu Watson, AFU Research Enterprises, Inc., 1993. Tsuba in question illustrated on page 14 and described as follows: " Tsuba mumei Ōnin. Tetsu ji maru gata ko-sukashi tsuchime shitate shinchū suemon ten zogan maru mimi. Brass suemon". My question remains: why such a text is called 'translation' while it looks more like transliteration of romanization?
English translation of the book indicated above Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1 by Harry Afu Watson, AFU Research Enterprises, Inc., 1993. Tsuba in question illustrated on page 14 and described as follows: " Tsuba mumei Ōnin. Tetsu ji maru gata ko-sukashi tsuchime shitate shinchū suemon ten zogan maru mimi. Brass suemon". My question remains: why such a text is called 'translation' while it looks more like transliteration of romanization?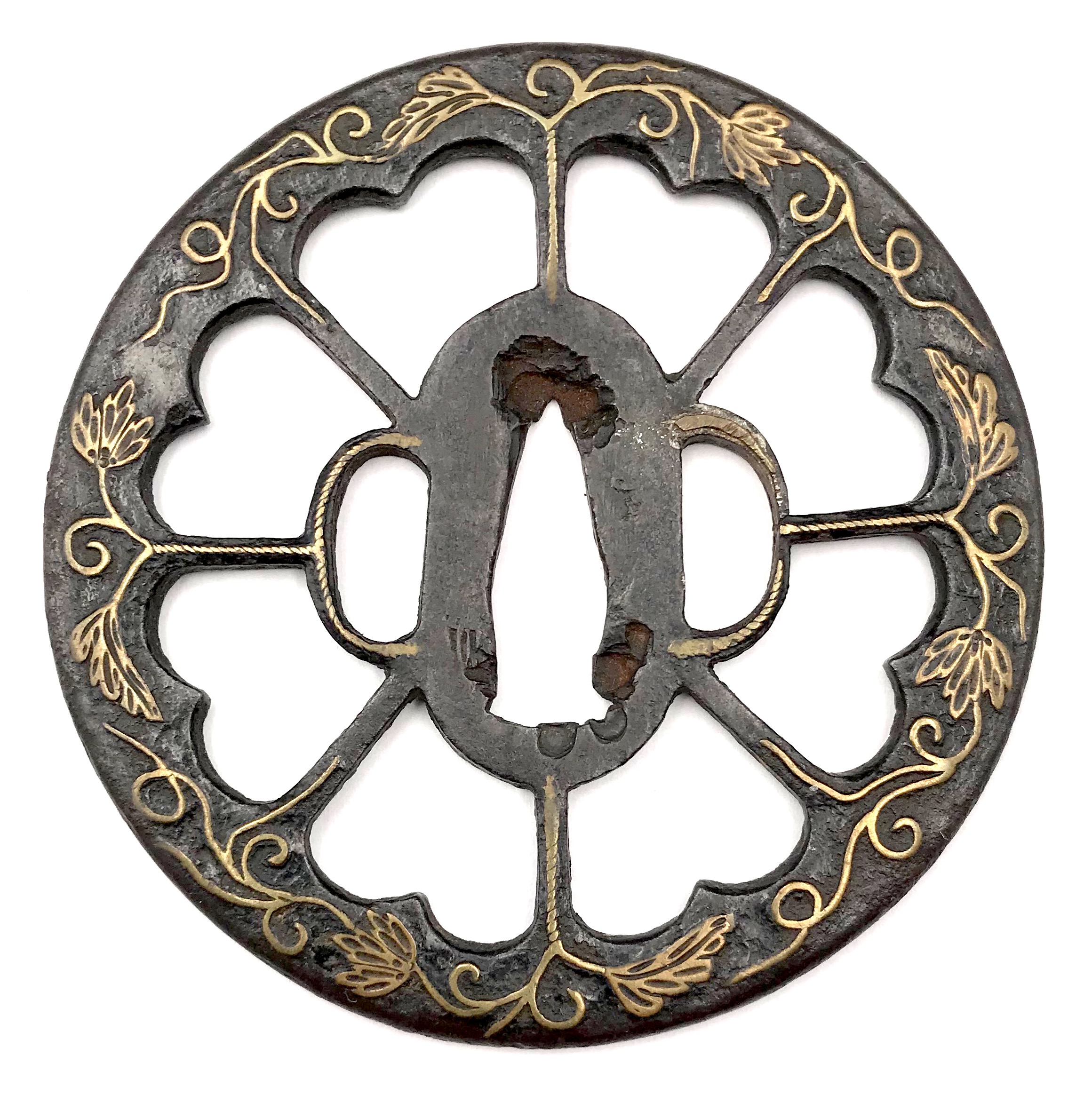 
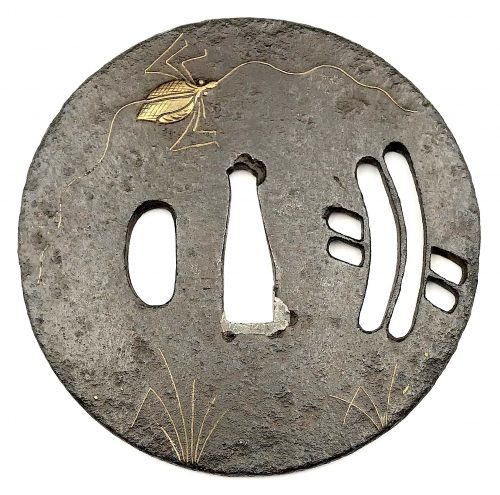
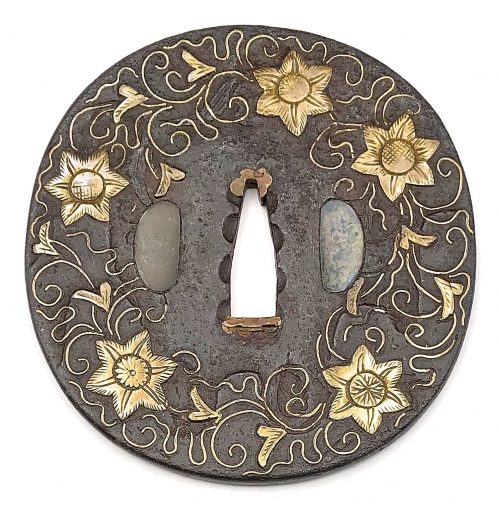
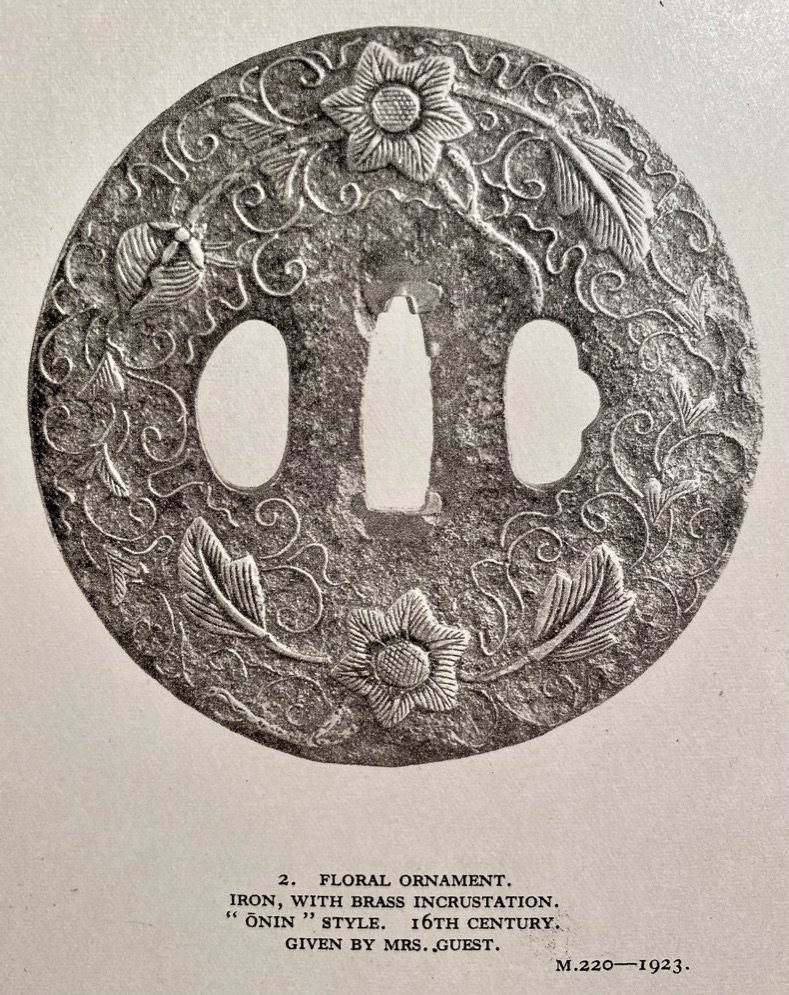
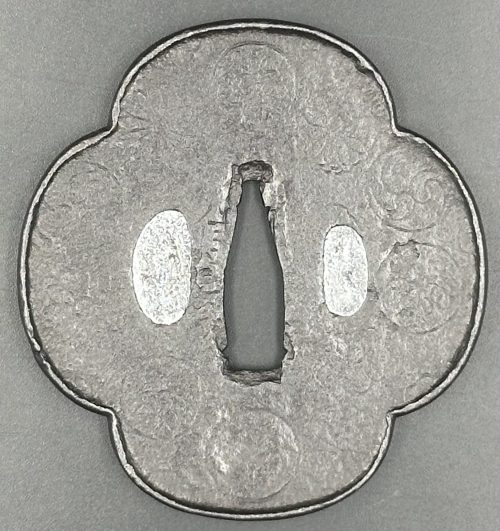
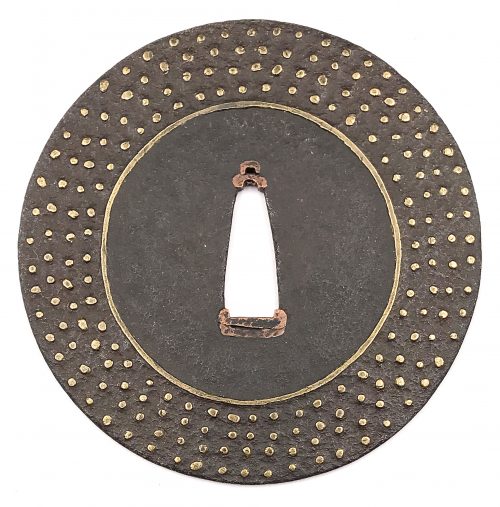
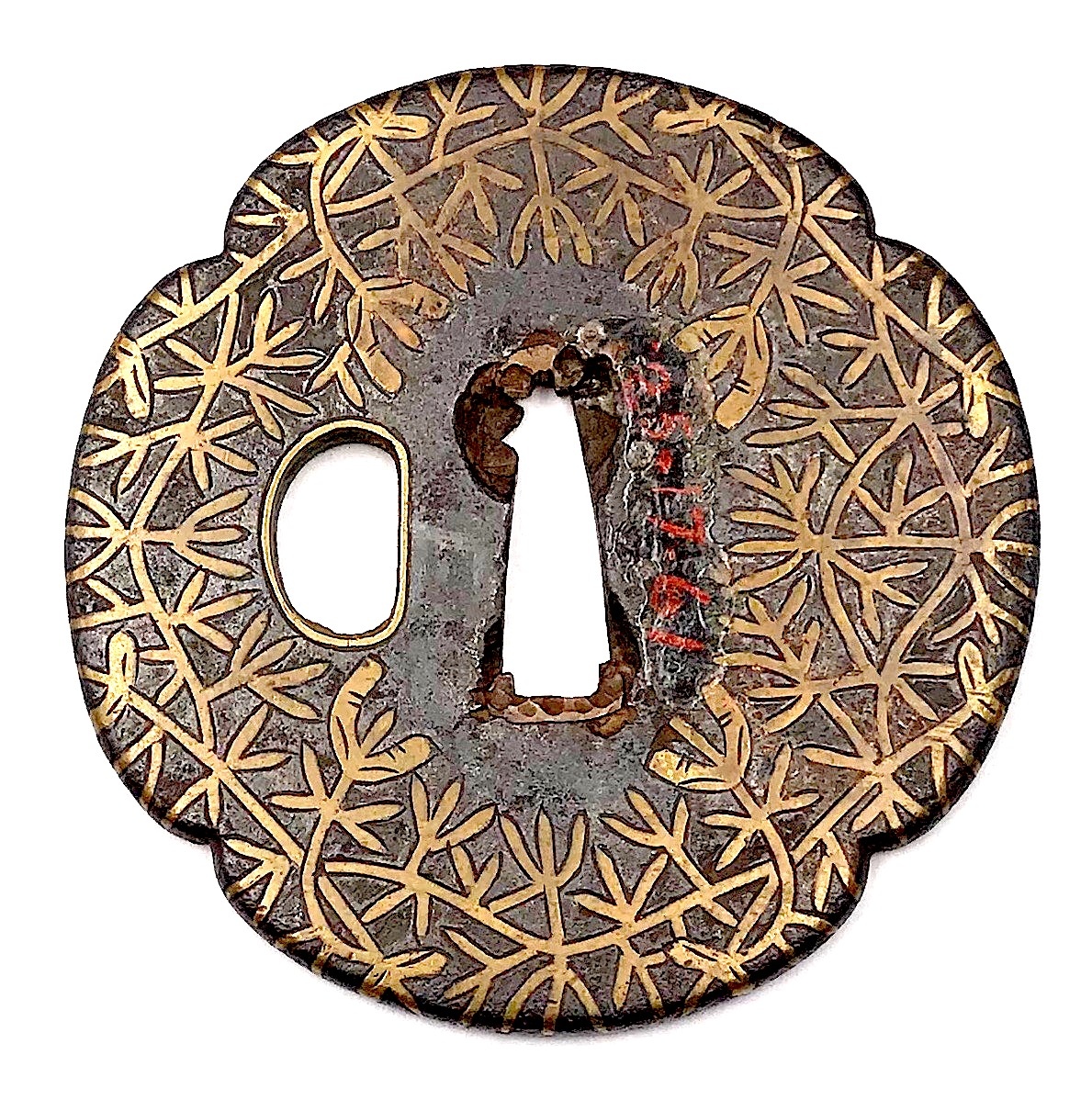
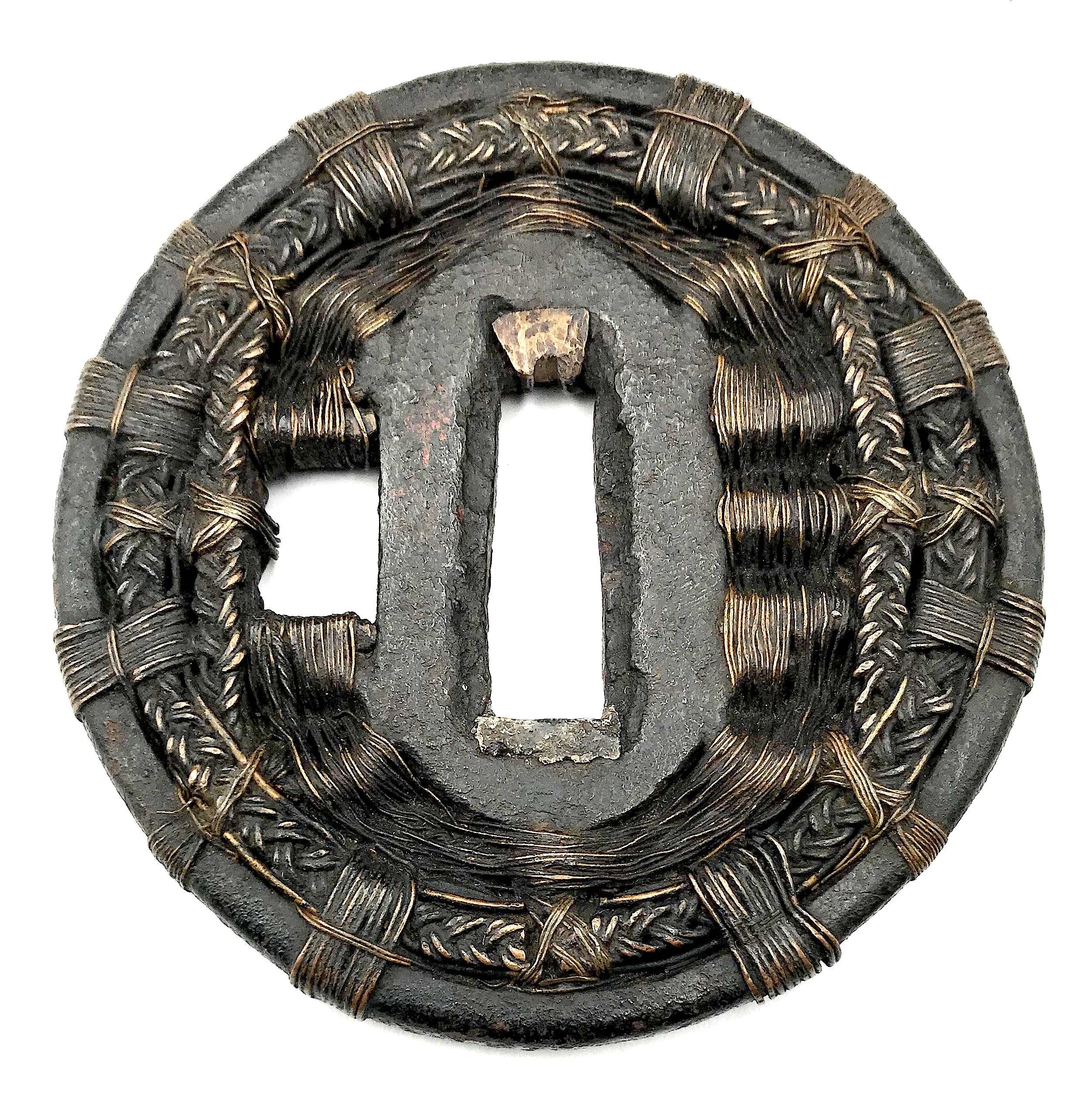
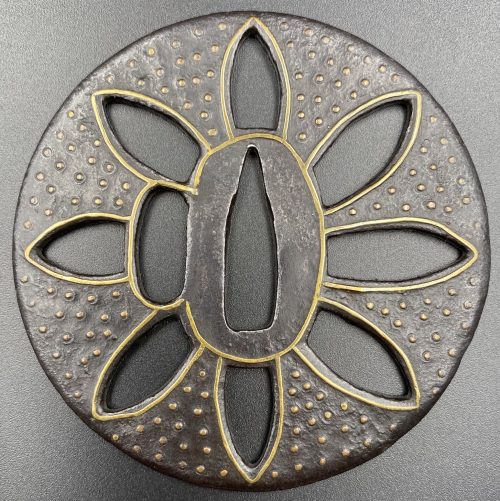
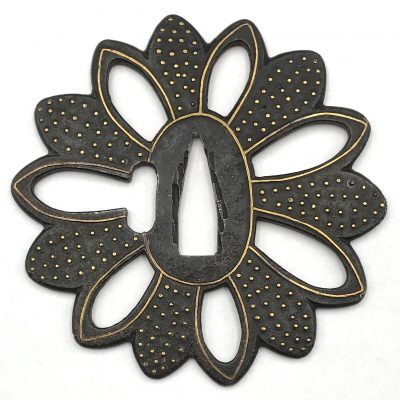
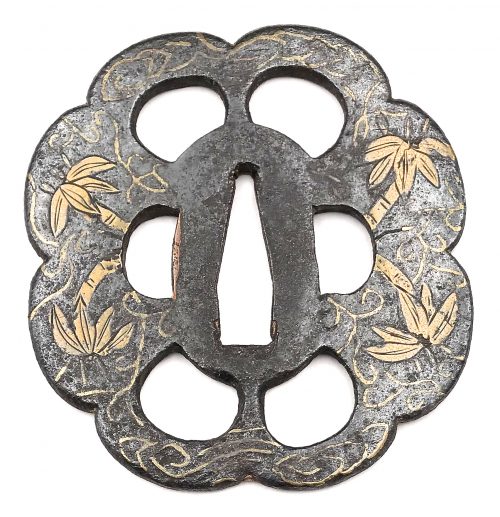
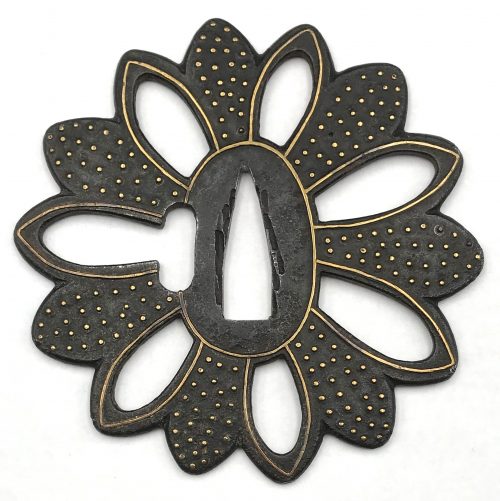
























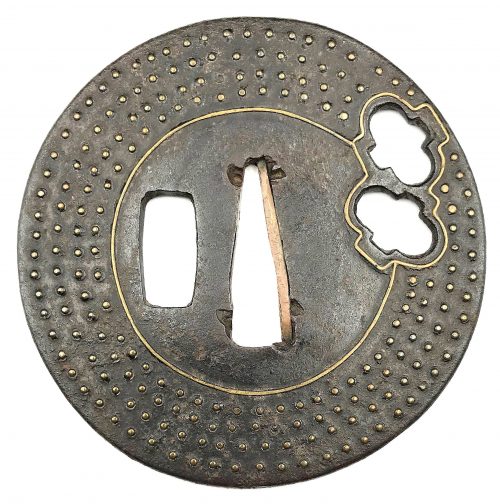
 Other similar specimens can be found at:
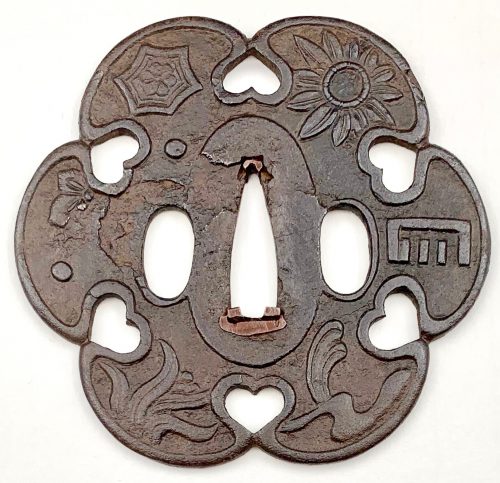
Henri L. Joly and Kumasaku Tomita, Japanese art and handicraft, "Swords and sword fittings" section, sub-section “Inlays of Ōnin, Kyoto, Fushimi-Yoshiro, and Kaga Province”, Plate CX, #128: Iron, chrysanthemoid, thin guard with alternate petals covered with brass spots. Ōnin style. 16th century.
Other similar specimens can be found at:
Henri L. Joly and Kumasaku Tomita, Japanese art and handicraft, "Swords and sword fittings" section, sub-section “Inlays of Ōnin, Kyoto, Fushimi-Yoshiro, and Kaga Province”, Plate CX, #128: Iron, chrysanthemoid, thin guard with alternate petals covered with brass spots. Ōnin style. 16th century.

