Gary D. Murtha's tsuba on page 61.


Gary D. Murtha's tsuba on page 61.
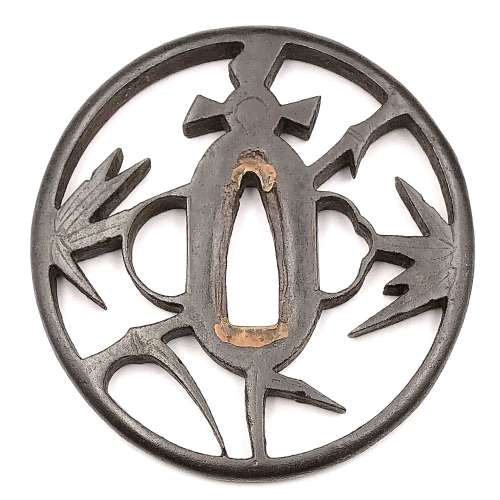
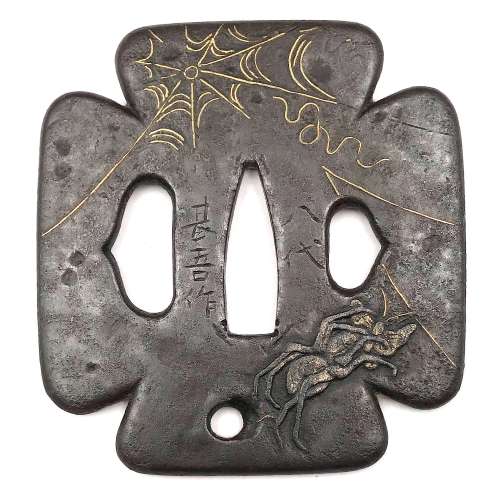






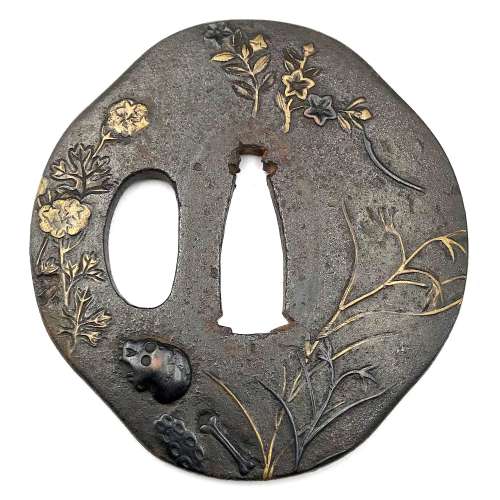
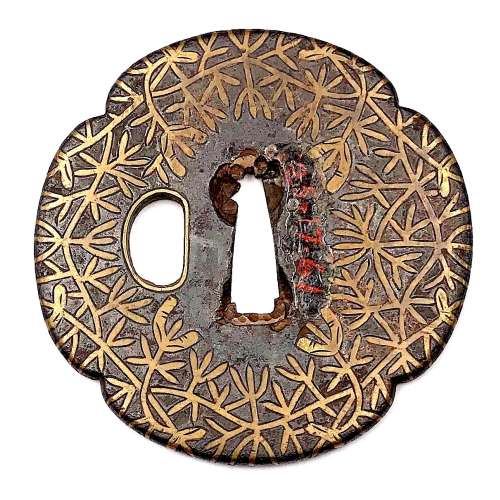
Very fine iron plate well hammered and turned, tapering and rolling to the rounded edge. Tsuba of a cross-form mokko shape (juji-mokko-gata) decorated with spider web inlaid in gold on both sides. The face is carved with a silver-damascened spider holding a gold-damascened butterfly (nunome-zōgan). Kozuka and kogai hitsu-ana of inome (boar's eye) form. The udenuki ana may be of purely decorative purpose.
Signed: Yatsushiro [八代] Jingo Saku [甚吾作], a signature of Chisokutei Amatsune, one of the last Jingo masters.
Late Edo period, Tenpō era, 1830-1844.Size: Height: 77.5 mm; Width: 72.8 mm; Thickness: 4.1 mm; Weight: 141 g.
In a custom wooden box.
Here is what Markus Sesko wrights in his book The Japanese toso-kinko Schools, 2012, on page 374:An artist who worked in the style of the Shimizu-Jingo school was Chisokutei Amatsune (知足亭天常). He was actually a samurai from Yatsushiro who made tsuba as a sideline. An extant old hakogaki of one of his pieces mentions that he died in Edo in the sixth month of An'ei eight (1779) at the age of 73. But the era of An'ei is probably wrong because Chikokutei (sic) is today dated by most experts around Tenpō (1830-1844). His relationships with the Shimizu school or under which Jingo master he had studied are unknown. From the point of view of production time and the finishing of nakago-ana, he is rather associated with the 5th and last gen. Shigenaga who died in the seventh year of Kaei (1854). A peculiarity of Chisokutei was that he signed his Jingo copies with "Yatsushiro Jingo Saku" ([八代甚吾作) but added the small syllable "chi" (チ) or the character "Chi" (知) for "Chisokutei" to identify them as copies.No longer available.


Tears That Brought Bamboo-shoots From the Frozen Earth: Meng Zong Meng Zong lived during the Three Kingdoms Period of China's past. His father died when he was young, and he and his mother struggled to survive. One winter his mother was stricken with a serious illness, and craved some bamboo-shoot broth as medicine. But in the depths of winter, with snow and ice blanketing the ground, where was anyone to find fresh bamboo shoots, shoots that emerge only in the warm months? Nonetheless, Meng Zong, to avoid disappointing his mother, bravely fetched his shovel and went out into the white landscape in search of bamboo shoots. In the thicket he found only frosted leaves and green stalks coated with snowflakes and ice. Look as he might, there were simply no fresh shoots growing in the winter. The thought of his poor mother lying sick on her bed, waiting for bamboo-broth medicine, made his heartache. Uncontrollably, tears began to fall in rivers to the ground beneath the tall, emerald canes. Even now, as his tears flowed down, he kept a light of faith in his heart. If he was truly sincere in his search, perhaps.... Just then Meng Zong nearly tripped and fell over a sharply protruding lump of earth. He quickly knelt down and knocked aside the dirt with his trembling fingers. How uncanny! Underneath his frozen hands he discovered a bed of fresh, tender bamboo shoots! Overjoyed, he gathered up a coatful and carried them back home. The broth that he quickly set stewing in the pot soon cured his mother's illness. The neighbors, hearing the story, exclaimed that it was the strength of his sincere, unselfish, filial resolve that inspired heaven and earth to respond, and to bring up, out of season, the fresh shoots that cured his mother's disease. Before Meng Zong's prayers generated this miracle, it was normally considered impossible for bamboo shoots to grow in the winter. After the nmiracle took place, however, people were able to gather and to eat bamboo shoots all year round. The winter variety that existed hereafter became known as "winter shoots." The villagers were deeply influenced by Meng Zong's courage and devotion. They renamed the spot where the event took place, "Meng Zong's Bamboo Grove". We can now enjoy bamboo sprouts during the winter as well, and as we do so, it is fitting to recollect Meng Zong's outstanding example of filial respect, and reflect on our conduct as sons and daughter of our parents. A verse in his honor says, His teardrops transformed winter at the roots; Up from the ice crept tender bamboo shoots. Instantly, the winter-sprouts matured; Heaven's will: a happy, peaceful world.


 SVJP-0179-6.2014 |
The Hour of the Dragon, Fifth Hour of Day (Tatsu no koku, Hi no itsutsu toki), from the series Twelve Hours of a Modern Clock (Imayo tokei jūniji) 「今世時計十二時 辰ノ刻 日ノ五つ時」 MFA impression: 11.15315. |
 SVJP-0179-1.2014 |
The Hour of the Rabbit, Sixth Hour of Day (U no koku, Ake muttsu toki), from the series Twelve Hours of a Modern Clock (Imayo tokei jūniji) 「今世時計十二時 卯ノ刻 明六つ時」. MFA impression: 11.15317 |
 SVJP-0179-2.2014 |
The Hour of the Monkey, Seventh Hour of Day (Saru no koku, Hi no nanatsu toki), from the series Twelve Hours of a Modern Clock (Imayo tokei jūniji) 「今様時計十二時 申ノ刻 日ノ七つ時」 MFA impression: 11.39692 |
 SVJP-0179-8.2014 |
The Hour of the Horse, Ninth Hour of Day (Uma no koku, Hi kokonotsu toki), from the series Twelve Hours of a Modern Clock (Imayo tokei jūniji) 「今世時計十二時 午ノ刻 日九つ時」. MFA impression: 11.15314 |
 SVJP-0179-4.2014 |
The Hour of the Boar, Fourth Hour of Night (I no koku, Yoru yottsu toki), from the series Twelve Hours of a Modern Clock (Imayo tokei jūniji) 「今世時計十二時 亥ノ刻 夜四つ時」. MFA impression: 11.15552 |
 SVJP-0179-3.2014 |
The Hour of the Tiger, Seventh Hour of Night (Tora no koku, Yoru nanatsu), from the series Twelve Hours of a Modern Clock (Imayo tokei jūniji) 「今世時計十二時 寅ノ刻 夜七つ」. MFA impression: 11.15313 Ref.: Izzard. Kunisada’s world [LIB-2970.2022]. |
 SVJP-0179-5.2014 |
The Hour of the Ox, Eight Hour of Night (Ushi no koku, Yoru no yattsu toki), from the series Twelve Hours of a Modern Clock (Imayo tokei jūniji) 「今世時計十二時 丑ノ刻 夜ノ八つ時」. MFA impression: 11.26906 |
 SVJP-0179-7.2014 |
The Hour of the Rat, Ninth Hour of Night (Ne no koku, Yoru kokonotsu toki), from the series Twelve Hours of a Modern Clock (Imayo tokei jūniji) 「今世時計十二時 子ノ刻 夜九つ時」. MFA impression: 11.15312 |
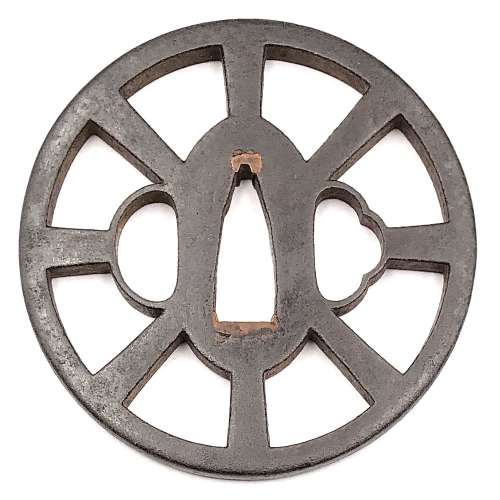



Merrily Baird in her book "Symbols of Japan" [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001] provides the following explanation of the Wheel-of-the-Law symbol: "The Wheel-of-the-Law or Golden Wheel (rimbo, kinrin) has its origins in India, where it is known as chakra. [...] In Buddhist practice, it has been represented with eight spokes, reflecting the eight-fold path to overcoming worldly desire, and it signifies that all illusions will be crushed by the faith's enlightenment. [...] The Wheel-of-the-Law is an attribute of such deities as Senju Kannon, the Thousand-Armed Kannon, and Dainichi Nyorai, the all-illuminating solar figure who is the principal deity for Shingon Buddhism. From the Edo period on, the wheel also has been used in a secular manner", e.g. on family crests.
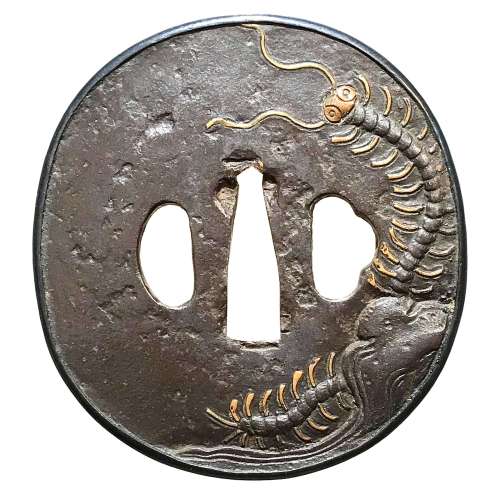

Iron tsuba of oval form with a shakudō fukurin and rough surface decorated by low relief carving and brass inlay with a centipede emerging from under the rock on both sides.
Edo period.Size: 78.9 x 73.6 x 3.8 mm
Unsigned. However, this tsuba may be (though with reservation) attributed to Misumi Kōji school. There is some information regarding this master(s) in Tsuba. An aesthetic study by Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes (from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997) on pages 163-4, though I was not able to locate the tsuba in the original publication. Possibly, this fragment of the book was added by Robert Haynes. Markus Sesko speculates about Misumi in his The Japanese toso-kinko Schools.// Lulu Inc., 2012 on pages 374-5: "Misumi Kōjo Tsuba. Iron plate, elliptical shape, shakudō takabori suemon, yamagane fukurin. Centipede." But of course, visual similarity does not prove anything. I was not able to find any traces of signature or a triangle on the seppa-dai.
Misumi Kōji Tsuba on p. 163.

References:
Jacob Pins #547 [p.217] - Ebisu drawing wakamizu, the first water drawn from a well on the New Year. TNM II (Tokyo National Museum Catalogue vol. 2) #1373.

Robert E. Haynes Catalog of April 9-11, 1982, № 36.
