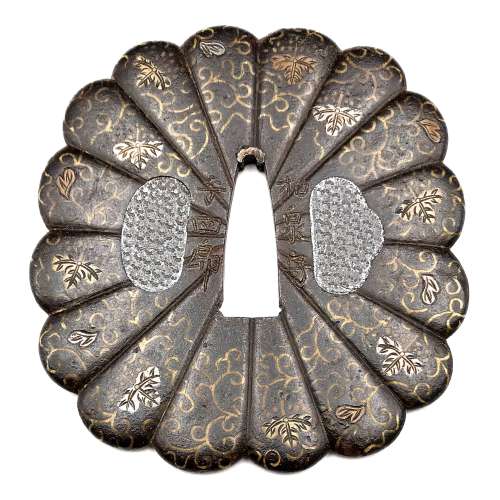
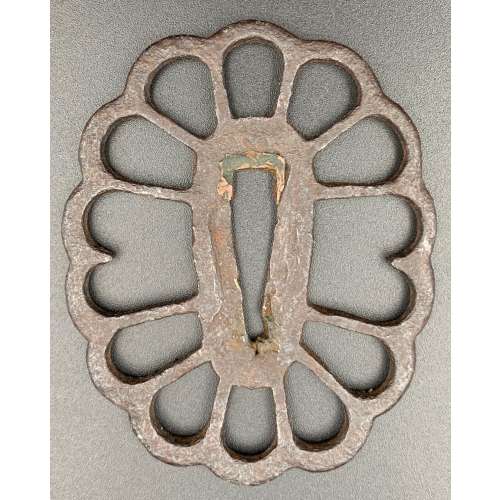
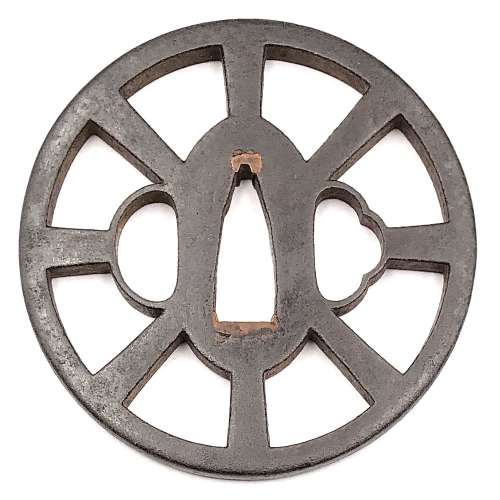
Iron tsuba with chrysanthemum design in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane.
Late Heian through Kamakura period (ca. 1150 - 1200's).
Size: 78.4 x 60.9 x 3.5 mm; weight: 45.7 g
Provenance: Boris Markhasin Message from Boris Markhasin (13-AUG-2019): It is a very rudimentary tachi tsuba, and the iron is old and really nothing to draw attention. However, this is a very old tsuba, and that is what makes it very special and an important study piece. This tsuba likely dates to the late Heian through Kamakura (ca. 1150 - 1200's) -- by consensus, since such examples are extremely rare, and none are mounted to my knowledge, so few direct analogues. The form is interesting for a variety of reasons. The smaller size, an oval form is associated more with 12th/13th c styles. The sukashi kiku motif is very interesting as it clearly pushes back the dating of large scale sukashi far back in time. This shouldn't be surprising, but for some reason, we (really mainly westerners) naively tend to associate sukashi with the Muromachi and younger. The two missing spokes are by consensus likely later removals to accommodate kozuka and kogai -- but this is not certain, and it could be an original styling. A key kantei point is the elongate, narrow, slightly squared seppa dai. This is a characteristic of early koshirae, which were much thinner and more delicate than the types we are used to seeing that date pretty much to the late Muromachi and later. I am always amazed when I have a chance to interrogate early koshirae at how thin they are - I want to call them fragile, but they were actually quite resilient. The walls were super thin, but the top and bottom edges were a bit thicker, providing a bit of structural support... but this is another thread topic. Of all the tsuba I have owned, this is the tsuba that has most clearly reflected the shape of the old style of saya / tsuka.
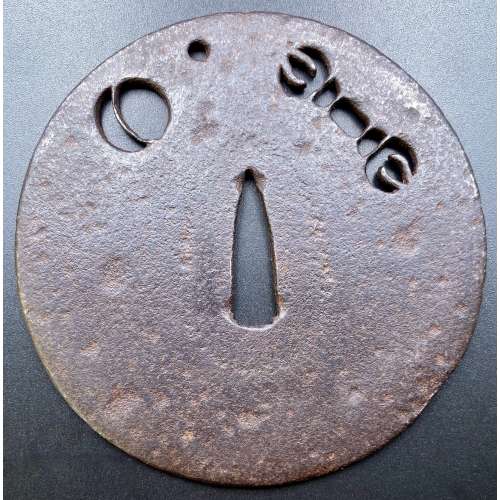
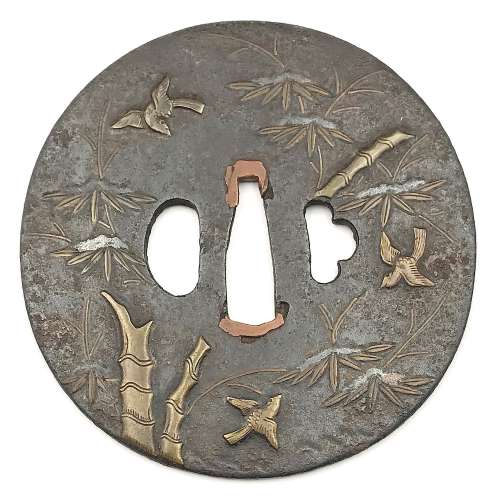
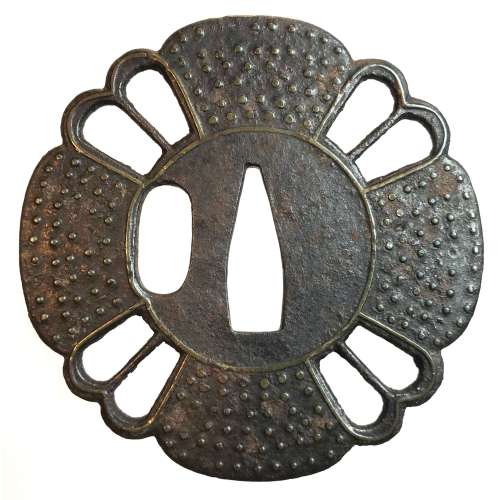
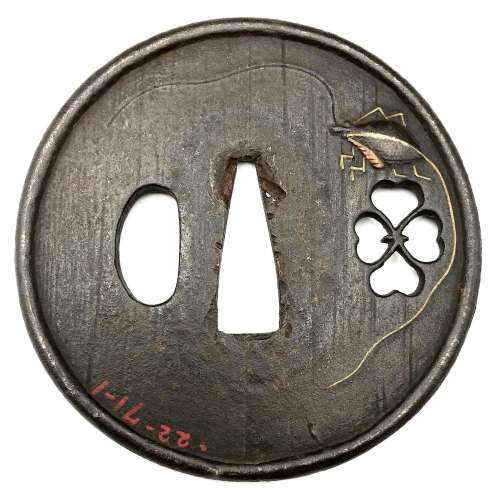
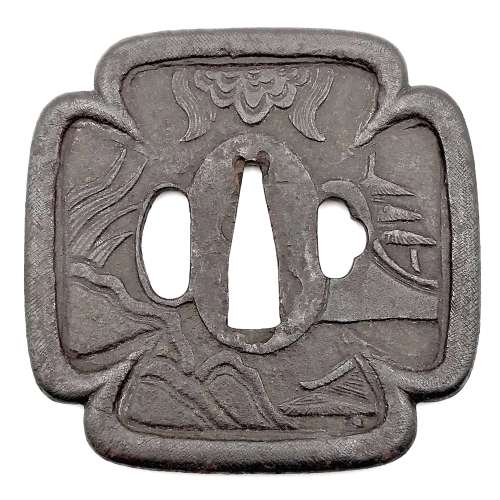
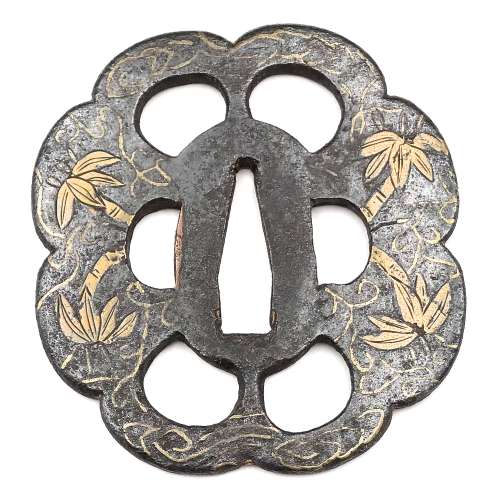
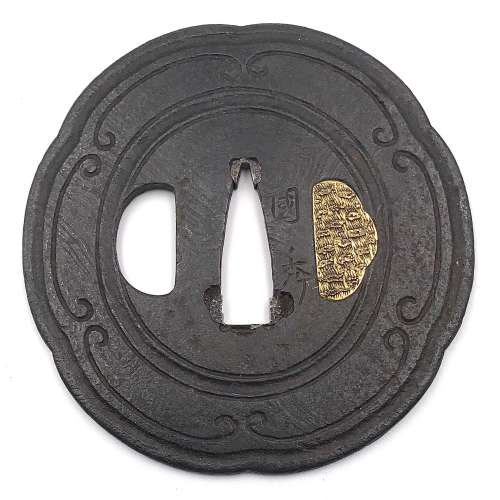















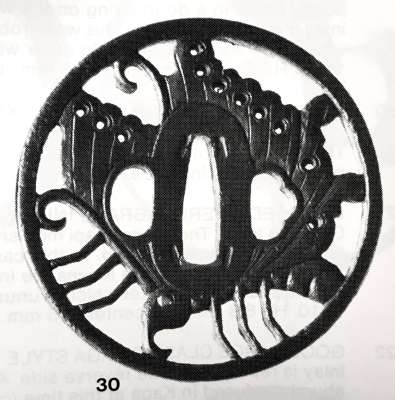




 Size: 77.4 x 74.9 x 2.7 mm
Size: 77.4 x 74.9 x 2.7 mm
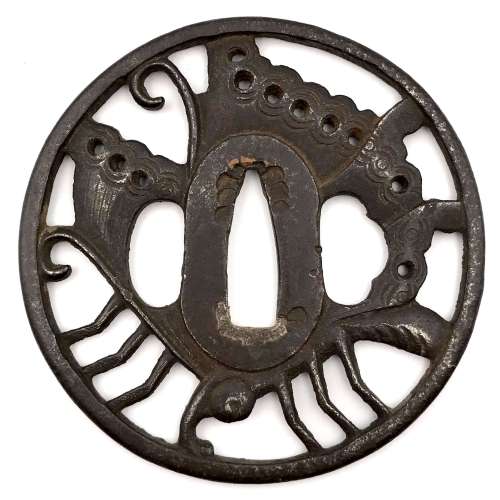
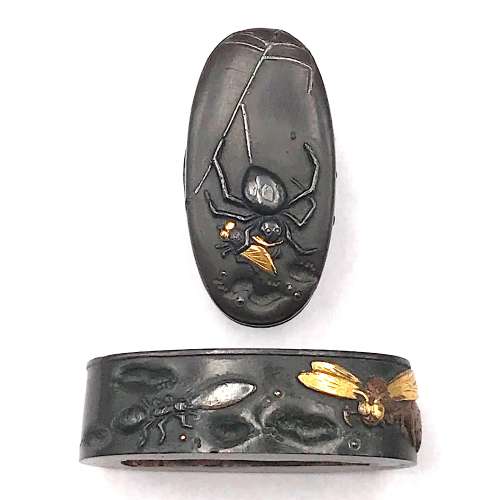
 3. And another one in Robert E. Haynes Catalog #9 on page 24-25 under №23: “Typical later Kamakura-bori style work. This type of plate and carving show the uniform work produced by several schools in the
3. And another one in Robert E. Haynes Catalog #9 on page 24-25 under №23: “Typical later Kamakura-bori style work. This type of plate and carving show the uniform work produced by several schools in the 
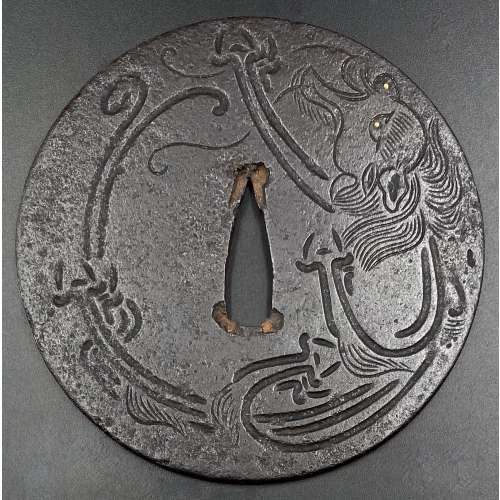
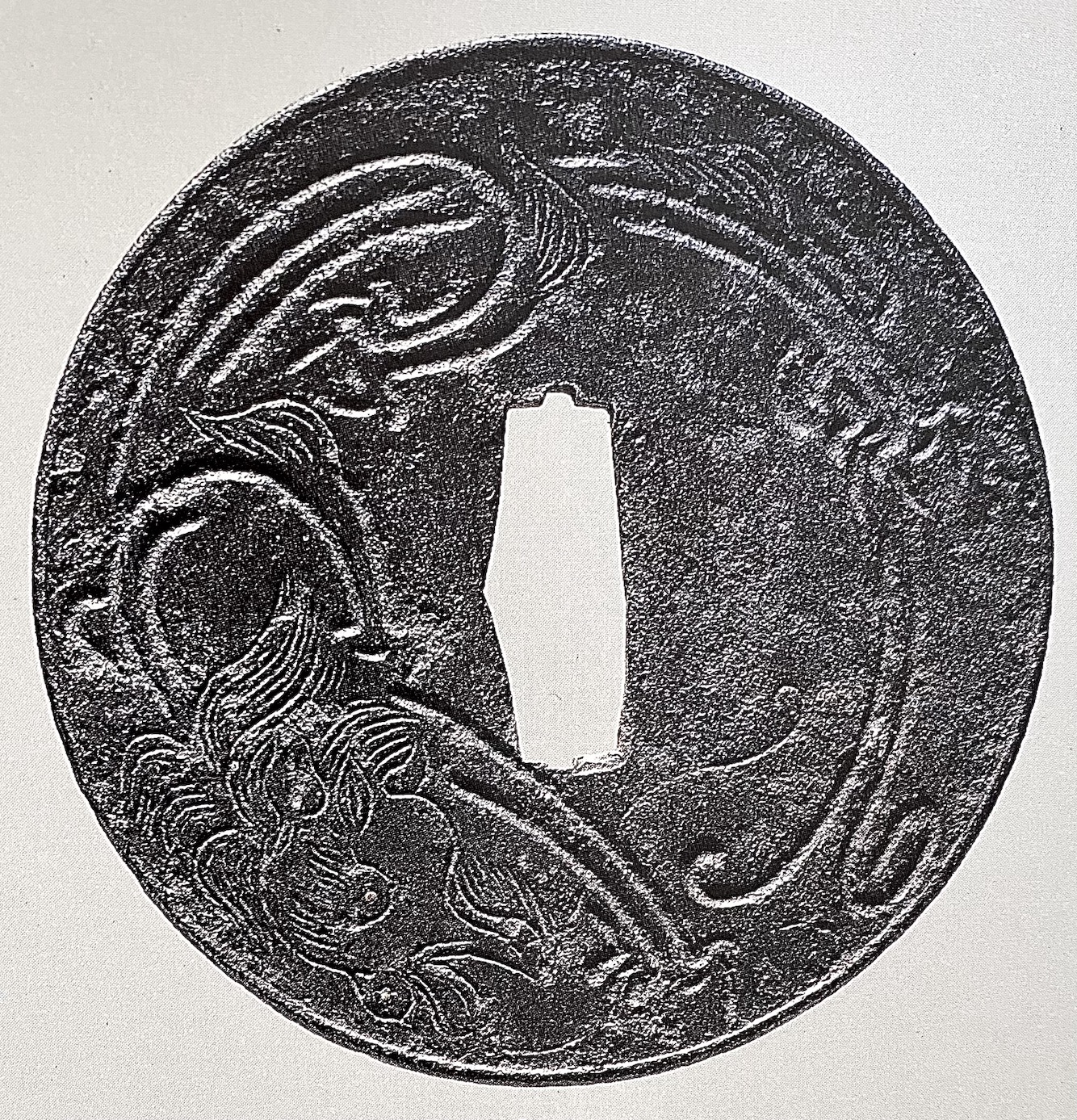
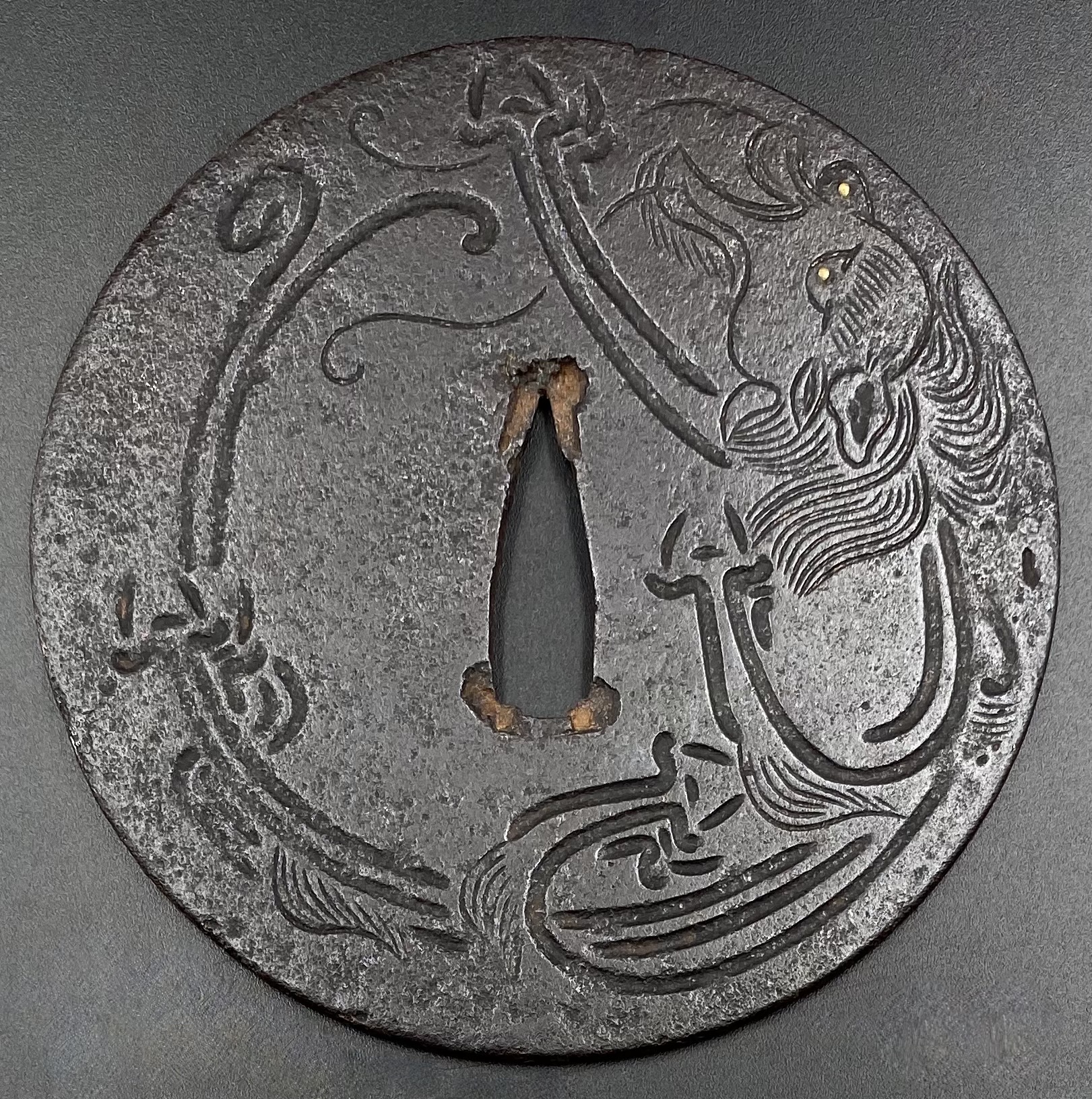

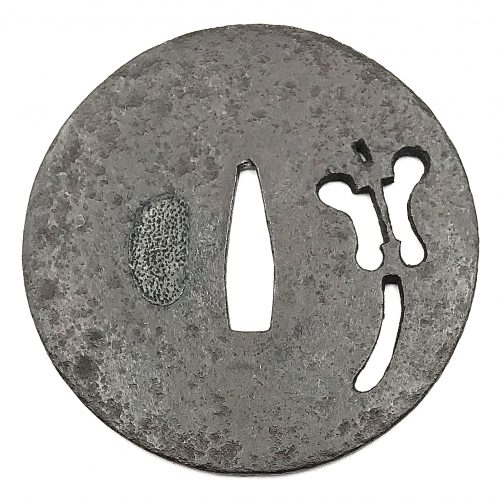
 Two other examples of the same design may be found at: (1) Christie, Manson & Woods auction sales “Kotetsu”, 1980, page 12, №10 and (2) Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections №36, pp. 18-19. Both have raised mimi, the latter classified as Katchushi tsuba.
More about
Two other examples of the same design may be found at: (1) Christie, Manson & Woods auction sales “Kotetsu”, 1980, page 12, №10 and (2) Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections №36, pp. 18-19. Both have raised mimi, the latter classified as Katchushi tsuba.
More about 




