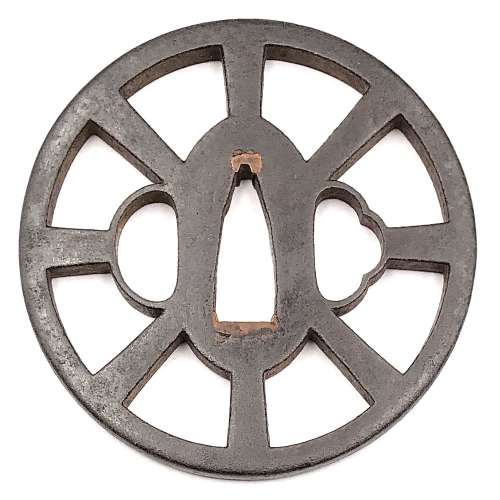
Merrily Baird in her book "Symbols of Japan" [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001] provides the following explanation of the Wheel-of-the-Law symbol: "The Wheel-of-the-Law or Golden Wheel (rimbo, kinrin) has its origins in India, where it is known as chakra. [...] In Buddhist practice, it has been represented with eight spokes, reflecting the eight-fold path to overcoming worldly desire, and it signifies that all illusions will be crushed by the faith's enlightenment. [...] The Wheel-of-the-Law is an attribute of such deities as Senju Kannon, the Thousand-Armed Kannon, and Dainichi Nyorai, the all-illuminating solar figure who is the principal deity for Shingon Buddhism. From the Edo period on, the wheel also has been used in a secular manner", e.g. on family crests.
-
 Iron tsuba of round form with design of wheel (kuruma) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Yagyu school. Signed of the face: Fukui Tsuguzaemon. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun/Enppo era). Height: 76.7 mm. Width: 76.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.2 mm. Center thickness: 5.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 203: "This design of spoke wheel relates to the 'circular principle' found in the Yagyu philosophy. Although it is very faint, Fukui Tsuguzaemon's signature is visible. Without a signature and based on appearance alone, it would undoubtable attributed to a later period".
Iron tsuba of round form with design of wheel (kuruma) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Yagyu school. Signed of the face: Fukui Tsuguzaemon. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun/Enppo era). Height: 76.7 mm. Width: 76.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.2 mm. Center thickness: 5.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 203: "This design of spoke wheel relates to the 'circular principle' found in the Yagyu philosophy. Although it is very faint, Fukui Tsuguzaemon's signature is visible. Without a signature and based on appearance alone, it would undoubtable attributed to a later period". -
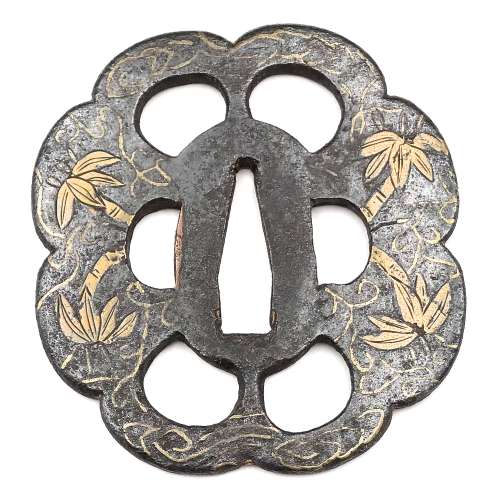 Iron tsuba of 8-lobed form pierced with six openings (sukashi) and decorated with design of bamboo and arabesque in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan). Two of the openings serve as hitsu-ana. The design on the face represents bamboo trunks and leaves, clouds, waves, and vines; on the back - vines and leaves, that forms an arabesque (karakusa) motif. Rounded square rim. 'Silver' patina. Hitsu-ana with copper sekigane. Heianjō (most probable) or Kaga-Yoshirō school. Late Muromachi or Momoyama period; 16th century. Size: Height: 74.6 mm; Width: 69.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.2 mm. Weight: 113.9 g. Provenance: Gary D. Murtha. This tsuba is illustrated at: Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro by Gary D. Murtha [GDM Publications, 2016, p. 48]: "Iron, 80x75x3 mm tsuba with brass karakusa vines and leaves on one side with bamboo, leaves, and clouds on the reverse. This tsuba is one of those pieces that might be classified as Onin or Heianjo work, but the flush inlay tips it to the Heianjo side. Late Muromachi period." I would like to add that it easily may also be classified as Kaga-Yoshirō. Robert Haynes in Study Collection.., page 32, illustrates a look-a-like example, and writes: "This style of inlay, where the designs on the face and the back are very different, was common to the work of artists in Kyoto in the Momoyama period."
Iron tsuba of 8-lobed form pierced with six openings (sukashi) and decorated with design of bamboo and arabesque in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan). Two of the openings serve as hitsu-ana. The design on the face represents bamboo trunks and leaves, clouds, waves, and vines; on the back - vines and leaves, that forms an arabesque (karakusa) motif. Rounded square rim. 'Silver' patina. Hitsu-ana with copper sekigane. Heianjō (most probable) or Kaga-Yoshirō school. Late Muromachi or Momoyama period; 16th century. Size: Height: 74.6 mm; Width: 69.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.2 mm. Weight: 113.9 g. Provenance: Gary D. Murtha. This tsuba is illustrated at: Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro by Gary D. Murtha [GDM Publications, 2016, p. 48]: "Iron, 80x75x3 mm tsuba with brass karakusa vines and leaves on one side with bamboo, leaves, and clouds on the reverse. This tsuba is one of those pieces that might be classified as Onin or Heianjo work, but the flush inlay tips it to the Heianjo side. Late Muromachi period." I would like to add that it easily may also be classified as Kaga-Yoshirō. Robert Haynes in Study Collection.., page 32, illustrates a look-a-like example, and writes: "This style of inlay, where the designs on the face and the back are very different, was common to the work of artists in Kyoto in the Momoyama period." -
-
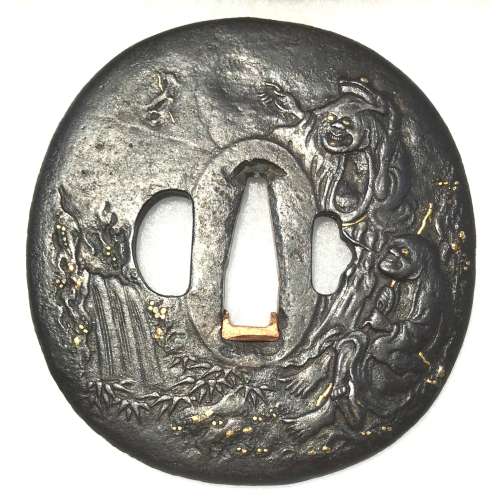

Iron tsuba of oval form with the design of two immortals (Gama Sennin with the toad upon his head and Tekkai Sennin with his iron crutch) beside a waterfall carved in low relief with a high relief effect (takabori) and with details inlaid in gold. A waterfall carved on the reverse. Nakago-ana is plugged with copper sekigane. Unsigned. Allegedly, Mito School.
Edo period, ca. 1700.
Size: Height: 87.0 mm; Width: 82.8 mm; Thickness: 4.4 mm; Weight: 179 g.
No longer available. -
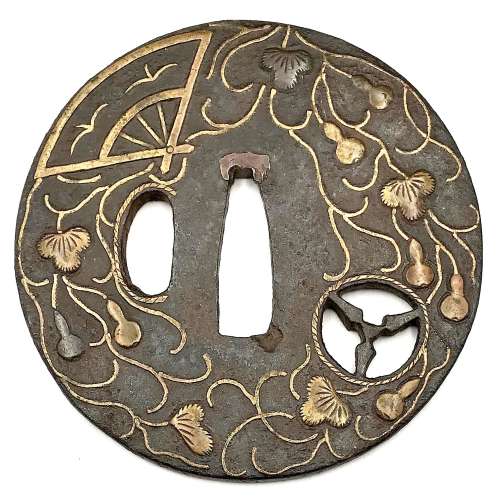

Iron tsuba of round form inlaid with brass and shakudo (suemon-zōgan) with a design of tendrils, leaves, double gourds, and folding fan with two wild geese on the face and the same design only with a fan with two interlocked rings (wachigai) on the back. Design is supplemented with a round family crest (mon) of three fans in openwork (sukashi). Hitsu-ana and the mon are outlined with brass rope. Copper sekigane.
Some attribute such tsuba as belonging to Heianjō or even Yoshirō School, and date them to Momoyama period. I keep this piece under Ōnin rubric, late Muromachi, but this is just a question of personal preference.Some inlay is missing, some repaired; traces of rust. Otherwise - decent condition.
Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Size: 77.4 x 77.1 x 3.8 (center), 3.2 (rim) mm -
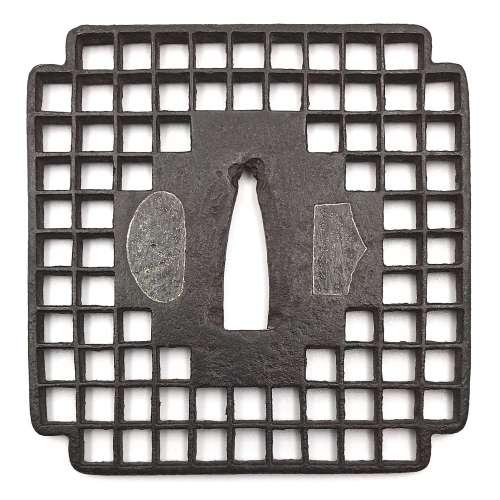

Iron tsuba of square with cut-off edges form (sumi-iri-kakugata) with lattice design in openwork (sukashi) and solid center. Hitsu-ana plugged with lead.
Unsigned. Late Muromachi period, ca. 16th century.
Size: 81.3 x 80.0 x 3.6 mm References: 1) Tsuba Kanshoki. Kazutaro Torogoye, 1975, p. 95, lower image. It's also called Kyō shōami. 2) KTK-11: Koshi motif, Late Muromachi (16th c.) -
 Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞]; a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865).
Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞]; a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865).Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche.
Publisher: Kojimaya Jūbei (c. 1797-1869), seal: Hanmoto, Jū [板元, 十] (Marks 19-043 | 264c).
Double nanushi censor seals: Mera & Watanabe – Kaei 4 (1851).
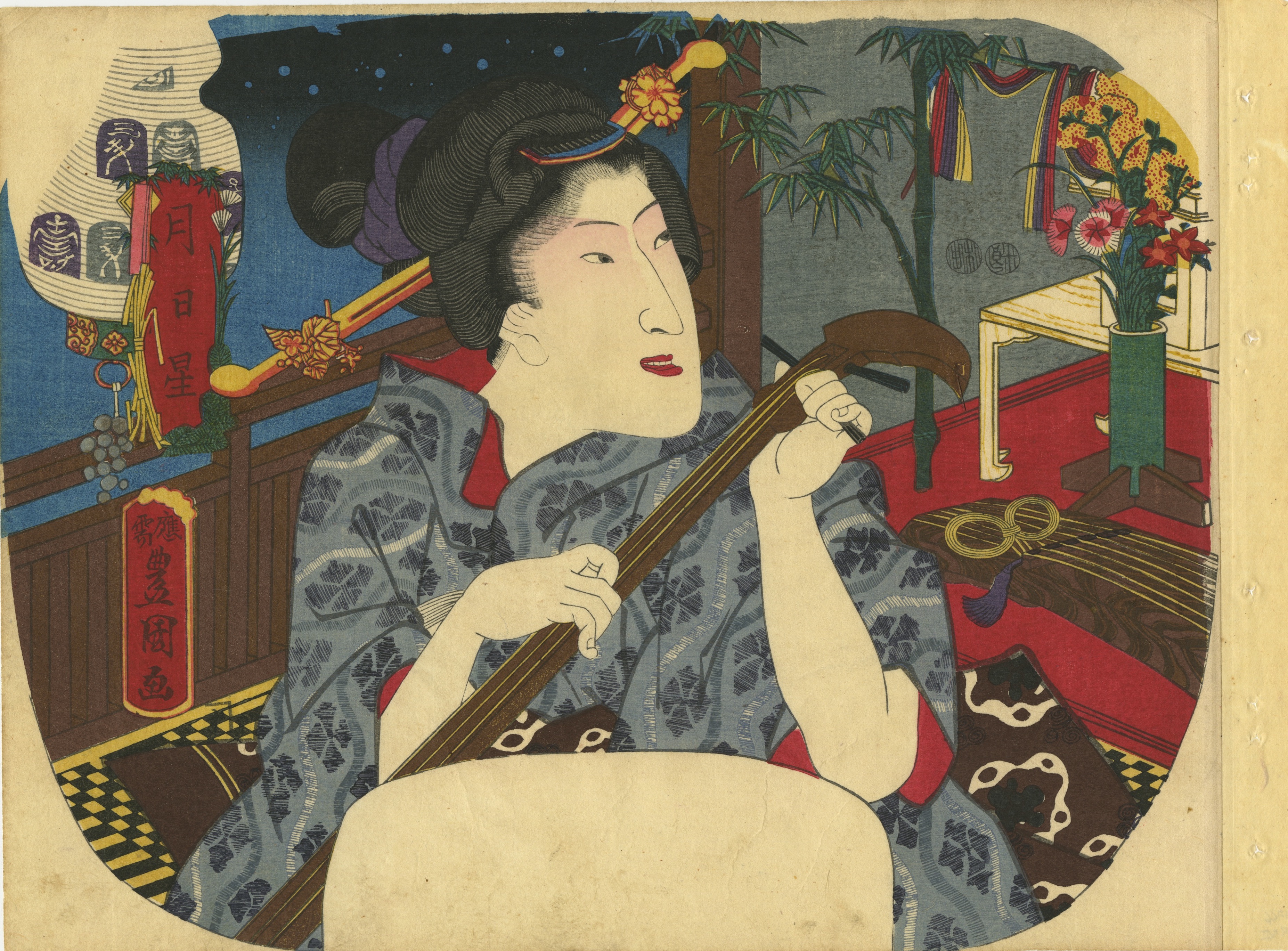
Uncut fan print (uchiwa-e), 298 x 228 mm depicting a young woman adjusting her hairpin and holding a portable lantern (andon) on a marine background with the full moon, nearby boats and distant cormorant fishers. -
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, c. 1815 – 1869). Double nanushi censor seals: Hama & Magome, Kaei 2-5 (1849 – 1852). An uncut fan print (uchiwa-e, 220 x 292 mm) depicts a beautiful woman sitting on a balcony overlooking a bay and reading a book. Above the book, there is an obi with a pattern of stripes or modified key fret motif, with lettering that reads: 菅原島 [Sugawara-jima] and 美立 [mitate]. The lettering and the blossoming plum branch next to the obi provide an allusion to Sugawara no Michizane [菅原 道真/菅原 道眞] (Japanese, 845 – 903) - a prominent scholar and poet of Heian period exiled from Kyoto to the island of Kyushu as a result of another courtier's slander. A legend says that his beloved plum tree was so fond of its master that it flew to Kyushu with Sugawara. The Davis Museum at Wellesley College describes the print as belonging to the series A Parody of Sugawara Stripe Patterns (Mitate Sugawara-jima). To make the fact of an allusion transparent, Kunisada had changed the usual way of writing "Sugawara stripes" from 菅原縞 to 菅原島 and "mitate" from 見立 to 美立. An unusual spelling was also used to provide additional information to the reader in other cultures. E.g. during the Prohibition Era, the West Coast United States speakeasy bars and bordellos misspelt the items on a menu ("scollops") or in a neon sign ("Martuni's") to tell: here we have more pleasures for you than you may have expected. After Tenpō reforms, the printing of bijin-ga (美人画, "picture of beautiful woman") images was restricted. Our print disguises a typical bijin-ga as an advertisement of an obi (帯, a kimono sash) fabric pattern. "The market of portraits was satisfied and the authorities fooled" [Rebecca Salter. Japanese popular prints. — Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press, 2006].
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, c. 1815 – 1869). Double nanushi censor seals: Hama & Magome, Kaei 2-5 (1849 – 1852). An uncut fan print (uchiwa-e, 220 x 292 mm) depicts a beautiful woman sitting on a balcony overlooking a bay and reading a book. Above the book, there is an obi with a pattern of stripes or modified key fret motif, with lettering that reads: 菅原島 [Sugawara-jima] and 美立 [mitate]. The lettering and the blossoming plum branch next to the obi provide an allusion to Sugawara no Michizane [菅原 道真/菅原 道眞] (Japanese, 845 – 903) - a prominent scholar and poet of Heian period exiled from Kyoto to the island of Kyushu as a result of another courtier's slander. A legend says that his beloved plum tree was so fond of its master that it flew to Kyushu with Sugawara. The Davis Museum at Wellesley College describes the print as belonging to the series A Parody of Sugawara Stripe Patterns (Mitate Sugawara-jima). To make the fact of an allusion transparent, Kunisada had changed the usual way of writing "Sugawara stripes" from 菅原縞 to 菅原島 and "mitate" from 見立 to 美立. An unusual spelling was also used to provide additional information to the reader in other cultures. E.g. during the Prohibition Era, the West Coast United States speakeasy bars and bordellos misspelt the items on a menu ("scollops") or in a neon sign ("Martuni's") to tell: here we have more pleasures for you than you may have expected. After Tenpō reforms, the printing of bijin-ga (美人画, "picture of beautiful woman") images was restricted. Our print disguises a typical bijin-ga as an advertisement of an obi (帯, a kimono sash) fabric pattern. "The market of portraits was satisfied and the authorities fooled" [Rebecca Salter. Japanese popular prints. — Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press, 2006]. -
 Artist: Utagawa Yoshikazu [歌川芳員] (Japanese, fl. c. 1850 – 1870). Publisher: Wakasaya Yoichi [若狭屋与市] (Japanese, fl. 1794 – 1897). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: 1861 (Man'en 2 / Bunkyū 1, from 19/02).
Artist: Utagawa Yoshikazu [歌川芳員] (Japanese, fl. c. 1850 – 1870). Publisher: Wakasaya Yoichi [若狭屋与市] (Japanese, fl. 1794 – 1897). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: 1861 (Man'en 2 / Bunkyū 1, from 19/02). -
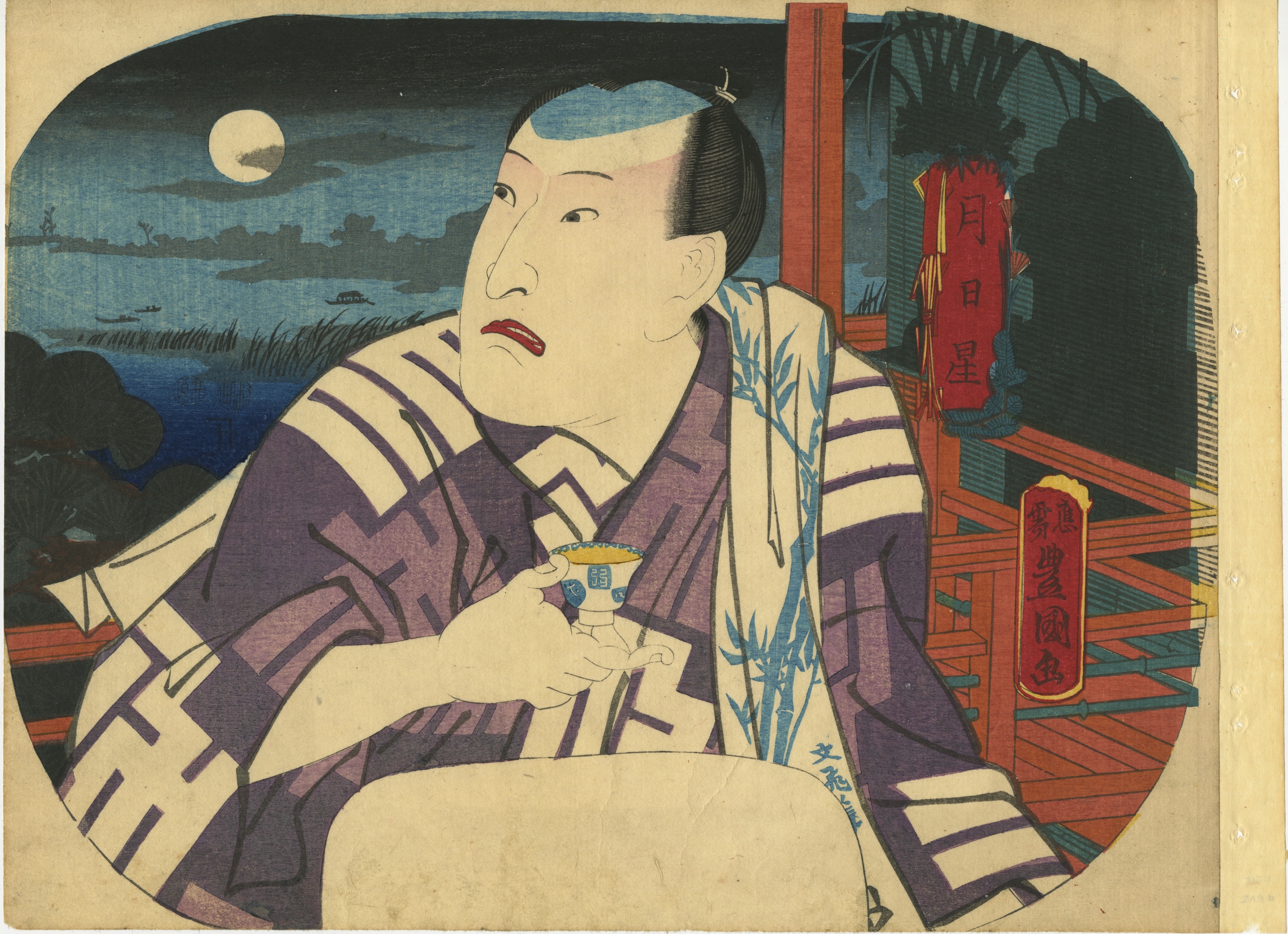
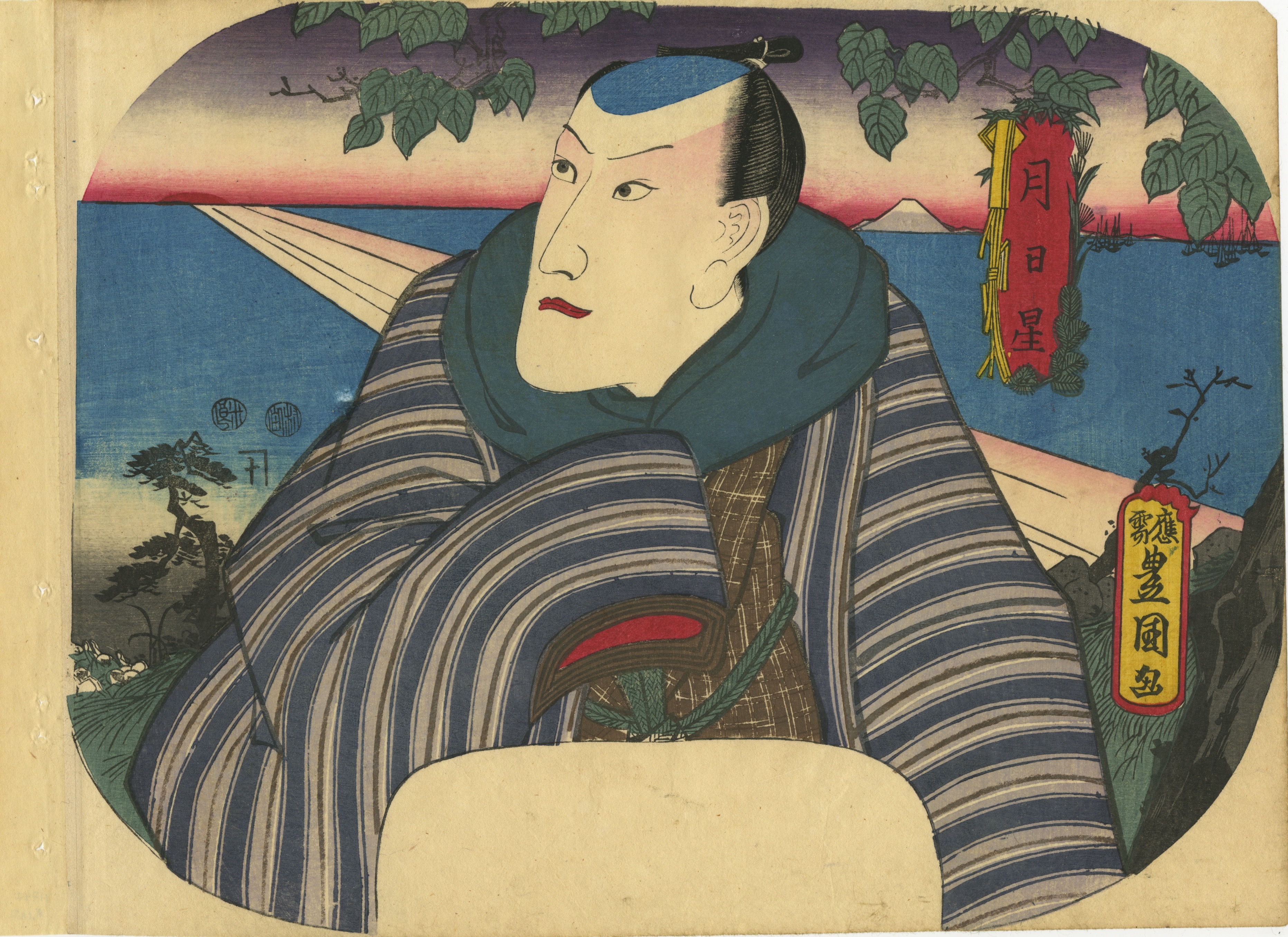
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Ōju Toyokuni ga [応需豊国画] in a toshidama cartouche. Double nanushi censor seals Mera & Murata (1846-50). Publisher: Kojimaya Jūbei [小嶋屋重兵衛] (Japanese, fl. c. 1797 – 1869). A gentleman, probably a kabuki actor Nakamura Utaemon IV [中村歌右衛門] (Nakamura Shikan II, Nakamura Tsurusuke I, Nakamura Tōtarō, Japanese, 1796 – 1852) drinking tea on a veranda under the shining moon. Series Moon, Sun, Stars [月日星] (tsuki-hi-hoshi/boshi), the three sources of light (sankō) [三光]:
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Ōju Toyokuni ga [応需豊国画] in a toshidama cartouche. Double nanushi censor seals Mera & Murata (1846-50). Publisher: Kojimaya Jūbei [小嶋屋重兵衛] (Japanese, fl. c. 1797 – 1869). A gentleman, probably a kabuki actor Nakamura Utaemon IV [中村歌右衛門] (Nakamura Shikan II, Nakamura Tsurusuke I, Nakamura Tōtarō, Japanese, 1796 – 1852) drinking tea on a veranda under the shining moon. Series Moon, Sun, Stars [月日星] (tsuki-hi-hoshi/boshi), the three sources of light (sankō) [三光]: -
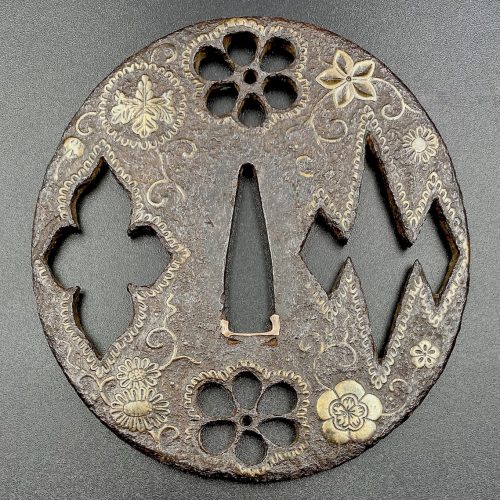 Iron tsuba of a round form (maru-gata) pierced (sukashi) with two six-petal flowers at 6 and 12 o’clock and modified lozenges at 3 and 9 o’clock, and inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils and flowers (chrysanthemum, cherry blossom, Chinese bellflower, paulownia); openings outlined with scalloped brass wire. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer on the surface. Nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Some elements of inlay missing. The rim with conspicuous tekkotsu, quite worn. Measurements: Height 92.0 mm; Width 86.3 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 3.2 mm, at rim 4.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier.
Iron tsuba of a round form (maru-gata) pierced (sukashi) with two six-petal flowers at 6 and 12 o’clock and modified lozenges at 3 and 9 o’clock, and inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils and flowers (chrysanthemum, cherry blossom, Chinese bellflower, paulownia); openings outlined with scalloped brass wire. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer on the surface. Nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Some elements of inlay missing. The rim with conspicuous tekkotsu, quite worn. Measurements: Height 92.0 mm; Width 86.3 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 3.2 mm, at rim 4.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier. -
 Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-124 (plates with photographs of 241 items), [2] 127-171 [3]. Kyō ware [京焼] (Kyō-yaki) – pottery from Kyoto. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-124 (plates with photographs of 241 items), [2] 127-171 [3]. Kyō ware [京焼] (Kyō-yaki) – pottery from Kyoto. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
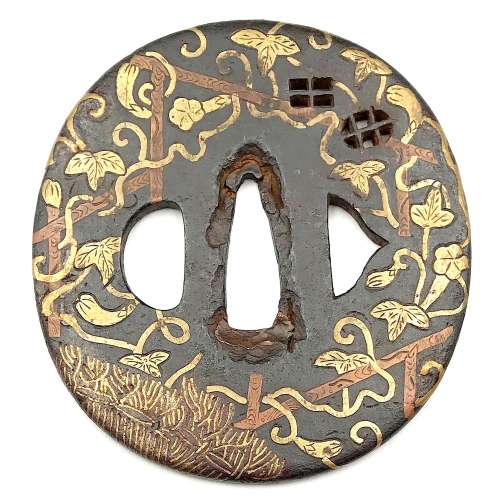 Iron tsuba of oval form with design of a gourd or aubergine vine with fruits, leaves, and blossoms climbing a trellis, and a fence in yellow brass and red copper flat inlay (hira-zōgan); inlay engraved. Two latticed windows represented by openwork (sukashi). The iron web has deep black patina. The seller attributes this tsuba to Heianjo-Namban school, whatever it means. Momoyama or early Edo period, 17th century. Kaga or Heianjō School. Unsigned. Height: 77.3, Width: 73.1, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm.
Iron tsuba of oval form with design of a gourd or aubergine vine with fruits, leaves, and blossoms climbing a trellis, and a fence in yellow brass and red copper flat inlay (hira-zōgan); inlay engraved. Two latticed windows represented by openwork (sukashi). The iron web has deep black patina. The seller attributes this tsuba to Heianjo-Namban school, whatever it means. Momoyama or early Edo period, 17th century. Kaga or Heianjō School. Unsigned. Height: 77.3, Width: 73.1, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. -
 Mori Sosen (1747-1821). Seated Monkey. Hanging scroll painting. Ink and colour on silk. Signed: Sosen. Sealed: Sosen. 28.8 x 33.3 cm.
Mori Sosen (1747-1821). Seated Monkey. Hanging scroll painting. Ink and colour on silk. Signed: Sosen. Sealed: Sosen. 28.8 x 33.3 cm. -
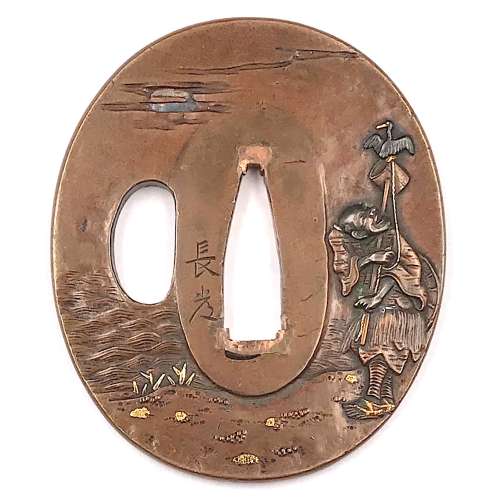 Copper (suaka) tsuba of oval form carved in relief, pierced and inlaid with soft metals (gold, shakudō, shibuichi or silver) with a cormorant fisherman (ushō) and moon motif on the face and a boat among the bank reeds on the reverse. Signed: Nagatsune. Box inscription: Tsuba with cormorant fishing, made by Nagatsune. Dimensions: 62.7 mm x 53.2 mm x 4.2 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th century. Nagatsune (1721-1787), 1st generation master of Inchinomiya School in Kyoto, adopted son of the gilder Nagayoshi, student of Yasui Takanaga [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', p. 26]. Detailed account of the school is given at The Japanese toso-kinko Schools.// Lulu Inc., 2012 by Markus Sesko, pp. 104-108. Nagatsune's biographical sketch can be found there on pp. 104-106. "What Sōminis in the East (Edo), Nagatsune is in the West (Kyōto)." “Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. […] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one’s master and keen eyesight.” – from Merrily Baird 'Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design.' //Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also in this collection: TSU-241 and TSU-0096
Copper (suaka) tsuba of oval form carved in relief, pierced and inlaid with soft metals (gold, shakudō, shibuichi or silver) with a cormorant fisherman (ushō) and moon motif on the face and a boat among the bank reeds on the reverse. Signed: Nagatsune. Box inscription: Tsuba with cormorant fishing, made by Nagatsune. Dimensions: 62.7 mm x 53.2 mm x 4.2 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th century. Nagatsune (1721-1787), 1st generation master of Inchinomiya School in Kyoto, adopted son of the gilder Nagayoshi, student of Yasui Takanaga [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', p. 26]. Detailed account of the school is given at The Japanese toso-kinko Schools.// Lulu Inc., 2012 by Markus Sesko, pp. 104-108. Nagatsune's biographical sketch can be found there on pp. 104-106. "What Sōminis in the East (Edo), Nagatsune is in the West (Kyōto)." “Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. […] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one’s master and keen eyesight.” – from Merrily Baird 'Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design.' //Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also in this collection: TSU-241 and TSU-0096The design was popular among the tsuba makers. We find one in the Alexander G. Moslé collection [Japanese Sword Fittings from the Alexander G. Moslé Collection; Sebastian Izzard LLC, 2004, page 90, №123] signed Nagatsune with kaō: Tsuba with cormorant fisherman, moon, and boat. Squared-oval shibuichi plate, slightly raised rim, engraved, pierced, and inlaid with soft metals in relief. 6.7 x 5.8 cm.

Alexander G. Moslé collection №123.
Another reference: Lundgren Collection, 1990, page 86 №207: Sword guard with design of ushō (person who fishes with cormorants). Signed by Nagatsune. Ichinomiya school. 6.45 x 5.95 x 0.40 cm. Polished shibuichi taka-bori relief, gold and silver inlay. Edo period, 18th century.

Lundgren Collection №207:
-
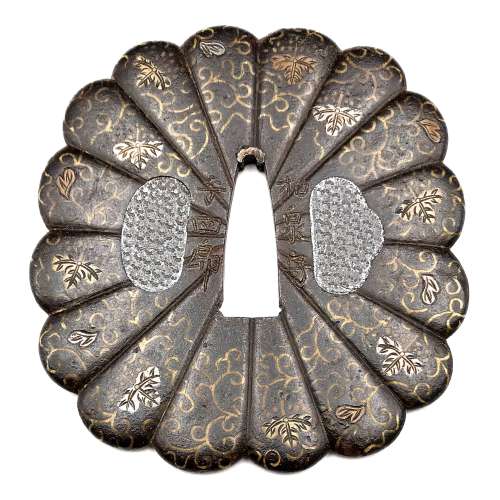 The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:
The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:"Early signed example of the work of Koike Naomasa. The kiku shape iron plate is well finished. The flush inlay is brass, for the scroll work on both sides, with the leaves and kiri mon in brass, copper and silver with strong detail carving. Some of the inlay goes almost over the edge, which is goishi gata. The large hitsuana are plugged in lead with starburst kokuin surface design. [...]The face is signed in deep bold kanji: Koike Naomasa; the back is signed: Izumi no Kami, on the right and Yoshiro on the left. There are one or two small pieces of inlay missing. Sold by Sotheby London, Oct. 27, 1981, lot 368. Height = 86 mm, thickness (seppa-dai) = 3.75 mm, (edge) = 4 mm."
Another similar example presented at: "Tsuba" by Günter Heckmann, 1995, №T55 — "Designation: Koike Naomasa. Mid Edo, end of the 17th century. Iron, hira-zogan in brass, copper, silver and shakudo, katakiri-bori. Tendrils and leaves. 87.0 x 78.0 x 4.0 mm." Reference: Japanische Schwertzierate by Lumir Jisl, 1967, page. 13. [SV: Actually, his tsuba is signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back; and Koike Naomasa on the front, exactly as Robert Haynes's tsuba. Dating this tsuba Mid-Edo, 17th century may be considered a misattribution]. More details regarding the Yoshirō tsuba. -
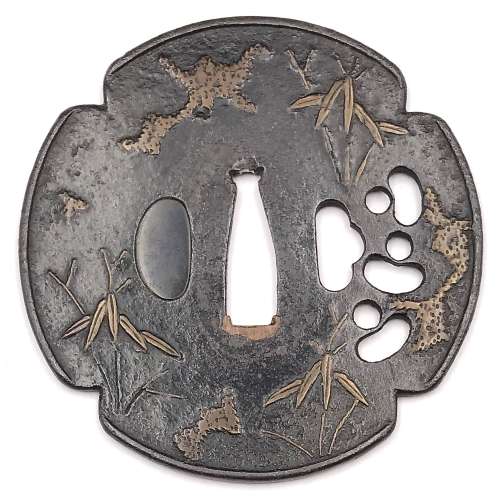 Iron tsuba of four-lobbed mokkō form (possibly it was circular and then altered to produce the mokkō) with slightly raised rim decorated with three kukurizaru ('tied up monkey' toy) in openwork (sukashi) next to kogai-hitsu-ana; inlaid in red-ish copper (suaka) with the design of bamboo stems and leaves, and shapeless masses which most probably represent snow. Kozuka-hitsu-ana plugged with shakudo. Probably original kogai-hitsu-ana. Copper sekigane. Surface still covered with lacquer (urushi). Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Size: 86.1 x 85.8 x 2.6 mm NBTHK Certificate №4002543: Hozon - "Worthy of preservation" (Attribution: Mumei Heianjō Zōgan)
Iron tsuba of four-lobbed mokkō form (possibly it was circular and then altered to produce the mokkō) with slightly raised rim decorated with three kukurizaru ('tied up monkey' toy) in openwork (sukashi) next to kogai-hitsu-ana; inlaid in red-ish copper (suaka) with the design of bamboo stems and leaves, and shapeless masses which most probably represent snow. Kozuka-hitsu-ana plugged with shakudo. Probably original kogai-hitsu-ana. Copper sekigane. Surface still covered with lacquer (urushi). Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Size: 86.1 x 85.8 x 2.6 mm NBTHK Certificate №4002543: Hozon - "Worthy of preservation" (Attribution: Mumei Heianjō Zōgan) -
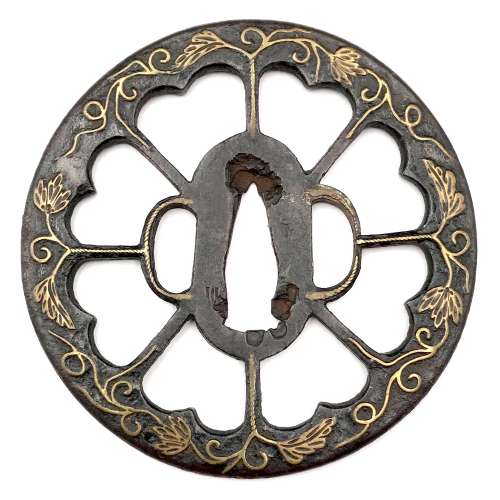 Iron tsuba of round form represents an eight-spoke Wheel-of-the-Law and in the same time (because of the inner shape of cut-outs) - a sixteen-petal imperial chrysanthemum in openwork (sukashi). Decorated on both sides with vines, leaves, and tendrils in suemon-zōgan and sen-zōgan. Spokes and hitsu-ana decorated with rope-like linear brass inlay (nawame-zōgan). A somewhat look-a-like tsuba is referenced in Gary D. Murtha's Japanese Sword Guards. Onin-Heianjo-Yoshiro book on page 61. Mr. Murtha attributes his piece to Heianjo school of Azuchi-Momoyama or early Edo period. However, tsuba in this collection looks older and bolder than the one in his book. It is larger (84 mm vs. his 66 mm), the spokes are longer, the inlay is of better quality, it is relatively thin, with deep black patina, and with the traces of lacquer (urushi). This may indicate that this tsuba belongs to Ōnin school and dates at least to late Muromachi period, ca. 1550, if not 1450 AD. Mid to late Muromachi period (ca. 1450-1550). Dimensions: 84.3 x 83.2 x 3.2 mm "In Japan, the Wheel-of-the-Law is an attribute of such deities as Senju Kannon, the Thousand-Armed Kannon, and Dainichi Nyorai, the principal deity of Shingon Buddhism [Merrily Baird]. May be used as a family crest (mon).
Iron tsuba of round form represents an eight-spoke Wheel-of-the-Law and in the same time (because of the inner shape of cut-outs) - a sixteen-petal imperial chrysanthemum in openwork (sukashi). Decorated on both sides with vines, leaves, and tendrils in suemon-zōgan and sen-zōgan. Spokes and hitsu-ana decorated with rope-like linear brass inlay (nawame-zōgan). A somewhat look-a-like tsuba is referenced in Gary D. Murtha's Japanese Sword Guards. Onin-Heianjo-Yoshiro book on page 61. Mr. Murtha attributes his piece to Heianjo school of Azuchi-Momoyama or early Edo period. However, tsuba in this collection looks older and bolder than the one in his book. It is larger (84 mm vs. his 66 mm), the spokes are longer, the inlay is of better quality, it is relatively thin, with deep black patina, and with the traces of lacquer (urushi). This may indicate that this tsuba belongs to Ōnin school and dates at least to late Muromachi period, ca. 1550, if not 1450 AD. Mid to late Muromachi period (ca. 1450-1550). Dimensions: 84.3 x 83.2 x 3.2 mm "In Japan, the Wheel-of-the-Law is an attribute of such deities as Senju Kannon, the Thousand-Armed Kannon, and Dainichi Nyorai, the principal deity of Shingon Buddhism [Merrily Baird]. May be used as a family crest (mon).
Gary D. Murtha's tsuba on page 61.





