-
 Hardcover volume, 35 x 26.8 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a slipcase, the outer case missing, pp.: [4] [1] 2-136 (plates with photographs of 211 items), [2] 139-166 [4]. Kutani ware [九谷焼] (Kutani-yaki); old kutani [古九谷] (kokutani) – ceramic objects produced in Kutani in the 17th century. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35 x 26.8 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a slipcase, the outer case missing, pp.: [4] [1] 2-136 (plates with photographs of 211 items), [2] 139-166 [4]. Kutani ware [九谷焼] (Kutani-yaki); old kutani [古九谷] (kokutani) – ceramic objects produced in Kutani in the 17th century. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35.1 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 27.8 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-108 (plates with photographs of 217 items), [2] [111] 112-150 [3]. Imari ware [伊万里焼] (Imari-yaki) – ceramics produced in and around the area of Arita, in the former Hizen Province, northwestern Kyūshū. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Old imari [古伊万里] (koimari) – book title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35.1 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 27.8 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-108 (plates with photographs of 217 items), [2] [111] 112-150 [3]. Imari ware [伊万里焼] (Imari-yaki) – ceramics produced in and around the area of Arita, in the former Hizen Province, northwestern Kyūshū. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Old imari [古伊万里] (koimari) – book title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a slipcase, the outer case missing, pp.: [4] [1] 2-116 (plates with photographs of 202 items), [2] 119-154 [4]. Ninsei [仁清] and Kenzan [乾山] ceramics produced by Ninsei Nonomura [野々村仁清] (Japanese, c. 1640 – c. 1690) and Ogata Kenzan [尾形 乾山] (Japanese, 1663 – 1743), respectively. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a slipcase, the outer case missing, pp.: [4] [1] 2-116 (plates with photographs of 202 items), [2] 119-154 [4]. Ninsei [仁清] and Kenzan [乾山] ceramics produced by Ninsei Nonomura [野々村仁清] (Japanese, c. 1640 – c. 1690) and Ogata Kenzan [尾形 乾山] (Japanese, 1663 – 1743), respectively. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-124 (plates with photographs of 241 items), [2] 127-171 [3]. Kyō ware [京焼] (Kyō-yaki) – pottery from Kyoto. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-124 (plates with photographs of 241 items), [2] 127-171 [3]. Kyō ware [京焼] (Kyō-yaki) – pottery from Kyoto. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche Block carver: Yokokawa Takejirō [横川竹二郎] (Japanese, fl. 1845 – 1863), seal: 彫竹 – hori Take. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. c. 1845 – 1847). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 238 x 304 mm. Title: Saiko (West River) [西江]; 西江 means the Xi River in China. Series: Chronicles of Elegant Women [風雅女史傳] (Fūga joshiden). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: Ansei 6 (1859). Other prints from the same series in this collection: SVJP-0216.2016 — Princess Sotoori:
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche Block carver: Yokokawa Takejirō [横川竹二郎] (Japanese, fl. 1845 – 1863), seal: 彫竹 – hori Take. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. c. 1845 – 1847). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 238 x 304 mm. Title: Saiko (West River) [西江]; 西江 means the Xi River in China. Series: Chronicles of Elegant Women [風雅女史傳] (Fūga joshiden). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: Ansei 6 (1859). Other prints from the same series in this collection: SVJP-0216.2016 — Princess Sotoori:

-
 Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):
Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):- Sake set [shuki, 酒器], namely flask, ladle, and cups
- Cloves [choji, 丁子]
- Purse of inexhaustible reaches [kinchaku, 巾着]
- Magic mallet [kozuchi, 小槌]
- Key to the storehouse of the Gods [kagi, 鍵]
- Rhombus, or Lozenge (hosho, 方勝), with the second ideograph meaning victory.
- Sacred (or wish-granting) gem, or jewel [hōju, 宝珠]
- Hats of invisibility [kakuregasa, 隠れ笠]
-
 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Kiri-mon
Katakura-mon
-
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche Publisher: Iseya Ichiemon [伊勢屋市右衛門] (Japanese, fl. c. 1820s – c. 1860s); seal Tsuji [辻] (Marks 16-029). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 225 x 295 mm, plus 10 mm paper strip glued on top (235 mm total height). Title: Plucking Popular Songs in Those Days [時世葉歌の爪弾] (Imayo ha-uta no tsuma-biki). Date seal and aratame seal: Ansei 3 (1856). Seller's Description: Uchiwa-e; picture intended for a summer fan. Here we see a relaxed beauty wearing loose layers of kimono and playing her shamisen instrument. She appears to be in the happy mood of spring, her singing inspired by the cherry blossoms in full bloom that we see outside of her window. She enjoys leisurely plucking with the plectrum of the shamisen and singing “ha-uta” (popular) songs. The title Ha-uta [葉歌] is normally written 端歌, which indicates a certain category of popular songs accompanied by shamisen with short texts that are drawn from daily life. Here however, the title葉歌 uses phonetically the same “ha葉“, referring to the title of the book of a collection of ha-uta songs, Matsu no ha [松の], which was published in five volumes in 1703 by Shûshôken 秀松軒. It is said that this collection of songs was written and sung by the blind (who were often musicians by livelihood). Behind her, lying on the window sill, we see two ha-uta songbooks, one open and one closed. The last half of the title tsuma-biki [爪弾] translates “to pluck with fingers” instead of a plectrum, which is the usual way of playing the shamisen.
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche Publisher: Iseya Ichiemon [伊勢屋市右衛門] (Japanese, fl. c. 1820s – c. 1860s); seal Tsuji [辻] (Marks 16-029). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 225 x 295 mm, plus 10 mm paper strip glued on top (235 mm total height). Title: Plucking Popular Songs in Those Days [時世葉歌の爪弾] (Imayo ha-uta no tsuma-biki). Date seal and aratame seal: Ansei 3 (1856). Seller's Description: Uchiwa-e; picture intended for a summer fan. Here we see a relaxed beauty wearing loose layers of kimono and playing her shamisen instrument. She appears to be in the happy mood of spring, her singing inspired by the cherry blossoms in full bloom that we see outside of her window. She enjoys leisurely plucking with the plectrum of the shamisen and singing “ha-uta” (popular) songs. The title Ha-uta [葉歌] is normally written 端歌, which indicates a certain category of popular songs accompanied by shamisen with short texts that are drawn from daily life. Here however, the title葉歌 uses phonetically the same “ha葉“, referring to the title of the book of a collection of ha-uta songs, Matsu no ha [松の], which was published in five volumes in 1703 by Shûshôken 秀松軒. It is said that this collection of songs was written and sung by the blind (who were often musicians by livelihood). Behind her, lying on the window sill, we see two ha-uta songbooks, one open and one closed. The last half of the title tsuma-biki [爪弾] translates “to pluck with fingers” instead of a plectrum, which is the usual way of playing the shamisen. -
 Utagawa Sadahide, a.k.a. Gountei Sadahide (Japanese, 1807 – c. 1878–1879), 五雲亭 貞秀, 歌川 貞秀, Yamaguchiya Tōbei, Yokohama kōeki seiyōjin nimotsu unsō no zu - Western traders loading cargo in Yokohama - 横浜交易西洋人荷物運送之圖, 1861, Woodblock print (nishiki-e); ink and color on paper, Horizontal Ōban Pentaptych: 5 x (37 x 25.5 cm), Alternative title: Picture of Western Traders at Yokohama Transporting Merchandise (Cat. Reisonée: Yokohama ukiyo-e, Yurindo, 1979: №50). Japanese pentaptych print shows an American ship in the harbor at Yokohama, Japan; small boats ferry cargo which is being carried up a gangplank contributing to the bustle of activity on the main deck. April, 1861. SOLD
Utagawa Sadahide, a.k.a. Gountei Sadahide (Japanese, 1807 – c. 1878–1879), 五雲亭 貞秀, 歌川 貞秀, Yamaguchiya Tōbei, Yokohama kōeki seiyōjin nimotsu unsō no zu - Western traders loading cargo in Yokohama - 横浜交易西洋人荷物運送之圖, 1861, Woodblock print (nishiki-e); ink and color on paper, Horizontal Ōban Pentaptych: 5 x (37 x 25.5 cm), Alternative title: Picture of Western Traders at Yokohama Transporting Merchandise (Cat. Reisonée: Yokohama ukiyo-e, Yurindo, 1979: №50). Japanese pentaptych print shows an American ship in the harbor at Yokohama, Japan; small boats ferry cargo which is being carried up a gangplank contributing to the bustle of activity on the main deck. April, 1861. SOLD -
 Iron tsuba of mokko form decorated with encircled family crests in low relief carving; niku from 3.0 mm in the centre to 4.0 mm at rim and full 1 mm raised uchikaeshi-mimi. Nobuie [信家] signature (hanare-mei) to the left of nakago-ana; on the reverse, to the right of nakago-ana, the inscription reads “62”, which may be how old the master was at the age of making the tsuba. Pewter or lead plugged hitsuana. In a wooden box, in a custom pouch. Size: H: 80 mm, W: 75, Th(c): 3.1 mm, Th(r): 4.0 mm Weight: 103.5 g
Iron tsuba of mokko form decorated with encircled family crests in low relief carving; niku from 3.0 mm in the centre to 4.0 mm at rim and full 1 mm raised uchikaeshi-mimi. Nobuie [信家] signature (hanare-mei) to the left of nakago-ana; on the reverse, to the right of nakago-ana, the inscription reads “62”, which may be how old the master was at the age of making the tsuba. Pewter or lead plugged hitsuana. In a wooden box, in a custom pouch. Size: H: 80 mm, W: 75, Th(c): 3.1 mm, Th(r): 4.0 mm Weight: 103.5 gSigned: Nobuie [信家] / 62
Probably the work of Shodai Nobuie (c. 1580).
Tokubetsu hozon certificate № 2002993 of the N.B.T.H.K., dated January 15, 2016. NOBUIE TSUBA by Steve Waszak The iron tsuba made by the two early Nobuie masters are regarded as the greatest sword guards ever made across hundreds of years of Japanese history. Only a small handful of other smiths' names are even mentioned in the same breath as that of Nobuie. Despite the well-deserved fame of the Nobuie name, virtually nothing is known with certainty about the lives of the two men who made the pieces carrying this name. They are thought to have been men of Owari Province, with the Nidai Nobuie also spending time in Aki Province at the end of the Momoyama Period. Two Nobuie tsubako are recognized. The man whom most consider to have been the Shodai signed his sword guards with finer and more elegantly inscribed characters than the smith seen by most as the Nidai. The term used to describe the mei of the Shodai is "hanare-mei" or "ga-mei," while that used to characterize the signature of the Nidai is "futoji-mei" or "chikara-mei." These terms refer to the fineness and grace of the Shodai's signature and the relatively more powerfully inscribed characters of the Nidai's. The Shodai is thought to have lived during the Eiroku and Tensho eras in the latter part of the 16th century, while the Nidai's years are considered to have been from Tensho into the Genna era. This locates both smiths well within the Golden Age of tsuba artists -- the Momoyama Period. Nobuie tsuba are esteemed and celebrated for the extraordinary beauty of their iron. The combination of the forging of the metal, the surface treatment by tsuchime and yakite married to powerfully expressive carving, the masterful manipulation of form, mass and shape, and the colour and patina of the iron makes Nobuie sword guards not only unique in the world of tsuba, but the greatest of the great. The sword guard here is a Shodai-made masterwork, done in mokko-gata form, a shape the early Nobuie smiths mastered to a degree unmatched by any others. The expanding of the mass of the tsuba from the seppa-dai to the mimi, increasing by 50% from the centre of the guard to the rim, creates a sense of exploding energy, which is then contained by the uchikaeshi-mimi, yielding a lightning-in-a-bottle effect of captured energy. The hammering the master has employed to finish the surface is subtle and sensitive, achieving a resonant profundity, and the deep blue-black colour -- augmented by a lustrous patina -- leaves the tsuba to positively glow in one's hand. In this piece, Nobuie has used a motif of several kamon, or family crests, each carved only lightly on the surface in a loose ring around the nakago-ana. Due to the shallow depth of this carving, together with the tsuchime finish of the plate, the effect is to leave the kamon with a sort of weathered appearance, recalling the prime aesthetic values of sabi and wabi, which had great circulation in the Tea Culture so ascendant in the Momoyama years. However, the effects of sabi and wabi expressed in the treatment described above are amplified and deepened by the color and patina of the iron, thereby adding yet another aesthetic value -- yuugen -- which is linked with the abiding mystery of the universe and one more — mono no aware — which alludes to the pathos of life's experiences and transitory nature. In short, this Nobuie tsuba joins poetry with power and therein exemplifies the unrivalled brilliance of Nobuie workmanship. -

Iron tsuba of round form with one hitsu ana; centre of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire broke by a circular opening 7 mm in diameter located between 4 and 5 o’clock of the plate and in its turn outlined with brass wire. Extraneous to the central wire, the plate is decorated with four rows of brass dots (ten-zogan). A few dots are missing. In a custom kiri wood box. The meaning of the emblem is probably either the sun or the moon.
Ōnin school. Unsigned.
Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century.
Dimensions: diameter 88 mm; thickness 3.3 mm.
-
 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form (nagamaru-gata) pierced on top and in the bottom (ko-sukashi) with simplified Genji-kō (incense game symbol) and two petals of bellflower; openings, seppa-dai, and plate along the rim are outlined with brass wire, kozuka-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire, missing on the front; kogai-ana pierced later. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer, decorated in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils, bellflowers, and Genji characters, and with brass dots (ten-zogan), many of which are missing. Measurements: Height 77.5 mm; Width 75.5 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.4 mm, at rim 3.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form (nagamaru-gata) pierced on top and in the bottom (ko-sukashi) with simplified Genji-kō (incense game symbol) and two petals of bellflower; openings, seppa-dai, and plate along the rim are outlined with brass wire, kozuka-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire, missing on the front; kogai-ana pierced later. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer, decorated in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils, bellflowers, and Genji characters, and with brass dots (ten-zogan), many of which are missing. Measurements: Height 77.5 mm; Width 75.5 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.4 mm, at rim 3.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier. -

Large iron tsuba of mokko form with the openwork (sukashi) design, described by some as rotten leaves swirling in the wind and boar eyes (inome, 猪目, heart-shaped elements); round rim (maru-mimi); no hitsu-ana; pronounced iron bones (tekkotsu); chocolate patina.
Signed to the left of nakaga-ana: Yamakichibei (山吉兵へ). Attributed to the First Generation (Shodai) master.
Dimensions: 90 x 82 mm, thickness 3.7 mm at centre, 4.9 mm at rim. Weight: 142 gReferences: similar handguards demonstrated at Yasukazu's Owari to Mikawa no tankō №176 and Kajima's Tsuba no Bi №28.
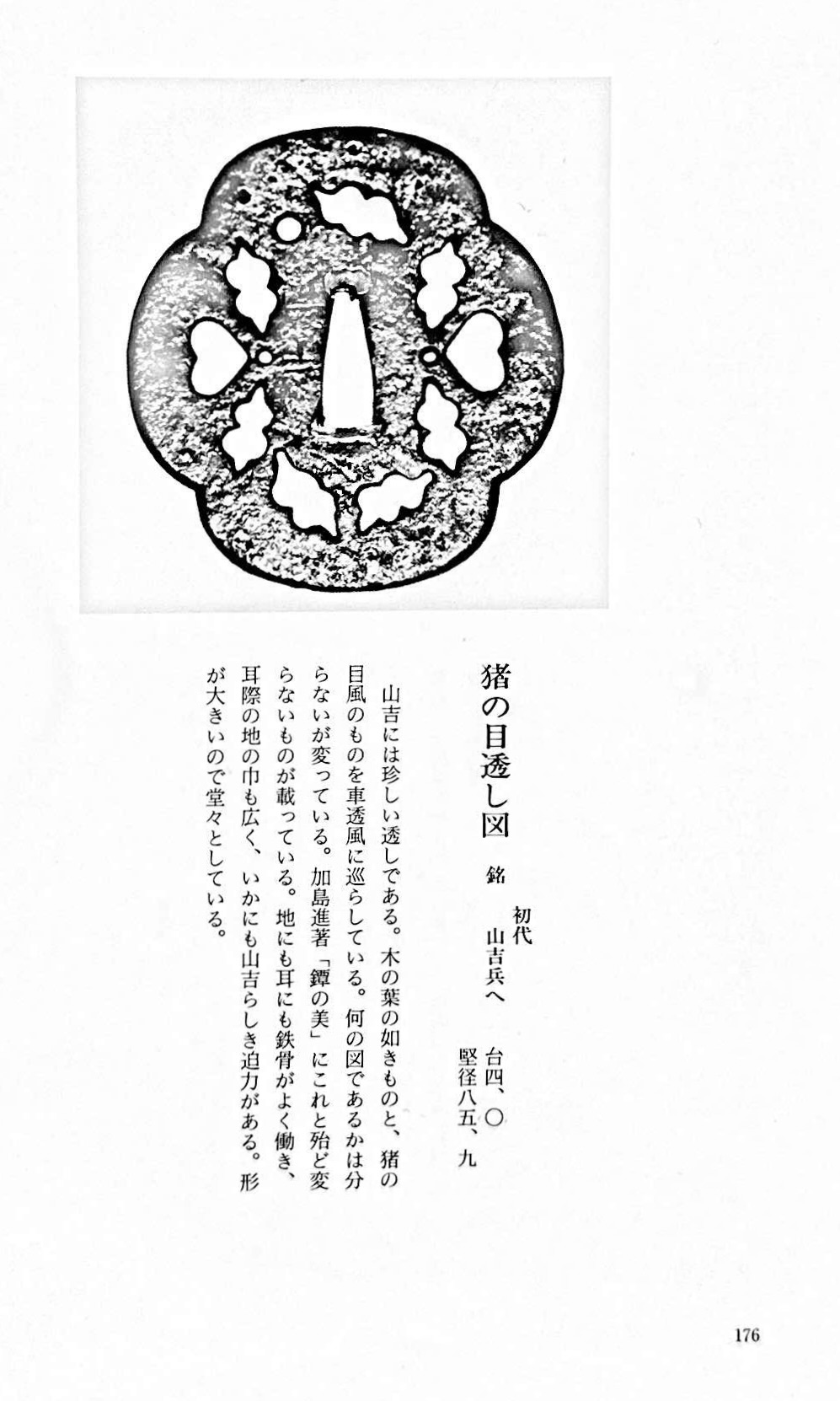
Owari to Mikawa no tankō №176

Tsuba no Bi №28
-
 Thin plate iron tsuba of round form with a military commander's fan (gunbai) design in openwork (sukashi); Ko-tosho school. Kamakura period (1185 – 1333), 13th to early 14th century (according to Nakamura Tessei). Dimensions: 91.2 x 89.5 mm, thickness: 1.5-2.5 mm. Provenance: Patrick Liebermann Collection. Reproduced in the exhibition catalogue Samurai. Guerriers et esthètes, BNU, Strasbourg, March 11 – July 13, 2022, №045, p.91 and in Patrick Liebermann, Tsuba. Itinéraires d'une collection, 2016, №72, p.111. Reference: a similar tsuba reproduced in LIB-3304.2024 (see below) and in this collection TSU-0332.2017 (provenance Sasano Masayuki).
Thin plate iron tsuba of round form with a military commander's fan (gunbai) design in openwork (sukashi); Ko-tosho school. Kamakura period (1185 – 1333), 13th to early 14th century (according to Nakamura Tessei). Dimensions: 91.2 x 89.5 mm, thickness: 1.5-2.5 mm. Provenance: Patrick Liebermann Collection. Reproduced in the exhibition catalogue Samurai. Guerriers et esthètes, BNU, Strasbourg, March 11 – July 13, 2022, №045, p.91 and in Patrick Liebermann, Tsuba. Itinéraires d'une collection, 2016, №72, p.111. Reference: a similar tsuba reproduced in LIB-3304.2024 (see below) and in this collection TSU-0332.2017 (provenance Sasano Masayuki).
Tsuba Collection (Tsuba shūsei, 鐔集成) by Nakamura Tessei (中村鐵青), p.36, fig. 12.
-

Netsuke with a design of an old man carrying a giant mushroom on his back. Possibly signed on his left foot. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, page. 93): ... This prominent use in the symbol-rich netsuke art form, however, reflects more their sexual symbolism than either their dietary appeal or interesting shapes. Mushrooms in Japan are generally a symbol of fertility, with some flat varieties, like shiitake, being associated with females. In contrast, the matsutake mushroom (Armillaria edodes) is a phallic symbol, as befits its thick, spearlike stem and the fact that it is consumed before cap opens.
Seller's description: "The old man carved walking, with one foot slightly raised, wearing a loose fitted robe and carrying a large long-stemmed mushroom on his back. The wood stained and bearing a fine patina. Himotoshi through the mushroom stem". See VO-0270.2018 for the same subject. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 62 mm tall -
 Finely carved as a rat (nezumi) seated on a shuro brush, bound naturalistically with thick bristles. The rodent with a long trailing tail and eyes inlaid in a dark horn. Generously excavated, asymmetrical himotoshi to the underside. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, p. 156): …The Japanese do not clearly differentiate between the rat and the mouse, and one word, nezumi [鼠], designates both. …Rat is a messenger of Daikokuten, a deity of grain and vegetation who is one of Japan’s Seven Gods of Good Luck. ...Depictions of the rat are most common in years of the zodiac represented by the animal. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 49 x 33 x 16 mm. Provenance: From the private collection of Armand Basi (Spanish, 1924-2009).
Finely carved as a rat (nezumi) seated on a shuro brush, bound naturalistically with thick bristles. The rodent with a long trailing tail and eyes inlaid in a dark horn. Generously excavated, asymmetrical himotoshi to the underside. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, p. 156): …The Japanese do not clearly differentiate between the rat and the mouse, and one word, nezumi [鼠], designates both. …Rat is a messenger of Daikokuten, a deity of grain and vegetation who is one of Japan’s Seven Gods of Good Luck. ...Depictions of the rat are most common in years of the zodiac represented by the animal. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 49 x 33 x 16 mm. Provenance: From the private collection of Armand Basi (Spanish, 1924-2009). -
 A large hardcover volume, 370 x 265 x 53 mm, bound in burgundy cloth with pasted-in b/w photograph and gilt lettering to front, gilt lettering to spine, in plastic dust jacket, in a slipcase, in a cardboard shipping box, pp. [2] 1-522 [2], 128 leaves total; limited edition of 1000 copies. Author: Nakamura Tessei [中村鐵青] Seller's description: Tsuba Shusei by Nakamura. 1963. Of a limited edition of 1,000. Clothbound with plastic jacket, slipcase, and cardboard storage box, 11 ½ x 14 ½”, 522 heavy stock pages in Japanese. This is a very impressive book. Thousands of tsuba, from Kamakura to late Edo and arranged by school. are illustrated (24 in colour photos and the rest in black & white) and described. If there is a tsuba bible this might be it; there can’t be a more comprehensive book on the subject. The storage box is shelf worn, the slipcase is just a bit toned; the book is in excellentt condition. Produced by Chuokoron-Shinsha, Inc. [株式会社中央公論新社] Publisher: 銀集成刊行会 Production details: 鐵集成 第617番 昭和38年2月10日発行 限定1,000部 定価 10,000円 オフセット単色印刷:マイク印刷 オフセット原色印刷:大日本印刷 著者中村鐵青 製作 中央公論事業出版 発行所 銀集成刊行会 活版印刷:精興社 製本:協和製本 本文用紙:三菱製紙 表紙:望月
A large hardcover volume, 370 x 265 x 53 mm, bound in burgundy cloth with pasted-in b/w photograph and gilt lettering to front, gilt lettering to spine, in plastic dust jacket, in a slipcase, in a cardboard shipping box, pp. [2] 1-522 [2], 128 leaves total; limited edition of 1000 copies. Author: Nakamura Tessei [中村鐵青] Seller's description: Tsuba Shusei by Nakamura. 1963. Of a limited edition of 1,000. Clothbound with plastic jacket, slipcase, and cardboard storage box, 11 ½ x 14 ½”, 522 heavy stock pages in Japanese. This is a very impressive book. Thousands of tsuba, from Kamakura to late Edo and arranged by school. are illustrated (24 in colour photos and the rest in black & white) and described. If there is a tsuba bible this might be it; there can’t be a more comprehensive book on the subject. The storage box is shelf worn, the slipcase is just a bit toned; the book is in excellentt condition. Produced by Chuokoron-Shinsha, Inc. [株式会社中央公論新社] Publisher: 銀集成刊行会 Production details: 鐵集成 第617番 昭和38年2月10日発行 限定1,000部 定価 10,000円 オフセット単色印刷:マイク印刷 オフセット原色印刷:大日本印刷 著者中村鐵青 製作 中央公論事業出版 発行所 銀集成刊行会 活版印刷:精興社 製本:協和製本 本文用紙:三菱製紙 表紙:望月 -
 NEWArtist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a yellow double-gourd. Publisher unknown. Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 228 x 298 mm. Series title: Six Jewel Faces (六玉颜, mu tama-gao), a pun on Six Jewel Rivers (六玉河, Mu Tamagawa). The date seal and censor seal are absent. Another print from the same series in the Metropolitan Museum of New York reads:
NEWArtist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a yellow double-gourd. Publisher unknown. Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 228 x 298 mm. Series title: Six Jewel Faces (六玉颜, mu tama-gao), a pun on Six Jewel Rivers (六玉河, Mu Tamagawa). The date seal and censor seal are absent. Another print from the same series in the Metropolitan Museum of New York reads:The colorful background, with explosions of tie-dyed floral motifs, is a reminder of how Kunisada made all his thousands of Genji-print designs a visual record of different textile patterns of the day. The title Six Jewel Faces (Mu tama-gao), along with its allusion to the literary theme of Six Jewel Rivers, suggests that this set of fan prints captures the appearance of a half-dozen attractive individuals, and, indeed, the other five works in the set show images of beautiful women, mostly courtesans of the pleasure quarters.
 Mitsuuji with Mountain Roses (Yamabuki), from the series “Six Jewel Faces” (Mu tama-gao).
MET Accession Number:2019.3
Ref.: [LIB-2967.2022] Utagawa Kunisada: His world revisited / Catalogue 17, Exhibition March 17-21, 2021. — NY: Sebastian Izzard, LLC., 2021.
Mitsuuji with Mountain Roses (Yamabuki), from the series “Six Jewel Faces” (Mu tama-gao).
MET Accession Number:2019.3
Ref.: [LIB-2967.2022] Utagawa Kunisada: His world revisited / Catalogue 17, Exhibition March 17-21, 2021. — NY: Sebastian Izzard, LLC., 2021.


