-
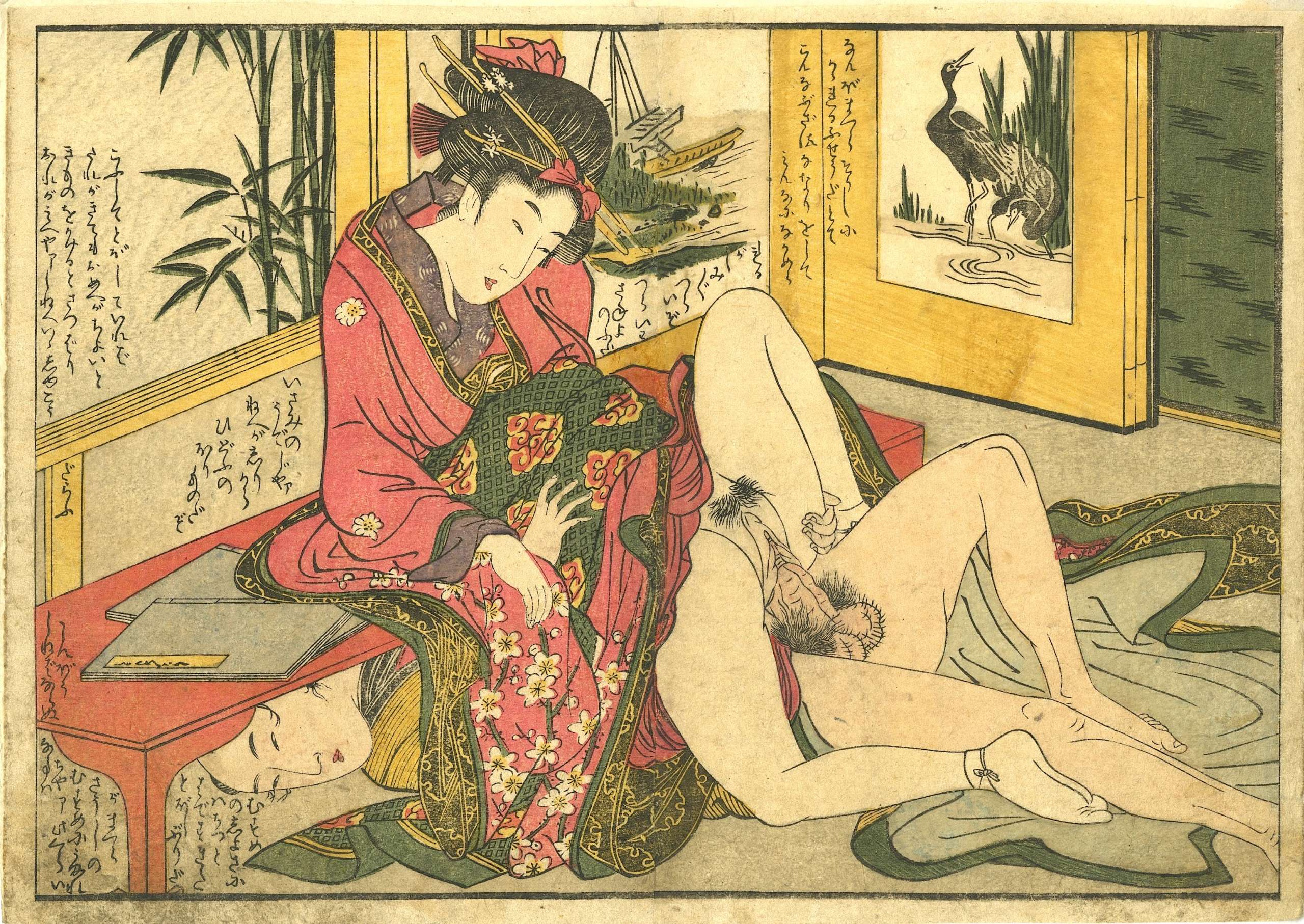 Kitagawa Utamaro. Illustration from book Ehon koi no Onamaki, published in 1799. Reference found by Chris Uhlenbeck: he found one of the designs in Hayashi Yoshikazu's 20-volume set Edo makura-e shi shusei: Kitagawa Utamaro. Size: Chuban (25.5 x 18.5 cm), two book pages glued together.
Kitagawa Utamaro. Illustration from book Ehon koi no Onamaki, published in 1799. Reference found by Chris Uhlenbeck: he found one of the designs in Hayashi Yoshikazu's 20-volume set Edo makura-e shi shusei: Kitagawa Utamaro. Size: Chuban (25.5 x 18.5 cm), two book pages glued together. -
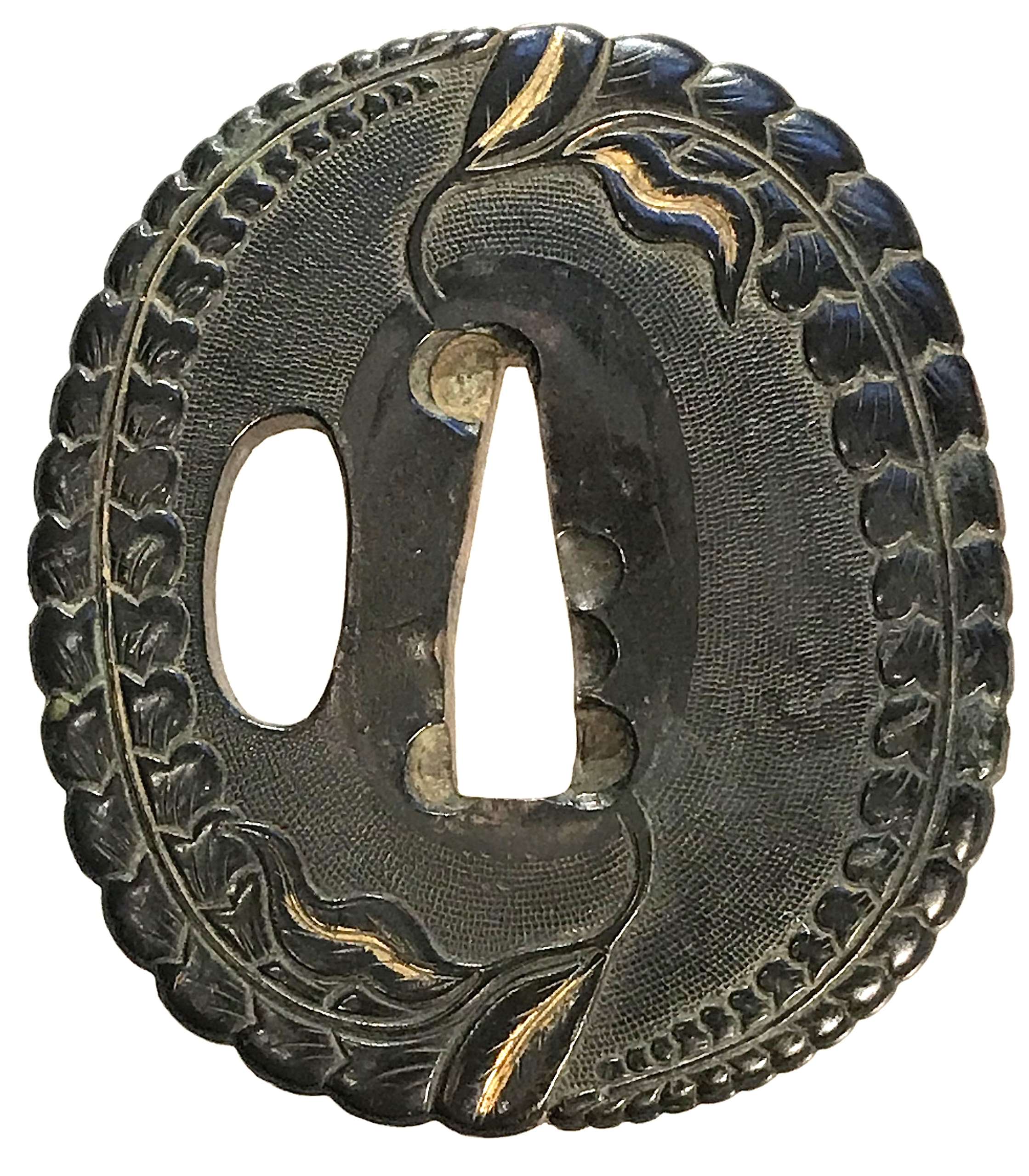

A yamagane tsuba of oval form with green-ish black patina decorated in usuniku-bori carving and gold iroe with wisteria (fuji) motif plus nanako-ji ground on both sides. Kozuka-hitsu-ana possibly cut later.
Unsigned.
Momoyama or may be even Muromachi period. Dimensions: 70.0 x 61.2 x 5.0 (center) mm -
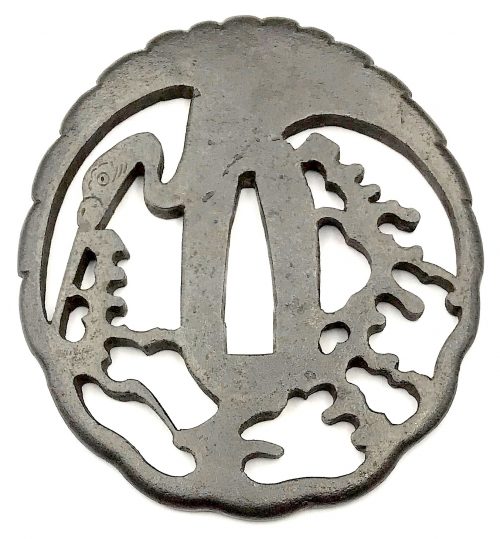

Iron tsuba of round form (tsurumaru) decorated with a design of crane and pines, or "nesting crane (sugomori-tsuru)" in openwork (sukashi). Details carved in kebori. Rounded rim.
Size: 74.7 x 69.8 x 4.8 mm.
Unsigned.
Edo period, ca. 17th century.
NBTHK Certificate № 463485. The certificate says it's a Higo School piece. The design was popular in both Akasaka and Higo schools. The Akasaka example: at Kodogu and tsuba. International collections not published in my books. (Toso Soran). Ph. D. Kazutaro Torigoye, 1978, p. 246: "Late Edo. Jiyūgata. Sined: Akasaka Tadanori saku."The Higo example can be found at Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 69, №56: Sugomori-tsuru sukashi-tsuba (Nesting Carne). Mumei: Matashichi (1st generation), early 17th century.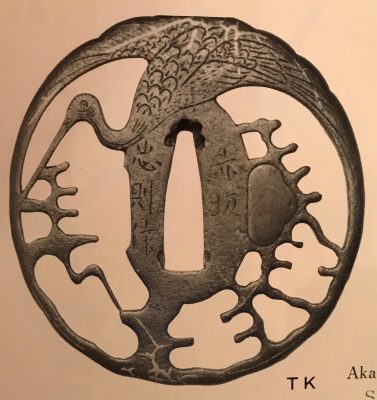
Torigoye, 1978, p. 246. Late Akasaka.
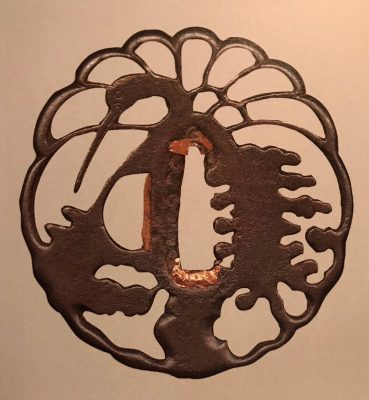
Kurogane no hana, 2014, p. 69, №56. Higo tsuba.
-
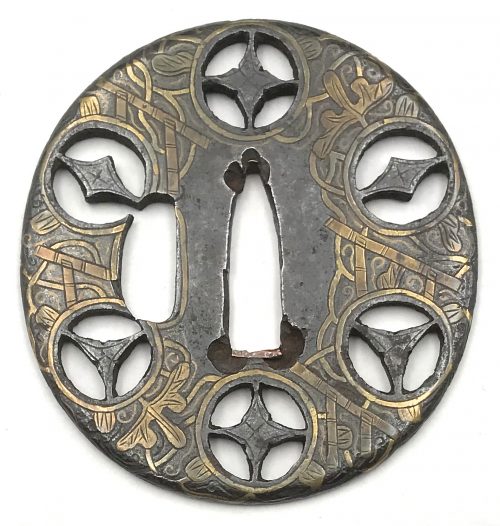

Tsuba of oval form decorated with vines, tendrils, and leaves on trellis in brass inlay with details carved in kebori, and pierced with six family crests (mon) with two, three and four pointing stars in openwork, each outlined with brass wire and carved in kebori. Original hitsu-ana outlined with brass wire was probably enlarged later. Copper sekigane.
Momoyama to early Edo period (end of the 16th - beginning of the 17th century). Dimensions: 68.3 x 64.5 x 3.4 mm. -
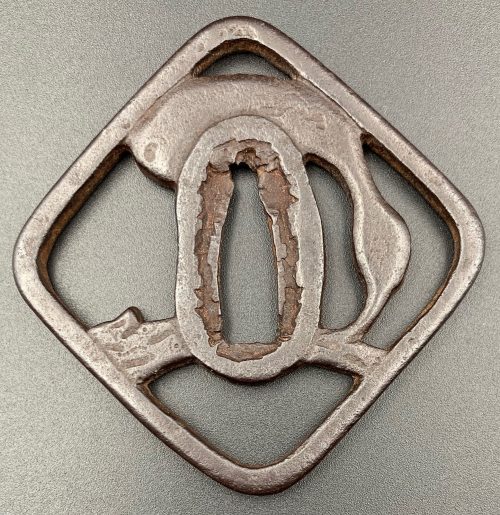

Iron tsuba of diamond form with rounded corners with the design of a double gourd on a branch in openwork. Dark brown patina. Ko-Shōami school. Custom kiri-wood box with hakogaki of Sasano Masayuki.
Momoyama Period (1574-1603)
Size: 77.1 x 75.7 x 4.6 mm; weight: 75.3 g.
Provenance: Sasano Masayuki[Translated by Markus Sesko]Hakogaki lid outside: 古正阿弥鐔 Ko-Shōami tsuba Hakogaki lid inside:Hyōtan-sukashi Mumei, Momoyama-ki saku Tetsu, ji-sukashi Koboku-aware no kasaku Heisei ninen Soshinkan Minazuki Openwork design of gourd Unsigned, Momoyama era work Iron, large openwork Masterwork full of classical charm. June of 1990, Soshinkan [pen name of Sasano Masayuki]瓢簞透 無銘 桃山期作 鉄地透
古撲惻之佳作 平成二年 素心鑑 水無月
-
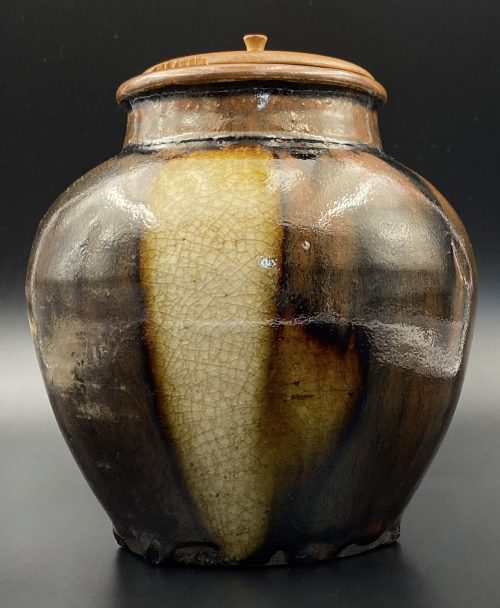 Seller's description: "pottery jar presenting a circular, concave base, an apple-form body, a cylindrical neck, and an annular flared rim. Boasting a lustrous burnish, the gorgeous vessel displays three narrow vertical panels in a hue of cream over mottled shades of chocolate brown and mocha on its body and a caramel-coloured neck and rim. The discoid lid features a lovely natural woodgrain surface incised with three decorative concentric circles around a petite knob-like handle. Note the beautiful globules of glaze that decorate the periphery of the base! This type of vessel is known as Seto ware." Size: Dia: 13 cm, H: 14 cm.
Seller's description: "pottery jar presenting a circular, concave base, an apple-form body, a cylindrical neck, and an annular flared rim. Boasting a lustrous burnish, the gorgeous vessel displays three narrow vertical panels in a hue of cream over mottled shades of chocolate brown and mocha on its body and a caramel-coloured neck and rim. The discoid lid features a lovely natural woodgrain surface incised with three decorative concentric circles around a petite knob-like handle. Note the beautiful globules of glaze that decorate the periphery of the base! This type of vessel is known as Seto ware." Size: Dia: 13 cm, H: 14 cm. -
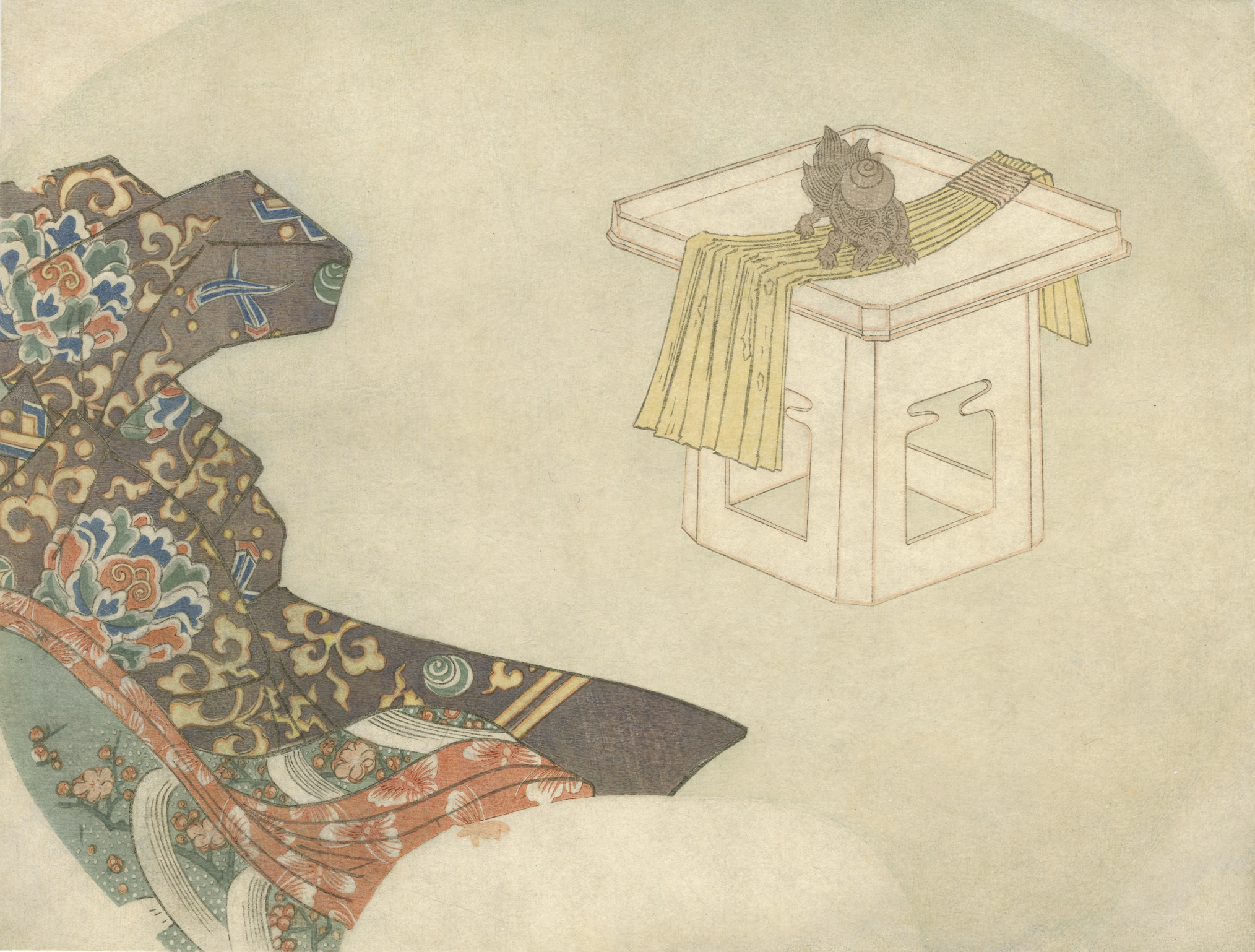
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Artists signature: Kunisada ga [国貞画] in a red double-gourd cartouche. Character: Kabuki actor Ichikawa Danjūrō VII [七代目 市川 團十郎]; other names: Ichikawa Ebizō V, Ichikawa Shinnosuke I (Japanese, 1791 – 1859). Series: Six choice modern flowers [當世六花撰] (Tosei rok’kasen). No publisher's seal, no date or censor's seal is present. Size: Fan print (aiban uchiwa-e); 232 x 289 mm. Provenance: Paul F. Walter. Izzard: "... six prints make up this set of fan prints, which compares contemporary artists with classic poets, in this case, Ichikawa Danjūrō VII with Ōtomo no Kuronushi [大友 黒主] (Japanese, dates unknown)". Rok'kasen [六歌仙] – six poetry immortals. According to Izzard, identification of the portrayed person is made possible by mimasu-mon [三升] on the robe, scrolling peony on the back of the mirror, and cloth decorated with the characters Yauan, one of the actor's poetry names, and other signs and symbols, including the inscription of the acter's guild name Naritaya. The absence of the publisher’s emblem and censorship seals may indicate that this was a privately issued print, not for public use. Ref: (1) [LIB-2967.2022] Utagawa Kunisada (1786 – 1865): His world revisited / Catalogue № 17, Exhibition March 17-21, 2021. — NY: Sebastian Izzard, LLC., 2021; p. 130-1, fig. 42). (2) Lyon Collection. Mimasu-mon, or Mitsumasu, is the Ichikawa Danjūrō family crest – three wooden measures, nested square boxes.
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Artists signature: Kunisada ga [国貞画] in a red double-gourd cartouche. Character: Kabuki actor Ichikawa Danjūrō VII [七代目 市川 團十郎]; other names: Ichikawa Ebizō V, Ichikawa Shinnosuke I (Japanese, 1791 – 1859). Series: Six choice modern flowers [當世六花撰] (Tosei rok’kasen). No publisher's seal, no date or censor's seal is present. Size: Fan print (aiban uchiwa-e); 232 x 289 mm. Provenance: Paul F. Walter. Izzard: "... six prints make up this set of fan prints, which compares contemporary artists with classic poets, in this case, Ichikawa Danjūrō VII with Ōtomo no Kuronushi [大友 黒主] (Japanese, dates unknown)". Rok'kasen [六歌仙] – six poetry immortals. According to Izzard, identification of the portrayed person is made possible by mimasu-mon [三升] on the robe, scrolling peony on the back of the mirror, and cloth decorated with the characters Yauan, one of the actor's poetry names, and other signs and symbols, including the inscription of the acter's guild name Naritaya. The absence of the publisher’s emblem and censorship seals may indicate that this was a privately issued print, not for public use. Ref: (1) [LIB-2967.2022] Utagawa Kunisada (1786 – 1865): His world revisited / Catalogue № 17, Exhibition March 17-21, 2021. — NY: Sebastian Izzard, LLC., 2021; p. 130-1, fig. 42). (2) Lyon Collection. Mimasu-mon, or Mitsumasu, is the Ichikawa Danjūrō family crest – three wooden measures, nested square boxes.
-
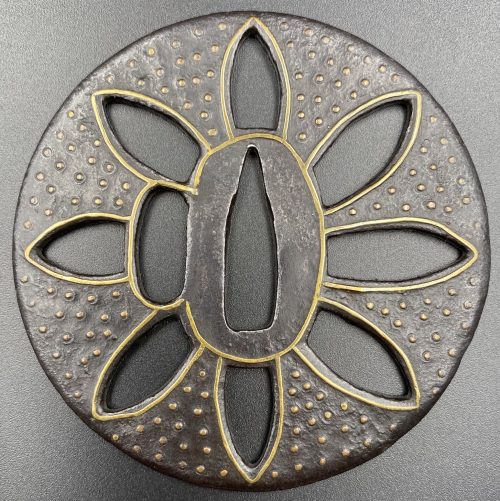 Iron tsuba of round form (maru-gata) with 8 openwork petals outlined with brass wire (sen-zōgan) and decorated with brass dots (ten-zōgan), on both sides. Seppa-dai and hitsu-ana outlined with brass wire. Late Muromachi period (Ca. 1514-1573). Ōnin school. Unsigned. Dimensions (mm): 80.4 x 79.8 x 3.6 (center) 3.2 (rim). Similar tsuba in this collection: TSU-0374.2018
Iron tsuba of round form (maru-gata) with 8 openwork petals outlined with brass wire (sen-zōgan) and decorated with brass dots (ten-zōgan), on both sides. Seppa-dai and hitsu-ana outlined with brass wire. Late Muromachi period (Ca. 1514-1573). Ōnin school. Unsigned. Dimensions (mm): 80.4 x 79.8 x 3.6 (center) 3.2 (rim). Similar tsuba in this collection: TSU-0374.2018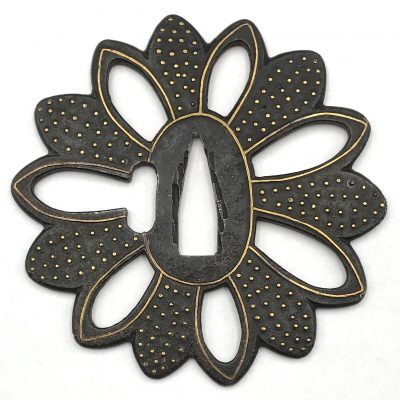
-
 Title: Early Spring [初春之図] (Hatsuharu no zu); Series: Fashionable Twelve Months [今様十二ヶ月] (Imayo juni-kagetsu). Another version of translation: Modern Beauties of Twelve Months. Artist: Utagawa Toyokuni I [歌川豊国] (1769–1825). Pubisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, 1815 – 1869), seal: Dansendō [伊場仙]. Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国画] and sealed with toshidama. Date-kiwame seal: Ushi (ox), Bunsei 5 (1822). Size: double-sheet uncut fan print ( aiban uchiwa-e), each 217 x 288 mm. Ref: Tokyo Museum Collection.
Title: Early Spring [初春之図] (Hatsuharu no zu); Series: Fashionable Twelve Months [今様十二ヶ月] (Imayo juni-kagetsu). Another version of translation: Modern Beauties of Twelve Months. Artist: Utagawa Toyokuni I [歌川豊国] (1769–1825). Pubisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, 1815 – 1869), seal: Dansendō [伊場仙]. Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国画] and sealed with toshidama. Date-kiwame seal: Ushi (ox), Bunsei 5 (1822). Size: double-sheet uncut fan print ( aiban uchiwa-e), each 217 x 288 mm. Ref: Tokyo Museum Collection.
Other five prints of this series: SVJP 0326.2020; SVJP-0362.2022; SVJP-0363.2022; SVJP-0364.2022; SVJP-0365.2022.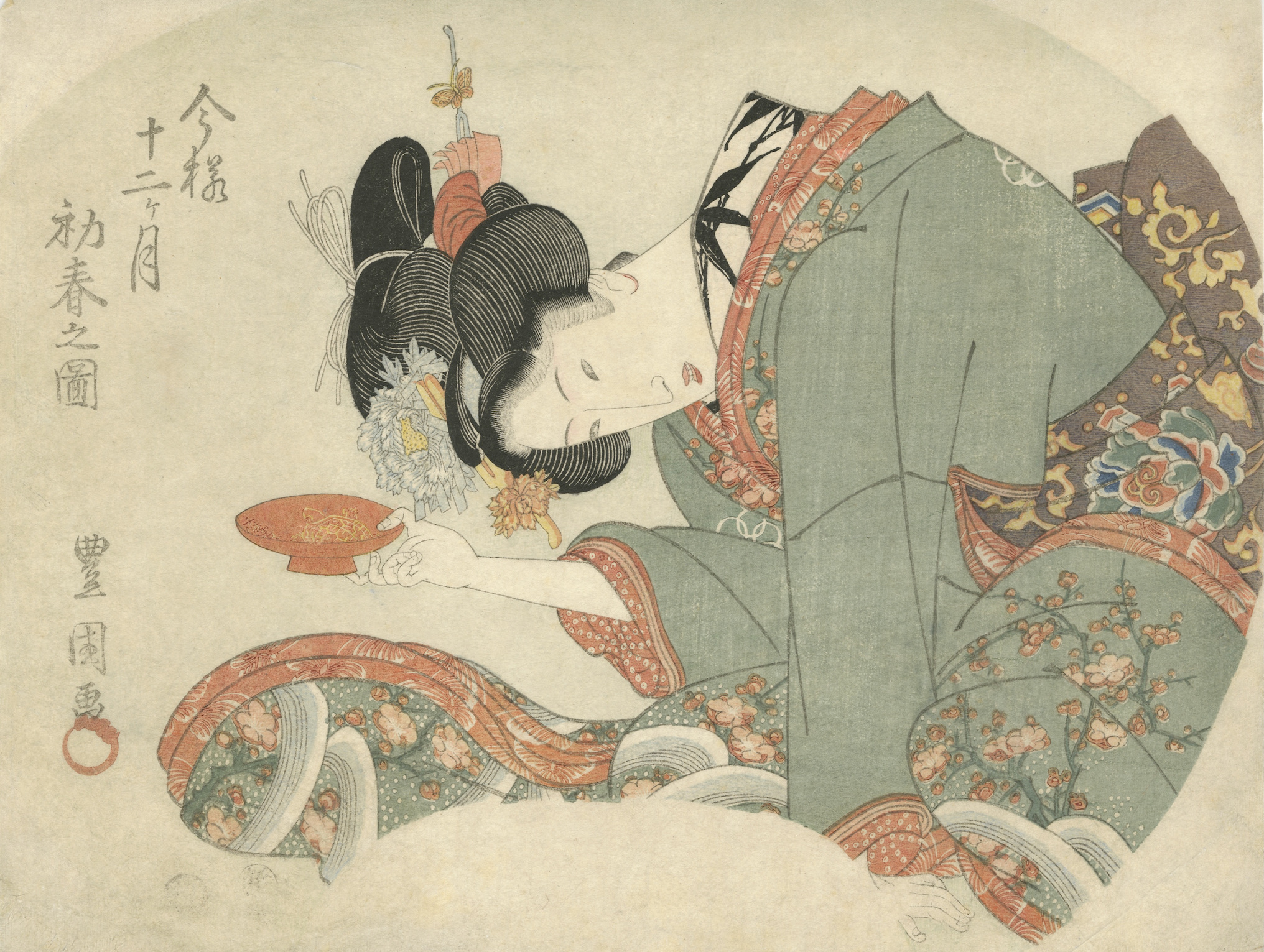
-
 Iron tsuba of mokko form decorated with encircled family crests in low relief carving; niku from 3.0 mm in the centre to 4.0 mm at rim and full 1 mm raised uchikaeshi-mimi. Nobuie [信家] signature (hanare-mei) to the left of nakago-ana; on the reverse, to the right of nakago-ana, the inscription reads “62”, which may be how old the master was at the age of making the tsuba. Pewter or lead plugged hitsuana. In a wooden box, in a custom pouch. Size: H: 80 mm, W: 75, Th(c): 3.1 mm, Th(r): 4.0 mm Weight: 103.5 g
Iron tsuba of mokko form decorated with encircled family crests in low relief carving; niku from 3.0 mm in the centre to 4.0 mm at rim and full 1 mm raised uchikaeshi-mimi. Nobuie [信家] signature (hanare-mei) to the left of nakago-ana; on the reverse, to the right of nakago-ana, the inscription reads “62”, which may be how old the master was at the age of making the tsuba. Pewter or lead plugged hitsuana. In a wooden box, in a custom pouch. Size: H: 80 mm, W: 75, Th(c): 3.1 mm, Th(r): 4.0 mm Weight: 103.5 gSigned: Nobuie [信家] / 62
Probably the work of Shodai Nobuie (c. 1580).
Tokubetsu hozon certificate № 2002993 of the N.B.T.H.K., dated January 15, 2016. NOBUIE TSUBA by Steve Waszak The iron tsuba made by the two early Nobuie masters are regarded as the greatest sword guards ever made across hundreds of years of Japanese history. Only a small handful of other smiths' names are even mentioned in the same breath as that of Nobuie. Despite the well-deserved fame of the Nobuie name, virtually nothing is known with certainty about the lives of the two men who made the pieces carrying this name. They are thought to have been men of Owari Province, with the Nidai Nobuie also spending time in Aki Province at the end of the Momoyama Period. Two Nobuie tsubako are recognized. The man whom most consider to have been the Shodai signed his sword guards with finer and more elegantly inscribed characters than the smith seen by most as the Nidai. The term used to describe the mei of the Shodai is "hanare-mei" or "ga-mei," while that used to characterize the signature of the Nidai is "futoji-mei" or "chikara-mei." These terms refer to the fineness and grace of the Shodai's signature and the relatively more powerfully inscribed characters of the Nidai's. The Shodai is thought to have lived during the Eiroku and Tensho eras in the latter part of the 16th century, while the Nidai's years are considered to have been from Tensho into the Genna era. This locates both smiths well within the Golden Age of tsuba artists -- the Momoyama Period. Nobuie tsuba are esteemed and celebrated for the extraordinary beauty of their iron. The combination of the forging of the metal, the surface treatment by tsuchime and yakite married to powerfully expressive carving, the masterful manipulation of form, mass and shape, and the colour and patina of the iron makes Nobuie sword guards not only unique in the world of tsuba, but the greatest of the great. The sword guard here is a Shodai-made masterwork, done in mokko-gata form, a shape the early Nobuie smiths mastered to a degree unmatched by any others. The expanding of the mass of the tsuba from the seppa-dai to the mimi, increasing by 50% from the centre of the guard to the rim, creates a sense of exploding energy, which is then contained by the uchikaeshi-mimi, yielding a lightning-in-a-bottle effect of captured energy. The hammering the master has employed to finish the surface is subtle and sensitive, achieving a resonant profundity, and the deep blue-black colour -- augmented by a lustrous patina -- leaves the tsuba to positively glow in one's hand. In this piece, Nobuie has used a motif of several kamon, or family crests, each carved only lightly on the surface in a loose ring around the nakago-ana. Due to the shallow depth of this carving, together with the tsuchime finish of the plate, the effect is to leave the kamon with a sort of weathered appearance, recalling the prime aesthetic values of sabi and wabi, which had great circulation in the Tea Culture so ascendant in the Momoyama years. However, the effects of sabi and wabi expressed in the treatment described above are amplified and deepened by the color and patina of the iron, thereby adding yet another aesthetic value -- yuugen -- which is linked with the abiding mystery of the universe and one more — mono no aware — which alludes to the pathos of life's experiences and transitory nature. In short, this Nobuie tsuba joins poetry with power and therein exemplifies the unrivalled brilliance of Nobuie workmanship. -
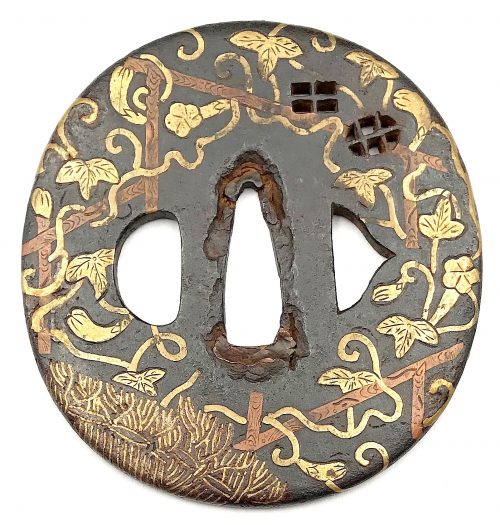 Iron tsuba of oval form with design of a gourd or aubergine vine with fruits, leaves, and blossoms climbing a trellis, and a fence in yellow brass and red copper flat inlay (hira-zōgan); inlay engraved. Two latticed windows represented by openwork (sukashi). The iron web has deep black patina. The seller attributes this tsuba to Heianjo-Namban school, whatever it means. Momoyama or early Edo period, 17th century. Kaga or Heianjō School. Unsigned. Height: 77.3, Width: 73.1, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm.
Iron tsuba of oval form with design of a gourd or aubergine vine with fruits, leaves, and blossoms climbing a trellis, and a fence in yellow brass and red copper flat inlay (hira-zōgan); inlay engraved. Two latticed windows represented by openwork (sukashi). The iron web has deep black patina. The seller attributes this tsuba to Heianjo-Namban school, whatever it means. Momoyama or early Edo period, 17th century. Kaga or Heianjō School. Unsigned. Height: 77.3, Width: 73.1, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. -
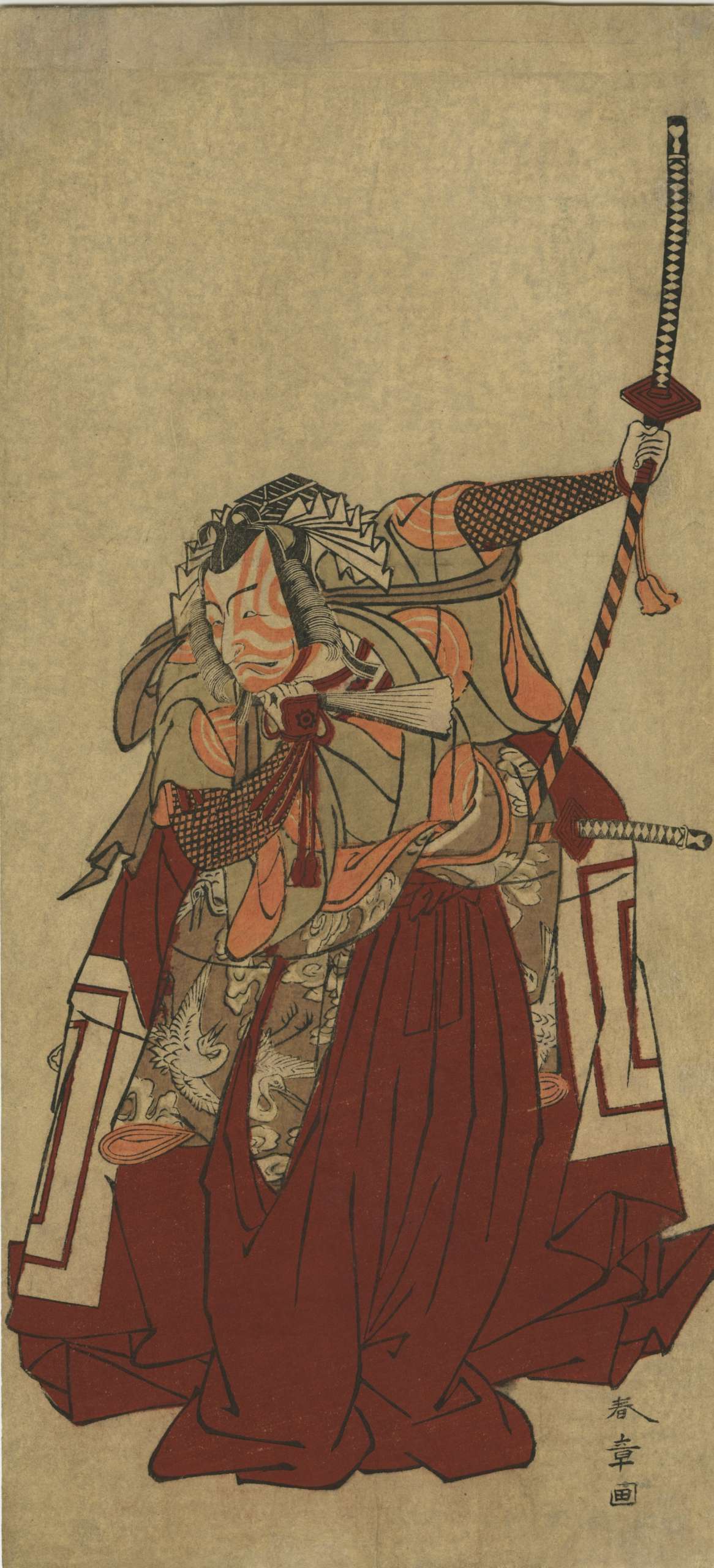 Katsukawa Shunshō ( 勝川 春章; 1726 – 19 January 1793).
Katsukawa Shunshō ( 勝川 春章; 1726 – 19 January 1793).SIZE: 12.5 x 5.75 in.
-
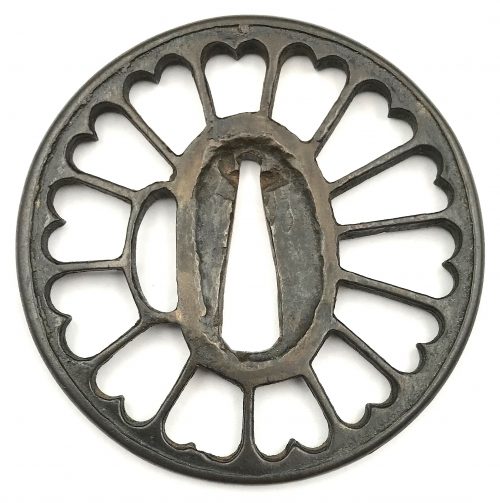 Yamagane tsuba of round form with design of a 14 petal chrysanthemum (kiku) in cast openwork (sukashi), with slightly raised rounded rim. Early Muromachi period (1393-1457). Size: Height: 64.5 mm; Width: 64.0 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.1 mm; Weight: 52.5 g. Provenance: Sasano collection (though not illustrated in the book 'Sasano: Japanese Sword Guard Masterpieces from the Sasano Collection, 1994', which only covers tsuba made of iron). Wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) by Sasano Masayuki. References: Illustrated on p. 140 at Tosogu: Treasure of the samurai by Graham Gemmell in the article Muromachi period tsuba by Robin Peverett, London, 1991, pp. 131-145. Sold at Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997 Sotheby's, London, 1997 [Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A.Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections], p. 16: "A ko-kinko bronze Tsuba, early Muromachi period (1393-1453) of circular form, with raised rounded rim, pierced with kiku petals and with a small elongated kozuka-hitsu, the work appearing to be cast and finished by hand. 6.4cm, thickness at centre 4.15mm, at rim 4.8mm. With a Tomobako, bearing a hakogaki by Masayuki Sasano, with rating Shu. Estimated: £1,000-1,500." Hakogaki (courtesy M. Sesko): 古金工 鐔 Ko-Kinkō tsuba 菊花透 無銘 山銅地透 時代 室町前期 古雅入念 秀作 昭和戊辰年伏月 素心鑑 kikka-sukashi, mumei yamagane, ji-sukashi jidai Muromachi-zenki koga nyūnen, shūsaku Showa tsuchinoe-tatsudoshi fukugetsu Soshinkan Kikka-sukashi, unsigned. Of yamagane and with ji-sukashi. Era is early Muromachi period. Excellent and carefully made work of classical elegance. June in the year of the dragon of the Shōwa era (1988) Soshinkan (pen name of Sasano Masayuki).
Yamagane tsuba of round form with design of a 14 petal chrysanthemum (kiku) in cast openwork (sukashi), with slightly raised rounded rim. Early Muromachi period (1393-1457). Size: Height: 64.5 mm; Width: 64.0 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.1 mm; Weight: 52.5 g. Provenance: Sasano collection (though not illustrated in the book 'Sasano: Japanese Sword Guard Masterpieces from the Sasano Collection, 1994', which only covers tsuba made of iron). Wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) by Sasano Masayuki. References: Illustrated on p. 140 at Tosogu: Treasure of the samurai by Graham Gemmell in the article Muromachi period tsuba by Robin Peverett, London, 1991, pp. 131-145. Sold at Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997 Sotheby's, London, 1997 [Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A.Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections], p. 16: "A ko-kinko bronze Tsuba, early Muromachi period (1393-1453) of circular form, with raised rounded rim, pierced with kiku petals and with a small elongated kozuka-hitsu, the work appearing to be cast and finished by hand. 6.4cm, thickness at centre 4.15mm, at rim 4.8mm. With a Tomobako, bearing a hakogaki by Masayuki Sasano, with rating Shu. Estimated: £1,000-1,500." Hakogaki (courtesy M. Sesko): 古金工 鐔 Ko-Kinkō tsuba 菊花透 無銘 山銅地透 時代 室町前期 古雅入念 秀作 昭和戊辰年伏月 素心鑑 kikka-sukashi, mumei yamagane, ji-sukashi jidai Muromachi-zenki koga nyūnen, shūsaku Showa tsuchinoe-tatsudoshi fukugetsu Soshinkan Kikka-sukashi, unsigned. Of yamagane and with ji-sukashi. Era is early Muromachi period. Excellent and carefully made work of classical elegance. June in the year of the dragon of the Shōwa era (1988) Soshinkan (pen name of Sasano Masayuki). -
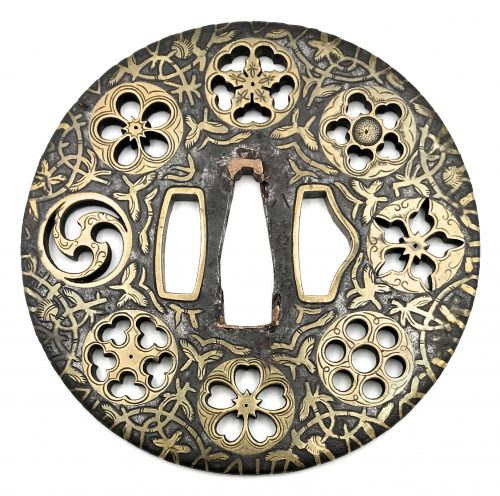 Well-forged iron plate of round shape (maru-gata) is decorated with water weeds or arabesque (karakusa) in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) all over and eight family crests (mon) of round form in cast brass with delicate linear carving (kebori) and openwork (sukashi). Crests represent: [at 9 hours] three counter-clockwise commas or swirls (tomoe); [at 10:30] plum blossom (ume); [at 12:00, 1:130, and 7:30] - stylized flower made by cutting out five suhama symblos (flower-shaped suhama); [at 3:00] bellflower (kikyō); [at 4:30] seven-star crest (shichiyō-mon); [at 6:00] cherry blossom (sakura). Brass-trimmed ryo-hitsu. Copper sekigane. Yoshirō school. Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Inscription on seppa-dai: 八幡 - Hachiman. Size: height 89.6 mm, width 89.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,0 mm. Weight 129.7 g. NBTHK certificate № 4007685, June 27, 2015: HOZON (Worthy of Preservation). As for the inscription, Nihonto Message Board blog discussion provides the following explanation of the inscription: "An expression of conviction as to being the best under the sun". On the other hand, there may be more in this confluence of symbols: the tomoe crest at 9:00 is "the kamon of Hachiman, the war god" [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007, p. 108]. The character 八 in the inscription cut stronger than the other kanji, and may be by a different hand in different time. 八 (hachi, eight): "The numeral eight was appreciated because its shape broadens toward the bottom, symbolizing eternal expansion" [ibid, p. 119]. It may be said that this tsuba is dedicated to Hachiman. Other crests (suhama, bellflower, seven-stars, plum and cherry blossoms) collectively allude to "good old times" when Fijiwara and Taira clans were in full bloom. Markus Sesko believes that the inscriptions reads: Hachiman: "the inscription is/was HACHIMAN (八幡), the God of War and a relatively popular inscription for tsuba, swords and armor." Elliott Long and Robert Haynes provide the following explanation of the inscription: "...hachi is correct and represents the name of the HACHI SHRINE. The inscription reads 'YAWATA' which is the name of the mountain in Mino Province where the HACHI Shrine is located". Details on Hachiman Shrine in Yawata (八幡市) can be found elsewhere, including Historical and geographical dictionary of Japan by Edmond Papinot. Van Ham auction house provides the following description: MON-SUKASHI TSUBA. MARUGATA. Japan. Momoyama period. Yoshiro school. Iron with inlays of brass. In hira-zogan technique with kebori engraving eight different family emblems (mon). An old inscription is dedicated to the deity Hachiman. D.4.5mm, Ø 8.3cm. Condition A/B. Supplement: Wooden box and NBTHK certificate.
Well-forged iron plate of round shape (maru-gata) is decorated with water weeds or arabesque (karakusa) in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) all over and eight family crests (mon) of round form in cast brass with delicate linear carving (kebori) and openwork (sukashi). Crests represent: [at 9 hours] three counter-clockwise commas or swirls (tomoe); [at 10:30] plum blossom (ume); [at 12:00, 1:130, and 7:30] - stylized flower made by cutting out five suhama symblos (flower-shaped suhama); [at 3:00] bellflower (kikyō); [at 4:30] seven-star crest (shichiyō-mon); [at 6:00] cherry blossom (sakura). Brass-trimmed ryo-hitsu. Copper sekigane. Yoshirō school. Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Inscription on seppa-dai: 八幡 - Hachiman. Size: height 89.6 mm, width 89.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,0 mm. Weight 129.7 g. NBTHK certificate № 4007685, June 27, 2015: HOZON (Worthy of Preservation). As for the inscription, Nihonto Message Board blog discussion provides the following explanation of the inscription: "An expression of conviction as to being the best under the sun". On the other hand, there may be more in this confluence of symbols: the tomoe crest at 9:00 is "the kamon of Hachiman, the war god" [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007, p. 108]. The character 八 in the inscription cut stronger than the other kanji, and may be by a different hand in different time. 八 (hachi, eight): "The numeral eight was appreciated because its shape broadens toward the bottom, symbolizing eternal expansion" [ibid, p. 119]. It may be said that this tsuba is dedicated to Hachiman. Other crests (suhama, bellflower, seven-stars, plum and cherry blossoms) collectively allude to "good old times" when Fijiwara and Taira clans were in full bloom. Markus Sesko believes that the inscriptions reads: Hachiman: "the inscription is/was HACHIMAN (八幡), the God of War and a relatively popular inscription for tsuba, swords and armor." Elliott Long and Robert Haynes provide the following explanation of the inscription: "...hachi is correct and represents the name of the HACHI SHRINE. The inscription reads 'YAWATA' which is the name of the mountain in Mino Province where the HACHI Shrine is located". Details on Hachiman Shrine in Yawata (八幡市) can be found elsewhere, including Historical and geographical dictionary of Japan by Edmond Papinot. Van Ham auction house provides the following description: MON-SUKASHI TSUBA. MARUGATA. Japan. Momoyama period. Yoshiro school. Iron with inlays of brass. In hira-zogan technique with kebori engraving eight different family emblems (mon). An old inscription is dedicated to the deity Hachiman. D.4.5mm, Ø 8.3cm. Condition A/B. Supplement: Wooden box and NBTHK certificate. -
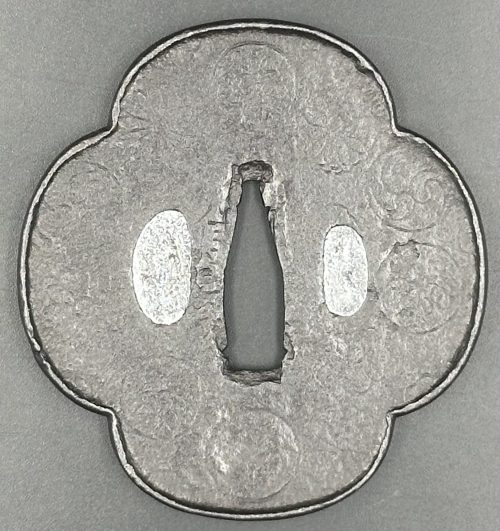
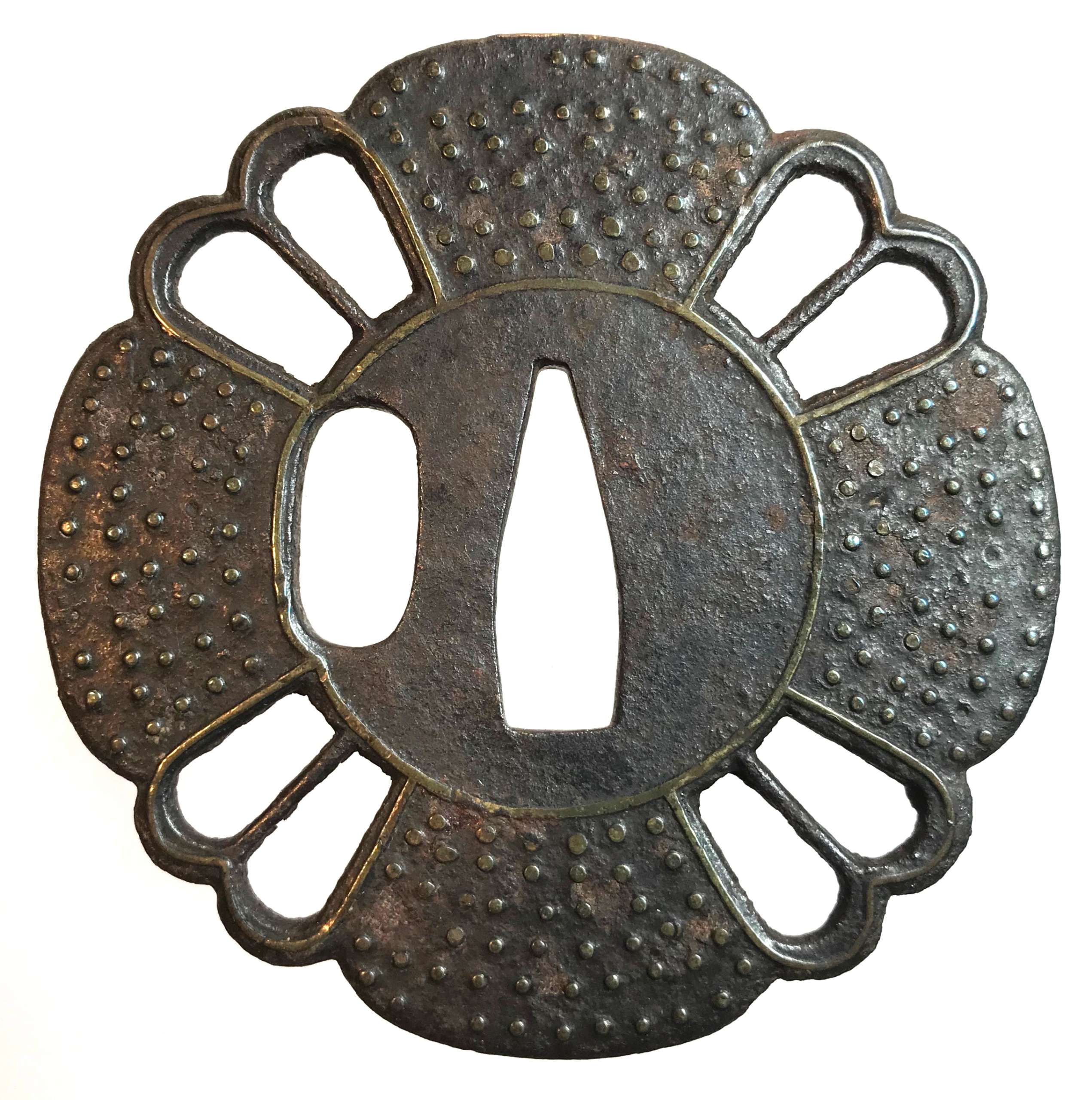 An iron tsuba of 12-lobed form with alternating four solid and four openwork areas, each with a central bar. Symbolism remains unclear, possibly - a gunbai, i.e. military leader's fan. The solid parts decorated with 5 to 6 rows of brass dots of nail heads inlaid in ten-zōgan. The center of the plate as well as the sukashi elements are outlined with brass wire. The kozuka-hitsu-ana seems original. Muromachi period. Dimensions: 77.9 x 77.5 x 3.2 mm.
An iron tsuba of 12-lobed form with alternating four solid and four openwork areas, each with a central bar. Symbolism remains unclear, possibly - a gunbai, i.e. military leader's fan. The solid parts decorated with 5 to 6 rows of brass dots of nail heads inlaid in ten-zōgan. The center of the plate as well as the sukashi elements are outlined with brass wire. The kozuka-hitsu-ana seems original. Muromachi period. Dimensions: 77.9 x 77.5 x 3.2 mm. -
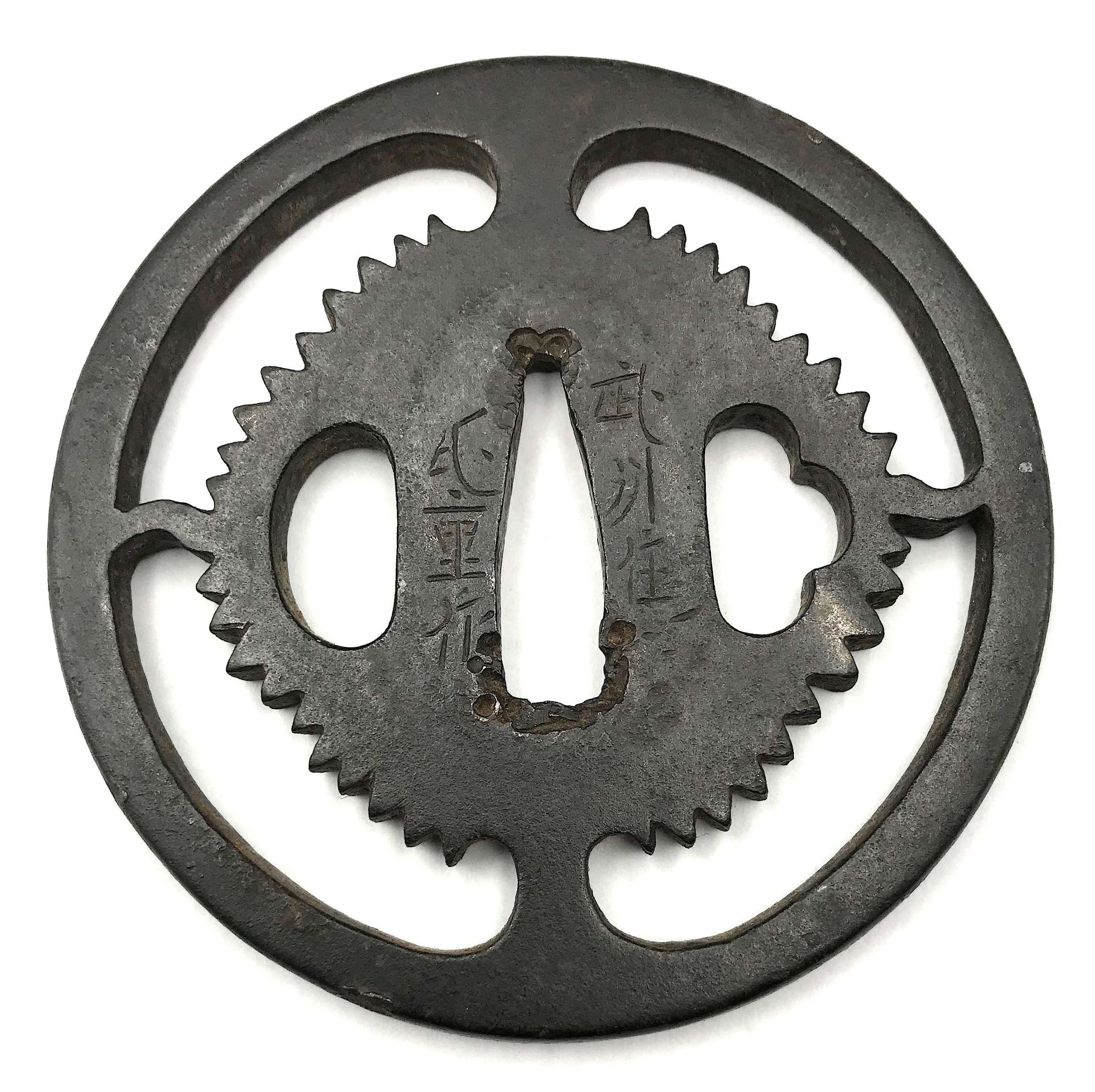 Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Edo period.
Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Edo period.Size: 83.4 x 83.1 x 4.4 mm
Signed Bushū-jū Ujishige saku (武州住氏重作) [Markus Sesko]. Ujishige (died 1677), 3rd generation of the Katsuki-Gondayu line; 1st gen. Ujiie came from Kyoto to Kaga to work for the Maeda family. There was another Ujishige, 4th generation Kaneko (?), who died in 1867 [M. Sesko, Genealogies...], but this tsuba looks a bit earlier than that. This particular Ujishige states in his signature that he is from Bushū, or Musashi Province, modern Tokyo Metropolis. He might have moved from Bushū to Kaga, of course. There is no artist with the name Ujishige in Bushū-Ito School anyway.
For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91. -
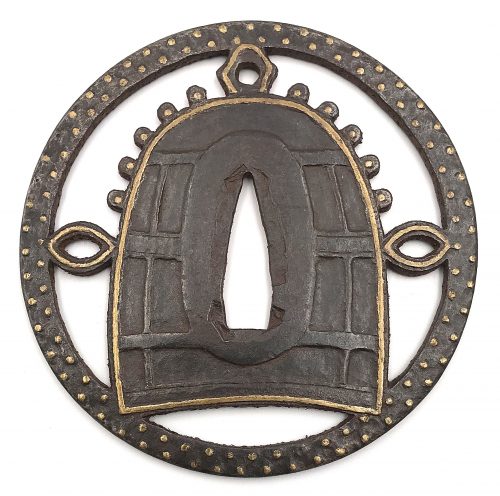

Iron tsuba of round form with brown patina decorated with the design of a Buddhist temple bell (tsurigane) in openwork (sukashi), with details outlined in brass wire (sen-zōgan), the outer ring decorated with two rows of brass dots (ten-zōgan), and the bell details carved in sukidashi-bori as on kamakura-bori pieces.
Ōnin school. Unsigned. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Dimensions: 88.8 x 88.3 x 3.0 mm. As per Merrily Baird, two legends are usually associated with the image of tsurigane, a large, suspended Buddhist bell: one is that of Dojo Temple (Dojo-ji), and the other is of Benkei stealing the tsurigane of Miidera Temple. Interestingly, this type of bell (tsurigane) is not described as a family crest (mon), while suzu and hansho bells are. -
 Utagawa Kunisada (Japanese: 歌川 国貞; also known as Utagawa Toyokuni III (三代歌川豊国); 1786 – 12 January 1865).
Utagawa Kunisada (Japanese: 歌川 国貞; also known as Utagawa Toyokuni III (三代歌川豊国); 1786 – 12 January 1865).A young woman adjusting her hairpins in the light of a paper lantern. Series: Arigataki miyo no kage-e (Shadow Pictures of an Auspicious Age). There are five known prints, half-length portraits of beauties, in this series, designed by Kunisada in ca. 1844. Another print from the series in this collection: SVJP-0309.2020: A young woman reading a book in the light of a lamp.
Signed: Kōchōrō Toyokuni ga (香蝶楼豊国画). Publisher: Maruya Kiyojiro.
Size: Vertical Ōban (37.5 x 25.4 cm). Utagawa (歌川) SOLD


