Artist:
Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865).
Block cutter: Horikō (Kiyomizu) Ryūzō [彫工 柳三].
Publisher:
Ebisuya Shoshichi [恵比寿屋庄七], Kinshōdō (Japanese, fl. c. 1846 – 1883).
Actor
Morita Kan'ya XI as Saito Tarozaemon Toshiyuki (
Morito Kan'ya, Saito Tarozaemon Toshiyuki)
Signed
Toyokuni ga within the artist's
Toshidama cartouche, publisher's seal
Sho, Kinshodo, carver's seal
Horiko Ryusan, censor's seal
aratame with date 1860, 3rd month.
Date: 3/1860.
Oban tate-e; 36.5 x 25.3 cm.
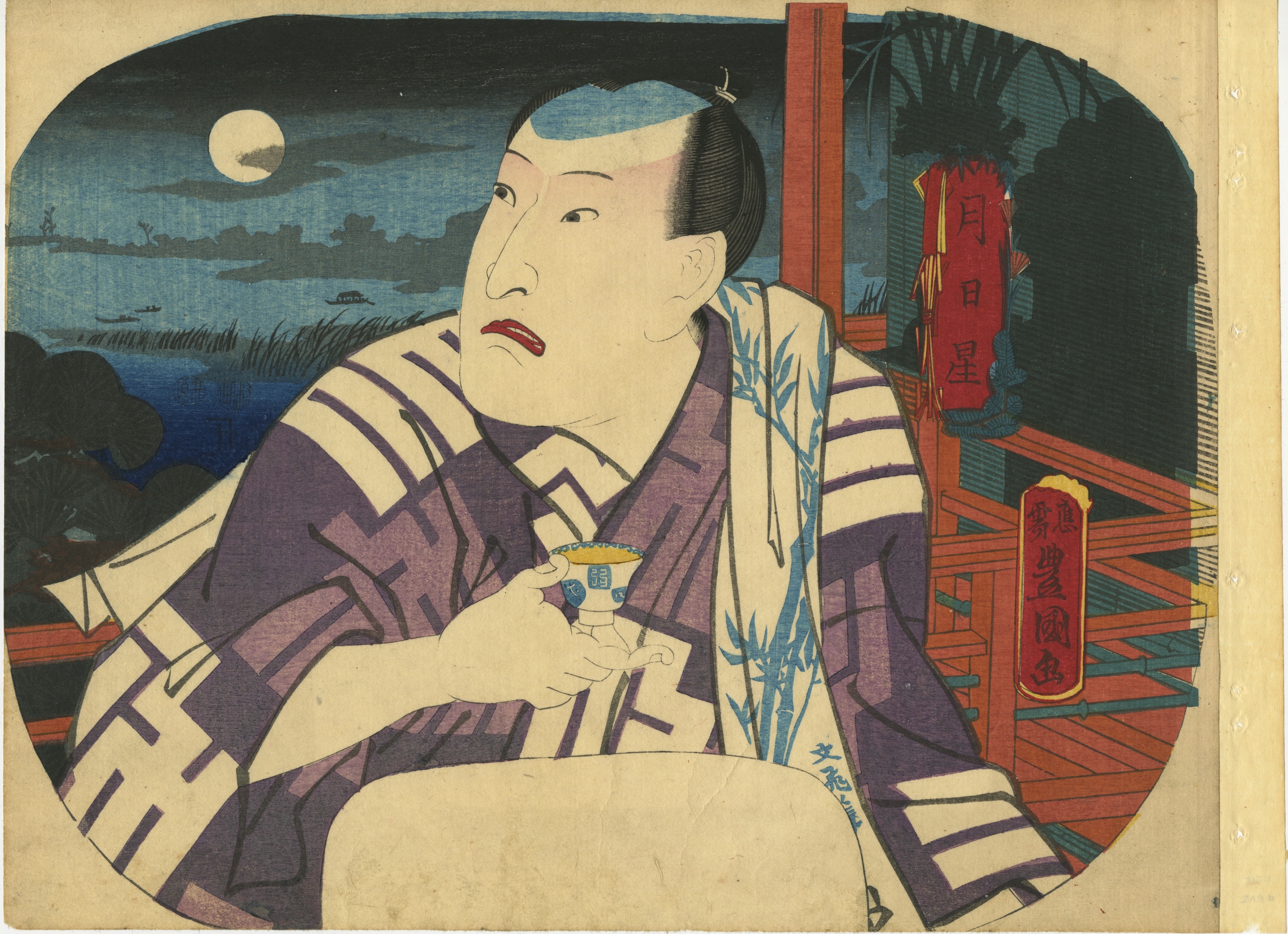
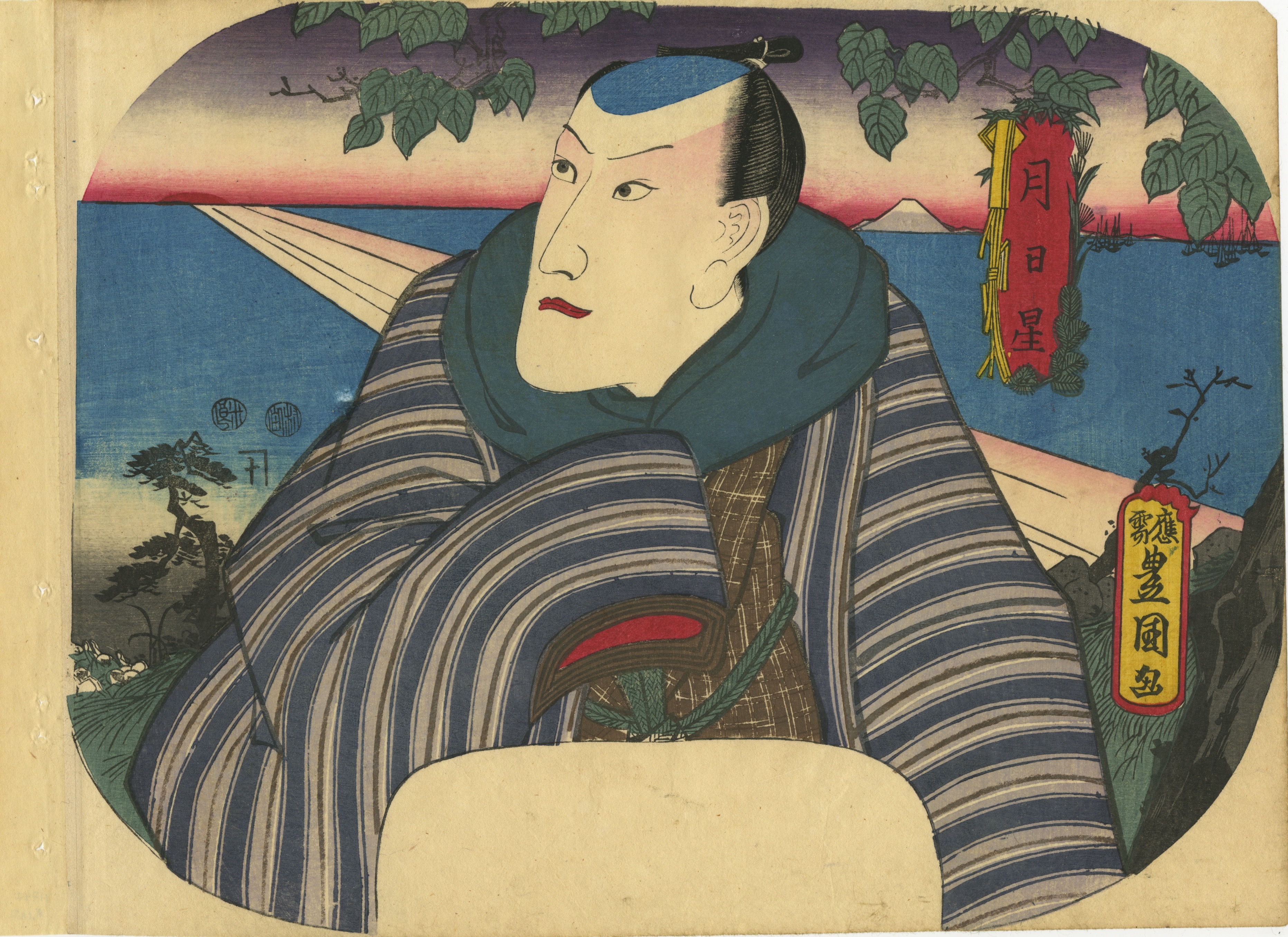
The actor Morita Kan'ya XI (1802-1863) is in the role of Saito Tarozaemon Toshiyuki from the play
Oto no Miya Asahi no Yoroi (Oto no Miyo and the Armor of the Rising Sun). The play picks up following the Genko War of 1331-33 in which Emperor Go-Daigo (1288-1339) led a failed uprising against the ruling Hojo clan. Tarozaemon was a Hojo warlord and is credited with much of the victory. After the conflict, his lord Norisada receives a summer festival lantern from the courtesan Sanmi-no-Tsubone, which bears a riddling inscription. He and Tarozaemon deliberate over the courtesan and her message for quite some time until they realize that she is attempting to manipulate Norisada in the hopes of returning the Emperor from exile. Following this revelation, Norisada reinterprets the message to mean
kiriko, literally "to cut a child," and determines that Sanmi-no-Tsubone's son must be killed. He instructs Tarozaemon to do the deed. However, unbeknownst to Norisada and in spite of his allegiance to the Hojo clan, Tarozaemon is sympathetic to Sanmi-no-Tsubone and her son. At one time, his own daughter had served in the Imperial Palace and was spared execution only through Sanmi-no-Tsubone's intervention. As repayment of that debt, he kills his own grandson in the other boy's stead and returns to Norisada to report that he had accomplished the mission.
This print is from a series of portraits that Kunisada undertook very late in life and has been named
Kinshodo-ban yakusha okubi-e (Kinshodo's Large-Head Actor Portraits) in reference to the publisher, Ebisuya Shochochi of Kinshodo. The series depicted great actors from the past and present in their famous roles. Kunisada was guided by images from his own oeuvre: he recorded Kan'ya in this role in the 8th month of 1829. As this was meant to be Kunisada's grandest actor series, it was executed on thick paper with the best possible pigments and the highest level of craftsmanship. In this unusual frontal portrait, Kunisada presents Morita Kan'ya XI as the loyal Tarozaemon with his eyes rolling upward and his jaw set in grim determination to commit the unthinkable act in an ultimate display of samurai honour.
Text by Scholten Japanese Art, New York.
Ref.: Waseda University Theatre Museum (enpaku.waseda.ac.jp),
accession no. 100-5261 (for 1829 portrait of the same); [
LIB-1212.2017] Robert Schaap. Kunisada: Imaging, drama and beauty. — Leiden: Hotei Publishing, 2016, p. 165 (№ 16).
Andreas Marks. Publishers of Japanese woodblock prints: A compendium. Ebisuya Shoshichi (1846-83) - P6032.
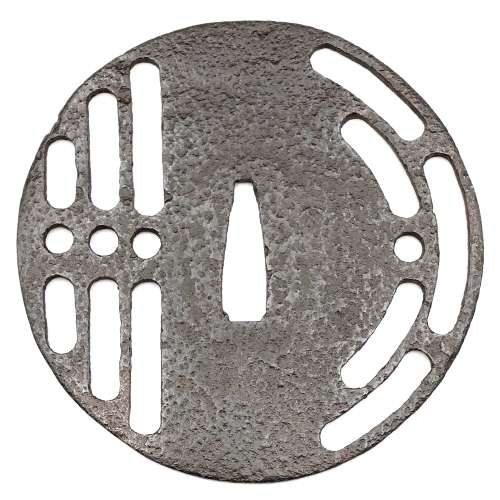
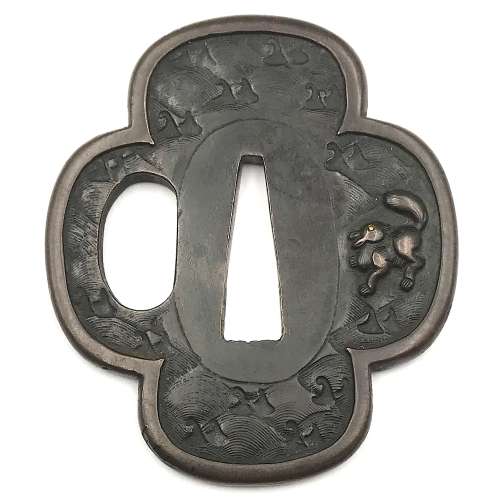
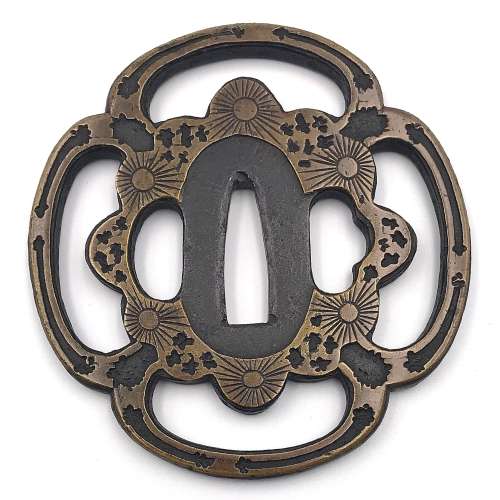
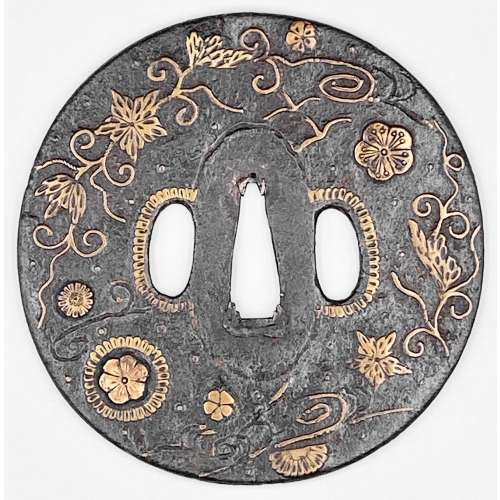
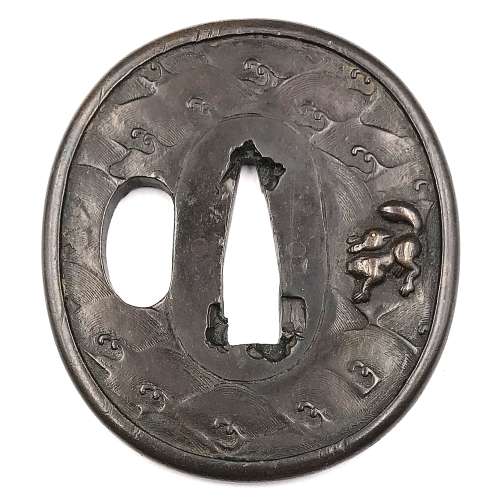
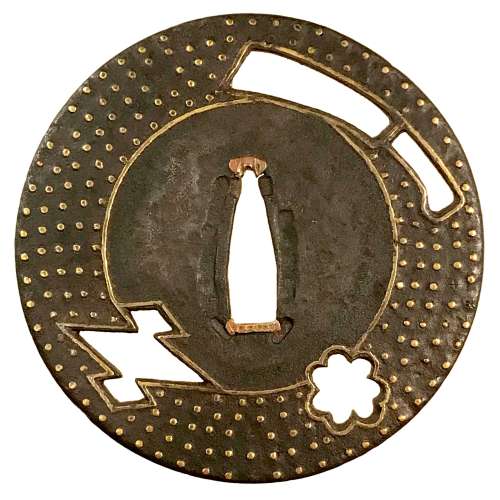
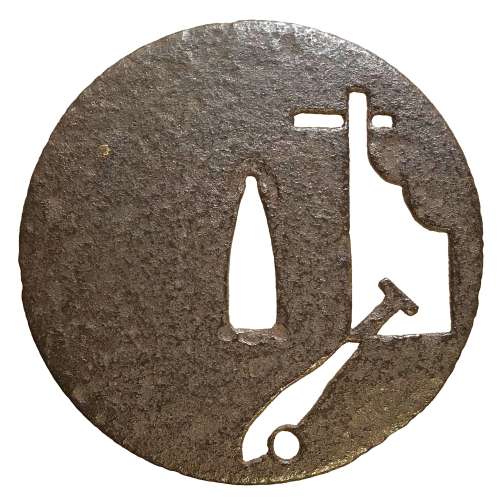
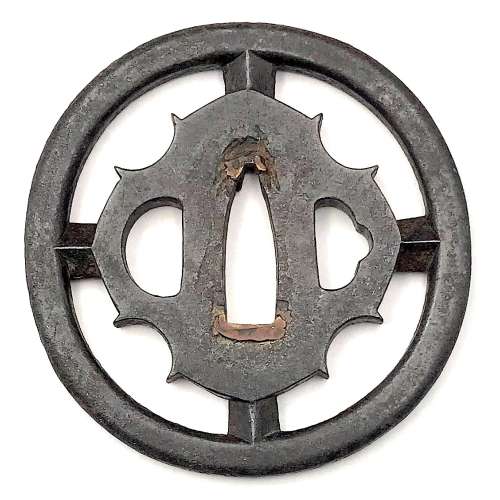
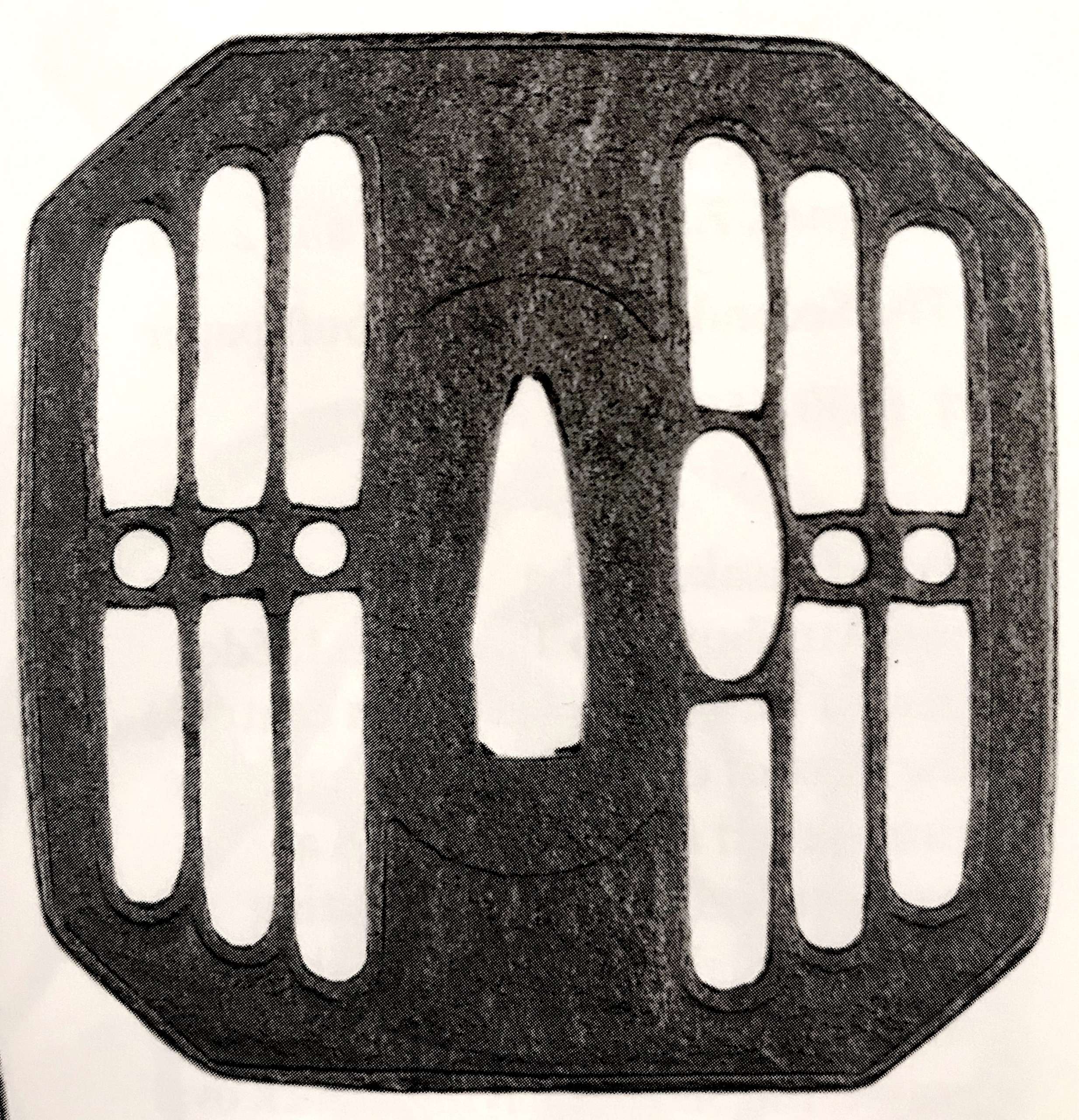
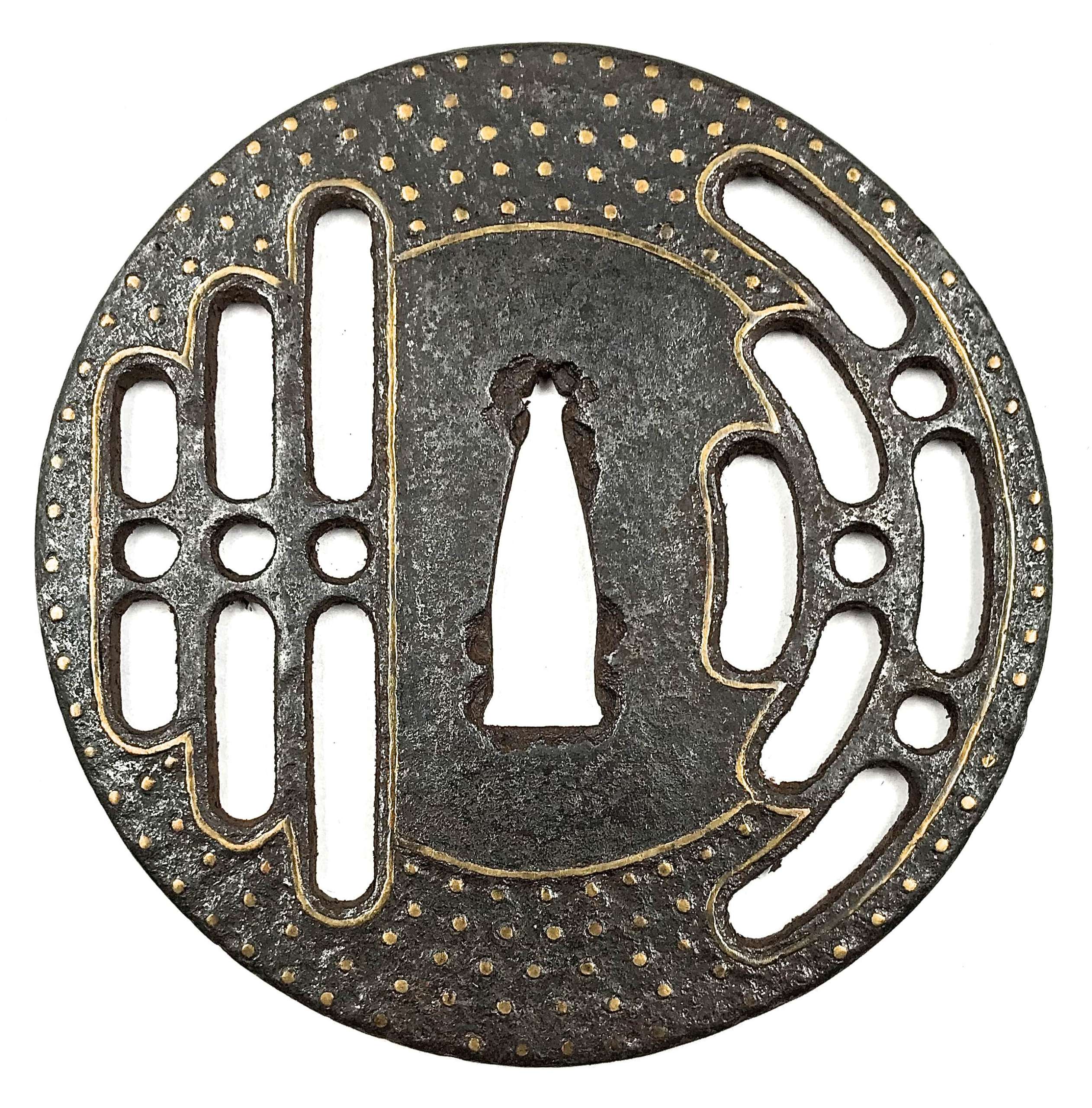 Reference to this design can be found in LIB-1359.2017 Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections, Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997; p. 18-19, lot № 37: "A Kamakura-bori Tsuba, Momoyama Period. ...pierced with two large formalised butterflies..."
Reference to this design can be found in LIB-1359.2017 Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections, Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997; p. 18-19, lot № 37: "A Kamakura-bori Tsuba, Momoyama Period. ...pierced with two large formalised butterflies..."