-
 An uncut aizuri fan print showing two travellers admiring the view of the Tama River [多摩川] (Tamagawa) and Mount Kōya [高野山] (Kōyasan) in Kii Province [紀伊国] (Kii no Kuni). Artist: Utagawa Sadahide [歌川貞秀] (Japanese, 1807 – 1879). Signed: Gountei Sadahide ga [五雲亭貞秀画] (Picture by Gountei Sadahide). Publisher: Unknown. Published: c. 1849. No date seal, no censor seal (privately printed?) Media: Fan print [団扇絵] (uchiwa-e), 235 x 300 mm.
An uncut aizuri fan print showing two travellers admiring the view of the Tama River [多摩川] (Tamagawa) and Mount Kōya [高野山] (Kōyasan) in Kii Province [紀伊国] (Kii no Kuni). Artist: Utagawa Sadahide [歌川貞秀] (Japanese, 1807 – 1879). Signed: Gountei Sadahide ga [五雲亭貞秀画] (Picture by Gountei Sadahide). Publisher: Unknown. Published: c. 1849. No date seal, no censor seal (privately printed?) Media: Fan print [団扇絵] (uchiwa-e), 235 x 300 mm. -
 An uncut aizuri fan print showing travellers arriving at Inba Lake [印旛沼] (Inba-numa) on Shimosa Plateau [下総台地] (Shimōsa-daichi). Artist: Utagawa Sadahide [歌川貞秀] (Japanese, 1807 – 1879) Publisher: Unknown. Published: c. 1849. Signed: Gountei Sadahide ga [五雲亭 貞秀画] (Picture by Gountei Sadahide). Inscription in cartouche: Shimosa Plateau, Inbanuma (Inba Lake) [下總國印幡沼]. No date seal, no censor seal (privately printed?) Media: Fan print [団扇絵] (uchiwa-e), 235 x 300 mm.
An uncut aizuri fan print showing travellers arriving at Inba Lake [印旛沼] (Inba-numa) on Shimosa Plateau [下総台地] (Shimōsa-daichi). Artist: Utagawa Sadahide [歌川貞秀] (Japanese, 1807 – 1879) Publisher: Unknown. Published: c. 1849. Signed: Gountei Sadahide ga [五雲亭 貞秀画] (Picture by Gountei Sadahide). Inscription in cartouche: Shimosa Plateau, Inbanuma (Inba Lake) [下總國印幡沼]. No date seal, no censor seal (privately printed?) Media: Fan print [団扇絵] (uchiwa-e), 235 x 300 mm. -
 An uncut fan print showing Otsu-e [大津絵] (Otsu pictures). Artist: Utagawa Sadahide [歌川貞秀] (Japanese, 1807 – 1879). Signed: Gountei Sadahide ga [五雲亭貞秀画] (Picture by Gountei Sadahide); characters on the Otsu-e. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, c. 1815 – 1869). Published: c. 1849. Inscription in a paper-weight shaped cartouche: [大津追 分絵の図] Ōtsu-oi wake-e no zu (Following Otsu – image of separate pictures) No date seal, no censor seal (privately printed?) Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 235 x 298 mm.
An uncut fan print showing Otsu-e [大津絵] (Otsu pictures). Artist: Utagawa Sadahide [歌川貞秀] (Japanese, 1807 – 1879). Signed: Gountei Sadahide ga [五雲亭貞秀画] (Picture by Gountei Sadahide); characters on the Otsu-e. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, c. 1815 – 1869). Published: c. 1849. Inscription in a paper-weight shaped cartouche: [大津追 分絵の図] Ōtsu-oi wake-e no zu (Following Otsu – image of separate pictures) No date seal, no censor seal (privately printed?) Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 235 x 298 mm. -
 Description: Hardcover 26.5 x 19 cm, grey cloth, red lettering in kanji over black stripe to front, lettering to spine, tan endpapers, pictorial slipcase 27 x 19.5 cm; pp.: [1-6] 7-95 [96], pasted frontispiece and 79 colour illustrations with captions, within a collation. Series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, №8. ISBN: 9780870110986; 0870110985. Ref.: Worldcat Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | "THE DECADENTS” | by Jūzō Suzuki and Isaburō Oka | translation by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A. || (Vertical text in kanji to the right, between rules). Artists: Utagawa Kunisada (Japanese [歌川 国貞], 1786 – 1865); Utagawa Kuniyoshi (Japanese [歌川 国芳], 1798 – 1861); Keisai Eisen [Japanese [渓斎 英泉], 1790 – 1848). Contributors: Jūzō Suzuki [鈴木重三] (Japanese, 1919 – 2010) – author. Isaburō Oka [岡畏三郎] (Japanese, 1914 –2010) – author. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – translator Kunisada's fan print in this collection (exactly the same copy) [SVJP-0380.2022]:
Description: Hardcover 26.5 x 19 cm, grey cloth, red lettering in kanji over black stripe to front, lettering to spine, tan endpapers, pictorial slipcase 27 x 19.5 cm; pp.: [1-6] 7-95 [96], pasted frontispiece and 79 colour illustrations with captions, within a collation. Series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, №8. ISBN: 9780870110986; 0870110985. Ref.: Worldcat Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | "THE DECADENTS” | by Jūzō Suzuki and Isaburō Oka | translation by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A. || (Vertical text in kanji to the right, between rules). Artists: Utagawa Kunisada (Japanese [歌川 国貞], 1786 – 1865); Utagawa Kuniyoshi (Japanese [歌川 国芳], 1798 – 1861); Keisai Eisen [Japanese [渓斎 英泉], 1790 – 1848). Contributors: Jūzō Suzuki [鈴木重三] (Japanese, 1919 – 2010) – author. Isaburō Oka [岡畏三郎] (Japanese, 1914 –2010) – author. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – translator Kunisada's fan print in this collection (exactly the same copy) [SVJP-0380.2022]:

-
 Title: Early Spring [初春之図] (Hatsuharu no zu); Series: Fashionable Twelve Months [今様十二ヶ月] (Imayo juni-kagetsu). Another version of translation: Modern Beauties of Twelve Months. Artist: Utagawa Toyokuni I [歌川豊国] (1769–1825). Pubisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, 1815 – 1869), seal: Dansendō [伊場仙]. Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国画] and sealed with toshidama. Date-kiwame seal: Ushi (ox), Bunsei 5 (1822). Size: double-sheet uncut fan print ( aiban uchiwa-e), each 217 x 288 mm. Ref: Tokyo Museum Collection.
Title: Early Spring [初春之図] (Hatsuharu no zu); Series: Fashionable Twelve Months [今様十二ヶ月] (Imayo juni-kagetsu). Another version of translation: Modern Beauties of Twelve Months. Artist: Utagawa Toyokuni I [歌川豊国] (1769–1825). Pubisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, 1815 – 1869), seal: Dansendō [伊場仙]. Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国画] and sealed with toshidama. Date-kiwame seal: Ushi (ox), Bunsei 5 (1822). Size: double-sheet uncut fan print ( aiban uchiwa-e), each 217 x 288 mm. Ref: Tokyo Museum Collection.
Other five prints of this series: SVJP 0326.2020; SVJP-0362.2022; SVJP-0363.2022; SVJP-0364.2022; SVJP-0365.2022.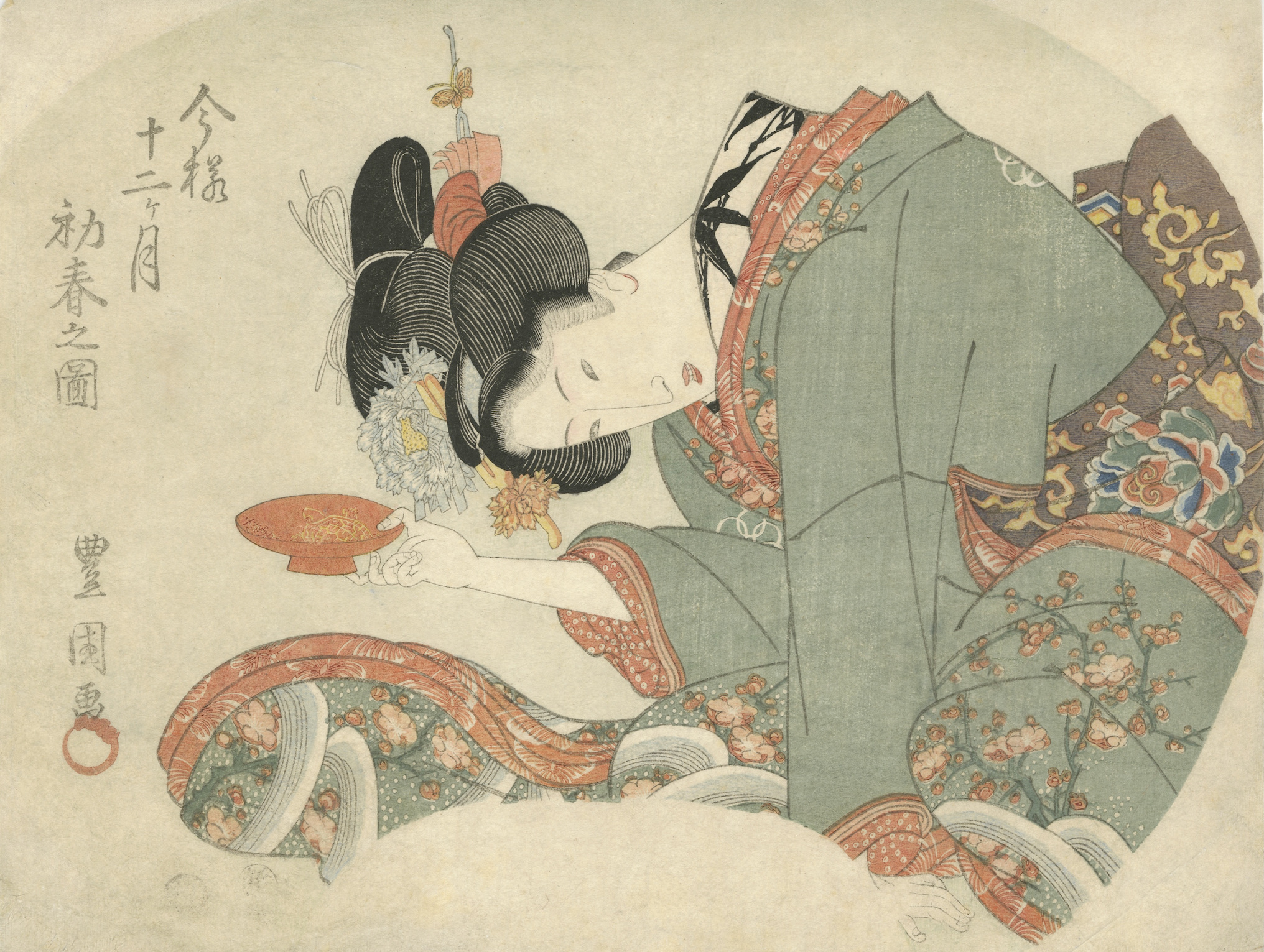
-
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Pubisher (accorfding to Suzuki & Oka): Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, 1815 – 1869), Dansendō [伊場仙]. Title: Beauty holding a roll of paper (by seller); A woman of Edo (by Suzuki & Oka) Date seal and aratame censor seal: 1822 (Bunsei 5). Signed: Gototei Kunisada ga [五渡亭国貞画]. Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 228 x 295 mm. Ref: [LIB-3085.2022] Jūzō Suzuki, Isaburō Oka. “The decadents”. — Tokyo: Kodansha International, 1969, p. 35, plate 30: exactly this print:
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Pubisher (accorfding to Suzuki & Oka): Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, 1815 – 1869), Dansendō [伊場仙]. Title: Beauty holding a roll of paper (by seller); A woman of Edo (by Suzuki & Oka) Date seal and aratame censor seal: 1822 (Bunsei 5). Signed: Gototei Kunisada ga [五渡亭国貞画]. Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 228 x 295 mm. Ref: [LIB-3085.2022] Jūzō Suzuki, Isaburō Oka. “The decadents”. — Tokyo: Kodansha International, 1969, p. 35, plate 30: exactly this print:
-
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). No publisher seal, no date or censor seal; probably a private printing. Signed: Kunisada ga [国貞画] in a red double gourd cartouche. Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 231 x 294 mm, with the use of mica and black lacquer.
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). No publisher seal, no date or censor seal; probably a private printing. Signed: Kunisada ga [国貞画] in a red double gourd cartouche. Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 231 x 294 mm, with the use of mica and black lacquer. -
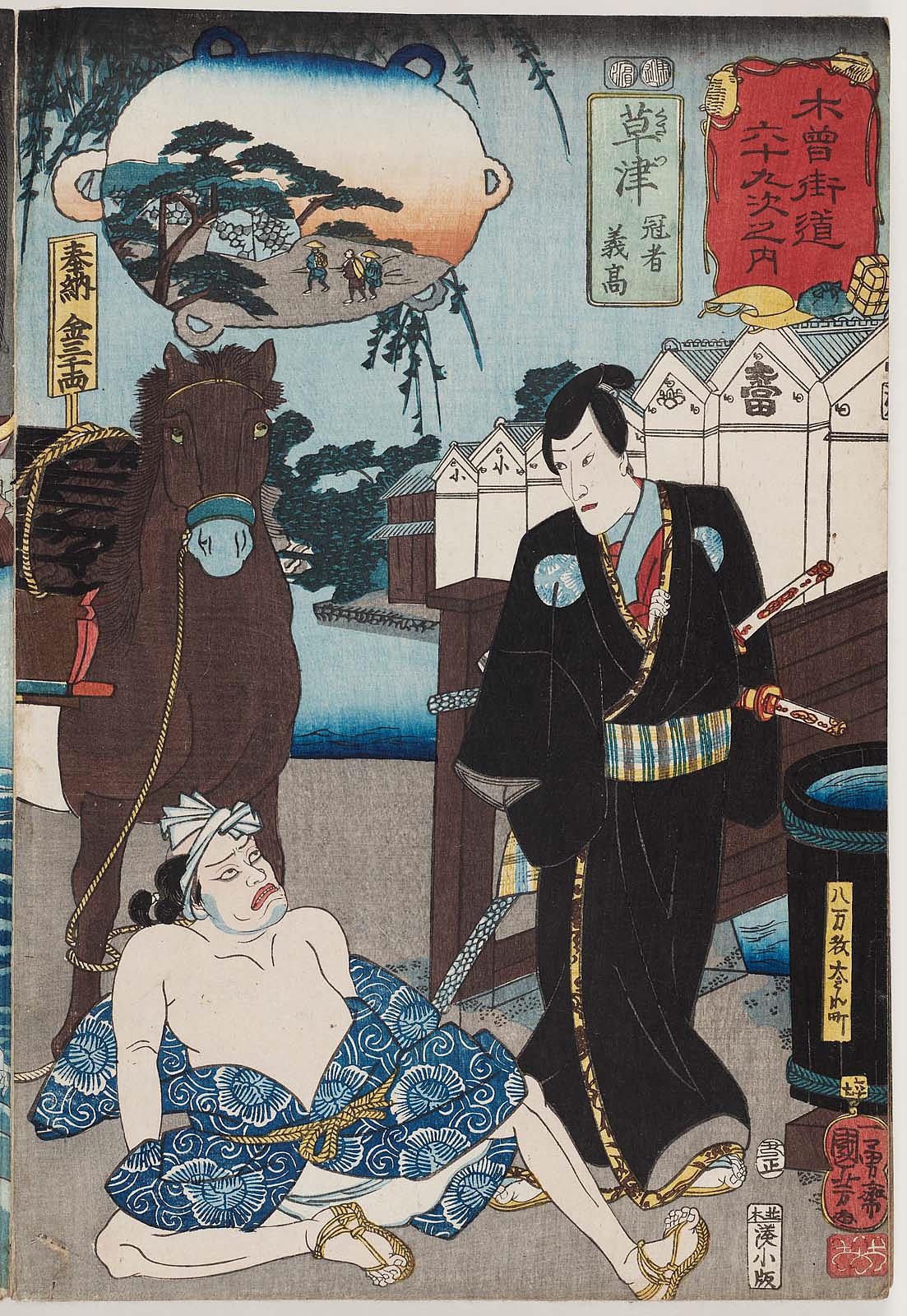
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Artist signature: By the brush of the 79-year-old Toyokuni [七十九歳豊國画] (Nanajūkyū-sai Toyokuni ga). Publisher: Ebiya Rinnosuke [海老屋林之助] (Japanese, fl. c. 1832 – 1895); seal: ト/ 海老林 (to, Ebirin). Block carver: Matsushima Masakichi [松島政吉]; seal: carved by Masa [彫政] (Hori Masa). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: [子極] 1864 (Bunkyū 4/Genji 1). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 223 x 297 mm. Inscription in the cartouches: (R) Wakana-hime [若菜姫], Sawamura Tanosuke III [沢村田之助]; (L) Ashikaga Sanshichirō [足利三七郎], Sawamura Tosshō II [沢村訥升]. Play: Kinoene Soga Daikoku-bashira [甲子曽我大国柱], performed at the Morita theatre [森田座・守田座] (Morita-za) in 1864 (Bunkyū 4/Genji 1), 2nd month (see playbill at MFA-Boston Collection). Playwright: Muraoka Kōji II [村岡幸治]. Actors and Characters: Sawamura Tanosuke III [三代目沢村田之助] (Japanese, 1859 – 1878); other names: Shozan [曙山] (poetry name), Sawamura Yoshijirō I [初代沢村由次郎], here in the role of Princess Wakana [若菜姫] (Wakana-hime) (R). The story about Princess Wakana, Shiranui Monogatari, was written by Ryukatei Tanekazu [柳下亭種員] (Japanese, 1807 – 1858) and published as a 90-volume book of comics between 1849 and 1855. ...The tale revolves around the clash between the Kikuchi and Ōtomo clans. Princess Wakana’s father Ōtomo Sōrin [大友 宗麟] (1530 – 1587) was killed in a battle, and his spirit demanded revenge. To appease her late father's spirit, Princes Wakana acquired the power of the Earth Spider. She often appears in prints with a magic scroll, which helps her fight various enemies. Sawamura Tosshō II [二代目沢村訥升] (Japanese, 1854 – 1879); other names: Kōga [高賀] (poetry name), Sawamura Genpei II [二代目沢村源平], Sawamura Sōjūrō [澤村宗十郎], Suketakaya Takasuke IV [四代目助高屋高助], Sawamura Tosshi VI [六代目澤村訥子] (poetry name), here in the role of Ashikaga Sanshichirō [足利三七郎] (L) with a horse. According to Markus Sesko, the scene comes from the kabuki play Umakiri (馬斬り) by Tatsuoka Mansaku [辰岡万作] (17432 – 1809), which premiered in 1794. It was later assimilated into the Kabuki play Kozotte Mimasu Kuruwa no Datezome [襷廓三升伊達染], which was staged in the 1st lunar month of 1853 at the Nakamura-za. Umakiri is based on a Kyōgen play featured in Hideyoshi’s biography Taikōki [太閤記]. Its plot is that Ashikaga Sanchichirō Yoshitaka [足利三七郎義孝・義高], who is supposed to allude to Nobunaga’s son Oda Sanshichirō Nobutaka [織田三七郎信孝], attacks and kills a horse that is carrying 3,000 ryō (金三千両), money Mashiba Hisayoshi [真柴久吉] (an allusion to Hashiba Hideyoshi [羽柴秀吉]) had sent to be donated to a shrine on Mt. Kōya. The surrounding people try to catch him, but when they hear it is Yoshitaka who killed the horse, they fall to the ground and prostrate, and Yoshitaka leisurely leaves with the money. The plot is very simple, but Yoshitaka’s dashing appearance makes it very pleasing to watch. There are also prints that quote the main protagonist as Ashikaga Sanshichirō Harutaka [足利三七郎春高], and there is another title for the play, Sanzen-Ryō Kogane no Kurairi [三千両黄金蔵入] (Pocketing 3,000 ryō of gold). For reference, see also the BLOG. What these two characters are doing in one play remains a riddle. As Mr Graebner comments: "Most kabuki plays were only performed for one season (two months), and the books were lost. The playwrights have repeatedly used parts of plots from other plays, they have adopted characters, sometimes with the same or similar names. What can be found is the Kabuki Playbill (Tsuji banzuke) with cast and roles; the content is lost". Acknowledgements: Special thanks to Horst Graebner of the Kunisada Project and to Markus Sesko of The Metropolitan Museum, NY, for the analysis of the image and their invaluable contribution. For reference, see also:
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞] a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代歌川豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Artist signature: By the brush of the 79-year-old Toyokuni [七十九歳豊國画] (Nanajūkyū-sai Toyokuni ga). Publisher: Ebiya Rinnosuke [海老屋林之助] (Japanese, fl. c. 1832 – 1895); seal: ト/ 海老林 (to, Ebirin). Block carver: Matsushima Masakichi [松島政吉]; seal: carved by Masa [彫政] (Hori Masa). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: [子極] 1864 (Bunkyū 4/Genji 1). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 223 x 297 mm. Inscription in the cartouches: (R) Wakana-hime [若菜姫], Sawamura Tanosuke III [沢村田之助]; (L) Ashikaga Sanshichirō [足利三七郎], Sawamura Tosshō II [沢村訥升]. Play: Kinoene Soga Daikoku-bashira [甲子曽我大国柱], performed at the Morita theatre [森田座・守田座] (Morita-za) in 1864 (Bunkyū 4/Genji 1), 2nd month (see playbill at MFA-Boston Collection). Playwright: Muraoka Kōji II [村岡幸治]. Actors and Characters: Sawamura Tanosuke III [三代目沢村田之助] (Japanese, 1859 – 1878); other names: Shozan [曙山] (poetry name), Sawamura Yoshijirō I [初代沢村由次郎], here in the role of Princess Wakana [若菜姫] (Wakana-hime) (R). The story about Princess Wakana, Shiranui Monogatari, was written by Ryukatei Tanekazu [柳下亭種員] (Japanese, 1807 – 1858) and published as a 90-volume book of comics between 1849 and 1855. ...The tale revolves around the clash between the Kikuchi and Ōtomo clans. Princess Wakana’s father Ōtomo Sōrin [大友 宗麟] (1530 – 1587) was killed in a battle, and his spirit demanded revenge. To appease her late father's spirit, Princes Wakana acquired the power of the Earth Spider. She often appears in prints with a magic scroll, which helps her fight various enemies. Sawamura Tosshō II [二代目沢村訥升] (Japanese, 1854 – 1879); other names: Kōga [高賀] (poetry name), Sawamura Genpei II [二代目沢村源平], Sawamura Sōjūrō [澤村宗十郎], Suketakaya Takasuke IV [四代目助高屋高助], Sawamura Tosshi VI [六代目澤村訥子] (poetry name), here in the role of Ashikaga Sanshichirō [足利三七郎] (L) with a horse. According to Markus Sesko, the scene comes from the kabuki play Umakiri (馬斬り) by Tatsuoka Mansaku [辰岡万作] (17432 – 1809), which premiered in 1794. It was later assimilated into the Kabuki play Kozotte Mimasu Kuruwa no Datezome [襷廓三升伊達染], which was staged in the 1st lunar month of 1853 at the Nakamura-za. Umakiri is based on a Kyōgen play featured in Hideyoshi’s biography Taikōki [太閤記]. Its plot is that Ashikaga Sanchichirō Yoshitaka [足利三七郎義孝・義高], who is supposed to allude to Nobunaga’s son Oda Sanshichirō Nobutaka [織田三七郎信孝], attacks and kills a horse that is carrying 3,000 ryō (金三千両), money Mashiba Hisayoshi [真柴久吉] (an allusion to Hashiba Hideyoshi [羽柴秀吉]) had sent to be donated to a shrine on Mt. Kōya. The surrounding people try to catch him, but when they hear it is Yoshitaka who killed the horse, they fall to the ground and prostrate, and Yoshitaka leisurely leaves with the money. The plot is very simple, but Yoshitaka’s dashing appearance makes it very pleasing to watch. There are also prints that quote the main protagonist as Ashikaga Sanshichirō Harutaka [足利三七郎春高], and there is another title for the play, Sanzen-Ryō Kogane no Kurairi [三千両黄金蔵入] (Pocketing 3,000 ryō of gold). For reference, see also the BLOG. What these two characters are doing in one play remains a riddle. As Mr Graebner comments: "Most kabuki plays were only performed for one season (two months), and the books were lost. The playwrights have repeatedly used parts of plots from other plays, they have adopted characters, sometimes with the same or similar names. What can be found is the Kabuki Playbill (Tsuji banzuke) with cast and roles; the content is lost". Acknowledgements: Special thanks to Horst Graebner of the Kunisada Project and to Markus Sesko of The Metropolitan Museum, NY, for the analysis of the image and their invaluable contribution. For reference, see also: -
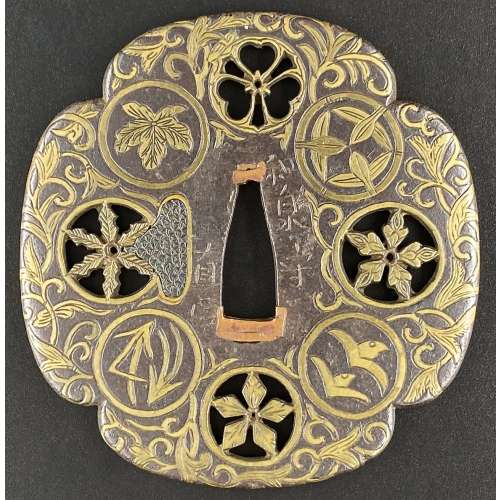 The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba.
The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba. -
 Artist: Utagawa Hiroshige II (二代目 歌川広重] (Japanese, 1826 – 1869). Signed: Hiroshige ga. Publisher: Enshūya Matabei [遠州屋又兵衛] (Japanese, fl. c. 1768 – 1881); (Enmata [遠又]), seal 22-009 (Marks). Block carver: Matsushima Masakichi (Japanese, fl. c. 1847-65); seal: [松嶋彫政] – Hori Masa (Frieze, 2009: 142). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: Bunkyū 2 (1862). Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 230 x 298 mm Series: Three Famous Views in Ise [伊勢名所三景] (Ise meisho sankei).
Artist: Utagawa Hiroshige II (二代目 歌川広重] (Japanese, 1826 – 1869). Signed: Hiroshige ga. Publisher: Enshūya Matabei [遠州屋又兵衛] (Japanese, fl. c. 1768 – 1881); (Enmata [遠又]), seal 22-009 (Marks). Block carver: Matsushima Masakichi (Japanese, fl. c. 1847-65); seal: [松嶋彫政] – Hori Masa (Frieze, 2009: 142). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: Bunkyū 2 (1862). Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 230 x 298 mm Series: Three Famous Views in Ise [伊勢名所三景] (Ise meisho sankei). -
 Title: Modori Kago [戻駕] (Returning palanquin). The dance-drama Modori Kago Iro ni Aikata [戻駕色相肩] premiered in the 11th lunar month of 1788 at the Nakamuraza [中村座], within Sakurada Jisuke I's kaomise [顔見世] (faceshowing) program Tôzumô Hana no Edogata [唐相撲花江戸方]", which celebrated the homecoming to Edo, after two years' absence, of Nakamura Nakazō I, and was intended to show off his particular talents in the role of Jirosaku (in reality Ishikawa Goemon [石川 五右衛門]) [kabuki21]. The symbol on a green book cover is the informal crest of tokiwazu-bushi [常磐津節] shaped like a water chestnut (Eleocharis dulcis) lozenge. Artist signature 国盛画 (Kunimori ga) with red toshidama. According to Samuel L. Leiter’s Kabuki Encyclopedia (1979), p. 243: The palanquin bearers Nanpa no Jirosaku and Azuma no Yōshirō, who are bearing a palanquin with a courtesan's young handmaiden in it, stop to rest at Kyoto's Murasakino, and each dances his regional dance. Then they call the girl, who does a dance showing the visitors to the famous pleasure quarters, Yoshiwara and Shimabara. The two men recognize each other as Ishikawa Goemon and Masashiba Hisayoshi, sworn enemies, and engage in a fight. This number is the only remaining section of an annual "faceshowing” (kaomize) work with a plot based on the medieval chronicle called the Toikōki. The full-length piece was called Kara Sumō Hanaeda no Kata. It is one of the most famous tokiwazu pieces and preserves the old-style Kabuki flavour. Nakamura Nakazō I played Jirosaku and Matsumoto Kōshirō IV was Yoshiro in the first production. The handmaiden was Matsumoto Komesaburō (probably Matsumoto Komasaburō I, an unknown actor [SV]). According to Egenolf Gallery: This work was first performed in 1788 at the Edo Nakamura-za as the season’s first performance and featured Nakamura Nakazō, who returned to Edo after three years in Osaka. It was a dance with tokiwazu chanting and was designed for him to play the lead role. In the piece, two palanquin carriers, one from Osaka, another from Edo, and a passenger – a kamuro, (a young geisha-in-training) exchange stories about the pleasure quarters of Shimabara and Yoshiwara. The text of the chanting book is open next to her, carrying the title “Collection of Practicing” [稽古尽くし], on which the green bundle cover carries the crest of Tokiwazu School, matsu-kawa-bishi, diamond variety of pine bark and the artist’s signature. Tokiwazu is a type of jōruri, narrative music, and accompanies dancing on the kabuki stage. Ref.: Christie's 27 Mar 2006. Publisher: Maruya Jinpachi, seal Marujin (Marks: 12-029 | 294e) Single nanushi censor seal: Mura (Murata Sahei, 1842-46). Provenance: Circular seal of the collector Huguette Bérès to verso. Contributors: Utagawa Kunimori [歌川国盛] (Japanese, fl. c. 1818 – 1943) – artist. Maruya Jinpachi [丸屋甚八] (Japanese, fl. 1770 – 1842) – publisher. Other mentioned: Nakamura Nakazō I [中村仲蔵] (Japanese, 1736 – 1790); other names: Nakayama Kojūrō VI, Nakamura Ichijūrō, Nakayama Manzō – actor. Matsumoto Kōshirō IV [松本幸四郎] (Japanese, 1737 – 1802); other names: Omegawa Kyōjūrō; Ichikawa Komazō II, Ichikawa Somegorô I, Ichikawa Takejūrō ; Segawa Kinji; Segawa Kingo – actor. Sakurada Jisuke I [桜田治助] (Japanese, 1734 – 1806) – dramatist.
Title: Modori Kago [戻駕] (Returning palanquin). The dance-drama Modori Kago Iro ni Aikata [戻駕色相肩] premiered in the 11th lunar month of 1788 at the Nakamuraza [中村座], within Sakurada Jisuke I's kaomise [顔見世] (faceshowing) program Tôzumô Hana no Edogata [唐相撲花江戸方]", which celebrated the homecoming to Edo, after two years' absence, of Nakamura Nakazō I, and was intended to show off his particular talents in the role of Jirosaku (in reality Ishikawa Goemon [石川 五右衛門]) [kabuki21]. The symbol on a green book cover is the informal crest of tokiwazu-bushi [常磐津節] shaped like a water chestnut (Eleocharis dulcis) lozenge. Artist signature 国盛画 (Kunimori ga) with red toshidama. According to Samuel L. Leiter’s Kabuki Encyclopedia (1979), p. 243: The palanquin bearers Nanpa no Jirosaku and Azuma no Yōshirō, who are bearing a palanquin with a courtesan's young handmaiden in it, stop to rest at Kyoto's Murasakino, and each dances his regional dance. Then they call the girl, who does a dance showing the visitors to the famous pleasure quarters, Yoshiwara and Shimabara. The two men recognize each other as Ishikawa Goemon and Masashiba Hisayoshi, sworn enemies, and engage in a fight. This number is the only remaining section of an annual "faceshowing” (kaomize) work with a plot based on the medieval chronicle called the Toikōki. The full-length piece was called Kara Sumō Hanaeda no Kata. It is one of the most famous tokiwazu pieces and preserves the old-style Kabuki flavour. Nakamura Nakazō I played Jirosaku and Matsumoto Kōshirō IV was Yoshiro in the first production. The handmaiden was Matsumoto Komesaburō (probably Matsumoto Komasaburō I, an unknown actor [SV]). According to Egenolf Gallery: This work was first performed in 1788 at the Edo Nakamura-za as the season’s first performance and featured Nakamura Nakazō, who returned to Edo after three years in Osaka. It was a dance with tokiwazu chanting and was designed for him to play the lead role. In the piece, two palanquin carriers, one from Osaka, another from Edo, and a passenger – a kamuro, (a young geisha-in-training) exchange stories about the pleasure quarters of Shimabara and Yoshiwara. The text of the chanting book is open next to her, carrying the title “Collection of Practicing” [稽古尽くし], on which the green bundle cover carries the crest of Tokiwazu School, matsu-kawa-bishi, diamond variety of pine bark and the artist’s signature. Tokiwazu is a type of jōruri, narrative music, and accompanies dancing on the kabuki stage. Ref.: Christie's 27 Mar 2006. Publisher: Maruya Jinpachi, seal Marujin (Marks: 12-029 | 294e) Single nanushi censor seal: Mura (Murata Sahei, 1842-46). Provenance: Circular seal of the collector Huguette Bérès to verso. Contributors: Utagawa Kunimori [歌川国盛] (Japanese, fl. c. 1818 – 1943) – artist. Maruya Jinpachi [丸屋甚八] (Japanese, fl. 1770 – 1842) – publisher. Other mentioned: Nakamura Nakazō I [中村仲蔵] (Japanese, 1736 – 1790); other names: Nakayama Kojūrō VI, Nakamura Ichijūrō, Nakayama Manzō – actor. Matsumoto Kōshirō IV [松本幸四郎] (Japanese, 1737 – 1802); other names: Omegawa Kyōjūrō; Ichikawa Komazō II, Ichikawa Somegorô I, Ichikawa Takejūrō ; Segawa Kinji; Segawa Kingo – actor. Sakurada Jisuke I [桜田治助] (Japanese, 1734 – 1806) – dramatist. -
 Artist: Utagawa Toyokuni I [歌川豊国] (1769–1825). Pubisher: Enshūya Matabei (遠州屋又兵衛) (c. 1768 – 1881), seal name: Enmata [ 遠又]. Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国画]. Date-aratame censor seal: 未改, Bunsei 6 (1823). Size: uchiwa-e; 233 x 262 mm. Ref: Israel Goldman. Japanese Prints, Paintings and Books / Catalogue 28, 2022: № 14.
Artist: Utagawa Toyokuni I [歌川豊国] (1769–1825). Pubisher: Enshūya Matabei (遠州屋又兵衛) (c. 1768 – 1881), seal name: Enmata [ 遠又]. Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国画]. Date-aratame censor seal: 未改, Bunsei 6 (1823). Size: uchiwa-e; 233 x 262 mm. Ref: Israel Goldman. Japanese Prints, Paintings and Books / Catalogue 28, 2022: № 14. -
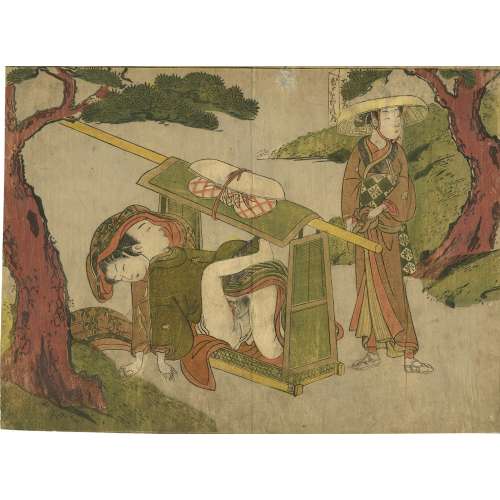 A shunga (erotic) print by Suzuki Harunobu [鈴木 春信] (Japanese, c. 1725 – 1770) depicting a woman making love with a man in the palanquin (のりもの/乗り物) while the other woman "ties a sash about her hips below her obi." The sheet is not signed; however, it is attributed to Harunobu. A reference image can be found in the Metropolitan Museum (NY) collection, Accession Number JP1635:According to the MET "the palanquin ... has carried these courtesans to the shore for a spring outing". Some time ago, a similar print was sold by Richard Kruml (description: A chuban shunga print showing the occupant of a kago in flagrante with one of the porters, having seized the opportunity of a stop on the journey. Published late 1760s. Rare). Another copy was sold at Sotheby's in Paris for €3,360 on November 27, 2002 (Lot 24), with a reproduction of the print's detail and description on p. 39: Suzuki Harunobu (1725 – 1770) | Shunga: couple dans un palanquin, vers 1768-1770, non-signe, cachet non identifé, cachets Charles Mitchell, Huguette Berès, Format chuban, 20.1 x 28.6 cm | 3000 – 4000 € | Il s’agit probablement de trois voyageurs, l’un d’entre eux debout près du palanquin faisant mine d’ignorer la scène. Bibliographie: Delay p. 87. Reference: [LIB-3121.2022] Sotheby's: Collection Huguette Berès – Estampes, dessins et livres illustrés japonais / 2 volumes; vol. 1. — Paris: Sotheby's, 2002.
A shunga (erotic) print by Suzuki Harunobu [鈴木 春信] (Japanese, c. 1725 – 1770) depicting a woman making love with a man in the palanquin (のりもの/乗り物) while the other woman "ties a sash about her hips below her obi." The sheet is not signed; however, it is attributed to Harunobu. A reference image can be found in the Metropolitan Museum (NY) collection, Accession Number JP1635:According to the MET "the palanquin ... has carried these courtesans to the shore for a spring outing". Some time ago, a similar print was sold by Richard Kruml (description: A chuban shunga print showing the occupant of a kago in flagrante with one of the porters, having seized the opportunity of a stop on the journey. Published late 1760s. Rare). Another copy was sold at Sotheby's in Paris for €3,360 on November 27, 2002 (Lot 24), with a reproduction of the print's detail and description on p. 39: Suzuki Harunobu (1725 – 1770) | Shunga: couple dans un palanquin, vers 1768-1770, non-signe, cachet non identifé, cachets Charles Mitchell, Huguette Berès, Format chuban, 20.1 x 28.6 cm | 3000 – 4000 € | Il s’agit probablement de trois voyageurs, l’un d’entre eux debout près du palanquin faisant mine d’ignorer la scène. Bibliographie: Delay p. 87. Reference: [LIB-3121.2022] Sotheby's: Collection Huguette Berès – Estampes, dessins et livres illustrés japonais / 2 volumes; vol. 1. — Paris: Sotheby's, 2002.
http://www.metmuseum.org/art/collection/search/45071
-
 Artist: Veronica Miller attributes the drawing to Utagawa Sadahide [歌川 貞秀] (Japanese, 1807 – 1879), also known as Gountei Sadahide [五雲亭 貞秀]. A preparatory drawing for a fan print depicts two women raking pine needles along the scenic beach at Harima. Inscription at top right "Maiko Beach in Harima" (Harima Maiko no Hama) [播磨 舞子濱], which is now located in Hyōgo Prefecture. The view must be of the Akashi Strait, looking towards Awaji Island. Drawn on thin hanshita paper, mounted lightly at the top to a backing paper, but unbacked. Size: 240 x 319 mm. Attribution to Sadahide based on his design titled "Suma Bay: Matsukaze and Murasame" (see below):
Artist: Veronica Miller attributes the drawing to Utagawa Sadahide [歌川 貞秀] (Japanese, 1807 – 1879), also known as Gountei Sadahide [五雲亭 貞秀]. A preparatory drawing for a fan print depicts two women raking pine needles along the scenic beach at Harima. Inscription at top right "Maiko Beach in Harima" (Harima Maiko no Hama) [播磨 舞子濱], which is now located in Hyōgo Prefecture. The view must be of the Akashi Strait, looking towards Awaji Island. Drawn on thin hanshita paper, mounted lightly at the top to a backing paper, but unbacked. Size: 240 x 319 mm. Attribution to Sadahide based on his design titled "Suma Bay: Matsukaze and Murasame" (see below):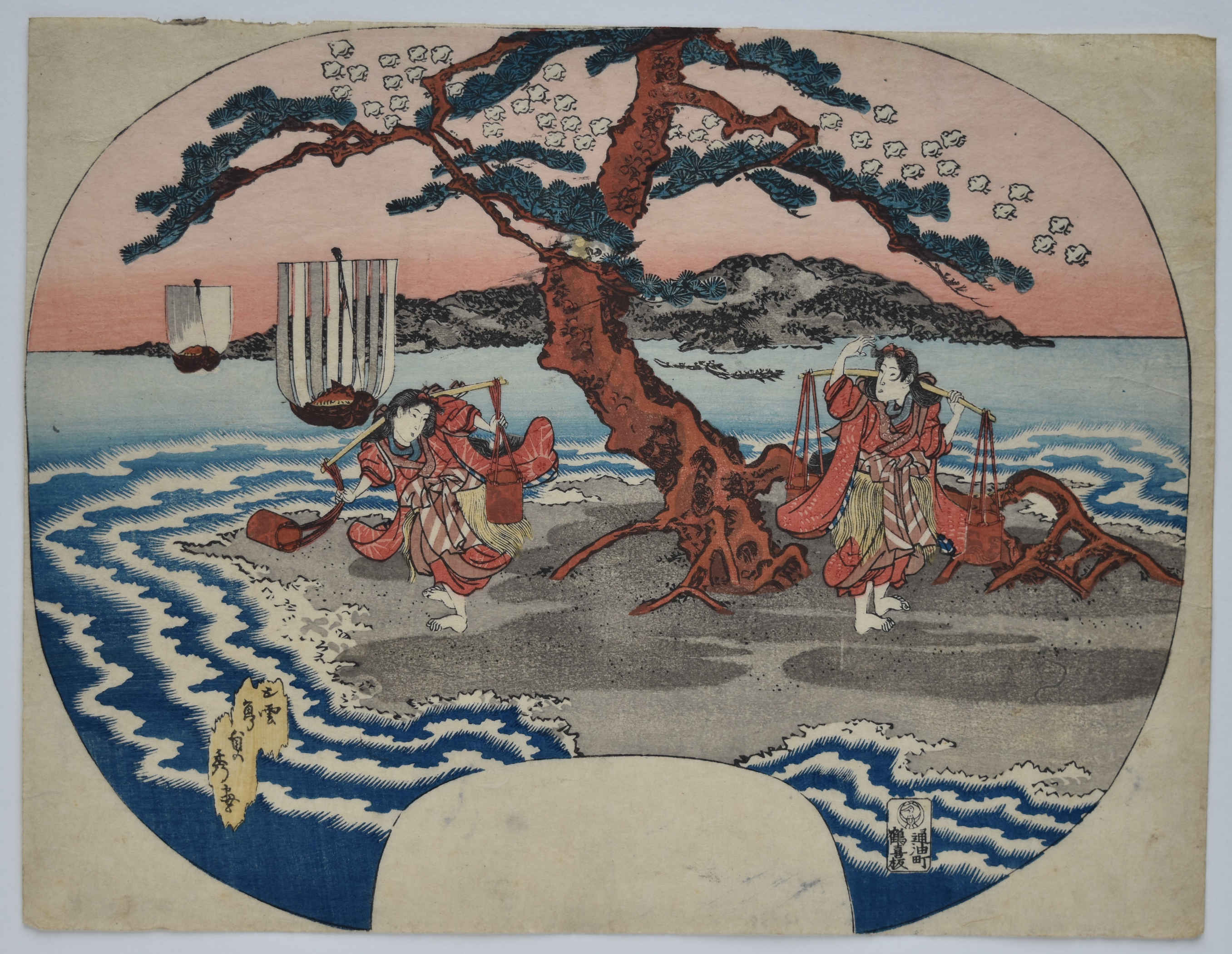 See also Maiko Beach, Harima Province, from the series Views of Famous Places in the Sixty-Odd Provinces,
See also Maiko Beach, Harima Province, from the series Views of Famous Places in the Sixty-Odd Provinces,
-
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada, a.k.a. Toyokuni III (Japanese, 1786 – 1865) [歌川 国貞]. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. C. 1845 – 1847). Date aratame seal: Bunsei 12 (1829). Signed: Gototei Kunisada ga [五渡亭国貞画]. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e), 238 x 267 mm (overtrimmed). Actor: Iwai Shijaku I [紫若] (Japanese, 1804 – 1845); other names: Iwai Matsunosuke I [岩井松之助]; Iwai Hanshirō VII, Iwai Shijaku I, Iwai Komurasaki I. The background is Arare-ko-mon [霰小紋] hail pattern. In the red cartouche at the top right is the series title "Edo no hana – itsutsu Karigane" (江戸の花 五雁金), to be translated as "Flowers of Edo - the five Karigane blood-brothers" (or "the five Karigane gang members"). Another print from the series in this collection: SVJP-0304.2019.
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada, a.k.a. Toyokuni III (Japanese, 1786 – 1865) [歌川 国貞]. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. C. 1845 – 1847). Date aratame seal: Bunsei 12 (1829). Signed: Gototei Kunisada ga [五渡亭国貞画]. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e), 238 x 267 mm (overtrimmed). Actor: Iwai Shijaku I [紫若] (Japanese, 1804 – 1845); other names: Iwai Matsunosuke I [岩井松之助]; Iwai Hanshirō VII, Iwai Shijaku I, Iwai Komurasaki I. The background is Arare-ko-mon [霰小紋] hail pattern. In the red cartouche at the top right is the series title "Edo no hana – itsutsu Karigane" (江戸の花 五雁金), to be translated as "Flowers of Edo - the five Karigane blood-brothers" (or "the five Karigane gang members"). Another print from the series in this collection: SVJP-0304.2019. -
 Kabuki actor Arashi Kichisaburō III [嵐吉三郎] as Sarushima Sōta [猿島惣太] in the play Hanamo Yoshida Iwao no Matsuwaka [花吉田岩尾松若] staged at Ichimura-za (市村座), theatre in Edo. Artist: Utagawa Kunisada, a.k.a. Toyokuni III (Japanese, 1786 – 1865) [歌川 国貞]. Publisher: Kojimaya Jūbei (Japanese, 1797-1869), seal: Hanmoto, Jū [板元, 十] (Marks 19-043 | 264c. Date seal and double nanushi censor seals Mera & Watanabe – 3rd month of Kaei 6 (1853). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e), 223 x 294 mm. Kabuki actor Arashi Kichisaburō III [嵐吉三郎] (Japanese, 1810 – 1864); other names: Arashi Daizaburō III, Arashi Kitsusaburō III Ref.: Art shop Ezoshi Ukiyoe new collection news, vol. 66, 2023.1 (Jan) # 30, p.8.
Kabuki actor Arashi Kichisaburō III [嵐吉三郎] as Sarushima Sōta [猿島惣太] in the play Hanamo Yoshida Iwao no Matsuwaka [花吉田岩尾松若] staged at Ichimura-za (市村座), theatre in Edo. Artist: Utagawa Kunisada, a.k.a. Toyokuni III (Japanese, 1786 – 1865) [歌川 国貞]. Publisher: Kojimaya Jūbei (Japanese, 1797-1869), seal: Hanmoto, Jū [板元, 十] (Marks 19-043 | 264c. Date seal and double nanushi censor seals Mera & Watanabe – 3rd month of Kaei 6 (1853). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e), 223 x 294 mm. Kabuki actor Arashi Kichisaburō III [嵐吉三郎] (Japanese, 1810 – 1864); other names: Arashi Daizaburō III, Arashi Kitsusaburō III Ref.: Art shop Ezoshi Ukiyoe new collection news, vol. 66, 2023.1 (Jan) # 30, p.8. -
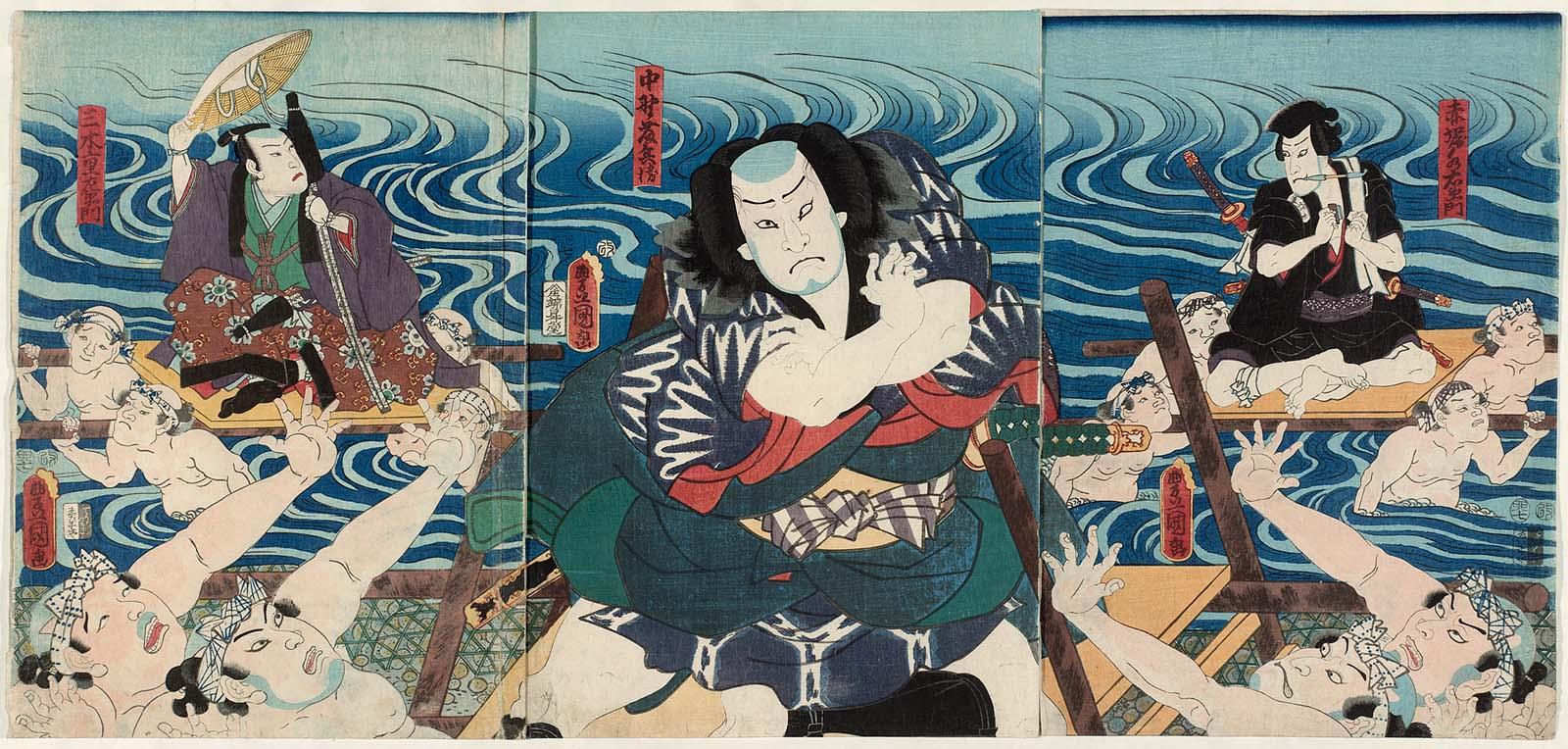
 Artist: Utagawa Kuniyoshi [歌川 國芳] (1798 – 1861). Kabuki actors Ichikawa Danjūrō VIII and Arashi Rikan III as sumo wrestlers Nuregami Chōgorō (L) and Hanaregoma Chōkichi (R), respectively. Signed: Ichiyûsai Kuniyoshi ga (一勇斎 國芳 画) in a double gourd-shaped cartouche with Yoshi Kiri seal. Publisher: No seal. Date seal and double nanushi censor seal: Mera & Watanabe, 1852. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 231 x 295 mm. Theme: Nine-act drama (11 scenes) Futatsu Chōchō Kuruwa Nikki [双蝶々曲輪日記] (A Diary of Two Butterflies in the Pleasure Quarters) written by Takeda Izumo II, Namiki Senryū I, Miyoshi Shōraku (7/1749) as puppet play Bunraku [文楽], adopted for Kabuki theatre by Arashi San'emon IV. “The sumo wrestler Nuregami Chōgorō is trying to ransom the courtesan Azuma for Yogoro, in whose debt he stands. Hiraoka Goemon, who is at odds with Yogorō and Azuma, is the patron of the amateur wrestler Hanaregoma Chōkichi. Chōgorō purposely loses to Chōkichi and then asks the latter to stop Goemon's ransoming of Azuma; Chōkichi refuses, however, and they quarrel. Admonished for his dissipation by his sister Oseki, Chōkichi is going to commit ritual suicide (seppuku) as an apology for his behavior, but Chōgorō, who happens along just then, prevents him. The two men swear blood brotherhood. […] The confrontation between Chōgorō and Chōkichi in the Sumōba scene, acted in the exaggerated style called aragoto, is a major highlight of the work. The scene in Yohei's home, known as Hikimado, presents the unfolding of Kabuki's eternal conflict between duty and feelings, here represented by the act of opening the skylight (hikimado) to which Chōgorō is tied”. [Samuel L. Leiter. Kabuki Encyclopedia: an English-language adaptation of Kabuki Jiten. — Westport, CT; London: Greenwood Press, 1979, pp. 70-71]. See also James R. Brandon and Samuel L. Leiter. Kabuki plays on stage, vol. 1, pp. 234-258. — Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press, 2002. Actors: Ichikawa Danjūrō VIII [市川団十郎] (Japanese, 1823 – 1854); other names: Ichikawa Ebizō VI, Ichikawa Shinnosuke II. Arashi Rikan III [嵐璃寛] (Japanese, 1812 – 1863); other names Arashi Tokusaburō III, Arashi Kicchō I, Onoe Wasaburō I. Another print in this collection with the same theme: SVJP-0331.2020.
Artist: Utagawa Kuniyoshi [歌川 國芳] (1798 – 1861). Kabuki actors Ichikawa Danjūrō VIII and Arashi Rikan III as sumo wrestlers Nuregami Chōgorō (L) and Hanaregoma Chōkichi (R), respectively. Signed: Ichiyûsai Kuniyoshi ga (一勇斎 國芳 画) in a double gourd-shaped cartouche with Yoshi Kiri seal. Publisher: No seal. Date seal and double nanushi censor seal: Mera & Watanabe, 1852. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 231 x 295 mm. Theme: Nine-act drama (11 scenes) Futatsu Chōchō Kuruwa Nikki [双蝶々曲輪日記] (A Diary of Two Butterflies in the Pleasure Quarters) written by Takeda Izumo II, Namiki Senryū I, Miyoshi Shōraku (7/1749) as puppet play Bunraku [文楽], adopted for Kabuki theatre by Arashi San'emon IV. “The sumo wrestler Nuregami Chōgorō is trying to ransom the courtesan Azuma for Yogoro, in whose debt he stands. Hiraoka Goemon, who is at odds with Yogorō and Azuma, is the patron of the amateur wrestler Hanaregoma Chōkichi. Chōgorō purposely loses to Chōkichi and then asks the latter to stop Goemon's ransoming of Azuma; Chōkichi refuses, however, and they quarrel. Admonished for his dissipation by his sister Oseki, Chōkichi is going to commit ritual suicide (seppuku) as an apology for his behavior, but Chōgorō, who happens along just then, prevents him. The two men swear blood brotherhood. […] The confrontation between Chōgorō and Chōkichi in the Sumōba scene, acted in the exaggerated style called aragoto, is a major highlight of the work. The scene in Yohei's home, known as Hikimado, presents the unfolding of Kabuki's eternal conflict between duty and feelings, here represented by the act of opening the skylight (hikimado) to which Chōgorō is tied”. [Samuel L. Leiter. Kabuki Encyclopedia: an English-language adaptation of Kabuki Jiten. — Westport, CT; London: Greenwood Press, 1979, pp. 70-71]. See also James R. Brandon and Samuel L. Leiter. Kabuki plays on stage, vol. 1, pp. 234-258. — Honolulu: University of Hawai'i Press, 2002. Actors: Ichikawa Danjūrō VIII [市川団十郎] (Japanese, 1823 – 1854); other names: Ichikawa Ebizō VI, Ichikawa Shinnosuke II. Arashi Rikan III [嵐璃寛] (Japanese, 1812 – 1863); other names Arashi Tokusaburō III, Arashi Kicchō I, Onoe Wasaburō I. Another print in this collection with the same theme: SVJP-0331.2020. Reference images:
Reference images:
-
 Artist: Utagawa Kuniyoshi [歌川 國芳] (1798 – 1861). A beauty leaning on a fence and watching a dragonfly hovering above a flowering plant. Signed: Ichiyûsai Kuniyoshi ga (一勇斎 國芳 画) in a double gourd-shaped red cartouche. Publisher: Maruya Jinpachi, seal Jin [甚] (Marks 08-088 | 294d). No date/censor seal. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 234 x 301 mm.
Artist: Utagawa Kuniyoshi [歌川 國芳] (1798 – 1861). A beauty leaning on a fence and watching a dragonfly hovering above a flowering plant. Signed: Ichiyûsai Kuniyoshi ga (一勇斎 國芳 画) in a double gourd-shaped red cartouche. Publisher: Maruya Jinpachi, seal Jin [甚] (Marks 08-088 | 294d). No date/censor seal. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 234 x 301 mm. -
 Artist: Utagawa Kuniyoshi [歌川 國芳] (Japanese, 1798 – 1861). Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. C. 1845 – 1847), seal: San [三] (Marks 11-001 | 127c). Carver: Matsushima Fusajirō [松嶋房次郎] (Japanese, fl. 1843 – 1850); seal [彫工房次郎] – Hori kō Fusajirō (Gordon Friese № 136) Signed: Chōōrō Kuniyoshi ga [朝櫻楼国芳画] in a red double gourd-shaped cartouche. Nanushi censor seal: Tanaka [田中]; V/1844 or II/1845. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 238 x 304 mm. Reference: Kuniyoshi Project. Series mentioned in Robert Schaap. Heroes and ghosts: Japanese prints by Kuniyoshi, 1797-1861.— Leiden: Hotei Publishing, 1998; p. 122 [LIB-1030.2016].
Artist: Utagawa Kuniyoshi [歌川 國芳] (Japanese, 1798 – 1861). Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. C. 1845 – 1847), seal: San [三] (Marks 11-001 | 127c). Carver: Matsushima Fusajirō [松嶋房次郎] (Japanese, fl. 1843 – 1850); seal [彫工房次郎] – Hori kō Fusajirō (Gordon Friese № 136) Signed: Chōōrō Kuniyoshi ga [朝櫻楼国芳画] in a red double gourd-shaped cartouche. Nanushi censor seal: Tanaka [田中]; V/1844 or II/1845. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 238 x 304 mm. Reference: Kuniyoshi Project. Series mentioned in Robert Schaap. Heroes and ghosts: Japanese prints by Kuniyoshi, 1797-1861.— Leiden: Hotei Publishing, 1998; p. 122 [LIB-1030.2016].
-
 Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.1 x 19 cm, bound in canvas, red characters on black strip to front, red and black lettering to spine, tan embossed endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/acknowledgements), 7-16 text, 17-96 (79 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | HOKUSAI | SKETCHES AND PAINTINGS | by Muneshige Narazaki | English adaptation by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules 漫画肉筆画} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 7. Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. Katsushika Hokusai [葛飾 北斎] (Japanese, 1760 – 1849) – artist. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – adaptation.
Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.1 x 19 cm, bound in canvas, red characters on black strip to front, red and black lettering to spine, tan embossed endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/acknowledgements), 7-16 text, 17-96 (79 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | HOKUSAI | SKETCHES AND PAINTINGS | by Muneshige Narazaki | English adaptation by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules 漫画肉筆画} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 7. Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. Katsushika Hokusai [葛飾 北斎] (Japanese, 1760 – 1849) – artist. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – adaptation. -
 Paperback volume, 25.7 x 18.6 cm, brown embossed wrappers with framed Japanese characters along the outer margin, pictorial dust jacket with series design (black lettering and vignette in silver border to wrappers, black lettering on silver to spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/blank), 7-32 text, 33-96 (59 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | EARLY PAINTINGS | by Muneshige Narazaki | English adaptation by Charles A. Pomeroy | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical between rules 初期 浮世絵} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 1. Contributors: Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. Charles A. Pomeroy (American, b. 1930) – adaptation.
Paperback volume, 25.7 x 18.6 cm, brown embossed wrappers with framed Japanese characters along the outer margin, pictorial dust jacket with series design (black lettering and vignette in silver border to wrappers, black lettering on silver to spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/blank), 7-32 text, 33-96 (59 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | EARLY PAINTINGS | by Muneshige Narazaki | English adaptation by Charles A. Pomeroy | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical between rules 初期 浮世絵} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 1. Contributors: Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. Charles A. Pomeroy (American, b. 1930) – adaptation. -
 Paperback volume, 25.8 x 18.6 cm, brown embossed wrappers with framed Japanese characters along the outer margin, pictorial dust jacket with series design (black lettering and vignette in silver border to wrappers, black lettering on silver to spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/blank), 7-32 text, 33-96 (59 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | SHARAKU | by Jūzō Suzuki | Translated by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical between rules 写楽} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 2. Contributors: Jūzō Suzuki [鈴木 重三] (Japanese, 1919 – 2010) – author. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – translator. Tōshūsai Sharaku [東洲斎 写楽] (Japanese, fl. 1794 – 1795) – artist.
Paperback volume, 25.8 x 18.6 cm, brown embossed wrappers with framed Japanese characters along the outer margin, pictorial dust jacket with series design (black lettering and vignette in silver border to wrappers, black lettering on silver to spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/blank), 7-32 text, 33-96 (59 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | SHARAKU | by Jūzō Suzuki | Translated by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical between rules 写楽} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 2. Contributors: Jūzō Suzuki [鈴木 重三] (Japanese, 1919 – 2010) – author. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – translator. Tōshūsai Sharaku [東洲斎 写楽] (Japanese, fl. 1794 – 1795) – artist. -
 Title: Illustrated Catalogues of Tokyo National Museum: Ukiyo-e Prints [東京国立博物館図版目録 | 浮世絵版画編] (Tōkyō Kokuritsu Hakubutsukan zuhan mokuroku | Ukiyoe hanga hen); Publisher: Tokyo National Museum [東京国立博物館] (Tōkyō Kokuritsu Hakubutsukan). Three volumes, 26.3 x 18.7 cm, uniformly bound in black cloth with white characters to front cover and spine. Title-page: ILLUSTRATED CATALOGUES OF | TOKYO NATIONAL MUSEUM | UKIYO-E PRINTS | <1 (2, 3) > | 東京国立博物館図版目録 | 浮世絵版画編 | < 上 (中, 下) > || Volume 1 [上]: unpaginated 1 t.p., 2 colour plates, 1 contents, 70 (1-1354) – b/w plates, 1 + 48 paginated leaves (1-95 [96]) – text. Volume 2 [中]: unpaginated 1 t.p., 2 colour plates, 1 contents, 67 (1355-2493) – b/w plates + 33 paginated leaves (1-65 [66]) – text. Volume 3 [下]: unpaginated 1 t.p., 2 colour plates, 1 contents, 83 (2494-3926) – b/w plates + 35 paginated leaves (1-69 [70]) – text. Black and white photomechanical reproduction of almost four thousand woodblock prints with titles by the artist and in chronological order.
Title: Illustrated Catalogues of Tokyo National Museum: Ukiyo-e Prints [東京国立博物館図版目録 | 浮世絵版画編] (Tōkyō Kokuritsu Hakubutsukan zuhan mokuroku | Ukiyoe hanga hen); Publisher: Tokyo National Museum [東京国立博物館] (Tōkyō Kokuritsu Hakubutsukan). Three volumes, 26.3 x 18.7 cm, uniformly bound in black cloth with white characters to front cover and spine. Title-page: ILLUSTRATED CATALOGUES OF | TOKYO NATIONAL MUSEUM | UKIYO-E PRINTS | <1 (2, 3) > | 東京国立博物館図版目録 | 浮世絵版画編 | < 上 (中, 下) > || Volume 1 [上]: unpaginated 1 t.p., 2 colour plates, 1 contents, 70 (1-1354) – b/w plates, 1 + 48 paginated leaves (1-95 [96]) – text. Volume 2 [中]: unpaginated 1 t.p., 2 colour plates, 1 contents, 67 (1355-2493) – b/w plates + 33 paginated leaves (1-65 [66]) – text. Volume 3 [下]: unpaginated 1 t.p., 2 colour plates, 1 contents, 83 (2494-3926) – b/w plates + 35 paginated leaves (1-69 [70]) – text. Black and white photomechanical reproduction of almost four thousand woodblock prints with titles by the artist and in chronological order. -
 Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.5 x 19.1 cm, bound in unprimed canvas, red characters on black strip to front 春信, red and black lettering to spine, cream embossed endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/blank), 7-30 text, [2] faux-title, 33-96 (66 colour plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | HARUNOBU | by Seiichirō Takahashi | English adaptation by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules 春信} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 6. Contributors: Seiichirō Takahashi [高橋誠一郎] (Japanese, 1884 – 1982) – author. Suzuki Harunobu [鈴木 春信] (Japanese, 1725 – 1770) – artist. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – adaptation.
Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.5 x 19.1 cm, bound in unprimed canvas, red characters on black strip to front 春信, red and black lettering to spine, cream embossed endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/blank), 7-30 text, [2] faux-title, 33-96 (66 colour plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | HARUNOBU | by Seiichirō Takahashi | English adaptation by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules 春信} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 6. Contributors: Seiichirō Takahashi [高橋誠一郎] (Japanese, 1884 – 1982) – author. Suzuki Harunobu [鈴木 春信] (Japanese, 1725 – 1770) – artist. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – adaptation. -
 Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.3 x 19 cm, bound in unprimed canvas, red characters on black strip to front, red and black lettering to spine, tan flat endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/acknowledgements), 7-67 text, 27-30 map, 31-32 f.t./blank, 33-96 (65 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | HIROSHIGE | FAMOUS VIEWS | by Muneshige Narazaki | English adaptation by Richard L. Gage | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules in ms 広重]} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 5. Edition: 1st edition ©1968, 2nd printing 1970. Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. Utagawa Hiroshige [歌川 広重] a.k.a. Andō Hiroshige [安藤 広重] (Japanese, 1797 – 1858) – artist. Richard L. Gage (American, b. 1934) – adaptation.
Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.3 x 19 cm, bound in unprimed canvas, red characters on black strip to front, red and black lettering to spine, tan flat endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/acknowledgements), 7-67 text, 27-30 map, 31-32 f.t./blank, 33-96 (65 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | HIROSHIGE | FAMOUS VIEWS | by Muneshige Narazaki | English adaptation by Richard L. Gage | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules in ms 広重]} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 5. Edition: 1st edition ©1968, 2nd printing 1970. Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. Utagawa Hiroshige [歌川 広重] a.k.a. Andō Hiroshige [安藤 広重] (Japanese, 1797 – 1858) – artist. Richard L. Gage (American, b. 1934) – adaptation. -
 Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.3 x 19.2 cm, bound in unprimed canvas, red characters on black strip to front, red and black lettering to spine, tan flat endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/acknowledgements), 7-31 text, [32] blank, 33-96 (58 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | STUDIES IN NATURE | HOKUSAI-HIROSHIGE | by Muneshige Narazaki | Translated by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules 花鳥風月} || 花鳥風月 (Kachou Fugetsu) – beauties of nature. Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 11. Contributors: Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – translator. Katsushika Hokusai [葛飾 北斎] (Japanese, 1760 – 1849) – artist. Utagawa Hiroshige [歌川 広重] a.k.a. Andō Hiroshige [安藤 広重] (Japanese, 1797 – 1858) – artist.
Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.3 x 19.2 cm, bound in unprimed canvas, red characters on black strip to front, red and black lettering to spine, tan flat endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/acknowledgements), 7-31 text, [32] blank, 33-96 (58 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | STUDIES IN NATURE | HOKUSAI-HIROSHIGE | by Muneshige Narazaki | Translated by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules 花鳥風月} || 花鳥風月 (Kachou Fugetsu) – beauties of nature. Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 11. Contributors: Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – translator. Katsushika Hokusai [葛飾 北斎] (Japanese, 1760 – 1849) – artist. Utagawa Hiroshige [歌川 広重] a.k.a. Andō Hiroshige [安藤 広重] (Japanese, 1797 – 1858) – artist. -
 Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.5 x 19 cm, bound in unprimed canvas, red ms characters on black strip to front, red and black lettering to spine, tan embossed endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/acknowledgements), 7-31 text, [32] blank, 33-96 (76 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | UTAMARO | by Muneshige Narazaki and Sadao Kikuchi | Translated by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules 歌麿} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 4. Contributors: Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. Sadao Kikuchi [菊地 貞雄] (Japanese, 1924 – 2017) – author. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – translator. Kitagawa Utamaro [喜多川 歌麿] (Japanese, c. 1753 – 1806) – artist.
Hardcover volume from the series Masterworks of ukiyo-e, 26.5 x 19 cm, bound in unprimed canvas, red ms characters on black strip to front, red and black lettering to spine, tan embossed endpapers, in a pictorial slipcase with series design (black lettering on silver spine); pp: [1-6]: h.t./frontis. (colour plate pasted in), t.p./imprint, contents/acknowledgements), 7-31 text, [32] blank, 33-96 (76 plates w/captions). Title-page (in frame): MASTERWORKS OF UKIYO-E | UTAMARO | by Muneshige Narazaki and Sadao Kikuchi | Translated by John Bester | {publisher’s device} | KODANSHA INTERNATIONAL LTD. | Tokyo, Japan & Palo-Alto, Calif., U.S.A | {vertical, between rules 歌麿} || Series: Masterworks of ukiyo-e, № 4. Contributors: Muneshige Narazaki [楢崎 宗重] (Japanese, 1904 – 2001) – author. Sadao Kikuchi [菊地 貞雄] (Japanese, 1924 – 2017) – author. John Bester (British, 1927 – 2010) – translator. Kitagawa Utamaro [喜多川 歌麿] (Japanese, c. 1753 – 1806) – artist. -
 Hardcover volume, 35 x 26.8 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28.2 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-144 (plates with photographs of 332 items), [2] 147-182 [4]. 鍋島 – Nabeshima – book title. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35 x 26.8 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28.2 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-144 (plates with photographs of 332 items), [2] 147-182 [4]. 鍋島 – Nabeshima – book title. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35.2 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-104 (plates with photographs of 206 items), [2] 107-138 [4]. Kakiemon [柿右衛門] – book title. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35.2 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-104 (plates with photographs of 206 items), [2] 107-138 [4]. Kakiemon [柿右衛門] – book title. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35.3 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-88 (plates with photographs of 129 items), [2] 91-108 [3]. Seto ware [瀬戸焼] (Seto-yaki) – ceramics produced in and around the city of Seto in Aichi Prefecture. Yellow seto [黄瀬戸] (Kiseto) – a yellow glaze seto ware. Black seto [瀬戸黒] (Setoguro) – a black glaze seto ware. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35.3 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-88 (plates with photographs of 129 items), [2] 91-108 [3]. Seto ware [瀬戸焼] (Seto-yaki) – ceramics produced in and around the city of Seto in Aichi Prefecture. Yellow seto [黄瀬戸] (Kiseto) – a yellow glaze seto ware. Black seto [瀬戸黒] (Setoguro) – a black glaze seto ware. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35 x 26.8 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a slipcase, the outer case missing, pp.: [4] [1] 2-136 (plates with photographs of 211 items), [2] 139-166 [4]. Kutani ware [九谷焼] (Kutani-yaki); old kutani [古九谷] (kokutani) – ceramic objects produced in Kutani in the 17th century. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35 x 26.8 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a slipcase, the outer case missing, pp.: [4] [1] 2-136 (plates with photographs of 211 items), [2] 139-166 [4]. Kutani ware [九谷焼] (Kutani-yaki); old kutani [古九谷] (kokutani) – ceramic objects produced in Kutani in the 17th century. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35.1 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 27.8 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-108 (plates with photographs of 217 items), [2] [111] 112-150 [3]. Imari ware [伊万里焼] (Imari-yaki) – ceramics produced in and around the area of Arita, in the former Hizen Province, northwestern Kyūshū. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Old imari [古伊万里] (koimari) – book title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35.1 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 27.8 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-108 (plates with photographs of 217 items), [2] [111] 112-150 [3]. Imari ware [伊万里焼] (Imari-yaki) – ceramics produced in and around the area of Arita, in the former Hizen Province, northwestern Kyūshū. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Old imari [古伊万里] (koimari) – book title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a slipcase, the outer case missing, pp.: [4] [1] 2-116 (plates with photographs of 202 items), [2] 119-154 [4]. Ninsei [仁清] and Kenzan [乾山] ceramics produced by Ninsei Nonomura [野々村仁清] (Japanese, c. 1640 – c. 1690) and Ogata Kenzan [尾形 乾山] (Japanese, 1663 – 1743), respectively. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a slipcase, the outer case missing, pp.: [4] [1] 2-116 (plates with photographs of 202 items), [2] 119-154 [4]. Ninsei [仁清] and Kenzan [乾山] ceramics produced by Ninsei Nonomura [野々村仁清] (Japanese, c. 1640 – c. 1690) and Ogata Kenzan [尾形 乾山] (Japanese, 1663 – 1743), respectively. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-124 (plates with photographs of 241 items), [2] 127-171 [3]. Kyō ware [京焼] (Kyō-yaki) – pottery from Kyoto. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher.
Hardcover volume, 35 x 27 cm, bound in grey cloth, blind stamped characters to front, brown characters to spine, in a glassine dust jacket, in a double slipcase, the outer case pictorial paper over cardboard, 36 x 28 cm, pp.: [4] [1] 2-124 (plates with photographs of 241 items), [2] 127-171 [3]. Kyō ware [京焼] (Kyō-yaki) – pottery from Kyoto. 日本の陶磁 – Japanese ceramics, series title. Contributors: Yasunari Kawabata [川端 康成] (Japanese, 1924 – 1972) – author. Tetsuzo Tanikawa [谷川 徹三] (Japanese, 1895 – 1989) – author. Seizo Hayashiya [林屋晴三] (Japanese, 1928 – 2017) – editor. Chūōkōron-sha [中央公論社] – publisher. -
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche Block carver: Yokokawa Takejirō [横川竹二郎] (Japanese, fl. 1845 – 1863), seal: 彫竹 – hori Take. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. c. 1845 – 1847). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 238 x 304 mm. Title: Saiko (West River) [西江]; 西江 means the Xi River in China. Series: Chronicles of Elegant Women [風雅女史傳] (Fūga joshiden). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: Ansei 6 (1859). Other prints from the same series in this collection: SVJP-0216.2016 — Princess Sotoori:
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche Block carver: Yokokawa Takejirō [横川竹二郎] (Japanese, fl. 1845 – 1863), seal: 彫竹 – hori Take. Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. c. 1845 – 1847). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 238 x 304 mm. Title: Saiko (West River) [西江]; 西江 means the Xi River in China. Series: Chronicles of Elegant Women [風雅女史傳] (Fūga joshiden). Combined date seal and kiwame censor seal: Ansei 6 (1859). Other prints from the same series in this collection: SVJP-0216.2016 — Princess Sotoori: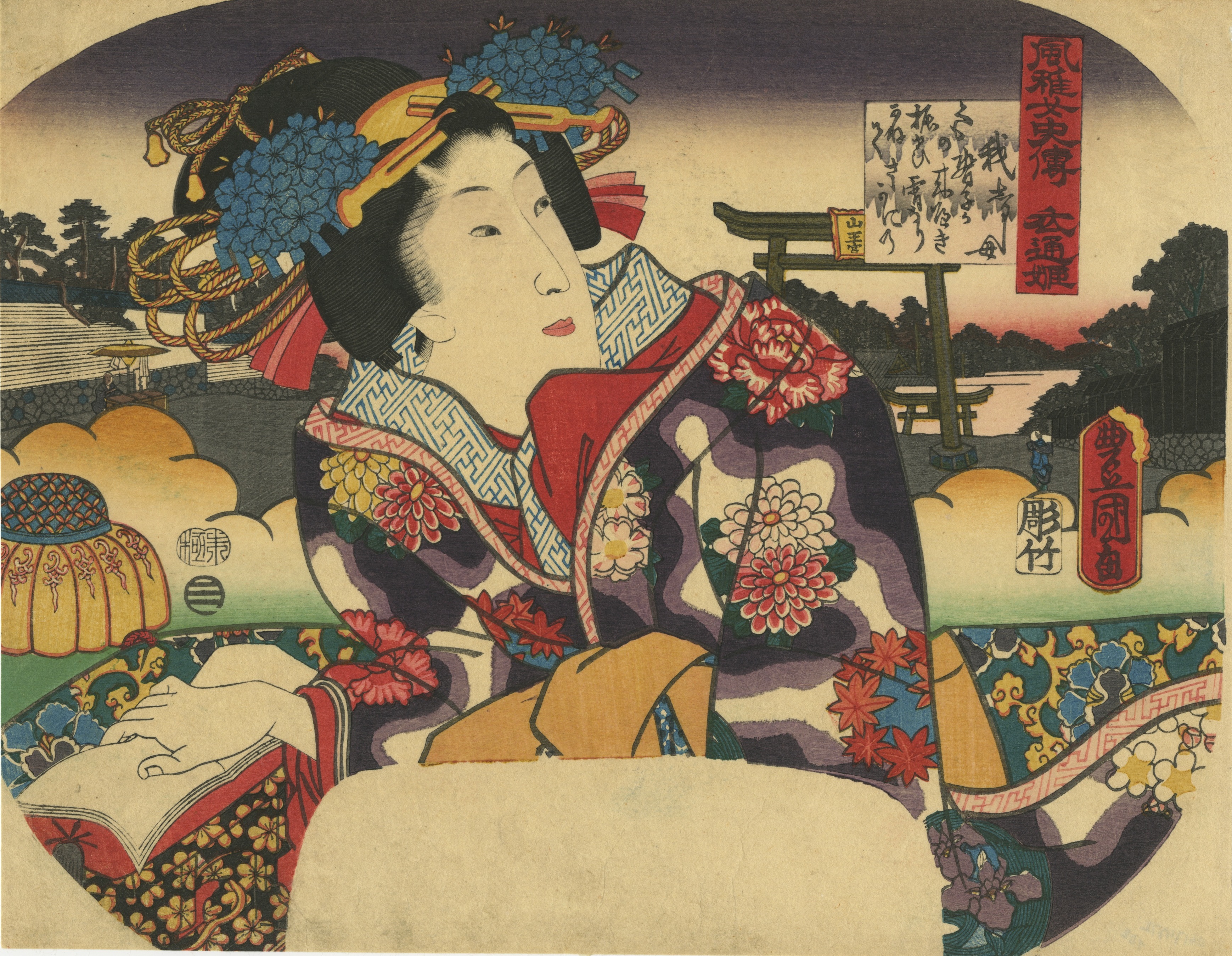

-
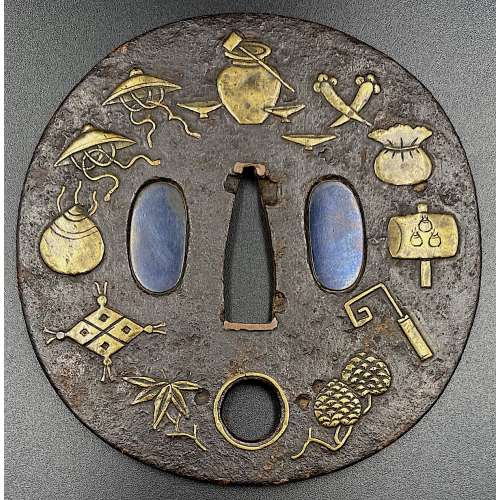 Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):
Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):- Sake set [shuki, 酒器], namely flask, ladle, and cups
- Cloves [choji, 丁子]
- Purse of inexhaustible reaches [kinchaku, 巾着]
- Magic mallet [kozuchi, 小槌]
- Key to the storehouse of the Gods [kagi, 鍵]
- Rhombus, or Lozenge (hosho, 方勝), with the second ideograph meaning victory.
- Sacred (or wish-granting) gem, or jewel [hōju, 宝珠]
- Hats of invisibility [kakuregasa, 隠れ笠]
-
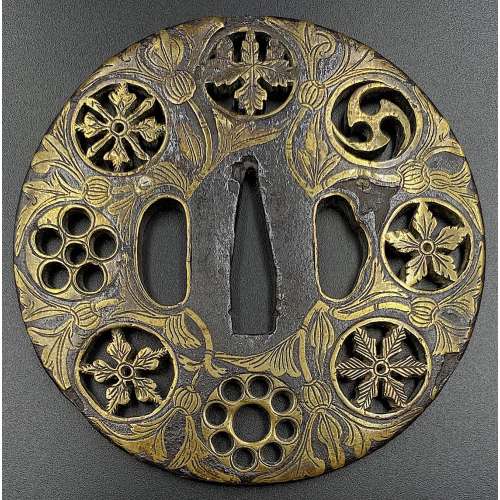 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Kiri-mon
Katakura-mon
-
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche Publisher: Iseya Ichiemon [伊勢屋市右衛門] (Japanese, fl. c. 1820s – c. 1860s); seal Tsuji [辻] (Marks 16-029). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 225 x 295 mm, plus 10 mm paper strip glued on top (235 mm total height). Title: Plucking Popular Songs in Those Days [時世葉歌の爪弾] (Imayo ha-uta no tsuma-biki). Date seal and aratame seal: Ansei 3 (1856). Seller's Description: Uchiwa-e; picture intended for a summer fan. Here we see a relaxed beauty wearing loose layers of kimono and playing her shamisen instrument. She appears to be in the happy mood of spring, her singing inspired by the cherry blossoms in full bloom that we see outside of her window. She enjoys leisurely plucking with the plectrum of the shamisen and singing “ha-uta” (popular) songs. The title Ha-uta [葉歌] is normally written 端歌, which indicates a certain category of popular songs accompanied by shamisen with short texts that are drawn from daily life. Here however, the title葉歌 uses phonetically the same “ha葉“, referring to the title of the book of a collection of ha-uta songs, Matsu no ha [松の], which was published in five volumes in 1703 by Shûshôken 秀松軒. It is said that this collection of songs was written and sung by the blind (who were often musicians by livelihood). Behind her, lying on the window sill, we see two ha-uta songbooks, one open and one closed. The last half of the title tsuma-biki [爪弾] translates “to pluck with fingers” instead of a plectrum, which is the usual way of playing the shamisen.
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche Publisher: Iseya Ichiemon [伊勢屋市右衛門] (Japanese, fl. c. 1820s – c. 1860s); seal Tsuji [辻] (Marks 16-029). Media: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 225 x 295 mm, plus 10 mm paper strip glued on top (235 mm total height). Title: Plucking Popular Songs in Those Days [時世葉歌の爪弾] (Imayo ha-uta no tsuma-biki). Date seal and aratame seal: Ansei 3 (1856). Seller's Description: Uchiwa-e; picture intended for a summer fan. Here we see a relaxed beauty wearing loose layers of kimono and playing her shamisen instrument. She appears to be in the happy mood of spring, her singing inspired by the cherry blossoms in full bloom that we see outside of her window. She enjoys leisurely plucking with the plectrum of the shamisen and singing “ha-uta” (popular) songs. The title Ha-uta [葉歌] is normally written 端歌, which indicates a certain category of popular songs accompanied by shamisen with short texts that are drawn from daily life. Here however, the title葉歌 uses phonetically the same “ha葉“, referring to the title of the book of a collection of ha-uta songs, Matsu no ha [松の], which was published in five volumes in 1703 by Shûshôken 秀松軒. It is said that this collection of songs was written and sung by the blind (who were often musicians by livelihood). Behind her, lying on the window sill, we see two ha-uta songbooks, one open and one closed. The last half of the title tsuma-biki [爪弾] translates “to pluck with fingers” instead of a plectrum, which is the usual way of playing the shamisen. -
 Utagawa Sadahide, a.k.a. Gountei Sadahide (Japanese, 1807 – c. 1878–1879), 五雲亭 貞秀, 歌川 貞秀, Yamaguchiya Tōbei, Yokohama kōeki seiyōjin nimotsu unsō no zu - Western traders loading cargo in Yokohama - 横浜交易西洋人荷物運送之圖, 1861, Woodblock print (nishiki-e); ink and color on paper, Horizontal Ōban Pentaptych: 5 x (37 x 25.5 cm), Alternative title: Picture of Western Traders at Yokohama Transporting Merchandise (Cat. Reisonée: Yokohama ukiyo-e, Yurindo, 1979: №50). Japanese pentaptych print shows an American ship in the harbor at Yokohama, Japan; small boats ferry cargo which is being carried up a gangplank contributing to the bustle of activity on the main deck. April, 1861. SOLD
Utagawa Sadahide, a.k.a. Gountei Sadahide (Japanese, 1807 – c. 1878–1879), 五雲亭 貞秀, 歌川 貞秀, Yamaguchiya Tōbei, Yokohama kōeki seiyōjin nimotsu unsō no zu - Western traders loading cargo in Yokohama - 横浜交易西洋人荷物運送之圖, 1861, Woodblock print (nishiki-e); ink and color on paper, Horizontal Ōban Pentaptych: 5 x (37 x 25.5 cm), Alternative title: Picture of Western Traders at Yokohama Transporting Merchandise (Cat. Reisonée: Yokohama ukiyo-e, Yurindo, 1979: №50). Japanese pentaptych print shows an American ship in the harbor at Yokohama, Japan; small boats ferry cargo which is being carried up a gangplank contributing to the bustle of activity on the main deck. April, 1861. SOLD -
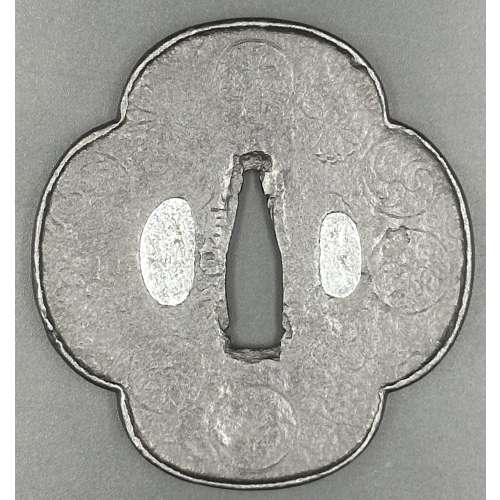 Iron tsuba of mokko form decorated with encircled family crests in low relief carving; niku from 3.0 mm in the centre to 4.0 mm at rim and full 1 mm raised uchikaeshi-mimi. Nobuie [信家] signature (hanare-mei) to the left of nakago-ana; on the reverse, to the right of nakago-ana, the inscription reads “62”, which may be how old the master was at the age of making the tsuba. Pewter or lead plugged hitsuana. In a wooden box, in a custom pouch. Size: H: 80 mm, W: 75, Th(c): 3.1 mm, Th(r): 4.0 mm Weight: 103.5 g
Iron tsuba of mokko form decorated with encircled family crests in low relief carving; niku from 3.0 mm in the centre to 4.0 mm at rim and full 1 mm raised uchikaeshi-mimi. Nobuie [信家] signature (hanare-mei) to the left of nakago-ana; on the reverse, to the right of nakago-ana, the inscription reads “62”, which may be how old the master was at the age of making the tsuba. Pewter or lead plugged hitsuana. In a wooden box, in a custom pouch. Size: H: 80 mm, W: 75, Th(c): 3.1 mm, Th(r): 4.0 mm Weight: 103.5 gSigned: Nobuie [信家] / 62
Probably the work of Shodai Nobuie (c. 1580).
Tokubetsu hozon certificate № 2002993 of the N.B.T.H.K., dated January 15, 2016. NOBUIE TSUBA by Steve Waszak The iron tsuba made by the two early Nobuie masters are regarded as the greatest sword guards ever made across hundreds of years of Japanese history. Only a small handful of other smiths' names are even mentioned in the same breath as that of Nobuie. Despite the well-deserved fame of the Nobuie name, virtually nothing is known with certainty about the lives of the two men who made the pieces carrying this name. They are thought to have been men of Owari Province, with the Nidai Nobuie also spending time in Aki Province at the end of the Momoyama Period. Two Nobuie tsubako are recognized. The man whom most consider to have been the Shodai signed his sword guards with finer and more elegantly inscribed characters than the smith seen by most as the Nidai. The term used to describe the mei of the Shodai is "hanare-mei" or "ga-mei," while that used to characterize the signature of the Nidai is "futoji-mei" or "chikara-mei." These terms refer to the fineness and grace of the Shodai's signature and the relatively more powerfully inscribed characters of the Nidai's. The Shodai is thought to have lived during the Eiroku and Tensho eras in the latter part of the 16th century, while the Nidai's years are considered to have been from Tensho into the Genna era. This locates both smiths well within the Golden Age of tsuba artists -- the Momoyama Period. Nobuie tsuba are esteemed and celebrated for the extraordinary beauty of their iron. The combination of the forging of the metal, the surface treatment by tsuchime and yakite married to powerfully expressive carving, the masterful manipulation of form, mass and shape, and the colour and patina of the iron makes Nobuie sword guards not only unique in the world of tsuba, but the greatest of the great. The sword guard here is a Shodai-made masterwork, done in mokko-gata form, a shape the early Nobuie smiths mastered to a degree unmatched by any others. The expanding of the mass of the tsuba from the seppa-dai to the mimi, increasing by 50% from the centre of the guard to the rim, creates a sense of exploding energy, which is then contained by the uchikaeshi-mimi, yielding a lightning-in-a-bottle effect of captured energy. The hammering the master has employed to finish the surface is subtle and sensitive, achieving a resonant profundity, and the deep blue-black colour -- augmented by a lustrous patina -- leaves the tsuba to positively glow in one's hand. In this piece, Nobuie has used a motif of several kamon, or family crests, each carved only lightly on the surface in a loose ring around the nakago-ana. Due to the shallow depth of this carving, together with the tsuchime finish of the plate, the effect is to leave the kamon with a sort of weathered appearance, recalling the prime aesthetic values of sabi and wabi, which had great circulation in the Tea Culture so ascendant in the Momoyama years. However, the effects of sabi and wabi expressed in the treatment described above are amplified and deepened by the color and patina of the iron, thereby adding yet another aesthetic value -- yuugen -- which is linked with the abiding mystery of the universe and one more — mono no aware — which alludes to the pathos of life's experiences and transitory nature. In short, this Nobuie tsuba joins poetry with power and therein exemplifies the unrivalled brilliance of Nobuie workmanship. -
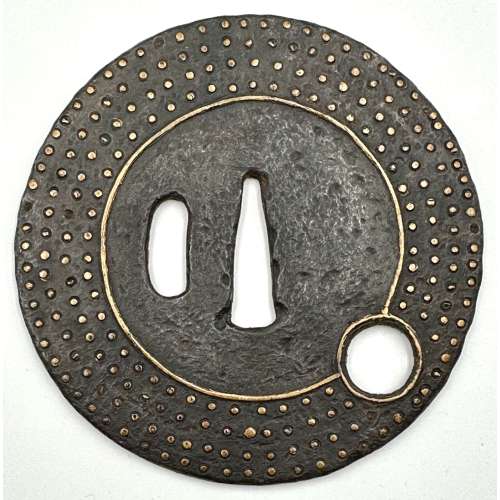

Iron tsuba of round form with one hitsu ana; centre of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire broke by a circular opening 7 mm in diameter located between 4 and 5 o’clock of the plate and in its turn outlined with brass wire. Extraneous to the central wire, the plate is decorated with four rows of brass dots (ten-zogan). A few dots are missing. In a custom kiri wood box. The meaning of the emblem is probably either the sun or the moon.
Ōnin school. Unsigned.
Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century.
Dimensions: diameter 88 mm; thickness 3.3 mm.
-
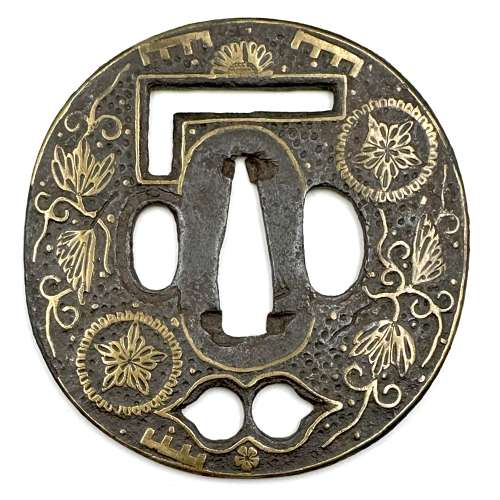 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form (nagamaru-gata) pierced on top and in the bottom (ko-sukashi) with simplified Genji-kō (incense game symbol) and two petals of bellflower; openings, seppa-dai, and plate along the rim are outlined with brass wire, kozuka-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire, missing on the front; kogai-ana pierced later. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer, decorated in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils, bellflowers, and Genji characters, and with brass dots (ten-zogan), many of which are missing. Measurements: Height 77.5 mm; Width 75.5 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.4 mm, at rim 3.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form (nagamaru-gata) pierced on top and in the bottom (ko-sukashi) with simplified Genji-kō (incense game symbol) and two petals of bellflower; openings, seppa-dai, and plate along the rim are outlined with brass wire, kozuka-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire, missing on the front; kogai-ana pierced later. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer, decorated in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils, bellflowers, and Genji characters, and with brass dots (ten-zogan), many of which are missing. Measurements: Height 77.5 mm; Width 75.5 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.4 mm, at rim 3.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier. -

Large iron tsuba of mokko form with the openwork (sukashi) design, described by some as rotten leaves swirling in the wind and boar eyes (inome, 猪目, heart-shaped elements); round rim (maru-mimi); no hitsu-ana; pronounced iron bones (tekkotsu); chocolate patina.
Signed to the left of nakaga-ana: Yamakichibei (山吉兵へ). Attributed to the First Generation (Shodai) master.
Dimensions: 90 x 82 mm, thickness 3.7 mm at centre, 4.9 mm at rim. Weight: 142 gReferences: similar handguards demonstrated at Yasukazu's Owari to Mikawa no tankō №176 and Kajima's Tsuba no Bi №28.
Owari to Mikawa no tankō №176

Tsuba no Bi №28
-
 Thin plate iron tsuba of round form with a military commander's fan (gunbai) design in openwork (sukashi); Ko-tosho school. Kamakura period (1185 – 1333), 13th to early 14th century (according to Nakamura Tessei). Dimensions: 91.2 x 89.5 mm, thickness: 1.5-2.5 mm. Provenance: Patrick Liebermann Collection. Reproduced in the exhibition catalogue Samurai. Guerriers et esthètes, BNU, Strasbourg, March 11 – July 13, 2022, №045, p.91 and in Patrick Liebermann, Tsuba. Itinéraires d'une collection, 2016, №72, p.111. Reference: a similar tsuba reproduced in LIB-3304.2024 (see below) and in this collection TSU-0332.2017 (provenance Sasano Masayuki).
Thin plate iron tsuba of round form with a military commander's fan (gunbai) design in openwork (sukashi); Ko-tosho school. Kamakura period (1185 – 1333), 13th to early 14th century (according to Nakamura Tessei). Dimensions: 91.2 x 89.5 mm, thickness: 1.5-2.5 mm. Provenance: Patrick Liebermann Collection. Reproduced in the exhibition catalogue Samurai. Guerriers et esthètes, BNU, Strasbourg, March 11 – July 13, 2022, №045, p.91 and in Patrick Liebermann, Tsuba. Itinéraires d'une collection, 2016, №72, p.111. Reference: a similar tsuba reproduced in LIB-3304.2024 (see below) and in this collection TSU-0332.2017 (provenance Sasano Masayuki).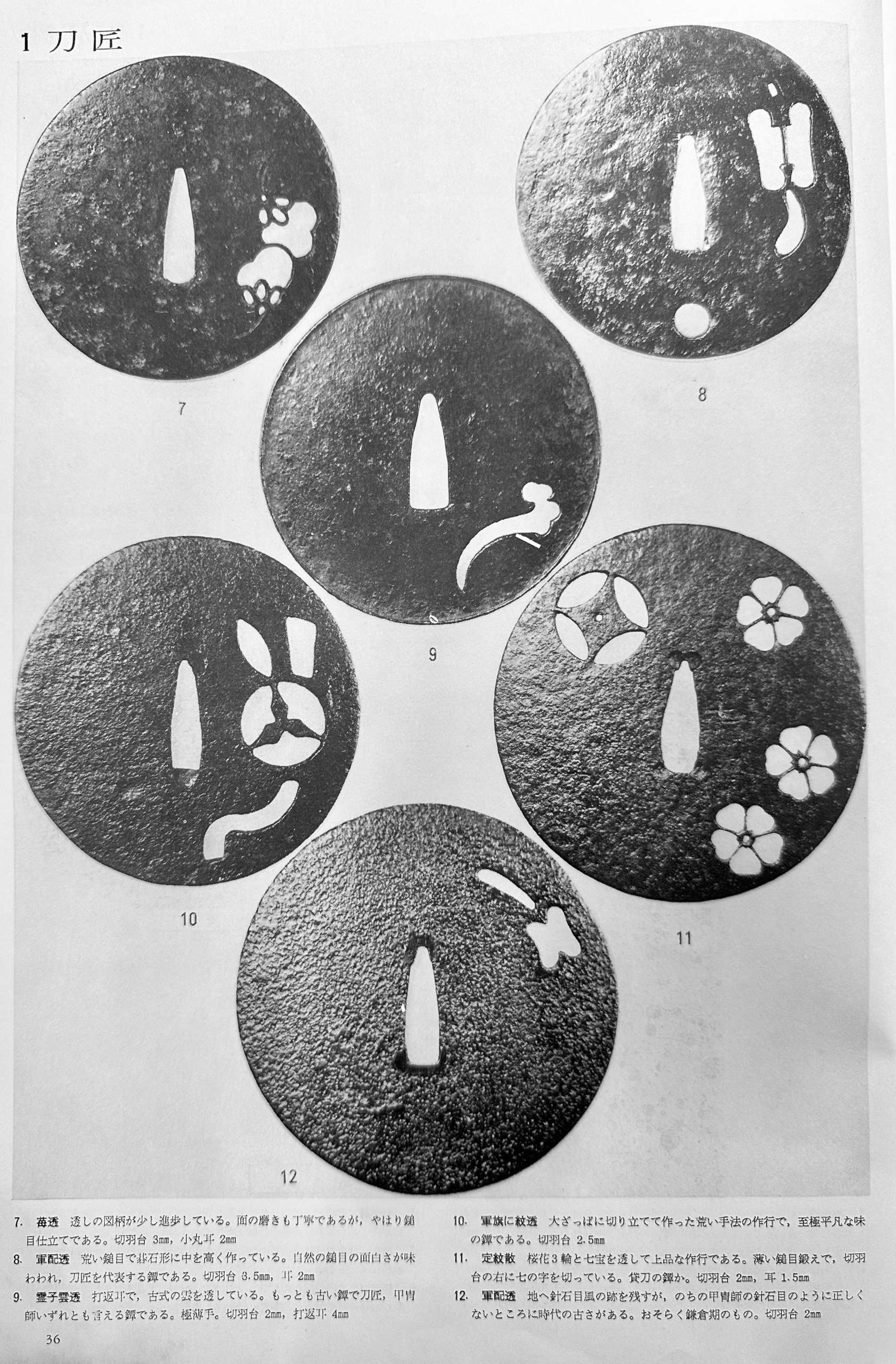
Tsuba Collection (Tsuba shūsei, 鐔集成) by Nakamura Tessei (中村鐵青), p.36, fig. 12.
-

Netsuke with a design of an old man carrying a giant mushroom on his back. Possibly signed on his left foot. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, page. 93): ... This prominent use in the symbol-rich netsuke art form, however, reflects more their sexual symbolism than either their dietary appeal or interesting shapes. Mushrooms in Japan are generally a symbol of fertility, with some flat varieties, like shiitake, being associated with females. In contrast, the matsutake mushroom (Armillaria edodes) is a phallic symbol, as befits its thick, spearlike stem and the fact that it is consumed before cap opens.
Seller's description: "The old man carved walking, with one foot slightly raised, wearing a loose fitted robe and carrying a large long-stemmed mushroom on his back. The wood stained and bearing a fine patina. Himotoshi through the mushroom stem". See VO-0270.2018 for the same subject. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 62 mm tall -
 Finely carved as a rat (nezumi) seated on a shuro brush, bound naturalistically with thick bristles. The rodent with a long trailing tail and eyes inlaid in a dark horn. Generously excavated, asymmetrical himotoshi to the underside. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, p. 156): …The Japanese do not clearly differentiate between the rat and the mouse, and one word, nezumi [鼠], designates both. …Rat is a messenger of Daikokuten, a deity of grain and vegetation who is one of Japan’s Seven Gods of Good Luck. ...Depictions of the rat are most common in years of the zodiac represented by the animal. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 49 x 33 x 16 mm. Provenance: From the private collection of Armand Basi (Spanish, 1924-2009).
Finely carved as a rat (nezumi) seated on a shuro brush, bound naturalistically with thick bristles. The rodent with a long trailing tail and eyes inlaid in a dark horn. Generously excavated, asymmetrical himotoshi to the underside. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, p. 156): …The Japanese do not clearly differentiate between the rat and the mouse, and one word, nezumi [鼠], designates both. …Rat is a messenger of Daikokuten, a deity of grain and vegetation who is one of Japan’s Seven Gods of Good Luck. ...Depictions of the rat are most common in years of the zodiac represented by the animal. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 49 x 33 x 16 mm. Provenance: From the private collection of Armand Basi (Spanish, 1924-2009). -
 A large hardcover volume, 370 x 265 x 53 mm, bound in burgundy cloth with pasted-in b/w photograph and gilt lettering to front, gilt lettering to spine, in plastic dust jacket, in a slipcase, in a cardboard shipping box, pp. [2] 1-522 [2], 128 leaves total; limited edition of 1000 copies. Author: Nakamura Tessei [中村鐵青] Seller's description: Tsuba Shusei by Nakamura. 1963. Of a limited edition of 1,000. Clothbound with plastic jacket, slipcase, and cardboard storage box, 11 ½ x 14 ½”, 522 heavy stock pages in Japanese. This is a very impressive book. Thousands of tsuba, from Kamakura to late Edo and arranged by school. are illustrated (24 in colour photos and the rest in black & white) and described. If there is a tsuba bible this might be it; there can’t be a more comprehensive book on the subject. The storage box is shelf worn, the slipcase is just a bit toned; the book is in excellentt condition. Produced by Chuokoron-Shinsha, Inc. [株式会社中央公論新社] Publisher: 銀集成刊行会 Production details: 鐵集成 第617番 昭和38年2月10日発行 限定1,000部 定価 10,000円 オフセット単色印刷:マイク印刷 オフセット原色印刷:大日本印刷 著者中村鐵青 製作 中央公論事業出版 発行所 銀集成刊行会 活版印刷:精興社 製本:協和製本 本文用紙:三菱製紙 表紙:望月
A large hardcover volume, 370 x 265 x 53 mm, bound in burgundy cloth with pasted-in b/w photograph and gilt lettering to front, gilt lettering to spine, in plastic dust jacket, in a slipcase, in a cardboard shipping box, pp. [2] 1-522 [2], 128 leaves total; limited edition of 1000 copies. Author: Nakamura Tessei [中村鐵青] Seller's description: Tsuba Shusei by Nakamura. 1963. Of a limited edition of 1,000. Clothbound with plastic jacket, slipcase, and cardboard storage box, 11 ½ x 14 ½”, 522 heavy stock pages in Japanese. This is a very impressive book. Thousands of tsuba, from Kamakura to late Edo and arranged by school. are illustrated (24 in colour photos and the rest in black & white) and described. If there is a tsuba bible this might be it; there can’t be a more comprehensive book on the subject. The storage box is shelf worn, the slipcase is just a bit toned; the book is in excellentt condition. Produced by Chuokoron-Shinsha, Inc. [株式会社中央公論新社] Publisher: 銀集成刊行会 Production details: 鐵集成 第617番 昭和38年2月10日発行 限定1,000部 定価 10,000円 オフセット単色印刷:マイク印刷 オフセット原色印刷:大日本印刷 著者中村鐵青 製作 中央公論事業出版 発行所 銀集成刊行会 活版印刷:精興社 製本:協和製本 本文用紙:三菱製紙 表紙:望月 -
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a yellow double-gourd cartouche. Publisher unknown (privately printed?) Media: Rigid fan print (Aiban Yoko-e Uchiwa-e, 合判横絵 団扇絵), 228 x 298 mm. Series title: Six Jewel Faces (六玉颜, mu tama-gao), a pun on Six Jewel Rivers (六玉河, Mu Tamagawa). The date seal and censor seal are absent. Another print from the same series in the Metropolitan Museum of New York reads:
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865). Signed: Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a yellow double-gourd cartouche. Publisher unknown (privately printed?) Media: Rigid fan print (Aiban Yoko-e Uchiwa-e, 合判横絵 団扇絵), 228 x 298 mm. Series title: Six Jewel Faces (六玉颜, mu tama-gao), a pun on Six Jewel Rivers (六玉河, Mu Tamagawa). The date seal and censor seal are absent. Another print from the same series in the Metropolitan Museum of New York reads:The colorful background, with explosions of tie-dyed floral motifs, is a reminder of how Kunisada made all his thousands of Genji-print designs a visual record of different textile patterns of the day. The title Six Jewel Faces (Mu tama-gao), along with its allusion to the literary theme of Six Jewel Rivers, suggests that this set of fan prints captures the appearance of a half-dozen attractive individuals, and, indeed, the other five works in the set show images of beautiful women, mostly courtesans of the pleasure quarters.
 Mitsuuji with Mountain Roses (Yamabuki), from the series “Six Jewel Faces” (Mu tama-gao).
MET Accession Number:2019.3
References:
1) [LIB-2967.2022] Utagawa Kunisada: His world revisited / Catalogue 17, Exhibition March 17-21, 2021. — NY: Sebastian Izzard, LLC., 2021.
2) [LIB-3428.2025] Christie’s, New York: Japanese Prints, Paintings, and Screens, Monday, 24 November 1997 / Sales Catalogue, №№ 84-89.
Description by the latter: "aiban uchiwa-e (22.7 × 29.8 cm.); a beauty against a background of tie-dyed fabric patterns holding a pipe looking at toy birds hanging from bamboo, from the series Mutamagao “Six jewel faces”, the bird decorations alluding to the Jewel River in Noda (Chidori no Tamagawa) in Rikuzen province, signed Kunisada ga".
Mitsuuji with Mountain Roses (Yamabuki), from the series “Six Jewel Faces” (Mu tama-gao).
MET Accession Number:2019.3
References:
1) [LIB-2967.2022] Utagawa Kunisada: His world revisited / Catalogue 17, Exhibition March 17-21, 2021. — NY: Sebastian Izzard, LLC., 2021.
2) [LIB-3428.2025] Christie’s, New York: Japanese Prints, Paintings, and Screens, Monday, 24 November 1997 / Sales Catalogue, №№ 84-89.
Description by the latter: "aiban uchiwa-e (22.7 × 29.8 cm.); a beauty against a background of tie-dyed fabric patterns holding a pipe looking at toy birds hanging from bamboo, from the series Mutamagao “Six jewel faces”, the bird decorations alluding to the Jewel River in Noda (Chidori no Tamagawa) in Rikuzen province, signed Kunisada ga".


-
 Artist: Utagawa Kunisada, a.k.a. Toyokuni III (Japanese, 1786 – 1865) [歌川 国貞]. Publisher: Unidentified, Marks 01-033|U335a To-Chū [ト忠] Date-aratame seal: Bunka 14 (1817). Signed: Kunisada ga [国貞画]. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e), 230 x 270 mm. Kabuki play Chūkō shōbu-gatana [忠孝菖蒲刀] performed at the Nakamura Theater in Tokyo (Edo) in 5/1817. Actor Seki Sanjūrō II [関三十郎], a.k.a. Seki Utasuke I; Nakamura Utasuke; Arashi Sôtarô; Meijin Seki; Sekisan (Japanese, 1786 – 1839) as Nakano Tōbei [中野藤兵衛] – top. Actor Bandō Mitsugorō III [坂東三津五郎], a.k.a. Bandô Minosuke I, Morita Kanjirô II, Bandô Mitahachi I, Bandô Minosuke I, Bandô Mitahachi (Japanese, 1775 – 1831) I as Miki Jūzaemon [三木十左衛門] – left. Actor Matsumoto Kōshirō V [松本幸四郎], a.k.a. Ichikawa Komazô III; Ichikawa Sumizô I (Japanese, 1764 – 1838) as Akabori Mizuemon [あかぼり水右衛門] – right. Reference images:
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada, a.k.a. Toyokuni III (Japanese, 1786 – 1865) [歌川 国貞]. Publisher: Unidentified, Marks 01-033|U335a To-Chū [ト忠] Date-aratame seal: Bunka 14 (1817). Signed: Kunisada ga [国貞画]. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e), 230 x 270 mm. Kabuki play Chūkō shōbu-gatana [忠孝菖蒲刀] performed at the Nakamura Theater in Tokyo (Edo) in 5/1817. Actor Seki Sanjūrō II [関三十郎], a.k.a. Seki Utasuke I; Nakamura Utasuke; Arashi Sôtarô; Meijin Seki; Sekisan (Japanese, 1786 – 1839) as Nakano Tōbei [中野藤兵衛] – top. Actor Bandō Mitsugorō III [坂東三津五郎], a.k.a. Bandô Minosuke I, Morita Kanjirô II, Bandô Mitahachi I, Bandô Minosuke I, Bandô Mitahachi (Japanese, 1775 – 1831) I as Miki Jūzaemon [三木十左衛門] – left. Actor Matsumoto Kōshirō V [松本幸四郎], a.k.a. Ichikawa Komazô III; Ichikawa Sumizô I (Japanese, 1764 – 1838) as Akabori Mizuemon [あかぼり水右衛門] – right. Reference images: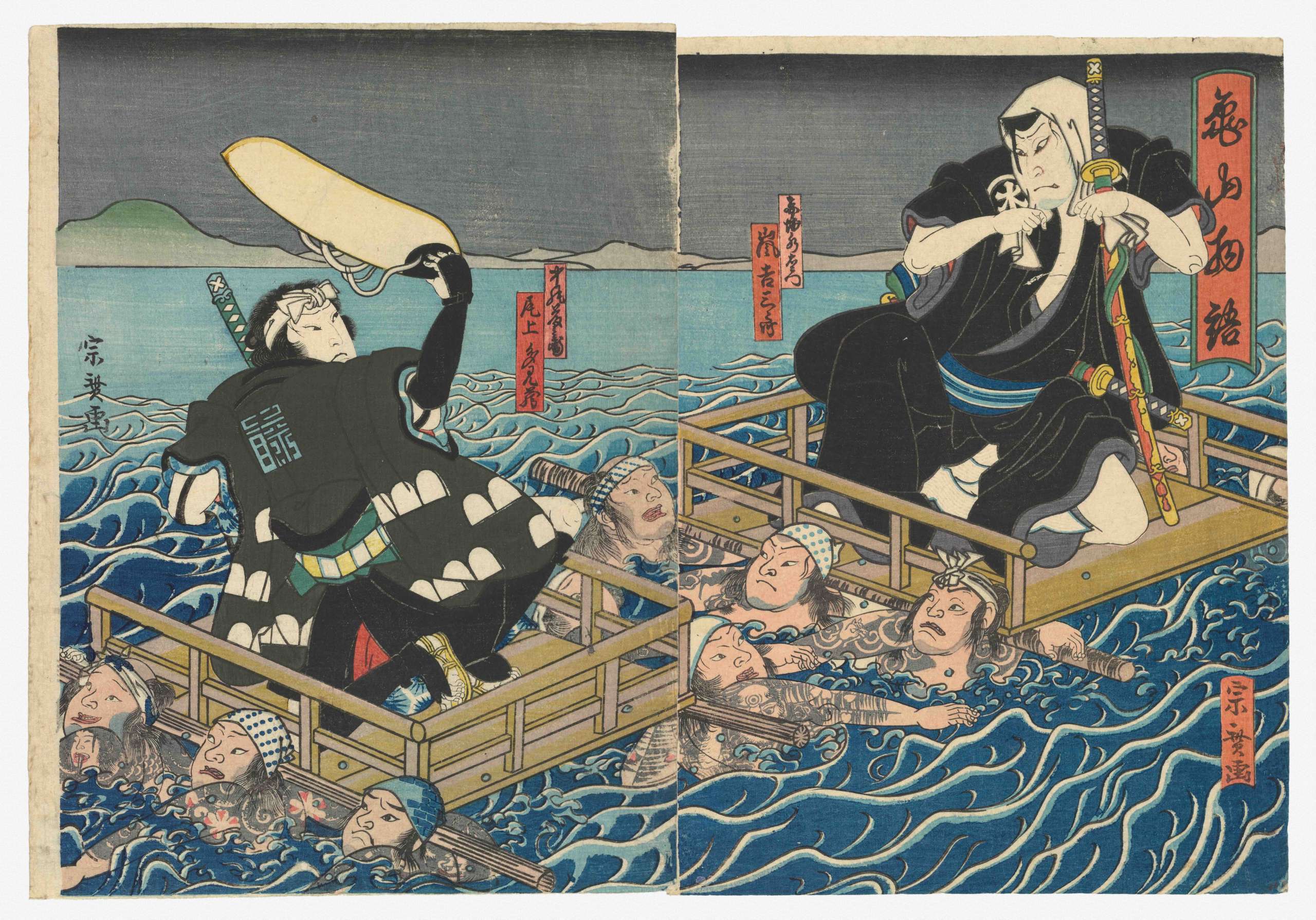
-
 Artist: Kawanabe Kyōsai [河鍋 暁斎] (Japanese, 1831 – 1889) Signed: Seisei Kyosai [惺々暁斎], and sealed. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 215 x 233 mm. Publisher: Unknown / No seal Date: Unknown / No seal Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 215 x 233 mm. Possibly, a private order. Wind chimes (fûrin, 風鈴) are associated with a Wind Chimes Festival [風鈴祭り], held in summer all over Japan. Seller's description: wo swallows streak by with seeming joy past a fûrin, a wind bell. These Japanese wind chimes were introduced to Japan in the Heian era, and in the Edo period, they began to be constructed out of glass. We see the hanging length of paper twisting in the breeze as it creates a delightful chime; these tones are a characteristic sound of summer in Japan. A layer of deluxe mica covers the entire design, lending sparkle. This work was meant to be pasted onto an uchiwa, or fan, for summer use.
Artist: Kawanabe Kyōsai [河鍋 暁斎] (Japanese, 1831 – 1889) Signed: Seisei Kyosai [惺々暁斎], and sealed. Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 215 x 233 mm. Publisher: Unknown / No seal Date: Unknown / No seal Media: Fan print (uchiwa-e, 団扇絵), 215 x 233 mm. Possibly, a private order. Wind chimes (fûrin, 風鈴) are associated with a Wind Chimes Festival [風鈴祭り], held in summer all over Japan. Seller's description: wo swallows streak by with seeming joy past a fûrin, a wind bell. These Japanese wind chimes were introduced to Japan in the Heian era, and in the Edo period, they began to be constructed out of glass. We see the hanging length of paper twisting in the breeze as it creates a delightful chime; these tones are a characteristic sound of summer in Japan. A layer of deluxe mica covers the entire design, lending sparkle. This work was meant to be pasted onto an uchiwa, or fan, for summer use. -
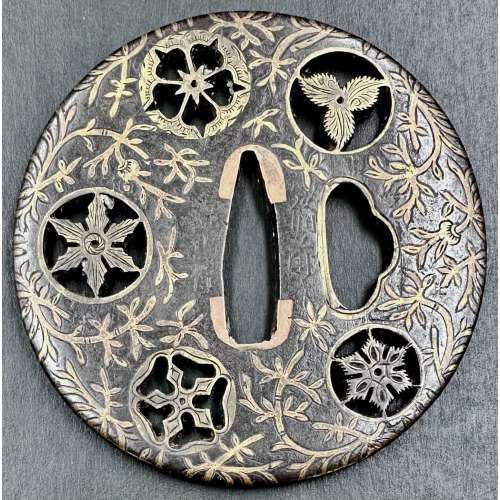 NEWIron tsuba of almost round form decorated with five roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Large hitsu-ana of ‘undulating cloud form’ outlined with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form, fitted with copper sekigane. Signed on both sides of seppa-dai on both sides of the plate: Made by Yoshirō, resident of Okayama in Bizen [備前岡山住・与四郎作之] (Bizen Okayama-jū – Yoshirō kore o tsukuru)
NEWIron tsuba of almost round form decorated with five roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Large hitsu-ana of ‘undulating cloud form’ outlined with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form, fitted with copper sekigane. Signed on both sides of seppa-dai on both sides of the plate: Made by Yoshirō, resident of Okayama in Bizen [備前岡山住・与四郎作之] (Bizen Okayama-jū – Yoshirō kore o tsukuru)According to Torigoye’s book “Tsuba Geijitsu Kō”, written in around 1962: “It is clear that there were two generations who used the name Bizen Yoshirō. The first generation worked about Kambun era (1661-1672). The second generation worked about the Genroku era (1688-1703). […] In the work of the first Bizen Yoshirō we see large hitsu-ana of undulating cloud forms. This would seem the sole characteristic separating his work from the other Bizen artists. In rare cases small nanako dots, or gold and silver ten-zōgan are to be found. Sometime after the middle of the Edo age the work of the Bizen Yoshirō school disappears, and there is no later work in the style of this school. The signatures found on tsuba are the following: Yoshirō saku, or Yoshirō kore (wo) tsukuru, this is the signature of the first Bizen Yoshirō. Other signatures are Umon Nagatsugu, or Koike Umon Nagatsugu, with Okayama jū nin on the back. Also Bizen Yoshirō Nagatsugu saku. Umon Nagatsugu and Koike Nagatsugu are the same person”.
Bizen Province [備前国] is located in southeastern Okayama Prefecture [岡山県]. Kanbun era [寛文] (April 1661 – September 1673). Dimensions: 68.5 x 68.0 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai 3.4 mm -
 NEWIn red cartouche: Famous places in Bushū and Kanagawa (Bushū Kanagawa meisho) [武州神奈河名昕] In yellow striped square: Gankirō in Yokohama (Yokohama Gankirō) [横濱巌亀楼] / new spelling 横浜岩亀楼. The three kanji [岩亀楼] (Gankirō) are also visible on the sign or lantern above the food tray, carried on the head by a man on the left. Gankirō – the largest 'tea house' (brothel) for foreigners in the Miyozaki pleasure quarters, similar to those in Yoshiwara, in Edo. Artist: Utagawa Hiroshige II [二代目 歌川広重] (Japanese, 1826 – 1869) – a son-in-law of Andō Hiroshige. Signature: Hiroshige ga [廣重画] Dimensions: Aiban yoko-e uchiwa-e, 223 x 289 mm. Combined date/censor seal: monkey (saru - 申) and kiwame (極), 1860. Publisher: Yama-Ta; seal: [板元, 太] – Hanmoto, Ta; Marks 19-044 | U421b: An unknown publisher in Edo, fl. c. 1815-61. Another Hiroshige II's print with the same subject and even the same characters, but in 3rd month, 1859: Entrance to the Gankirō Tea House in the Miyozaki District, Yokohama, Bushu (Bushu Yokohama Gankirō) [諸国名所百景 武州横浜岩亀楼]. Utagawa Yoshikazu's [歌川芳員] depiction of the place in c. 1861 from the inside:[Thanks to Horst Graebner].
NEWIn red cartouche: Famous places in Bushū and Kanagawa (Bushū Kanagawa meisho) [武州神奈河名昕] In yellow striped square: Gankirō in Yokohama (Yokohama Gankirō) [横濱巌亀楼] / new spelling 横浜岩亀楼. The three kanji [岩亀楼] (Gankirō) are also visible on the sign or lantern above the food tray, carried on the head by a man on the left. Gankirō – the largest 'tea house' (brothel) for foreigners in the Miyozaki pleasure quarters, similar to those in Yoshiwara, in Edo. Artist: Utagawa Hiroshige II [二代目 歌川広重] (Japanese, 1826 – 1869) – a son-in-law of Andō Hiroshige. Signature: Hiroshige ga [廣重画] Dimensions: Aiban yoko-e uchiwa-e, 223 x 289 mm. Combined date/censor seal: monkey (saru - 申) and kiwame (極), 1860. Publisher: Yama-Ta; seal: [板元, 太] – Hanmoto, Ta; Marks 19-044 | U421b: An unknown publisher in Edo, fl. c. 1815-61. Another Hiroshige II's print with the same subject and even the same characters, but in 3rd month, 1859: Entrance to the Gankirō Tea House in the Miyozaki District, Yokohama, Bushu (Bushu Yokohama Gankirō) [諸国名所百景 武州横浜岩亀楼]. Utagawa Yoshikazu's [歌川芳員] depiction of the place in c. 1861 from the inside:[Thanks to Horst Graebner].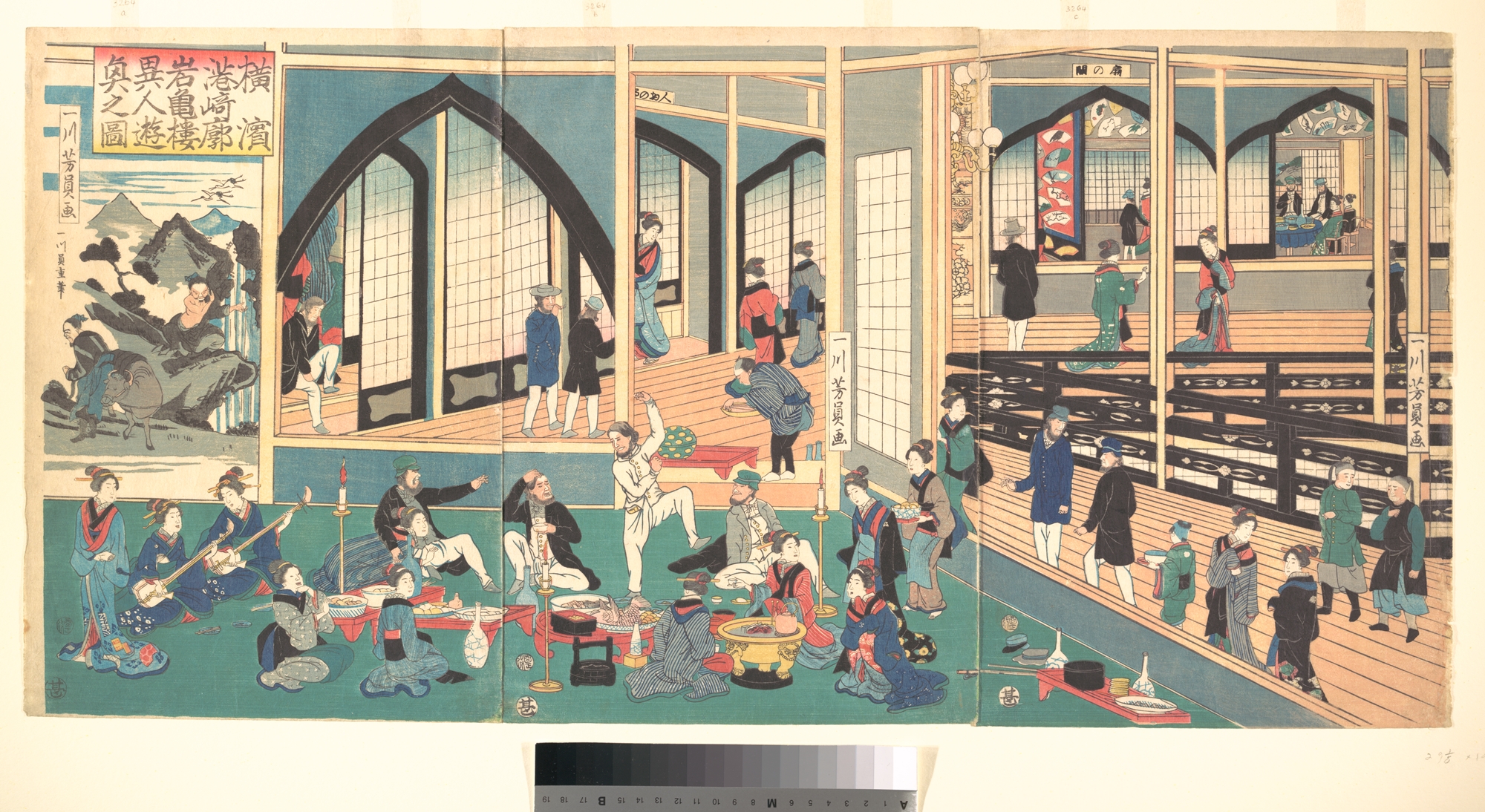
Foreigners Enjoying Themselves in the Gankirō. MET JP3264.
-
 NEWTitle: Flower calendar for the famous cherry blossoms (Hana goyomi meisho sakura) [花暦名所櫻]. A scene from an imaginary (mitate) kabuki play. Names of the characters (left to right): Kiyomizu/Shimizu Seigen [清水清玄]; Yakko (footman) Yodohei [奴淀平]; koshimoto (court lady) [こしもと]; Sakura hime (princess) [桜姫]. The same characters appear in a few real kabuki plays. Artist: Utagawa Hiroshige [歌川 広重] a.k.a. Andō Hiroshige [安藤 広重] (Japanese, 1797 – 1858) Signature: Hiroshige ga [廣重画] Dimensions: Aiban yoko-e uchiwa-e, 232 x 295 mm. Censor seal: "Mura" [村] for Murata Sahei [村田佐兵衛], used from VI/1842 to V/1846 (Tenpō 13 – Kōka 3). Publisher: Enshūya Matabei [遠州屋又兵衛] (Enterprise, active c. 1768 – 1881); seal: "To" (ト) (Marks 01-031 | 057a). [Thanks to Horst Graebner].
NEWTitle: Flower calendar for the famous cherry blossoms (Hana goyomi meisho sakura) [花暦名所櫻]. A scene from an imaginary (mitate) kabuki play. Names of the characters (left to right): Kiyomizu/Shimizu Seigen [清水清玄]; Yakko (footman) Yodohei [奴淀平]; koshimoto (court lady) [こしもと]; Sakura hime (princess) [桜姫]. The same characters appear in a few real kabuki plays. Artist: Utagawa Hiroshige [歌川 広重] a.k.a. Andō Hiroshige [安藤 広重] (Japanese, 1797 – 1858) Signature: Hiroshige ga [廣重画] Dimensions: Aiban yoko-e uchiwa-e, 232 x 295 mm. Censor seal: "Mura" [村] for Murata Sahei [村田佐兵衛], used from VI/1842 to V/1846 (Tenpō 13 – Kōka 3). Publisher: Enshūya Matabei [遠州屋又兵衛] (Enterprise, active c. 1768 – 1881); seal: "To" (ト) (Marks 01-031 | 057a). [Thanks to Horst Graebner]. -
 NEWTitle: The Secret Meeting between Ushiwakamaru and the Daughter of Kiichi Hōgen (Kiichi Hōgen ga hisho o miro) [鬼一法眼が秘書をみる] Series: Scenes from the life of Ushiwaka (Ushiwaka zue) [牛若図会] Artist: Utagawa Hiroshige [歌川 広重] a.k.a. Andō Hiroshige [安藤 広重] (Japanese, 1797 – 1858) Signature: Hiroshige ga [廣重画] Dimensions: Aiban yoko-e uchiwa-e, 226 x 303 mm. Censor seal: Hama & Magome [濱 / 馬込]: 1/1849 – 2/1852 (Kaei 2-5) Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. C. 1845 – 1847), seal: San [三] (Marks 11-001 | 127c). According to Rupert Faulkner (2001), another copy of this fan print is housed at Ōta Memorial Museum (ŌMM 1998, № 258). There are four other known prints from this series: (1) The Meeting at Yahagi: The Beginnings of the Jorurijunidan Story (Yahagi no Shuku Jorurijunidan no Hajime); (2) Ushiwakamaru practising swordsmanship at Sojogatani (ŌMM 1998, no.256); (3) Ushiwakamaru's encounter with Benkei on Gojo Bridge (Matsuki 1924, no.93); and (4) Ise no Saburo swearing an oath of loyalty to Ushiwakamaru (Kanagawa Prefectural Museum of Cultural History). Kiichi Hōgen [鬼一法眼] is a legendary monk and warrior who trained Ushiwakamaru (young Minamoto no Yoshitsune) in swordsmanship, tactics, and magic.Another print (Ushiwakamaru's encounter with Benkei on Gojo Bridge) from this series is in the collection of the Art Institute of Chicago under the title Killing One Thousand People at Gojo Bridge (Gojo no hashi sennin kiri).
NEWTitle: The Secret Meeting between Ushiwakamaru and the Daughter of Kiichi Hōgen (Kiichi Hōgen ga hisho o miro) [鬼一法眼が秘書をみる] Series: Scenes from the life of Ushiwaka (Ushiwaka zue) [牛若図会] Artist: Utagawa Hiroshige [歌川 広重] a.k.a. Andō Hiroshige [安藤 広重] (Japanese, 1797 – 1858) Signature: Hiroshige ga [廣重画] Dimensions: Aiban yoko-e uchiwa-e, 226 x 303 mm. Censor seal: Hama & Magome [濱 / 馬込]: 1/1849 – 2/1852 (Kaei 2-5) Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. C. 1845 – 1847), seal: San [三] (Marks 11-001 | 127c). According to Rupert Faulkner (2001), another copy of this fan print is housed at Ōta Memorial Museum (ŌMM 1998, № 258). There are four other known prints from this series: (1) The Meeting at Yahagi: The Beginnings of the Jorurijunidan Story (Yahagi no Shuku Jorurijunidan no Hajime); (2) Ushiwakamaru practising swordsmanship at Sojogatani (ŌMM 1998, no.256); (3) Ushiwakamaru's encounter with Benkei on Gojo Bridge (Matsuki 1924, no.93); and (4) Ise no Saburo swearing an oath of loyalty to Ushiwakamaru (Kanagawa Prefectural Museum of Cultural History). Kiichi Hōgen [鬼一法眼] is a legendary monk and warrior who trained Ushiwakamaru (young Minamoto no Yoshitsune) in swordsmanship, tactics, and magic.Another print (Ushiwakamaru's encounter with Benkei on Gojo Bridge) from this series is in the collection of the Art Institute of Chicago under the title Killing One Thousand People at Gojo Bridge (Gojo no hashi sennin kiri).
Rupert Faulkner (2001)
Reference: (1) Rupert Faulkner. Hiroshige Fan Prints / Victoria and Albert Museum, Far Eastern Series. — London: V&A Publications; NY: Harry N. Abrams, Inc., 2001. (2) Christophe Marquet. Hiroshige: Les éventails d'Edo / Estampes de la collection Georges Leskowicz. — Paris: In fine, 2022. [Thanks to Horst Graebner].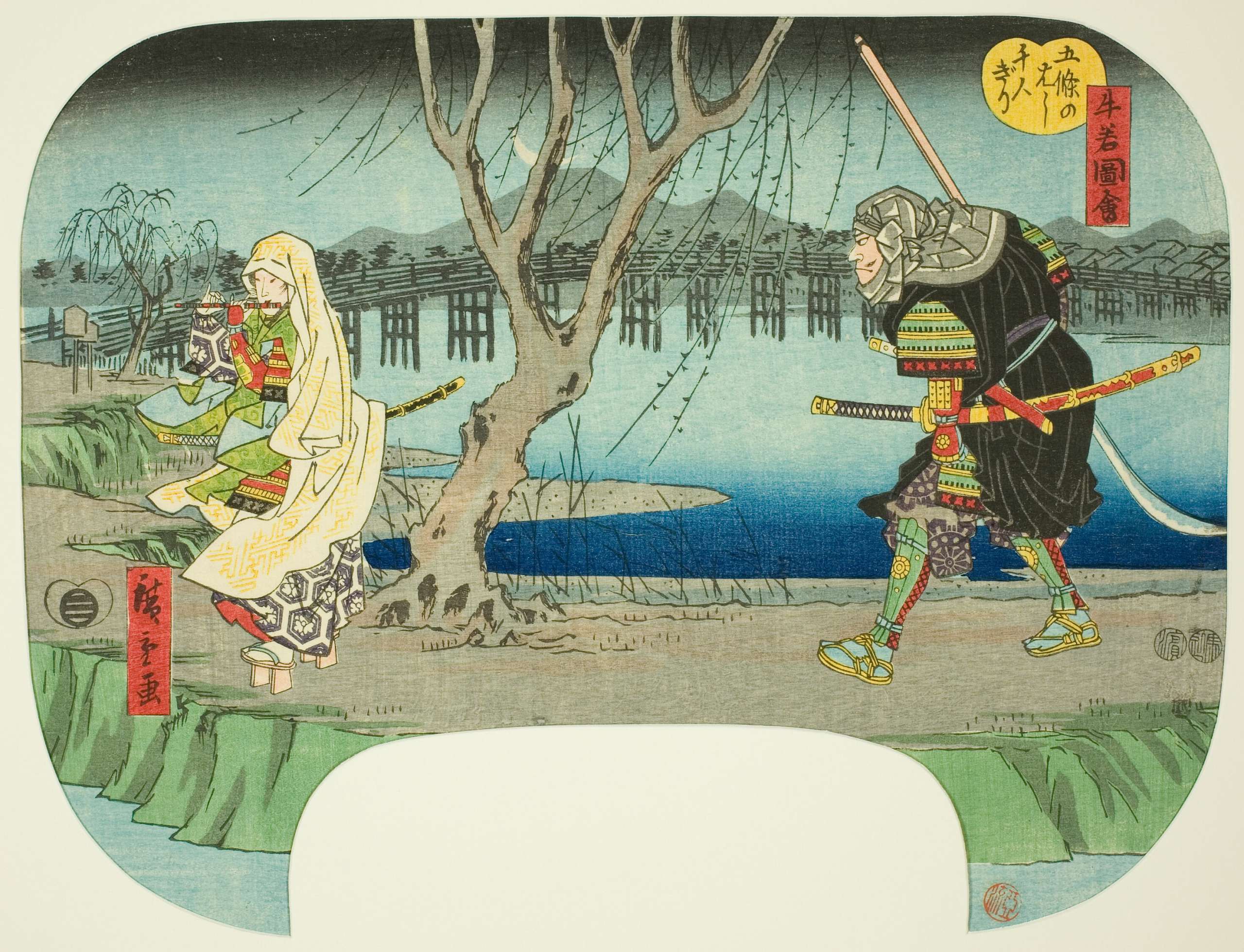
AIC Reference Number 1925.3802









