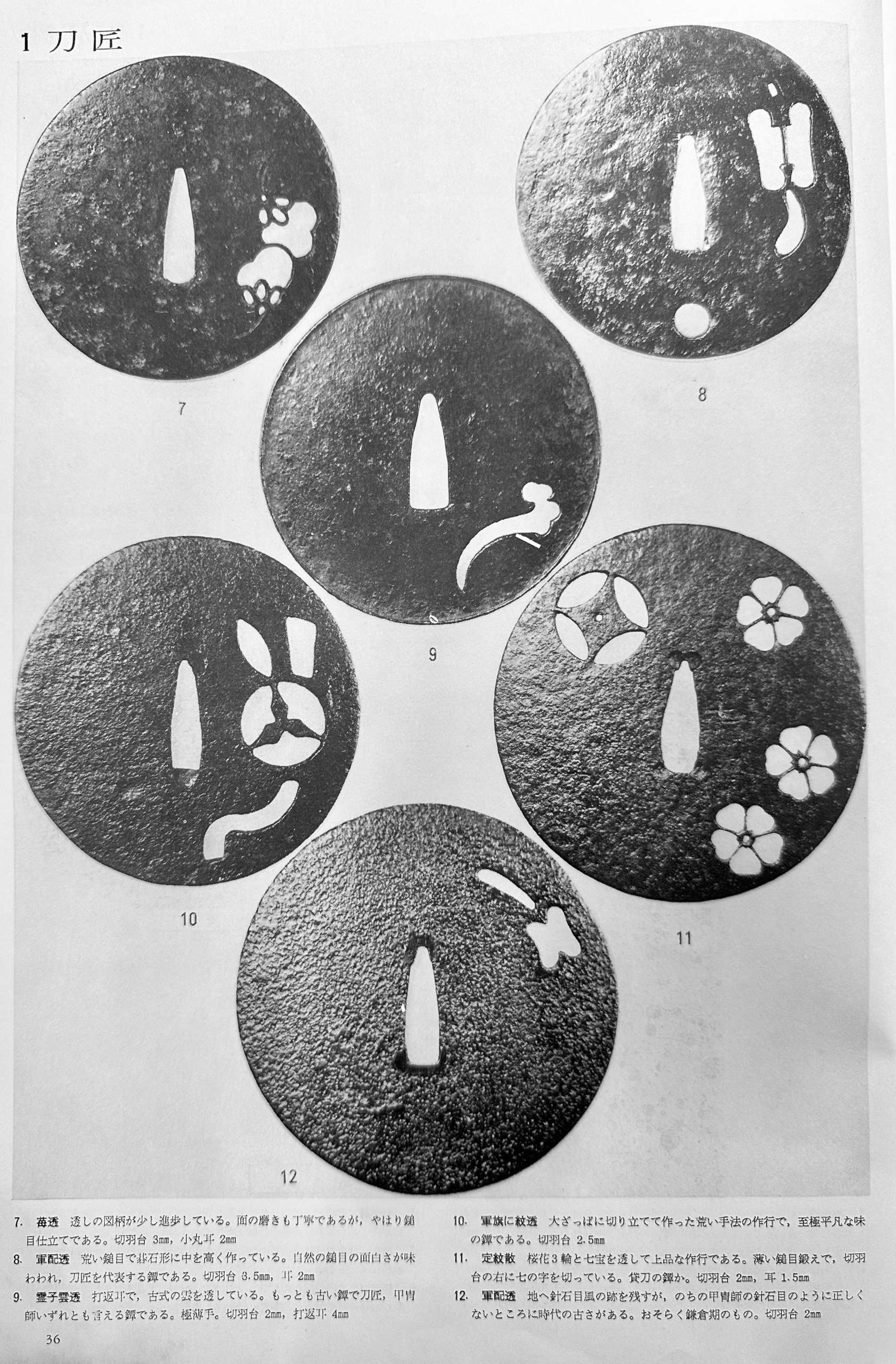
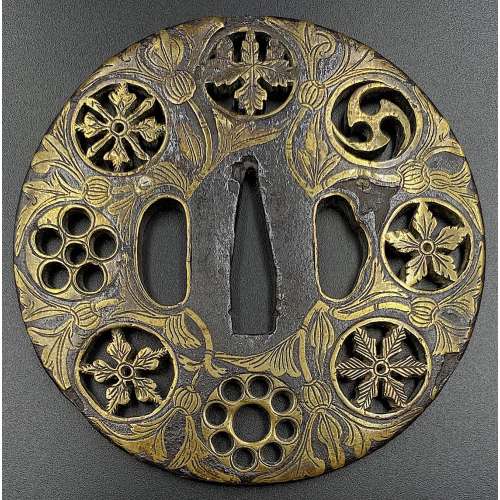
Tsuba Collection (Tsuba shūsei, 鐔集成) by Nakamura Tessei (中村鐵青), p.36, fig. 12.


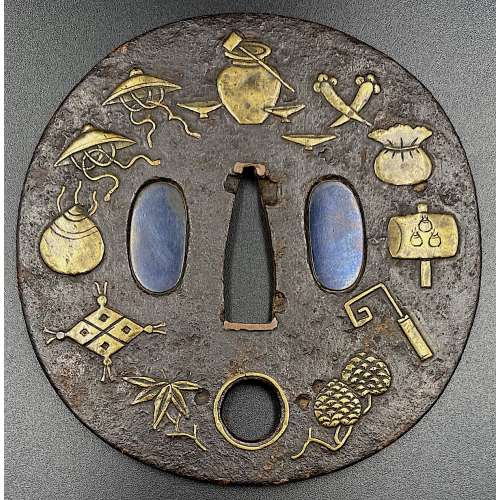
Tsuba Collection (Tsuba shūsei, 鐔集成) by Nakamura Tessei (中村鐵青), p.36, fig. 12.

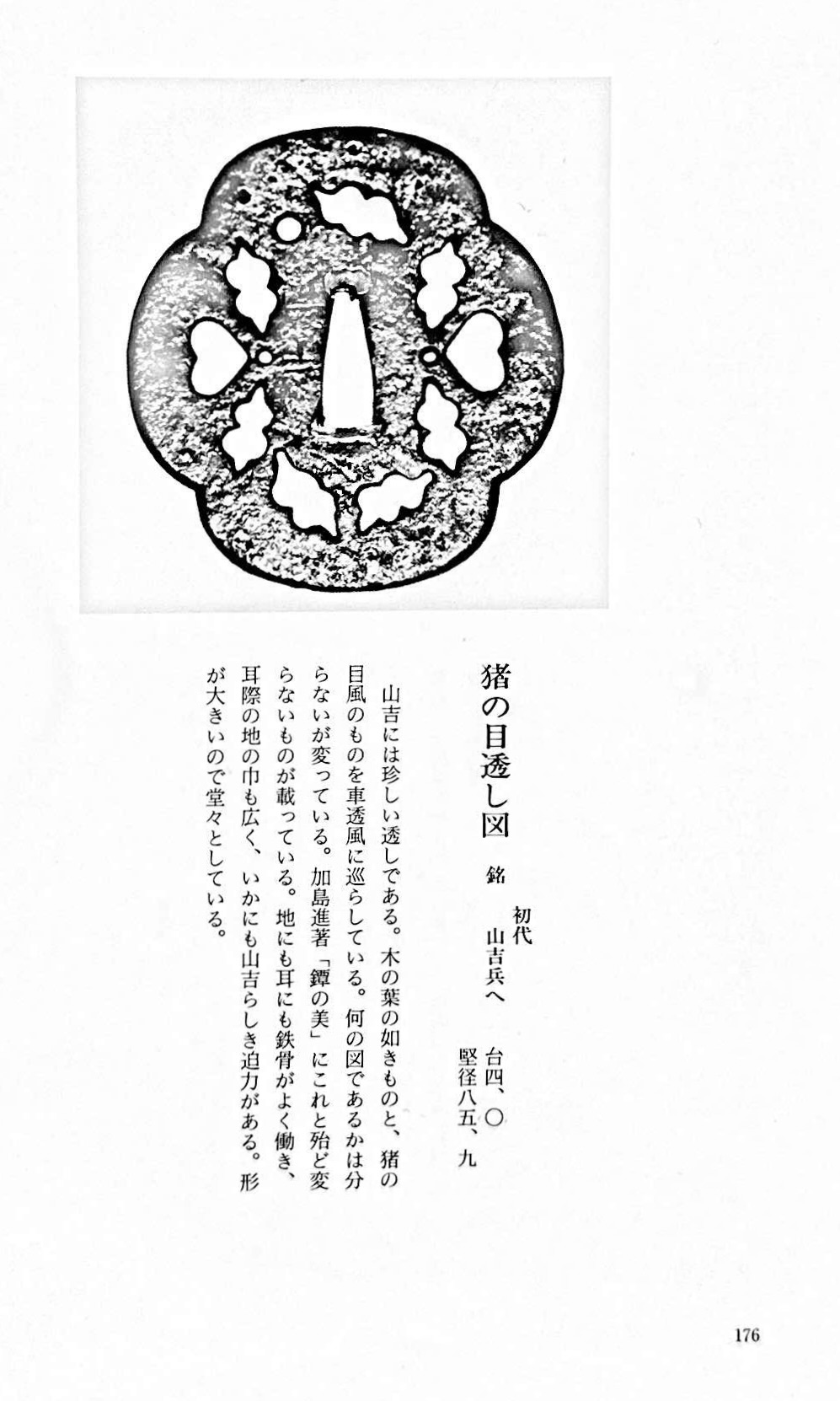
Large iron tsuba of mokko form with the openwork (sukashi) design, described by some as rotten leaves swirling in the wind and boar eyes (inome, 猪目, heart-shaped elements); round rim (maru-mimi); no hitsu-ana; pronounced iron bones (tekkotsu); chocolate patina.
Signed to the left of nakaga-ana: Yamakichibei (山吉兵へ). Attributed to the First Generation (Shodai) master.
Dimensions: 90 x 82 mm, thickness 3.7 mm at centre, 4.9 mm at rim. Weight: 142 gReferences: similar handguards demonstrated at Yasukazu's Owari to Mikawa no tankō №176 and Kajima's Tsuba no Bi №28.
Owari to Mikawa no tankō №176

Tsuba no Bi №28

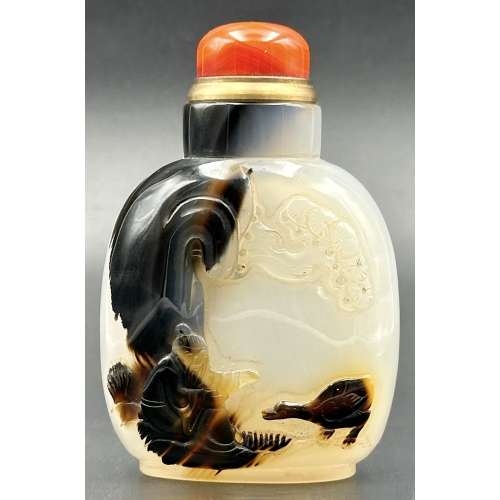
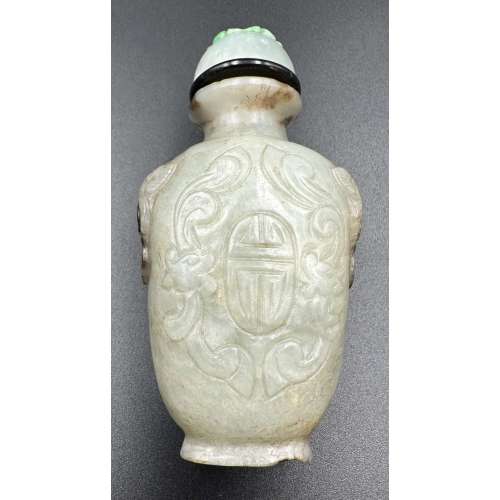
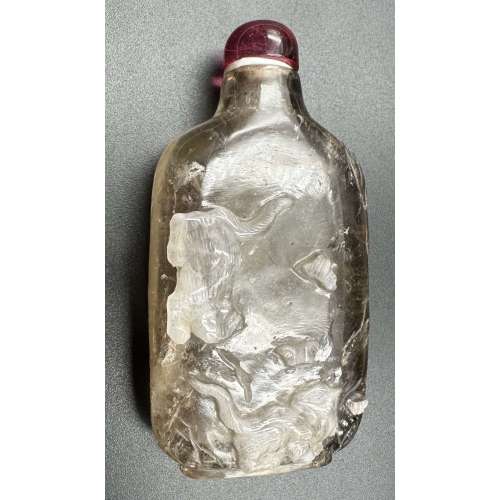
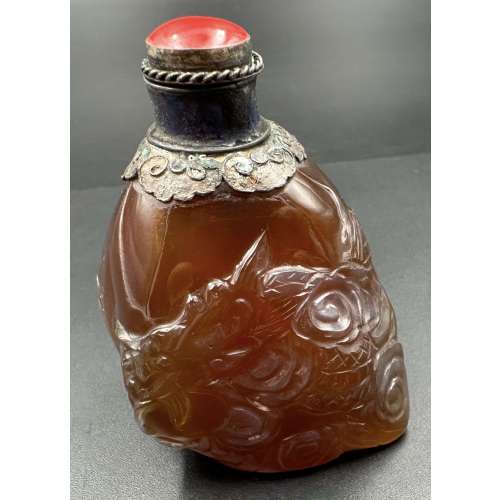
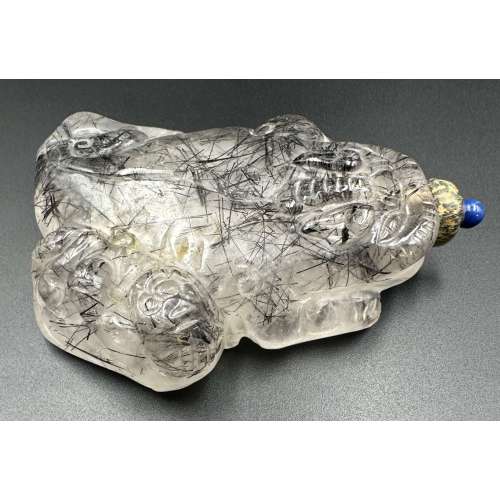
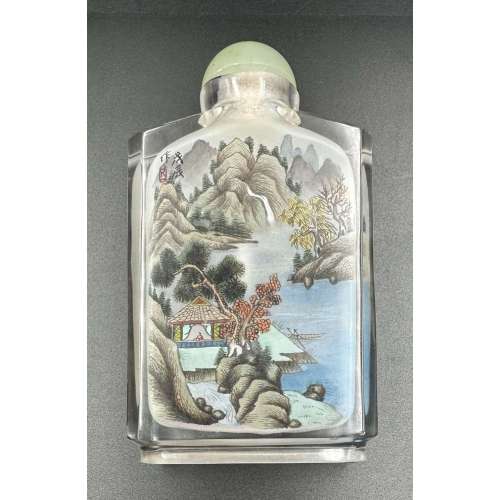
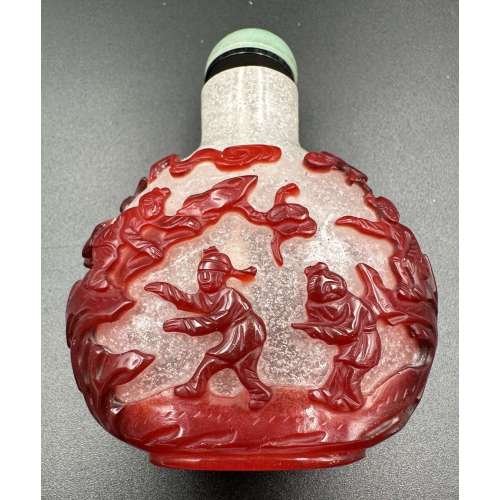
The Eastern dragon is not the gruesome monster of medieval imagination, but the genius of strength and goodness. He is the spirit of change, therefore of life itself. Hidden in the caverns of inaccessible mountains, or coiled in the unfathomed depth of the sea, he awaits the time when he slowly rouses himself into activity. He unfolds himself in the storm clouds; he washes his mane in the blackness of the seething whirlpools. His claws are in the fork of the lightning, his scales begin to glisten in the bark of rain-swept pine trees. His voice is heard in the hurricane, which, scattering the withered leaves of the forest, a dragon quickens a new spring [C. A. S. Williams. Chinese Symbolism and Art Motifs / 3rd Revised Edition. — Rutland, Vermont & Tokyo, Japan: Charles E. Tuttle Company, 1993].The Qing dynasty (1644–1911). Mid-19th century. Dimensions: H90 x W52 x D30 mm
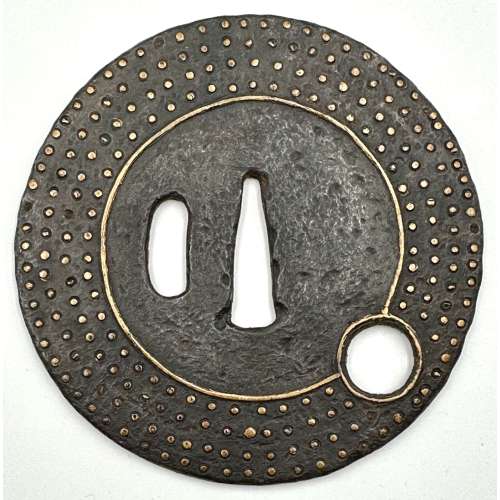


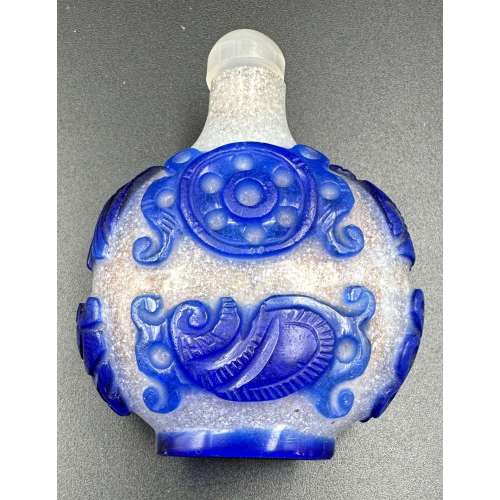
Iron tsuba of round form with one hitsu ana; centre of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire broke by a circular opening 7 mm in diameter located between 4 and 5 o’clock of the plate and in its turn outlined with brass wire. Extraneous to the central wire, the plate is decorated with four rows of brass dots (ten-zogan). A few dots are missing. In a custom kiri wood box. The meaning of the emblem is probably either the sun or the moon.
Ōnin school. Unsigned.
Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century.
Dimensions: diameter 88 mm; thickness 3.3 mm.











 Kiri-mon |
 Katakura-mon |

