Tears That Brought Bamboo-shoots From the Frozen Earth: Meng Zong Meng Zong lived during the Three Kingdoms Period of China's past. His father died when he was young, and he and his mother struggled to survive. One winter his mother was stricken with a serious illness, and craved some bamboo-shoot broth as medicine. But in the depths of winter, with snow and ice blanketing the ground, where was anyone to find fresh bamboo shoots, shoots that emerge only in the warm months? Nonetheless, Meng Zong, to avoid disappointing his mother, bravely fetched his shovel and went out into the white landscape in search of bamboo shoots. In the thicket he found only frosted leaves and green stalks coated with snowflakes and ice. Look as he might, there were simply no fresh shoots growing in the winter. The thought of his poor mother lying sick on her bed, waiting for bamboo-broth medicine, made his heartache. Uncontrollably, tears began to fall in rivers to the ground beneath the tall, emerald canes. Even now, as his tears flowed down, he kept a light of faith in his heart. If he was truly sincere in his search, perhaps.... Just then Meng Zong nearly tripped and fell over a sharply protruding lump of earth. He quickly knelt down and knocked aside the dirt with his trembling fingers. How uncanny! Underneath his frozen hands he discovered a bed of fresh, tender bamboo shoots! Overjoyed, he gathered up a coatful and carried them back home. The broth that he quickly set stewing in the pot soon cured his mother's illness. The neighbors, hearing the story, exclaimed that it was the strength of his sincere, unselfish, filial resolve that inspired heaven and earth to respond, and to bring up, out of season, the fresh shoots that cured his mother's disease. Before Meng Zong's prayers generated this miracle, it was normally considered impossible for bamboo shoots to grow in the winter. After the nmiracle took place, however, people were able to gather and to eat bamboo shoots all year round. The winter variety that existed hereafter became known as "winter shoots." The villagers were deeply influenced by Meng Zong's courage and devotion. They renamed the spot where the event took place, "Meng Zong's Bamboo Grove". We can now enjoy bamboo sprouts during the winter as well, and as we do so, it is fitting to recollect Meng Zong's outstanding example of filial respect, and reflect on our conduct as sons and daughter of our parents. A verse in his honor says, His teardrops transformed winter at the roots; Up from the ice crept tender bamboo shoots. Instantly, the winter-sprouts matured; Heaven's will: a happy, peaceful world.
-
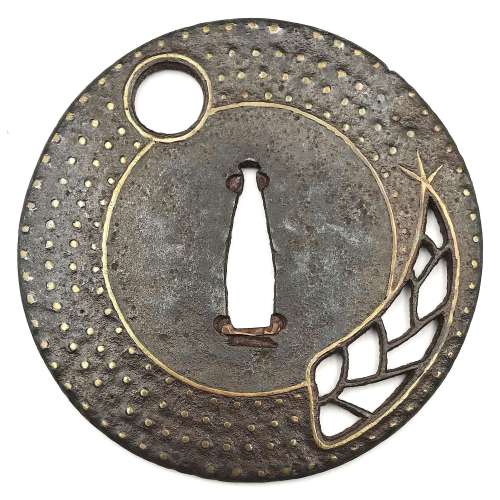 Ōnin shinchū ten-zōgan tsuba. Iron tsuba of round form decorated with full moon and bamboo shoot (takenoko) motif executed in openwork (sukashi) and inlaid with four concentric rows of brass dots (ten-zōgan). The innermost row of dots as well as the sukashi openings outlined with the inlaid linear brass wire. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Diameter: 82.0 mm; Thickness: 2.8 mm Cited from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 72: "In Japanese art, the appearance of bamboo shoots is often without symbolic meaning. In other cases, however, the shoots are emblematic of Moso (Chinese: Meng Tsung/Meng Zong), a paragon of filial piety who dug through snow to find shoots for his mother. ... especially in miniature art forms, let bamboo shoots alone speak for the full story." The full story is this (See THE TWENTY-FOUR PARAGONS OF FILIAL PIETY [ERSHISI XIAO]):
Ōnin shinchū ten-zōgan tsuba. Iron tsuba of round form decorated with full moon and bamboo shoot (takenoko) motif executed in openwork (sukashi) and inlaid with four concentric rows of brass dots (ten-zōgan). The innermost row of dots as well as the sukashi openings outlined with the inlaid linear brass wire. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Diameter: 82.0 mm; Thickness: 2.8 mm Cited from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 72: "In Japanese art, the appearance of bamboo shoots is often without symbolic meaning. In other cases, however, the shoots are emblematic of Moso (Chinese: Meng Tsung/Meng Zong), a paragon of filial piety who dug through snow to find shoots for his mother. ... especially in miniature art forms, let bamboo shoots alone speak for the full story." The full story is this (See THE TWENTY-FOUR PARAGONS OF FILIAL PIETY [ERSHISI XIAO]): -
 Onin Tsuba with two overlapping lozenges, or interlocked diamond shapes. Iron and brass. Sukashi and ten-zogan technique. Muromachi period. Diameter: 81.0 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm The symbol of two overlapping lozenges (or, interlocked diamond shapes), presumably a family crest (kamon) may be deciphered as chigai kuginuki (nail extraction tool => 'conquered nine castles' ) or as chigai bishi (overlapping lozenges). Similar symbol can be found at Butterfield & Butterfield. IMPORTANT JAPANESE SWORDS, SWORD FITTINGS AND ARMOR. Auction Monday, November 19th, 1979. Sale # 3063], №94 with the following explanation: " This was the mon (crest) of the Yonekura family of Kaga Prov., at Kanazawa". An interesting insight is provided by Robert E. Haynes at Important Japanese kodogu, gaiso and works of art. San Francisco, April 9-11, 1982. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd., № 36 (see photo): "This would seem to be the Yonekura family mon. They were Seiwa-Genji Daimyō family made noble in 1696 and resided in Kanazawa in Kaga". Would it be possible that this is a late 17th century Ōnin tsuba?
Onin Tsuba with two overlapping lozenges, or interlocked diamond shapes. Iron and brass. Sukashi and ten-zogan technique. Muromachi period. Diameter: 81.0 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm The symbol of two overlapping lozenges (or, interlocked diamond shapes), presumably a family crest (kamon) may be deciphered as chigai kuginuki (nail extraction tool => 'conquered nine castles' ) or as chigai bishi (overlapping lozenges). Similar symbol can be found at Butterfield & Butterfield. IMPORTANT JAPANESE SWORDS, SWORD FITTINGS AND ARMOR. Auction Monday, November 19th, 1979. Sale # 3063], №94 with the following explanation: " This was the mon (crest) of the Yonekura family of Kaga Prov., at Kanazawa". An interesting insight is provided by Robert E. Haynes at Important Japanese kodogu, gaiso and works of art. San Francisco, April 9-11, 1982. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd., № 36 (see photo): "This would seem to be the Yonekura family mon. They were Seiwa-Genji Daimyō family made noble in 1696 and resided in Kanazawa in Kaga". Would it be possible that this is a late 17th century Ōnin tsuba?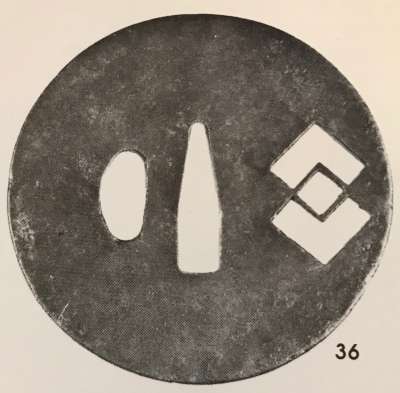
Robert E. Haynes Catalog of April 9-11, 1982, № 36.
-
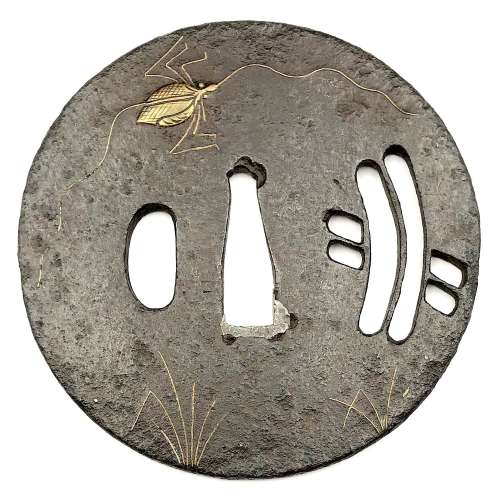 Iron tsuba with design of a cricket and grass inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) and a bridge over a stream in openwork (sukashi) on both sides. Inlay of distant part of the cricket's antenna is missing. Heianjō School. Momoyama period. Diameter: 79.5 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.3 mm NBTHK # 4002100.
Iron tsuba with design of a cricket and grass inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) and a bridge over a stream in openwork (sukashi) on both sides. Inlay of distant part of the cricket's antenna is missing. Heianjō School. Momoyama period. Diameter: 79.5 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.3 mm NBTHK # 4002100. -
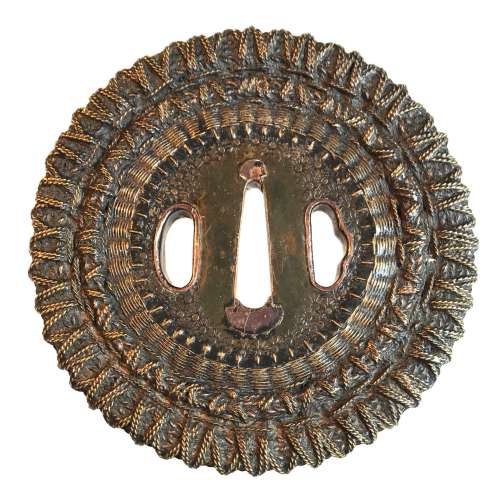 Shingen school (or style) tsuba of round form with an iron core of spoked-wheel shape, with its centre covered with a copper plate decorated with star-shaped punch marks. From this copper plate outward, the body is formed by brass and copper wire (flat and twisted) in a weave pattern. Both hitsu-ana are outlined in brass with a raised rim. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Edo period, 18th century. SOLD Height: 98.0 mm, Width: 97.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 6.0 mm. Weight: 290 g. NBTHK certificate №436696: 'Hozon' attestation. Citing "JAPANESE SWORD-MOUNTS IN THE COLLECTIONS OF FIELD MUSEUM" by Helen C. Gunsaulus, Assistant Curator of Japanese Ethnology. 61 plates. Berthold Laufer, Curator of Anthropology. Field Museum of Natural History, Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p.45: "An unusual group of tsuba popular in the late sixteenth century and afterwards is made up of those guards known as Shingen tsuba, a name which was derived from a sixteenth-century warrior, Takeda Shingen (Takeda Harunobu, 1521-73), who is said to have preferred this style of guard, as it combined strength and lightness. Under the category of "Shingen", four different types abd generally listed, though a fifth appears in the drawings in the Boston Catalogue of Okabe Kakuya "Japanese Sword Guards" (p. 21). It is square, that form which is said to have been used in Ashikaga days for scaling walls, the sword having been set up as a step. [...] The following descriptions include, however, the Shingen tsuba usually met with.
Shingen school (or style) tsuba of round form with an iron core of spoked-wheel shape, with its centre covered with a copper plate decorated with star-shaped punch marks. From this copper plate outward, the body is formed by brass and copper wire (flat and twisted) in a weave pattern. Both hitsu-ana are outlined in brass with a raised rim. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Edo period, 18th century. SOLD Height: 98.0 mm, Width: 97.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 6.0 mm. Weight: 290 g. NBTHK certificate №436696: 'Hozon' attestation. Citing "JAPANESE SWORD-MOUNTS IN THE COLLECTIONS OF FIELD MUSEUM" by Helen C. Gunsaulus, Assistant Curator of Japanese Ethnology. 61 plates. Berthold Laufer, Curator of Anthropology. Field Museum of Natural History, Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p.45: "An unusual group of tsuba popular in the late sixteenth century and afterwards is made up of those guards known as Shingen tsuba, a name which was derived from a sixteenth-century warrior, Takeda Shingen (Takeda Harunobu, 1521-73), who is said to have preferred this style of guard, as it combined strength and lightness. Under the category of "Shingen", four different types abd generally listed, though a fifth appears in the drawings in the Boston Catalogue of Okabe Kakuya "Japanese Sword Guards" (p. 21). It is square, that form which is said to have been used in Ashikaga days for scaling walls, the sword having been set up as a step. [...] The following descriptions include, however, the Shingen tsuba usually met with.- So-called Mukade ("centipede") tsuba are made of iron in which a centepede is inlaid in brass or copper wire. Mukade tsuba of Myōchin and Umetada warkmanship have been found with the inscription, "Made to the taste of Takeda Shingen".
- There are those of solid iron, with need centers of brass, to the edges of which is affixed a weaving of brass and copper wires which is bound to the foundation disk by a rim, usually decorated simply.
- Another type is of solid iron, bored at intervals and laced with braided or twisted wires of copper and brass.
- The fourth type is a chrysanthemoid form, chiselled in open work and laced or woven tightly with copper and brass wire."

Compton Collection, Part II, p.p. 26-27, №54.
-
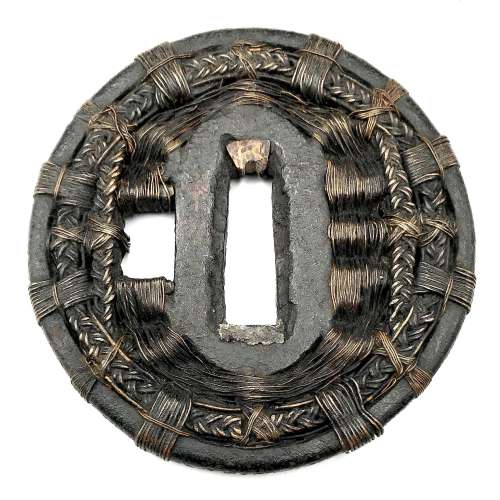 Shingen school tsuba with woven wire pattern. Iron core, woven brass wire. Height: 72.5 mm; Width 69.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm. Weight 88.8 g. Late Muromachi, 16th century. SOLD http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Shingen school tsuba with woven wire pattern. Iron core, woven brass wire. Height: 72.5 mm; Width 69.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm. Weight 88.8 g. Late Muromachi, 16th century. SOLD http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ -
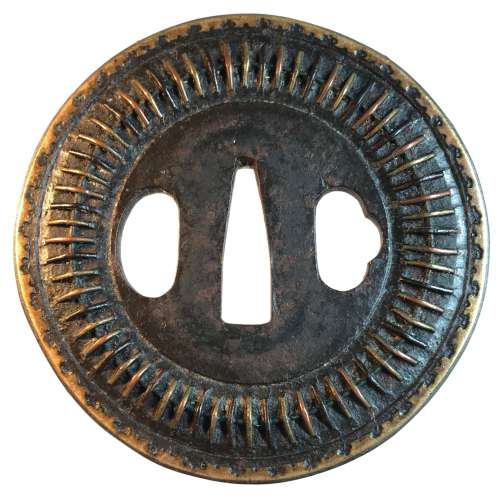 Iron tsuba of round form inlaid with brass, copper, and shakudō wire fastened to the surface with metal staples (mukade-zōgan); Scalloped brass inlay around the rim. Early Edo, 17th century. Height: 84.8 mm; Width 84.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.7 mm. Weight 161.6 g. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] See also: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Iron tsuba of round form inlaid with brass, copper, and shakudō wire fastened to the surface with metal staples (mukade-zōgan); Scalloped brass inlay around the rim. Early Edo, 17th century. Height: 84.8 mm; Width 84.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.7 mm. Weight 161.6 g. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] See also: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ -
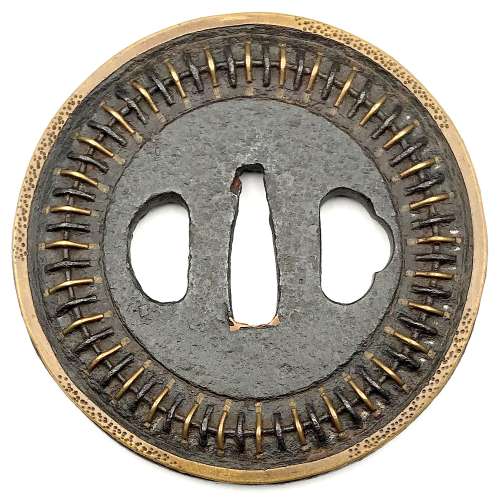 Iron tsuba of round form with circular iron wire fastened to the surface with iron and brass staples (mukade-zōgan); brass ring about 2.5 mm wide along the rim with chisel marks. Design repeats on the reverse. Copper sekigane. Early Edo, 17th century. Size: Height: 83.3 mm; width 83.9 mm; thickness at seppa-dai: 4.5 mm. Weight 173.6 g. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] See also: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ SOLD
Iron tsuba of round form with circular iron wire fastened to the surface with iron and brass staples (mukade-zōgan); brass ring about 2.5 mm wide along the rim with chisel marks. Design repeats on the reverse. Copper sekigane. Early Edo, 17th century. Size: Height: 83.3 mm; width 83.9 mm; thickness at seppa-dai: 4.5 mm. Weight 173.6 g. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] See also: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ SOLD -
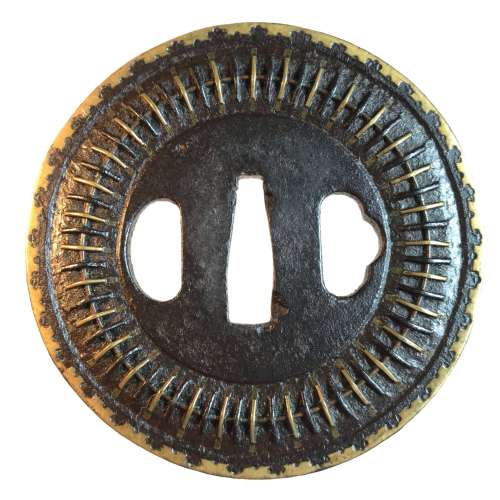 Mukade-zōgan tsuba with two types of wires. Iron, inlaid with brass and iron wire fastened to the surface with metal staples (mukade-zōgan); Brass inlay around the rim. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] Height: 85.8 mm; Width 86.2 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.3 mm. Weight 177.6 g. Early Edo, 17th century. http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Mukade-zōgan tsuba with two types of wires. Iron, inlaid with brass and iron wire fastened to the surface with metal staples (mukade-zōgan); Brass inlay around the rim. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] Height: 85.8 mm; Width 86.2 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.3 mm. Weight 177.6 g. Early Edo, 17th century. http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ -
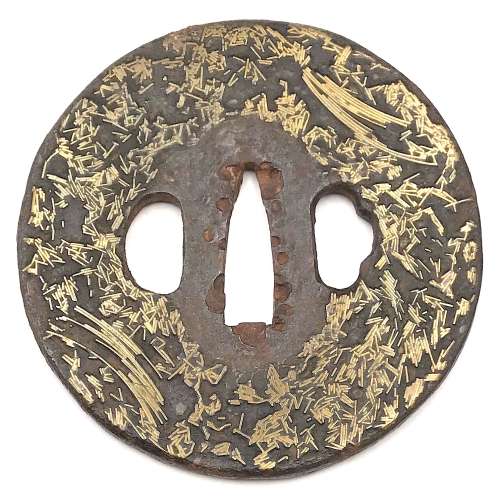 Gomoku-zōgan tsuba. Iron, inlaid with brass scrap (gomoku-zōgan), and polished. Height: 75.3 mm; Width 74.9 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. Weight 130.2 g. Edo, 18th century. Gary D. Murtha dedicates 10 pages to this type of tsuba: "...they were made by soldering brass overlay scraps to the iron plate". Actual gomoku-zōgan tsuba are seldom found in collections most likely because they have little if any artistic attributes. In addition, many have rough surfaces making them questionable for use on a sword. It is said that many of these were produced in Yokohama for export to the West during the late Edo period". G. D. Murtha then describes the technique of making gomoku-zōgan in every detail, and states that "The brass pieces are said to represent 'fallen pine needles', a description most likely created to add aesthetic value to help market the tsuba" [see:Gary D. Murtha. Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro. GDM Publications, 2016; pp. 160-161].
Gomoku-zōgan tsuba. Iron, inlaid with brass scrap (gomoku-zōgan), and polished. Height: 75.3 mm; Width 74.9 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. Weight 130.2 g. Edo, 18th century. Gary D. Murtha dedicates 10 pages to this type of tsuba: "...they were made by soldering brass overlay scraps to the iron plate". Actual gomoku-zōgan tsuba are seldom found in collections most likely because they have little if any artistic attributes. In addition, many have rough surfaces making them questionable for use on a sword. It is said that many of these were produced in Yokohama for export to the West during the late Edo period". G. D. Murtha then describes the technique of making gomoku-zōgan in every detail, and states that "The brass pieces are said to represent 'fallen pine needles', a description most likely created to add aesthetic value to help market the tsuba" [see:Gary D. Murtha. Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro. GDM Publications, 2016; pp. 160-161]. -
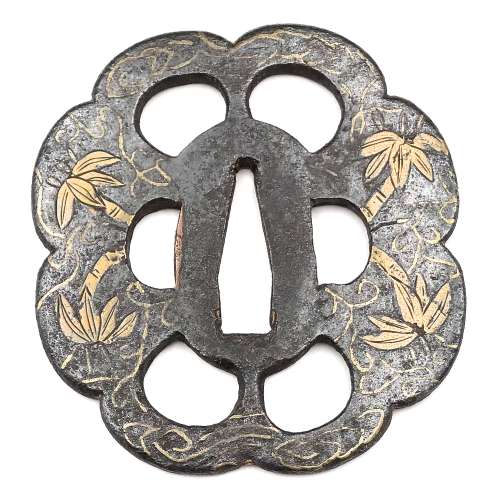 Iron tsuba of 8-lobed form pierced with six openings (sukashi) and decorated with design of bamboo and arabesque in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan). Two of the openings serve as hitsu-ana. The design on the face represents bamboo trunks and leaves, clouds, waves, and vines; on the back - vines and leaves, that forms an arabesque (karakusa) motif. Rounded square rim. 'Silver' patina. Hitsu-ana with copper sekigane. Heianjō (most probable) or Kaga-Yoshirō school. Late Muromachi or Momoyama period; 16th century. Size: Height: 74.6 mm; Width: 69.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.2 mm. Weight: 113.9 g. Provenance: Gary D. Murtha. This tsuba is illustrated at: Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro by Gary D. Murtha [GDM Publications, 2016, p. 48]: "Iron, 80x75x3 mm tsuba with brass karakusa vines and leaves on one side with bamboo, leaves, and clouds on the reverse. This tsuba is one of those pieces that might be classified as Onin or Heianjo work, but the flush inlay tips it to the Heianjo side. Late Muromachi period." I would like to add that it easily may also be classified as Kaga-Yoshirō. Robert Haynes in Study Collection.., page 32, illustrates a look-a-like example, and writes: "This style of inlay, where the designs on the face and the back are very different, was common to the work of artists in Kyoto in the Momoyama period."
Iron tsuba of 8-lobed form pierced with six openings (sukashi) and decorated with design of bamboo and arabesque in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan). Two of the openings serve as hitsu-ana. The design on the face represents bamboo trunks and leaves, clouds, waves, and vines; on the back - vines and leaves, that forms an arabesque (karakusa) motif. Rounded square rim. 'Silver' patina. Hitsu-ana with copper sekigane. Heianjō (most probable) or Kaga-Yoshirō school. Late Muromachi or Momoyama period; 16th century. Size: Height: 74.6 mm; Width: 69.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.2 mm. Weight: 113.9 g. Provenance: Gary D. Murtha. This tsuba is illustrated at: Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro by Gary D. Murtha [GDM Publications, 2016, p. 48]: "Iron, 80x75x3 mm tsuba with brass karakusa vines and leaves on one side with bamboo, leaves, and clouds on the reverse. This tsuba is one of those pieces that might be classified as Onin or Heianjo work, but the flush inlay tips it to the Heianjo side. Late Muromachi period." I would like to add that it easily may also be classified as Kaga-Yoshirō. Robert Haynes in Study Collection.., page 32, illustrates a look-a-like example, and writes: "This style of inlay, where the designs on the face and the back are very different, was common to the work of artists in Kyoto in the Momoyama period." -
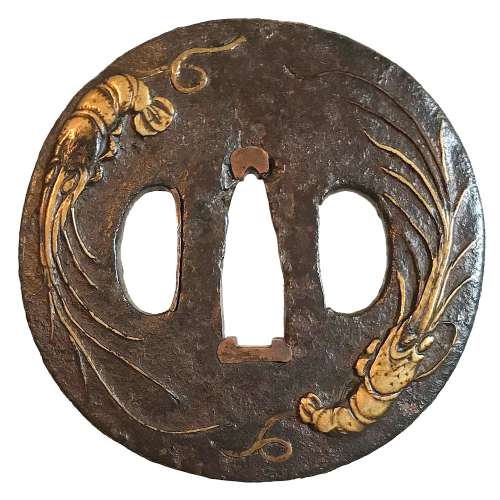 Iron tsuba of round form with two ebi (lobster) on omote (obverse side) and shika (deer) among scattered momiji (maple leaves) on ura (reverse side) motif in brass takabori (high relief) suemon-zōgan. Traces of lacquer. Unsigned. Late Muromachi / Momoyama period (late 16th / Early 17th century). Dimensions: 69.0.6 mm (H) x 69.6 mm (W) x 3.4 mm (T, seppa-dai). Weight: 92.6 g. Illustrated at: The Lundgren Collection of Japanese Swords, Sword Fittings and A Group of Miochin School Metalwork. Christie's Auction: Tuesday, 18 November 1997, London. Sales "GOTO-5881". Christie's, 1997. - #2 at page 7. Provenance: The second John Harding; The Lundgren Collection. Description at Christie's: "The iron plate depicting two lobsters in takabory and brass takazogan, the reverse similarly decorated with deer among scattered maple leaves, square mimi, late Muromachi / early Momoyama period (late 16th/early 17th century) Diameter 68 mm, mimi thickness 4 mm. Provenance: The second John Harding." Also at: JAPANESE SWORD-FITTINGS & METALWORK IN THE LUNDGREN COLLECTION. Published by Otsuka Kogeisha, Tokyo 1992. № 134. Description on page 173: Sword guard with design of shrimps in inlay (scarlet [sic] maple leaves and deer on the reverse side). Unsigned. Heianjō inlay school. Vertical 6.85 cm, horizontal 6.90 cm, Th. of rim 0.40 cm. Iron. Taka-bori relief and brass inlay. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. According to Merrily Baird, maple leaves, especially if paired with the deer, allude to autumnal tradition of Japanese aristocracy of viewing the seasonal changes of color in the Nara area. The lobster is typical Japanese ebi, - it lacks prominent claws, and has a spiny shell. As a symbol of longevity and good fortune, lobster is a staple of New Year's decoration.
Iron tsuba of round form with two ebi (lobster) on omote (obverse side) and shika (deer) among scattered momiji (maple leaves) on ura (reverse side) motif in brass takabori (high relief) suemon-zōgan. Traces of lacquer. Unsigned. Late Muromachi / Momoyama period (late 16th / Early 17th century). Dimensions: 69.0.6 mm (H) x 69.6 mm (W) x 3.4 mm (T, seppa-dai). Weight: 92.6 g. Illustrated at: The Lundgren Collection of Japanese Swords, Sword Fittings and A Group of Miochin School Metalwork. Christie's Auction: Tuesday, 18 November 1997, London. Sales "GOTO-5881". Christie's, 1997. - #2 at page 7. Provenance: The second John Harding; The Lundgren Collection. Description at Christie's: "The iron plate depicting two lobsters in takabory and brass takazogan, the reverse similarly decorated with deer among scattered maple leaves, square mimi, late Muromachi / early Momoyama period (late 16th/early 17th century) Diameter 68 mm, mimi thickness 4 mm. Provenance: The second John Harding." Also at: JAPANESE SWORD-FITTINGS & METALWORK IN THE LUNDGREN COLLECTION. Published by Otsuka Kogeisha, Tokyo 1992. № 134. Description on page 173: Sword guard with design of shrimps in inlay (scarlet [sic] maple leaves and deer on the reverse side). Unsigned. Heianjō inlay school. Vertical 6.85 cm, horizontal 6.90 cm, Th. of rim 0.40 cm. Iron. Taka-bori relief and brass inlay. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. According to Merrily Baird, maple leaves, especially if paired with the deer, allude to autumnal tradition of Japanese aristocracy of viewing the seasonal changes of color in the Nara area. The lobster is typical Japanese ebi, - it lacks prominent claws, and has a spiny shell. As a symbol of longevity and good fortune, lobster is a staple of New Year's decoration. -
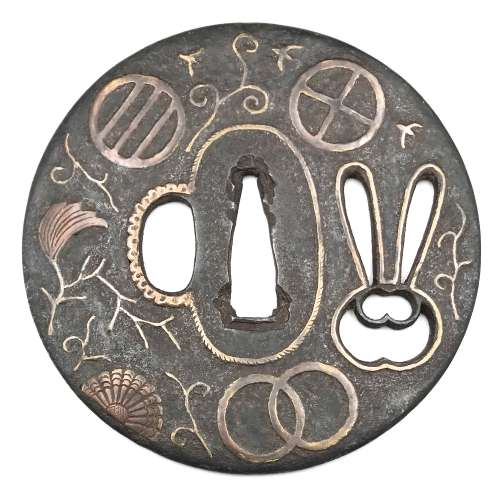 Iron tsuba of round form with design of rabbit (usagi) in openwork (sukashi) and inlaid with designs of plants and family crests (mon) in suemon-zōgan. A branch with lonely leaf, half chrysanthemum, and flying wild geese on the face represent autumnal connotations. The same motif is complemented by a clove (choji) on the reverse. The family crests (mon) include: interlocked rings (kanawa; wachigai), three encircled lines or stripes (hikiryo), bit or muzzle (kutsuwa - horse's harness element with possible christian symbolism), and encircled triangle (uroko, fish scale). Brass wire trim around the openwork elements and the seppa-dai, scalloped wire inlay around the hitsu-ana. Iron is dark, almost black. Brass or copper elements vary in shades of lighter and darker yellow with red-ish hue. Ōnin school. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Height: 89.6 mm; Width: 89.3 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.0 mm. Weight: 129.7 g.
Iron tsuba of round form with design of rabbit (usagi) in openwork (sukashi) and inlaid with designs of plants and family crests (mon) in suemon-zōgan. A branch with lonely leaf, half chrysanthemum, and flying wild geese on the face represent autumnal connotations. The same motif is complemented by a clove (choji) on the reverse. The family crests (mon) include: interlocked rings (kanawa; wachigai), three encircled lines or stripes (hikiryo), bit or muzzle (kutsuwa - horse's harness element with possible christian symbolism), and encircled triangle (uroko, fish scale). Brass wire trim around the openwork elements and the seppa-dai, scalloped wire inlay around the hitsu-ana. Iron is dark, almost black. Brass or copper elements vary in shades of lighter and darker yellow with red-ish hue. Ōnin school. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Height: 89.6 mm; Width: 89.3 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.0 mm. Weight: 129.7 g. -
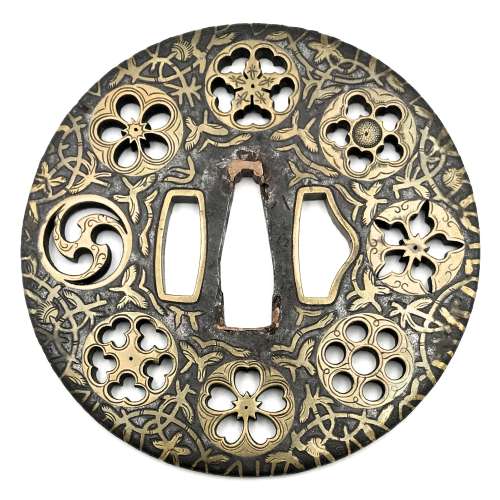 Well-forged iron plate of round shape (maru-gata) is decorated with water weeds or arabesque (karakusa) in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) all over and eight family crests (mon) of round form in cast brass with delicate linear carving (kebori) and openwork (sukashi). Crests represent: [at 9 hours] three counter-clockwise commas or swirls (tomoe); [at 10:30] plum blossom (ume); [at 12:00, 1:130, and 7:30] - stylized flower made by cutting out five suhama symblos (flower-shaped suhama); [at 3:00] bellflower (kikyō); [at 4:30] seven-star crest (shichiyō-mon); [at 6:00] cherry blossom (sakura). Brass-trimmed ryo-hitsu. Copper sekigane. Yoshirō school. Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Inscription on seppa-dai: 八幡 - Hachiman. Size: height 89.6 mm, width 89.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,0 mm. Weight 129.7 g. NBTHK certificate № 4007685, June 27, 2015: HOZON (Worthy of Preservation). As for the inscription, Nihonto Message Board blog discussion provides the following explanation of the inscription: "An expression of conviction as to being the best under the sun". On the other hand, there may be more in this confluence of symbols: the tomoe crest at 9:00 is "the kamon of Hachiman, the war god" [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007, p. 108]. The character 八 in the inscription cut stronger than the other kanji, and may be by a different hand in different time. 八 (hachi, eight): "The numeral eight was appreciated because its shape broadens toward the bottom, symbolizing eternal expansion" [ibid, p. 119]. It may be said that this tsuba is dedicated to Hachiman. Other crests (suhama, bellflower, seven-stars, plum and cherry blossoms) collectively allude to "good old times" when Fijiwara and Taira clans were in full bloom. Markus Sesko believes that the inscriptions reads: Hachiman: "the inscription is/was HACHIMAN (八幡), the God of War and a relatively popular inscription for tsuba, swords and armor." Elliott Long and Robert Haynes provide the following explanation of the inscription: "...hachi is correct and represents the name of the HACHI SHRINE. The inscription reads 'YAWATA' which is the name of the mountain in Mino Province where the HACHI Shrine is located". Details on Hachiman Shrine in Yawata (八幡市) can be found elsewhere, including Historical and geographical dictionary of Japan by Edmond Papinot. Van Ham auction house provides the following description: MON-SUKASHI TSUBA. MARUGATA. Japan. Momoyama period. Yoshiro school. Iron with inlays of brass. In hira-zogan technique with kebori engraving eight different family emblems (mon). An old inscription is dedicated to the deity Hachiman. D.4.5mm, Ø 8.3cm. Condition A/B. Supplement: Wooden box and NBTHK certificate.
Well-forged iron plate of round shape (maru-gata) is decorated with water weeds or arabesque (karakusa) in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) all over and eight family crests (mon) of round form in cast brass with delicate linear carving (kebori) and openwork (sukashi). Crests represent: [at 9 hours] three counter-clockwise commas or swirls (tomoe); [at 10:30] plum blossom (ume); [at 12:00, 1:130, and 7:30] - stylized flower made by cutting out five suhama symblos (flower-shaped suhama); [at 3:00] bellflower (kikyō); [at 4:30] seven-star crest (shichiyō-mon); [at 6:00] cherry blossom (sakura). Brass-trimmed ryo-hitsu. Copper sekigane. Yoshirō school. Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Inscription on seppa-dai: 八幡 - Hachiman. Size: height 89.6 mm, width 89.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,0 mm. Weight 129.7 g. NBTHK certificate № 4007685, June 27, 2015: HOZON (Worthy of Preservation). As for the inscription, Nihonto Message Board blog discussion provides the following explanation of the inscription: "An expression of conviction as to being the best under the sun". On the other hand, there may be more in this confluence of symbols: the tomoe crest at 9:00 is "the kamon of Hachiman, the war god" [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007, p. 108]. The character 八 in the inscription cut stronger than the other kanji, and may be by a different hand in different time. 八 (hachi, eight): "The numeral eight was appreciated because its shape broadens toward the bottom, symbolizing eternal expansion" [ibid, p. 119]. It may be said that this tsuba is dedicated to Hachiman. Other crests (suhama, bellflower, seven-stars, plum and cherry blossoms) collectively allude to "good old times" when Fijiwara and Taira clans were in full bloom. Markus Sesko believes that the inscriptions reads: Hachiman: "the inscription is/was HACHIMAN (八幡), the God of War and a relatively popular inscription for tsuba, swords and armor." Elliott Long and Robert Haynes provide the following explanation of the inscription: "...hachi is correct and represents the name of the HACHI SHRINE. The inscription reads 'YAWATA' which is the name of the mountain in Mino Province where the HACHI Shrine is located". Details on Hachiman Shrine in Yawata (八幡市) can be found elsewhere, including Historical and geographical dictionary of Japan by Edmond Papinot. Van Ham auction house provides the following description: MON-SUKASHI TSUBA. MARUGATA. Japan. Momoyama period. Yoshiro school. Iron with inlays of brass. In hira-zogan technique with kebori engraving eight different family emblems (mon). An old inscription is dedicated to the deity Hachiman. D.4.5mm, Ø 8.3cm. Condition A/B. Supplement: Wooden box and NBTHK certificate. -
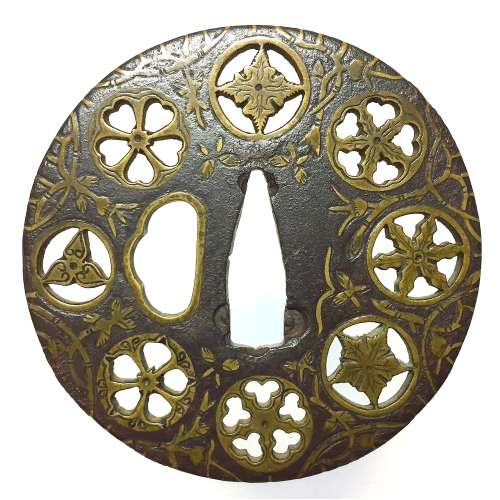 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm -
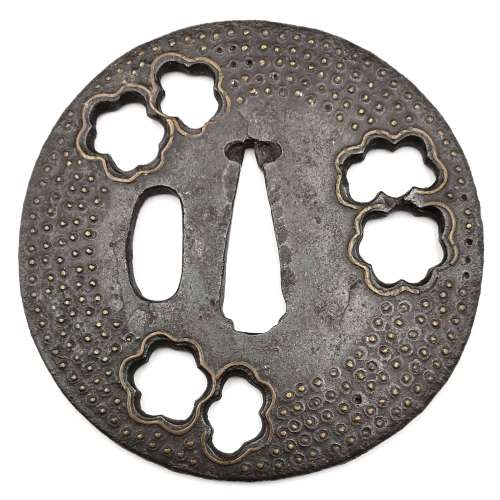 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form decorated with three pairs of snowflake-form small perforations (ko-sukashi), each outlined with brass wire; five concentric circular rows of dots inlaid in brass or copper ten-zōgan (some dots are missing). Hitsu-ana of oval form. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Late Muromachi period. Dimensions: 75.6 mm x74.6 mm x 3.0 mm. Weight: 78.0 g. Old NBTHK certificate (green paper): Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work". Unlike most Ōnin ten-zōgan tsuba this one does not have circular brass wire inlay inside the dots area; neither it has brass trim around seppa-dai or hitsu-ana.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form decorated with three pairs of snowflake-form small perforations (ko-sukashi), each outlined with brass wire; five concentric circular rows of dots inlaid in brass or copper ten-zōgan (some dots are missing). Hitsu-ana of oval form. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Late Muromachi period. Dimensions: 75.6 mm x74.6 mm x 3.0 mm. Weight: 78.0 g. Old NBTHK certificate (green paper): Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work". Unlike most Ōnin ten-zōgan tsuba this one does not have circular brass wire inlay inside the dots area; neither it has brass trim around seppa-dai or hitsu-ana. -
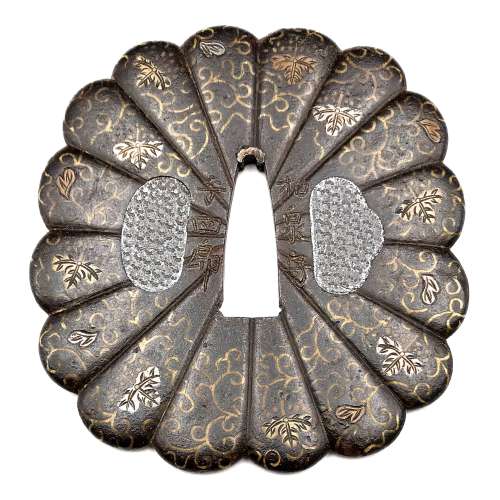 The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:
The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:"Early signed example of the work of Koike Naomasa. The kiku shape iron plate is well finished. The flush inlay is brass, for the scroll work on both sides, with the leaves and kiri mon in brass, copper and silver with strong detail carving. Some of the inlay goes almost over the edge, which is goishi gata. The large hitsuana are plugged in lead with starburst kokuin surface design. [...]The face is signed in deep bold kanji: Koike Naomasa; the back is signed: Izumi no Kami, on the right and Yoshiro on the left. There are one or two small pieces of inlay missing. Sold by Sotheby London, Oct. 27, 1981, lot 368. Height = 86 mm, thickness (seppa-dai) = 3.75 mm, (edge) = 4 mm."
Another similar example presented at: "Tsuba" by Günter Heckmann, 1995, №T55 — "Designation: Koike Naomasa. Mid Edo, end of the 17th century. Iron, hira-zogan in brass, copper, silver and shakudo, katakiri-bori. Tendrils and leaves. 87.0 x 78.0 x 4.0 mm." Reference: Japanische Schwertzierate by Lumir Jisl, 1967, page. 13. [SV: Actually, his tsuba is signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back; and Koike Naomasa on the front, exactly as Robert Haynes's tsuba. Dating this tsuba Mid-Edo, 17th century may be considered a misattribution]. More details regarding the Yoshirō tsuba. -
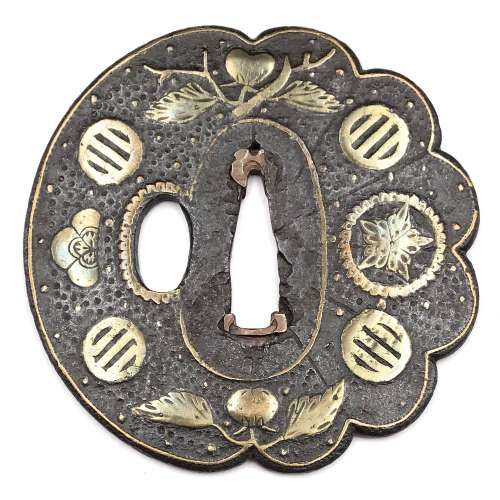 Iron tsuba of half round and half lobed (chrysanthemoid) form decorated with plants and family crests (mon) in cast brass inlay (suemon-zōgan), and scattered brass dots inlay (ten-zōgan); brass wire inlay outlining the rim, seppa-dai, and hitsu-ana (scalloped wire) on both sides. Surface treated with hummer punch marks. The chrysanthemoid half of the plate chiseled with thin shallow grooves, outlining the petals. Copper sekigane. On the face the inlay represents: mandarin orange (tachibana), half karahana, encircled bellflower, and four encircled three-stipe family crest (mitsubiki-mon of Sakuma and Abe clans, and some others). On the reverse the design is similar but two of the mitsubiki-mon symbols replaced with two comb-shaped Genji-mon ideographs. Ōnin school. The end of mid-Muromachi period, beginning of the 16th century. Size: 74.3 x 72.7 x 2.4 mm.
Iron tsuba of half round and half lobed (chrysanthemoid) form decorated with plants and family crests (mon) in cast brass inlay (suemon-zōgan), and scattered brass dots inlay (ten-zōgan); brass wire inlay outlining the rim, seppa-dai, and hitsu-ana (scalloped wire) on both sides. Surface treated with hummer punch marks. The chrysanthemoid half of the plate chiseled with thin shallow grooves, outlining the petals. Copper sekigane. On the face the inlay represents: mandarin orange (tachibana), half karahana, encircled bellflower, and four encircled three-stipe family crest (mitsubiki-mon of Sakuma and Abe clans, and some others). On the reverse the design is similar but two of the mitsubiki-mon symbols replaced with two comb-shaped Genji-mon ideographs. Ōnin school. The end of mid-Muromachi period, beginning of the 16th century. Size: 74.3 x 72.7 x 2.4 mm. -
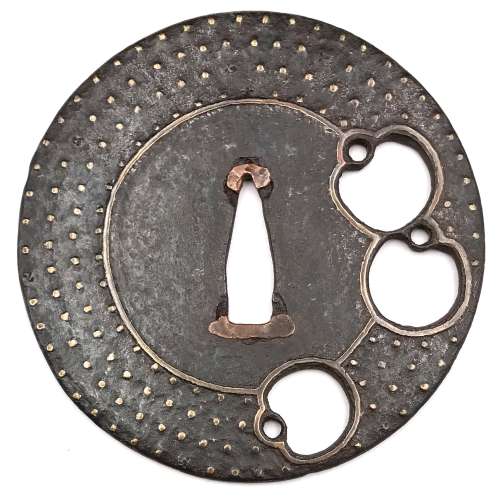 A circular iron tsuba with a design of three monkey toys (kukurizaru) in small openwork (ko-sukashi); the plate further decorated with four rows of brass dot inlay (ten-zogan). The center of the plate and the openings are outlined with brass wire. Copper sekigane. A few dots missing. Muromachi period. Dimensions: 89.0 x 88.2 x 2.9 mm. Kukurizaru was an often used motif on old tsuba. The symbol has two explanations: (1) "upright" monkey, a sort of roly-poly toy, alludes to 'never-ever give up' property of the samurai; (2) monkeys are represented with their hands and feet tied to their back to symbolize self-control. Other examples of the same design:
A circular iron tsuba with a design of three monkey toys (kukurizaru) in small openwork (ko-sukashi); the plate further decorated with four rows of brass dot inlay (ten-zogan). The center of the plate and the openings are outlined with brass wire. Copper sekigane. A few dots missing. Muromachi period. Dimensions: 89.0 x 88.2 x 2.9 mm. Kukurizaru was an often used motif on old tsuba. The symbol has two explanations: (1) "upright" monkey, a sort of roly-poly toy, alludes to 'never-ever give up' property of the samurai; (2) monkeys are represented with their hands and feet tied to their back to symbolize self-control. Other examples of the same design:
The Henry D. Rosin Collection №9.

Lundgren Collection №7.


