-
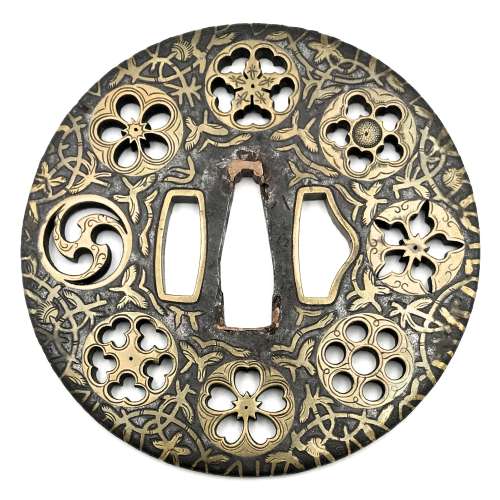 Well-forged iron plate of round shape (maru-gata) is decorated with water weeds or arabesque (karakusa) in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) all over and eight family crests (mon) of round form in cast brass with delicate linear carving (kebori) and openwork (sukashi). Crests represent: [at 9 hours] three counter-clockwise commas or swirls (tomoe); [at 10:30] plum blossom (ume); [at 12:00, 1:130, and 7:30] - stylized flower made by cutting out five suhama symblos (flower-shaped suhama); [at 3:00] bellflower (kikyō); [at 4:30] seven-star crest (shichiyō-mon); [at 6:00] cherry blossom (sakura). Brass-trimmed ryo-hitsu. Copper sekigane. Yoshirō school. Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Inscription on seppa-dai: 八幡 - Hachiman. Size: height 89.6 mm, width 89.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,0 mm. Weight 129.7 g. NBTHK certificate № 4007685, June 27, 2015: HOZON (Worthy of Preservation). As for the inscription, Nihonto Message Board blog discussion provides the following explanation of the inscription: "An expression of conviction as to being the best under the sun". On the other hand, there may be more in this confluence of symbols: the tomoe crest at 9:00 is "the kamon of Hachiman, the war god" [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007, p. 108]. The character 八 in the inscription cut stronger than the other kanji, and may be by a different hand in different time. 八 (hachi, eight): "The numeral eight was appreciated because its shape broadens toward the bottom, symbolizing eternal expansion" [ibid, p. 119]. It may be said that this tsuba is dedicated to Hachiman. Other crests (suhama, bellflower, seven-stars, plum and cherry blossoms) collectively allude to "good old times" when Fijiwara and Taira clans were in full bloom. Markus Sesko believes that the inscriptions reads: Hachiman: "the inscription is/was HACHIMAN (八幡), the God of War and a relatively popular inscription for tsuba, swords and armor." Elliott Long and Robert Haynes provide the following explanation of the inscription: "...hachi is correct and represents the name of the HACHI SHRINE. The inscription reads 'YAWATA' which is the name of the mountain in Mino Province where the HACHI Shrine is located". Details on Hachiman Shrine in Yawata (八幡市) can be found elsewhere, including Historical and geographical dictionary of Japan by Edmond Papinot. Van Ham auction house provides the following description: MON-SUKASHI TSUBA. MARUGATA. Japan. Momoyama period. Yoshiro school. Iron with inlays of brass. In hira-zogan technique with kebori engraving eight different family emblems (mon). An old inscription is dedicated to the deity Hachiman. D.4.5mm, Ø 8.3cm. Condition A/B. Supplement: Wooden box and NBTHK certificate.
Well-forged iron plate of round shape (maru-gata) is decorated with water weeds or arabesque (karakusa) in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) all over and eight family crests (mon) of round form in cast brass with delicate linear carving (kebori) and openwork (sukashi). Crests represent: [at 9 hours] three counter-clockwise commas or swirls (tomoe); [at 10:30] plum blossom (ume); [at 12:00, 1:130, and 7:30] - stylized flower made by cutting out five suhama symblos (flower-shaped suhama); [at 3:00] bellflower (kikyō); [at 4:30] seven-star crest (shichiyō-mon); [at 6:00] cherry blossom (sakura). Brass-trimmed ryo-hitsu. Copper sekigane. Yoshirō school. Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Inscription on seppa-dai: 八幡 - Hachiman. Size: height 89.6 mm, width 89.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,0 mm. Weight 129.7 g. NBTHK certificate № 4007685, June 27, 2015: HOZON (Worthy of Preservation). As for the inscription, Nihonto Message Board blog discussion provides the following explanation of the inscription: "An expression of conviction as to being the best under the sun". On the other hand, there may be more in this confluence of symbols: the tomoe crest at 9:00 is "the kamon of Hachiman, the war god" [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007, p. 108]. The character 八 in the inscription cut stronger than the other kanji, and may be by a different hand in different time. 八 (hachi, eight): "The numeral eight was appreciated because its shape broadens toward the bottom, symbolizing eternal expansion" [ibid, p. 119]. It may be said that this tsuba is dedicated to Hachiman. Other crests (suhama, bellflower, seven-stars, plum and cherry blossoms) collectively allude to "good old times" when Fijiwara and Taira clans were in full bloom. Markus Sesko believes that the inscriptions reads: Hachiman: "the inscription is/was HACHIMAN (八幡), the God of War and a relatively popular inscription for tsuba, swords and armor." Elliott Long and Robert Haynes provide the following explanation of the inscription: "...hachi is correct and represents the name of the HACHI SHRINE. The inscription reads 'YAWATA' which is the name of the mountain in Mino Province where the HACHI Shrine is located". Details on Hachiman Shrine in Yawata (八幡市) can be found elsewhere, including Historical and geographical dictionary of Japan by Edmond Papinot. Van Ham auction house provides the following description: MON-SUKASHI TSUBA. MARUGATA. Japan. Momoyama period. Yoshiro school. Iron with inlays of brass. In hira-zogan technique with kebori engraving eight different family emblems (mon). An old inscription is dedicated to the deity Hachiman. D.4.5mm, Ø 8.3cm. Condition A/B. Supplement: Wooden box and NBTHK certificate. -
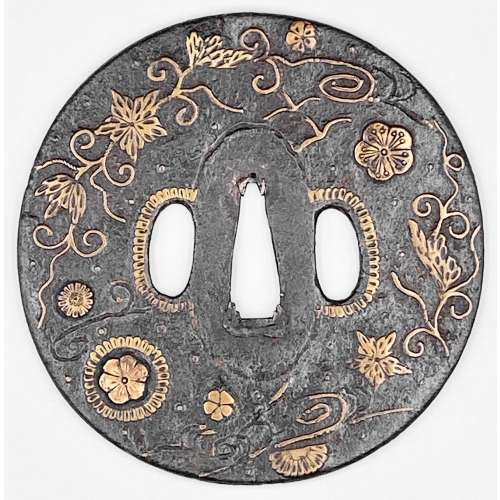 Iron tsuba of round form adorned with the design of stars, wild geese, floating blossoms, leaves and tendrils realized in brass inlay. The inlay technique includes suemon-zōgan and ten-zōgan. Two smaller openings (hitsu-ana) surrounded by a scalloped brass border. The seppa-dai border inlay is missing, as well as a few other fragments of inlay on both sides. Sword cut at 12 o'clock on the reverse. A tsuba with a strong autumnal connotation, which once belonged to a great battle weapon. One of only three known jūyō Ōnin tsuba. Translation of the paper, issued by the Japanese sword fittings (tosogu) examination board: Designated as jūyō-tosogu at the 34th jūyō-shinsa held on April 14th 1988 Kaki-karimon zōgan-tsuba (花卉雁文象嵌鐔) — Tsuba with zōgan design of flowers and wild geese. Mumei: Onin (応仁) Tokyo. Nakasono Tokumi (中園とくみ) Measurements: height 9.5 cm, width 9.4 cm, thickness at rim 0.35 cm Interpretation: marugata, iron, brass zōgan, two hitsu-ana Time: end of Muromachi Explanation: Ōnin-tsuba are thin iron ita-tsuba which show a brass zōgan ornamentation. All of them are mumei and there is the theory that they were made in the Onin era (1467-1469) although today more and more the theory is accepted that they are in general late Muromachi period works. There are two kinds of brass zōgan interpretations: One depicts irregularly arranged tachibana branches, wild geese, chrysanthemums, flowers, or karakusa for example, and the other one shows punctual zōgan elements, which are referred to as hoshi-zōgan or ro-zōgan, and concentrical zōgan elements between the nakago-ana and the rim. The latter interpretations might also be accompanied by simple ko-sukashi in the form of butterflies, clouds, hats, or stylized mountains. This tsuba is a typical work from the former category. It is large and feels massive and the powerful and impressive zōgan and the excellent iron make it a highly tasteful piece. Back side: Issued to: Nakasono Tokumi Address: Tokyo-to, Suginami-ku, Kamitakaido 2-17-26 Date of issue: May 30th 1989
Iron tsuba of round form adorned with the design of stars, wild geese, floating blossoms, leaves and tendrils realized in brass inlay. The inlay technique includes suemon-zōgan and ten-zōgan. Two smaller openings (hitsu-ana) surrounded by a scalloped brass border. The seppa-dai border inlay is missing, as well as a few other fragments of inlay on both sides. Sword cut at 12 o'clock on the reverse. A tsuba with a strong autumnal connotation, which once belonged to a great battle weapon. One of only three known jūyō Ōnin tsuba. Translation of the paper, issued by the Japanese sword fittings (tosogu) examination board: Designated as jūyō-tosogu at the 34th jūyō-shinsa held on April 14th 1988 Kaki-karimon zōgan-tsuba (花卉雁文象嵌鐔) — Tsuba with zōgan design of flowers and wild geese. Mumei: Onin (応仁) Tokyo. Nakasono Tokumi (中園とくみ) Measurements: height 9.5 cm, width 9.4 cm, thickness at rim 0.35 cm Interpretation: marugata, iron, brass zōgan, two hitsu-ana Time: end of Muromachi Explanation: Ōnin-tsuba are thin iron ita-tsuba which show a brass zōgan ornamentation. All of them are mumei and there is the theory that they were made in the Onin era (1467-1469) although today more and more the theory is accepted that they are in general late Muromachi period works. There are two kinds of brass zōgan interpretations: One depicts irregularly arranged tachibana branches, wild geese, chrysanthemums, flowers, or karakusa for example, and the other one shows punctual zōgan elements, which are referred to as hoshi-zōgan or ro-zōgan, and concentrical zōgan elements between the nakago-ana and the rim. The latter interpretations might also be accompanied by simple ko-sukashi in the form of butterflies, clouds, hats, or stylized mountains. This tsuba is a typical work from the former category. It is large and feels massive and the powerful and impressive zōgan and the excellent iron make it a highly tasteful piece. Back side: Issued to: Nakasono Tokumi Address: Tokyo-to, Suginami-ku, Kamitakaido 2-17-26 Date of issue: May 30th 1989 -
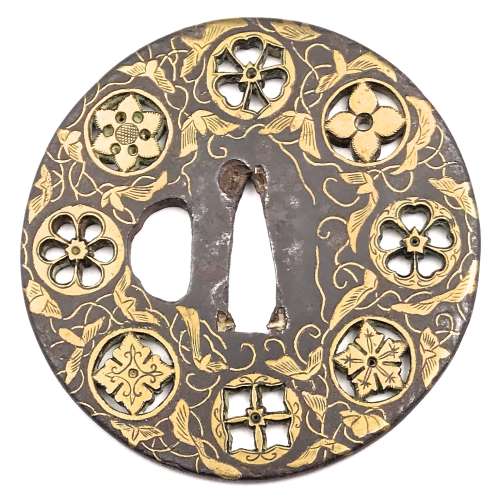 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, as well as with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines, leaves, and flowers all over the plate. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, 17th century. Size: diameter 80 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,6 mm. Symbols: [12:00 o'clock] - Wood sorrel (katabami) and swords ; [9:00] - Cherry blossom (sakura); [7:30] - Bellflower (kikyō), kamon of Toki clan; [3:00] - possibly, a six-petal Chrysanthemum (kiku) or a Passion flower (tessen); [1:30] - Hemp (asanoha). The symbols at 6:00, 10:30, and 4:30 o'clock seem to be geometrical patterns of auspicious meaning: a cross in a square, a four pointing star, and a diamond, respectively. Alternatively, we may look at this piece as purely decorative, with patterns at 12:00, 3:00, 6:00, and 9:00 o'clock in negative openwork (in-sukashi), and at 1:30, 4:40, 7:20, and 10:30 o'clock - in positive openwork (ji-sukashi, or yō-sukashi). Markus Sesko in his Handbook of sword fittings related terms [Herstellung und Verlag: Books on Demand GmbH, Norderstedt, 2011] discriminates this type of openwork in a separate class: Ranma-sukashi: "This term is applied to circular sukashi with family crests to their inside, which are arranged running along the rim area. The description goes back to the opened boards (ranma) between the sliding doors and the ceiling of Japanese rooms. Ranma-sukashi are mostly seen on old Heianjō- or Yoshirō-zōgan-tsuba but also on works of Hayashi Matashichi" [page 30].
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, as well as with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines, leaves, and flowers all over the plate. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, 17th century. Size: diameter 80 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,6 mm. Symbols: [12:00 o'clock] - Wood sorrel (katabami) and swords ; [9:00] - Cherry blossom (sakura); [7:30] - Bellflower (kikyō), kamon of Toki clan; [3:00] - possibly, a six-petal Chrysanthemum (kiku) or a Passion flower (tessen); [1:30] - Hemp (asanoha). The symbols at 6:00, 10:30, and 4:30 o'clock seem to be geometrical patterns of auspicious meaning: a cross in a square, a four pointing star, and a diamond, respectively. Alternatively, we may look at this piece as purely decorative, with patterns at 12:00, 3:00, 6:00, and 9:00 o'clock in negative openwork (in-sukashi), and at 1:30, 4:40, 7:20, and 10:30 o'clock - in positive openwork (ji-sukashi, or yō-sukashi). Markus Sesko in his Handbook of sword fittings related terms [Herstellung und Verlag: Books on Demand GmbH, Norderstedt, 2011] discriminates this type of openwork in a separate class: Ranma-sukashi: "This term is applied to circular sukashi with family crests to their inside, which are arranged running along the rim area. The description goes back to the opened boards (ranma) between the sliding doors and the ceiling of Japanese rooms. Ranma-sukashi are mostly seen on old Heianjō- or Yoshirō-zōgan-tsuba but also on works of Hayashi Matashichi" [page 30]. -
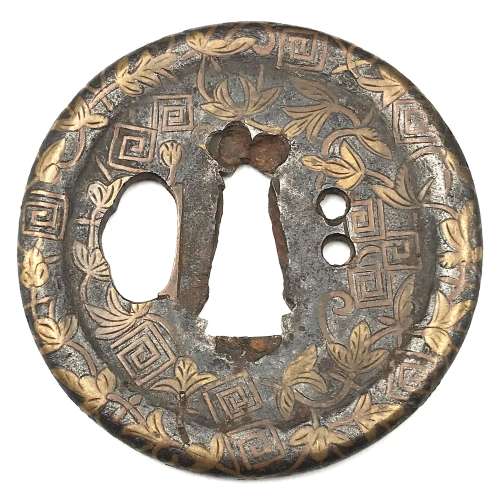

Iron tsuba of round form with dam-shaped rim (dote-mimi) pierced with hitsu-ana and two udenuki-ana (probably cut later on) decorated in flat inlay (hira-zōgan) with vines and symbols of thunder or lightning (possibly - family crest, mon). Hitsu-ana and nakago-ana with copper sekigane.
Ōnin or Heianjō school, or, possibly Kaga or Umetada school. Momoyama period or earlier (Muromachi), 16th century. Unsigned.Size: 64.5 x 63.8 x 2.2 (center), 4.2 (rim) mm.
Provenance: Lundgren Collection: [Japanese sword-fittings and metalwork in the Lundgren Collection. Published by Otsuka Kogeisha Co., Ltd., Tokyo 1992], №31; The Lundgren Collection of Japanese Swords, Sword Fittings and A Group of Miochin School Metalwork. Christie's Auction: Tuesday, 18 November 1997, London. Sales "GOTO-5881". Christie's, 1997, №2. Lundgren's description at Christie's: Heianjo tsuba. Unsigned. The circular plate decorated in brass hirazogan with flowers, plants and symbols of thunder, dote mimi and udenuki ana, late Muromachi period (16th century). Tokyo 1992 description: Sword guard with design of flowering plants and frets in inlay. Unsigned. Heianjo inlay school. 6.35 x 6.3 cm, thickness of rim 0.40 cm. Iron. Flat brass inlay. Muromachi-Momoyama Period, 16th century. Provenance: The Second John Harding. A somewhat look-a-like pieces can be found in various catalogues. The one in Naunton Collection, №172, is signed: Umetada of Yamashiro: "Iron, small, almost circular, with raised oval rim, inlaid all over with leaves and scrolls in brass hirazōgan." -
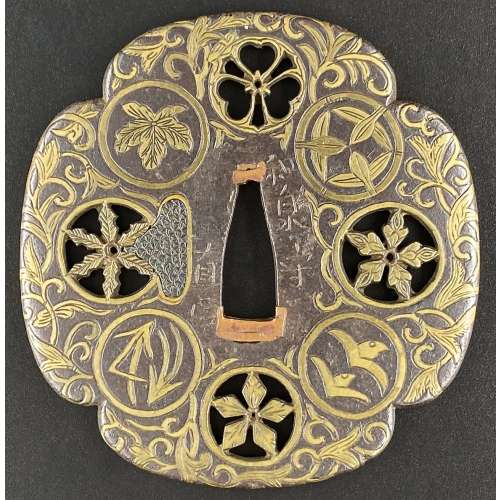 The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba.
The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba. -
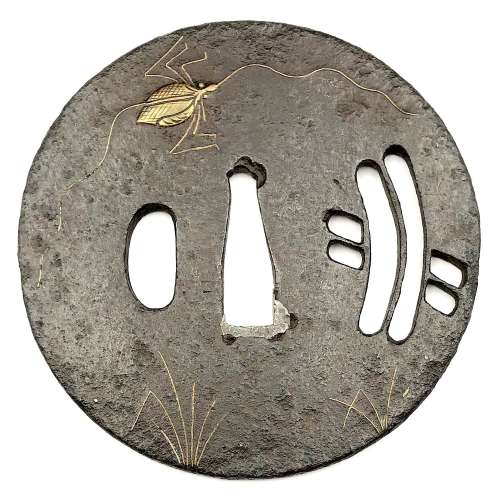 Iron tsuba with design of a cricket and grass inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) and a bridge over a stream in openwork (sukashi) on both sides. Inlay of distant part of the cricket's antenna is missing. Heianjō School. Momoyama period. Diameter: 79.5 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.3 mm NBTHK # 4002100.
Iron tsuba with design of a cricket and grass inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) and a bridge over a stream in openwork (sukashi) on both sides. Inlay of distant part of the cricket's antenna is missing. Heianjō School. Momoyama period. Diameter: 79.5 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.3 mm NBTHK # 4002100. -
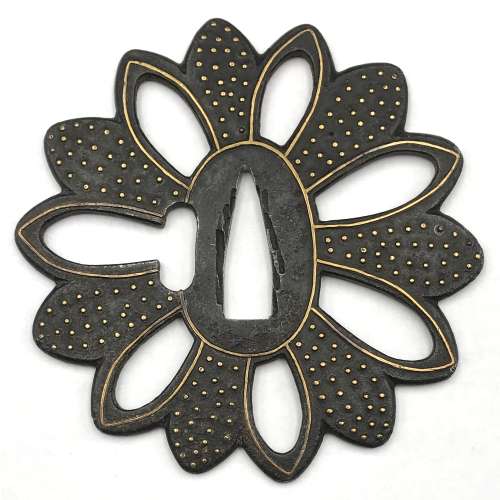 Iron tsuba of 14-petal chrysanthemoid form (kikka-gata) with alternating solid and openwork petals, the latter outlined with brass wire (sen-zōgan) and the former decorated with brass dots (ten-zōgan), on both sides. Seppa-dai is outlined with brass wire. Small hitsu-ana probably cut later. Late Muromachi period (Ca. 1514-1573). Ōnin school. Unsigned. Dimensions: 87.0 x 87.8 x 3.2 mm. Similar tsuba in this collection: TSU-0420.2022
Iron tsuba of 14-petal chrysanthemoid form (kikka-gata) with alternating solid and openwork petals, the latter outlined with brass wire (sen-zōgan) and the former decorated with brass dots (ten-zōgan), on both sides. Seppa-dai is outlined with brass wire. Small hitsu-ana probably cut later. Late Muromachi period (Ca. 1514-1573). Ōnin school. Unsigned. Dimensions: 87.0 x 87.8 x 3.2 mm. Similar tsuba in this collection: TSU-0420.2022 Other similar specimens can be found at:
Henri L. Joly and Kumasaku Tomita, Japanese art and handicraft, "Swords and sword fittings" section, sub-section “Inlays of Ōnin, Kyoto, Fushimi-Yoshiro, and Kaga Province”, Plate CX, #128: Iron, chrysanthemoid, thin guard with alternate petals covered with brass spots. Ōnin style. 16th century.
Compton Collection, Part I, #7: The iron plate is of flowerhead shape with each of the fourteen petals alternating between solid and openwork. The apertures are outlined in inlaid brass as is the seppa-dai and hitsu-ana. The remainder of the plate is similarly inlaid with plum flowers, birds, dots of dew, Genji mon and sambiki mon. 87 mm x 85 mm x 3.5 mm.
Other similar specimens can be found at:
Henri L. Joly and Kumasaku Tomita, Japanese art and handicraft, "Swords and sword fittings" section, sub-section “Inlays of Ōnin, Kyoto, Fushimi-Yoshiro, and Kaga Province”, Plate CX, #128: Iron, chrysanthemoid, thin guard with alternate petals covered with brass spots. Ōnin style. 16th century.
Compton Collection, Part I, #7: The iron plate is of flowerhead shape with each of the fourteen petals alternating between solid and openwork. The apertures are outlined in inlaid brass as is the seppa-dai and hitsu-ana. The remainder of the plate is similarly inlaid with plum flowers, birds, dots of dew, Genji mon and sambiki mon. 87 mm x 85 mm x 3.5 mm.
Japanese art and handicraft, Plate CX, #128.
And at Jim Gilbert website: Onin ten zogan tsuba, mid Muromachi. Size: 7.7 cm T x 7.6 cm W x 0.3 cm. Iron plate with brass inlay. Kiku gata. The Ōnin ten zogan style is characterized by the decoration of small brass “nail heads” and wires on a thin iron plate. The iron often has a soft, granular texture and seems to be prone to rust. Unfortunately, this rust will undermine the brass inlay and result in the loss of some of the inlay. This example is in reasonably good but far from perfect condition. As is often the case, the backside is better preserved, with the wire around the seppa-dai and kozuka-ana, and all petals still intact.
Compton Collection, Part I, #7.
-
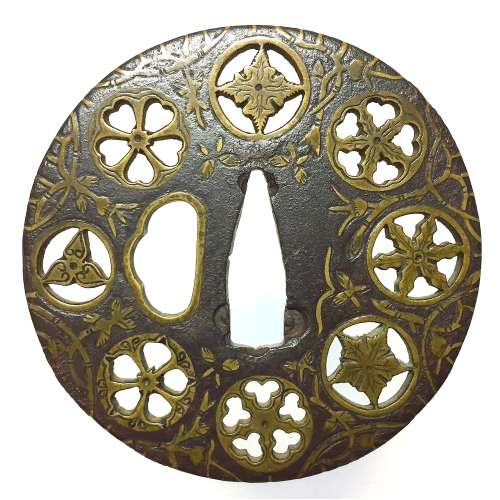 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm -
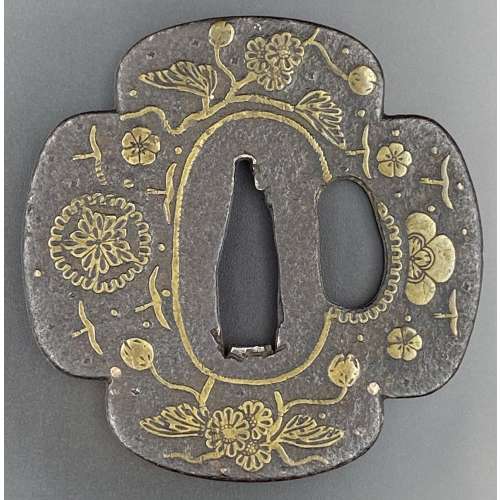 Iron tsuba of quatrefoil form (mokka-gata) adorned with the design of stars, wild geese, blossoms, leaves and tendrils realized in the brass inlay. The inlay technique includes suemon-zōgan and ten-zōgan. A smaller opening (kozuka hitsu-ana) surrounded by a scalloped brass border. The seppa-dai bordered with linear inlay. A few dots of inlay on both sides are missing. Measurements: height 71 mm, width 70 mm, thickness at centre 2.7 cm Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573)
Iron tsuba of quatrefoil form (mokka-gata) adorned with the design of stars, wild geese, blossoms, leaves and tendrils realized in the brass inlay. The inlay technique includes suemon-zōgan and ten-zōgan. A smaller opening (kozuka hitsu-ana) surrounded by a scalloped brass border. The seppa-dai bordered with linear inlay. A few dots of inlay on both sides are missing. Measurements: height 71 mm, width 70 mm, thickness at centre 2.7 cm Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) -
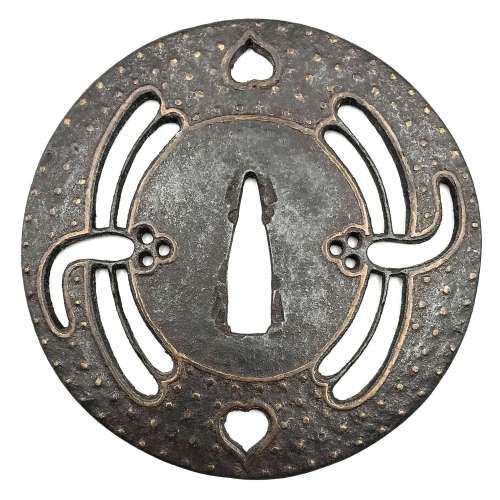 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with two boar's eyes (inome) and two dragonflies (tombo) in small openwork (ko-sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate also decorated with 2 to 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. The inlaid metal is of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, and not brass. The surface has remnants of lacquer. Ōnin school. Mid Muromachi period, middle of 15th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 90 mm, thickness: 3.2 mm. Notes regarding design: "According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13]. Two other cutouts - in the form of what in European tradition symbolizes the heart, on the top and in the bottom of tsuba disc - may have two different explanations. The most usual one, inome - "Heart-shaped pattern, which is said to go back to the shape of a wild boar's eye" [Markus Sesko. Encyclopedia of Japanese Swords. Print and publishing: Lulu Enterprises, Inc., 2014.]. This understanding is shared by Robert Haynes [Robert E. Haynes. Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010.] and elsewhere, with an exception of Okabe-Kakuya [Okabe-Kakuya. JAPANESE SWORD GUARDS. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. In cooperation with the department of Chinese and Japanese art; - 1908, p. 14], who provides the illustration of inome-shaped cut-outs with the following explanation: " The tsuba shown in Fig. 13 approaches a square form with rounded corners and is perforated with Aoi decoration. But this book was written long time ago, when people even at MFA might not know enough...
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with two boar's eyes (inome) and two dragonflies (tombo) in small openwork (ko-sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate also decorated with 2 to 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. The inlaid metal is of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, and not brass. The surface has remnants of lacquer. Ōnin school. Mid Muromachi period, middle of 15th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 90 mm, thickness: 3.2 mm. Notes regarding design: "According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13]. Two other cutouts - in the form of what in European tradition symbolizes the heart, on the top and in the bottom of tsuba disc - may have two different explanations. The most usual one, inome - "Heart-shaped pattern, which is said to go back to the shape of a wild boar's eye" [Markus Sesko. Encyclopedia of Japanese Swords. Print and publishing: Lulu Enterprises, Inc., 2014.]. This understanding is shared by Robert Haynes [Robert E. Haynes. Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010.] and elsewhere, with an exception of Okabe-Kakuya [Okabe-Kakuya. JAPANESE SWORD GUARDS. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. In cooperation with the department of Chinese and Japanese art; - 1908, p. 14], who provides the illustration of inome-shaped cut-outs with the following explanation: " The tsuba shown in Fig. 13 approaches a square form with rounded corners and is perforated with Aoi decoration. But this book was written long time ago, when people even at MFA might not know enough... The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.
The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.
 There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
 Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."
Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."
-
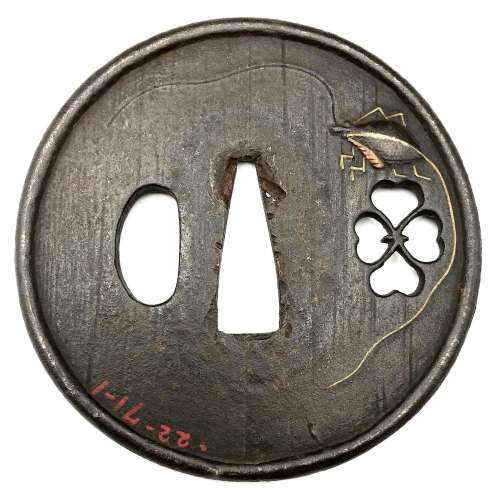 Iron tsuba of round form with a Marsilea (water clover, paddy plant, denjiso) in openwork (sukashi) and a cricket carved in low relief (katakiribori) with extremities and one antenna inlaid with brass; the other antenna is carved in kebori (which antenna is inlaid and which is carved alternates on the face and on the reverse). The plate decorated with vertical file stroke ornamentation (tate-yasurime). Raised dam-shaped rim (dote-mimi). Inscription from a previous collector in red oil paint: 22-71-1. Edo period, possibly 17th century. Katchushi school.
Iron tsuba of round form with a Marsilea (water clover, paddy plant, denjiso) in openwork (sukashi) and a cricket carved in low relief (katakiribori) with extremities and one antenna inlaid with brass; the other antenna is carved in kebori (which antenna is inlaid and which is carved alternates on the face and on the reverse). The plate decorated with vertical file stroke ornamentation (tate-yasurime). Raised dam-shaped rim (dote-mimi). Inscription from a previous collector in red oil paint: 22-71-1. Edo period, possibly 17th century. Katchushi school.Size: 75.0 x 74.4 x 3.6 (center), 5.0 (rim) mm.
The plant Marsilea (paddy plant, denjiso), common names include water clover and four-leaf clover because the long-stalked leaves have four clover-like lobes and are either held above water or submerged. In The elements of Japanese design by John W. Dower, this motif is listed under the numbers 634-35 Paddy Plant (denjiso). Obviously, as a four-leaf clover it is an auspicious symbol. The four leaves radiate out as the shape of the kanji 田 (romaji 'ta'), which means 'rice paddy'. This symbol may be used as a family crest (mon), and this would be the most probable explanation of the sukashi on this tsuba. -
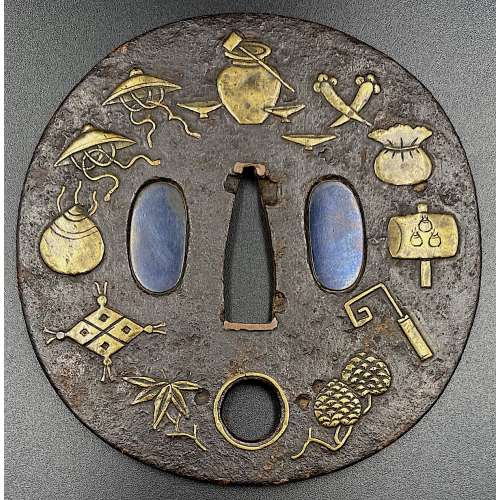 Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):
Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):- Sake set [shuki, 酒器], namely flask, ladle, and cups
- Cloves [choji, 丁子]
- Purse of inexhaustible reaches [kinchaku, 巾着]
- Magic mallet [kozuchi, 小槌]
- Key to the storehouse of the Gods [kagi, 鍵]
- Rhombus, or Lozenge (hosho, 方勝), with the second ideograph meaning victory.
- Sacred (or wish-granting) gem, or jewel [hōju, 宝珠]
- Hats of invisibility [kakuregasa, 隠れ笠]
-
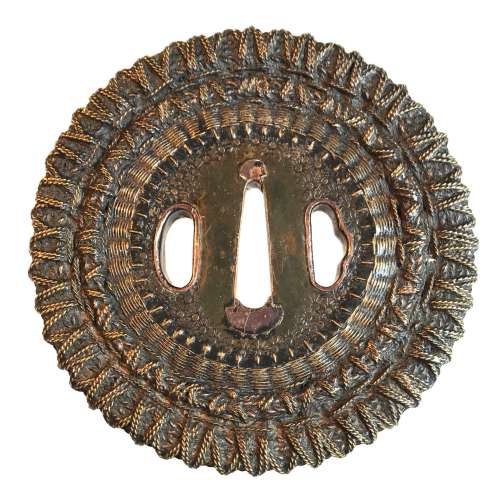 Shingen school (or style) tsuba of round form with an iron core of spoked-wheel shape, with its centre covered with a copper plate decorated with star-shaped punch marks. From this copper plate outward, the body is formed by brass and copper wire (flat and twisted) in a weave pattern. Both hitsu-ana are outlined in brass with a raised rim. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Edo period, 18th century. SOLD Height: 98.0 mm, Width: 97.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 6.0 mm. Weight: 290 g. NBTHK certificate №436696: 'Hozon' attestation. Citing "JAPANESE SWORD-MOUNTS IN THE COLLECTIONS OF FIELD MUSEUM" by Helen C. Gunsaulus, Assistant Curator of Japanese Ethnology. 61 plates. Berthold Laufer, Curator of Anthropology. Field Museum of Natural History, Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p.45: "An unusual group of tsuba popular in the late sixteenth century and afterwards is made up of those guards known as Shingen tsuba, a name which was derived from a sixteenth-century warrior, Takeda Shingen (Takeda Harunobu, 1521-73), who is said to have preferred this style of guard, as it combined strength and lightness. Under the category of "Shingen", four different types abd generally listed, though a fifth appears in the drawings in the Boston Catalogue of Okabe Kakuya "Japanese Sword Guards" (p. 21). It is square, that form which is said to have been used in Ashikaga days for scaling walls, the sword having been set up as a step. [...] The following descriptions include, however, the Shingen tsuba usually met with.
Shingen school (or style) tsuba of round form with an iron core of spoked-wheel shape, with its centre covered with a copper plate decorated with star-shaped punch marks. From this copper plate outward, the body is formed by brass and copper wire (flat and twisted) in a weave pattern. Both hitsu-ana are outlined in brass with a raised rim. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Edo period, 18th century. SOLD Height: 98.0 mm, Width: 97.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 6.0 mm. Weight: 290 g. NBTHK certificate №436696: 'Hozon' attestation. Citing "JAPANESE SWORD-MOUNTS IN THE COLLECTIONS OF FIELD MUSEUM" by Helen C. Gunsaulus, Assistant Curator of Japanese Ethnology. 61 plates. Berthold Laufer, Curator of Anthropology. Field Museum of Natural History, Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p.45: "An unusual group of tsuba popular in the late sixteenth century and afterwards is made up of those guards known as Shingen tsuba, a name which was derived from a sixteenth-century warrior, Takeda Shingen (Takeda Harunobu, 1521-73), who is said to have preferred this style of guard, as it combined strength and lightness. Under the category of "Shingen", four different types abd generally listed, though a fifth appears in the drawings in the Boston Catalogue of Okabe Kakuya "Japanese Sword Guards" (p. 21). It is square, that form which is said to have been used in Ashikaga days for scaling walls, the sword having been set up as a step. [...] The following descriptions include, however, the Shingen tsuba usually met with.- So-called Mukade ("centipede") tsuba are made of iron in which a centepede is inlaid in brass or copper wire. Mukade tsuba of Myōchin and Umetada warkmanship have been found with the inscription, "Made to the taste of Takeda Shingen".
- There are those of solid iron, with need centers of brass, to the edges of which is affixed a weaving of brass and copper wires which is bound to the foundation disk by a rim, usually decorated simply.
- Another type is of solid iron, bored at intervals and laced with braided or twisted wires of copper and brass.
- The fourth type is a chrysanthemoid form, chiselled in open work and laced or woven tightly with copper and brass wire."

Compton Collection, Part II, p.p. 26-27, №54.
-
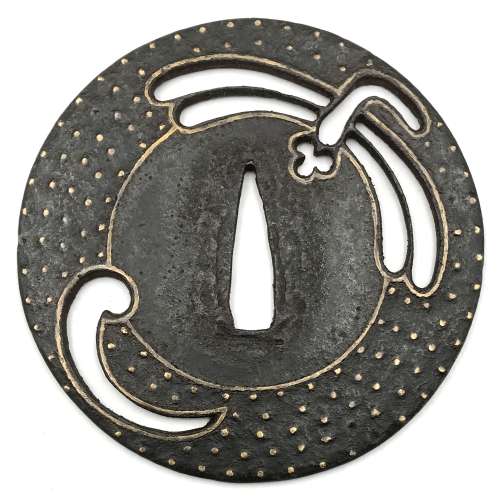 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with dragonfly (tombo) and comma (comma-like swirl, tomoe) in openwork (sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate decorated with 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire (sen-zōgan). Ōnin school. Unsigned. Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 89.5 mm, thickness: 3.1 mm. Notes regarding design: "According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13]. Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with dragonfly (tombo) and comma (comma-like swirl, tomoe) in openwork (sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate decorated with 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire (sen-zōgan). Ōnin school. Unsigned. Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 89.5 mm, thickness: 3.1 mm. Notes regarding design: "According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13]. Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc." -
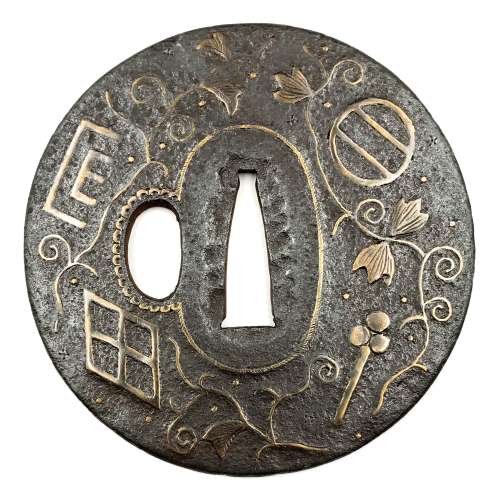 Thin iron tsuba of round form with design of family crests (mon) and arabesque (karakusa) in brass or copper inlay (suemon-zōgan) and occasional scattered brass dots or nail heads in ten-zōgan. Seppa-dai outlined with brass wire in the shape of a rope; kozuka-hitsu-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire. Rounded rim with iron bones (tekkotsu). The surface covered with lacquer (urushi). Ōnin school. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Family crests on the face: 1:30: Two lines (double stripe) encircled (maruni futatsu biki). 4:30: Stylized clove (choji). 7:30: Divided rhombus, or four lozenges incorporated in one (wari-bishi); it is also called Takeda-bishi, the family crest of warrior Takeda Shingen (among the others). 10:00: Stylized Genji-mon (Genji kō-zu) or incense symbol. On the reverse: 2:00 - "Chinese cloud" not a crest. 5:00: Bit (Kutsuwa) 7:30: Number four in a fan (ōgi-san) 10:30: Two dots in a well frame (igeta).
Thin iron tsuba of round form with design of family crests (mon) and arabesque (karakusa) in brass or copper inlay (suemon-zōgan) and occasional scattered brass dots or nail heads in ten-zōgan. Seppa-dai outlined with brass wire in the shape of a rope; kozuka-hitsu-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire. Rounded rim with iron bones (tekkotsu). The surface covered with lacquer (urushi). Ōnin school. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Family crests on the face: 1:30: Two lines (double stripe) encircled (maruni futatsu biki). 4:30: Stylized clove (choji). 7:30: Divided rhombus, or four lozenges incorporated in one (wari-bishi); it is also called Takeda-bishi, the family crest of warrior Takeda Shingen (among the others). 10:00: Stylized Genji-mon (Genji kō-zu) or incense symbol. On the reverse: 2:00 - "Chinese cloud" not a crest. 5:00: Bit (Kutsuwa) 7:30: Number four in a fan (ōgi-san) 10:30: Two dots in a well frame (igeta). -
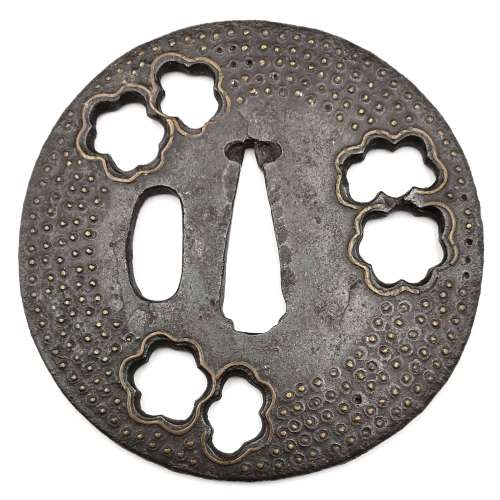 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form decorated with three pairs of snowflake-form small perforations (ko-sukashi), each outlined with brass wire; five concentric circular rows of dots inlaid in brass or copper ten-zōgan (some dots are missing). Hitsu-ana of oval form. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Late Muromachi period. Dimensions: 75.6 mm x74.6 mm x 3.0 mm. Weight: 78.0 g. Old NBTHK certificate (green paper): Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work". Unlike most Ōnin ten-zōgan tsuba this one does not have circular brass wire inlay inside the dots area; neither it has brass trim around seppa-dai or hitsu-ana.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form decorated with three pairs of snowflake-form small perforations (ko-sukashi), each outlined with brass wire; five concentric circular rows of dots inlaid in brass or copper ten-zōgan (some dots are missing). Hitsu-ana of oval form. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Late Muromachi period. Dimensions: 75.6 mm x74.6 mm x 3.0 mm. Weight: 78.0 g. Old NBTHK certificate (green paper): Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work". Unlike most Ōnin ten-zōgan tsuba this one does not have circular brass wire inlay inside the dots area; neither it has brass trim around seppa-dai or hitsu-ana. -
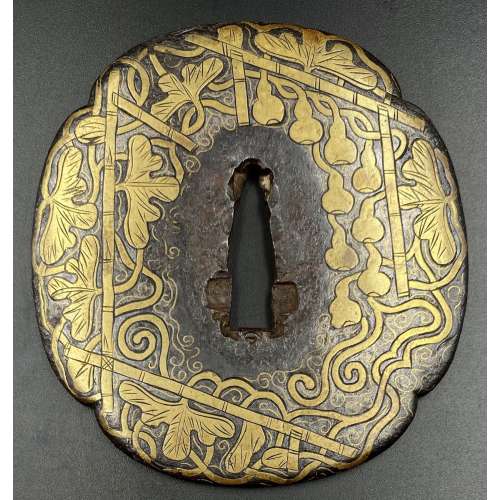

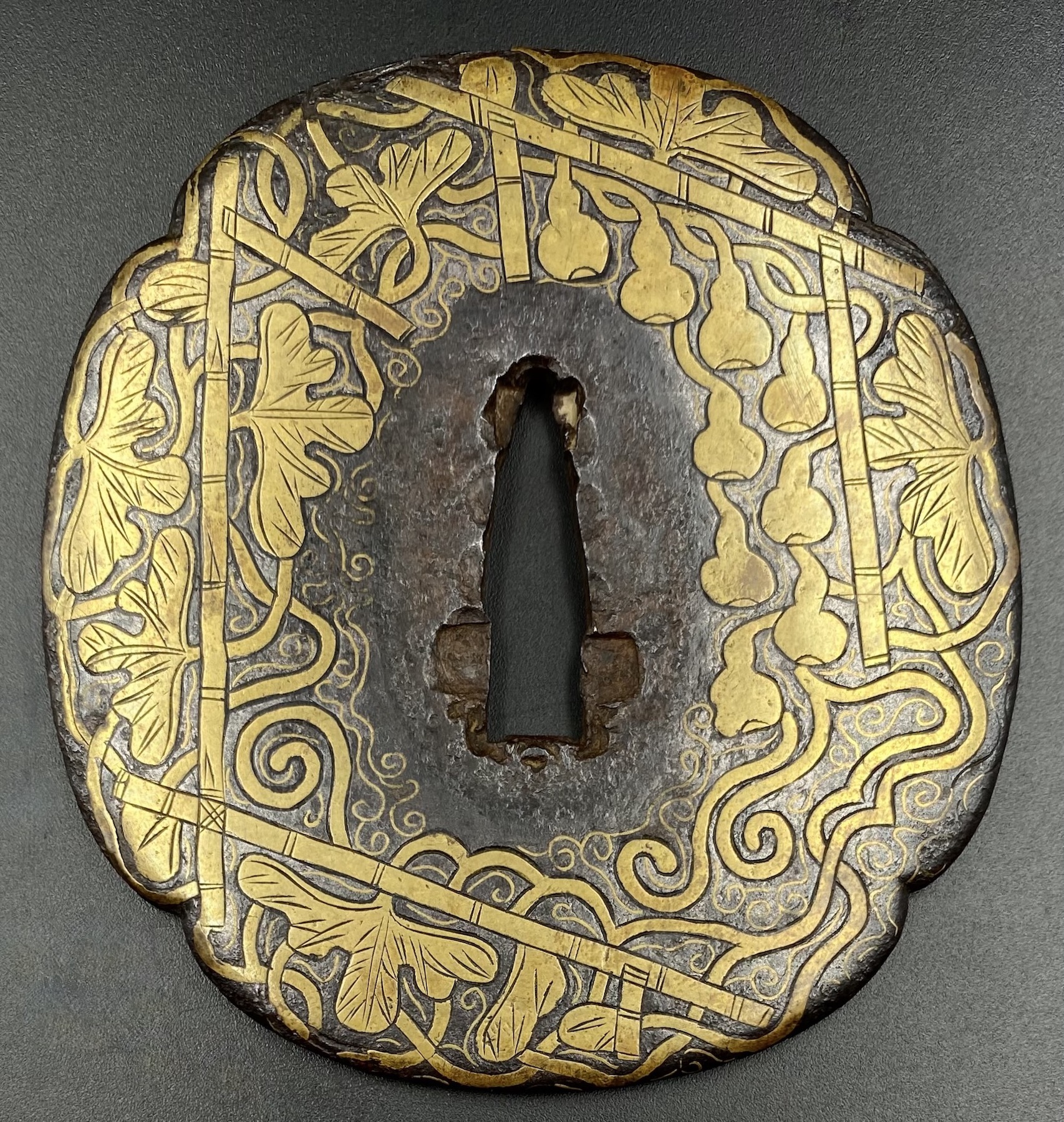
Iron tsuba of mokko form decorated with trellis, vines, foliage, and gourds inlaid in brass with details carved in low relief.
NBTHK: Tokubetsu Hozon №2003186.
Momoyama period (1574 – 1603). Dimensions: H: 85.5 cm, W: 79 mm, Thickness (centre): 4.8 mm. Tsuba of a similar design can be found in this collection [TSU-0373]. In that example, the plate was later pierced with geometrical mon-like openwork to resemble Koike Yoshirō's handguards. More about this type of tsuba here.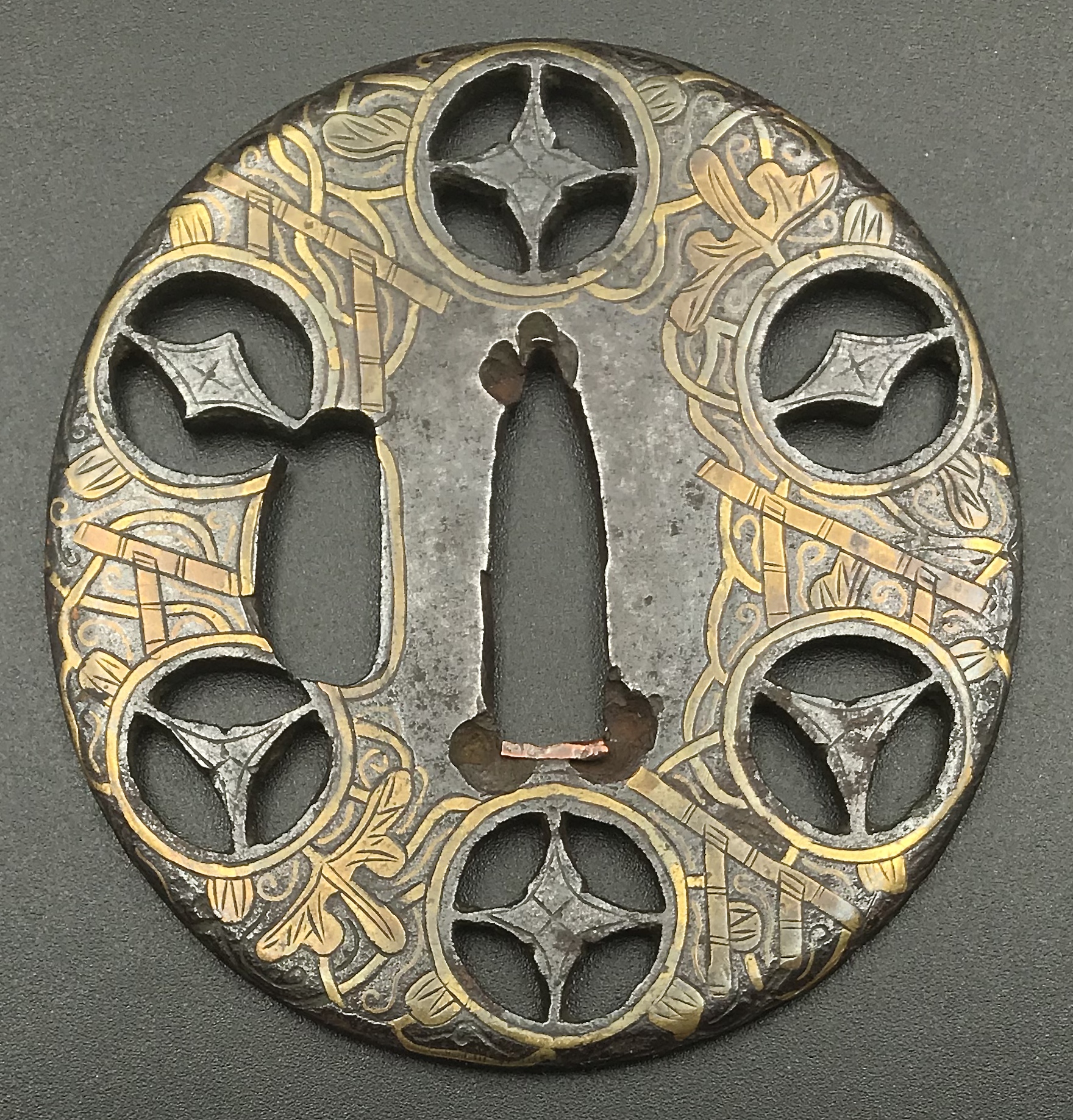

-
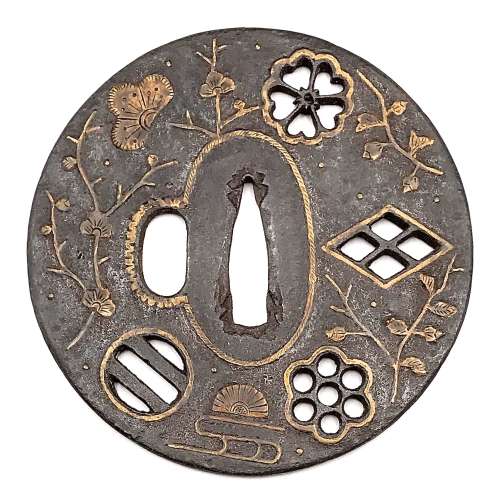 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with floral motif in brass or copper inlay (suemon-zōgan) and family crests (mon) in small openwork (ko-sukashi). Occasional brass dots or nail heads in brass ten-zōgan. Sukashi elements outlined with inlaid brass wire. Seppa-dai outlined with rope-shaped brass wire (nawame-zōgan); kozuka-hitsu-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire. Ōnin school. Mid to late Muromachi period, 15th or 16th century. Height: 88.9 mm; Width: 88.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.9 mm. Family crests (mon) in openwork: cherry blossom (sakura) - kamon of Sakurai and Yoshino clans, four-section lozenge (waribishi) - kamon of Takeda clan, the seven stars of the big dipper (maru ni nanatsuboshi) - kamon of Chiba clan, two encircled stripes (futatsubiki) - kamon of Ashikaga clan. Brass inlays represent flowers, branches and leaves, as well as halved plum blossom, halved chrysanthemum blossom, cloud, and chrysanthemum-on-water symbol - the mon of Kusunoki Masashige. Abundance of family crests of so many powerful warrior clans symbolizes heritage. "The brass trim around the kozuka hitsu-ana andd the seppa-dai are characteristics of Onin work" [Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro. Gary D. Murtha. GDM Publications, 2016; p. 27.]
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with floral motif in brass or copper inlay (suemon-zōgan) and family crests (mon) in small openwork (ko-sukashi). Occasional brass dots or nail heads in brass ten-zōgan. Sukashi elements outlined with inlaid brass wire. Seppa-dai outlined with rope-shaped brass wire (nawame-zōgan); kozuka-hitsu-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire. Ōnin school. Mid to late Muromachi period, 15th or 16th century. Height: 88.9 mm; Width: 88.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.9 mm. Family crests (mon) in openwork: cherry blossom (sakura) - kamon of Sakurai and Yoshino clans, four-section lozenge (waribishi) - kamon of Takeda clan, the seven stars of the big dipper (maru ni nanatsuboshi) - kamon of Chiba clan, two encircled stripes (futatsubiki) - kamon of Ashikaga clan. Brass inlays represent flowers, branches and leaves, as well as halved plum blossom, halved chrysanthemum blossom, cloud, and chrysanthemum-on-water symbol - the mon of Kusunoki Masashige. Abundance of family crests of so many powerful warrior clans symbolizes heritage. "The brass trim around the kozuka hitsu-ana andd the seppa-dai are characteristics of Onin work" [Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro. Gary D. Murtha. GDM Publications, 2016; p. 27.]


