-
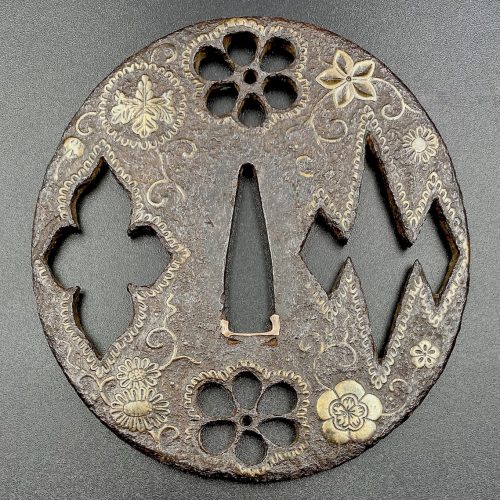 Iron tsuba of a round form (maru-gata) pierced (sukashi) with two six-petal flowers at 6 and 12 o’clock and modified lozenges at 3 and 9 o’clock, and inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils and flowers (chrysanthemum, cherry blossom, Chinese bellflower, paulownia); openings outlined with scalloped brass wire. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer on the surface. Nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Some elements of inlay missing. The rim with conspicuous tekkotsu, quite worn. Measurements: Height 92.0 mm; Width 86.3 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 3.2 mm, at rim 4.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier.
Iron tsuba of a round form (maru-gata) pierced (sukashi) with two six-petal flowers at 6 and 12 o’clock and modified lozenges at 3 and 9 o’clock, and inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils and flowers (chrysanthemum, cherry blossom, Chinese bellflower, paulownia); openings outlined with scalloped brass wire. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer on the surface. Nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Some elements of inlay missing. The rim with conspicuous tekkotsu, quite worn. Measurements: Height 92.0 mm; Width 86.3 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 3.2 mm, at rim 4.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier. -
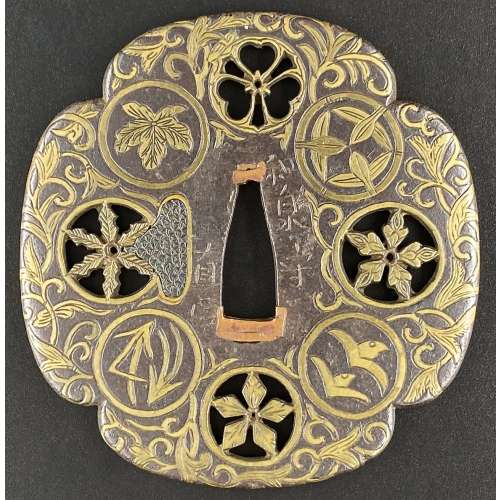 The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba.
The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba. -
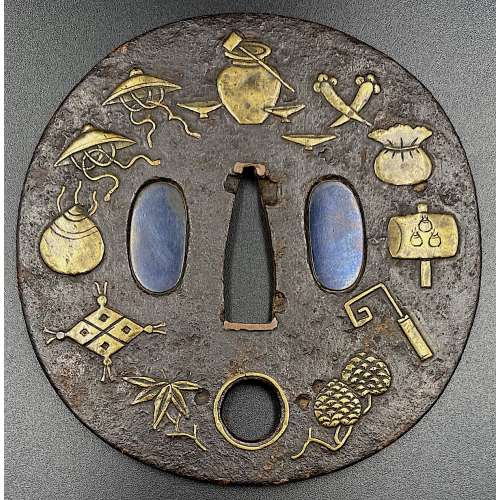 Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):
Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):- Sake set [shuki, 酒器], namely flask, ladle, and cups
- Cloves [choji, 丁子]
- Purse of inexhaustible reaches [kinchaku, 巾着]
- Magic mallet [kozuchi, 小槌]
- Key to the storehouse of the Gods [kagi, 鍵]
- Rhombus, or Lozenge (hosho, 方勝), with the second ideograph meaning victory.
- Sacred (or wish-granting) gem, or jewel [hōju, 宝珠]
- Hats of invisibility [kakuregasa, 隠れ笠]
-
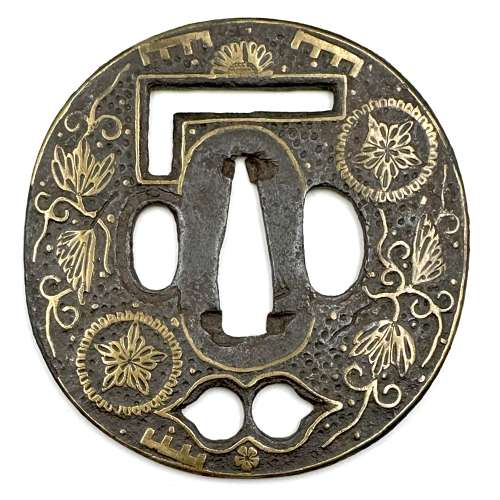
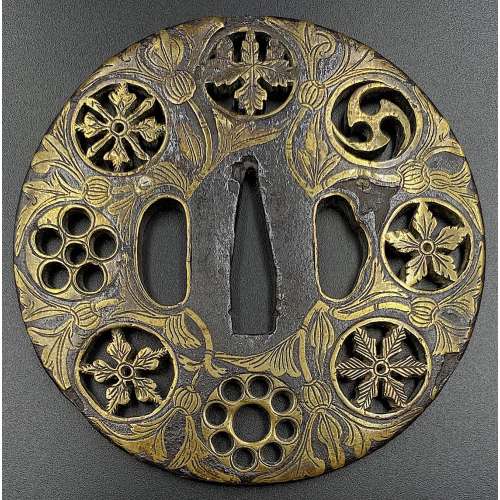 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Kiri-mon
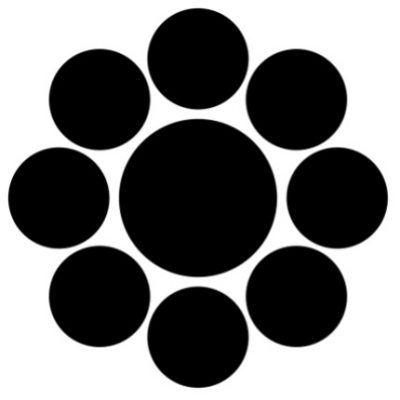
Katakura-mon
-
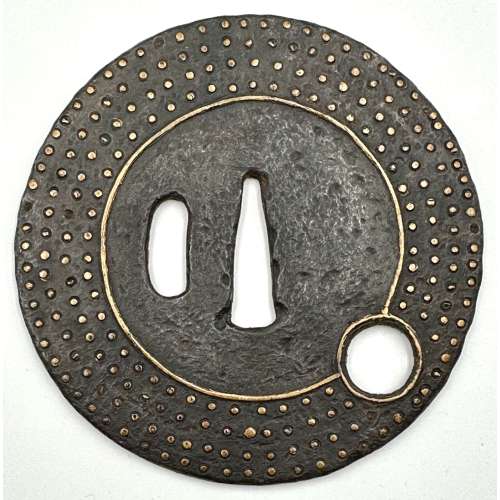

Iron tsuba of round form with one hitsu ana; centre of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire broke by a circular opening 7 mm in diameter located between 4 and 5 o’clock of the plate and in its turn outlined with brass wire. Extraneous to the central wire, the plate is decorated with four rows of brass dots (ten-zogan). A few dots are missing. In a custom kiri wood box. The meaning of the emblem is probably either the sun or the moon.
Ōnin school. Unsigned.
Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century.
Dimensions: diameter 88 mm; thickness 3.3 mm.
-
 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form (nagamaru-gata) pierced on top and in the bottom (ko-sukashi) with simplified Genji-kō (incense game symbol) and two petals of bellflower; openings, seppa-dai, and plate along the rim are outlined with brass wire, kozuka-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire, missing on the front; kogai-ana pierced later. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer, decorated in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils, bellflowers, and Genji characters, and with brass dots (ten-zogan), many of which are missing. Measurements: Height 77.5 mm; Width 75.5 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.4 mm, at rim 3.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form (nagamaru-gata) pierced on top and in the bottom (ko-sukashi) with simplified Genji-kō (incense game symbol) and two petals of bellflower; openings, seppa-dai, and plate along the rim are outlined with brass wire, kozuka-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire, missing on the front; kogai-ana pierced later. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer, decorated in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils, bellflowers, and Genji characters, and with brass dots (ten-zogan), many of which are missing. Measurements: Height 77.5 mm; Width 75.5 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.4 mm, at rim 3.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier.


