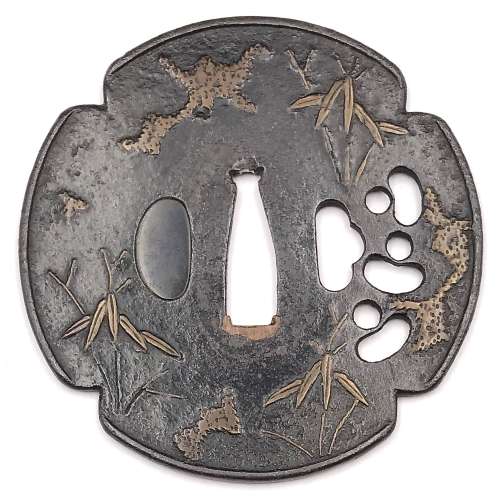
Small iron tsuba (tantō size) of aoi form with the design of paulownia leaves and blossoms in copper and brass flat inlay (hira-zōgan). Brass sekigane. Open kozuka hitsu-ana.
Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 53.4 x 40.7 x 4.4 mm; weight: 47.4 g
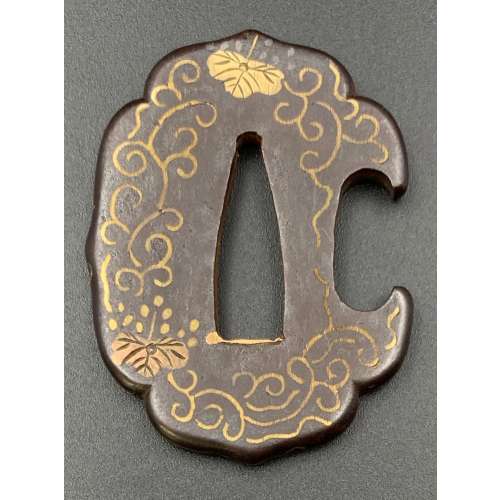

Small iron tsuba (tantō size) of aoi form with the design of paulownia leaves and blossoms in copper and brass flat inlay (hira-zōgan). Brass sekigane. Open kozuka hitsu-ana.
Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 53.4 x 40.7 x 4.4 mm; weight: 47.4 g
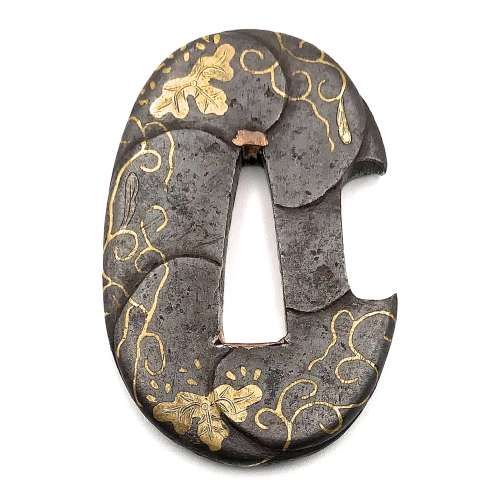

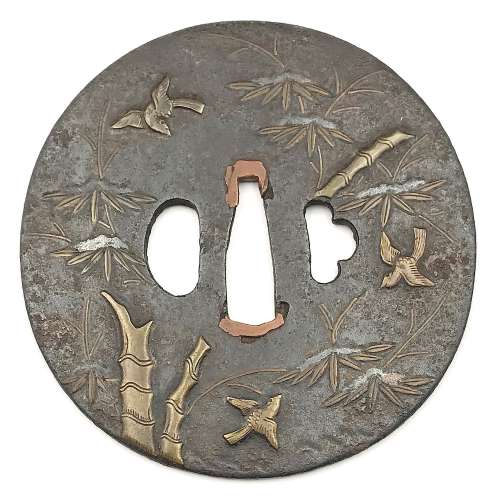
Small iron tsuba (tantō size) of oval form carved with imitation of six overlapping plates, decorated with paulownia blossoms, leaves, and tendrils in brass and copper hira-zōgan. Copper sekigane. Open kozuka hitsu-ana.
Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 50.5 x 34.0 x 4.9 mm.


Compton Collection, Part II, p.p. 26-27, №54.
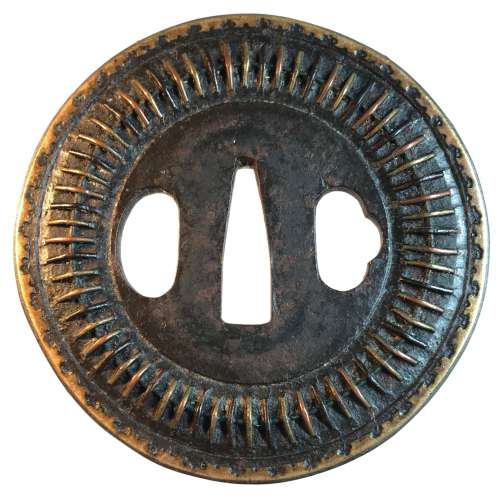
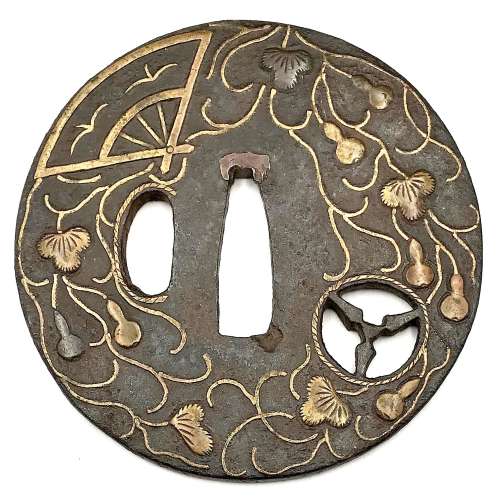


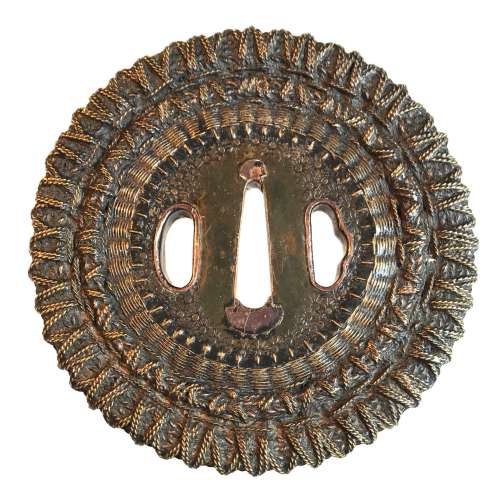
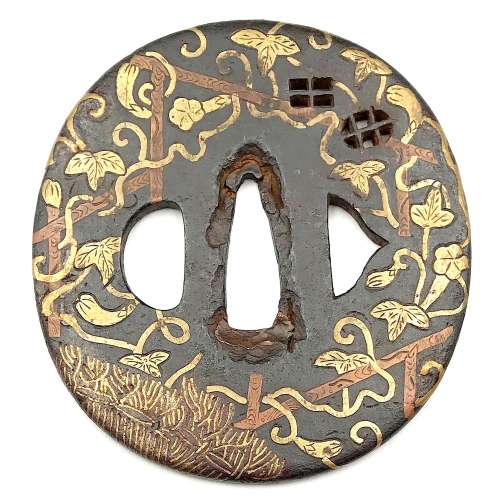
Iron tsuba of round form inlaid with brass and shakudo (suemon-zōgan) with a design of tendrils, leaves, double gourds, and folding fan with two wild geese on the face and the same design only with a fan with two interlocked rings (wachigai) on the back. Design is supplemented with a round family crest (mon) of three fans in openwork (sukashi). Hitsu-ana and the mon are outlined with brass rope. Copper sekigane.
Some attribute such tsuba as belonging to Heianjō or even Yoshirō School, and date them to Momoyama period. I keep this piece under Ōnin rubric, late Muromachi, but this is just a question of personal preference.Some inlay is missing, some repaired; traces of rust. Otherwise - decent condition.
Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Size: 77.4 x 77.1 x 3.8 (center), 3.2 (rim) mm
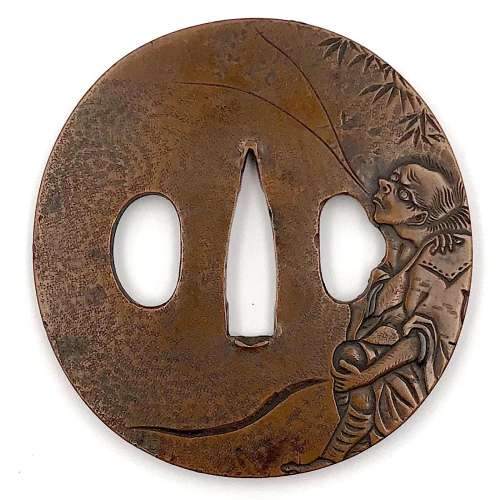

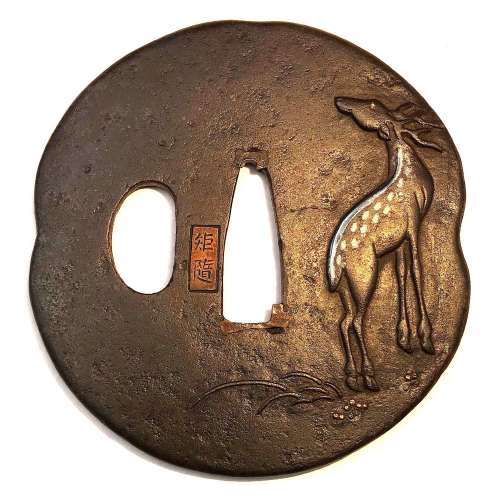
Copper tsuba of oval form carved in kebori and katakiribori with Tekkai Sennin sitting under bamboo on the face and with a pine tree on the back. Ishime-ji treated surface.
Signed on the reverse: Jōi (乗 意).
Edo period (First half of 18th century). Dimensions: 69.6 x 66.5 x 4.5 mm Sugiura Jōi (杉 浦 乗 意) was a master of Nara School in Edo; he was a student of Toshinaga [M. Sesko, 'Genealogies', p. 32]. "Sugiura Jōi (1701-1761) made many fuchigashira and kozuka, tsuba are rather rare." [M. Sesko, The Japanese toso-kinko Schools].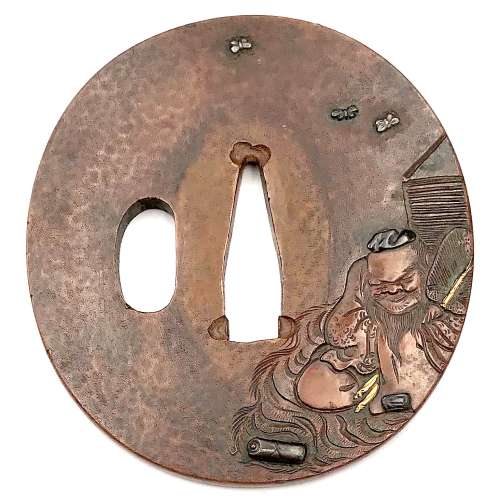
Copper tsuba of slightly elongated round form carved in low relief (shishiaibori and sukisagebori) and inlaid in gold, silver and shakudō with the design of dreaming Rosei (Lu Sheng): he is half-sitting by the pillow with his eyes closed, holding his fan, with a scroll by his feet, surrounded by flying butterflies.
Edo period, first half of the 18th century.
Dimensions: 70.8 x 67.1 x 5.0 mm. Signed on the reverse: Jōi (乗 意) + Kaō. Sugiura Jōi [杉 浦 乗 意] (1701-1761) was a master of Nara School in Edo; he was a student of Toshinaga [M. Sesko, ‘Genealogies’, p. 32]. “Sugiura Jōi (1701-1761) made many fuchigashira and kozuka, tsuba are rather rare.” [M. Sesko, The Japanese toso-kinko Schools, pp. 148-149]. On Rosei (Lu Sheng) dream's legend see Legend in Japanese Art by Henri L. Joly (1908 edition) on page 293.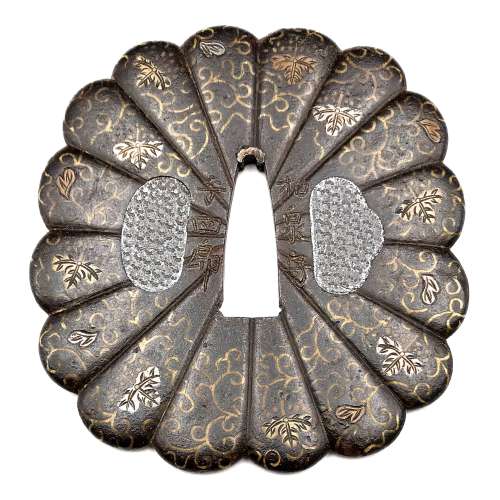
"Early signed example of the work of Koike Naomasa. The kiku shape iron plate is well finished. The flush inlay is brass, for the scroll work on both sides, with the leaves and kiri mon in brass, copper and silver with strong detail carving. Some of the inlay goes almost over the edge, which is goishi gata. The large hitsuana are plugged in lead with starburst kokuin surface design. [...]The face is signed in deep bold kanji: Koike Naomasa; the back is signed: Izumi no Kami, on the right and Yoshiro on the left. There are one or two small pieces of inlay missing. Sold by Sotheby London, Oct. 27, 1981, lot 368. Height = 86 mm, thickness (seppa-dai) = 3.75 mm, (edge) = 4 mm."Another similar example presented at: "Tsuba" by Günter Heckmann, 1995, №T55 — "Designation: Koike Naomasa. Mid Edo, end of the 17th century. Iron, hira-zogan in brass, copper, silver and shakudo, katakiri-bori. Tendrils and leaves. 87.0 x 78.0 x 4.0 mm." Reference: Japanische Schwertzierate by Lumir Jisl, 1967, page. 13. [SV: Actually, his tsuba is signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back; and Koike Naomasa on the front, exactly as Robert Haynes's tsuba. Dating this tsuba Mid-Edo, 17th century may be considered a misattribution]. More details regarding the Yoshirō tsuba.

Size: 71.5 x 70.0 x 3.0 mm.
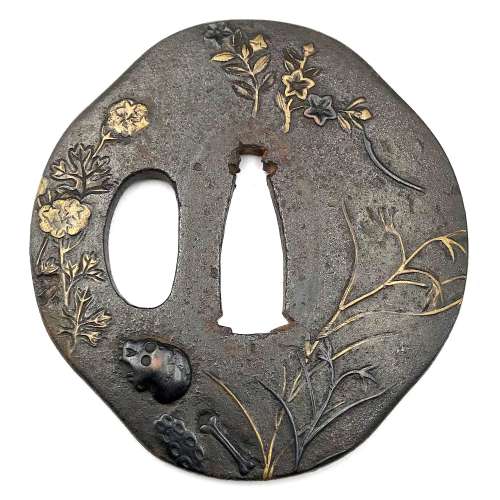
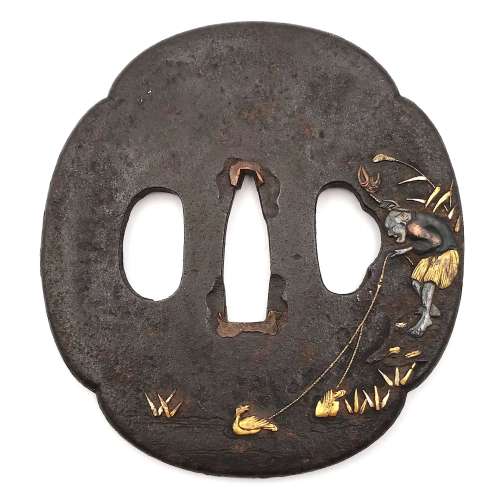
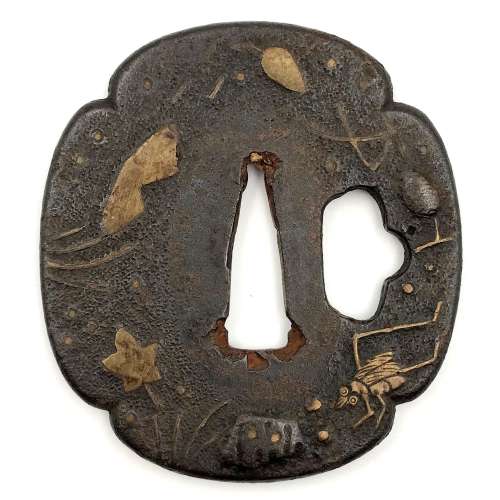




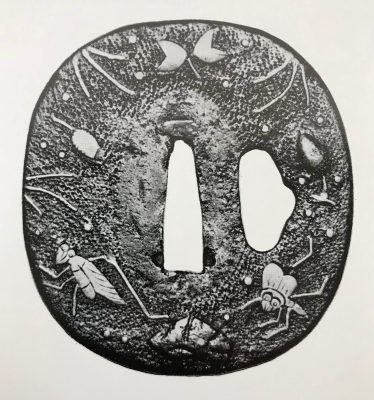
Tsuba Kanshoki, 1975, p. 61: Heianjō tsuba, Momoyama Period.



