Size: 71.5 x 70.0 x 3.0 mm.
-
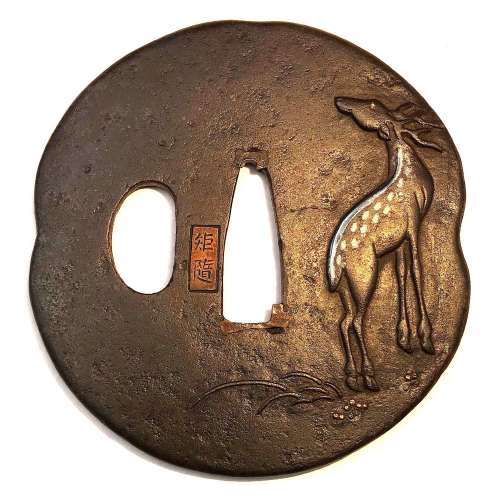 Iron tsuba of ryō-mokko-gata form decorated with a spotted deer (Nara deer or sika deer) motif in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori) and flat silver inlay (hara-zōgan); deer's eyes and details in gold inlay. Signed on a copper cartouche: Noriyuki. Grass in low relief carving on the reverse. There were two Noriyuki in Hamano school - father (Noriyuki I, 1736-1787) and son (Noriyuki II, 1771-1852). Frankly speaking, I don't know which one made this particular piece. Edo period, late 18th or early 19th century.
Iron tsuba of ryō-mokko-gata form decorated with a spotted deer (Nara deer or sika deer) motif in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori) and flat silver inlay (hara-zōgan); deer's eyes and details in gold inlay. Signed on a copper cartouche: Noriyuki. Grass in low relief carving on the reverse. There were two Noriyuki in Hamano school - father (Noriyuki I, 1736-1787) and son (Noriyuki II, 1771-1852). Frankly speaking, I don't know which one made this particular piece. Edo period, late 18th or early 19th century. -
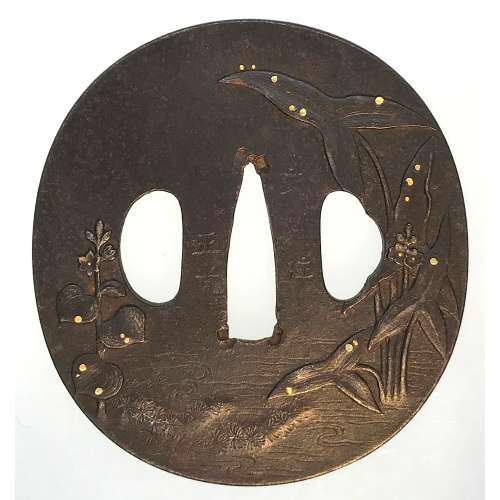

An iron tsuba of oval form decorated with a water plantain (omodaka) carved in low relief and water drops inlaid in gold.
Signed: Bushū jū Masamitsu.
Bushū-Itō school.Height: 71.8; Width: 67.3; Thickness: 3.6; Weight: 96 g.
Mid to late Edo period; 18th-19th century.
There were several tsuba artists with the name of Masamitsu. The one who worked with iron and spelled [正光] is mentioned at Markus Sesko's 'Genealogies' on page 106 in Akasaka School of Edo section as Masamitsu Gorōbei , student of Tadatoki, 4th generation Akasaka master. The name is not mentioned at Torigoye/Haynes 'Tsuba. An Aesthetic Study' in the list of Bushū-Itō family masters on page 181. -
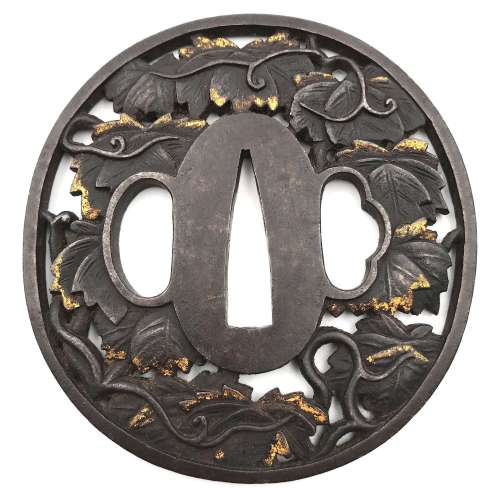

An iron tsuba of slightly vertically elongated circular form carved and pierced with a mass of ivy (tsuta) leaves and tendrils, details damascened with gold in nunome-zōgan technique. Hitsu-ana with raised rim.
Unsigned.
Chōshū school.Height: 72.0 mm; width: 69.0 mm; thickness: 4.7 mm; Weight: 92 g.
According to John W. Dower, "ivy bears fairly close resemblance to both maple leaf and grape leaf". However, I consider this tsuba decorated with ivy leaves for several reasons, such as the lack of racemations in the presence of tendrils. -
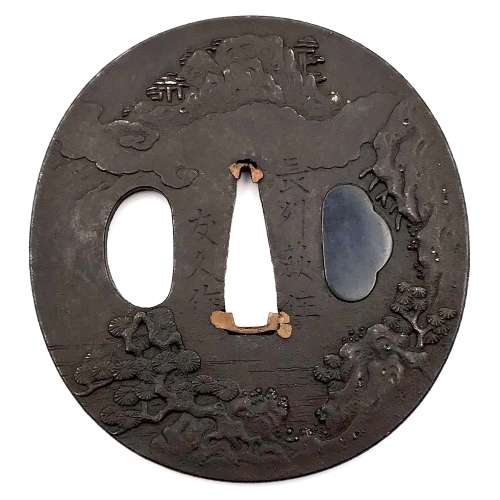

Iron tsuba of oval form carved with a landscape motif. Kogai-hitsu-ana plugged with shakudo. Sekigane of copper.
Signed: Chōshū Hagi-jū Tomohisa saku (長州萩住友久作).
Tomohisa, adopted son of Rokurō'emon, was 3rd generation master of Kawaji School from Hagi in Nagato (Chōshū), lived 1687-1743 [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 117].
Edo period, circa 1700. Dimensions: 71.1 x 66.8 x 2.9 mm For his adopted son Hisatsugu work see TSU-0103 in this collection. -
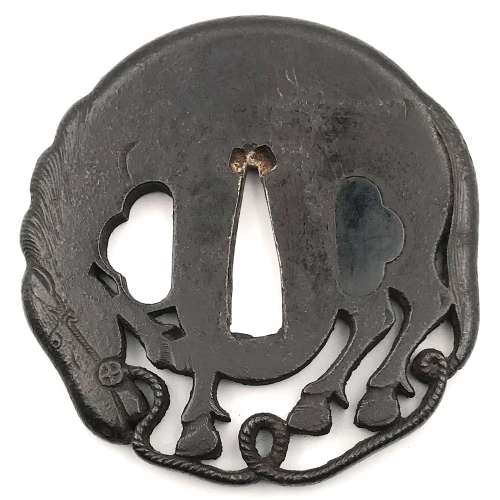

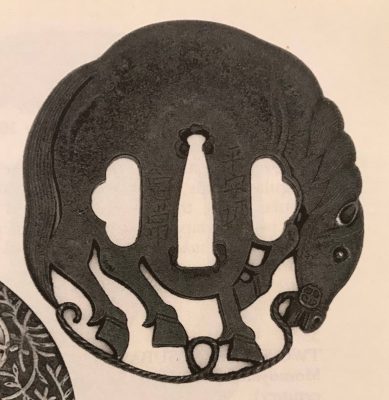
Iron tsuba pierced and carved (marubori-sukashi) with the 'horse in the round' design. Possibly, Bushū-Ito school, 19th century (ca. 1800). Kogai-hitsu-ana plugged with shakudō.
Size: 67.6 x 66.8 x 5.1 mm
Unsigned.
See:
-
- Robert E. Haynes. Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010, p. 120: Iron plate carved and formed in the round as a tethered bull...Signed: Bushū jū Sadayasu saku.
- Robert E. Haynes. Masterpiece and highly important tsuba, etc... San Francisco, 1984 // Catalog #9.: Signed: Bushū jū Yoshifusa. Ca. 1800, H 6.7 cm, Th. 4.75 mm.
- The Hartman collection of Japanese metalwork. Christie's, 1976, p. 29, №59: Bushū type, 19th century. Reference to Takezawa, Nihon Toban Zuetsu №411 for a similar design signed Bushū Yoshifusa.
4. Japanese Sword Fittings from the R. B. Caldwell Collection. Sale LN4188 "HIGO". Sotheby's, 30th March 1994, p. 17, №24: An iron tsuba, by Heianjo Sadatsune, Edo period (18th century). In the form of a horse, standing with its head lowered and a rope halter attached to its bit and trailing beneath. Signed Heianjo Sadatsune, 7.3 cm. With NBTHK Tokubetsu kicho paper, dated Showa 49 (1974). GBP 600-700.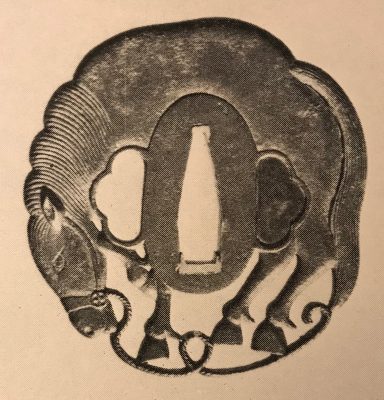
Hartman collection, №59.
The Caldwell Collection. Heianjo Sadatsune, Edo period (18th century).
-
-
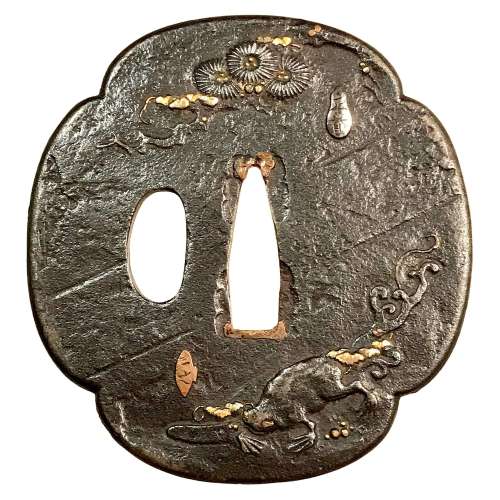

Iron tsuba of mokkō-form with a pine and a frog on the face and a snail on the back, carved and inlaid with gold. Each figurative element of the design is signed on three inlaid cartouches: Masaharu (正春), Kazuyuki (一之), and Yoshikazu (良一) [read by Markus Sesko]. Snake, snail, and frog together make a design called "SANSUKUMI" - Three Cringing Ones [Merrily Baird]. The snail can poison the snake, the frog eats the snail, and the snake eats the frog. It's unclear whether the pine replaces the snake on this tsuba, or the snake is hiding in the pine? Anyway, the frog and the snail are clearly represented. "Maybe we have here a joint work with Masaharu (the silver cartouche next to the pine) being the master and making the plate and Kazuyuki and Yoshikazu as his students carving out the frog and the snail respectively". Copper sekigane.
Dimensions: 70.9 x 67.2 x 3.0 mm. Edo period (18th century).Markus Sesko writes: "I agree, the frog and the snail most likely allude to the san-sukumi motif. It is possible that we have here an artist's choice to deliberately leave out the snake, maybe he thought that the motif is already obvious and there is no need to add a snake to make it clear that the tsuba shows the san-sukumi motif." [Markus Sesko].
Kazuyuki (一之): adopted son of Kumagai Yoshiyuki, student of Ichijō (Gotō-Ichijō Scool) [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 19.] Masaharu (正春): Kasuya fam., student of Masamichi (1707-1757) who was the 4th generation Nomura School master in Edo. [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 49.] -

Iron tsuba of circular form with a branch of loquat (biwa) pierced in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi) and carved in marubori technique (marubori-sukashi). Kozuka and kogai hitsu-ana are plugged with shakudo.
Signature: Choshu Kawaji ju Hisatsugu saku. Chōshū school in Nagato province.
According to M. Sesko 'Genealogies' Hisatsugu was a 4th generation Kawaji School master from Chōshū (present day Nagato), with the name Gonbei, formerly Toramatsu, adopted son of Tomohisa (1687-1743) [page 117]. For Tomohisa work see TSU-0104 in this collection. -

Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of distant pines, torii, and crescent moon in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane.
Size: 84.9 x 84.8 x 5.8 mm.
Unsigned.
Edo period, ca. 1750.
Tosa Myochin or Akasaka school.Japanese Swords and Sword Fittings from the Collection of Dr. Walter Ames Compton (Part I). Christie's, New York, March 31, 1992, pp. 28-29, № 53:
"A Tosa Myochin School Tsuba. Edo period (circa 1750), signed Toshu ju Kuniyoshi saku. The round iron plate pierced with a design of a temple gate (torii) and a pine tree. It has a round rim and there are some carved details on the surface of the design. The Tosa Myochin school, despite its foundation in the classic Myochin armor school tradition, worked mainly in the style of Akasaka school of Edo. [...] Many are equal to the mid to later Akasaka school work and the two types have frequently been confused. Signed examples are rare. Estimated price $1,500-2,000."

Compton Collection, Vol. 1, №53
-
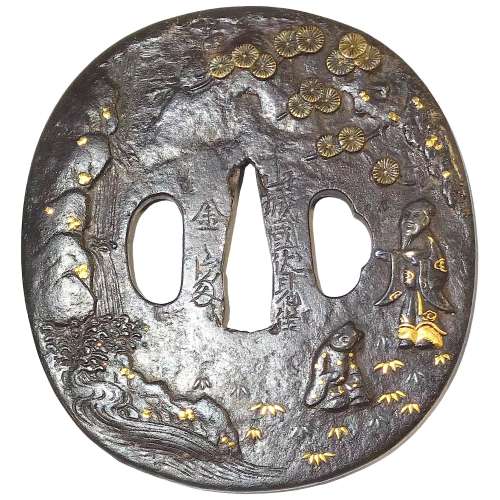

Large oval form tsuba decorated with two human figures (scholar and attendant) under the pine tree admiring a view of a waterfall on the face of the plate, and with stylized dragons carved on the reverse among the symbols of thunder inlaid in gold. The plate is carved in low relief with details inlaid with gold and silver.
Signed: Yamashiro no kuni Fushimi no ju Kaneie [Kaneie of Fushimi in Yamashiro Province] [山城國伏見住金家], with Kaō. It is a fake signature (
gimei). Size: Height: 91.9 mm; Width: 85.6 mm; Thickness: 3.4 mm; Weight: 169 g.
This is a late Edo period, 19th-century export work to cater to the tastes of the European tsuba collectors. It does not have anything in common with the work of great Kaneie masters.
SOLD -

Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of keys to the storehouse of the gods in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane.
Unsigned. Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 71.0 x 70.9 x 6.0 mm.Merrily Baird, Symbols..: The Key to the Storehouse of the Gods, one of the Myriad Treasures.
-
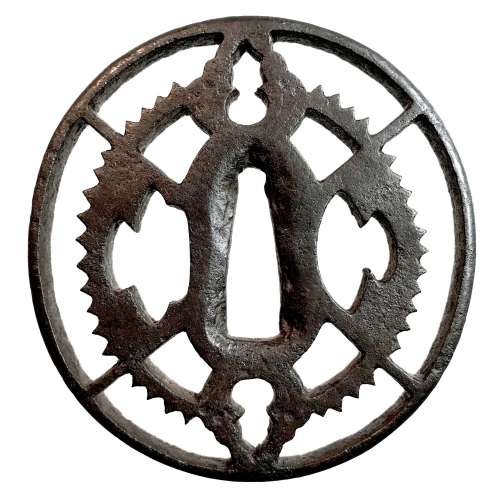

Iron tsuba of oval form pierced with design of slanting rays of light (shakoh), a Christian motif (Jesuit’s IHS symbol), and a pair of tassels in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi). Details on tassels carved in low relief. Traditional description of this kind of design is called “tokei”, or “clock gear”. Rounded rim.
Unsigned.
Edo period, 17th or 18th century. Possibly - Owari school.
Size: 76.0 x 73.0 x 6.2 mm. -
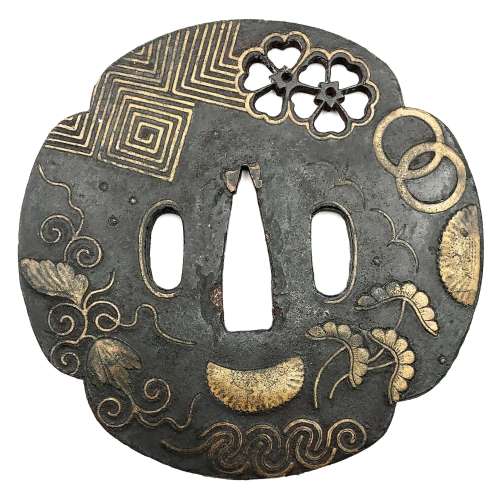 Iron tsuba of mokko form (quatrefoil) decorated with a pair of cherry blossoms (sakura) in small openwork (ko-sukashi) and inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) with designs of waves, distant pines, chrysanthemum flowers in halves, tendrils and leaves, lightning or thunder symbol (inazuma), flying geese and family chrests (mon): two interlocked rings (wachigai) on the face, and three encircled stripes (maru-no-uchi-ni-mitsuhikiryo) - kamon of the Kikkawa clan - on the reverse. Hitsu-ana outlined with inlay of brass wire. Surface treated with lacquer. Copper sekigane. Though some consider this type of tsuba to resemble Heianjo school, “...the brass trim around the hitsu-ana is a characteristics of Ōnin work” [Japanese sword guards. Onin – Heianjo – Yoshiro. Gary D. Murtha. GDM Publications, 2016; p. 27.]. The Ōnin origin is reinforced by scattered ten-zōgan elements here and there through the plate. It is possible that the tsuba was initially of round form and later trimmed to mokko shape. Mid Muromachi period; 15th century. Dimensions: Height: 87.2 mm; Width: 87.9 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm.
Iron tsuba of mokko form (quatrefoil) decorated with a pair of cherry blossoms (sakura) in small openwork (ko-sukashi) and inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) with designs of waves, distant pines, chrysanthemum flowers in halves, tendrils and leaves, lightning or thunder symbol (inazuma), flying geese and family chrests (mon): two interlocked rings (wachigai) on the face, and three encircled stripes (maru-no-uchi-ni-mitsuhikiryo) - kamon of the Kikkawa clan - on the reverse. Hitsu-ana outlined with inlay of brass wire. Surface treated with lacquer. Copper sekigane. Though some consider this type of tsuba to resemble Heianjo school, “...the brass trim around the hitsu-ana is a characteristics of Ōnin work” [Japanese sword guards. Onin – Heianjo – Yoshiro. Gary D. Murtha. GDM Publications, 2016; p. 27.]. The Ōnin origin is reinforced by scattered ten-zōgan elements here and there through the plate. It is possible that the tsuba was initially of round form and later trimmed to mokko shape. Mid Muromachi period; 15th century. Dimensions: Height: 87.2 mm; Width: 87.9 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. -
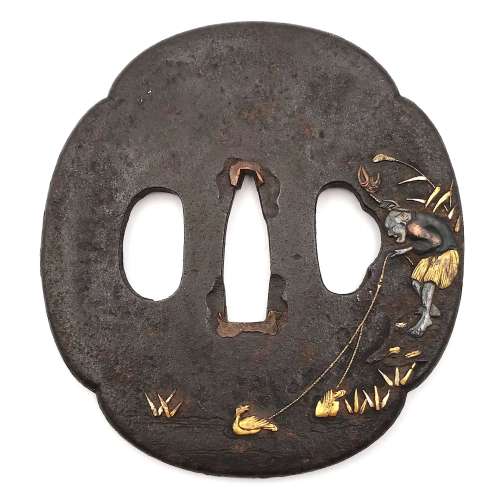 Mokkō form iron tsuba carved in relief and inlaid with soft metals (copper, gold, silver) with the design of a cormorant fisherman on the face and a boat on the reverse. Unsigned. Dimensions: 77 mm x 69 mm x 3.0 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th or 19th century. "Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. [...] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one's master and keen eyesight." - from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also in this collection TSU-0212 and TSU-0241.
Mokkō form iron tsuba carved in relief and inlaid with soft metals (copper, gold, silver) with the design of a cormorant fisherman on the face and a boat on the reverse. Unsigned. Dimensions: 77 mm x 69 mm x 3.0 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th or 19th century. "Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. [...] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one's master and keen eyesight." - from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also in this collection TSU-0212 and TSU-0241. -
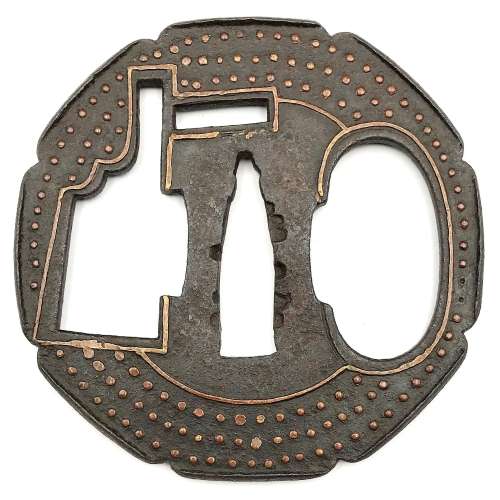 Iron tsuba of octafoil form with design of rudder (kaji) and lake in openwork (sukashi) outlined with brass wire. Thin plate also decorated with three concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. Cut-outs for kozuka and kogai probably added later. Slightly raised rim between the indentations (suki-nokoshi-mimi). The inlaid metal of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, not brass. Sekigane, visible on the NBTHK paper photo, are missing, possibly removed by a previous owner. Muromachi period. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Dimensions: 81.2 mm x 81.8 mm x 2.7 mm. Weight: 79.0 g. Large nakago-ana: 34 mm high and 10 mm wide. NBTHK certificate №455786: Hozon. Note regarding design: it was quite hard to interpret the big oval opening. The first suggestion was 'sea cucubmer', and it was based on a design published by Kazutaro Torigoye [Kodogu and tsuba. International collections not published in my books (Toso Soran), 1978] on page 202: Katchūshi tsuba: Sea cucumber and butterfly. Look and judge yourself:The second suggestion - 'lake' - came from [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014], page 14 №5:
Iron tsuba of octafoil form with design of rudder (kaji) and lake in openwork (sukashi) outlined with brass wire. Thin plate also decorated with three concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. Cut-outs for kozuka and kogai probably added later. Slightly raised rim between the indentations (suki-nokoshi-mimi). The inlaid metal of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, not brass. Sekigane, visible on the NBTHK paper photo, are missing, possibly removed by a previous owner. Muromachi period. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Dimensions: 81.2 mm x 81.8 mm x 2.7 mm. Weight: 79.0 g. Large nakago-ana: 34 mm high and 10 mm wide. NBTHK certificate №455786: Hozon. Note regarding design: it was quite hard to interpret the big oval opening. The first suggestion was 'sea cucubmer', and it was based on a design published by Kazutaro Torigoye [Kodogu and tsuba. International collections not published in my books (Toso Soran), 1978] on page 202: Katchūshi tsuba: Sea cucumber and butterfly. Look and judge yourself:The second suggestion - 'lake' - came from [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014], page 14 №5:
Torigoye: sea cucumber and butterfly.
Opening on my tsuba looks more like the 'lake'. Also, rudder and lake make more sense than rudder and sea cucumber. At least to me...
Ko-Katchūshi tsuba: Lake and pine.
-
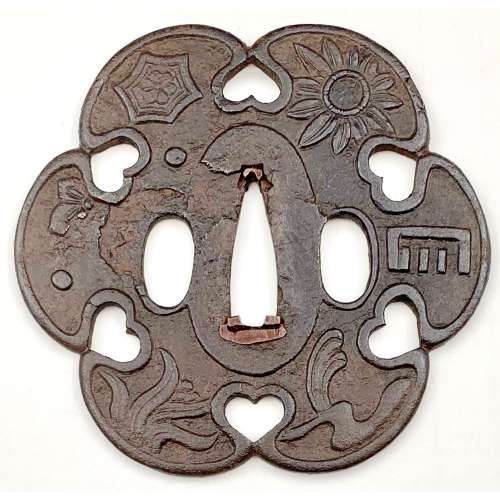 Iron tsuba of six-lobed (mutsu-mokkō-gata) form, with six wild boar's eye shape (inome) openings (sukashi). Ryo-Hitsu and the entire perimeter of tsuba have typical for this school raised rim; raised seppa dai. Lobes are decorated in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori). On the obverse: chrysanthemum, Genji mon, waves and rocks, grasses and star, bellflower, star and flower in tortoiseshell (kikko). On the reverse: Stars and different flowers, and flying geese. The plate is damaged to the left of nakago-ana and around the left hitsu-ana. Kamakura-bori school. Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Diameter: 89 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm; Weight: 108.8 g [large]. There is a similar tsuba in this collection, TSU-0345.2018, but with a different motif and much smaller: diameter 74.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, weight: 62.8 g.Another look-a-like tsuba can be found at the Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17, though his tsuba is more massive (80 x 84 x 4 mm).
Iron tsuba of six-lobed (mutsu-mokkō-gata) form, with six wild boar's eye shape (inome) openings (sukashi). Ryo-Hitsu and the entire perimeter of tsuba have typical for this school raised rim; raised seppa dai. Lobes are decorated in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori). On the obverse: chrysanthemum, Genji mon, waves and rocks, grasses and star, bellflower, star and flower in tortoiseshell (kikko). On the reverse: Stars and different flowers, and flying geese. The plate is damaged to the left of nakago-ana and around the left hitsu-ana. Kamakura-bori school. Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Diameter: 89 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm; Weight: 108.8 g [large]. There is a similar tsuba in this collection, TSU-0345.2018, but with a different motif and much smaller: diameter 74.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, weight: 62.8 g.Another look-a-like tsuba can be found at the Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17, though his tsuba is more massive (80 x 84 x 4 mm).
Varshavsky Collection: TSU-0345.2018
This tsuba, TSU-0401.2019, is the biggest of all three (another mine and the one from Campton Collection). The presence of a flower in a tortoiseshell symbol (crest or mon) on this tsuba alludes to Izumo Shrine. The overall piece, with symbols of grasses, waves, flowers, incense, stars, and flying geese, is full of autumnal connotations.
Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17: Kamakura-bori tsuba, ca. 1450.
-
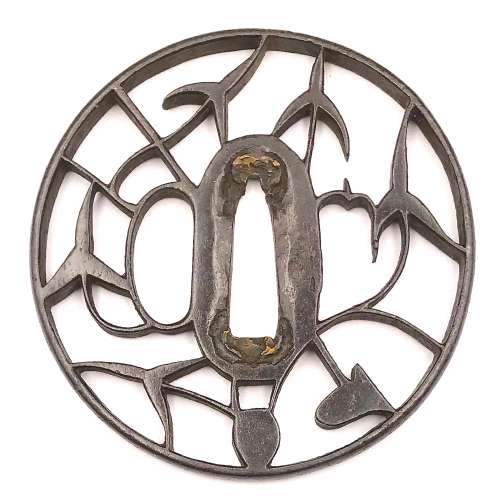 Iron tsuba of round form with design of water plantain (omodaka) and wild goose in openwork (sukashi). Slightly rounded, square rim. Copper sekigane. Kyo school. Late Muromachi period: Early 16th century (Tenbun era) [Sasano's attribution]. Height: 76.2 mm. Width: 75.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.3 mm. Center thickness: 4.5 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 68: "The water plantain (omodaka) first appeared as a design for sword fittings in the Heian period. From such early beginnings, this decorative plant has shared a long history with the samurai. Also known as shogun's grass (shogununso), it was held in high esteem as a symbol of victory". The same tsuba was found at Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections. Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997, page 22, item 60, saying that this is a "Kyo-sukashi tsuba, early to middle Edo period (late 17th/18th century) [Sotheby's attribution], and that it represents "a small bird among omodaka and aoi plants".
Iron tsuba of round form with design of water plantain (omodaka) and wild goose in openwork (sukashi). Slightly rounded, square rim. Copper sekigane. Kyo school. Late Muromachi period: Early 16th century (Tenbun era) [Sasano's attribution]. Height: 76.2 mm. Width: 75.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.3 mm. Center thickness: 4.5 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 68: "The water plantain (omodaka) first appeared as a design for sword fittings in the Heian period. From such early beginnings, this decorative plant has shared a long history with the samurai. Also known as shogun's grass (shogununso), it was held in high esteem as a symbol of victory". The same tsuba was found at Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections. Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997, page 22, item 60, saying that this is a "Kyo-sukashi tsuba, early to middle Edo period (late 17th/18th century) [Sotheby's attribution], and that it represents "a small bird among omodaka and aoi plants". -
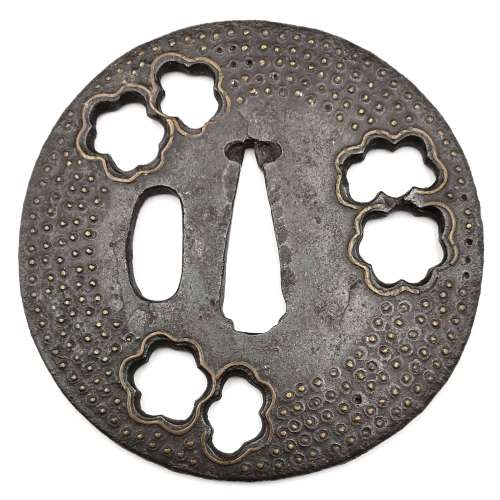 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form decorated with three pairs of snowflake-form small perforations (ko-sukashi), each outlined with brass wire; five concentric circular rows of dots inlaid in brass or copper ten-zōgan (some dots are missing). Hitsu-ana of oval form. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Late Muromachi period. Dimensions: 75.6 mm x74.6 mm x 3.0 mm. Weight: 78.0 g. Old NBTHK certificate (green paper): Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work". Unlike most Ōnin ten-zōgan tsuba this one does not have circular brass wire inlay inside the dots area; neither it has brass trim around seppa-dai or hitsu-ana.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form decorated with three pairs of snowflake-form small perforations (ko-sukashi), each outlined with brass wire; five concentric circular rows of dots inlaid in brass or copper ten-zōgan (some dots are missing). Hitsu-ana of oval form. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Late Muromachi period. Dimensions: 75.6 mm x74.6 mm x 3.0 mm. Weight: 78.0 g. Old NBTHK certificate (green paper): Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work". Unlike most Ōnin ten-zōgan tsuba this one does not have circular brass wire inlay inside the dots area; neither it has brass trim around seppa-dai or hitsu-ana. -
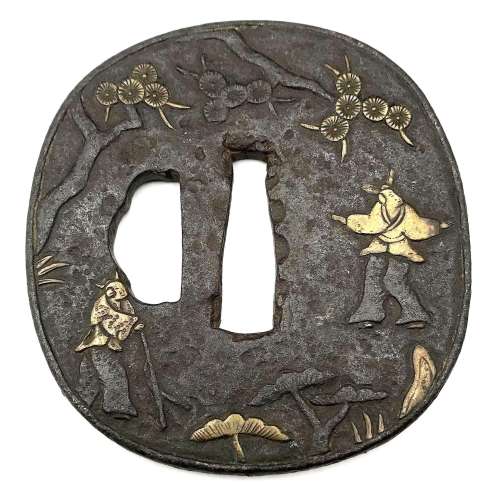 Relatively thick iron tsuba of rounded square form with slightly elevated rim decorated in carving (sukidashi-bori) and yellow brass (shinchū) inlay (suemon-zōgan) with legendary creatures (humans with cow heads) in a pine tree forrest on the face, and a horned man with a stick hunting a rabbit in the woods on the reverse. Large hitsu-ana possibly cut off later on. In the beginning of the 20th century such tsuba were usually attributed to Fushimi-Kaga school. This one may be attributed to either Ōnin or to Heianjō. The latter seems most plosible because of the thick web and dull patina. The technique may also be called "shinchū-zōgan". Momoyama or early Edo period. Unsigned. Dimensions: 72.3 x 68.4 x 4.1 mm
Relatively thick iron tsuba of rounded square form with slightly elevated rim decorated in carving (sukidashi-bori) and yellow brass (shinchū) inlay (suemon-zōgan) with legendary creatures (humans with cow heads) in a pine tree forrest on the face, and a horned man with a stick hunting a rabbit in the woods on the reverse. Large hitsu-ana possibly cut off later on. In the beginning of the 20th century such tsuba were usually attributed to Fushimi-Kaga school. This one may be attributed to either Ōnin or to Heianjō. The latter seems most plosible because of the thick web and dull patina. The technique may also be called "shinchū-zōgan". Momoyama or early Edo period. Unsigned. Dimensions: 72.3 x 68.4 x 4.1 mm


