-
 [Jean de LA FONTAINE]. Contes et nouvelles en vers. De Monsieur de La Fontaine. Nouvelle édition enrichie de tailles-douces. À Amsterdam | Chez Henry Desbordes, MDCLXXXV [1685]. — 2 vol. in 1. Pagination: [1] - frontispiece with pasted illustr., [*1] - title p. with blank verso, *2-*5 (only recto numbered) - advertisement, [1] - preface vol. 1, [2] table, 1-236; [6] - preface vol. 2, 1-216, illustr. (in text). Etched frontispiece plate and 58 half-page etchings at the head of each chapter as well as endpiece vignettes, all by R. de Hooge (Romeyn de Hooghe, 1645 – 1708, a Dutch painter, sculptor, engraver and caricaturist. First illustrated edition. "Publication of the scandalous fables was forbidden in France from 1674. According to Van Eeghen, this edition was published without the knowledge of La Fontaine. ...This is the edition with ‘Le Juge de Nêle’ (instead of Mesle) in the contents of the first volume, as well as page 211 for 'Dissertation sur la Joconde'; 16 lines of text on page 211; and 19 lines of text on the first page of the preface of volume 2" [1]. Pott 8vo (15.4 x 10 cm), hardcover; owner's later tan polished half-calf, marbled boards, marbled pastedowns and flyleaves, 5 raised bands, dark brown labels with gilt lettering and gilt roll patterns on spine, tail of the spine slightly damaged. Corners bumped, spotted stains on leather. Henri Desbordes (d. ca. 1722) was a Huguenot printer who was exiled from his business in France and set up as a publisher in Amsterdam in the 17th century.
[Jean de LA FONTAINE]. Contes et nouvelles en vers. De Monsieur de La Fontaine. Nouvelle édition enrichie de tailles-douces. À Amsterdam | Chez Henry Desbordes, MDCLXXXV [1685]. — 2 vol. in 1. Pagination: [1] - frontispiece with pasted illustr., [*1] - title p. with blank verso, *2-*5 (only recto numbered) - advertisement, [1] - preface vol. 1, [2] table, 1-236; [6] - preface vol. 2, 1-216, illustr. (in text). Etched frontispiece plate and 58 half-page etchings at the head of each chapter as well as endpiece vignettes, all by R. de Hooge (Romeyn de Hooghe, 1645 – 1708, a Dutch painter, sculptor, engraver and caricaturist. First illustrated edition. "Publication of the scandalous fables was forbidden in France from 1674. According to Van Eeghen, this edition was published without the knowledge of La Fontaine. ...This is the edition with ‘Le Juge de Nêle’ (instead of Mesle) in the contents of the first volume, as well as page 211 for 'Dissertation sur la Joconde'; 16 lines of text on page 211; and 19 lines of text on the first page of the preface of volume 2" [1]. Pott 8vo (15.4 x 10 cm), hardcover; owner's later tan polished half-calf, marbled boards, marbled pastedowns and flyleaves, 5 raised bands, dark brown labels with gilt lettering and gilt roll patterns on spine, tail of the spine slightly damaged. Corners bumped, spotted stains on leather. Henri Desbordes (d. ca. 1722) was a Huguenot printer who was exiled from his business in France and set up as a publisher in Amsterdam in the 17th century. -
 Title: ACADEMIE | DES | SCIENCES | ET DES | ARTS, | Contenant les Vies & les Eloges Historiques des | Hommes Illustres, | Qui ont excellé en ces Professions depuis environ quatre Siécles | parmy diverses Nations de l’Europe : |Avec leurs Pourtraits tirez sur des Originaux au Naturel, & plusieurs Inscriptions | funebres, exactement recueïlies de leurs Tombeaux | Par Isaac Bullart , Chevalier de l’Ordre de Saint Michel. | TOME PREMIER | {allegorical vignette, signed Abr. A Diepenbeke delineavit – Pet. Clouwet sculp.} | Imprimé par les soins de l’Autheur. | A AMSTERDAM, | Se vendent chez les Heritiers de Daniel Elzevier, 1682. || Pagination : [2] – h.t. / blank ; [2] – 1st vol. t.p. in black and red with vignette engraved by Pet. Clouwet after Abr. Diepenbeke / blank; [7] – dedication to Jacques Theodore de Brias {Jacques-Théodore de Bryas (Dutch, 1630 – 1694)}, [9] – preface, [2] – table demonstrative / stanza by Guilielmus Riverius, [2] vinette “Tardius sed grandius” with an elephant in ornamental frame / text; [2] – Advis au lecteur; [1, 2] – f.t. livre premiere, illustres politiques / blank; [2] – noms politiques / blank (A1, after f.t.), 3(A2)-421, [422-424] – table eloges. Collation: [*]6, **8, A6 B-Ggg4. (14 prelim. leaves, as in LIB-2675.2021; the LIB-2676.2021 copy has 12) Binding: 34.5 x 22 x 4.3 cm.34.5 x 22 x 4.3 cm, hardbound; full calf, raised bands. The title is drawn by Abraham van Diepenbeeck (Dutch, 1596 - 1675) and engraved by Peeter Clouwet (Flemish, 1629–1670). The first volume of a two-volume set contains 119 copperplate burin-engraved portraits of selected politicians, historians, jurists, writers, and Italian artists. 26 portraits engraved by Esme de Boulonois (French,1645 – 1681), 3 unsigned, and the rest engraved by Nicolas de Larmessin I (French, 1632 – 1694)Lavinia Vecellio, (Italian, 1530 – 1575), Titian' daughter, engraved by Lamerssin after Titian, Portrait of Jacques Auguste de Thou engraved by de Boulonois after Daniel Dumonstier. Politicians: Antoine Perrenot, Cardinal de Granvelle; Arnaud d'Ossat, Cardinal; Auger Busbeque; Bessarion, Cardinal; François Ximenes, Cardinal; George d'Amboise, Cardinal; Gille Albornoz, Cardinal; Guillaume de Croy; Guy du Faur de Pybrac; Jacques Auguste de Thou; Jean de Selve; Jean Zamoski; Jean de Barnevelt; Jean Armand du Plessis, Cardinal de Richelieu; Jule Mazarin, Cardinal; Michel de l'Hospital; Renaud Pole, Cardinal; Stanislas Hosius, Cardinal; Thomas Morus; Thomas Wolsey, Cardinal. Historians: Bertrand d'Argentré; Cæsar Baronius, Cardinal; Emanuel de Meteren; Enguerand de Monstrelet; Florimond de Remond; François Guicciardin; Fulve Ursin; Guillaume Camden; Henry Catherine d'Avila; Hubert Goltzius; Jacques Amiot; Jean Aventin; Jean Baptiste Platina; Jean Barclay; Jean Froissard; Jean Papirius Masson; Nicolas le Febure; Olivier de la Marche; Onuphre Panuinius; Pandolphe Collenuce; Paul Jove; Philippe de Commines; Pontus Heuterus; Regino Abbé de Prumy; Robert Gaguin; Wolfgang Lazius. Jurists: Alexandre de Tartagnis; André Alciat; André Tiraqueau; Antoine Augustin; Antoine le Febvre; Boece Epo; Charles du Moulin; François Bauduin; Gabriel Mudée; Jacques Cuias; Jason Mainus; Jean Wamese; Mathieu Wesenbec; Philippe Dece; Pierre Peckius; Pierre Pithou; Tibere Decian; Viglius de Zuichem. Writers/Linguists: Ange Politian; Demetrius Chalcondyles; Emanuel Chrysoloras; François Philelphe; François Raphelenge; Guillaume Postel; Jean Argyropilus; Jean Bocace; Jean Lascaris; Jean Passerat; Jean Pierius Valerianus; Jeanne Gray; Nicolas Clenard; Pierre Nannius; Rudolphe Agricola; Theodore Gaza. Italian painters, architects, and sculptors: André Mantegna; André Organa; André del Sarto; André Tafi; André Verrochio; Antoine de Correge; Antoine de Messine; Arnoud di Lappo; Baccio Bandinel; Balthazar Perusi; Bramante d'Urbin; Daniel Ricciarelli; Dominique Beccafumi; Donato; François Mazzuoli; François Primatici; Frere Philippe Lippi; Giorgion; Giotto; Jacques Barozzi de Vignole; Jean Antoine Licinio de Pordenone; Jean Cimabue; Jean d'Udine; Jean François Rustici; Jule Romain; Le Rosso; Leonard de Vinci; Masaccio; Michel-Ange Buonarotti; Perin del Vaga; Philippe Bruneleschi; Philippe Lippi; Polidore de Caravage; Propertia de Rossi; Raphael Sanzio d'Urbin; Sandro Boticelli; Simon Memmi; Taddée Gaddi; Titian Uccello.
Title: ACADEMIE | DES | SCIENCES | ET DES | ARTS, | Contenant les Vies & les Eloges Historiques des | Hommes Illustres, | Qui ont excellé en ces Professions depuis environ quatre Siécles | parmy diverses Nations de l’Europe : |Avec leurs Pourtraits tirez sur des Originaux au Naturel, & plusieurs Inscriptions | funebres, exactement recueïlies de leurs Tombeaux | Par Isaac Bullart , Chevalier de l’Ordre de Saint Michel. | TOME PREMIER | {allegorical vignette, signed Abr. A Diepenbeke delineavit – Pet. Clouwet sculp.} | Imprimé par les soins de l’Autheur. | A AMSTERDAM, | Se vendent chez les Heritiers de Daniel Elzevier, 1682. || Pagination : [2] – h.t. / blank ; [2] – 1st vol. t.p. in black and red with vignette engraved by Pet. Clouwet after Abr. Diepenbeke / blank; [7] – dedication to Jacques Theodore de Brias {Jacques-Théodore de Bryas (Dutch, 1630 – 1694)}, [9] – preface, [2] – table demonstrative / stanza by Guilielmus Riverius, [2] vinette “Tardius sed grandius” with an elephant in ornamental frame / text; [2] – Advis au lecteur; [1, 2] – f.t. livre premiere, illustres politiques / blank; [2] – noms politiques / blank (A1, after f.t.), 3(A2)-421, [422-424] – table eloges. Collation: [*]6, **8, A6 B-Ggg4. (14 prelim. leaves, as in LIB-2675.2021; the LIB-2676.2021 copy has 12) Binding: 34.5 x 22 x 4.3 cm.34.5 x 22 x 4.3 cm, hardbound; full calf, raised bands. The title is drawn by Abraham van Diepenbeeck (Dutch, 1596 - 1675) and engraved by Peeter Clouwet (Flemish, 1629–1670). The first volume of a two-volume set contains 119 copperplate burin-engraved portraits of selected politicians, historians, jurists, writers, and Italian artists. 26 portraits engraved by Esme de Boulonois (French,1645 – 1681), 3 unsigned, and the rest engraved by Nicolas de Larmessin I (French, 1632 – 1694)Lavinia Vecellio, (Italian, 1530 – 1575), Titian' daughter, engraved by Lamerssin after Titian, Portrait of Jacques Auguste de Thou engraved by de Boulonois after Daniel Dumonstier. Politicians: Antoine Perrenot, Cardinal de Granvelle; Arnaud d'Ossat, Cardinal; Auger Busbeque; Bessarion, Cardinal; François Ximenes, Cardinal; George d'Amboise, Cardinal; Gille Albornoz, Cardinal; Guillaume de Croy; Guy du Faur de Pybrac; Jacques Auguste de Thou; Jean de Selve; Jean Zamoski; Jean de Barnevelt; Jean Armand du Plessis, Cardinal de Richelieu; Jule Mazarin, Cardinal; Michel de l'Hospital; Renaud Pole, Cardinal; Stanislas Hosius, Cardinal; Thomas Morus; Thomas Wolsey, Cardinal. Historians: Bertrand d'Argentré; Cæsar Baronius, Cardinal; Emanuel de Meteren; Enguerand de Monstrelet; Florimond de Remond; François Guicciardin; Fulve Ursin; Guillaume Camden; Henry Catherine d'Avila; Hubert Goltzius; Jacques Amiot; Jean Aventin; Jean Baptiste Platina; Jean Barclay; Jean Froissard; Jean Papirius Masson; Nicolas le Febure; Olivier de la Marche; Onuphre Panuinius; Pandolphe Collenuce; Paul Jove; Philippe de Commines; Pontus Heuterus; Regino Abbé de Prumy; Robert Gaguin; Wolfgang Lazius. Jurists: Alexandre de Tartagnis; André Alciat; André Tiraqueau; Antoine Augustin; Antoine le Febvre; Boece Epo; Charles du Moulin; François Bauduin; Gabriel Mudée; Jacques Cuias; Jason Mainus; Jean Wamese; Mathieu Wesenbec; Philippe Dece; Pierre Peckius; Pierre Pithou; Tibere Decian; Viglius de Zuichem. Writers/Linguists: Ange Politian; Demetrius Chalcondyles; Emanuel Chrysoloras; François Philelphe; François Raphelenge; Guillaume Postel; Jean Argyropilus; Jean Bocace; Jean Lascaris; Jean Passerat; Jean Pierius Valerianus; Jeanne Gray; Nicolas Clenard; Pierre Nannius; Rudolphe Agricola; Theodore Gaza. Italian painters, architects, and sculptors: André Mantegna; André Organa; André del Sarto; André Tafi; André Verrochio; Antoine de Correge; Antoine de Messine; Arnoud di Lappo; Baccio Bandinel; Balthazar Perusi; Bramante d'Urbin; Daniel Ricciarelli; Dominique Beccafumi; Donato; François Mazzuoli; François Primatici; Frere Philippe Lippi; Giorgion; Giotto; Jacques Barozzi de Vignole; Jean Antoine Licinio de Pordenone; Jean Cimabue; Jean d'Udine; Jean François Rustici; Jule Romain; Le Rosso; Leonard de Vinci; Masaccio; Michel-Ange Buonarotti; Perin del Vaga; Philippe Bruneleschi; Philippe Lippi; Polidore de Caravage; Propertia de Rossi; Raphael Sanzio d'Urbin; Sandro Boticelli; Simon Memmi; Taddée Gaddi; Titian Uccello. -
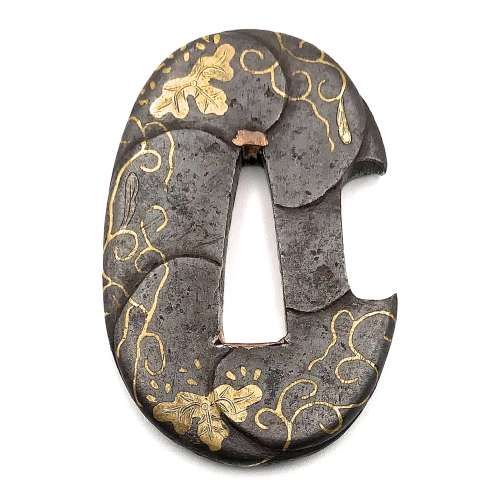

Small iron tsuba (tantō size) of oval form carved with imitation of six overlapping plates, decorated with paulownia blossoms, leaves, and tendrils in brass and copper hira-zōgan. Copper sekigane. Open kozuka hitsu-ana.
Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 50.5 x 34.0 x 4.9 mm.
-
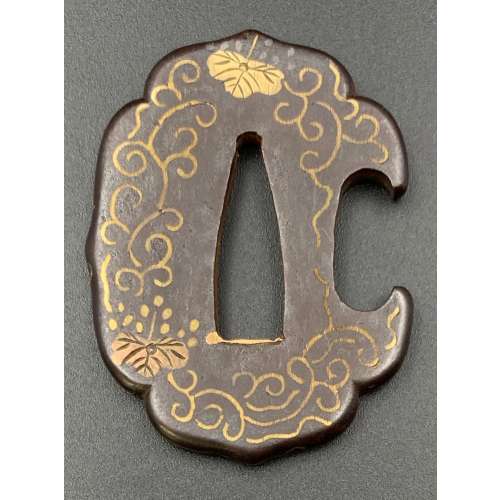

Small iron tsuba (tantō size) of aoi form with the design of paulownia leaves and blossoms in copper and brass flat inlay (hira-zōgan). Brass sekigane. Open kozuka hitsu-ana.
Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 53.4 x 40.7 x 4.4 mm; weight: 47.4 g
-
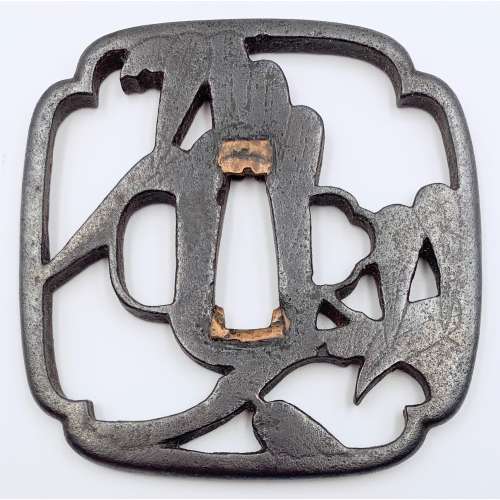 Iron tsuba of quatrefoil form with design of bamboo stems and leaves in openwork (sukashi) decorated with carving (kebori) . Copper sekigane. Early Edo period, late 17th century (Kanbun / Enppo era). First generation Kanshiro of Nishigaki school in Higo Province died in the sixth year of Genroku, 1693, at the age of 81). Height: 74.4 mm; Width: 74.2 mm; Centre thickness: 4.9 mm. Rounded rim. The design was quite popular among the Higo masters.
Iron tsuba of quatrefoil form with design of bamboo stems and leaves in openwork (sukashi) decorated with carving (kebori) . Copper sekigane. Early Edo period, late 17th century (Kanbun / Enppo era). First generation Kanshiro of Nishigaki school in Higo Province died in the sixth year of Genroku, 1693, at the age of 81). Height: 74.4 mm; Width: 74.2 mm; Centre thickness: 4.9 mm. Rounded rim. The design was quite popular among the Higo masters.
Kanshiro III, early 18th century (Sasano 1994 №267)

Matashichi I, late 17th century (Sasano 1994 №270)
The design of my tsuba closely resembles the one at the last example (Sasano 1994 №280), however, the form (mine is quatrefoil) and the execution (strength) are very different, which result in a very different spirit of my piece.
Shigemitsu II, early 18th century (Sasano 1994 №280)
-
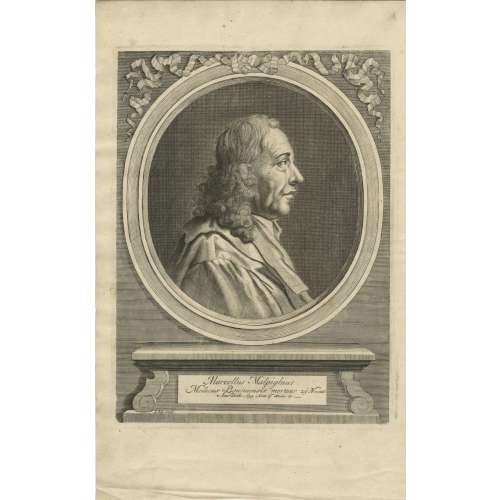

A portrait of Marcello Malpighi from his book Opera posthuma: figuris aeneis illustrata, quibus praefixa est ejusdem vita a seipso scripta, Londini:Churchill, 1697. Inscription: Marcellus Malpighius | Medicus Bononiensis mortuus 29 Novemb. Anno Dom. 1694. Anno aetatis 67. I. Kip. sculp.
Marcello Malpighi (10 March 1628 – 29 November 1694) was an Italian biologist and physician, who is referred to as the "Father of microscopical anatomy, histology, physiology and embryology" [Wikipedia].
From European Journal of Anatomy 22(5):433-439 · September 2018, an article by Sanjib Ghosh and Ashutosh Kumar 'Marcello Malpighi (1628-1694): Pioneer of microscopic anatomy and exponent of the scientific revolution of the 17th Century': Italian anatomist and an eminent scientist who significantly contributed to the advancement of the anatomical sciences in the 17th century. Malpighi was one of the first to use the compound microscope (an instrument designed by Galileo in 1609) and made the most important discovery of his life in 1661 when he identified capillaries as connecting vessels between small arteries and veins in the lungs. Malpighi thus provided the missing link in William Harvey's theory of blood circulation. He made significant contributions in the field of embryology based on his observations on chick embryo, and his efforts provided deep insights into the development of the heart and the nervous system. His communications based on microscopic studies scripted valuable details on the structural organization of organs like the liver, kidney and spleen. He identified the hepatic lobule as the fundamental unit of the liver and noted that bile was being secreted by these lobules and not from the gall bladder (the popular belief then). In the kidney, he discovered the glomerulus (Malpighian Corpuscle) and was the first to observe the convoluted tubules in the renal cortex. He was the first to describe the presence of lymphatic bodies (Malpighi's Corpuscle) in the spleen. Although he was exceedingly successful in his scientific activities, his life was fraught with unfortunate events and savage criticism from detractors arising out of professional jealousy and personal feuds. Nevertheless, his exploits were instrumental in understanding the human microscopic anatomy (histology) and his accomplishments have etched his name in the pages of medical science forever.
The portrait was engraved by Johannes "Jan" Kip (1652/53, Amsterdam – 1722, Westminster) - a Dutch draftsman, engraver and print dealer.
-
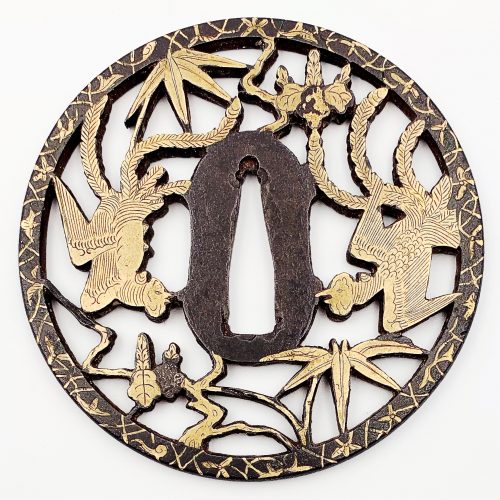

Iron tsuba of round form pierced (sukashi) and inlaid in flat (hira-zōgan) and cast brass (suemon-zōgan), details carved in kebori, with design of two phoenixes, bamboo, and paulownia leaves and flowers (kiri-mon) on both sides. According to seller: Bizen-Yoshirō school (or Heianjō school). Unsigned.
Momoyama period. End of the 16th - beginning of the 17th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 99.5 mm; Thickness: 2.1 mm at centre; 4.3 mm at the rim. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan), "bamboo teamed with paulownia blossoms or with paulownia and the phoenix, in reference to the Chinese legend that the phoenix perches only on the paulownia and eats only the bamboo". Citation from http://www.clevelandart.org/art/1986.2.1: "The immense heraldic birds on display [...] reflect the Momoyama era's spirit of newly gained self-confidence and an affinity for grand expressive statements in painting, architecture, the textile and ceramic arts, as well as garden design. While that period preceded the arrival of prosperity, it clearly marked an extraordinary moment in Japanese cultural history, one frequently compared with the twelfth century of the Heian period. [...] Rather than an emblem of immortality, as it is in Western lore, in Japan, the phoenix evolved out of its origins in Chinese mythology to become, by the sixteenth century, an auspicious symbol of political authority. Together with clusters of the distinctively shaped paulownia leaves, this long-tailed, mythical bird [...] proclaiming an air of graceful command". -
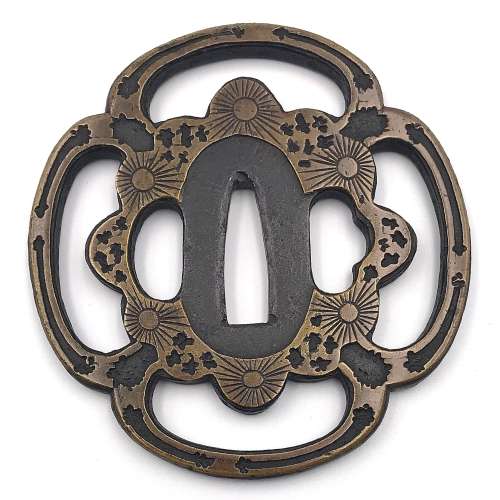

Iron tsuba of mokkō form (mokkōgata) pierced (sukashi) and inlaid with precast dark brass inlay (taka-zōgan) with somewhat abstract/geometrical design that can be liberally described as pines, mist, and snow.
Momoyama or early Edo period. End of the 16th - beginning of the 17th century. Heianjō school. Unsigned. Dimensions: 86.8 x 82.9 x 4.5 mm. -
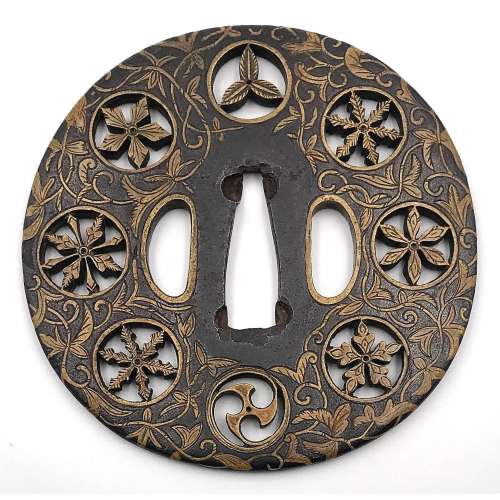 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 6 hours depicting tomoe (comma). Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). Attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa himself. Unsigned. The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: Diameter 82.0 mm, thickness 3.8 mm at seppa-dai, 3.4 mm at rim.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 6 hours depicting tomoe (comma). Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). Attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa himself. Unsigned. The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: Diameter 82.0 mm, thickness 3.8 mm at seppa-dai, 3.4 mm at rim. -
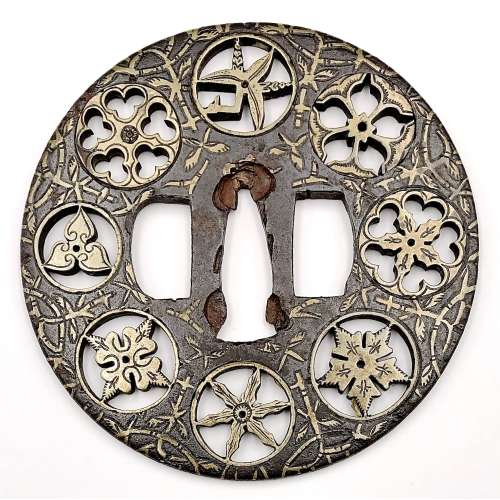

Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana could have been trimmed with brass now lacking. Nakago-ana of triangular form, possibly enlarged, with copper sekigane. All typical emblems with bellflower, two variations on suhama theme, and 3, 4, 5, and 6-poinitng mon variations. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours depicting water plantain (omodaka).
“Omodaka was also called shōgunsō (victorious army grass); because of this martial connotation, it was a design favored for the crests of samurai families” [Family crests of Japan, Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, California]. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: Height: 81.4 mm; width: 81.2; thickness 3.8 mm at seppa-dai. -
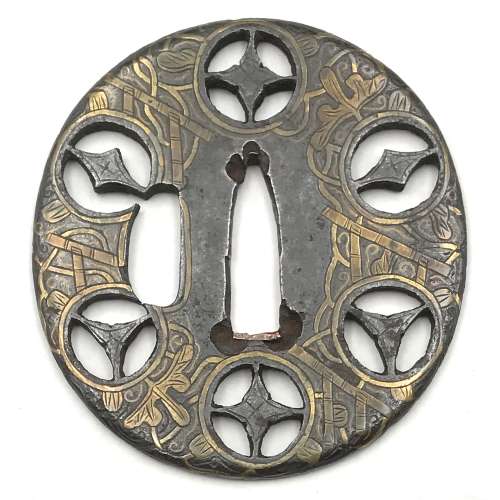

Tsuba of oval form decorated with vines, tendrils, and leaves on trellis in brass inlay with details carved in kebori, and pierced with six family crests (mon) with two, three and four pointing stars in openwork, each outlined with brass wire and carved in kebori. Original hitsu-ana outlined with brass wire was probably enlarged later. Copper sekigane.
Momoyama to early Edo period (end of the 16th - beginning of the 17th century). Dimensions: 68.3 x 64.5 x 3.4 mm. -
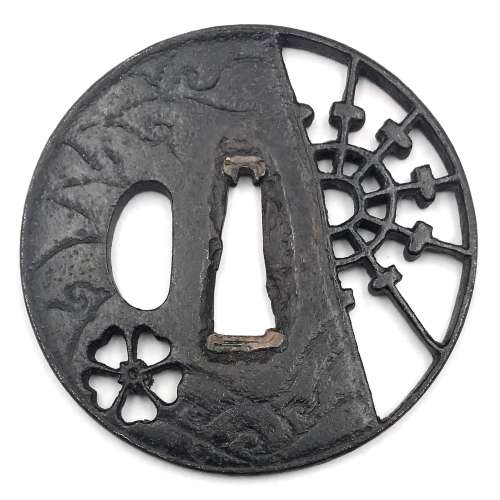 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of sea waves in low relief carving (kebori) and pierced with design of cherry blossom in negative silhouette (in-sukashi) and water wheel in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi). The solid portion of the plate has a shallow groove just before the edge. Copper sekigane. School attribution is unclear. Unsigned. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. Dimensions: Height: 70.3 mm, width: 71.1 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 4.4 mm, at rim 4.1 mm. Provenance: Robert E. Haynes, Mark Weisman. This is what shibuiswords.com says about this tsuba:
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of sea waves in low relief carving (kebori) and pierced with design of cherry blossom in negative silhouette (in-sukashi) and water wheel in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi). The solid portion of the plate has a shallow groove just before the edge. Copper sekigane. School attribution is unclear. Unsigned. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. Dimensions: Height: 70.3 mm, width: 71.1 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 4.4 mm, at rim 4.1 mm. Provenance: Robert E. Haynes, Mark Weisman. This is what shibuiswords.com says about this tsuba:"A very unusual iron plate tsuba. The solid plate is carved with waves on both sides. A cherry bloom in sukashi, lower left, and the right third of the plate in openwork with design of a water wheel. The rim with some iron bones. The hitsu-ana is original but the shape may have been slightly changed. One would expect this to be the work of the early Edo period, but the age of the walls of the sukashi would suggest that this is a work of the middle Muromachi period. This must be the forerunner for the Edo examples we see of this type of design." (Haynes)
I managed to find a look-a-like tsuba in Haynes Catalog #5, 1983, pp. 20-21, №44: "Typical later Heianjo brass inlay example. Ca. 1725. Ht. 7 cm., Th. 4.5 mm., $100/200".We see that the plate design of both tsuba is the same, and the only difference is the trim. It would be logical to assume that both pieces were made at about the same time, rather than 225 years apart. To be fair, let's accept that they were made in Momoyama period.
Haynes Catalog #5, 1983, pp. 20-21, №44.
-

Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of keys to the storehouse of the gods in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane.
Unsigned. Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 71.0 x 70.9 x 6.0 mm.Merrily Baird, Symbols..: The Key to the Storehouse of the Gods, one of the Myriad Treasures.
-
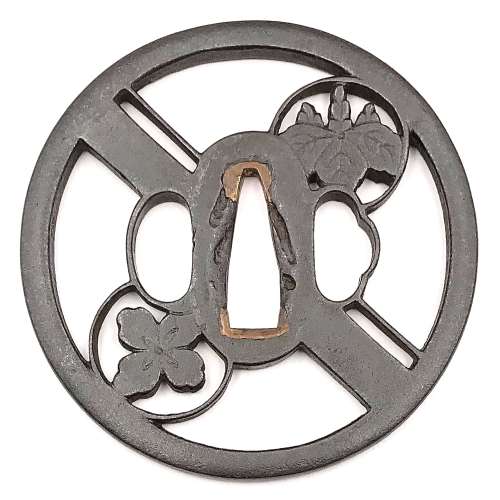 Iron tsuba of round form with design of double crossbar and two family crests (hikiryo-ni-kamon) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Owari school. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun / Enppo era). Height: 80.9 mm. Width: 80.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.0 mm. Center thickness: 4.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 172: "A paulownia and a clover are diagonally opposite two crossbars. This expressive design suggests a Higo origin, but the iron and the finish are certainly of the Owari school. Work of this nature may have been influenced by Hayashi Matashichi (1613-1699)."
Iron tsuba of round form with design of double crossbar and two family crests (hikiryo-ni-kamon) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Owari school. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun / Enppo era). Height: 80.9 mm. Width: 80.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.0 mm. Center thickness: 4.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 172: "A paulownia and a clover are diagonally opposite two crossbars. This expressive design suggests a Higo origin, but the iron and the finish are certainly of the Owari school. Work of this nature may have been influenced by Hayashi Matashichi (1613-1699)." -

Iron tsuba of round form (tsurumaru) decorated with a design of crane and pines, or "nesting crane (sugomori-tsuru)" in openwork (sukashi). Details carved in kebori. Rounded rim.
Size: 74.7 x 69.8 x 4.8 mm.
Unsigned.
Edo period, ca. 17th century.
NBTHK Certificate № 463485. The certificate says it's a Higo School piece. The design was popular in both Akasaka and Higo schools. The Akasaka example: at Kodogu and tsuba. International collections not published in my books. (Toso Soran). Ph. D. Kazutaro Torigoye, 1978, p. 246: "Late Edo. Jiyūgata. Sined: Akasaka Tadanori saku."The Higo example can be found at Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 69, №56: Sugomori-tsuru sukashi-tsuba (Nesting Carne). Mumei: Matashichi (1st generation), early 17th century.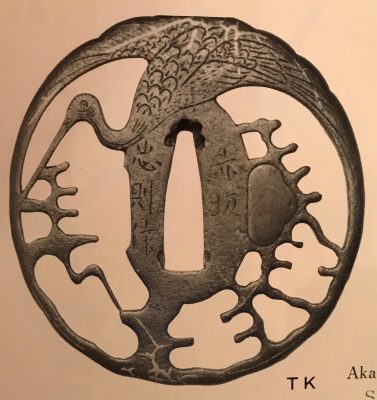
Torigoye, 1978, p. 246. Late Akasaka.
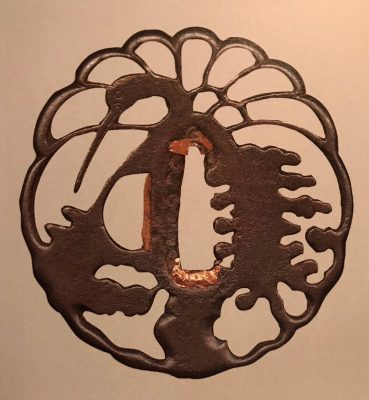
Kurogane no hana, 2014, p. 69, №56. Higo tsuba.
-
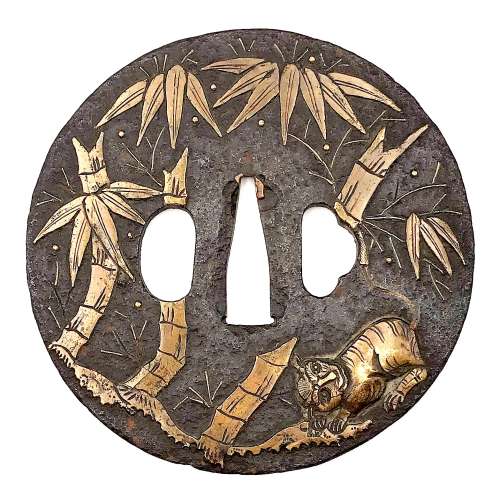 Large and thin iron tsuba of round form (width > height) decorated with the design of a tiger sheltering in bamboo in suemon-zōgan brass inlay. A fragment of tail inlay is missing. Bamboo leaves on the reverse. According to Merrily Baird [Symbols, p. 166], tiger sheltering in bamboo symbolizes "weak giving shelter to the strong". Momoyama period. Unsigned. Dimensions: 90.8 x 91.2 x 3.4 (center), 3.1 (rim) mm. Custom wooden box. NBTHK Certificate № 4001593.
Large and thin iron tsuba of round form (width > height) decorated with the design of a tiger sheltering in bamboo in suemon-zōgan brass inlay. A fragment of tail inlay is missing. Bamboo leaves on the reverse. According to Merrily Baird [Symbols, p. 166], tiger sheltering in bamboo symbolizes "weak giving shelter to the strong". Momoyama period. Unsigned. Dimensions: 90.8 x 91.2 x 3.4 (center), 3.1 (rim) mm. Custom wooden box. NBTHK Certificate № 4001593. -
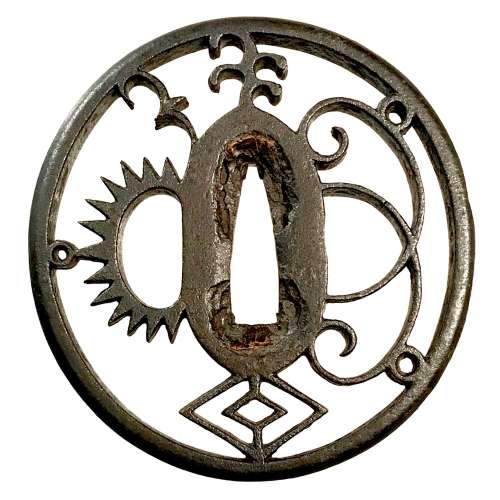 Iron tsuba of round form with a dense combination of symbols: slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol), also often described as "tokei" or "clock gear", wild goose in flight, bracken, and lozenges in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Edo period.
Iron tsuba of round form with a dense combination of symbols: slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol), also often described as "tokei" or "clock gear", wild goose in flight, bracken, and lozenges in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Edo period.Size: 76.0 x 72.6 x 6.2 mm
Unsigned.
For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91.
-
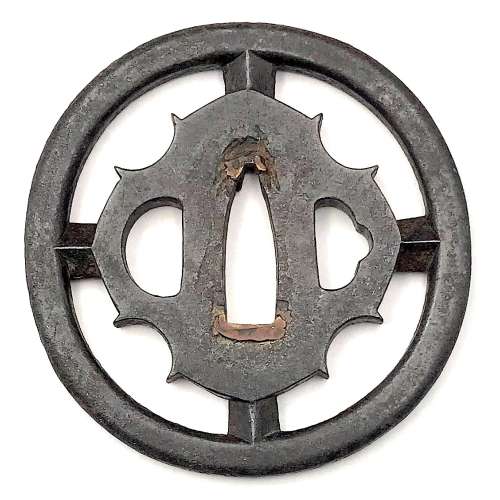 Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Edo period.
Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Edo period.Size: 77.7 x 76.1 x 6.7 mm.
For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba" by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91.


