Magazine article by
Edgar Jepson: The Iron Tsuba of Japan (Section: Oriental Art), published in volume Vol. 70 (September–December) of The Connoisseur: An Illustrated Magazine for Collectors, Vol. 70 (September–December); pp. 143-152 / C. Reginald Grundy [ed.] — London: Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, 1924.
Owner's half black morocco, gilt lettering to spine, blue cloth boards. Two volumes bound together without original covers. Size 28.5 x 22 cm.
Vol. 1: The Connoisseur | An Illustrated Magazine | For Collectors | Edited by C. Reginald Grundy | Vol. LXIX. | (MAY—AUGUST, 1924) | LONDON | Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the | Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, | at 1, Duke Street, St. James's, S.W. 1 | 1924 || Pp.: [i-ii] iii-xviii [xix] [1, 2 - plate] 3-249 [250].
Vol. 2: The Connoisseur | An Illustrated Magazine | For Collectors | Edited by C. Reginald Grundy | Vol. LXX. | (SEPTEMBER—DECEMBER, 1924) | LONDON | Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the | Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, | at 1, Duke Street, St. James's, S.W. 1 | 1924 || Pp.: [i-ii] iii-xxii [2 blanks] [1, 2 - plate] 3-261 [262].
The Iron Tsuba of Japan by Edgar Jepson
The heart of Japan was in the sword. However admirable may be the paintings, the prints, the netsuke, the lacquer, or the bronzes of the Japanese masters, the supreme artistic achievements of Japan were the blades of Masamune, Muramasa, Sadamune, and Rai Kunitsugu. But not a little of the heart of Japan went also in the tsuba, the guard which protected the hand that wielded the blade, into the iron tsuba of the fighting Samurai. Beside the forgers of the iron tsuba of Japan the ironsmiths of the rest of the world have been mere children.
The earliest tsuba were of bronze or copper, often gilded. It is probable that they were replaced by iron tsuba during the Kamakura period, the great fighting era, which lasted from
A.D. 1185 to 1333. During the later half of the twelfth century leather tsuba, strengthened by thin iron plates or a metal rim, also replaced the bronze and copper tsuba. It was at this time that a family of armourers of the name of Masuda, and in particular Masuda Munesuke, the founder of the Myochin family, began to forge iron tsuba — thin, round plates of great hardness and density. But it is probable that no tsuba perforated with a view to decorative effects were forged before the end of the fourteenth century.
These fourteenth-century tsuba are exceedingly rare in England. I have seen none in the museums, none in the famous collections that have been sold during the last ten years. Those photographed in Herr Oeder's book might easily be the fifteenth century. No. 1 is a curious cup-shape tsuba decorated with a bronze and copper inlay. No. 2, with its edges curiously twisted in the forging, looks like Myochin work. But it is not of the Myochin iron.
The Myochin family produced some of the greatest ironsmiths of Japan. Armourers first of all, tsubasmiths, forgers of sake-kettles, articulated reptiles, crustacea, and insects — everything that can be done with iron they did; they pushed their medium to its limit. They were forging iron tsuba in 1160, and they were still forging them in 1860. And it was their own iron, or rather their own steel. They discovered the secret of it early, and they kept that secret in the family for all those hundreds of years. There is no mistaking a Myochin tsuba: balance it on your finger and tap it with a piece of metal, always it gives forth a clear bell-like ring that you get from the work of no other ironsmith, Japanese or European. Always the Myochin tsuba is before everything a protection to the hand of the swordsman; to that everything is, as it should be, subordinated. No. 3 is a Myochin tsuba of the fifteenth century, and probably of the early fifteenth century. No. 4, by Myochin Munetaka, perforated with a grotesque figure, is an example of that twisting and twisting of the iron in the forging till it forms a pattern like the grain of wood. The Myochin smiths invented these wood-grain tsuba, and no other smiths equalled them in their forging.
In the sixteenth century, the fighting tsuba was probably at its best. It was a century of great tsubasmiths. Then the first Nobuiye, whose tsuba fetched £100 apiece,
circa 1800, in Japan, and the first Kaneiye flourished. No. 5 is a tsuba forged by a great smith, Iyesada of Sotome, in the manner of Nobuiye I, decorated with the karakusa tendrils that Nobuiye delighted in, with lightning and clouds. No. 6 is a guard of Sanada Tembo, the chief smith of the Tembo family, stamped, punning fashion, with the character Tembo. Akin to the Tembo tsuba were those of the Kiami and Hoan smiths. Then also the Heianjo smiths and the Owari smiths, especially those of Nagoya and the Yamakichi family, forged their strongest tsuba. Those of the Yamakichi were tested after the forging by being pounded in iron mortars — at least, so the legend runs. But they were a sternly utilitarian family, and I have never seen a Yamakichi tsuba of any beauty.
In the later half of the fifteenth century arose the fashion of decorating tsuba with an inlay, zogan, of bronze. The Heianjo tsuba, forged at Kyoto in the latter half of the fifteenth and the beginning of the sixteenth century, were often thus inlaid. The earliest of them were called "Onin", of which No. 7 is an example. In addition to the bronze inlay around the edge, it is inlaid with a representation, some say, of snow; others say, of the duckweed on a pond. No. 8 is probably a Heianjo tsuba, but I am not quite sure about it. The inlaid acacia branches might be very early Shoami work. But to judge by the iron, it is a fifteenth-century tsuba; and the authorities place the beginning of the Shoami school not later than early in the sixteenth century.
No. 10 is an example of the Fushimi-zogan, a flat inlay of a light-coloured bronze. These tsuba took their name from the fact that they were first forged at Fushimi, in Yamashiro, in the sixteenth century. It is of the type known as Mon-zukashi, perforated with crests (mon)
à jour. The Yoshiro-zogan tsuba were also first forged at Fushimi by Yoshiro Naomasa. They were distinguished from the Fushimi-zogan by the fact that their inlay was generally a little raised-not always-for the inlay of No. 9, a tsuba forged by a later nineteenth-century Yoshiro, is quite flat. It is an interesting tsuba, for, with its decoration grown florid and excessive, it marks the intermediate stage between the simple and delightful designs of the genuine fighting tsuba and the elaborate pictures in gold and silver on the tsuba of the eighteenth-century smiths of Awa and Kyoto, which have become mere ornaments of the goldsmith.
The Gomoku-zogan (No. 11) tsuba were probably first forged earlier than the Fushimi and Yoshiro-zogan tsuba. This inlay, in slight relief, is a representation in a light-coloured bronze and copper of twigs caught in the eddies of streams. The seventeenth century and early eighteenth century were the great periods of perforated tsuba. The designs, and they are often admirable, are for the most part in plain fretwork; but they are also chased. No. 12, a crane under an acacia, is a tsuba of a Higo smith, great forgers of fighting tsuba during this period. These smiths also excelled in nunome zogan, a very thin gold and silver inlay, with which they further decorated their perforated guards. The smiths of the Umetada and Shoami families also forged iron tsuba during this period; but their designs, though sometimes pleasing enough, are rarely fine. The best work of Myoju Umetada is in sentoku, not iron.
The Choshu smiths, coming later, surpass the perforated guards of both the Umetada and Shoami smiths in beauty of design. No. 13, a lotus in the round, not only fretwork, but also engraved, is a good example of the admirable balance they so often attained in their designs. It is a sufficiently realistic lotus, but yet of a delightful simplicity. In considerable contrast is No. 14, the dragon by Soheishi Soten — one of the only two authentic tsuba of his forging known — the first forger of hikone-bori tsuba, which were in extraordinary favour in Japan during the eighteenth century, and illustrated every important event in Japanese history. It is on the elaborate side, but fine, strong work, and an excellent guard to the hand, for the lighter and more open part, which gives the design its admirable balance, is on the inside, and not exposed to the full swing of an opponent's blade.
A few years ago there was a tendency to decry the Namban tsuba as having sprung too directly from foreign sources. But though the original suggestion may have been Chinese, or, as some say, Portuguese, the Japanese made it entirely their own, as characteristically Japanese as anything can well be, but, it must be admitted, of a decadent period. The school took its rise at the beginning of the seventeenth century, and the early tsuba were forged of a specially hard iron, the Wootz, imported from Southern India. No. 15, the signs of the Zodiac, is an excellent tsuba from the fighting point of view. Both it and No. 16 are of quite charming, if elaborate, design, and both of them, with their delicate scroll-work, so astonishingly undercut, are the very last word in the work of the ironsmith-veritable iron lace.
To return to the simpler perforated tsuba, the smiths of Akasaka, a suburb of Tokyo, produced probably the most charming designs. Their style derives considerably from the Higo smiths, and their earlier fighting tsuba are very like the Higo tsuba. But always their work was just a little lighter than that of the Higo smiths, and in the end they moved right away from them and became the forgers of very light guards indeed.
No. 17, is a representation of the Hiyokudori, the fabulous double bird, in which were reincarnated the souls of the two lovers, Gompachi and Komurasaki; and No. 18, “the tsuba of a hundred ducks "— there are about forty — are characteristic designs of the school. In the work of the Akasaka smiths the balance, which makes the design of a good tsuba so admirable and delightful, attains its height. This admirable balance seems often to be obtained by a deliberate sacrifice of symmetry. About nine hundred and ninety-nine European ironsmiths out of a thousand would have made the right and left sides of the Hiyoku-dori line by line, and perforation by perforation, exactly alike; he would have cut out exactly as many ducks on the one side of “the tsuba of a hundred ducks” as on the other, and made each duck on the right side correspond exactly in position and attitude with a duck on the left side. By variations the tsubasmith attained a finer balance, almost a higher symmetry.
No. 19, often called by collectors the "rose-window" tsuba, but really a stylised chrysanthemum, is a favourite design of the Akasaka smiths, but Hizen work and inlaid in the Hizen manner with gold nunome. No. 20 is a Satsuma tsuba of the middle period. The Satsuma smiths of the nineteenth century produced probably the most ornate of all the iron guards, for the most part calibashes and beans with their leaves and tendrils realistic in the extreme, but of charming design.
Few crafts have been carried further than that of the tsubasmith; few crafts working in a difficult medium have handled more subjects with greater feeling for beauty or greater liveliness of fancy. It is interesting to note again and again how school influences school, and smith influences smith. But, as in all the applied arts, the finest tsuba were forged by men who never lost sight of the purpose of a tsuba, that it is before everything a protection to the hand, and never subjected that purpose to a passion for virtuosity.
Illustrations:
No 1. FOURTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA, WITH BRONZE AND COPPER INLAY
No. 2. FOURTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA, RESEMBLING MYOCHIN WORK
No. 3. MYOCHIN TSUBA, FIFTEENTH CENTURY
No. 4. MYOCHIN TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY
No. 5. SIXTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA
No. 6. SIXTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA BY IYESADA OF SOTOME BY SANADA TEMBO
No. 7. ONIN TSUBA
No. 8. HEIANJO (?) TSUBA
No. 9. YOSHIRO TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY
No. 10. FUSHIMI-ZOGAN, NINETEENTH CENTURY
No. 11.- GOMOKU-ZOGAN, SIXTEENTH CENTURY
No. 12. HIGO TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY
No. 13. CHOSHU TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY
No. 14. SOTEN TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY
No. 15. NAMBAN TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY
No. 16. NAMBAN TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY
Nos. 17. AND 18. AKASAKA TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY
No. 19. HIZEN TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY
No. 20. SATSUMA TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY
 Publisher's flapped portfolio 32.8 x 26.8 cm, gilt-ruled and gilt-lettered quarter faux-parchment waxed paper over brown paper boards with pasted illustration after von Bayros within gilt arabesque frame. Possibly published in Vienna by Heinrich Conrad in 1905 or 1908. The portfolio contains the title page with a vignette and 15 loose wove paper sheets 32 x 26.2 cm of collotype reproductions after drawings by Franz von Bayros. Cover gilt lettering: Choisÿ | le Conin | Erzählungen | am | Toiletten- | tische || Title-page: Erzählungen | am Toilettentische | von | CHOISY LE CONIN | {vignette} || Title-page verso: Inhalt: | 1. Die Tabaksdose | 2. Viola de Gamba | 3. Der Bote | 4. Nicht drängeln, Kinder! | 5. Die blaue Feder | 6. O what a pretty like-place! | 7. Die Sonnenuhr |8. Der Temel der der Cotÿs | 9. Der Fetischist | 10. Jupiter und Europa | 11. Die Witwe | 12. Paroxÿsme-erotique | 13. Der Rivale | 14. Die rote Lehrerin | 15. Tantalus | Nicht im Handel. || Catalogue raisonné: The amorous drawings of the Marquis von Bayros / Part I and II. — NY: Cythera Press, 1968; pp. 95-111 [LIB-2246.2019]
Publisher's flapped portfolio 32.8 x 26.8 cm, gilt-ruled and gilt-lettered quarter faux-parchment waxed paper over brown paper boards with pasted illustration after von Bayros within gilt arabesque frame. Possibly published in Vienna by Heinrich Conrad in 1905 or 1908. The portfolio contains the title page with a vignette and 15 loose wove paper sheets 32 x 26.2 cm of collotype reproductions after drawings by Franz von Bayros. Cover gilt lettering: Choisÿ | le Conin | Erzählungen | am | Toiletten- | tische || Title-page: Erzählungen | am Toilettentische | von | CHOISY LE CONIN | {vignette} || Title-page verso: Inhalt: | 1. Die Tabaksdose | 2. Viola de Gamba | 3. Der Bote | 4. Nicht drängeln, Kinder! | 5. Die blaue Feder | 6. O what a pretty like-place! | 7. Die Sonnenuhr |8. Der Temel der der Cotÿs | 9. Der Fetischist | 10. Jupiter und Europa | 11. Die Witwe | 12. Paroxÿsme-erotique | 13. Der Rivale | 14. Die rote Lehrerin | 15. Tantalus | Nicht im Handel. || Catalogue raisonné: The amorous drawings of the Marquis von Bayros / Part I and II. — NY: Cythera Press, 1968; pp. 95-111 [LIB-2246.2019] Softcover, 258 x 166 mm, publisher’s olive French flapped wrappers in owner’s glassine dustcover, edges untrimmed, some pages uncut, printed on thick wove paper with watermark “Hollande van Gelder Zonen”, in a slipcase. Pp.: [1-10] 11-129 [5], pages in wrappers included in the count, total 67 leaves; two-tone woodcuts by Jean-Gabriel Daragnès within the pagination. Title-page (red and black, in a double-fillet frame): PAUL VERLAINE | femmes | ÉDITION ORNÉE | DE TRENTE ET UNE | GRAVURES S/ BOIS | {vignette} | (under the bottom frame) PARIS | 1917 | {red triangle} || Limitation: Il a été tiré de cet ouvrage : 11 15 Exemplaires sur vieux papier de Japon numérotés de I à XV; 15 20 Exemplaires sur papier de Chine numérotés de XVI à XXXV; auxquels on a joint une suite des fumés sur même papier. 250 Exemplaires sur papier vélin de Hollande Van Gelder Zonen numérotés de 1 à 250. Après le tirage les bois ont été détruits. № 1. Numbers “15” and “20” corrected manually by Daragnès (per Dutel). This is copy № 1 of vélin de Hollande print run. Catalogue raisonné: Dutel II: № 295; Nordmann II № 544. Seller’s description: Un volume broché in-8° sous couverture illustrée et rempliée. Etui cartonné. Illustré de 31 gravures sur bois en camaïeu, attribuées à DARAGNES, la plupart très libres, dont 18 à pleine page. Tiré à [226 ou 285] ex. numérotés. 1 des [200 ou 250] sur Hollande Van Gelder Zonen. Le nôtre porte le n°1. (Dutel : 295. Pia : 501. Carteret : IV, 392 : Belle édition rare, très estimée ». Monod : 11086). Dorgelès commenta ainsi ces illustrations : « Dans ces nus voluptueux et tragiques, qui semblent à la fois s’aimer et se haïr, on retrouve la même frénésie amère qui tourmente les poèmes interdits de Verlaine » (in Catalogue de livres... Daragnès, Drouot 1924, n°55). Très rares rousseurs. TRES BON EXEMPLAIRE, toujours recherché. Contributors: Paul Verlaine (French, 1844 – 1896) – author. Jean-Gabriel Daragnès (French, 1886 – 1950) – artist/publisher.
Softcover, 258 x 166 mm, publisher’s olive French flapped wrappers in owner’s glassine dustcover, edges untrimmed, some pages uncut, printed on thick wove paper with watermark “Hollande van Gelder Zonen”, in a slipcase. Pp.: [1-10] 11-129 [5], pages in wrappers included in the count, total 67 leaves; two-tone woodcuts by Jean-Gabriel Daragnès within the pagination. Title-page (red and black, in a double-fillet frame): PAUL VERLAINE | femmes | ÉDITION ORNÉE | DE TRENTE ET UNE | GRAVURES S/ BOIS | {vignette} | (under the bottom frame) PARIS | 1917 | {red triangle} || Limitation: Il a été tiré de cet ouvrage : 11 15 Exemplaires sur vieux papier de Japon numérotés de I à XV; 15 20 Exemplaires sur papier de Chine numérotés de XVI à XXXV; auxquels on a joint une suite des fumés sur même papier. 250 Exemplaires sur papier vélin de Hollande Van Gelder Zonen numérotés de 1 à 250. Après le tirage les bois ont été détruits. № 1. Numbers “15” and “20” corrected manually by Daragnès (per Dutel). This is copy № 1 of vélin de Hollande print run. Catalogue raisonné: Dutel II: № 295; Nordmann II № 544. Seller’s description: Un volume broché in-8° sous couverture illustrée et rempliée. Etui cartonné. Illustré de 31 gravures sur bois en camaïeu, attribuées à DARAGNES, la plupart très libres, dont 18 à pleine page. Tiré à [226 ou 285] ex. numérotés. 1 des [200 ou 250] sur Hollande Van Gelder Zonen. Le nôtre porte le n°1. (Dutel : 295. Pia : 501. Carteret : IV, 392 : Belle édition rare, très estimée ». Monod : 11086). Dorgelès commenta ainsi ces illustrations : « Dans ces nus voluptueux et tragiques, qui semblent à la fois s’aimer et se haïr, on retrouve la même frénésie amère qui tourmente les poèmes interdits de Verlaine » (in Catalogue de livres... Daragnès, Drouot 1924, n°55). Très rares rousseurs. TRES BON EXEMPLAIRE, toujours recherché. Contributors: Paul Verlaine (French, 1844 – 1896) – author. Jean-Gabriel Daragnès (French, 1886 – 1950) – artist/publisher.![Insel-Almanach auf das Jahr 1907. Kalender für 1907. (with illustration by Franz von Bayros on p. 50). — 150 + [2] pp.](https://varshavskycollection.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/LIB-2250.2019-a-500x500.jpeg) Half-title: ÜBERREICHT VON | GILHOFER UND RANSCHBURG | SORTIMENT–, BÜCHER– UND KUNST– | ANTIQUARIAT | WIEN 1, BOGNERGASSE 2 || Title: Red letterpress lettering in black ornamental frame: Insel- | Almanach | auf das Jahr | 1907 || Pagination: [6] – h.t., frontis., title; [1-16] 17-150 [2], + 2 folding plates (op. p. 30 and 32), and 2 plates op. p. 50 (Franz von Bayros "Francine" for Die Bohème by Henri Murger) and 112 (colour). Binding: 17.3 x 9.9 cm; original olive paper wrappers with gilt lettering and elements to cover, lettering to spine. Catalogue raisonné: Heinz Sarkowski (1999): № 1986, pp. 329-30, with contents. Contributors: Gilhofer und Ranschburg – antiquarian bookstore in Vienna. Schröder, Rudolf Alexander (German, 1878 – 1962) – title and cover. Wieynk, Heinrich (German, 1874 – 1931) – typeset. Kippenberg, Anton Hermann Friedrich (German, 1874 – 1950) – editor. Brandstetter, Oscar (German, 1844 – ?) – printer.
Half-title: ÜBERREICHT VON | GILHOFER UND RANSCHBURG | SORTIMENT–, BÜCHER– UND KUNST– | ANTIQUARIAT | WIEN 1, BOGNERGASSE 2 || Title: Red letterpress lettering in black ornamental frame: Insel- | Almanach | auf das Jahr | 1907 || Pagination: [6] – h.t., frontis., title; [1-16] 17-150 [2], + 2 folding plates (op. p. 30 and 32), and 2 plates op. p. 50 (Franz von Bayros "Francine" for Die Bohème by Henri Murger) and 112 (colour). Binding: 17.3 x 9.9 cm; original olive paper wrappers with gilt lettering and elements to cover, lettering to spine. Catalogue raisonné: Heinz Sarkowski (1999): № 1986, pp. 329-30, with contents. Contributors: Gilhofer und Ranschburg – antiquarian bookstore in Vienna. Schröder, Rudolf Alexander (German, 1878 – 1962) – title and cover. Wieynk, Heinrich (German, 1874 – 1931) – typeset. Kippenberg, Anton Hermann Friedrich (German, 1874 – 1950) – editor. Brandstetter, Oscar (German, 1844 – ?) – printer. Title page: A | BIBLIOGRAPHY | OF | THE WRITINGS OF | JOSEPH CONRAD (1895–1920) | BY THOMAS J. WISE | ❦ | LONDON: | PRINTED FOR PRIVATE CIRCULATION ONLY | By Richard Clay & Sons, Ltd. | 1920 || Pagination: [i-viii] ix-xiii [xiv-xvi], [1, 2] 3-105 [106-112], frontispiece with tissue guard in collation; 128 pages total. Collation: 8vo; [A]-H8, 64 leaves total. Binding: 22.5 x 18 cm; terracotta paper boards, black lettering to front and spine; uncut. The device on the recto of the last leaf inscribed: The Ashley library. Privately printed. 1920. Insert: ALS from Thomas J. Wise dated 22/3/21 on watermarked paper (King of Kent | Extra Fine) with letterhead “Kirkstead”, 25 Heath Drive, Hampstead, N.W.3. The letter is a response to a request for two copies of Volume II of Wise’s Swinburne bibliography, which Wise promises to supply the next day to Stevens & Brown (founded in 1864, Literary and Fine Arts Agents). Limitation: 150 copies, private printing. Contributors: Joseph Conrad [Józef Teodor Konrad Korzeniowski] (British-Polish, 1857 – 1924) Wise, Thomas James (British, 1859 – 1937) – compiler, bibliographer. R. Clay & Sons Ltd. (London); Clay, Richard (British, 1789 – 1877) – publisher. The Ashley Library (London) – printer.
Title page: A | BIBLIOGRAPHY | OF | THE WRITINGS OF | JOSEPH CONRAD (1895–1920) | BY THOMAS J. WISE | ❦ | LONDON: | PRINTED FOR PRIVATE CIRCULATION ONLY | By Richard Clay & Sons, Ltd. | 1920 || Pagination: [i-viii] ix-xiii [xiv-xvi], [1, 2] 3-105 [106-112], frontispiece with tissue guard in collation; 128 pages total. Collation: 8vo; [A]-H8, 64 leaves total. Binding: 22.5 x 18 cm; terracotta paper boards, black lettering to front and spine; uncut. The device on the recto of the last leaf inscribed: The Ashley library. Privately printed. 1920. Insert: ALS from Thomas J. Wise dated 22/3/21 on watermarked paper (King of Kent | Extra Fine) with letterhead “Kirkstead”, 25 Heath Drive, Hampstead, N.W.3. The letter is a response to a request for two copies of Volume II of Wise’s Swinburne bibliography, which Wise promises to supply the next day to Stevens & Brown (founded in 1864, Literary and Fine Arts Agents). Limitation: 150 copies, private printing. Contributors: Joseph Conrad [Józef Teodor Konrad Korzeniowski] (British-Polish, 1857 – 1924) Wise, Thomas James (British, 1859 – 1937) – compiler, bibliographer. R. Clay & Sons Ltd. (London); Clay, Richard (British, 1789 – 1877) – publisher. The Ashley Library (London) – printer. One volume in-4o, 26.5 x 21 x 4.4 cm, bound by Durvand (signed) in yellow ¾ morocco over marbled boards outlined in gilt, spine with raised bands, gilt lettering, vignettes after Félicien Rops in compartments, top margin gilt, marbled endpapers, publisher’s wrappers preserved; enriched with 57 original prints after Félicien Rops and an etched portrait of Félicien Rops by Robert Kastor. Collation: 3 blanks, π4 (orig. front wrapper ‘En souscription…./Etudes sur…’, La tentation…/Érastène Ramiro..., h.t./justification, t.p/blank), 1-274 (paginated 1-215 [216]) χ2 plus 58 leaves of bound-in original prints by various printers on different papers, some on India paper pasted on vergé, with tissue guards, and 1 leave of manuscript ‘Table de gravures dans le texte’; back wrapper with ‘Table des gravures ajoutées’ manuscript to recto, original spine, 2 blanks. Title-page (red and black): Études sur quelques Artistes originaux | — | FÉLICIEN ROPS | par | ÉRASTÈNE RAMIRO | {fleuron} | PARIS | (left): G. PELLET | 51, Rue Le Peletier, 51 | (right): H. FLOURY | 1, Boulevard des Capucines, 1 | 1905 || Limitation: 125 copies, of which 100 copies on Japon à la forme and 25 copies 0n papier de Chine. Photographs here represent the original prints only. Contributors: Eugène Rodrigues-Henriques [Eugène Rodrigues, Erastène Ramiro] (French, 1853 –1928) – author. Félicien Rops (Belgian, 1833 – 1898) – artist. Robert Kastor (French, 1872 – 1935) – artist. Imprimerie Charles Hérissey (Évreux) – printer Gustave Pellet (French, 1859 – 1919) – publisher. Henri Floury (French, 1862 –1961) – publisher. Lucien Durvand (French, 1852 – 1924) – bookbinder.
One volume in-4o, 26.5 x 21 x 4.4 cm, bound by Durvand (signed) in yellow ¾ morocco over marbled boards outlined in gilt, spine with raised bands, gilt lettering, vignettes after Félicien Rops in compartments, top margin gilt, marbled endpapers, publisher’s wrappers preserved; enriched with 57 original prints after Félicien Rops and an etched portrait of Félicien Rops by Robert Kastor. Collation: 3 blanks, π4 (orig. front wrapper ‘En souscription…./Etudes sur…’, La tentation…/Érastène Ramiro..., h.t./justification, t.p/blank), 1-274 (paginated 1-215 [216]) χ2 plus 58 leaves of bound-in original prints by various printers on different papers, some on India paper pasted on vergé, with tissue guards, and 1 leave of manuscript ‘Table de gravures dans le texte’; back wrapper with ‘Table des gravures ajoutées’ manuscript to recto, original spine, 2 blanks. Title-page (red and black): Études sur quelques Artistes originaux | — | FÉLICIEN ROPS | par | ÉRASTÈNE RAMIRO | {fleuron} | PARIS | (left): G. PELLET | 51, Rue Le Peletier, 51 | (right): H. FLOURY | 1, Boulevard des Capucines, 1 | 1905 || Limitation: 125 copies, of which 100 copies on Japon à la forme and 25 copies 0n papier de Chine. Photographs here represent the original prints only. Contributors: Eugène Rodrigues-Henriques [Eugène Rodrigues, Erastène Ramiro] (French, 1853 –1928) – author. Félicien Rops (Belgian, 1833 – 1898) – artist. Robert Kastor (French, 1872 – 1935) – artist. Imprimerie Charles Hérissey (Évreux) – printer Gustave Pellet (French, 1859 – 1919) – publisher. Henri Floury (French, 1862 –1961) – publisher. Lucien Durvand (French, 1852 – 1924) – bookbinder. Title: GESCHICHTEN | AUS | ARETINO | MIT FÜNFZEHN BILDERN | VON | CHOISI-NÉRAC | NICHT IM HANDEL | GEDRUCKT FÜR HEINRICH CONRAD | UND SEINE FREUNDE | SIENA 1907 || Collation: 8vo; 1-128 137; frontispiece, t.p. and 14 plates, extraneous to collation. Pagination: [2] f.t. / blank, 3-203 [2], il. Binding: Full cream vellum, ruled with gilt double-fillet, grey label with gilt lettering to spine. Bookplate by von Bayros Par Avi Cigno to front pastedown. Note: Private edition of Aretino's Ragionamenti in German as Geschichten aus Aretino by translater and publisher Heinrich Conrad (German, 1866 – 1918), whose real name was Hugo Storm, this copy №394, illustrated by Franz von Bayros (Austrian, 1866 – of Choisi-Nérac.
Title: GESCHICHTEN | AUS | ARETINO | MIT FÜNFZEHN BILDERN | VON | CHOISI-NÉRAC | NICHT IM HANDEL | GEDRUCKT FÜR HEINRICH CONRAD | UND SEINE FREUNDE | SIENA 1907 || Collation: 8vo; 1-128 137; frontispiece, t.p. and 14 plates, extraneous to collation. Pagination: [2] f.t. / blank, 3-203 [2], il. Binding: Full cream vellum, ruled with gilt double-fillet, grey label with gilt lettering to spine. Bookplate by von Bayros Par Avi Cigno to front pastedown. Note: Private edition of Aretino's Ragionamenti in German as Geschichten aus Aretino by translater and publisher Heinrich Conrad (German, 1866 – 1918), whose real name was Hugo Storm, this copy №394, illustrated by Franz von Bayros (Austrian, 1866 – of Choisi-Nérac. Description: owner’s quarter green morocco over marbled boards, 21.5 x 16.5 cm, collated 8vo, illustrated with numerous in-text and 5 full-page coloured etchings after drawings by Chas Laborde. Original publisher’s wrappers preserved, enriched with a set of 17 plates in black and white (bound in). Front wrapper (black and red): LÉO LARGUIER | LA POUPÉE | DESSINS DE CHAS LABORDE | {vignette} | COLLECTION | “LA ROSE ET LE LAURIER” | G. BRIFFAUT, Éditeur | 4, RUE DE FURSTENBERG, PARIS || Title-page: LÉO LARGUIER | — | LA POUPÉE | DESSINS DE | CHAS LABORDE | {vignette} | COLLECTION DE | “LA ROSE ET LE LAURIER” | G. BRIFFAUT, Éditeur | 4, RUE DE FURSTENBERG, PARIS (VIe) | M CM XXV || Collation: Three binder’s blanks, 1 front wrapper, 1 blank, 1 h.t./limit., 1 t.p., 1 epigraph, 1-68 74 (last blank), plates within collation, 1 back wrapper, three binder’s blanks, plus 17 leaves of b/w plates. Pagination: not counting wrappers, [6] (h.t., t.p., epigraph) 1-99 [100] [4], ils. Limitation: A print run of 770 copies on April 25, 1925, by Coulouma (Argenteuil) under the direction of H. Barthélemy , of which 10 copies on Japon Impérial (№ 1-10) + one drawing + one b/w suite, 10 copies on Japon Impérial (№ 11-20) + one drawing, 750 copies on Vélin (№ 21-770). This is copy № 1 (on Japon Impérial with b/w suite of plates but without the drawing). Contributors: Léo Larguier (French, 1878 – 1950) – author. Chas Laborde [Charles Laborde] (French, 1886 – 1941) – artist. Georges Briffaut (French, 1886 – 1973) – publisher.
Description: owner’s quarter green morocco over marbled boards, 21.5 x 16.5 cm, collated 8vo, illustrated with numerous in-text and 5 full-page coloured etchings after drawings by Chas Laborde. Original publisher’s wrappers preserved, enriched with a set of 17 plates in black and white (bound in). Front wrapper (black and red): LÉO LARGUIER | LA POUPÉE | DESSINS DE CHAS LABORDE | {vignette} | COLLECTION | “LA ROSE ET LE LAURIER” | G. BRIFFAUT, Éditeur | 4, RUE DE FURSTENBERG, PARIS || Title-page: LÉO LARGUIER | — | LA POUPÉE | DESSINS DE | CHAS LABORDE | {vignette} | COLLECTION DE | “LA ROSE ET LE LAURIER” | G. BRIFFAUT, Éditeur | 4, RUE DE FURSTENBERG, PARIS (VIe) | M CM XXV || Collation: Three binder’s blanks, 1 front wrapper, 1 blank, 1 h.t./limit., 1 t.p., 1 epigraph, 1-68 74 (last blank), plates within collation, 1 back wrapper, three binder’s blanks, plus 17 leaves of b/w plates. Pagination: not counting wrappers, [6] (h.t., t.p., epigraph) 1-99 [100] [4], ils. Limitation: A print run of 770 copies on April 25, 1925, by Coulouma (Argenteuil) under the direction of H. Barthélemy , of which 10 copies on Japon Impérial (№ 1-10) + one drawing + one b/w suite, 10 copies on Japon Impérial (№ 11-20) + one drawing, 750 copies on Vélin (№ 21-770). This is copy № 1 (on Japon Impérial with b/w suite of plates but without the drawing). Contributors: Léo Larguier (French, 1878 – 1950) – author. Chas Laborde [Charles Laborde] (French, 1886 – 1941) – artist. Georges Briffaut (French, 1886 – 1973) – publisher. A set of sixteen planographic prints, signed and titled in pencil by owner “Chevalier F. de Bouval” (pseudonym of Franz von Bayros (Austrian, 1866 – 1924). Titles include: 1) Ouverture, 2) champagne brut, 3) maternité, 4) piano, 5) crudité délicieuse, 6. la belle vue, 7) au pensionnat, 8) le collier, 9) languelles pénètrelles, 10) introduction, 11) le sourrogat, 12) variation amoureuse, 13) la surprise, 14) le clef délicat, 15) le monstre gomme, 16) fruits de sud. Printed on wove paper, possibly engraved on wood after ink drawings by Franz von Bayros (Austrian, 1866 – 1924) under the pseudonym Chevalier F. de Bouval. Size: sheet 30 x 24 cm, image 18 x 17.5 cm. In another source, there are two more images from the same set: le passe-partout and la doublette, making 18 images altogether; the set is titled “Lesbia: XVIII sujets”, signed by Chevalier François René de Bouval.
A set of sixteen planographic prints, signed and titled in pencil by owner “Chevalier F. de Bouval” (pseudonym of Franz von Bayros (Austrian, 1866 – 1924). Titles include: 1) Ouverture, 2) champagne brut, 3) maternité, 4) piano, 5) crudité délicieuse, 6. la belle vue, 7) au pensionnat, 8) le collier, 9) languelles pénètrelles, 10) introduction, 11) le sourrogat, 12) variation amoureuse, 13) la surprise, 14) le clef délicat, 15) le monstre gomme, 16) fruits de sud. Printed on wove paper, possibly engraved on wood after ink drawings by Franz von Bayros (Austrian, 1866 – 1924) under the pseudonym Chevalier F. de Bouval. Size: sheet 30 x 24 cm, image 18 x 17.5 cm. In another source, there are two more images from the same set: le passe-partout and la doublette, making 18 images altogether; the set is titled “Lesbia: XVIII sujets”, signed by Chevalier François René de Bouval.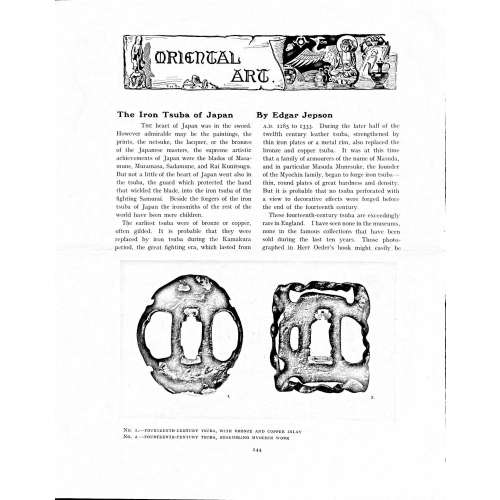 Magazine article by Edgar Jepson: The Iron Tsuba of Japan (Section: Oriental Art), published in volume Vol. 70 (September–December) of The Connoisseur: An Illustrated Magazine for Collectors, Vol. 70 (September–December); pp. 143-152 / C. Reginald Grundy [ed.] — London: Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, 1924. Owner's half black morocco, gilt lettering to spine, blue cloth boards. Two volumes bound together without original covers. Size 28.5 x 22 cm. Vol. 1: The Connoisseur | An Illustrated Magazine | For Collectors | Edited by C. Reginald Grundy | Vol. LXIX. | (MAY—AUGUST, 1924) | LONDON | Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the | Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, | at 1, Duke Street, St. James's, S.W. 1 | 1924 || Pp.: [i-ii] iii-xviii [xix] [1, 2 - plate] 3-249 [250]. Vol. 2: The Connoisseur | An Illustrated Magazine | For Collectors | Edited by C. Reginald Grundy | Vol. LXX. | (SEPTEMBER—DECEMBER, 1924) | LONDON | Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the | Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, | at 1, Duke Street, St. James's, S.W. 1 | 1924 || Pp.: [i-ii] iii-xxii [2 blanks] [1, 2 - plate] 3-261 [262]. The Iron Tsuba of Japan by Edgar Jepson The heart of Japan was in the sword. However admirable may be the paintings, the prints, the netsuke, the lacquer, or the bronzes of the Japanese masters, the supreme artistic achievements of Japan were the blades of Masamune, Muramasa, Sadamune, and Rai Kunitsugu. But not a little of the heart of Japan went also in the tsuba, the guard which protected the hand that wielded the blade, into the iron tsuba of the fighting Samurai. Beside the forgers of the iron tsuba of Japan the ironsmiths of the rest of the world have been mere children. The earliest tsuba were of bronze or copper, often gilded. It is probable that they were replaced by iron tsuba during the Kamakura period, the great fighting era, which lasted from A.D. 1185 to 1333. During the later half of the twelfth century leather tsuba, strengthened by thin iron plates or a metal rim, also replaced the bronze and copper tsuba. It was at this time that a family of armourers of the name of Masuda, and in particular Masuda Munesuke, the founder of the Myochin family, began to forge iron tsuba — thin, round plates of great hardness and density. But it is probable that no tsuba perforated with a view to decorative effects were forged before the end of the fourteenth century. These fourteenth-century tsuba are exceedingly rare in England. I have seen none in the museums, none in the famous collections that have been sold during the last ten years. Those photographed in Herr Oeder's book might easily be the fifteenth century. No. 1 is a curious cup-shape tsuba decorated with a bronze and copper inlay. No. 2, with its edges curiously twisted in the forging, looks like Myochin work. But it is not of the Myochin iron. The Myochin family produced some of the greatest ironsmiths of Japan. Armourers first of all, tsubasmiths, forgers of sake-kettles, articulated reptiles, crustacea, and insects — everything that can be done with iron they did; they pushed their medium to its limit. They were forging iron tsuba in 1160, and they were still forging them in 1860. And it was their own iron, or rather their own steel. They discovered the secret of it early, and they kept that secret in the family for all those hundreds of years. There is no mistaking a Myochin tsuba: balance it on your finger and tap it with a piece of metal, always it gives forth a clear bell-like ring that you get from the work of no other ironsmith, Japanese or European. Always the Myochin tsuba is before everything a protection to the hand of the swordsman; to that everything is, as it should be, subordinated. No. 3 is a Myochin tsuba of the fifteenth century, and probably of the early fifteenth century. No. 4, by Myochin Munetaka, perforated with a grotesque figure, is an example of that twisting and twisting of the iron in the forging till it forms a pattern like the grain of wood. The Myochin smiths invented these wood-grain tsuba, and no other smiths equalled them in their forging. In the sixteenth century, the fighting tsuba was probably at its best. It was a century of great tsubasmiths. Then the first Nobuiye, whose tsuba fetched £100 apiece, circa 1800, in Japan, and the first Kaneiye flourished. No. 5 is a tsuba forged by a great smith, Iyesada of Sotome, in the manner of Nobuiye I, decorated with the karakusa tendrils that Nobuiye delighted in, with lightning and clouds. No. 6 is a guard of Sanada Tembo, the chief smith of the Tembo family, stamped, punning fashion, with the character Tembo. Akin to the Tembo tsuba were those of the Kiami and Hoan smiths. Then also the Heianjo smiths and the Owari smiths, especially those of Nagoya and the Yamakichi family, forged their strongest tsuba. Those of the Yamakichi were tested after the forging by being pounded in iron mortars — at least, so the legend runs. But they were a sternly utilitarian family, and I have never seen a Yamakichi tsuba of any beauty. In the later half of the fifteenth century arose the fashion of decorating tsuba with an inlay, zogan, of bronze. The Heianjo tsuba, forged at Kyoto in the latter half of the fifteenth and the beginning of the sixteenth century, were often thus inlaid. The earliest of them were called "Onin", of which No. 7 is an example. In addition to the bronze inlay around the edge, it is inlaid with a representation, some say, of snow; others say, of the duckweed on a pond. No. 8 is probably a Heianjo tsuba, but I am not quite sure about it. The inlaid acacia branches might be very early Shoami work. But to judge by the iron, it is a fifteenth-century tsuba; and the authorities place the beginning of the Shoami school not later than early in the sixteenth century. No. 10 is an example of the Fushimi-zogan, a flat inlay of a light-coloured bronze. These tsuba took their name from the fact that they were first forged at Fushimi, in Yamashiro, in the sixteenth century. It is of the type known as Mon-zukashi, perforated with crests (mon) à jour. The Yoshiro-zogan tsuba were also first forged at Fushimi by Yoshiro Naomasa. They were distinguished from the Fushimi-zogan by the fact that their inlay was generally a little raised-not always-for the inlay of No. 9, a tsuba forged by a later nineteenth-century Yoshiro, is quite flat. It is an interesting tsuba, for, with its decoration grown florid and excessive, it marks the intermediate stage between the simple and delightful designs of the genuine fighting tsuba and the elaborate pictures in gold and silver on the tsuba of the eighteenth-century smiths of Awa and Kyoto, which have become mere ornaments of the goldsmith. The Gomoku-zogan (No. 11) tsuba were probably first forged earlier than the Fushimi and Yoshiro-zogan tsuba. This inlay, in slight relief, is a representation in a light-coloured bronze and copper of twigs caught in the eddies of streams. The seventeenth century and early eighteenth century were the great periods of perforated tsuba. The designs, and they are often admirable, are for the most part in plain fretwork; but they are also chased. No. 12, a crane under an acacia, is a tsuba of a Higo smith, great forgers of fighting tsuba during this period. These smiths also excelled in nunome zogan, a very thin gold and silver inlay, with which they further decorated their perforated guards. The smiths of the Umetada and Shoami families also forged iron tsuba during this period; but their designs, though sometimes pleasing enough, are rarely fine. The best work of Myoju Umetada is in sentoku, not iron. The Choshu smiths, coming later, surpass the perforated guards of both the Umetada and Shoami smiths in beauty of design. No. 13, a lotus in the round, not only fretwork, but also engraved, is a good example of the admirable balance they so often attained in their designs. It is a sufficiently realistic lotus, but yet of a delightful simplicity. In considerable contrast is No. 14, the dragon by Soheishi Soten — one of the only two authentic tsuba of his forging known — the first forger of hikone-bori tsuba, which were in extraordinary favour in Japan during the eighteenth century, and illustrated every important event in Japanese history. It is on the elaborate side, but fine, strong work, and an excellent guard to the hand, for the lighter and more open part, which gives the design its admirable balance, is on the inside, and not exposed to the full swing of an opponent's blade. A few years ago there was a tendency to decry the Namban tsuba as having sprung too directly from foreign sources. But though the original suggestion may have been Chinese, or, as some say, Portuguese, the Japanese made it entirely their own, as characteristically Japanese as anything can well be, but, it must be admitted, of a decadent period. The school took its rise at the beginning of the seventeenth century, and the early tsuba were forged of a specially hard iron, the Wootz, imported from Southern India. No. 15, the signs of the Zodiac, is an excellent tsuba from the fighting point of view. Both it and No. 16 are of quite charming, if elaborate, design, and both of them, with their delicate scroll-work, so astonishingly undercut, are the very last word in the work of the ironsmith-veritable iron lace. To return to the simpler perforated tsuba, the smiths of Akasaka, a suburb of Tokyo, produced probably the most charming designs. Their style derives considerably from the Higo smiths, and their earlier fighting tsuba are very like the Higo tsuba. But always their work was just a little lighter than that of the Higo smiths, and in the end they moved right away from them and became the forgers of very light guards indeed. No. 17, is a representation of the Hiyokudori, the fabulous double bird, in which were reincarnated the souls of the two lovers, Gompachi and Komurasaki; and No. 18, “the tsuba of a hundred ducks "— there are about forty — are characteristic designs of the school. In the work of the Akasaka smiths the balance, which makes the design of a good tsuba so admirable and delightful, attains its height. This admirable balance seems often to be obtained by a deliberate sacrifice of symmetry. About nine hundred and ninety-nine European ironsmiths out of a thousand would have made the right and left sides of the Hiyoku-dori line by line, and perforation by perforation, exactly alike; he would have cut out exactly as many ducks on the one side of “the tsuba of a hundred ducks” as on the other, and made each duck on the right side correspond exactly in position and attitude with a duck on the left side. By variations the tsubasmith attained a finer balance, almost a higher symmetry. No. 19, often called by collectors the "rose-window" tsuba, but really a stylised chrysanthemum, is a favourite design of the Akasaka smiths, but Hizen work and inlaid in the Hizen manner with gold nunome. No. 20 is a Satsuma tsuba of the middle period. The Satsuma smiths of the nineteenth century produced probably the most ornate of all the iron guards, for the most part calibashes and beans with their leaves and tendrils realistic in the extreme, but of charming design. Few crafts have been carried further than that of the tsubasmith; few crafts working in a difficult medium have handled more subjects with greater feeling for beauty or greater liveliness of fancy. It is interesting to note again and again how school influences school, and smith influences smith. But, as in all the applied arts, the finest tsuba were forged by men who never lost sight of the purpose of a tsuba, that it is before everything a protection to the hand, and never subjected that purpose to a passion for virtuosity. Illustrations: No 1. FOURTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA, WITH BRONZE AND COPPER INLAY No. 2. FOURTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA, RESEMBLING MYOCHIN WORK No. 3. MYOCHIN TSUBA, FIFTEENTH CENTURY No. 4. MYOCHIN TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY No. 5. SIXTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA No. 6. SIXTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA BY IYESADA OF SOTOME BY SANADA TEMBO No. 7. ONIN TSUBA No. 8. HEIANJO (?) TSUBA No. 9. YOSHIRO TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY No. 10. FUSHIMI-ZOGAN, NINETEENTH CENTURY No. 11.- GOMOKU-ZOGAN, SIXTEENTH CENTURY No. 12. HIGO TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY No. 13. CHOSHU TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY No. 14. SOTEN TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY No. 15. NAMBAN TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY No. 16. NAMBAN TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY Nos. 17. AND 18. AKASAKA TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY No. 19. HIZEN TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY No. 20. SATSUMA TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY
Magazine article by Edgar Jepson: The Iron Tsuba of Japan (Section: Oriental Art), published in volume Vol. 70 (September–December) of The Connoisseur: An Illustrated Magazine for Collectors, Vol. 70 (September–December); pp. 143-152 / C. Reginald Grundy [ed.] — London: Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, 1924. Owner's half black morocco, gilt lettering to spine, blue cloth boards. Two volumes bound together without original covers. Size 28.5 x 22 cm. Vol. 1: The Connoisseur | An Illustrated Magazine | For Collectors | Edited by C. Reginald Grundy | Vol. LXIX. | (MAY—AUGUST, 1924) | LONDON | Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the | Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, | at 1, Duke Street, St. James's, S.W. 1 | 1924 || Pp.: [i-ii] iii-xviii [xix] [1, 2 - plate] 3-249 [250]. Vol. 2: The Connoisseur | An Illustrated Magazine | For Collectors | Edited by C. Reginald Grundy | Vol. LXX. | (SEPTEMBER—DECEMBER, 1924) | LONDON | Published by the Proprietor, W. CLAUSE JOHNSON, at the | Editorial and Advertisement Offices of The Connoisseur, | at 1, Duke Street, St. James's, S.W. 1 | 1924 || Pp.: [i-ii] iii-xxii [2 blanks] [1, 2 - plate] 3-261 [262]. The Iron Tsuba of Japan by Edgar Jepson The heart of Japan was in the sword. However admirable may be the paintings, the prints, the netsuke, the lacquer, or the bronzes of the Japanese masters, the supreme artistic achievements of Japan were the blades of Masamune, Muramasa, Sadamune, and Rai Kunitsugu. But not a little of the heart of Japan went also in the tsuba, the guard which protected the hand that wielded the blade, into the iron tsuba of the fighting Samurai. Beside the forgers of the iron tsuba of Japan the ironsmiths of the rest of the world have been mere children. The earliest tsuba were of bronze or copper, often gilded. It is probable that they were replaced by iron tsuba during the Kamakura period, the great fighting era, which lasted from A.D. 1185 to 1333. During the later half of the twelfth century leather tsuba, strengthened by thin iron plates or a metal rim, also replaced the bronze and copper tsuba. It was at this time that a family of armourers of the name of Masuda, and in particular Masuda Munesuke, the founder of the Myochin family, began to forge iron tsuba — thin, round plates of great hardness and density. But it is probable that no tsuba perforated with a view to decorative effects were forged before the end of the fourteenth century. These fourteenth-century tsuba are exceedingly rare in England. I have seen none in the museums, none in the famous collections that have been sold during the last ten years. Those photographed in Herr Oeder's book might easily be the fifteenth century. No. 1 is a curious cup-shape tsuba decorated with a bronze and copper inlay. No. 2, with its edges curiously twisted in the forging, looks like Myochin work. But it is not of the Myochin iron. The Myochin family produced some of the greatest ironsmiths of Japan. Armourers first of all, tsubasmiths, forgers of sake-kettles, articulated reptiles, crustacea, and insects — everything that can be done with iron they did; they pushed their medium to its limit. They were forging iron tsuba in 1160, and they were still forging them in 1860. And it was their own iron, or rather their own steel. They discovered the secret of it early, and they kept that secret in the family for all those hundreds of years. There is no mistaking a Myochin tsuba: balance it on your finger and tap it with a piece of metal, always it gives forth a clear bell-like ring that you get from the work of no other ironsmith, Japanese or European. Always the Myochin tsuba is before everything a protection to the hand of the swordsman; to that everything is, as it should be, subordinated. No. 3 is a Myochin tsuba of the fifteenth century, and probably of the early fifteenth century. No. 4, by Myochin Munetaka, perforated with a grotesque figure, is an example of that twisting and twisting of the iron in the forging till it forms a pattern like the grain of wood. The Myochin smiths invented these wood-grain tsuba, and no other smiths equalled them in their forging. In the sixteenth century, the fighting tsuba was probably at its best. It was a century of great tsubasmiths. Then the first Nobuiye, whose tsuba fetched £100 apiece, circa 1800, in Japan, and the first Kaneiye flourished. No. 5 is a tsuba forged by a great smith, Iyesada of Sotome, in the manner of Nobuiye I, decorated with the karakusa tendrils that Nobuiye delighted in, with lightning and clouds. No. 6 is a guard of Sanada Tembo, the chief smith of the Tembo family, stamped, punning fashion, with the character Tembo. Akin to the Tembo tsuba were those of the Kiami and Hoan smiths. Then also the Heianjo smiths and the Owari smiths, especially those of Nagoya and the Yamakichi family, forged their strongest tsuba. Those of the Yamakichi were tested after the forging by being pounded in iron mortars — at least, so the legend runs. But they were a sternly utilitarian family, and I have never seen a Yamakichi tsuba of any beauty. In the later half of the fifteenth century arose the fashion of decorating tsuba with an inlay, zogan, of bronze. The Heianjo tsuba, forged at Kyoto in the latter half of the fifteenth and the beginning of the sixteenth century, were often thus inlaid. The earliest of them were called "Onin", of which No. 7 is an example. In addition to the bronze inlay around the edge, it is inlaid with a representation, some say, of snow; others say, of the duckweed on a pond. No. 8 is probably a Heianjo tsuba, but I am not quite sure about it. The inlaid acacia branches might be very early Shoami work. But to judge by the iron, it is a fifteenth-century tsuba; and the authorities place the beginning of the Shoami school not later than early in the sixteenth century. No. 10 is an example of the Fushimi-zogan, a flat inlay of a light-coloured bronze. These tsuba took their name from the fact that they were first forged at Fushimi, in Yamashiro, in the sixteenth century. It is of the type known as Mon-zukashi, perforated with crests (mon) à jour. The Yoshiro-zogan tsuba were also first forged at Fushimi by Yoshiro Naomasa. They were distinguished from the Fushimi-zogan by the fact that their inlay was generally a little raised-not always-for the inlay of No. 9, a tsuba forged by a later nineteenth-century Yoshiro, is quite flat. It is an interesting tsuba, for, with its decoration grown florid and excessive, it marks the intermediate stage between the simple and delightful designs of the genuine fighting tsuba and the elaborate pictures in gold and silver on the tsuba of the eighteenth-century smiths of Awa and Kyoto, which have become mere ornaments of the goldsmith. The Gomoku-zogan (No. 11) tsuba were probably first forged earlier than the Fushimi and Yoshiro-zogan tsuba. This inlay, in slight relief, is a representation in a light-coloured bronze and copper of twigs caught in the eddies of streams. The seventeenth century and early eighteenth century were the great periods of perforated tsuba. The designs, and they are often admirable, are for the most part in plain fretwork; but they are also chased. No. 12, a crane under an acacia, is a tsuba of a Higo smith, great forgers of fighting tsuba during this period. These smiths also excelled in nunome zogan, a very thin gold and silver inlay, with which they further decorated their perforated guards. The smiths of the Umetada and Shoami families also forged iron tsuba during this period; but their designs, though sometimes pleasing enough, are rarely fine. The best work of Myoju Umetada is in sentoku, not iron. The Choshu smiths, coming later, surpass the perforated guards of both the Umetada and Shoami smiths in beauty of design. No. 13, a lotus in the round, not only fretwork, but also engraved, is a good example of the admirable balance they so often attained in their designs. It is a sufficiently realistic lotus, but yet of a delightful simplicity. In considerable contrast is No. 14, the dragon by Soheishi Soten — one of the only two authentic tsuba of his forging known — the first forger of hikone-bori tsuba, which were in extraordinary favour in Japan during the eighteenth century, and illustrated every important event in Japanese history. It is on the elaborate side, but fine, strong work, and an excellent guard to the hand, for the lighter and more open part, which gives the design its admirable balance, is on the inside, and not exposed to the full swing of an opponent's blade. A few years ago there was a tendency to decry the Namban tsuba as having sprung too directly from foreign sources. But though the original suggestion may have been Chinese, or, as some say, Portuguese, the Japanese made it entirely their own, as characteristically Japanese as anything can well be, but, it must be admitted, of a decadent period. The school took its rise at the beginning of the seventeenth century, and the early tsuba were forged of a specially hard iron, the Wootz, imported from Southern India. No. 15, the signs of the Zodiac, is an excellent tsuba from the fighting point of view. Both it and No. 16 are of quite charming, if elaborate, design, and both of them, with their delicate scroll-work, so astonishingly undercut, are the very last word in the work of the ironsmith-veritable iron lace. To return to the simpler perforated tsuba, the smiths of Akasaka, a suburb of Tokyo, produced probably the most charming designs. Their style derives considerably from the Higo smiths, and their earlier fighting tsuba are very like the Higo tsuba. But always their work was just a little lighter than that of the Higo smiths, and in the end they moved right away from them and became the forgers of very light guards indeed. No. 17, is a representation of the Hiyokudori, the fabulous double bird, in which were reincarnated the souls of the two lovers, Gompachi and Komurasaki; and No. 18, “the tsuba of a hundred ducks "— there are about forty — are characteristic designs of the school. In the work of the Akasaka smiths the balance, which makes the design of a good tsuba so admirable and delightful, attains its height. This admirable balance seems often to be obtained by a deliberate sacrifice of symmetry. About nine hundred and ninety-nine European ironsmiths out of a thousand would have made the right and left sides of the Hiyoku-dori line by line, and perforation by perforation, exactly alike; he would have cut out exactly as many ducks on the one side of “the tsuba of a hundred ducks” as on the other, and made each duck on the right side correspond exactly in position and attitude with a duck on the left side. By variations the tsubasmith attained a finer balance, almost a higher symmetry. No. 19, often called by collectors the "rose-window" tsuba, but really a stylised chrysanthemum, is a favourite design of the Akasaka smiths, but Hizen work and inlaid in the Hizen manner with gold nunome. No. 20 is a Satsuma tsuba of the middle period. The Satsuma smiths of the nineteenth century produced probably the most ornate of all the iron guards, for the most part calibashes and beans with their leaves and tendrils realistic in the extreme, but of charming design. Few crafts have been carried further than that of the tsubasmith; few crafts working in a difficult medium have handled more subjects with greater feeling for beauty or greater liveliness of fancy. It is interesting to note again and again how school influences school, and smith influences smith. But, as in all the applied arts, the finest tsuba were forged by men who never lost sight of the purpose of a tsuba, that it is before everything a protection to the hand, and never subjected that purpose to a passion for virtuosity. Illustrations: No 1. FOURTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA, WITH BRONZE AND COPPER INLAY No. 2. FOURTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA, RESEMBLING MYOCHIN WORK No. 3. MYOCHIN TSUBA, FIFTEENTH CENTURY No. 4. MYOCHIN TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY No. 5. SIXTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA No. 6. SIXTEENTH-CENTURY TSUBA BY IYESADA OF SOTOME BY SANADA TEMBO No. 7. ONIN TSUBA No. 8. HEIANJO (?) TSUBA No. 9. YOSHIRO TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY No. 10. FUSHIMI-ZOGAN, NINETEENTH CENTURY No. 11.- GOMOKU-ZOGAN, SIXTEENTH CENTURY No. 12. HIGO TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY No. 13. CHOSHU TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY No. 14. SOTEN TSUBA, SEVENTEENTH CENTURY No. 15. NAMBAN TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY No. 16. NAMBAN TSUBA, NINETEENTH CENTURY Nos. 17. AND 18. AKASAKA TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY No. 19. HIZEN TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY No. 20. SATSUMA TSUBA, EIGHTEENTH CENTURY Title: THE IDEALS OF THE EAST | WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE | TO THE ART OF JAPAN | BY KAKASU OKAKURA | LONDON | JOHN MURRAY, ALBEMARLE STREET | 1903 || Collation: 8vo; ffl, [2] (t.p., prep. note) [a]4 b4, A-P8 Q4. Pagination: ffl, [I, ii] – h.t. / blank, [iii, iv] – t.p. / blank, [v, vi] – preparatory note / blank, vii-xxii, [1] 2-244, [1] 2-4 (Works for art lovers). Binding: Burgundy cloth, red flowers and lettering to cover, gilt lettering to spine. Size: 19.5 x 13 cm Contributors: Author: Okakura Kakuzō [岡倉 覚三] (1863 – 1913). Publisher: Murray, Sir John IV (1851–1928); John Murray (publishing house). Printer: Ballantyne, Hanson & Co., Edinburgh, London.
Title: THE IDEALS OF THE EAST | WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE | TO THE ART OF JAPAN | BY KAKASU OKAKURA | LONDON | JOHN MURRAY, ALBEMARLE STREET | 1903 || Collation: 8vo; ffl, [2] (t.p., prep. note) [a]4 b4, A-P8 Q4. Pagination: ffl, [I, ii] – h.t. / blank, [iii, iv] – t.p. / blank, [v, vi] – preparatory note / blank, vii-xxii, [1] 2-244, [1] 2-4 (Works for art lovers). Binding: Burgundy cloth, red flowers and lettering to cover, gilt lettering to spine. Size: 19.5 x 13 cm Contributors: Author: Okakura Kakuzō [岡倉 覚三] (1863 – 1913). Publisher: Murray, Sir John IV (1851–1928); John Murray (publishing house). Printer: Ballantyne, Hanson & Co., Edinburgh, London. Description: 4to, 26 x 21 cm, hardcover ¾ brown percaline over marbled boards, gilt lettering to spine, marbled endpapers, publisher’s original wrappers preserved (bound-in), engraved bookplate “EX LIBRIS | Rodolfo …“ to verso of the 1st blank leaf. Printed in 1905 by Imprimerie Humbert Allegretti (Milan). Collation: 4to; front wrapper, π3 (blank, h.t., t.p.), 1-684, back wrapper; total 275 leaves within the wrappers. Pagination: [6] [1] 2-542 [2], total 550 pages. Contributors: Alessandro Baudi di Vesme [Alexandre de Vesme] (Italian, 1854 – 1923) Adam Bartsch (Austrian, 1757 – 1821) Ulrico Hoepli [Johannes Ulrich Höpli] (Swiss-Italian, 1846 – 1935) U. Hoepli (Milan)
Description: 4to, 26 x 21 cm, hardcover ¾ brown percaline over marbled boards, gilt lettering to spine, marbled endpapers, publisher’s original wrappers preserved (bound-in), engraved bookplate “EX LIBRIS | Rodolfo …“ to verso of the 1st blank leaf. Printed in 1905 by Imprimerie Humbert Allegretti (Milan). Collation: 4to; front wrapper, π3 (blank, h.t., t.p.), 1-684, back wrapper; total 275 leaves within the wrappers. Pagination: [6] [1] 2-542 [2], total 550 pages. Contributors: Alessandro Baudi di Vesme [Alexandre de Vesme] (Italian, 1854 – 1923) Adam Bartsch (Austrian, 1757 – 1821) Ulrico Hoepli [Johannes Ulrich Höpli] (Swiss-Italian, 1846 – 1935) U. Hoepli (Milan) Set of 21 etchings by Martin van Maele for the English edition of ‘Thais’ by Anatole France published in London by Charles Carrington in 1901. Printed on vowe paper without a watermark in two colours with the black image and sepia historiated border. All etchings are inscribed with the artist's monogram; one of the etchings bears inscriptions ORGUEIL, LUXURE, DOUTE (mirror image). Dimensions: sheet: 317 x 250 mm; plate: 170 x 115 mm; image: 155 x 100 mm. Catalogue raisonné: S. A. Perry: № 64. Per Perry, the edition was printed in 500 copies on 'handmade paper watermarked 'Van Gelder'. Contributor: Martin van Maële [Martin, Maurice François Alfred] (French, 1863 – 1926)
Set of 21 etchings by Martin van Maele for the English edition of ‘Thais’ by Anatole France published in London by Charles Carrington in 1901. Printed on vowe paper without a watermark in two colours with the black image and sepia historiated border. All etchings are inscribed with the artist's monogram; one of the etchings bears inscriptions ORGUEIL, LUXURE, DOUTE (mirror image). Dimensions: sheet: 317 x 250 mm; plate: 170 x 115 mm; image: 155 x 100 mm. Catalogue raisonné: S. A. Perry: № 64. Per Perry, the edition was printed in 500 copies on 'handmade paper watermarked 'Van Gelder'. Contributor: Martin van Maële [Martin, Maurice François Alfred] (French, 1863 – 1926)

