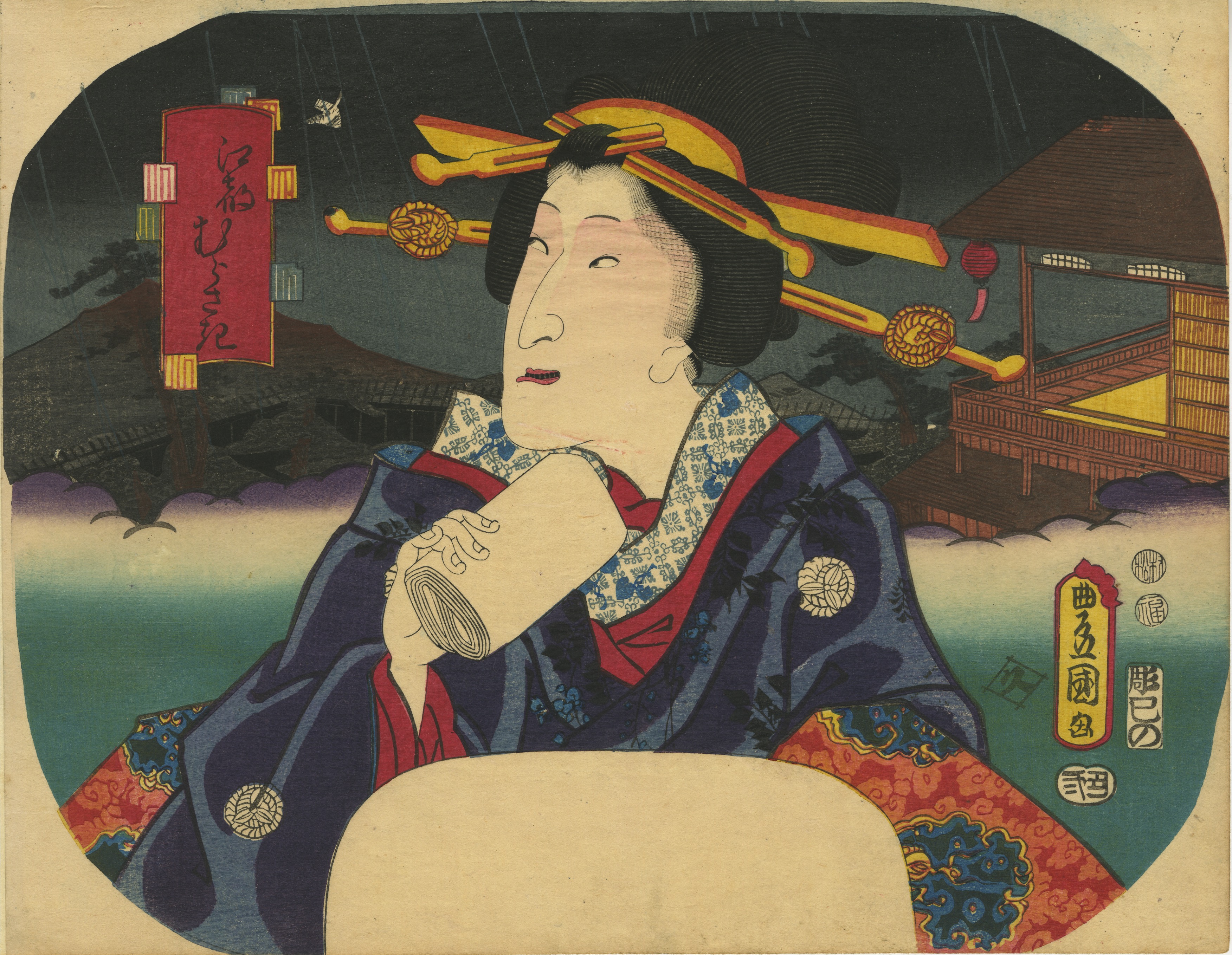
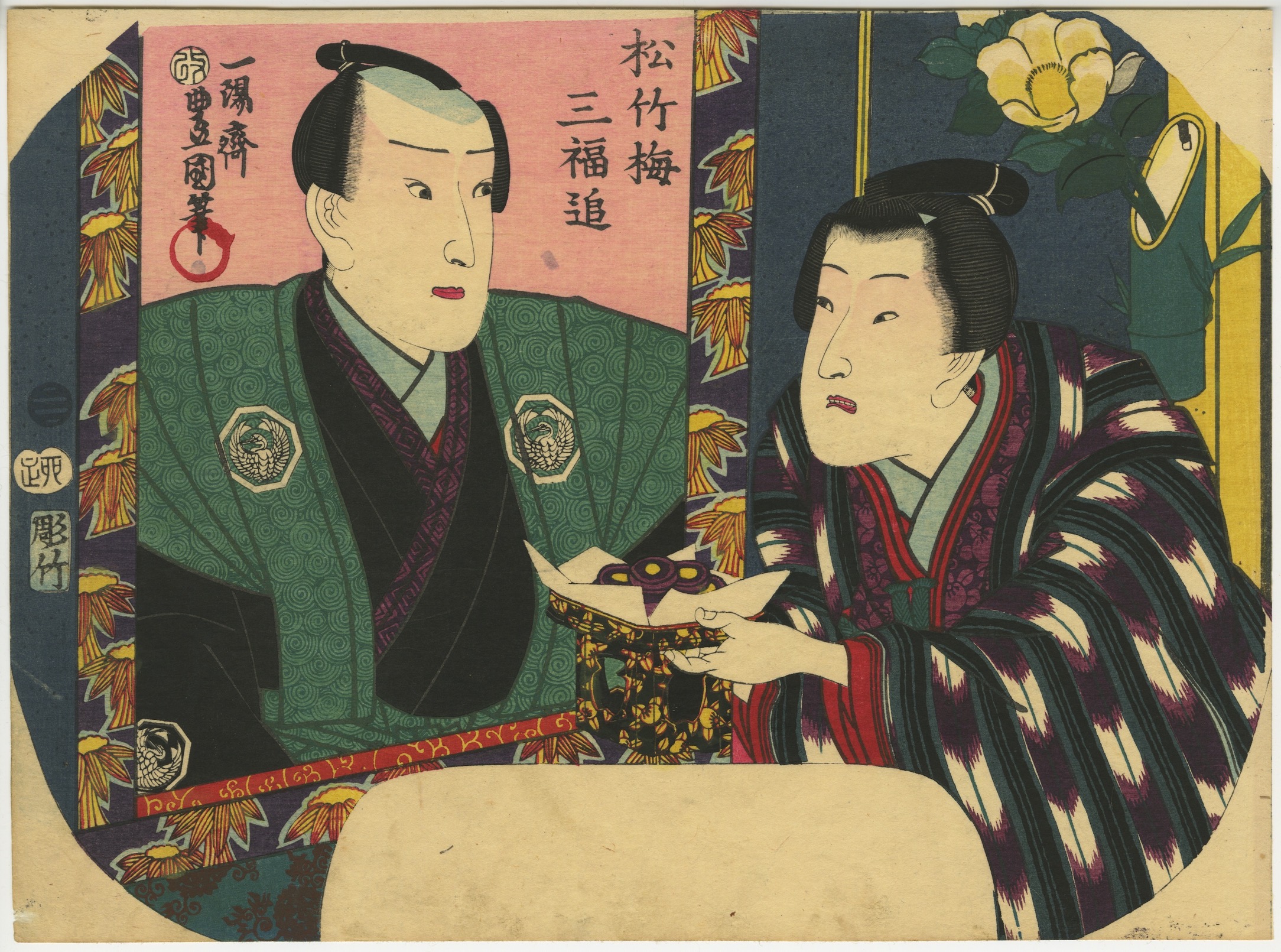
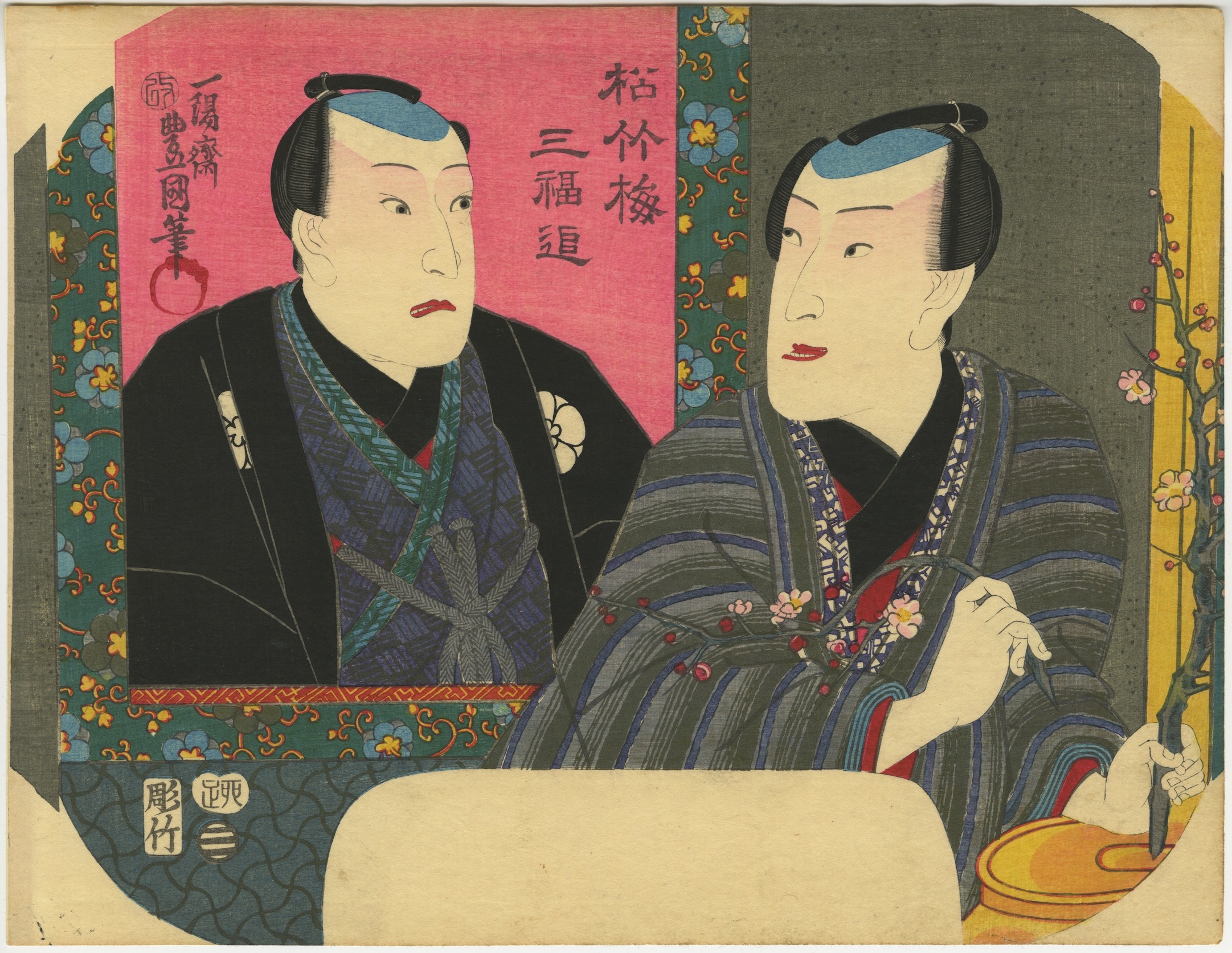
Artist: Utagawa Kunisada [歌川 国貞], a.k.a. Utagawa Toyokuni III [三代 歌川 豊国] (Japanese, 1786 – 1865).
Signed:
Toyokuni ga [豊国 画] in a red toshidama cartouche
Block carver:
Yokokawa Takejirō [横川竹二郎] (Japanese, fl. 1845 – 1863), seal: 彫竹 – Hori Take.
Publisher: Ibaya Senzaburō [伊場屋仙三郎] (Japanese, fl. c. 1845 – 1847).
Combined date and kiwame seal: Ansei 5 (II-XII/1858).
Size: Untrimmed fan print (uchiwa-e), 300 x 232 mm.
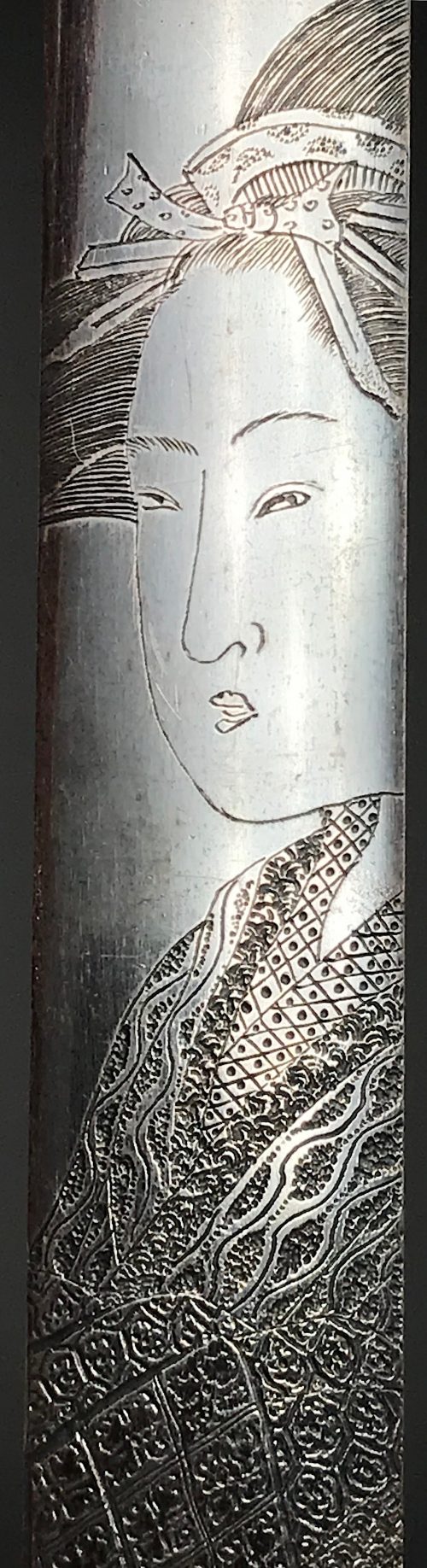
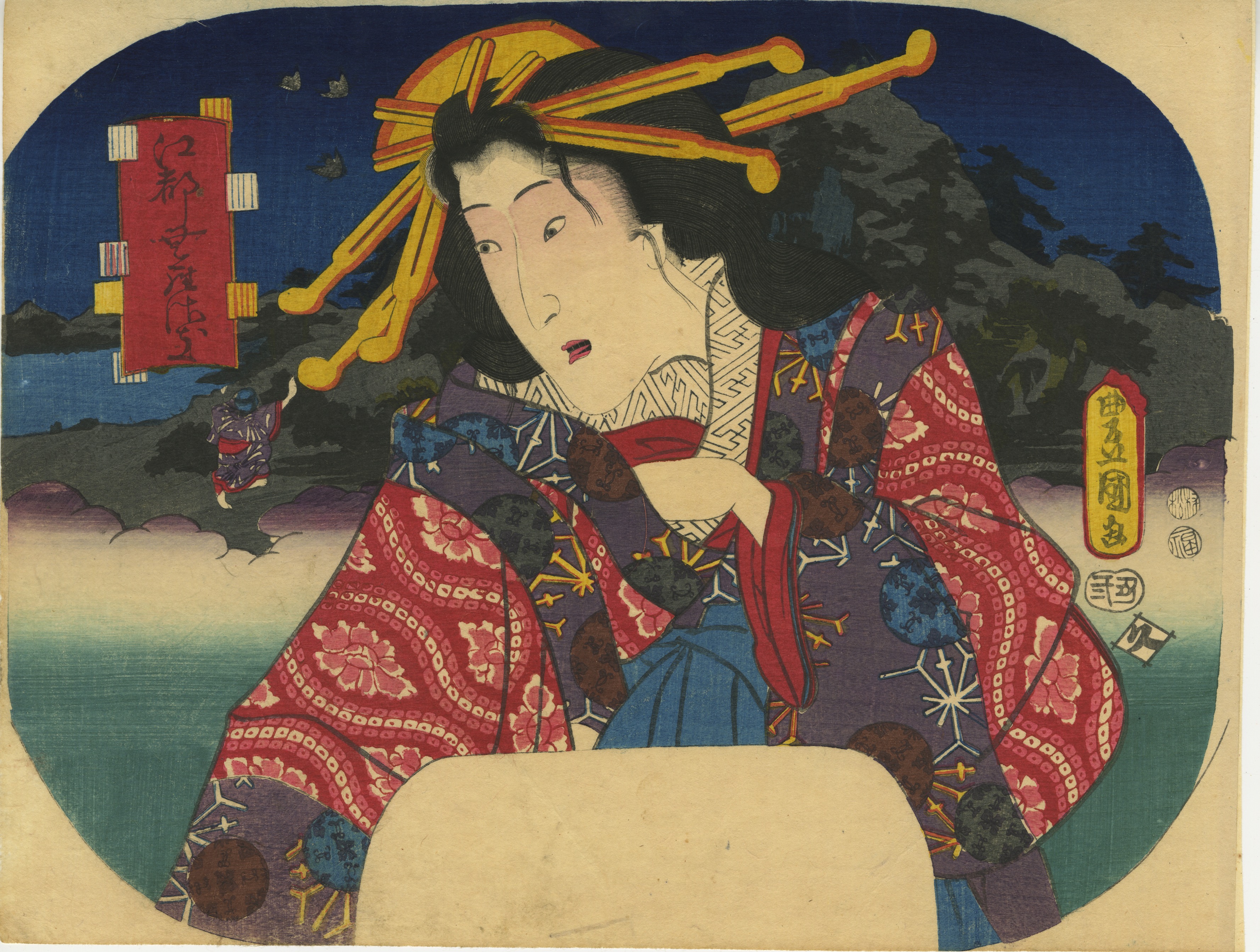
A young woman adjusting her hairpin on a balcony during the Tanabata festival, as inscribed on the white folding fan: [七夕] (Tanabata).
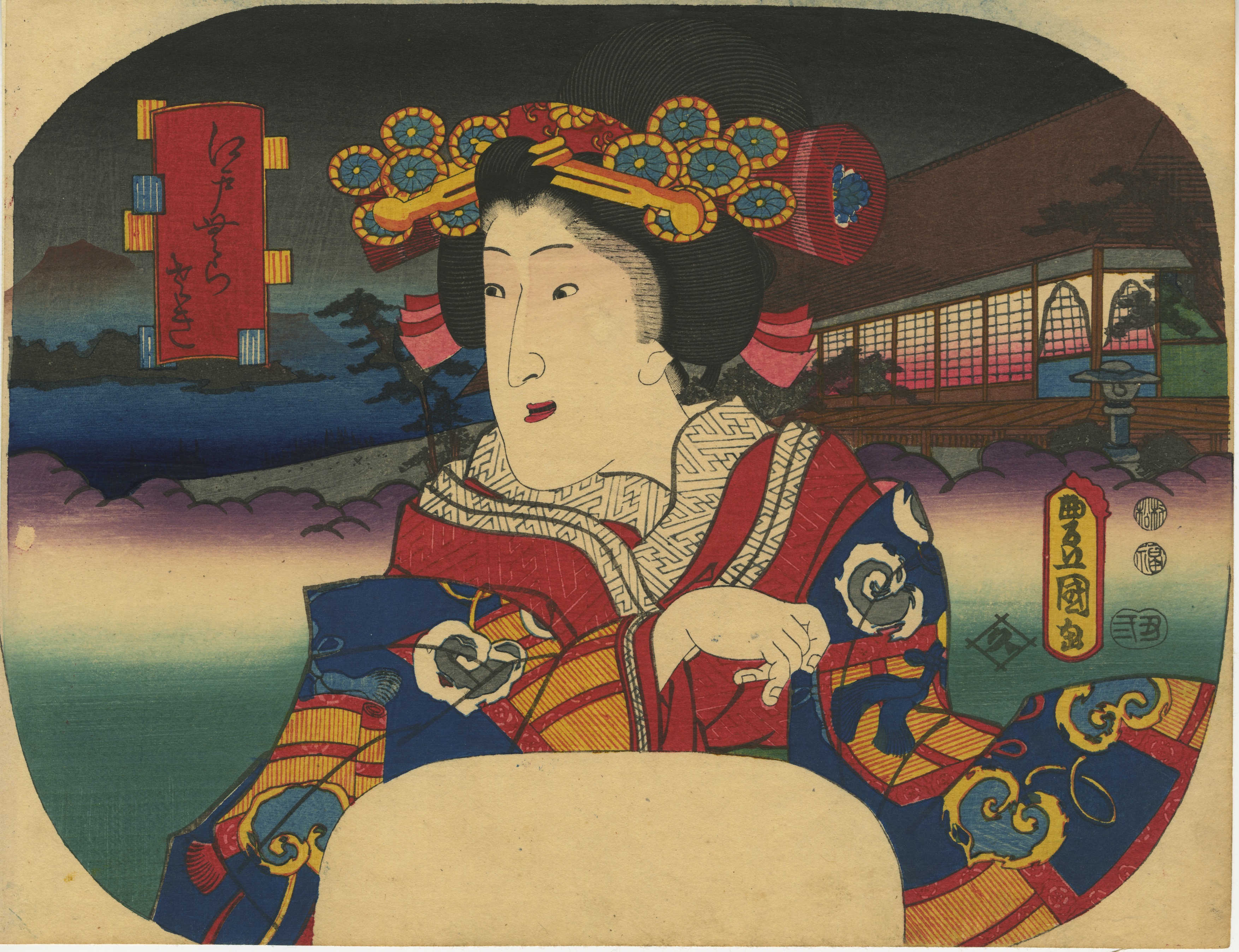
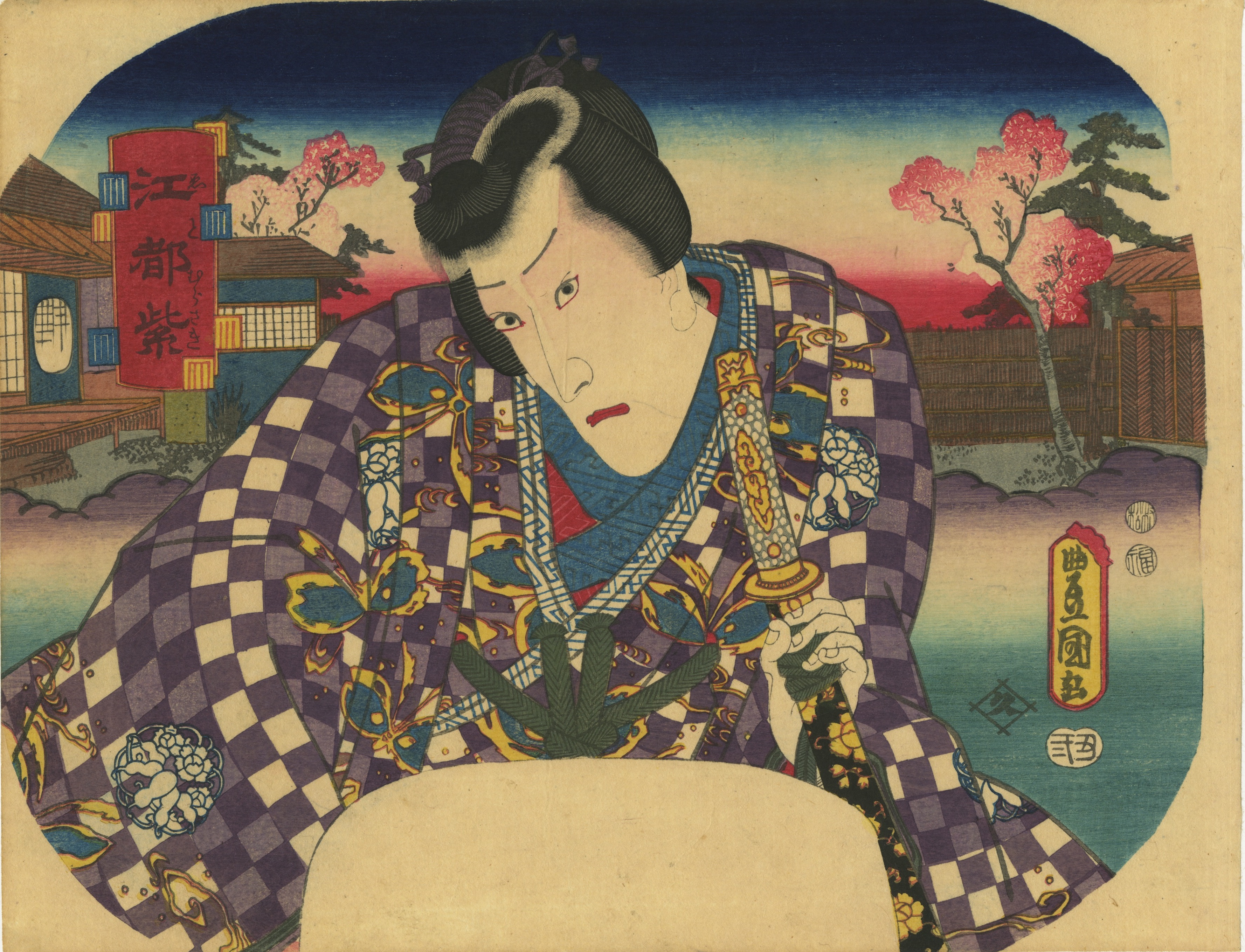
Inscription on the blue book (print title): Early autumn [はつ秋や] (hatsu akiya), inscription on the purple book (series title): Short love songs, second volume [端唄の意 二編] (Hauta no kokoro nihen). According to Marks (2010), Hauta no kokoro nihen series of fan prints was published by Ibaya in 1858 (p. 267|P6871).
The series refers to love songs of a certain type popular in late Edo. They were performed with the accompaniment of a shamisen, “Seven herbs of autumn, the song of the insects is not heard; the bodies of lightning bugs are burnt, and the precious writings of love are getting thinner like the song of the insects as I am waiting for you. So, on an early autumn evening, I spot the glitter of a lightning bug that lingered among the autumn grasses, and while listening to the pine cricket, I am singing with my heart troubled by love". [
Tokyo National Museum; translation provided by Elena Varshavsky].
Tanabata [たなばた] or [七夕] – meaning "Evening of the seventh", also known as the Star Festival [星祭] (Hoshi matsuri) – is a Japanese festival originating from the Chinese Qixi Festival. One popular Tanabata custom is to write one's wishes on a piece of paper and hang that piece of paper on a specially erected bamboo tree, in the hope that the wishes become true.