According to Torigoye’s book “Tsuba Geijitsu Kō”, written in around 1962: “It is clear that there were two generations who used the name Bizen Yoshirō. The first generation worked about Kambun era (1661-1672). The second generation worked about the Genroku era (1688-1703). […] In the work of the first Bizen Yoshirō we see large hitsu-ana of undulating cloud forms. This would seem the sole characteristic separating his work from the other Bizen artists. In rare cases small nanako dots, or gold and silver ten-zōgan are to be found. Sometime after the middle of the Edo age the work of the Bizen Yoshirō school disappears, and there is no later work in the style of this school. The signatures found on tsuba are the following: Yoshirō saku, or Yoshirō kore (wo) tsukuru, this is the signature of the first Bizen Yoshirō. Other signatures are Umon Nagatsugu, or Koike Umon Nagatsugu, with Okayama jū nin on the back. Also Bizen Yoshirō Nagatsugu saku. Umon Nagatsugu and Koike Nagatsugu are the same person”.Bizen Province [備前国] is located in southeastern Okayama Prefecture [岡山県]. Kanbun era [寛文] (April 1661 – September 1673). Dimensions: 68.5 x 68.0 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai 3.4 mm
-
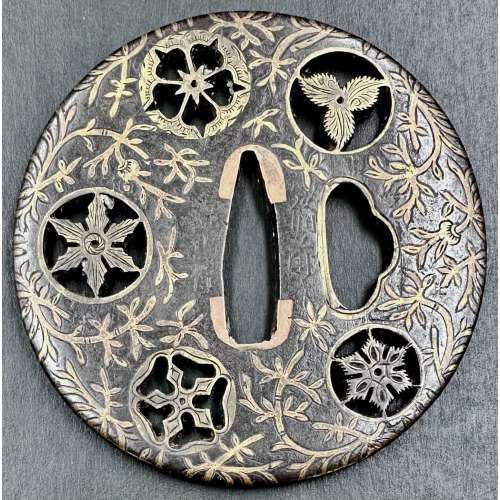 NEWIron tsuba of almost round form decorated with five roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Large hitsu-ana of ‘undulating cloud form’ outlined with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form, fitted with copper sekigane. Signed on both sides of seppa-dai on both sides of the plate: Made by Yoshirō, resident of Okayama in Bizen [備前岡山住・与四郎作之] (Bizen Okayama-jū – Yoshirō kore o tsukuru)
NEWIron tsuba of almost round form decorated with five roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Large hitsu-ana of ‘undulating cloud form’ outlined with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form, fitted with copper sekigane. Signed on both sides of seppa-dai on both sides of the plate: Made by Yoshirō, resident of Okayama in Bizen [備前岡山住・与四郎作之] (Bizen Okayama-jū – Yoshirō kore o tsukuru) -
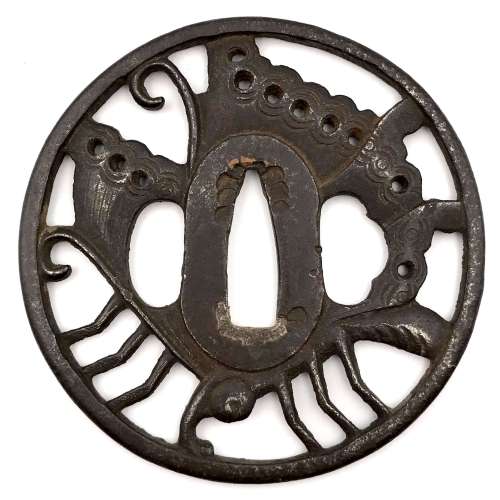 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of a butterfly in openwork (sukashi) with details carved in kebori. Eyes inlaid in brass (one inlay is missing). Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 80.4 x 80.6 x 4.4 mm References At Haynes Catalog #6, p. 18-19, Lot 30: "Famous Ikeda butterfly design" (Ikeda family of Inaba and Okayama, and at least 7 other families). Ca. 1700. Shōami of Kyoto, no doubt. Ht 8.2 cm, Th. 5 mm. ["Important tsuba, menuki, bokuto, woodblock prints, koshirae, sword pistol and kana mono". San Francisco, June 1-26, 1983. Catalog #6. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd.]Similar tsuba at Haynes Catalog #9, p.71, lot 143: the classic Shoami tsuba of the mon of the Ikeda family. This example, as most, seems to be made by the same hand as the others. See Haynes sale number 6, lot 30, for an identical example. The eye is brass. From an old French collection. Ht. 7.9 cm., Th. 5 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of a butterfly in openwork (sukashi) with details carved in kebori. Eyes inlaid in brass (one inlay is missing). Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 80.4 x 80.6 x 4.4 mm References At Haynes Catalog #6, p. 18-19, Lot 30: "Famous Ikeda butterfly design" (Ikeda family of Inaba and Okayama, and at least 7 other families). Ca. 1700. Shōami of Kyoto, no doubt. Ht 8.2 cm, Th. 5 mm. ["Important tsuba, menuki, bokuto, woodblock prints, koshirae, sword pistol and kana mono". San Francisco, June 1-26, 1983. Catalog #6. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd.]Similar tsuba at Haynes Catalog #9, p.71, lot 143: the classic Shoami tsuba of the mon of the Ikeda family. This example, as most, seems to be made by the same hand as the others. See Haynes sale number 6, lot 30, for an identical example. The eye is brass. From an old French collection. Ht. 7.9 cm., Th. 5 mm.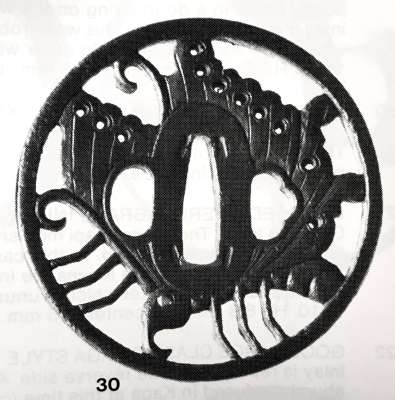
Haynes Catalog #6, lot 30.
Similar tsuba in the Randolph B. Caldwell Collection, 1994, page 24, №13: "A circular iron tsuba pierced in positive sukashi with a butterfly within an angular rim, details engraved. The eye inlaid in brass [in my specimen the inlay is missing on the omote side]. Unsigned. Bizen Shōami, Momoyama period. Dimensions: 8.0 x 8.2 x 0.5 cm. Similar example: Durand-Ruel, collection Ch. Gilloz, number 1302. [SV: that's possibly the 'old French collection' of Robert Haynes.]
Haynes Catalog #9, lot 143.
If we accept Haynes' theory regarding the genealogy and history of Bizen Shōami family, Momoyama period attribution would seem unlikely. I am leaning towards the early to mid 17th century.
Caldwell Collection, #13.
-
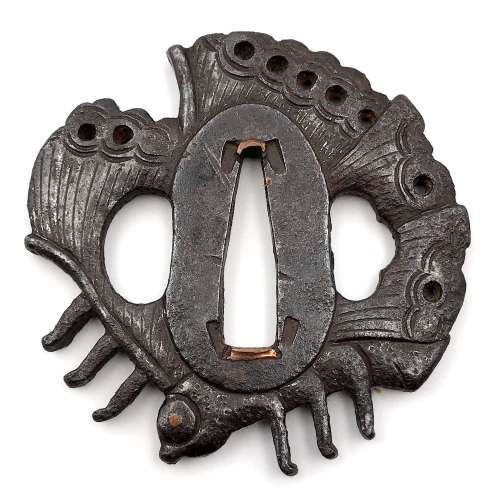 This tsuba is a cut from a typical Bizen Shōami butterfly tsuba (see TSU-0100 in this collection), which normally would have had a circular rim around the butterfly. In this particular example of altered guard we have both eyes of the insect (inlaid in brass or copper) intact. The kebori carving is more pronounced than in TSU-0100 example. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 64.7 x 63.7 x 5.2 mm References: see TSU-0100.
This tsuba is a cut from a typical Bizen Shōami butterfly tsuba (see TSU-0100 in this collection), which normally would have had a circular rim around the butterfly. In this particular example of altered guard we have both eyes of the insect (inlaid in brass or copper) intact. The kebori carving is more pronounced than in TSU-0100 example. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 64.7 x 63.7 x 5.2 mm References: see TSU-0100. -
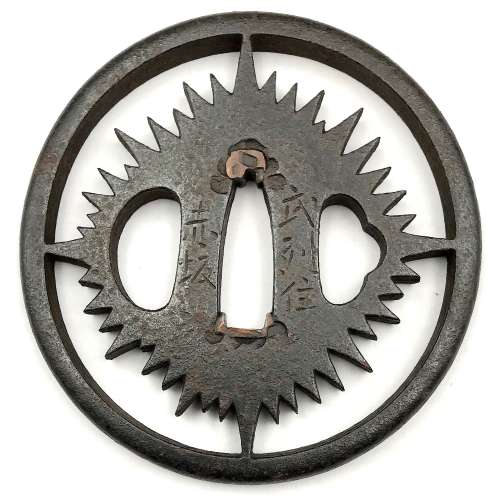 Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit’s IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called “tokei”, or “clock gear”. Signed: On the face: Bushu ju Akasaka; On the back: Tadatoki Saku [Made by Tadatoki, resident of Bushu]. Probably, 4th generation of Akasaka School master Tadatoki (忠時), who died in 1746. Akasaka School. Edo period, first half of the 18th century. Size: 79.8 x 78.5 x 6.5 mm
Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit’s IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called “tokei”, or “clock gear”. Signed: On the face: Bushu ju Akasaka; On the back: Tadatoki Saku [Made by Tadatoki, resident of Bushu]. Probably, 4th generation of Akasaka School master Tadatoki (忠時), who died in 1746. Akasaka School. Edo period, first half of the 18th century. Size: 79.8 x 78.5 x 6.5 mm -
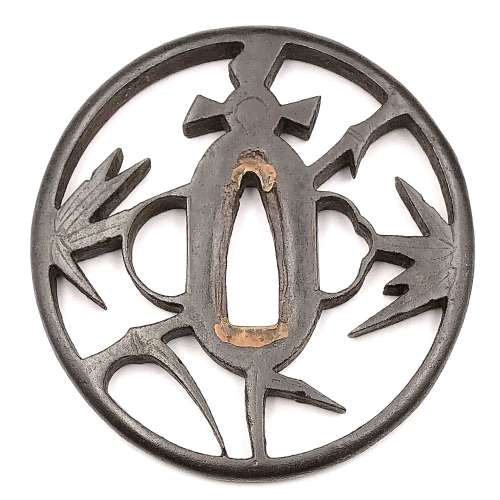 Iron tsuba with design of bamboo and sparrow (take-ni-suzume) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane. Akasaka school. Unsigned. Attributed to second generation Tadamasa Shōzaemon (died in in the fifth year of Enppo, 1677). Early Edo period: 17th century (Kan-ei / Kanbun era). Height: 79.0 mm. Width: 77.5 mm. Rim thickness: 5.5 mm. Center thickness: 6.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 222: "It is believed that sparrows nest in a bamboo grove". According to Merrily Baird [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001], "a bamboo grove is said to be emblematic of security as the bamboo is resilient even in the face of high winds and heavy rains. [...] The association of the sparrow (suzume) with bamboo is an old one found in Japanese poetry, paining, and design. The bird is said to be obsessed with its honor, especially the repaying of debts".
Iron tsuba with design of bamboo and sparrow (take-ni-suzume) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane. Akasaka school. Unsigned. Attributed to second generation Tadamasa Shōzaemon (died in in the fifth year of Enppo, 1677). Early Edo period: 17th century (Kan-ei / Kanbun era). Height: 79.0 mm. Width: 77.5 mm. Rim thickness: 5.5 mm. Center thickness: 6.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 222: "It is believed that sparrows nest in a bamboo grove". According to Merrily Baird [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001], "a bamboo grove is said to be emblematic of security as the bamboo is resilient even in the face of high winds and heavy rains. [...] The association of the sparrow (suzume) with bamboo is an old one found in Japanese poetry, paining, and design. The bird is said to be obsessed with its honor, especially the repaying of debts". -
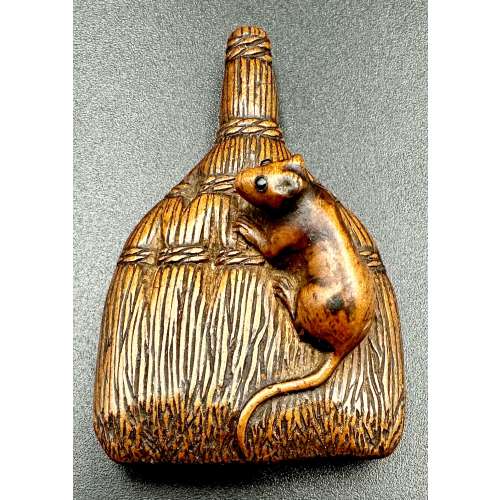 Finely carved as a rat (nezumi) seated on a shuro brush, bound naturalistically with thick bristles. The rodent with a long trailing tail and eyes inlaid in a dark horn. Generously excavated, asymmetrical himotoshi to the underside. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, p. 156): …The Japanese do not clearly differentiate between the rat and the mouse, and one word, nezumi [鼠], designates both. …Rat is a messenger of Daikokuten, a deity of grain and vegetation who is one of Japan’s Seven Gods of Good Luck. ...Depictions of the rat are most common in years of the zodiac represented by the animal. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 49 x 33 x 16 mm. Provenance: From the private collection of Armand Basi (Spanish, 1924-2009).
Finely carved as a rat (nezumi) seated on a shuro brush, bound naturalistically with thick bristles. The rodent with a long trailing tail and eyes inlaid in a dark horn. Generously excavated, asymmetrical himotoshi to the underside. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, p. 156): …The Japanese do not clearly differentiate between the rat and the mouse, and one word, nezumi [鼠], designates both. …Rat is a messenger of Daikokuten, a deity of grain and vegetation who is one of Japan’s Seven Gods of Good Luck. ...Depictions of the rat are most common in years of the zodiac represented by the animal. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 49 x 33 x 16 mm. Provenance: From the private collection of Armand Basi (Spanish, 1924-2009). -
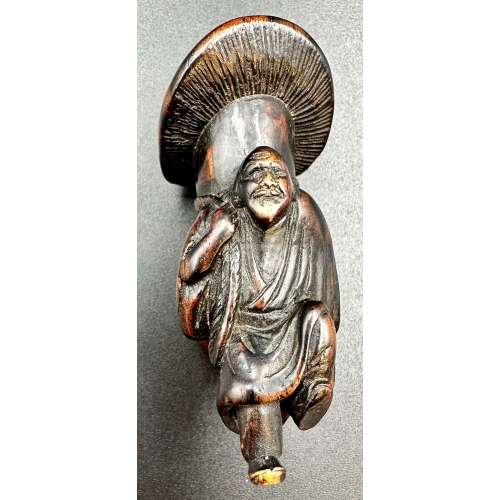

Netsuke with a design of an old man carrying a giant mushroom on his back. Possibly signed on his left foot. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, page. 93): ... This prominent use in the symbol-rich netsuke art form, however, reflects more their sexual symbolism than either their dietary appeal or interesting shapes. Mushrooms in Japan are generally a symbol of fertility, with some flat varieties, like shiitake, being associated with females. In contrast, the matsutake mushroom (Armillaria edodes) is a phallic symbol, as befits its thick, spearlike stem and the fact that it is consumed before cap opens.
Seller's description: "The old man carved walking, with one foot slightly raised, wearing a loose fitted robe and carrying a large long-stemmed mushroom on his back. The wood stained and bearing a fine patina. Himotoshi through the mushroom stem". See VO-0270.2018 for the same subject. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 62 mm tall -
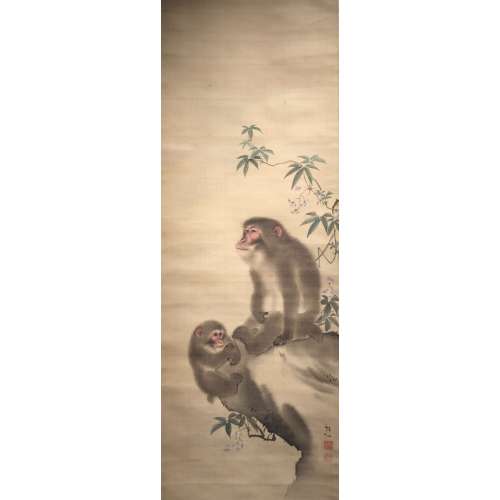 Mori Sosen (1747-1821). A Monkey Seated on a Rock with an Infant Monkey. Hanging scroll painting. Ink and colour on silk. Signed: Sosen. Sealed: Sosen. 108.3 x 38.3 cm. Provenance: According to the box inscriptions, the painting was in the possession of Itakura Katsunao, a daimyo lord in present-day Gunma, in 1808. In 1881, the painting was subsequently acquired by Negishi Shôrei (1833-1897) a master swordsman who established the Negishi school of shuriken ("The only specialist school to have survived is the Negishi-ryū, which was founded by Negishi Shorei in the mid-1800s".)
Mori Sosen (1747-1821). A Monkey Seated on a Rock with an Infant Monkey. Hanging scroll painting. Ink and colour on silk. Signed: Sosen. Sealed: Sosen. 108.3 x 38.3 cm. Provenance: According to the box inscriptions, the painting was in the possession of Itakura Katsunao, a daimyo lord in present-day Gunma, in 1808. In 1881, the painting was subsequently acquired by Negishi Shôrei (1833-1897) a master swordsman who established the Negishi school of shuriken ("The only specialist school to have survived is the Negishi-ryū, which was founded by Negishi Shorei in the mid-1800s".) -
 An uncut fan print uchiwa-e, size 22.7 x 28.7cm, by an unknown artist.
An uncut fan print uchiwa-e, size 22.7 x 28.7cm, by an unknown artist.


