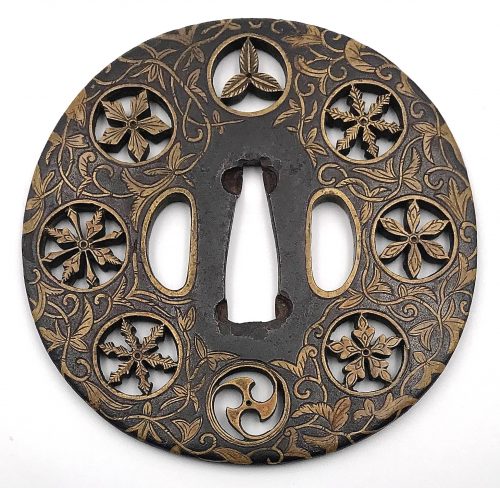
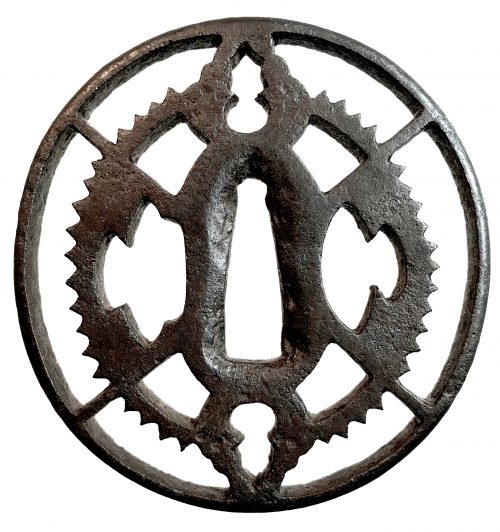
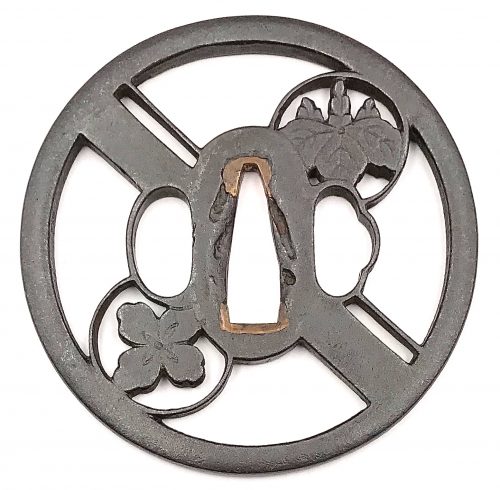
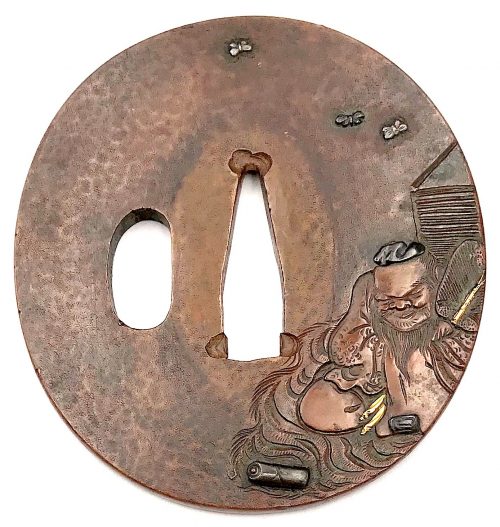
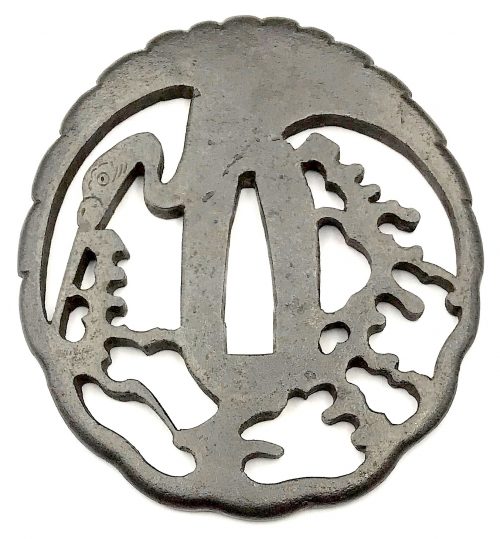
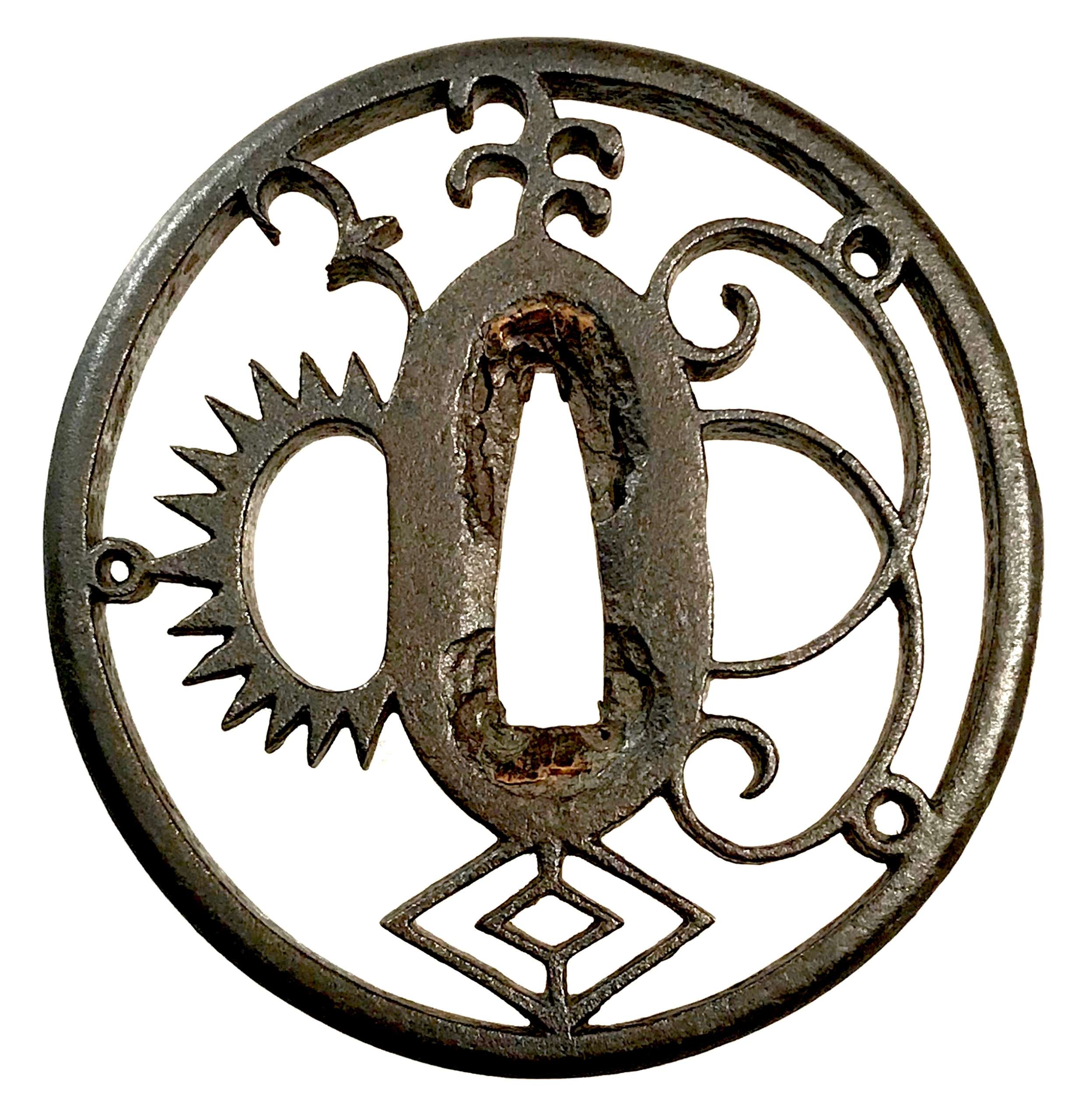
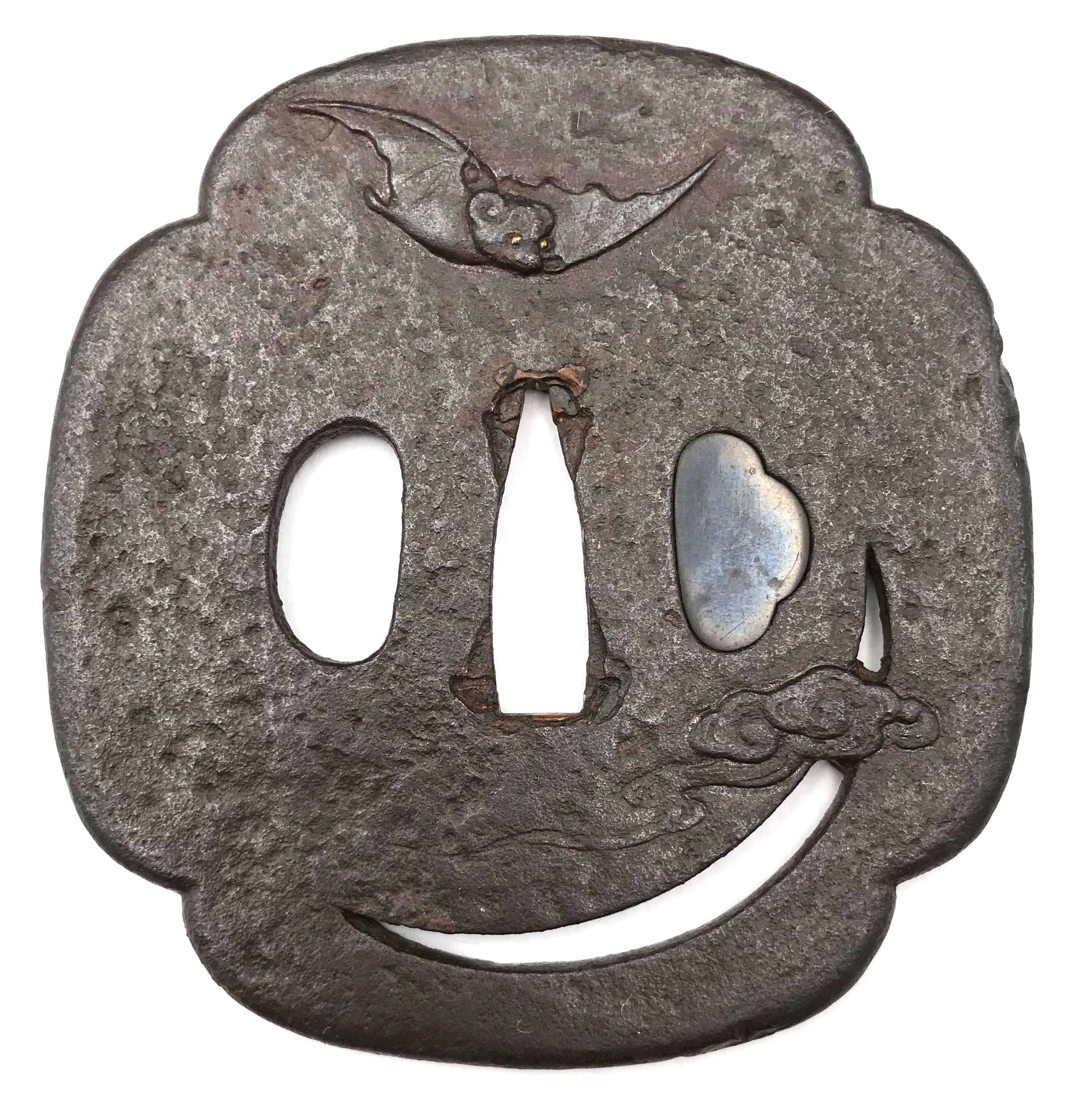
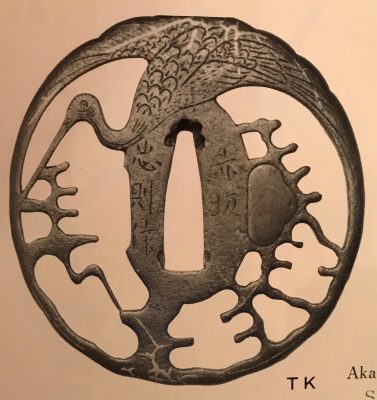
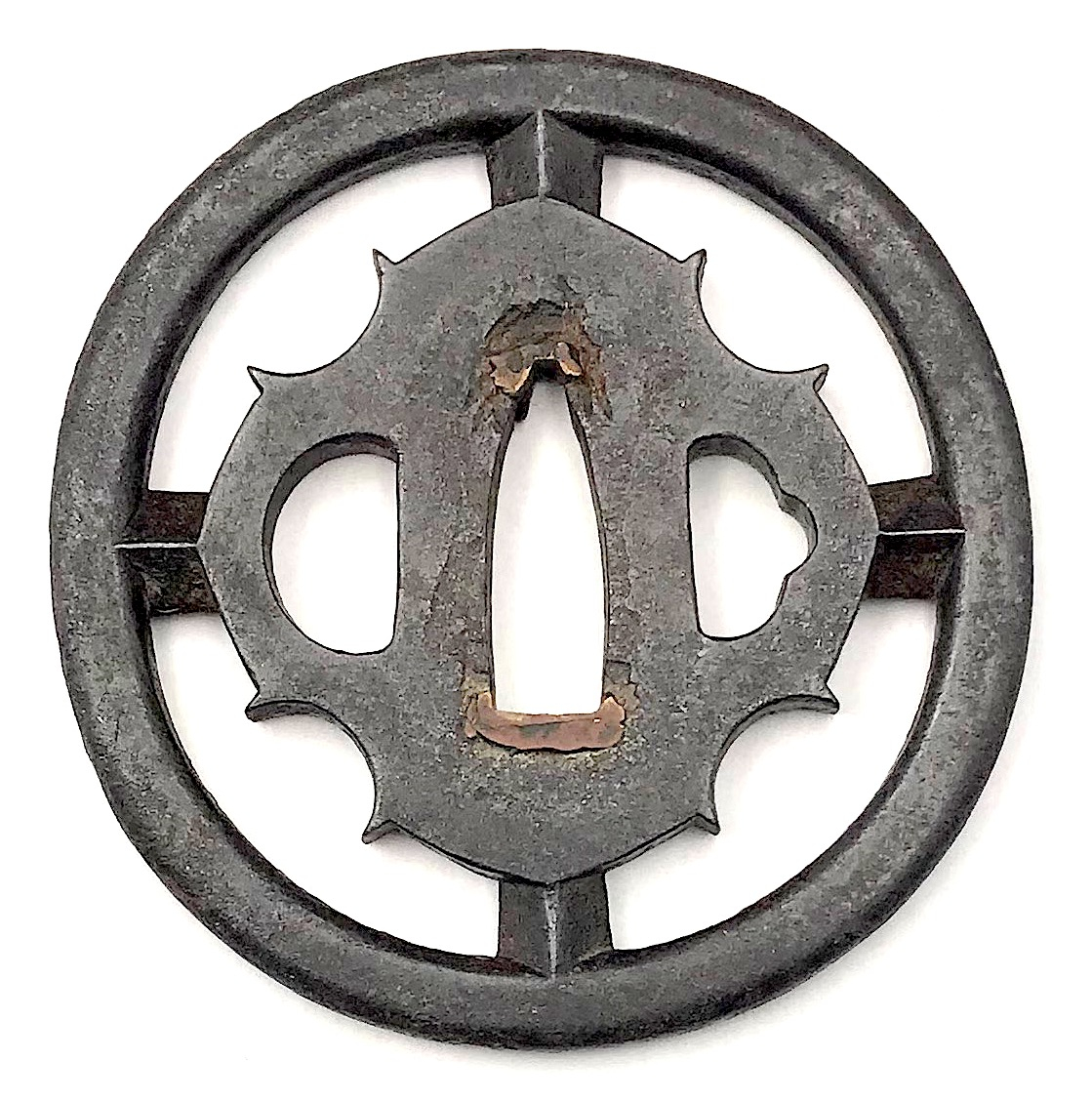
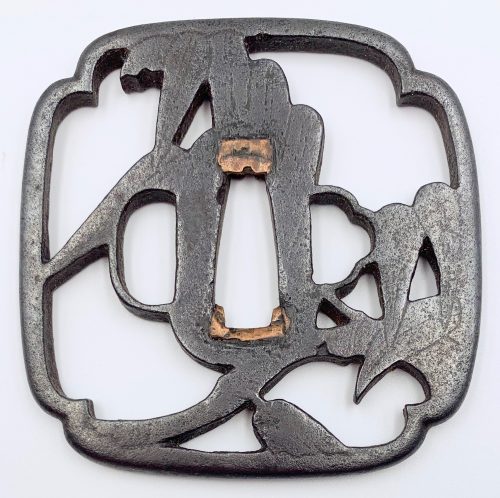
Thin six-lobed iron plate of brownish color is carved on each side with a groove that follows the rim and a concentric grooves around the center of the plate, also carved with six thin scroll lines (mokkō or handles, kan) that follow the shape of the rim. Mokume surface treatment. Hitsu-ana possibly added at a later date, and kogai-hitsu-ana plugged with gold. Silver sekigane.
Signed: Kunihide [國秀]. Higo school, 1st generation swordsmith.
Mid Edo period, ca. 1800.
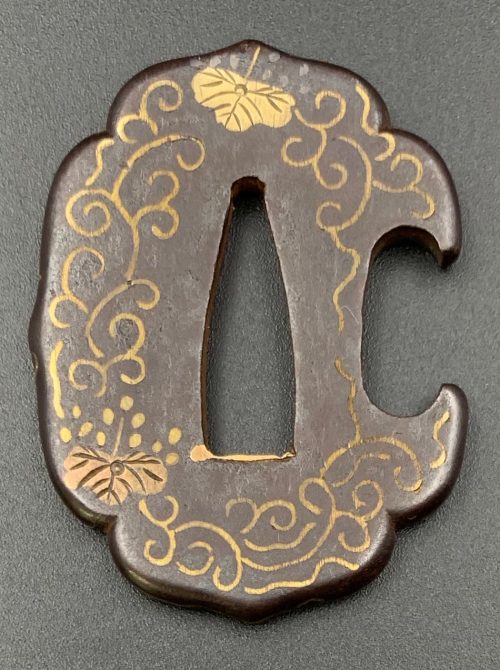
Would be possibly attributed to Kamakura-bori school revival of the 19th century.
References: Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI / Japanese Sword / Kodōgu Part 1, page 231: Enju Kunihide, a tōshō from Higo: "...forging of the jigane is excellent, and there are also pieces with mokume hada."
Haynes Index Vol. 1, p. 741, H 03569.0: "Enju Kunihide in Higo province, died 1830, student of Suishinshi Masahide. Retainer of the Hosokawa Daimyō, etc."
Additional Information from Markus Sesko: This tsuba indeed is made by Enju Kunihide, who in his later years signed the HIDE [
秀] character as HI [日] and DE [出], as here:

Size: 77.4 x 74.9 x 2.7 mm
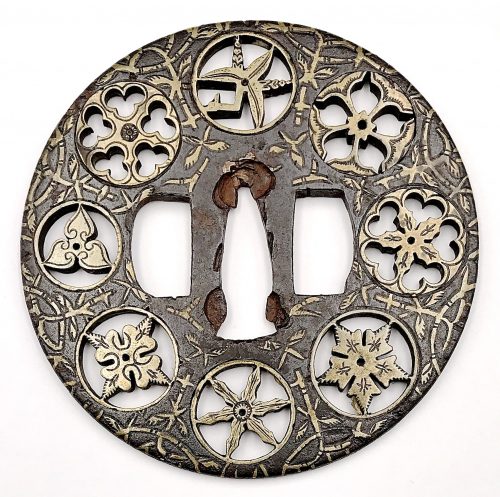
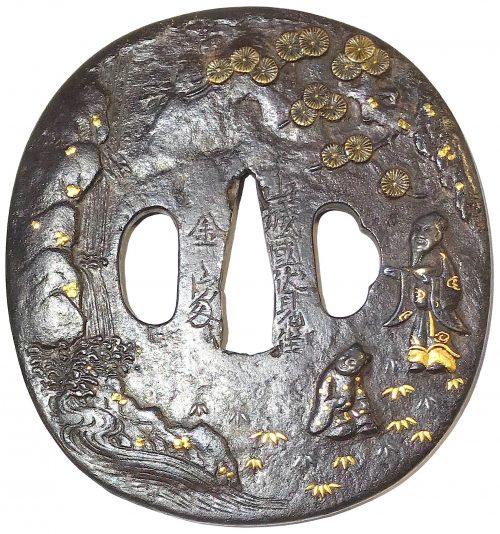
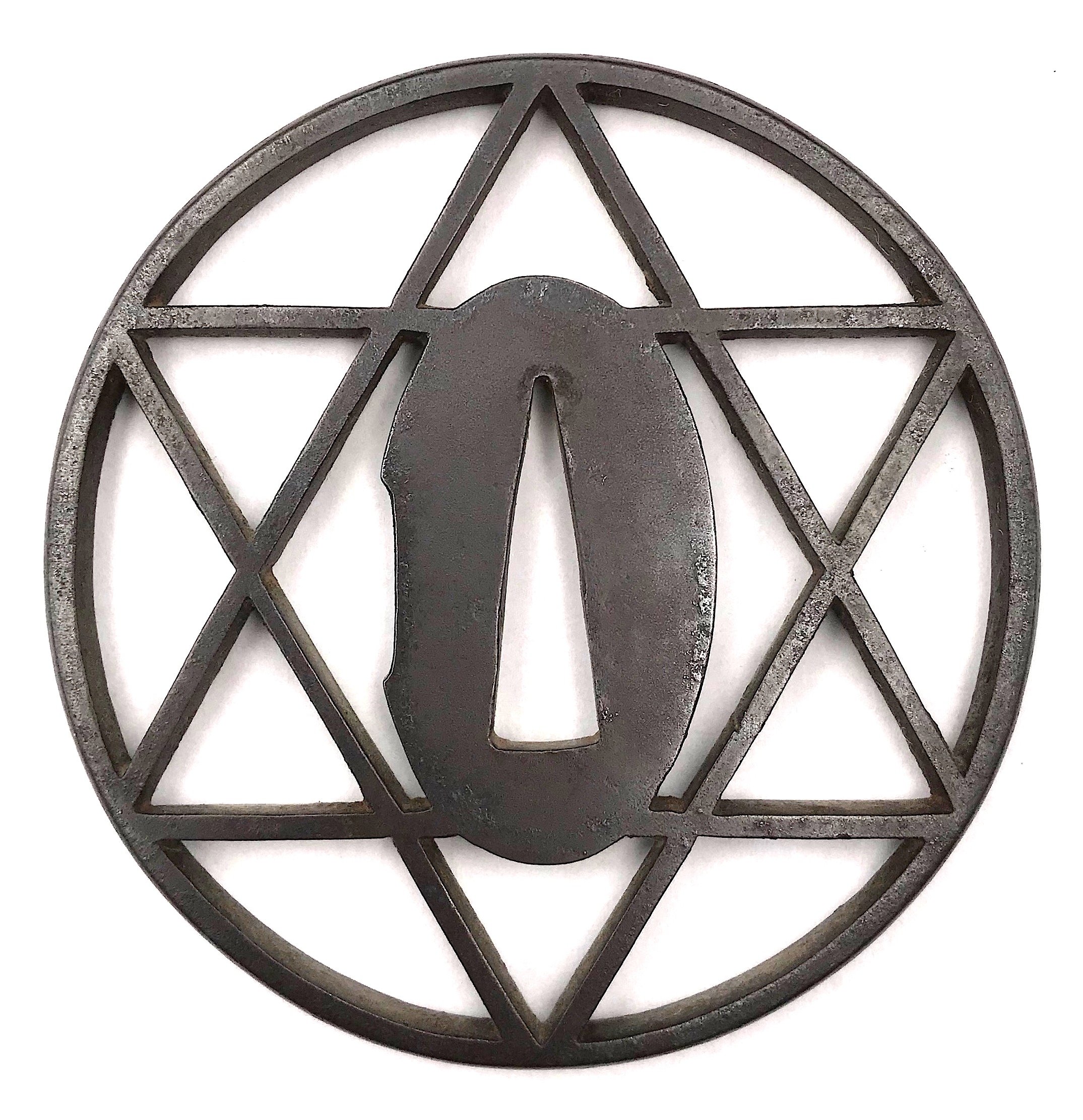
Similar pieces are:
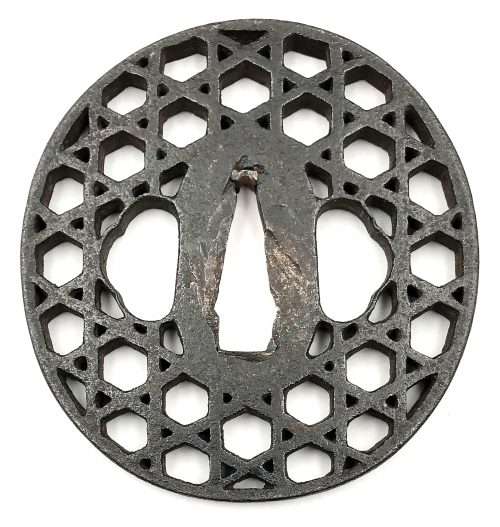
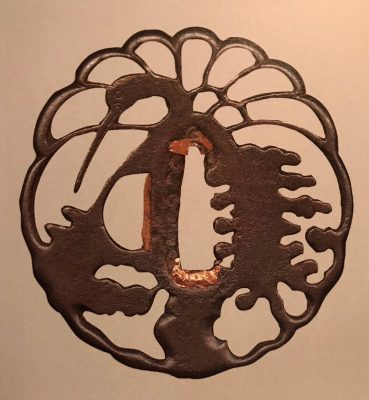
1. In this collection №
TSU-0341: Kamakura-bori tsuba with mokkō motif.
Muromachi period, 15th - 16th century.
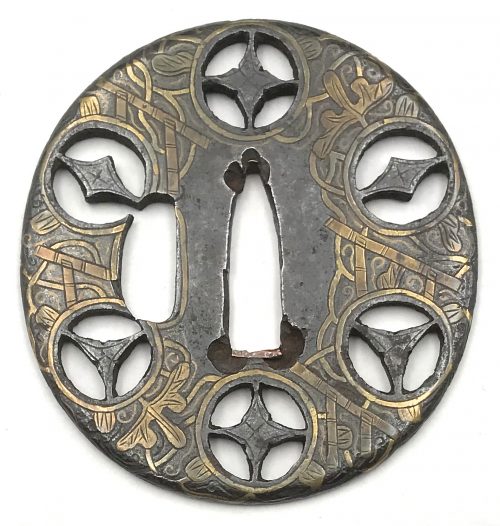
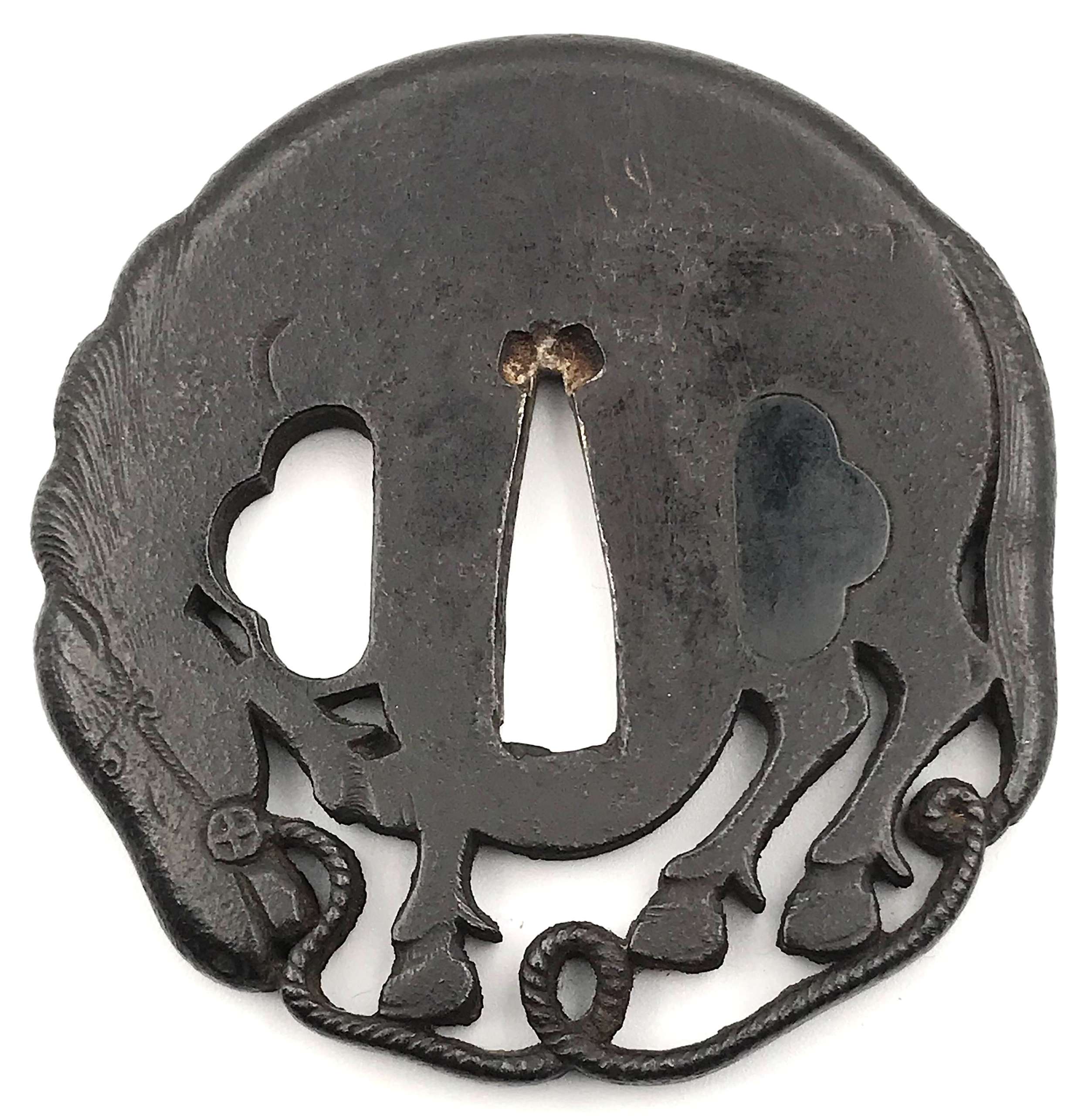
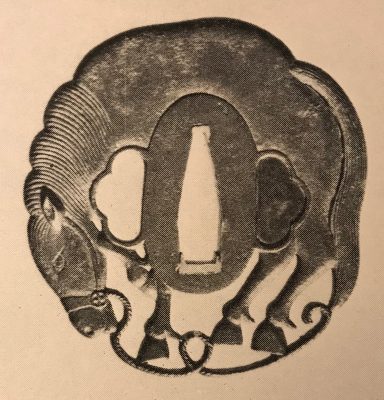
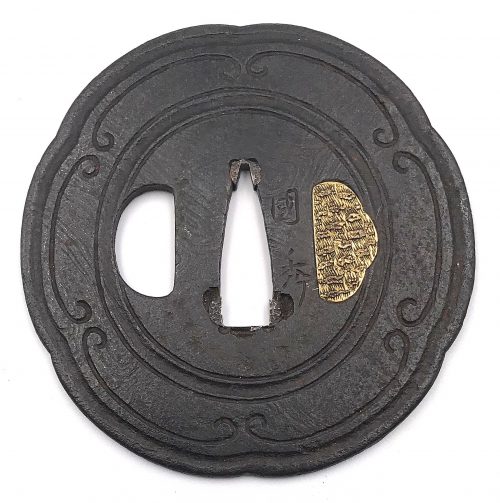
2. Dr. Walter A. Compton Collection, 1992, Christie’s auction, Part II, pp. 14-15, №16: “A
kamakurabori type tsuba,
Muromachi period, circa 1400. The thin, six-lobed iron plate is carved on each side with a wide groove that follows the shape of the rim, and with six scroll lines and a single thin circular groove. […] The
hitsu-ana was added at a later date, circa 1500-1550. Height 8.3 cm, width 8.6 cm, thickness 2.5 mm. The tsuba was initially intended to be mounted on a
tachi of the battle type in use from
Nambokucho to early
Muromachi period (1333-1400)”. Sold at $935.

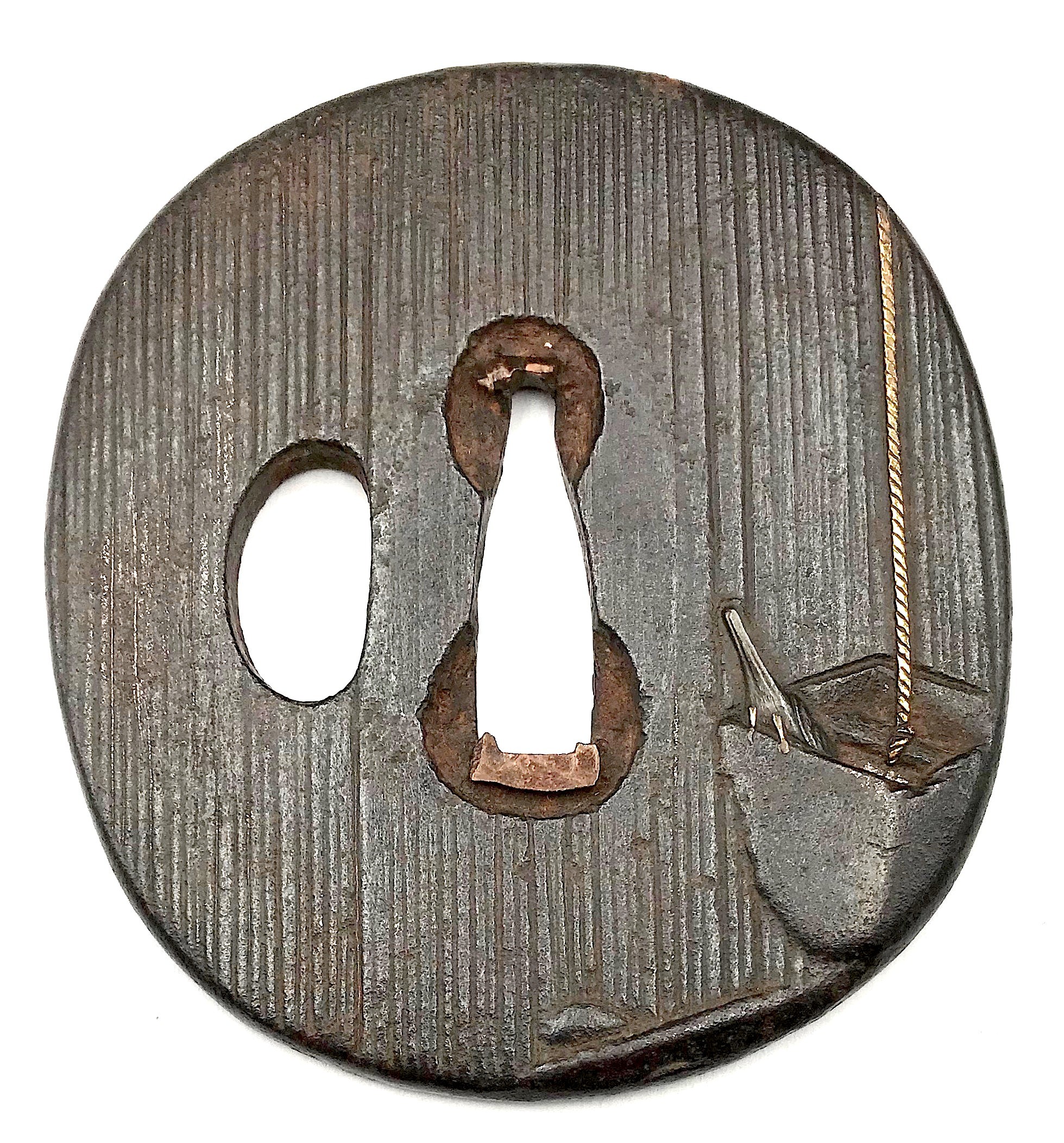
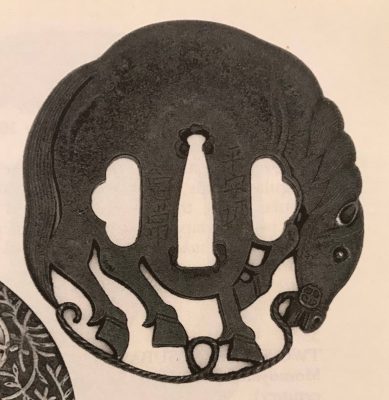
3. And another one in Robert E. Haynes Catalog #9 on page 24-25 under №23: “Typical later
Kamakura-bori style work. This type of plate and carving show the uniform work produced by several schools in the
Muromachi </em period. Some had brass inlay and others were just carved as this one is. The hitsu are later. Ca. 1550. Ht. 8.8 cm, Th. 3.25 mm”. Sold for $175.
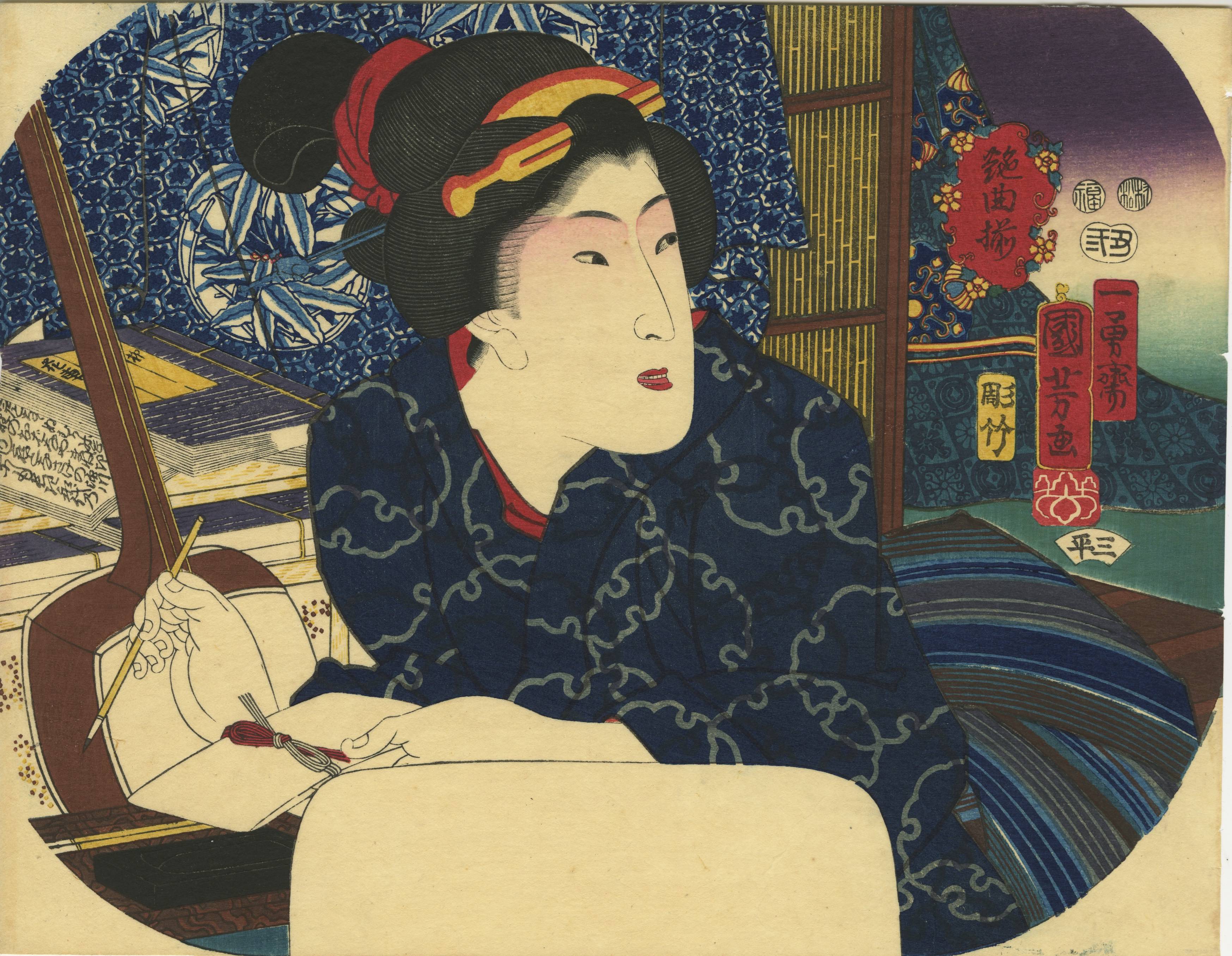
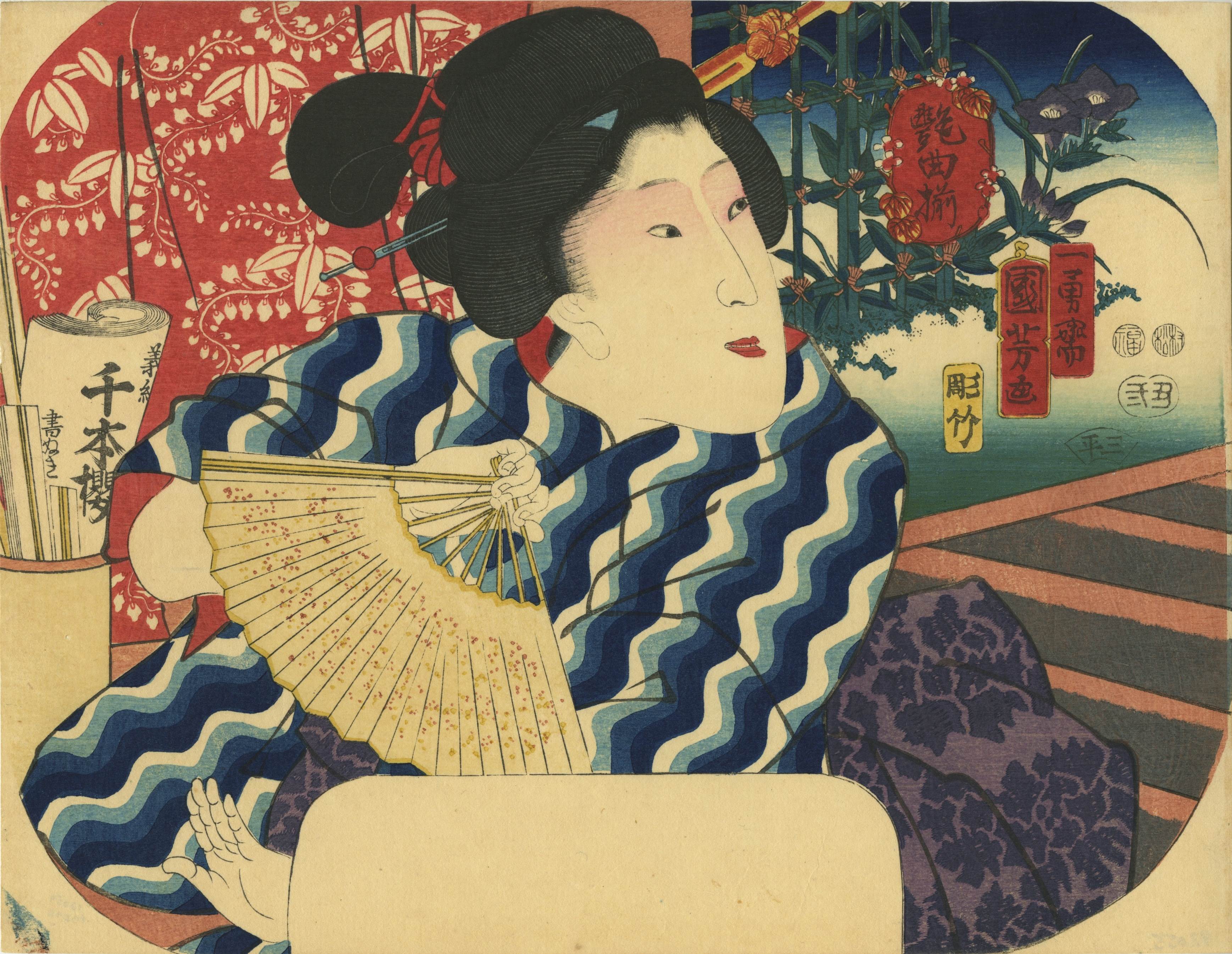
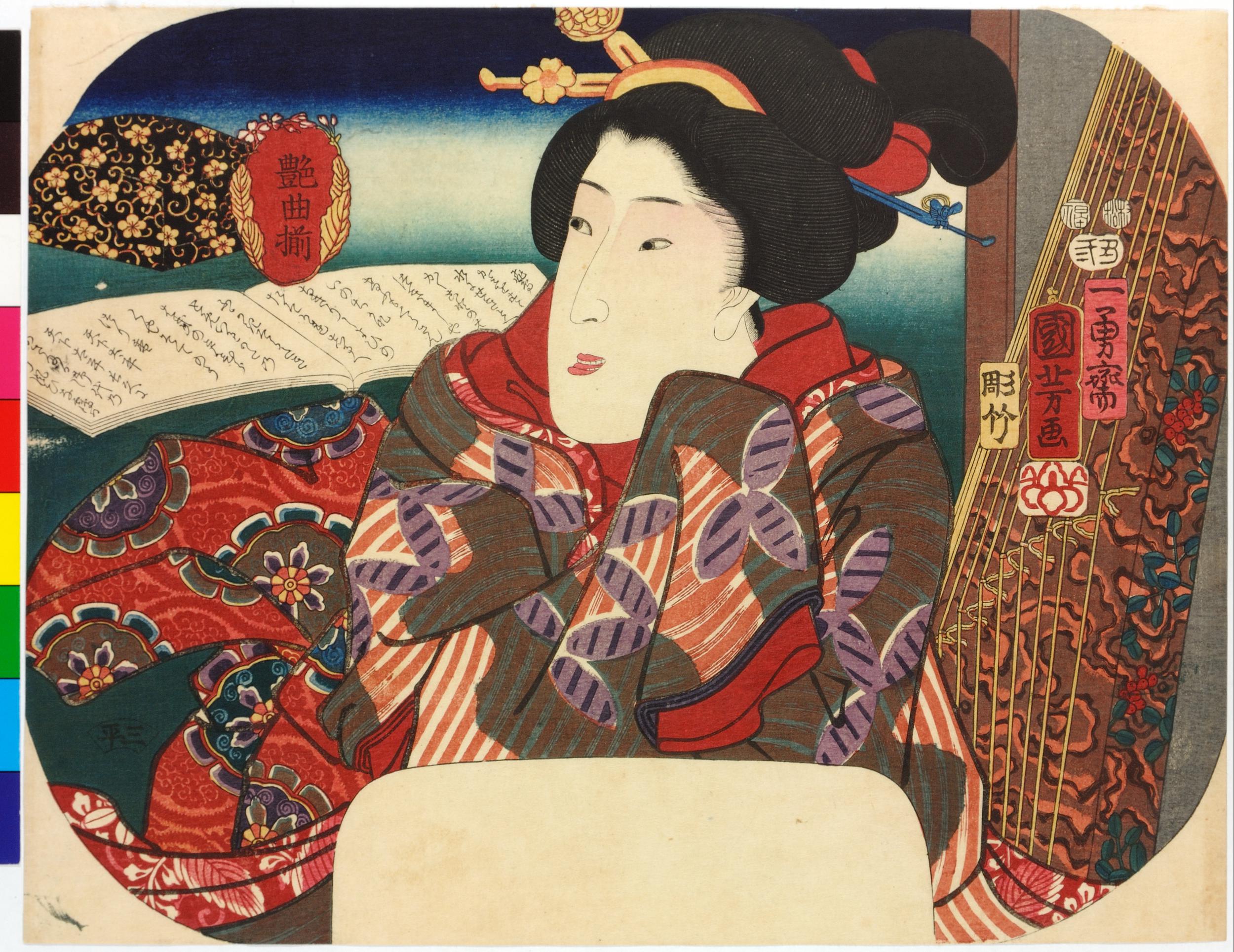














 Uncut fan print (uchiwa-e) depicting Onoe Kikugorō IV as Karukaya Dōshin parting from his son, Ishidomaru (played by Ichimura Uzaemon XIII), and Kawarasaki Gonjūrō I as Yamazakiya Yogoro in the kabuki play Karukaya Dōshin Tsukushi no Iezuto [苅萱桑門筑紫𨏍], written by
Uncut fan print (uchiwa-e) depicting Onoe Kikugorō IV as Karukaya Dōshin parting from his son, Ishidomaru (played by Ichimura Uzaemon XIII), and Kawarasaki Gonjūrō I as Yamazakiya Yogoro in the kabuki play Karukaya Dōshin Tsukushi no Iezuto [苅萱桑門筑紫𨏍], written by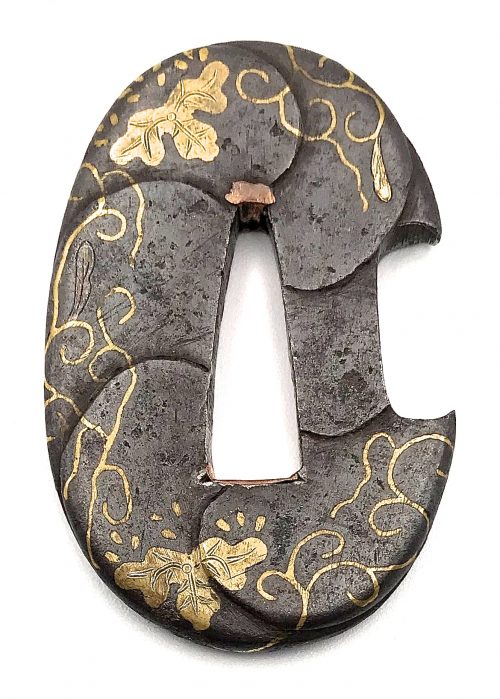 









 Size: 77.4 x 74.9 x 2.7 mm
Size: 77.4 x 74.9 x 2.7 mm
 3. And another one in Robert E. Haynes Catalog #9 on page 24-25 under №23: “Typical later Kamakura-bori style work. This type of plate and carving show the uniform work produced by several schools in the
3. And another one in Robert E. Haynes Catalog #9 on page 24-25 under №23: “Typical later Kamakura-bori style work. This type of plate and carving show the uniform work produced by several schools in the