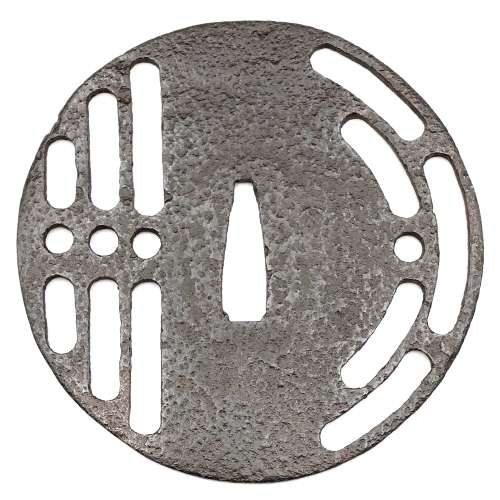
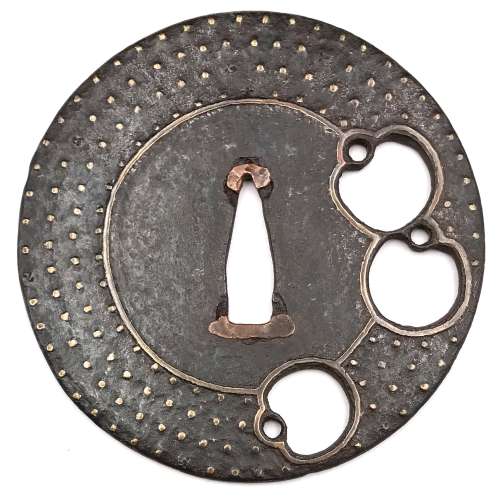
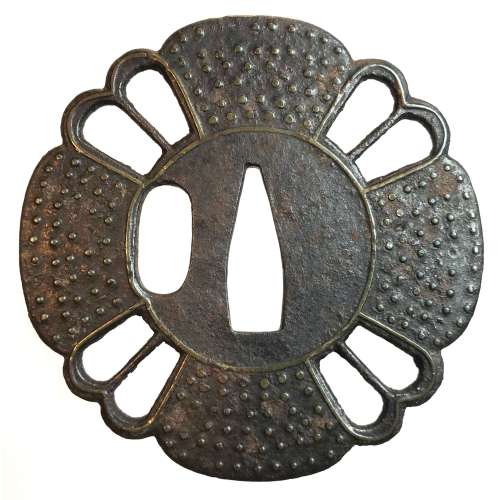
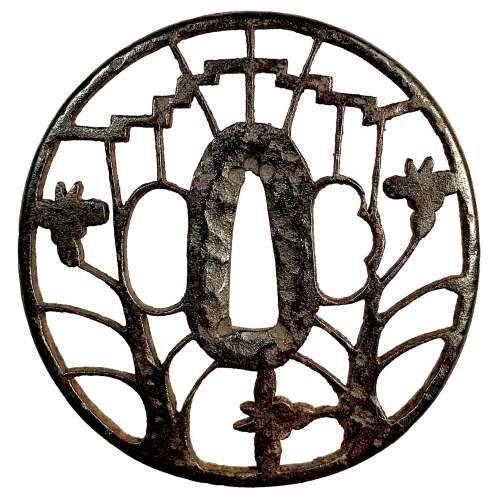
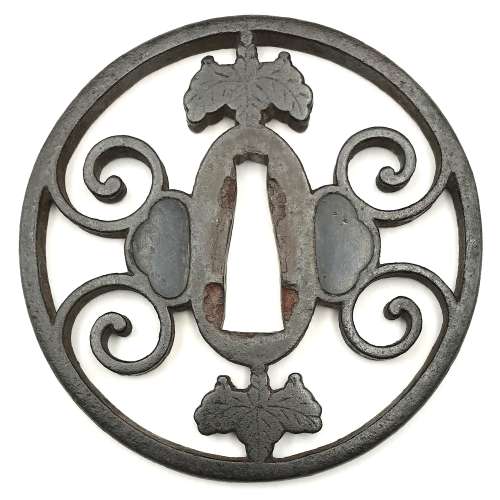
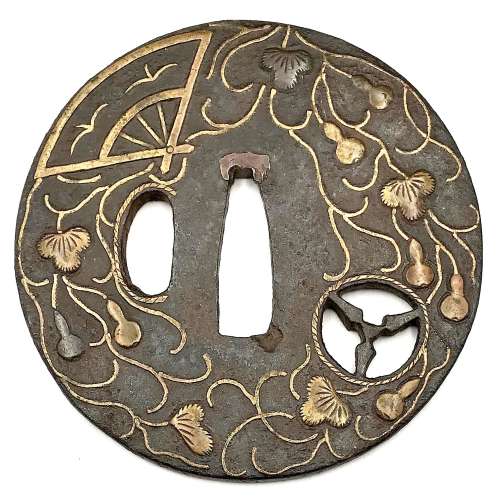
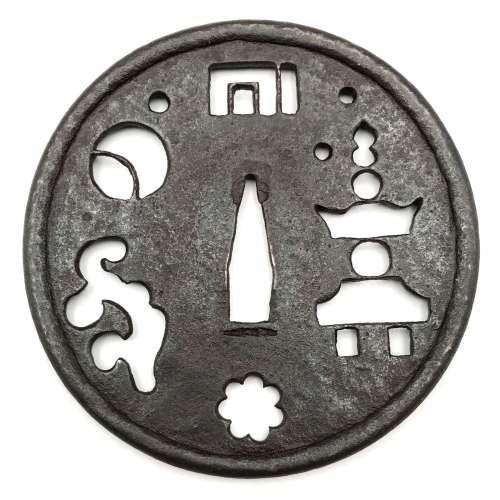
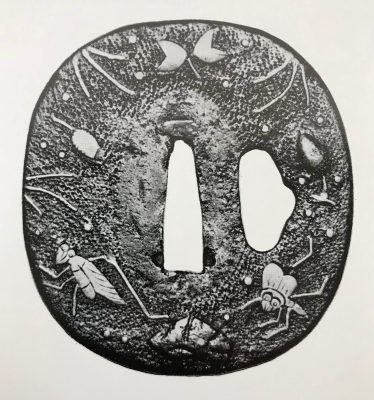
"Traditionally the old iron plate tsuba are classified into Ko Tosho (old sword smith), and Ko Katchushi (old armor maker) styles. It is sometimes difficult to justify attribution of a given tsuba to the Tosho or Katchushi category. Generally guards with raised rims or relatively complex designs tend to be assigned to Katchushi. This is basically a convention we follow out of habit and convenience." [...] "In Token Kai-Shi part six, Articles by Akiyama Kyusaku, Robert Haynes comments: "…from 1300 to 1400 over 150,000 MOUNTED swords were made in Japan for export alone. This means that over four tsuba a day were made for 100 years. This would mean that at least 3000 persons were making nothing but tsuba, let alone all the other fittings needed to complete these swords. With sword smiths, fittings makers and all the other artists need to complete a sword for export, at least 10,000 sword artists were working together, in any one of these hundred years."Another tsuba of similar design, Tōshō school, is illustrated in this collection; see TSU-0319.2015.
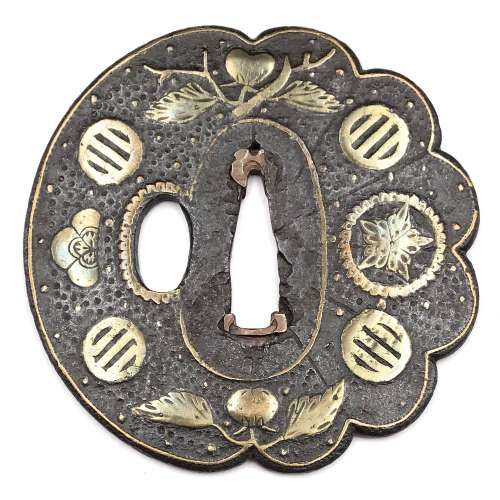
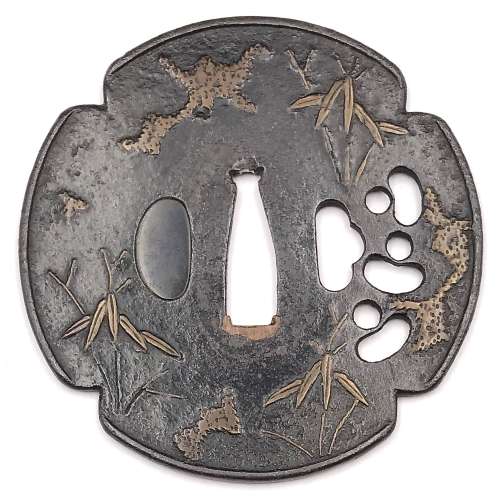
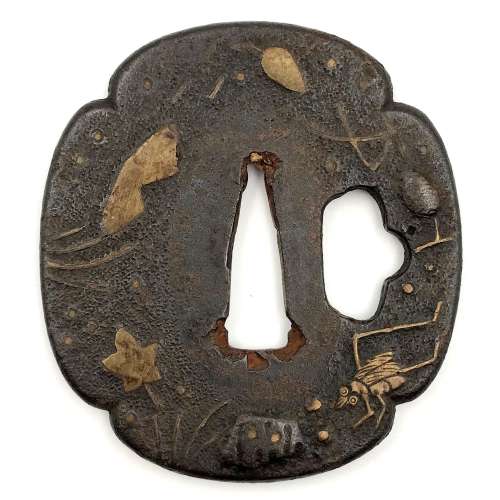
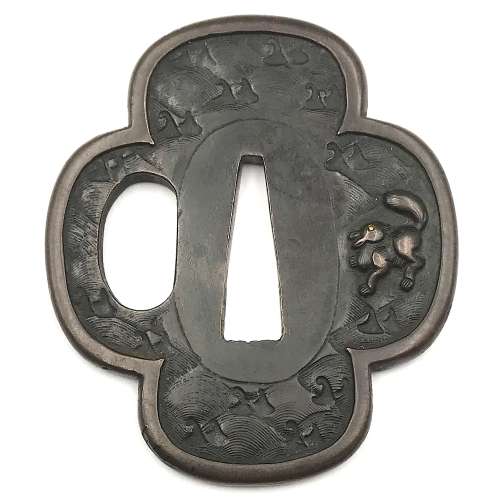
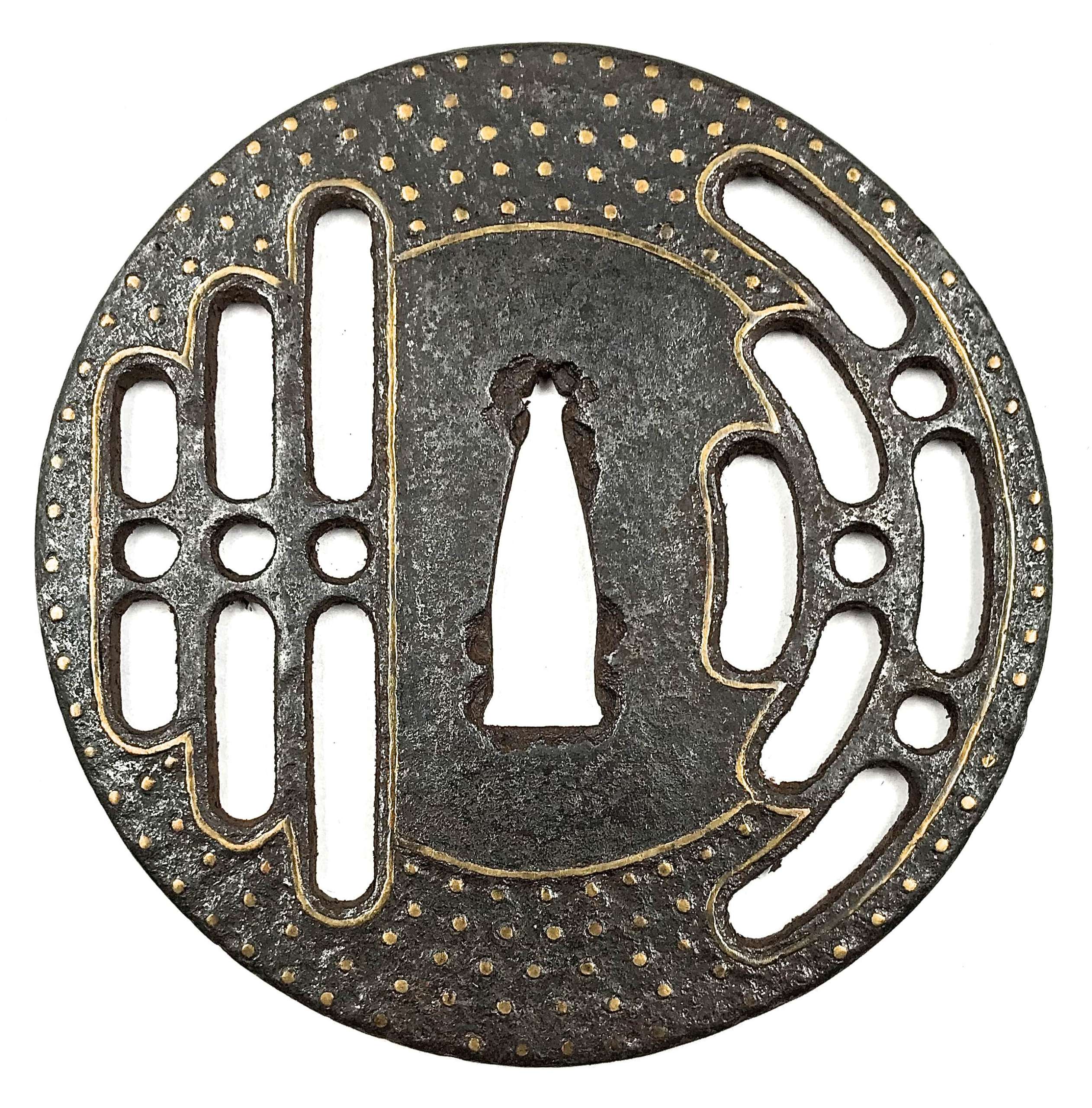 Reference to this design can be found in LIB-1359.2017 Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections, Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997; p. 18-19, lot № 37: "A Kamakura-bori Tsuba, Momoyama Period. ...pierced with two large formalised butterflies..."
Reference to this design can be found in LIB-1359.2017 Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections, Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997; p. 18-19, lot № 37: "A Kamakura-bori Tsuba, Momoyama Period. ...pierced with two large formalised butterflies..."
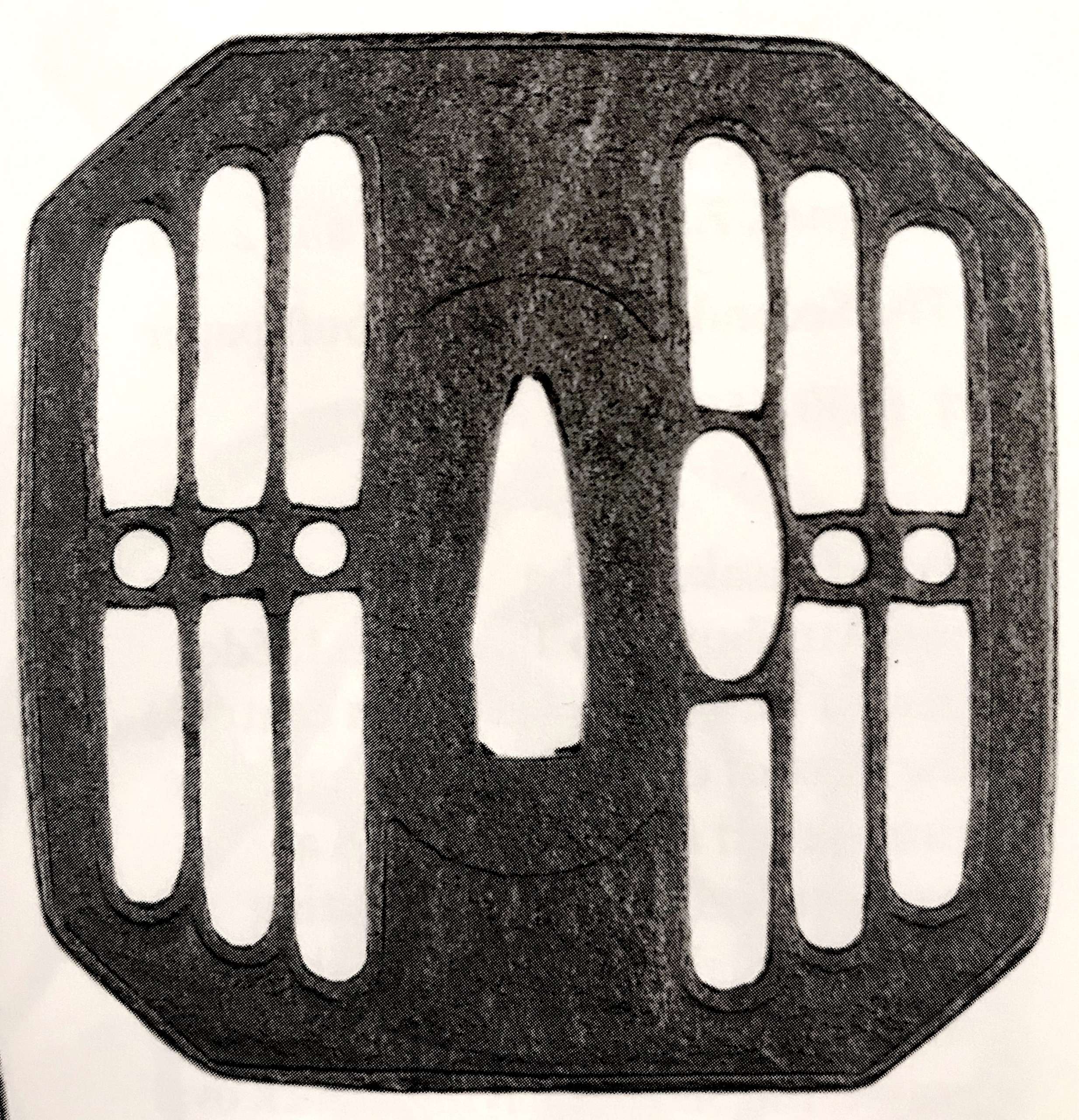
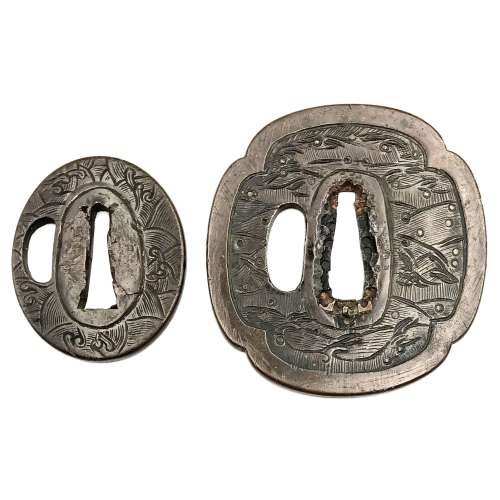
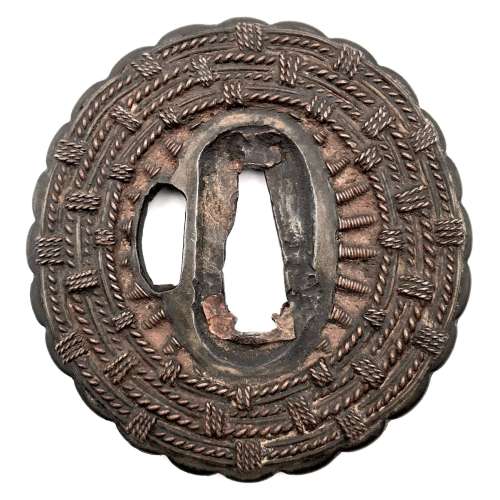
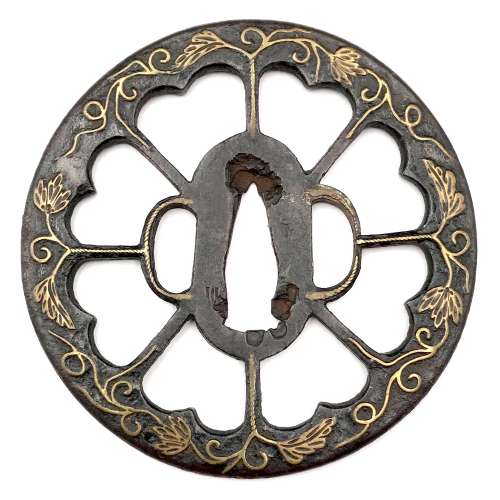
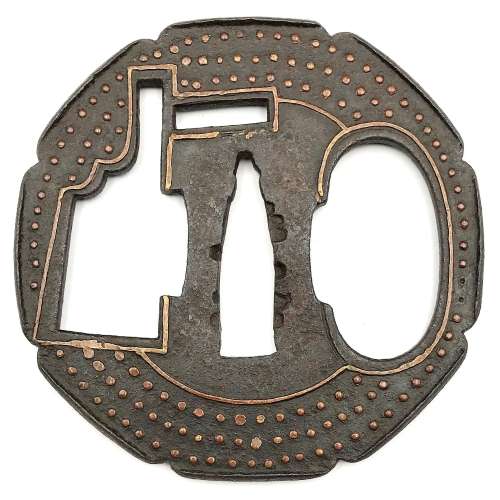
A Kamakura-bori tsuba of octagonal form, Momoyama period.