 Kiri-mon |
 Katakura-mon |
-
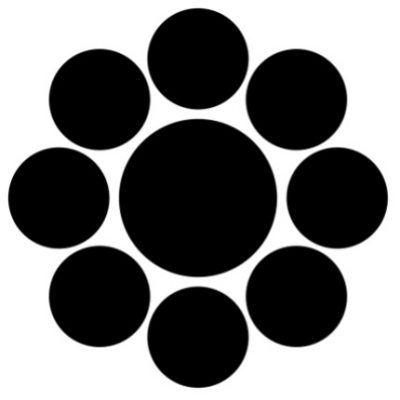
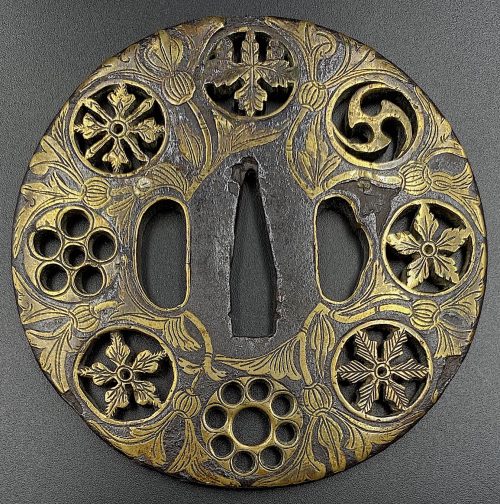 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm. -
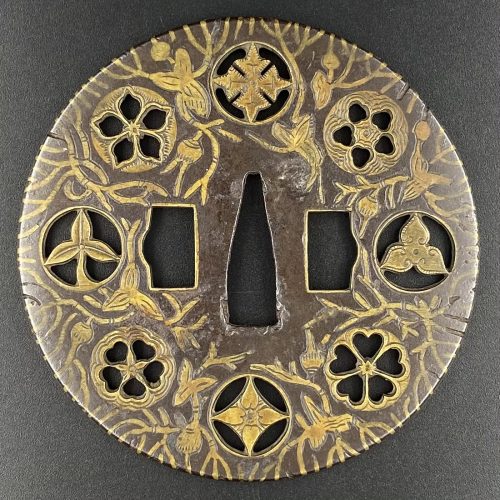 Iron tsuba of round form, tapering from centre to the rim, decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of water plantain (omodaka) and seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 6-, 9-, and 12 – pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels – bellflower, cherry and plum blossoms. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). Unsigned. The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: H: 88.3 mm; W: 88.7 mm; Thickness 4.0 mm (Seppa-dai), 3,2 cm (rim). Other Kaga-Yoshiro tsuba in this collection: TSU-0334: 7.7 cm; TSU-0342.2017: 89.6 cm; TSU-0344: 8.1 cm; TSU-0329: 8.0 cm; TSU-0376.2018: 8.1 cm; TSU-0379.2018: 8.2 cm. We see that the usual size is about 8 cm; larger pieces, such as this one and TSU-0342.2017 dedicated to Hachiman, are rare. Article about Yoshiro tsuba.
Iron tsuba of round form, tapering from centre to the rim, decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of water plantain (omodaka) and seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 6-, 9-, and 12 – pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels – bellflower, cherry and plum blossoms. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). Unsigned. The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: H: 88.3 mm; W: 88.7 mm; Thickness 4.0 mm (Seppa-dai), 3,2 cm (rim). Other Kaga-Yoshiro tsuba in this collection: TSU-0334: 7.7 cm; TSU-0342.2017: 89.6 cm; TSU-0344: 8.1 cm; TSU-0329: 8.0 cm; TSU-0376.2018: 8.1 cm; TSU-0379.2018: 8.2 cm. We see that the usual size is about 8 cm; larger pieces, such as this one and TSU-0342.2017 dedicated to Hachiman, are rare. Article about Yoshiro tsuba. -
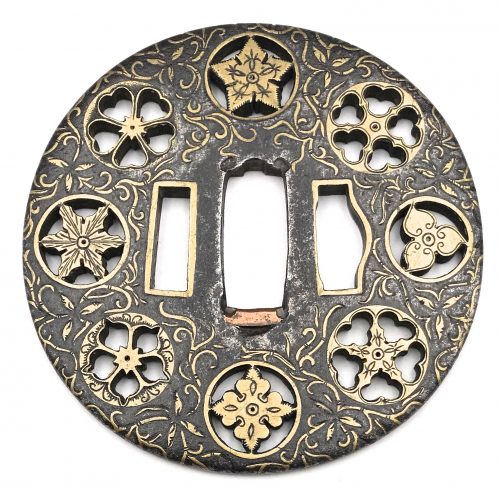 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana trimmed in brass. Nakago-ana of rectangular form, with copper sekigane. Four positive openwork (ji-sukashi) roundels at 12, 3, 6, and 9 o'clock; and four negative openwork (in-sukashi) roundels with cherry blossom, bellflower, and two variations on suhama theme. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, late 16th to early 17th century. Size: diameter 81.4 mm, thickness 4.7 mmat seppa-dai, 4.0 mm at rim. Christie's lot description: AN IRON TSUBA; EDO PERIOD (17TH CENTURY). THE DOLPHYN COLLECTION OF SAMURAI ART. The round iron tsuba pierced with roundels of various floral motifs interspersed among scrolling foliage, all inlaid with brass. 8.1 cm. high. Provenance: Pabst Collection (no. 338).
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana trimmed in brass. Nakago-ana of rectangular form, with copper sekigane. Four positive openwork (ji-sukashi) roundels at 12, 3, 6, and 9 o'clock; and four negative openwork (in-sukashi) roundels with cherry blossom, bellflower, and two variations on suhama theme. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, late 16th to early 17th century. Size: diameter 81.4 mm, thickness 4.7 mmat seppa-dai, 4.0 mm at rim. Christie's lot description: AN IRON TSUBA; EDO PERIOD (17TH CENTURY). THE DOLPHYN COLLECTION OF SAMURAI ART. The round iron tsuba pierced with roundels of various floral motifs interspersed among scrolling foliage, all inlaid with brass. 8.1 cm. high. Provenance: Pabst Collection (no. 338). -
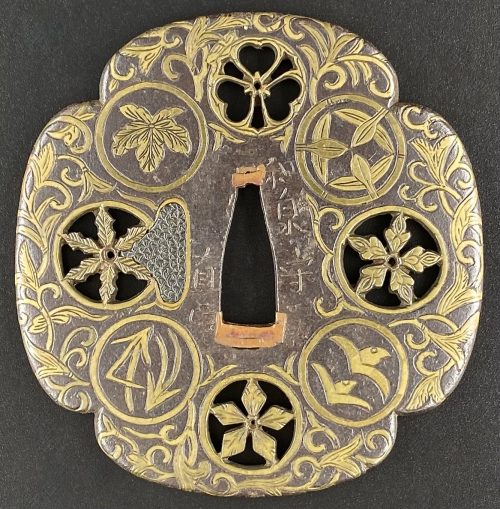 The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba.
The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba. -
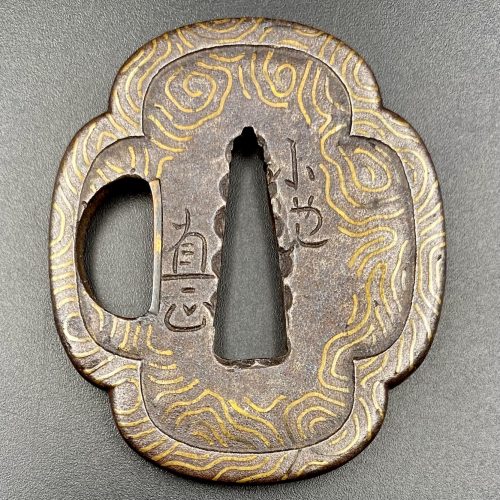

Small iron tsuba for a dagger (tantō), of quatrefoil form (mokkō-gata), with raised rim (mimi), decorated with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) to form an abstract design alluding to the mushroom of immortality (reishi). Opening (hitsu-ana) to the left of nakaga-ana probably cut later and fitted with shakudo sekigane. Maker's signature on seppa-dai: Koike Naomasa (小池 直正).
Momoyama period: End of the 16th - beginning of the 17th century. Dimensions: Height 53.7 mm; Width: 45.5 mm; Thickness at centre: 3.5 mm; at rim: 4.9 mm. Other examples of signed Koike Naomasa work in this collection: TSU-0346. Reference: The closest example in literature is in Compton Collection (II): №11 with the description: “A Koike School tsuba, Edo period (circa 1625), signed Koike Yoshiro. Sheet-brass flush inlay of cloud forms and wire inlay creating the same shape. Koike Yoshiro Naomasa worked from the Keicho to the Genna periods (1596-1623). He arrived in Kyoto from Kaga.” [Japanese Swords and Sword Fittings from the Collection of Dr. Walter Ames Compton (Part II) / Sebastian Izzard, Yoshinori Munemura. — Christie's, New York, October 22, 1992]. See: Yoshirō tsuba.
-
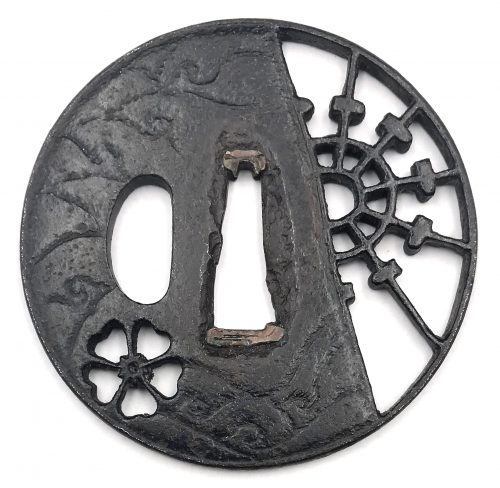 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of sea waves in low relief carving (kebori) and pierced with design of cherry blossom in negative silhouette (in-sukashi) and water wheel in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi). The solid portion of the plate has a shallow groove just before the edge. Copper sekigane. School attribution is unclear. Unsigned. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. Dimensions: Height: 70.3 mm, width: 71.1 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 4.4 mm, at rim 4.1 mm. Provenance: Robert E. Haynes, Mark Weisman. This is what shibuiswords.com says about this tsuba:
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of sea waves in low relief carving (kebori) and pierced with design of cherry blossom in negative silhouette (in-sukashi) and water wheel in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi). The solid portion of the plate has a shallow groove just before the edge. Copper sekigane. School attribution is unclear. Unsigned. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. Dimensions: Height: 70.3 mm, width: 71.1 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 4.4 mm, at rim 4.1 mm. Provenance: Robert E. Haynes, Mark Weisman. This is what shibuiswords.com says about this tsuba:"A very unusual iron plate tsuba. The solid plate is carved with waves on both sides. A cherry bloom in sukashi, lower left, and the right third of the plate in openwork with design of a water wheel. The rim with some iron bones. The hitsu-ana is original but the shape may have been slightly changed. One would expect this to be the work of the early Edo period, but the age of the walls of the sukashi would suggest that this is a work of the middle Muromachi period. This must be the forerunner for the Edo examples we see of this type of design." (Haynes)
I managed to find a look-a-like tsuba in Haynes Catalog #5, 1983, pp. 20-21, №44: "Typical later Heianjo brass inlay example. Ca. 1725. Ht. 7 cm., Th. 4.5 mm., $100/200".We see that the plate design of both tsuba is the same, and the only difference is the trim. It would be logical to assume that both pieces were made at about the same time, rather than 225 years apart. To be fair, let's accept that they were made in Momoyama period.
Haynes Catalog #5, 1983, pp. 20-21, №44.
-
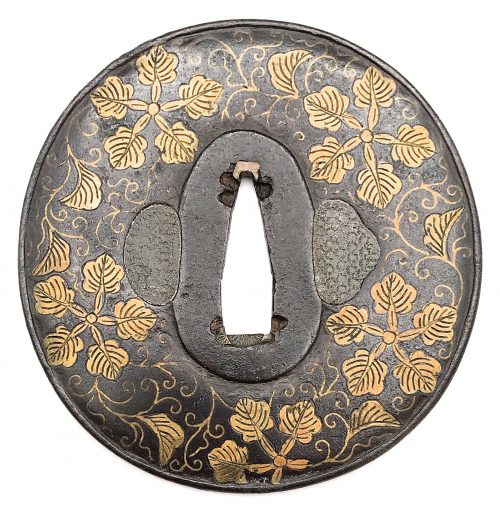 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form decorated with design of melon flowers, vines, and leaves in brass flat inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Slightly raised rim (mimi) carved in a way to simulate ring-shaped covering (fukurin). Kozuka hitsu-ana and kogai hitsu-ana both plugged with soft metal (tim or lead). Copper sekigane. Heianjō or Kaga School. Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Iron, hira-zōgan brass inlay. Round (maru gata) form, diameter 79 mm. Size: 80.3 x 78.4 mm; thickness at seppa-dai: 3.4 mm; at the middle: 3.8 mm; before the rim: 2.4 mm, rim: 2.8 mm. Note on design: though this design resembles family crests with oak and mulberry leaves, I believe it's a melon flower [see Jeanne Allen. Designer's guide to Samurai Patterns. Chronicle Books, San Francisco, 1990, page 114, №130 "Melon Flowers":Note about the distribution of thickness (niku-oki): "this tsuba has toroid features, niku raises from the rim towards the centre but thins once more out when approaching the seppa-dai" [M. Sesko, "Handbook...", p. 48].
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form decorated with design of melon flowers, vines, and leaves in brass flat inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Slightly raised rim (mimi) carved in a way to simulate ring-shaped covering (fukurin). Kozuka hitsu-ana and kogai hitsu-ana both plugged with soft metal (tim or lead). Copper sekigane. Heianjō or Kaga School. Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Iron, hira-zōgan brass inlay. Round (maru gata) form, diameter 79 mm. Size: 80.3 x 78.4 mm; thickness at seppa-dai: 3.4 mm; at the middle: 3.8 mm; before the rim: 2.4 mm, rim: 2.8 mm. Note on design: though this design resembles family crests with oak and mulberry leaves, I believe it's a melon flower [see Jeanne Allen. Designer's guide to Samurai Patterns. Chronicle Books, San Francisco, 1990, page 114, №130 "Melon Flowers":Note about the distribution of thickness (niku-oki): "this tsuba has toroid features, niku raises from the rim towards the centre but thins once more out when approaching the seppa-dai" [M. Sesko, "Handbook...", p. 48].
Jeanne Allen. Designer's guide to Samurai Patterns. Chronicle Books, San Francisco, 1990. Page 114, №130.
-
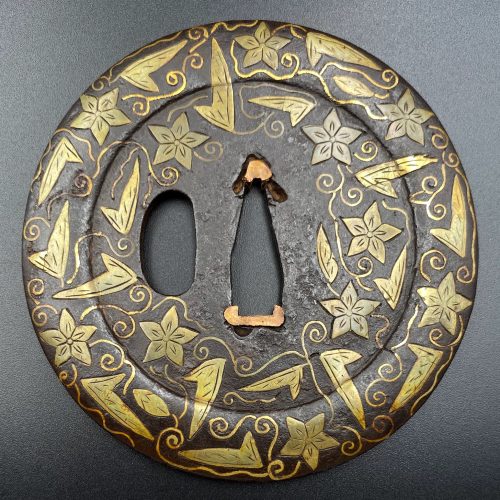 Iron tsuba of the round form (丸型, maru–gata), decorated with brass flat inlay (平象嵌, hira-zōgan) of bellflowers, leaves, and vines on both sides, inlaid brass is carved in low relief; wide rim (dote-mimi) also inlaid; the plate is pierced with hitsu-ana (probably original); nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Dimensions: Height: 84.1 mm; Width: 82.0 mm; Thickness (centre): 2.8 mm; mimi is 11.8 mm wide and 4.7 mm thick. Produced at the end of the 16th century, in the Momoyama period (1674–1703).
Iron tsuba of the round form (丸型, maru–gata), decorated with brass flat inlay (平象嵌, hira-zōgan) of bellflowers, leaves, and vines on both sides, inlaid brass is carved in low relief; wide rim (dote-mimi) also inlaid; the plate is pierced with hitsu-ana (probably original); nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Dimensions: Height: 84.1 mm; Width: 82.0 mm; Thickness (centre): 2.8 mm; mimi is 11.8 mm wide and 4.7 mm thick. Produced at the end of the 16th century, in the Momoyama period (1674–1703). -
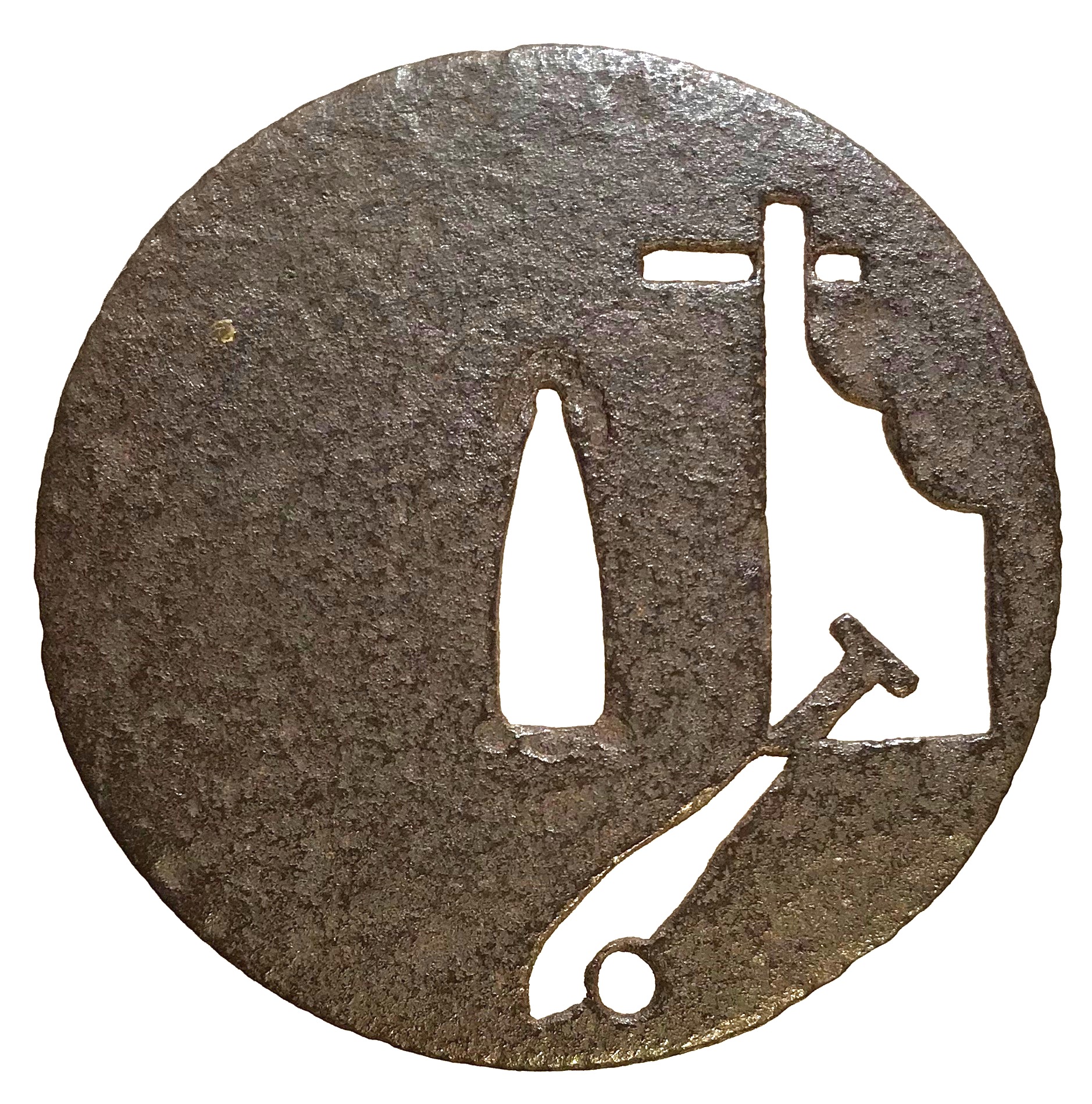 Round tsuba of iron; well forged thin plate decorated with a rudder (kaji) and an oar, or paddle (kai) with a water drop, executed in a combination of negative (in-sukashi) and positive (ji-sukashi) openwork. It may be Ko-Tōshō (old Tōshō) or just Tōshō school, without a 'Ko'. The characteristics of the plate point toward an older piece, however the combination of negative and positive silhouettes pulls the date of manufacture in an opposite direction. Muromachi period. Height: 90.0 mm. Width: 89.0 mm. Rim thickness: 2.1 mm. Center thickness: 2.3 mm. Nakago-ana: height = 29 mm, width = 8.8 mm. A rudder and an oar design is classified by John W. Dower as "Sailing vessels and gear": "Unlike many other motifs, sailing vessels and sailing gear failed to collect an interesting lore or to develop levels of meaning." Merrily Baird does not say anything about these symbols. Yuzuri Okada says: "Ships, sails, rudders, etc. also supply motive of the same class as wheels." He does not provide us with the description of the motive supplied by the wheel. The same motif is used on Ōnin tsuba in this collection:
Round tsuba of iron; well forged thin plate decorated with a rudder (kaji) and an oar, or paddle (kai) with a water drop, executed in a combination of negative (in-sukashi) and positive (ji-sukashi) openwork. It may be Ko-Tōshō (old Tōshō) or just Tōshō school, without a 'Ko'. The characteristics of the plate point toward an older piece, however the combination of negative and positive silhouettes pulls the date of manufacture in an opposite direction. Muromachi period. Height: 90.0 mm. Width: 89.0 mm. Rim thickness: 2.1 mm. Center thickness: 2.3 mm. Nakago-ana: height = 29 mm, width = 8.8 mm. A rudder and an oar design is classified by John W. Dower as "Sailing vessels and gear": "Unlike many other motifs, sailing vessels and sailing gear failed to collect an interesting lore or to develop levels of meaning." Merrily Baird does not say anything about these symbols. Yuzuri Okada says: "Ships, sails, rudders, etc. also supply motive of the same class as wheels." He does not provide us with the description of the motive supplied by the wheel. The same motif is used on Ōnin tsuba in this collection:
-
 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of dragonfly in negative openwork (in-sukashi). It may be Ko-Tōshō (old Tōshō) or just Tōshō school, without a 'Ko'. Probably the dragonfly here is used as a family crest (mon). Muromachi period. Dimensions: Height: 95.0 mm. Width: 93.6 mm. Rim thickness: 2.1 mm. Center thickness: 2.3 mm. Nakago-ana: height = 30 mm, width = 7.8 mm. A dragonfly design is described by John W. Dower as following "During the period of feudal warfare, the dragonfly is reputed to have been am especially popular design applied to arrow quivers, and some warriors adopted it as a family crest. One reason for this was the insect's alternative names of katsu mushi and shogun mushi, both meaning 'victory insect'." Merrily Baird is even more talkative regarding the matter: "The dragonfly (tombo) in Japan is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato. This legacy has led to the use of dragonfly as an emblem on arrow quivers and as family crest. It also appears occasionally in conjunction with such imperial motifs as the chrysanthemum. Used in a context devoid of historical associations, the dragonfly is a seasonal symbol of late summer and early autumn." Dragonfly was an extremely often motif for the tsuba in all times, primarily in earlier times, before Tokugawa pacified the nation. The same motif is used on Ōnin tsuba in this collection:
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of dragonfly in negative openwork (in-sukashi). It may be Ko-Tōshō (old Tōshō) or just Tōshō school, without a 'Ko'. Probably the dragonfly here is used as a family crest (mon). Muromachi period. Dimensions: Height: 95.0 mm. Width: 93.6 mm. Rim thickness: 2.1 mm. Center thickness: 2.3 mm. Nakago-ana: height = 30 mm, width = 7.8 mm. A dragonfly design is described by John W. Dower as following "During the period of feudal warfare, the dragonfly is reputed to have been am especially popular design applied to arrow quivers, and some warriors adopted it as a family crest. One reason for this was the insect's alternative names of katsu mushi and shogun mushi, both meaning 'victory insect'." Merrily Baird is even more talkative regarding the matter: "The dragonfly (tombo) in Japan is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato. This legacy has led to the use of dragonfly as an emblem on arrow quivers and as family crest. It also appears occasionally in conjunction with such imperial motifs as the chrysanthemum. Used in a context devoid of historical associations, the dragonfly is a seasonal symbol of late summer and early autumn." Dragonfly was an extremely often motif for the tsuba in all times, primarily in earlier times, before Tokugawa pacified the nation. The same motif is used on Ōnin tsuba in this collection:
-
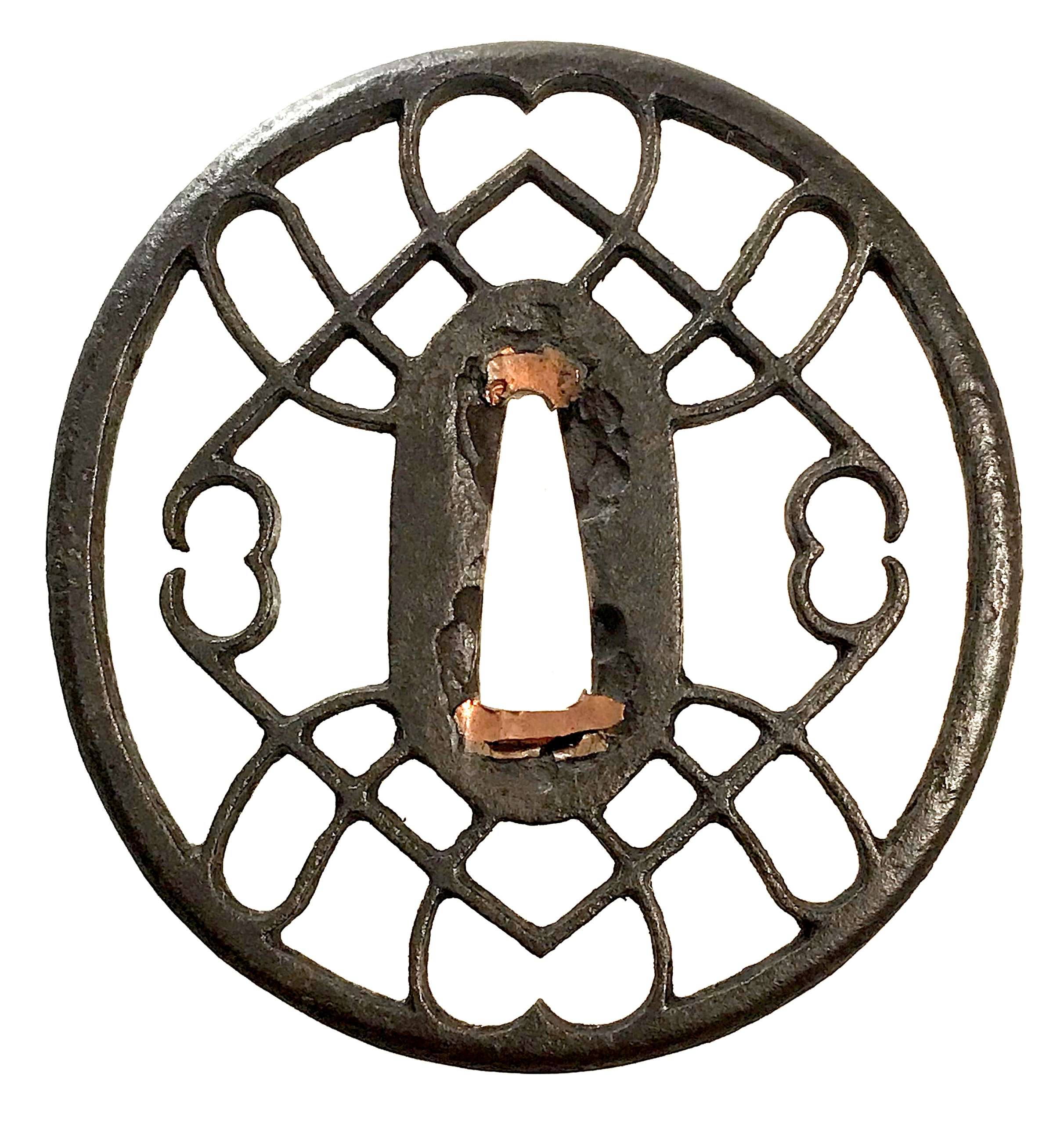 Iron tsuba of oval form with the motif of horse trappings in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Iron bones (tekkotsu) on the rim.
Iron tsuba of oval form with the motif of horse trappings in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Iron bones (tekkotsu) on the rim.Size: 80.4 x 75.8 x 5.2 mm
NBTHK Certificate №454567, allegedly saying that it is Akasaka School, Muromachi period. A look-a-like tsuba in Robert. E. Haynes Catalog #7, 1983 on page 57 under №48 is described as follows: "A masterpiece second period Owari sukashi tsuba. The plate is of beautiful color and quality almost like velvet. The design is very hard to discern, it might be the horse trappings, or even a moon. The style and type of Owari tsuba shows the great tradition of the Momoyama period and why it was the renaissance in time, as well as the arts produced, through the long history of all Japanese art. Ca. 1580. Ht. 7.7 cm, Th. (center) 5.5 mm, (edge) 5.25 to 5.75 mm."I believe we can safely attribute this tsuba to Owari School, c. 1580.
Robert. E. Haynes Catalog #7, 1983, p. 57, №48.
-
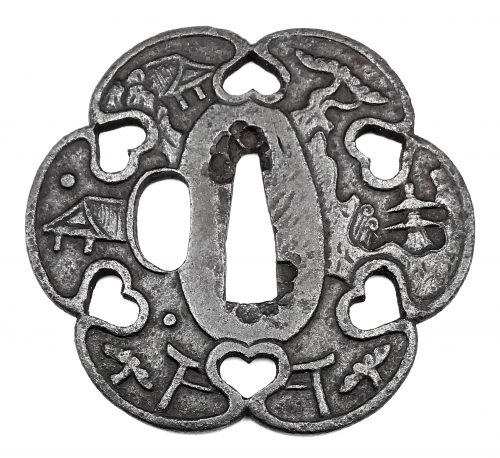 Iron tsuba of six-lobed (mutsu-mokkō-gata) form, with six wild boar's eye shape (inome) openings (sukashi). Hitsu-ana and the entire perimeter of tsuba have typical for this school raised rim. Lobes are decorated with landscape motifs in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori). On the obverse: A hut under a full moon, Shinto shrine gates (torii) with pines and a full moon, rocks, a large pine tree, and a temple (pagoda) surrounded by rocks and waves. On the reverse: waves, fishing boat, wild gees in flight under full moon, maple, hexagon (tortoiseshell, kikko) with a dot inside and a dot outside (inclusion/exclusion symbol), and chrysanthemum (the last two may be family crests, mon). Kamakura-bori school. Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Height: 64.2 mm, width: 74.3 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, at rim 2.6 mm. Weight: 62.8 g (light). NBTHK old green certificate №561: Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work". A look-a-like tsuba can be found at the Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17, though his tsuba is more massive (80 x 84 x 4 mm).NBTHK paper says that the motif is Hakkei (八景), i.e. "Eight Views," so several interpretations are possible (the original Chinese ones, Omi Hakkei, etc.). However, most likely it is the 'Eight views of Omi' (近江八景 - 'Omi Hakkei'). Why the artist selected a 6-lobed form for depicting 8 views remains unclear, and thus we are in our right to raise the question whether the motif is indeed Hakkei. The term Omi hakkei (eight views of Omi) refers to painting or print sets which illustrate life on the shores of Lake Biwa in Omi (now Shiga Prefecture). The model for such paintings came from China, where, from the eleventh century onward, painters had produced eight views of the Hsiao and Hsiang lake areas of Hunan Province. The themes, which follow the original Chinese models, are: geese descending to land, returning fishing boats, clearing rain, a snow-covered evening landscape, the autumn moon, night rain, a temple bell at evening, and the glow of sunset. Japanese artists have also used the eight-theme approach for other parts of country - including cities - and applied it to subject matter other than landscapes. [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, page 308-9]. Japan Encyclopedia by Louis Frédéric also mentions Omi Hakkei as "Eight landscapes of Omi", and states that this theme was often cited in poetry after 1500. It is likely that the tsuba in focus is designed under the influence of the theme popularity in the 16th century. The theme was effectively exploited by prominent ukiyo-e artists Suzuki Harunobu and Utagawa Hiroshige in the 18th and 19th century, respectively. These are the eight scenes of the theme (see Wikipedia):
Iron tsuba of six-lobed (mutsu-mokkō-gata) form, with six wild boar's eye shape (inome) openings (sukashi). Hitsu-ana and the entire perimeter of tsuba have typical for this school raised rim. Lobes are decorated with landscape motifs in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori). On the obverse: A hut under a full moon, Shinto shrine gates (torii) with pines and a full moon, rocks, a large pine tree, and a temple (pagoda) surrounded by rocks and waves. On the reverse: waves, fishing boat, wild gees in flight under full moon, maple, hexagon (tortoiseshell, kikko) with a dot inside and a dot outside (inclusion/exclusion symbol), and chrysanthemum (the last two may be family crests, mon). Kamakura-bori school. Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Height: 64.2 mm, width: 74.3 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, at rim 2.6 mm. Weight: 62.8 g (light). NBTHK old green certificate №561: Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work". A look-a-like tsuba can be found at the Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17, though his tsuba is more massive (80 x 84 x 4 mm).NBTHK paper says that the motif is Hakkei (八景), i.e. "Eight Views," so several interpretations are possible (the original Chinese ones, Omi Hakkei, etc.). However, most likely it is the 'Eight views of Omi' (近江八景 - 'Omi Hakkei'). Why the artist selected a 6-lobed form for depicting 8 views remains unclear, and thus we are in our right to raise the question whether the motif is indeed Hakkei. The term Omi hakkei (eight views of Omi) refers to painting or print sets which illustrate life on the shores of Lake Biwa in Omi (now Shiga Prefecture). The model for such paintings came from China, where, from the eleventh century onward, painters had produced eight views of the Hsiao and Hsiang lake areas of Hunan Province. The themes, which follow the original Chinese models, are: geese descending to land, returning fishing boats, clearing rain, a snow-covered evening landscape, the autumn moon, night rain, a temple bell at evening, and the glow of sunset. Japanese artists have also used the eight-theme approach for other parts of country - including cities - and applied it to subject matter other than landscapes. [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, page 308-9]. Japan Encyclopedia by Louis Frédéric also mentions Omi Hakkei as "Eight landscapes of Omi", and states that this theme was often cited in poetry after 1500. It is likely that the tsuba in focus is designed under the influence of the theme popularity in the 16th century. The theme was effectively exploited by prominent ukiyo-e artists Suzuki Harunobu and Utagawa Hiroshige in the 18th and 19th century, respectively. These are the eight scenes of the theme (see Wikipedia):
Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17: Kamakura-bori tsuba, ca. 1450.
- Returning sails at Yabase (矢橋の帰帆) - Yabase. Yabase is an old harbour on the east side of the lake. Near the Tokaido, it was used for a shortcut to Otsu by boat.
- Evening glow at Seta (勢多(瀬田)の夕照) - The Chinese Bridge at Seta. The long bridge across the Seta was used by the Tokaido. In the background the "Fuji of Omi", the Mikamiyama. It is just above 400 m, but indeed well visible.
- Autumn moon at Ishiyama (石山の秋月) - Ishiyama Temple. The Ishiyamadera was located on a hillside next to the Seta River. It got his name form the strange rocks on which it is built, partly on supporting beams. A hut at the upper end of the site allows a view of the lake, and the moon.
- Clear breeze at Awazu (粟津の晴嵐) - Awazuhara. Awazu is well known for its pine wood, Awazu-ga-hara.
- Evening bell at Miidera (三井晩鐘) - Mii-dera. Miidera temple was built in the 8th century. Its famous bell is one of the "Three bells of Japan", the other two being those at Byoodo-in, Uji and at Jingoji, Kyoto.
- Evening rain at Karasaki (唐崎の夜雨) - Karasaki Shrine. Karasaki is a small cape with a single large pine tree, a hitsu-matsu.
- Wild geese returning home at Katata (堅田の落雁) - Ukimido. Alighting geese cannot be seen always, however the little temple near Katata in the square hōkyō-style, detached from the lakeside, connected by a bridge. The first part of the name uki is the same as in Ukiyo-e, meaning floating. Midō means temple.
- Evening snow at Hira (比良の暮雪) - Hira Mountains. The Hira mountains on the west side of the lake experience the hard winter, when the winter monsoon brings much snow from the continent.
-
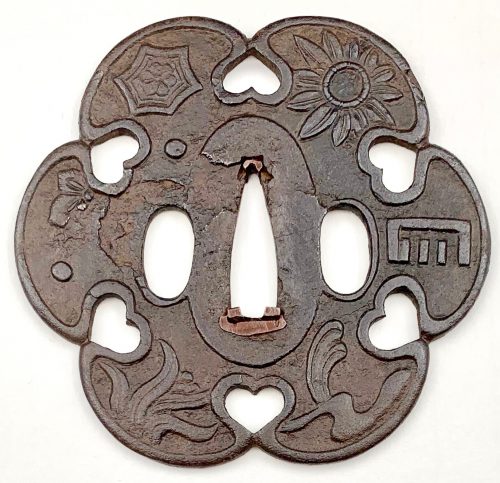 Iron tsuba of six-lobed (mutsu-mokkō-gata) form, with six wild boar's eye shape (inome) openings (sukashi). Ryo-Hitsu and the entire perimeter of tsuba have typical for this school raised rim; raised seppa dai. Lobes are decorated in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori). On the obverse: chrysanthemum, Genji mon, waves and rocks, grasses and star, bellflower, star and flower in tortoiseshell (kikko). On the reverse: Stars and different flowers, and flying geese. The plate is damaged to the left of nakago-ana and around the left hitsu-ana. Kamakura-bori school. Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Diameter: 89 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm; Weight: 108.8 g [large]. There is a similar tsuba in this collection, TSU-0345.2018, but with a different motif and much smaller: diameter 74.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, weight: 62.8 g.Another look-a-like tsuba can be found at the Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17, though his tsuba is more massive (80 x 84 x 4 mm).
Iron tsuba of six-lobed (mutsu-mokkō-gata) form, with six wild boar's eye shape (inome) openings (sukashi). Ryo-Hitsu and the entire perimeter of tsuba have typical for this school raised rim; raised seppa dai. Lobes are decorated in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori). On the obverse: chrysanthemum, Genji mon, waves and rocks, grasses and star, bellflower, star and flower in tortoiseshell (kikko). On the reverse: Stars and different flowers, and flying geese. The plate is damaged to the left of nakago-ana and around the left hitsu-ana. Kamakura-bori school. Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Diameter: 89 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm; Weight: 108.8 g [large]. There is a similar tsuba in this collection, TSU-0345.2018, but with a different motif and much smaller: diameter 74.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, weight: 62.8 g.Another look-a-like tsuba can be found at the Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17, though his tsuba is more massive (80 x 84 x 4 mm).
Varshavsky Collection: TSU-0345.2018
This tsuba, TSU-0401.2019, is the biggest of all three (another mine and the one from Campton Collection). The presence of a flower in a tortoiseshell symbol (crest or mon) on this tsuba alludes to Izumo Shrine. The overall piece, with symbols of grasses, waves, flowers, incense, stars, and flying geese, is full of autumnal connotations.
Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17: Kamakura-bori tsuba, ca. 1450.
-
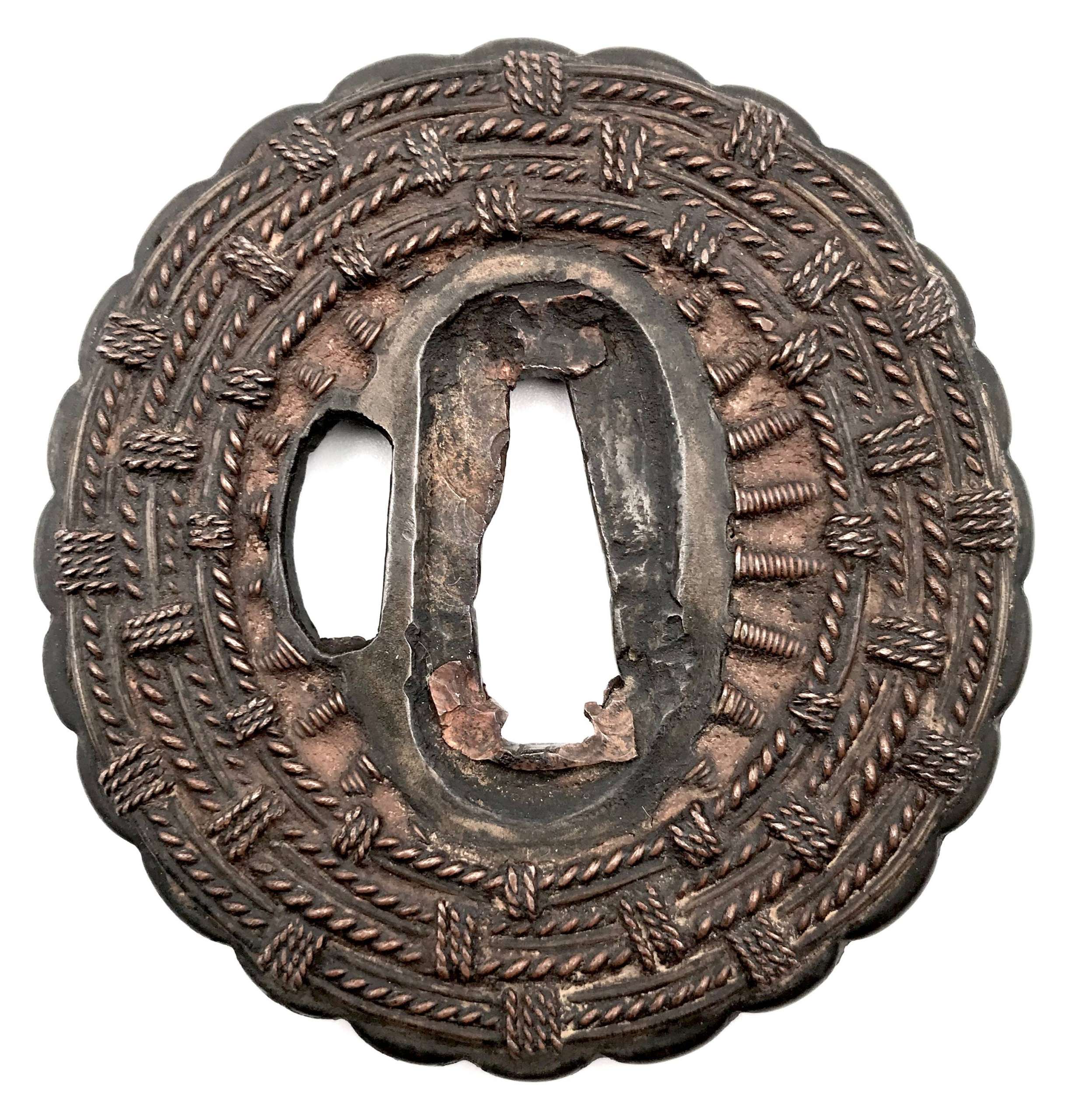 Tsuba of chrysanthemoid form (kikka-gata) with yamagane core and woven copper wire pattern. Copper sekigane. Shingen school. Height: 70.2 mm; Width 67.2 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.4-3.6 mm, overall 7.3 mm. Weight 82.7 g Inscription on the wooden box reads: "Muromachi period Mumei Zōgan Shingen Tsuba" Muromachi period, 16th century. Age attribution is based on the fact that the core is made of yamagane; later copies of Edo period are usually made of iron. This small and light tsuba was likely mounted on a combat sword, while larger and much heavier woven wire Shingen tsuba of Edo period were of purely decorative purpose. http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Tsuba of chrysanthemoid form (kikka-gata) with yamagane core and woven copper wire pattern. Copper sekigane. Shingen school. Height: 70.2 mm; Width 67.2 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.4-3.6 mm, overall 7.3 mm. Weight 82.7 g Inscription on the wooden box reads: "Muromachi period Mumei Zōgan Shingen Tsuba" Muromachi period, 16th century. Age attribution is based on the fact that the core is made of yamagane; later copies of Edo period are usually made of iron. This small and light tsuba was likely mounted on a combat sword, while larger and much heavier woven wire Shingen tsuba of Edo period were of purely decorative purpose. http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ -
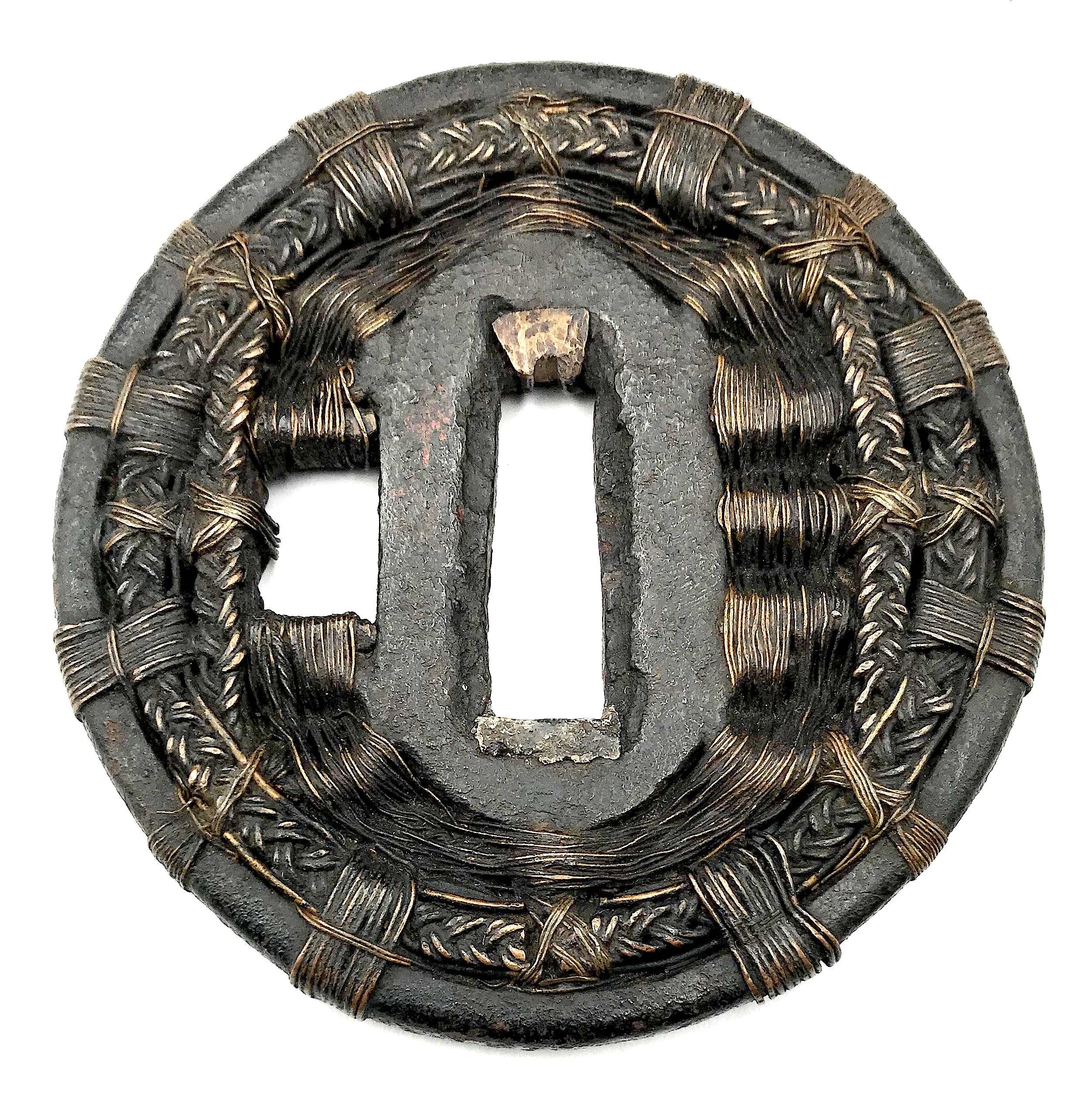 Shingen school tsuba with woven wire pattern. Iron core, woven brass wire. Height: 72.5 mm; Width 69.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm. Weight 88.8 g. Late Muromachi, 16th century. SOLD http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Shingen school tsuba with woven wire pattern. Iron core, woven brass wire. Height: 72.5 mm; Width 69.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm. Weight 88.8 g. Late Muromachi, 16th century. SOLD http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ -
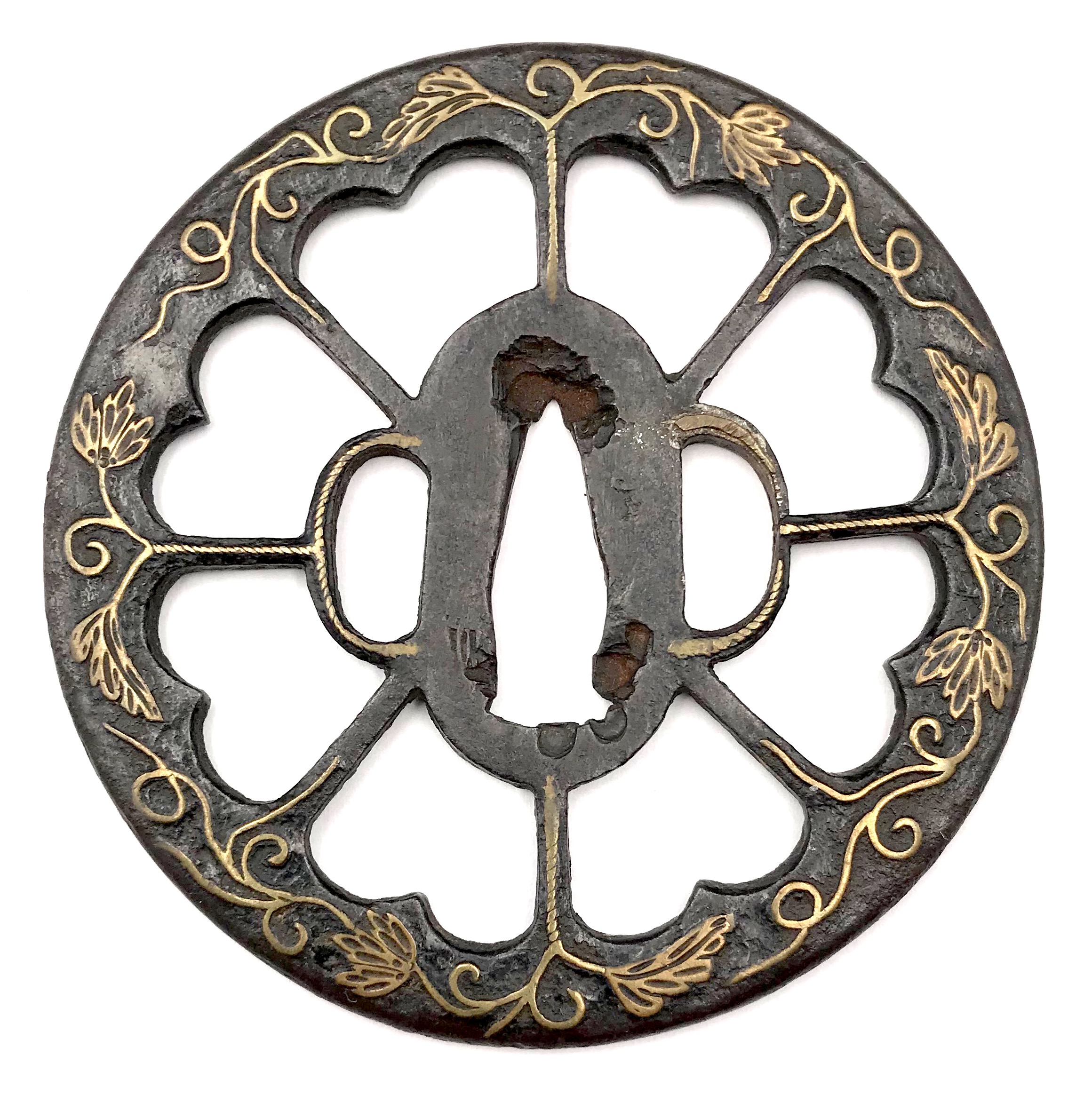 Iron tsuba of round form represents an eight-spoke Wheel-of-the-Law and in the same time (because of the inner shape of cut-outs) - a sixteen-petal imperial chrysanthemum in openwork (sukashi). Decorated on both sides with vines, leaves, and tendrils in suemon-zōgan and sen-zōgan. Spokes and hitsu-ana decorated with rope-like linear brass inlay (nawame-zōgan). A somewhat look-a-like tsuba is referenced in Gary D. Murtha's Japanese Sword Guards. Onin-Heianjo-Yoshiro book on page 61. Mr. Murtha attributes his piece to Heianjo school of Azuchi-Momoyama or early Edo period. However, tsuba in this collection looks older and bolder than the one in his book. It is larger (84 mm vs. his 66 mm), the spokes are longer, the inlay is of better quality, it is relatively thin, with deep black patina, and with the traces of lacquer (urushi). This may indicate that this tsuba belongs to Ōnin school and dates at least to late Muromachi period, ca. 1550, if not 1450 AD. Mid to late Muromachi period (ca. 1450-1550). Dimensions: 84.3 x 83.2 x 3.2 mm "In Japan, the Wheel-of-the-Law is an attribute of such deities as Senju Kannon, the Thousand-Armed Kannon, and Dainichi Nyorai, the principal deity of Shingon Buddhism [Merrily Baird]. May be used as a family crest (mon).
Iron tsuba of round form represents an eight-spoke Wheel-of-the-Law and in the same time (because of the inner shape of cut-outs) - a sixteen-petal imperial chrysanthemum in openwork (sukashi). Decorated on both sides with vines, leaves, and tendrils in suemon-zōgan and sen-zōgan. Spokes and hitsu-ana decorated with rope-like linear brass inlay (nawame-zōgan). A somewhat look-a-like tsuba is referenced in Gary D. Murtha's Japanese Sword Guards. Onin-Heianjo-Yoshiro book on page 61. Mr. Murtha attributes his piece to Heianjo school of Azuchi-Momoyama or early Edo period. However, tsuba in this collection looks older and bolder than the one in his book. It is larger (84 mm vs. his 66 mm), the spokes are longer, the inlay is of better quality, it is relatively thin, with deep black patina, and with the traces of lacquer (urushi). This may indicate that this tsuba belongs to Ōnin school and dates at least to late Muromachi period, ca. 1550, if not 1450 AD. Mid to late Muromachi period (ca. 1450-1550). Dimensions: 84.3 x 83.2 x 3.2 mm "In Japan, the Wheel-of-the-Law is an attribute of such deities as Senju Kannon, the Thousand-Armed Kannon, and Dainichi Nyorai, the principal deity of Shingon Buddhism [Merrily Baird]. May be used as a family crest (mon).
Gary D. Murtha's tsuba on page 61.
-
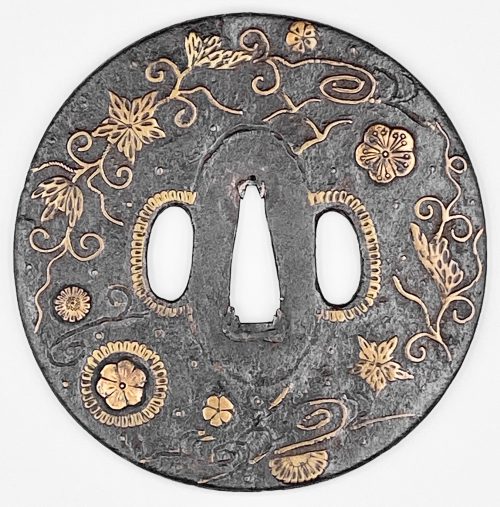 Iron tsuba of round form adorned with the design of stars, wild geese, floating blossoms, leaves and tendrils realized in brass inlay. The inlay technique includes suemon-zōgan and ten-zōgan. Two smaller openings (hitsu-ana) surrounded by a scalloped brass border. The seppa-dai border inlay is missing, as well as a few other fragments of inlay on both sides. Sword cut at 12 o'clock on the reverse. A tsuba with a strong autumnal connotation, which once belonged to a great battle weapon. One of only three known jūyō Ōnin tsuba. Translation of the paper, issued by the Japanese sword fittings (tosogu) examination board: Designated as jūyō-tosogu at the 34th jūyō-shinsa held on April 14th 1988 Kaki-karimon zōgan-tsuba (花卉雁文象嵌鐔) — Tsuba with zōgan design of flowers and wild geese. Mumei: Onin (応仁) Tokyo. Nakasono Tokumi (中園とくみ) Measurements: height 9.5 cm, width 9.4 cm, thickness at rim 0.35 cm Interpretation: marugata, iron, brass zōgan, two hitsu-ana Time: end of Muromachi Explanation: Ōnin-tsuba are thin iron ita-tsuba which show a brass zōgan ornamentation. All of them are mumei and there is the theory that they were made in the Onin era (1467-1469) although today more and more the theory is accepted that they are in general late Muromachi period works. There are two kinds of brass zōgan interpretations: One depicts irregularly arranged tachibana branches, wild geese, chrysanthemums, flowers, or karakusa for example, and the other one shows punctual zōgan elements, which are referred to as hoshi-zōgan or ro-zōgan, and concentrical zōgan elements between the nakago-ana and the rim. The latter interpretations might also be accompanied by simple ko-sukashi in the form of butterflies, clouds, hats, or stylized mountains. This tsuba is a typical work from the former category. It is large and feels massive and the powerful and impressive zōgan and the excellent iron make it a highly tasteful piece. Back side: Issued to: Nakasono Tokumi Address: Tokyo-to, Suginami-ku, Kamitakaido 2-17-26 Date of issue: May 30th 1989
Iron tsuba of round form adorned with the design of stars, wild geese, floating blossoms, leaves and tendrils realized in brass inlay. The inlay technique includes suemon-zōgan and ten-zōgan. Two smaller openings (hitsu-ana) surrounded by a scalloped brass border. The seppa-dai border inlay is missing, as well as a few other fragments of inlay on both sides. Sword cut at 12 o'clock on the reverse. A tsuba with a strong autumnal connotation, which once belonged to a great battle weapon. One of only three known jūyō Ōnin tsuba. Translation of the paper, issued by the Japanese sword fittings (tosogu) examination board: Designated as jūyō-tosogu at the 34th jūyō-shinsa held on April 14th 1988 Kaki-karimon zōgan-tsuba (花卉雁文象嵌鐔) — Tsuba with zōgan design of flowers and wild geese. Mumei: Onin (応仁) Tokyo. Nakasono Tokumi (中園とくみ) Measurements: height 9.5 cm, width 9.4 cm, thickness at rim 0.35 cm Interpretation: marugata, iron, brass zōgan, two hitsu-ana Time: end of Muromachi Explanation: Ōnin-tsuba are thin iron ita-tsuba which show a brass zōgan ornamentation. All of them are mumei and there is the theory that they were made in the Onin era (1467-1469) although today more and more the theory is accepted that they are in general late Muromachi period works. There are two kinds of brass zōgan interpretations: One depicts irregularly arranged tachibana branches, wild geese, chrysanthemums, flowers, or karakusa for example, and the other one shows punctual zōgan elements, which are referred to as hoshi-zōgan or ro-zōgan, and concentrical zōgan elements between the nakago-ana and the rim. The latter interpretations might also be accompanied by simple ko-sukashi in the form of butterflies, clouds, hats, or stylized mountains. This tsuba is a typical work from the former category. It is large and feels massive and the powerful and impressive zōgan and the excellent iron make it a highly tasteful piece. Back side: Issued to: Nakasono Tokumi Address: Tokyo-to, Suginami-ku, Kamitakaido 2-17-26 Date of issue: May 30th 1989 -
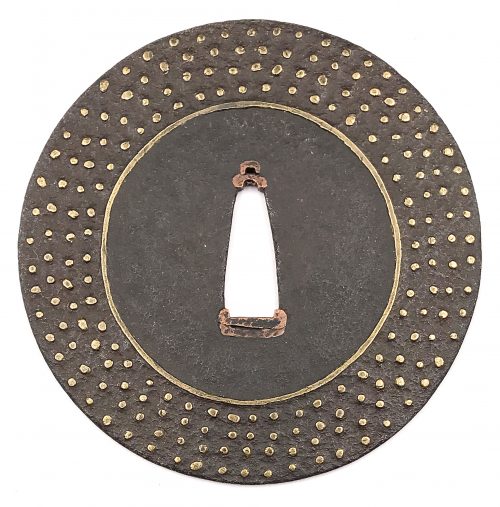 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with inlay of four concentric rows of brass dots or nail heads (ten-zōgan) and a circular brass wire inlay inside the innermost row of dots. Copper sekigane. Muromachi period, 15th or 16th century. Unsigned. Ōnin school. Size: 87.9 x 87.8 x 2.2 mm. Ōnin school got its name from the Ōnin War (応仁の乱 - Ōnin no Ran) - a civil war that lasted 10 years (1467–1477) during the Muromachi period in Japan.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with inlay of four concentric rows of brass dots or nail heads (ten-zōgan) and a circular brass wire inlay inside the innermost row of dots. Copper sekigane. Muromachi period, 15th or 16th century. Unsigned. Ōnin school. Size: 87.9 x 87.8 x 2.2 mm. Ōnin school got its name from the Ōnin War (応仁の乱 - Ōnin no Ran) - a civil war that lasted 10 years (1467–1477) during the Muromachi period in Japan.


