-
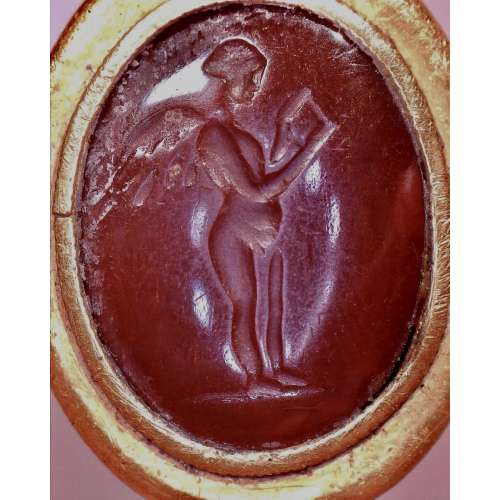 NEWThe intaglio depicts the ancient Greek god Eros looking into a mirror, which he holds in his left hand. Dimensions: 26 x 21 x 20 mm; weight: 11 g. US ring size: 4.25. High-karat gold. Ref.: J. Ogden, A Golden Past: Jewelry from the Ancient World (Catalogue), 1990, p. 10, no. 26 (not seen).
NEWThe intaglio depicts the ancient Greek god Eros looking into a mirror, which he holds in his left hand. Dimensions: 26 x 21 x 20 mm; weight: 11 g. US ring size: 4.25. High-karat gold. Ref.: J. Ogden, A Golden Past: Jewelry from the Ancient World (Catalogue), 1990, p. 10, no. 26 (not seen). -
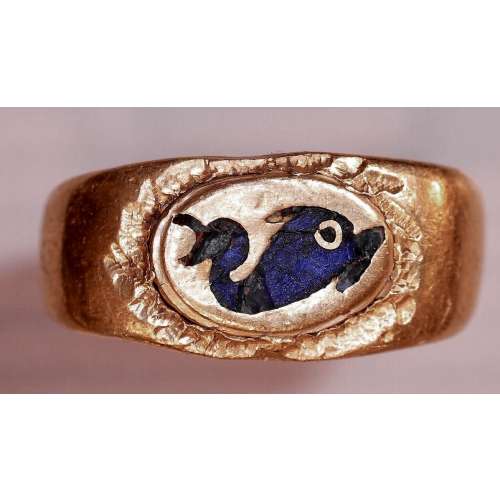 NEWA gold ring with a raised oval face featuring an inlaid blue glass dolphin. Dimensions: 17.7 x 18.8 mm; weight: 4.2 g. US ring size: 4.25. Gold Quality: 96.29% (<23 kt).
NEWA gold ring with a raised oval face featuring an inlaid blue glass dolphin. Dimensions: 17.7 x 18.8 mm; weight: 4.2 g. US ring size: 4.25. Gold Quality: 96.29% (<23 kt). -
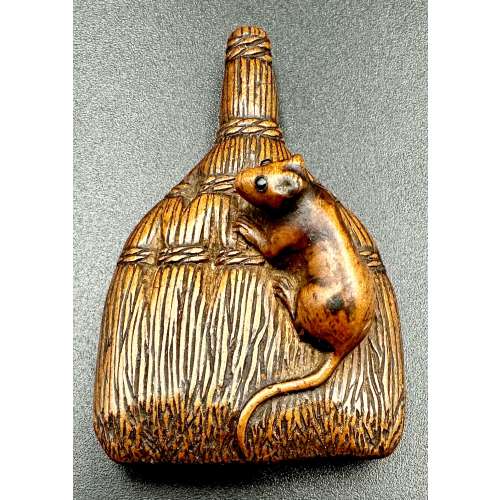 NEWFinely carved as a rat (nezumi) seated on a shuro brush, bound naturalistically with thick bristles. The rodent with a long trailing tail and eyes inlaid in a dark horn. Generously excavated, asymmetrical himotoshi to the underside. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, p. 156): …The Japanese do not clearly differentiate between the rat and the mouse, and one word, nezumi [鼠], designates both. …Rat is a messenger of Daikokuten, a deity of grain and vegetation who is one of Japan’s Seven Gods of Good Luck. ...Depictions of the rat are most common in years of the zodiac represented by the animal. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 49 x 33 x 16 mm. Provenance: From the private collection of Armand Basi (Spanish, 1924-2009).
NEWFinely carved as a rat (nezumi) seated on a shuro brush, bound naturalistically with thick bristles. The rodent with a long trailing tail and eyes inlaid in a dark horn. Generously excavated, asymmetrical himotoshi to the underside. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, p. 156): …The Japanese do not clearly differentiate between the rat and the mouse, and one word, nezumi [鼠], designates both. …Rat is a messenger of Daikokuten, a deity of grain and vegetation who is one of Japan’s Seven Gods of Good Luck. ...Depictions of the rat are most common in years of the zodiac represented by the animal. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 49 x 33 x 16 mm. Provenance: From the private collection of Armand Basi (Spanish, 1924-2009). -
 NEW
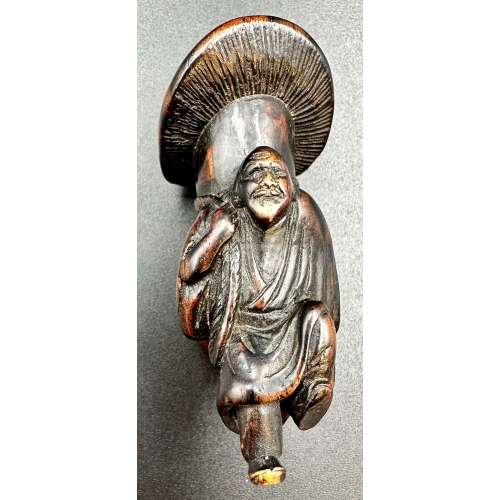
NEWNetsuke with a design of an old man carrying a giant mushroom on his back. Possibly signed on his left foot. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, page. 93): ... This prominent use in the symbol-rich netsuke art form, however, reflects more their sexual symbolism than either their dietary appeal or interesting shapes. Mushrooms in Japan are generally a symbol of fertility, with some flat varieties, like shiitake, being associated with females. In contrast, the matsutake mushroom (Armillaria edodes) is a phallic symbol, as befits its thick, spearlike stem and the fact that it is consumed before cap opens.
Seller's description: "The old man carved walking, with one foot slightly raised, wearing a loose fitted robe and carrying a large long-stemmed mushroom on his back. The wood stained and bearing a fine patina. Himotoshi through the mushroom stem". See VO-0270.2018 for the same subject. Late 18th century. Dimensions: 62 mm tall -
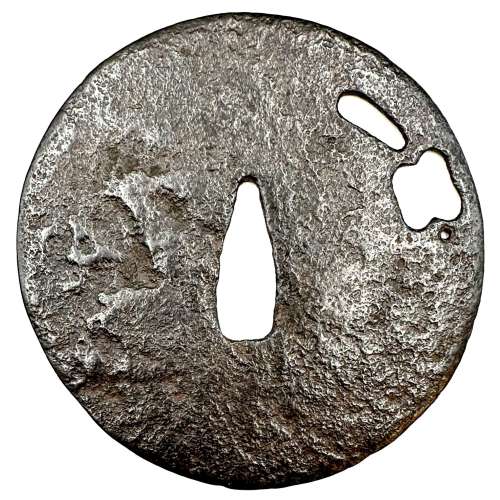 NEWThin plate iron tsuba of round form with a military commander's fan (gunbai) design in openwork (sukashi); Ko-tosho school. Kamakura period (1185 – 1333), 13th to early 14th century (according to Nakamura Tessei). Dimensions: 91.2 x 89.5 mm, thickness: 1.5-2.5 mm. Provenance: Patrick Liebermann Collection. Reproduced in the exhibition catalogue Samurai. Guerriers et esthètes, BNU, Strasbourg, March 11 – July 13, 2022, №045, p.91 and in Patrick Liebermann, Tsuba. Itinéraires d'une collection, 2016, №72, p.111. Reference: a similar tsuba reproduced in LIB-3304.2024 (see below) and in this collection TSU-0332.2017 (provenance Sasano Masayuki).
NEWThin plate iron tsuba of round form with a military commander's fan (gunbai) design in openwork (sukashi); Ko-tosho school. Kamakura period (1185 – 1333), 13th to early 14th century (according to Nakamura Tessei). Dimensions: 91.2 x 89.5 mm, thickness: 1.5-2.5 mm. Provenance: Patrick Liebermann Collection. Reproduced in the exhibition catalogue Samurai. Guerriers et esthètes, BNU, Strasbourg, March 11 – July 13, 2022, №045, p.91 and in Patrick Liebermann, Tsuba. Itinéraires d'une collection, 2016, №72, p.111. Reference: a similar tsuba reproduced in LIB-3304.2024 (see below) and in this collection TSU-0332.2017 (provenance Sasano Masayuki).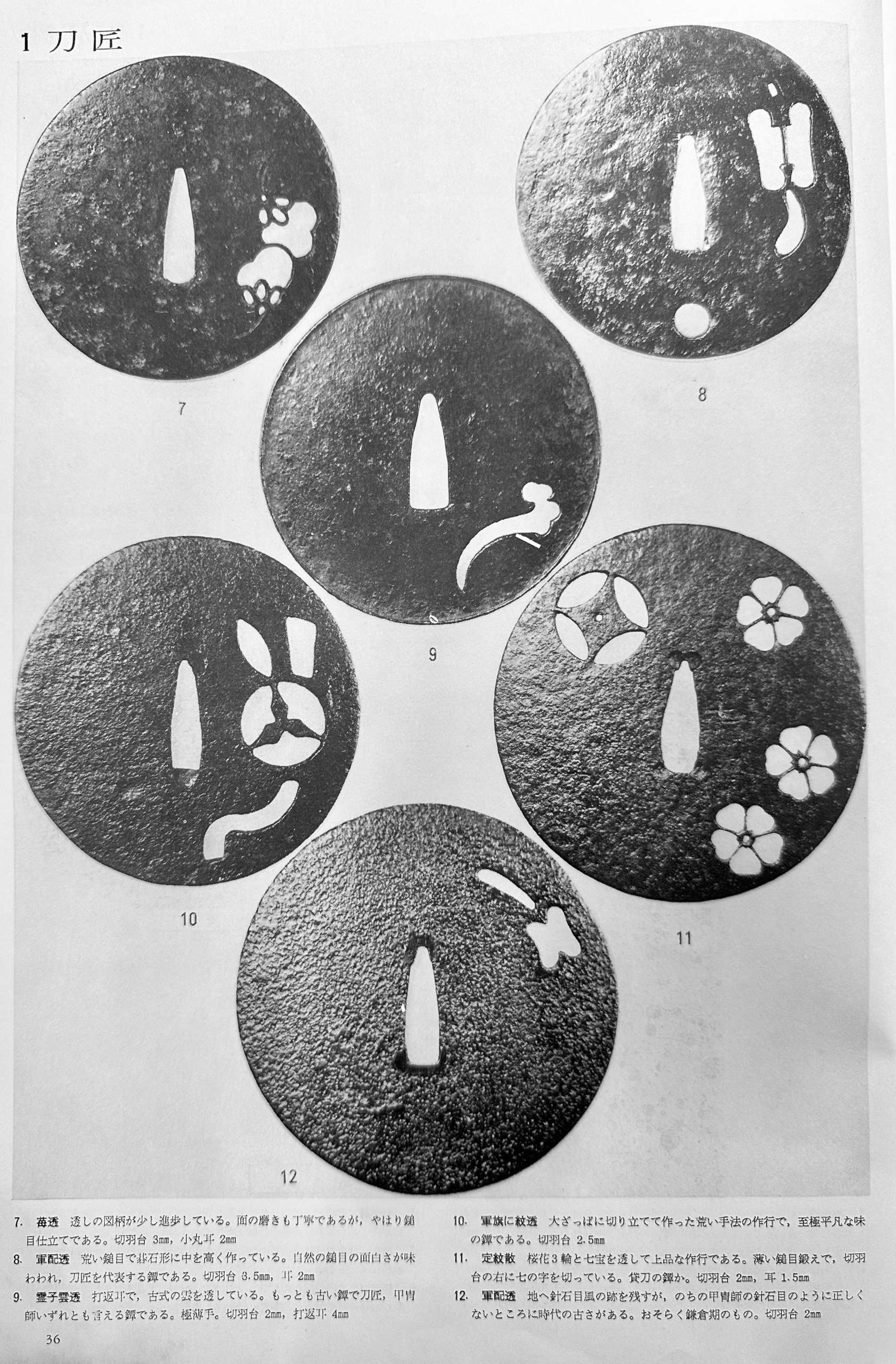
Tsuba Collection (Tsuba shūsei, 鐔集成) by Nakamura Tessei (中村鐵青), p.36, fig. 12.
-
 NEW
NEWLarge iron tsuba of mokko form with the openwork (sukashi) design, described by some as rotten leaves swirling in the wind and boar eyes (inome, 猪目, heart-shaped elements); round rim (maru-mimi); no hitsu-ana; pronounced iron bones (tekkotsu); chocolate patina.
Signed to the left of nakaga-ana: Yamakichibei (山吉兵へ). Attributed to the First Generation (Shodai) master.
Dimensions: 90 x 82 mm, thickness 3.7 mm at centre, 4.9 mm at rim. Weight: 142 gReferences: similar handguards demonstrated at Yasukazu's Owari to Mikawa no tankō №176 and Kajima's Tsuba no Bi №28.
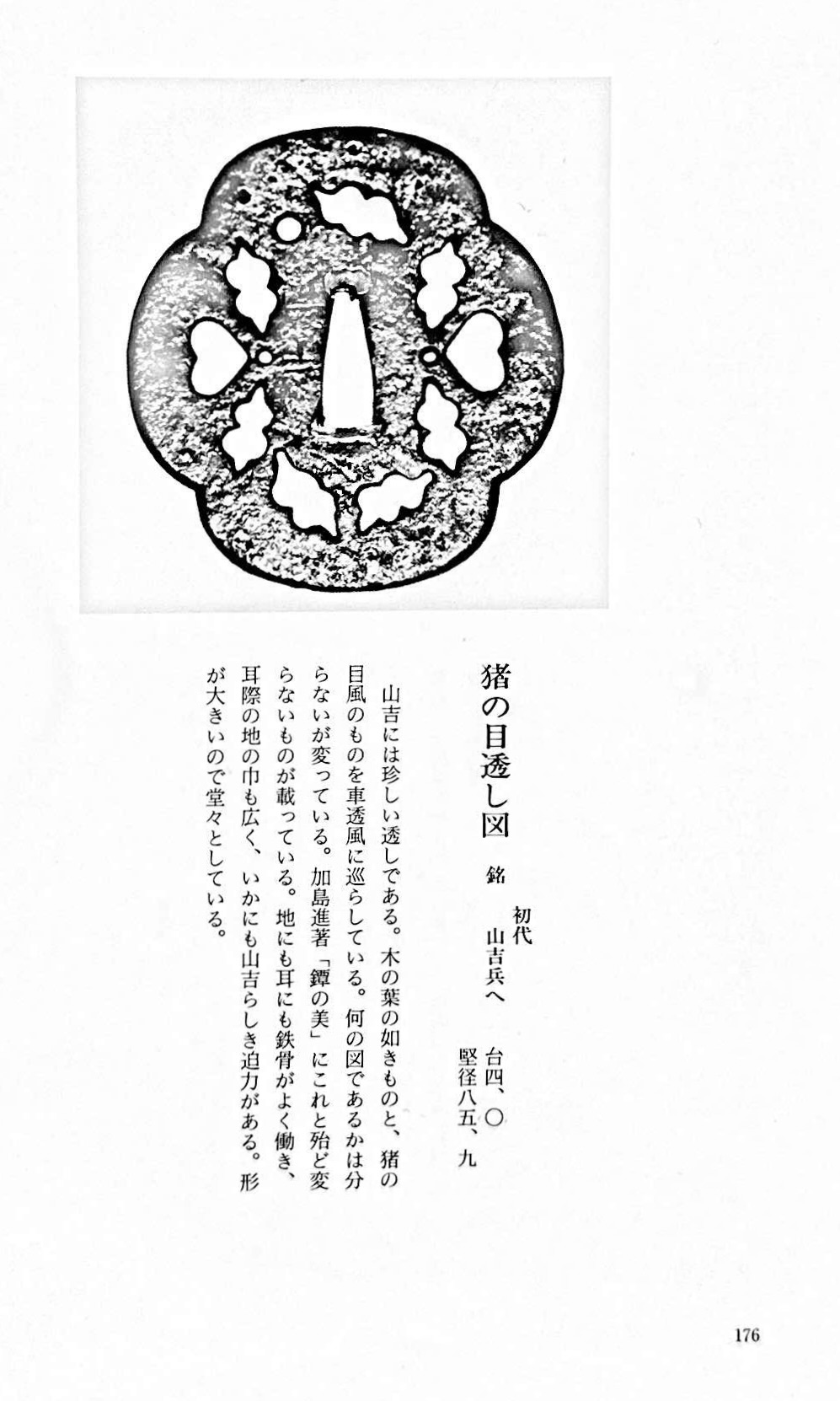
Owari to Mikawa no tankō №176

Tsuba no Bi №28
-
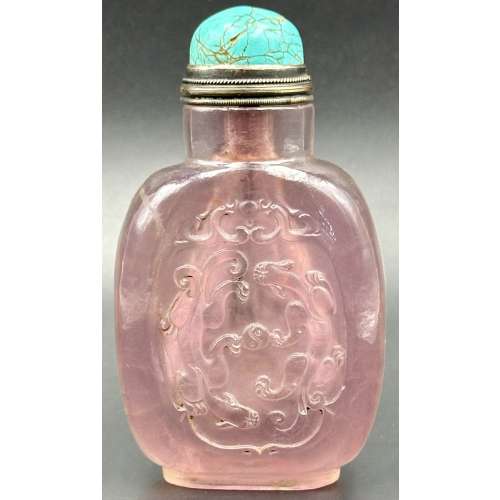 Rose quartz snuff bottle of rounded rectangular form on raised foot with round neck, carved in relief with a double dragon in a cartouche; round turquoise stopper with silver collar.
Rose quartz snuff bottle of rounded rectangular form on raised foot with round neck, carved in relief with a double dragon in a cartouche; round turquoise stopper with silver collar.The Eastern dragon is not the gruesome monster of medieval imagination, but the genius of strength and goodness. He is the spirit of change, therefore of life itself. Hidden in the caverns of inaccessible mountains, or coiled in the unfathomed depth of the sea, he awaits the time when he slowly rouses himself into activity. He unfolds himself in the storm clouds; he washes his mane in the blackness of the seething whirlpools. His claws are in the fork of the lightning, his scales begin to glisten in the bark of rain-swept pine trees. His voice is heard in the hurricane, which, scattering the withered leaves of the forest, a dragon quickens a new spring [C. A. S. Williams. Chinese Symbolism and Art Motifs / 3rd Revised Edition. — Rutland, Vermont & Tokyo, Japan: Charles E. Tuttle Company, 1993].
The Qing dynasty (1644–1911). Mid-19th century. Dimensions: H90 x W52 x D30 mm -
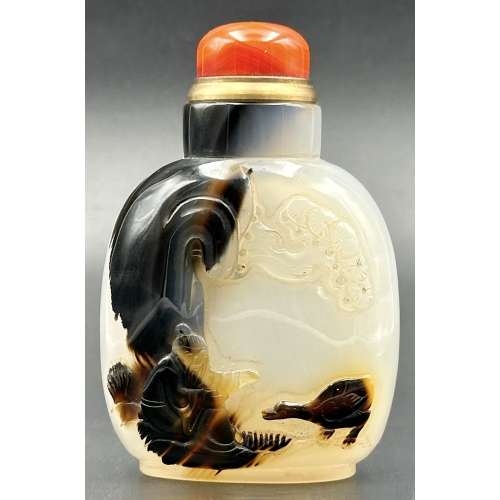 Agate snuff bottle of rounded rectangular form on raised foot with round neck, cream body with dark brown inclusion, carved in relief with a sage seated under a wooded rock, and a duck; round red agate stopper with brass collar. Late 18th or 19th century. The Qing dynasty (1644–1911). Dimensions: H72 x W48 x D28 mm
Agate snuff bottle of rounded rectangular form on raised foot with round neck, cream body with dark brown inclusion, carved in relief with a sage seated under a wooded rock, and a duck; round red agate stopper with brass collar. Late 18th or 19th century. The Qing dynasty (1644–1911). Dimensions: H72 x W48 x D28 mm -
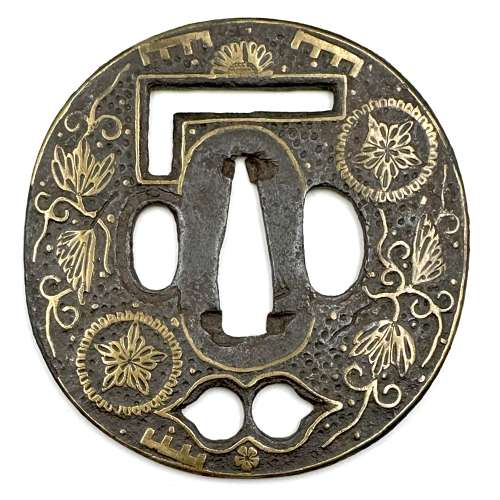 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form (nagamaru-gata) pierced on top and in the bottom (ko-sukashi) with simplified Genji-kō (incense game symbol) and two petals of bellflower; openings, seppa-dai, and plate along the rim are outlined with brass wire, kozuka-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire, missing on the front; kogai-ana pierced later. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer, decorated in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils, bellflowers, and Genji characters, and with brass dots (ten-zogan), many of which are missing. Measurements: Height 77.5 mm; Width 75.5 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.4 mm, at rim 3.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form (nagamaru-gata) pierced on top and in the bottom (ko-sukashi) with simplified Genji-kō (incense game symbol) and two petals of bellflower; openings, seppa-dai, and plate along the rim are outlined with brass wire, kozuka-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire, missing on the front; kogai-ana pierced later. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer, decorated in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils, bellflowers, and Genji characters, and with brass dots (ten-zogan), many of which are missing. Measurements: Height 77.5 mm; Width 75.5 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.4 mm, at rim 3.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier. -
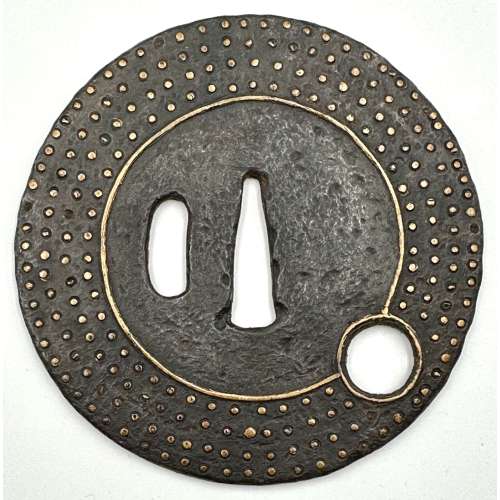

Iron tsuba of round form with one hitsu ana; centre of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire broke by a circular opening 7 mm in diameter located between 4 and 5 o’clock of the plate and in its turn outlined with brass wire. Extraneous to the central wire, the plate is decorated with four rows of brass dots (ten-zogan). A few dots are missing. In a custom kiri wood box. The meaning of the emblem is probably either the sun or the moon.
Ōnin school. Unsigned.
Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century.
Dimensions: diameter 88 mm; thickness 3.3 mm.
-
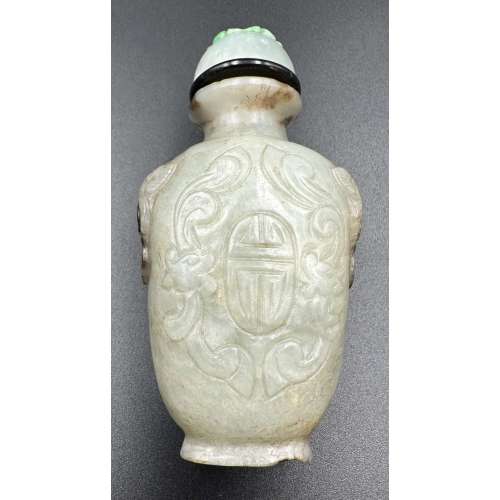 Jadeite snuff bottle carved with shou character and foo dog handles, with a black collar and jadeite stopper carved with a blossom design. Late 19th century. Dimensions: H74 x W39 x D26 mm
Jadeite snuff bottle carved with shou character and foo dog handles, with a black collar and jadeite stopper carved with a blossom design. Late 19th century. Dimensions: H74 x W39 x D26 mm -
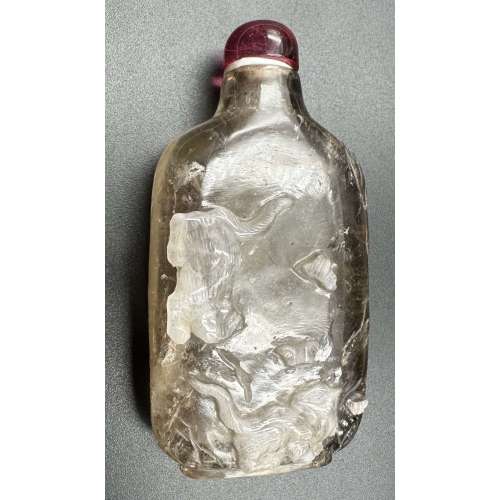 Snuff bottle made of smoky quartz with white skin carved with cats hunting butterflies design; cherry quartz stopper. Late 19th century. Dimensions: H70 x W36 x D17 mm
Snuff bottle made of smoky quartz with white skin carved with cats hunting butterflies design; cherry quartz stopper. Late 19th century. Dimensions: H70 x W36 x D17 mm -
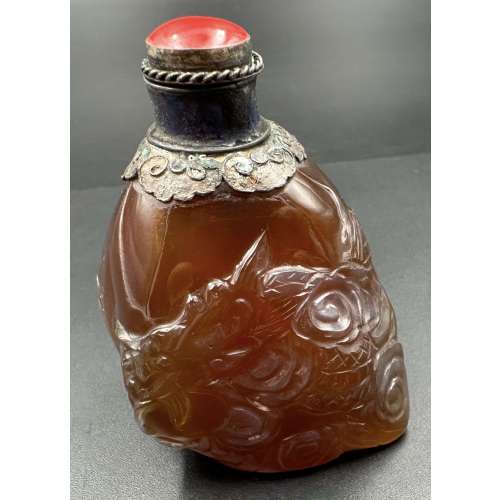 Agate snuff bottle carved with a dragon in clouds design; tin-mounted lapis lazuli collar with red coral stopper. Late 19th century. Dimensions: H56 x W52 x D34 mm.
Agate snuff bottle carved with a dragon in clouds design; tin-mounted lapis lazuli collar with red coral stopper. Late 19th century. Dimensions: H56 x W52 x D34 mm. -
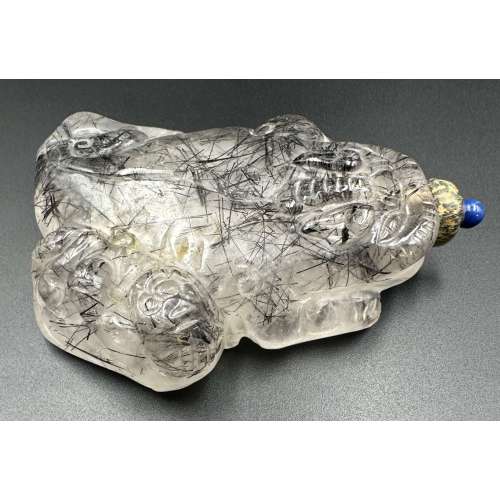 Snuff bottle in the form of Fo (or Fu) dog (lion-dog) guarding a cub carved of tourmalinated quartz with lapis lazuli and serpentine stopper. Late 19th century. Dimensions: L81 x W59 x H19 mm.
Snuff bottle in the form of Fo (or Fu) dog (lion-dog) guarding a cub carved of tourmalinated quartz with lapis lazuli and serpentine stopper. Late 19th century. Dimensions: L81 x W59 x H19 mm. -
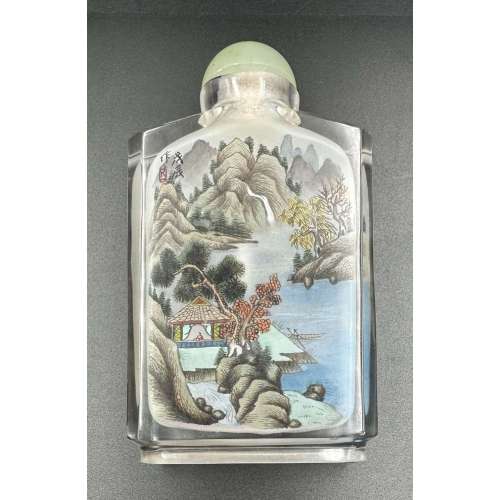 Large inside-painted glass snuff bottle with a mountain landscape design, signed and sealed Wu Chen Zuo, with a serpentine stopper. Mid-20th century. Dimensions: H105 x W61 x D27 mm.
Large inside-painted glass snuff bottle with a mountain landscape design, signed and sealed Wu Chen Zuo, with a serpentine stopper. Mid-20th century. Dimensions: H105 x W61 x D27 mm. -
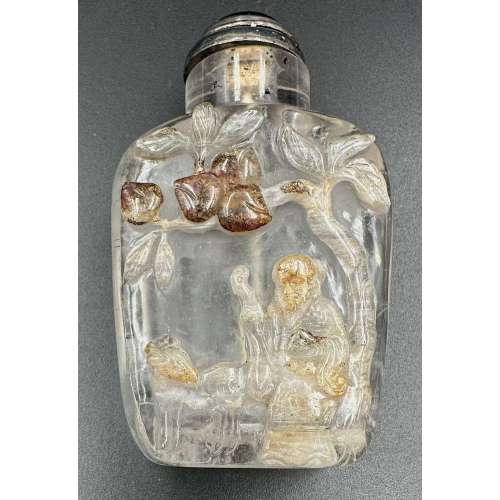 Snuff bottle made of rock crystal with brown skin carved with a sage and a deer under the peach tree on one side and a cuckoo on a plum tree on the other, with a chrysotile stopper and tin collar. Late 19th century. Dimensions: H68 x W40 x D21 mm.
Snuff bottle made of rock crystal with brown skin carved with a sage and a deer under the peach tree on one side and a cuckoo on a plum tree on the other, with a chrysotile stopper and tin collar. Late 19th century. Dimensions: H68 x W40 x D21 mm. -
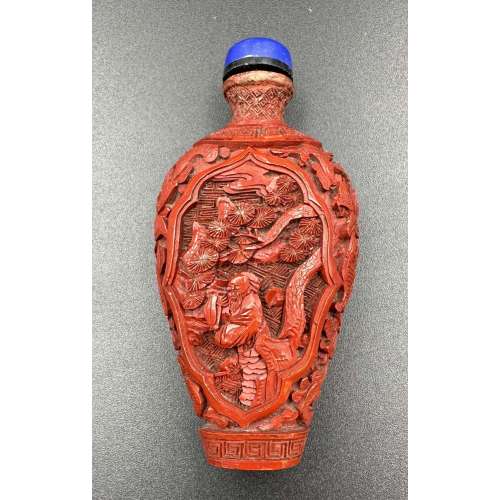 Cinnabar lacquer snuff bottle carved in low relief with a scholar under a pine tree and another under a maple, with lapis lazuli stopper and black collar. Early 20th century Dimansions: H77 x W36 x D19 mm.
Cinnabar lacquer snuff bottle carved in low relief with a scholar under a pine tree and another under a maple, with lapis lazuli stopper and black collar. Early 20th century Dimansions: H77 x W36 x D19 mm. -
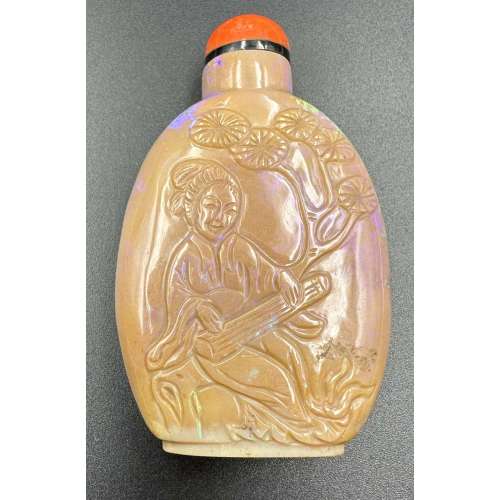 Opal jasper snuff bottle carved in low relief with a beauty playing Guqin under a pine tree and another on the veranda with a folding fan; bamboo, pine, and plum (the three friends of winter); carnelian agate stopper and black collar. Mid-20th century Dimensions: H67 x W41 x D15 mm
Opal jasper snuff bottle carved in low relief with a beauty playing Guqin under a pine tree and another on the veranda with a folding fan; bamboo, pine, and plum (the three friends of winter); carnelian agate stopper and black collar. Mid-20th century Dimensions: H67 x W41 x D15 mm


