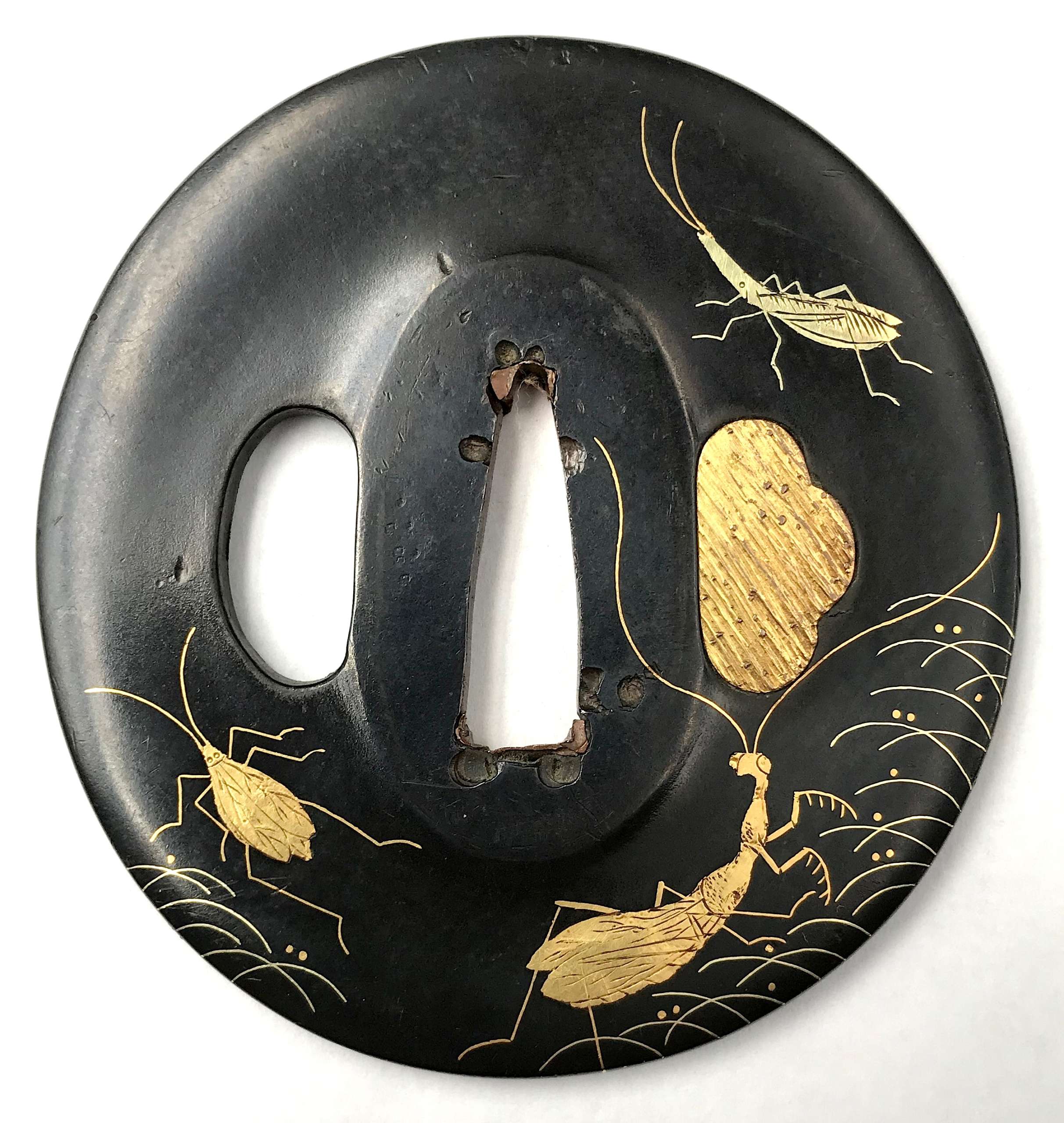
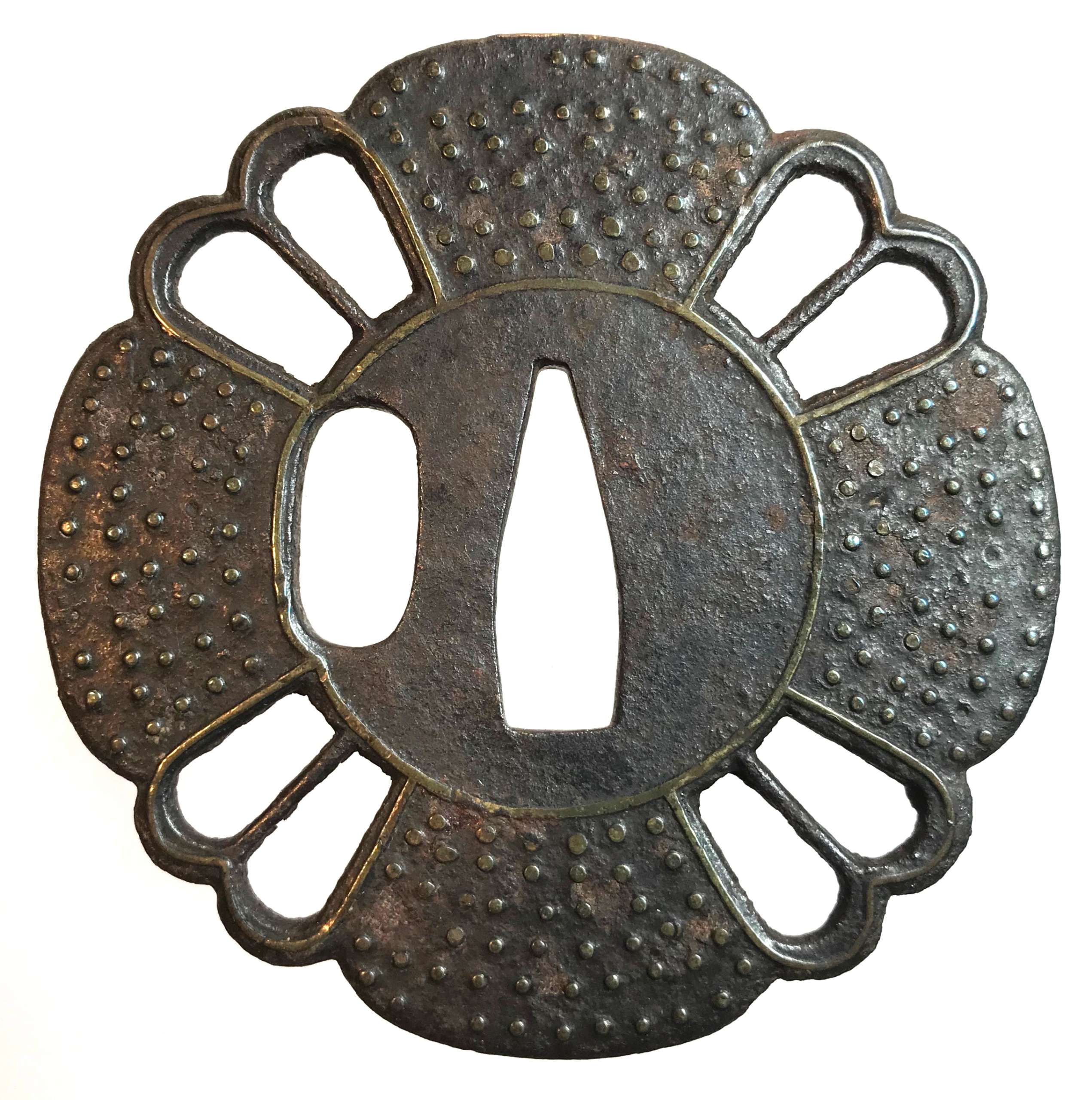
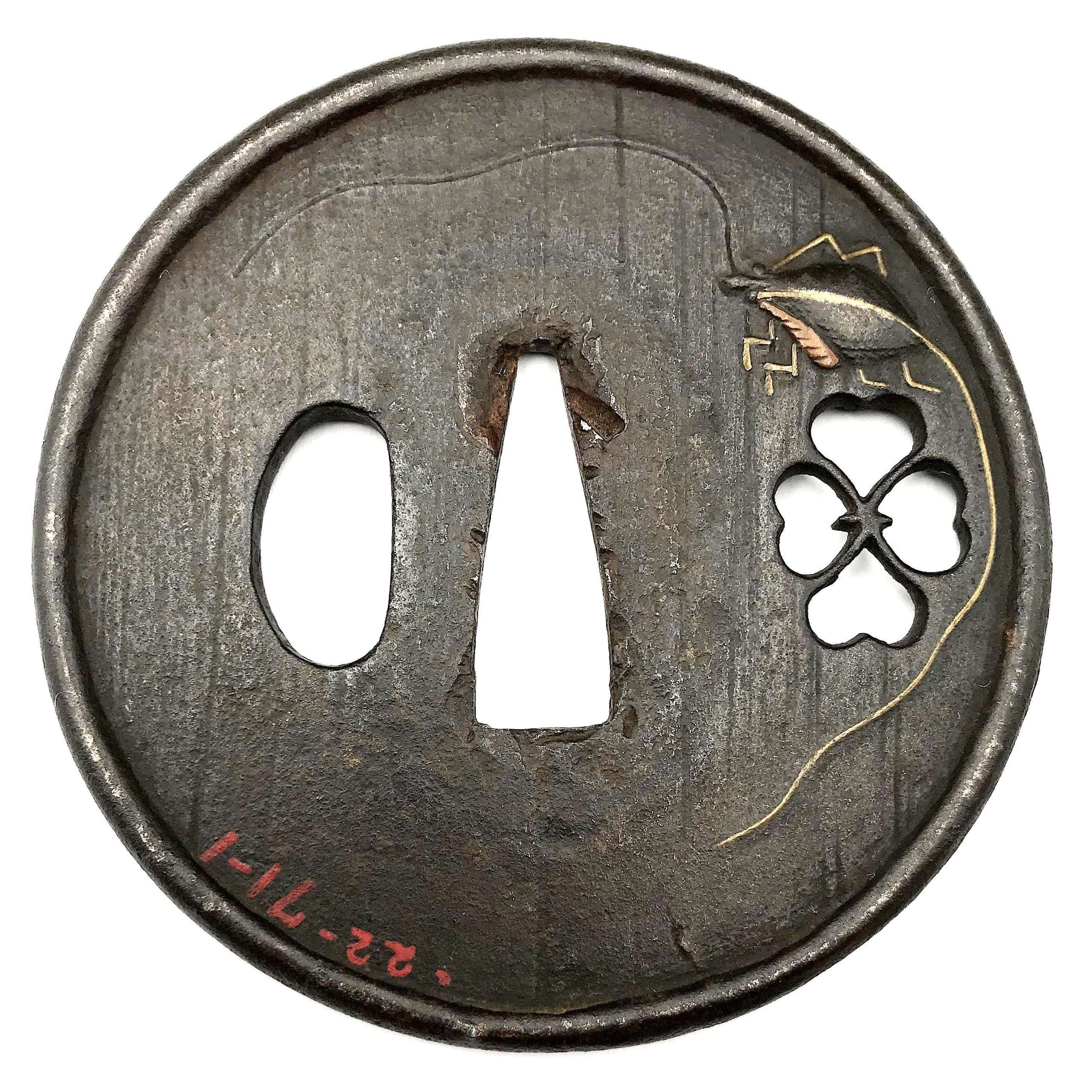
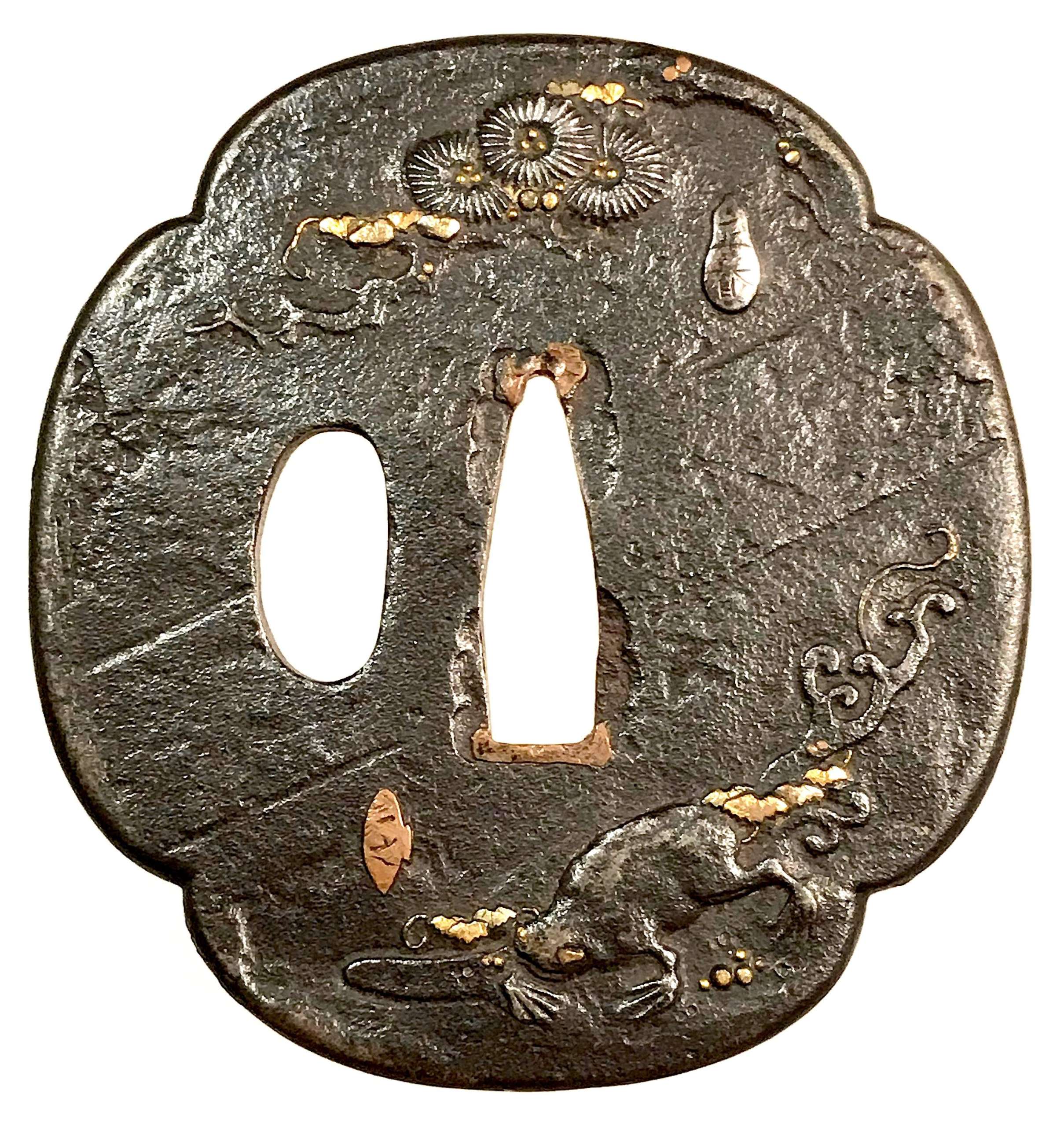
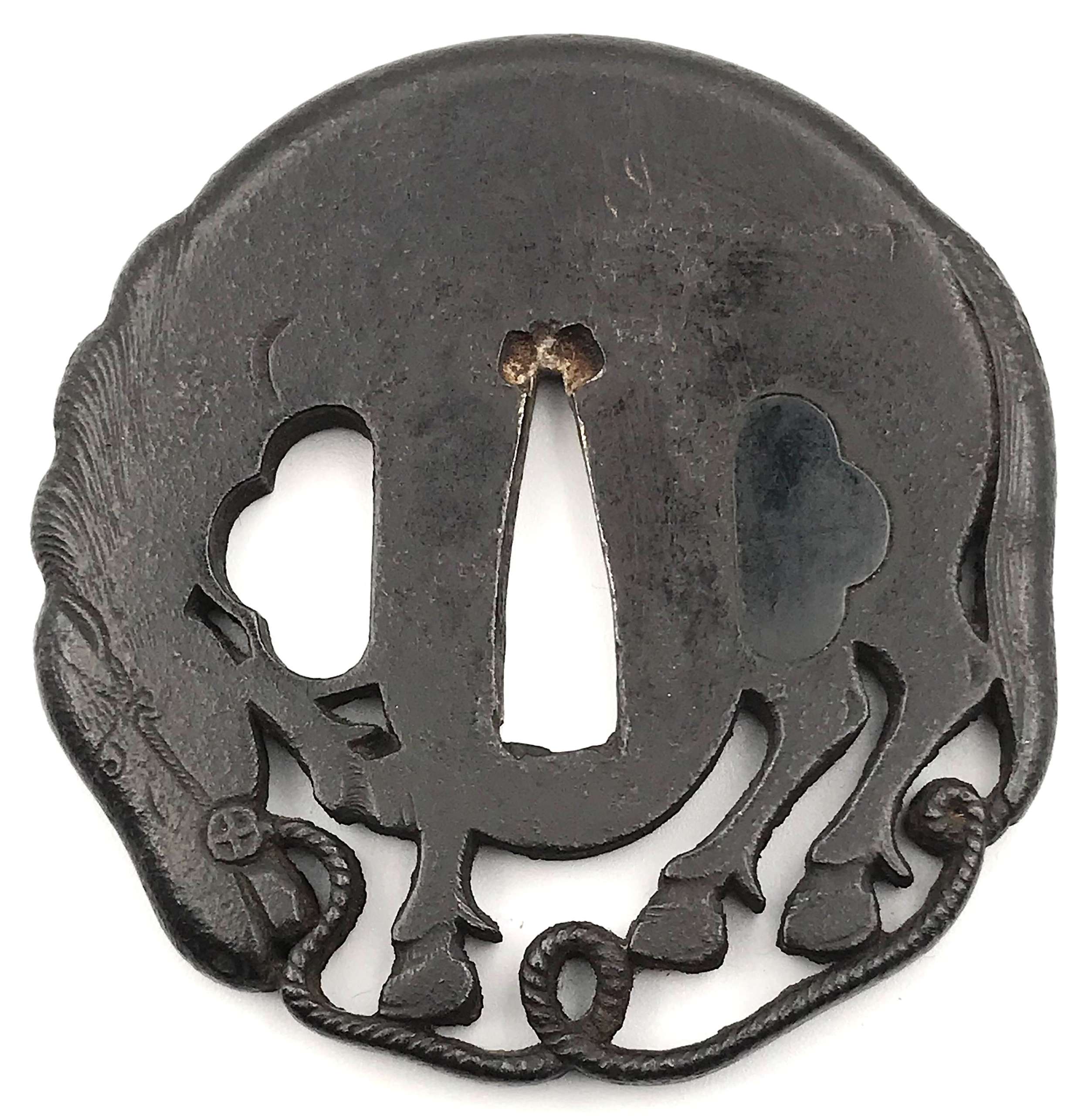
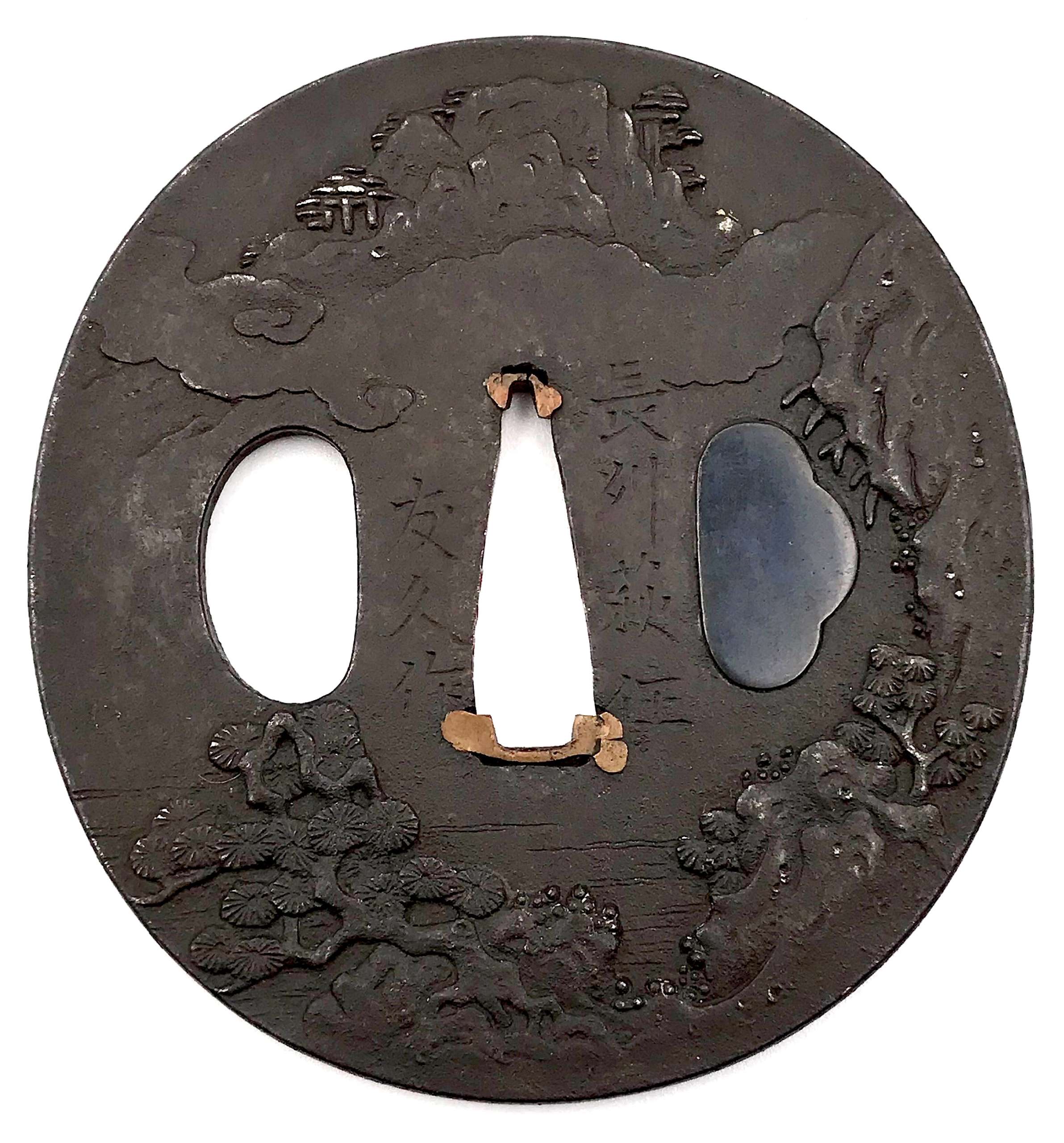
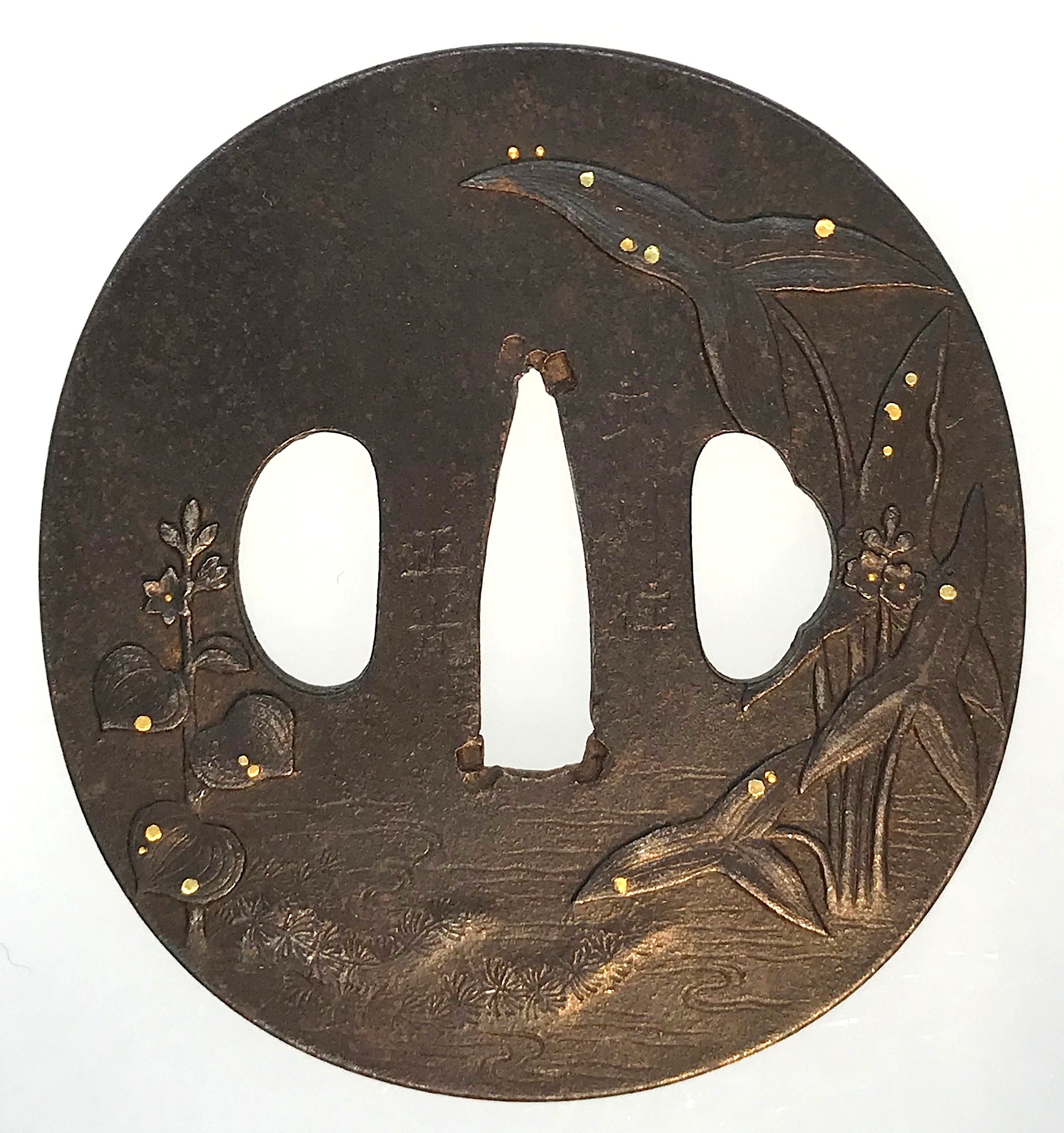
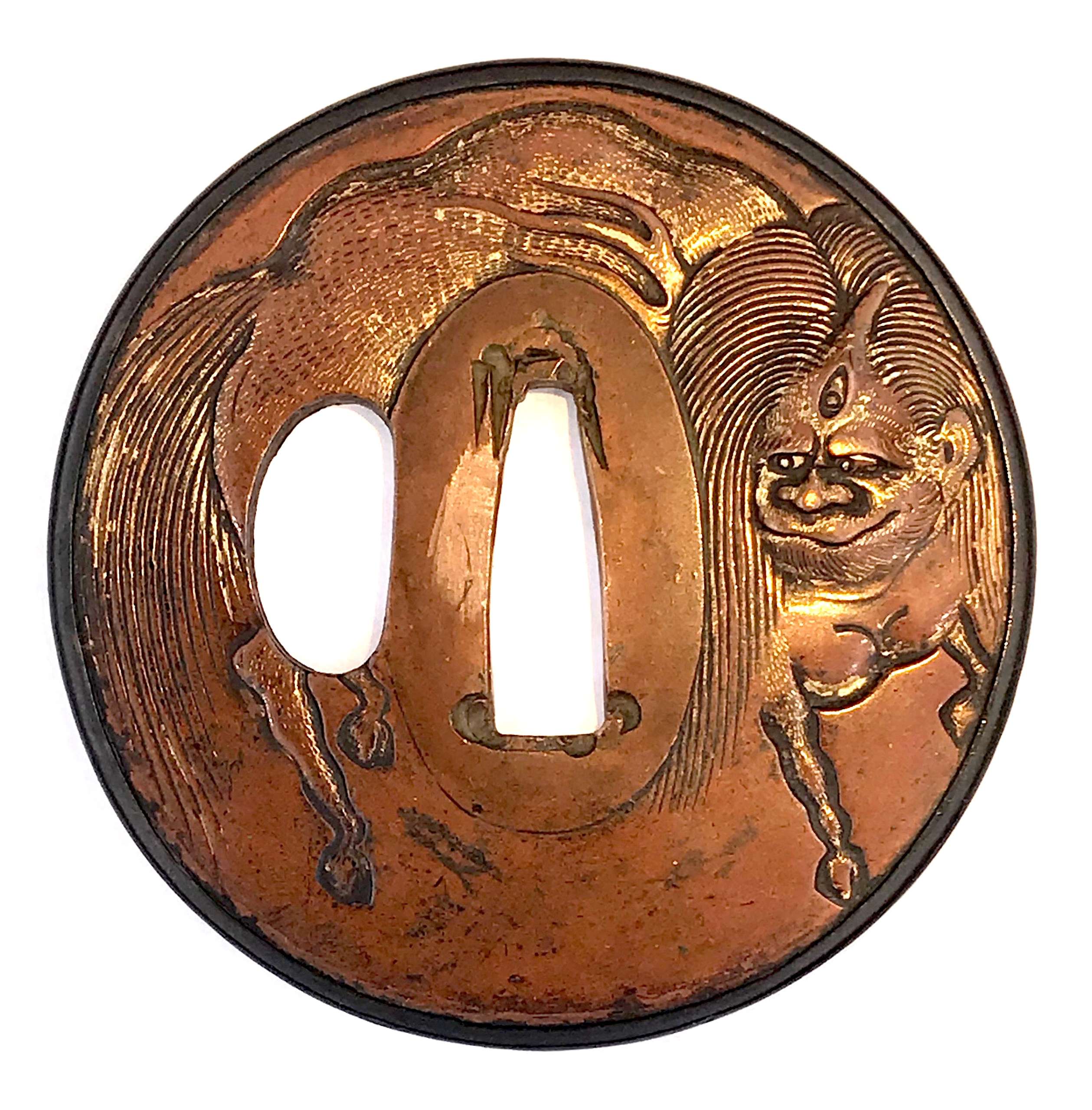
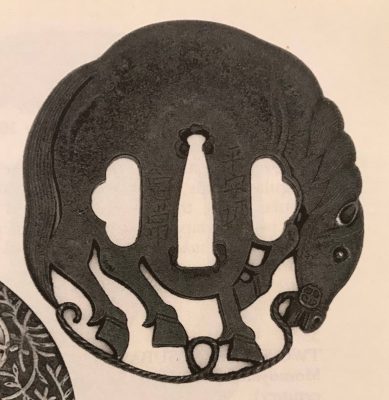
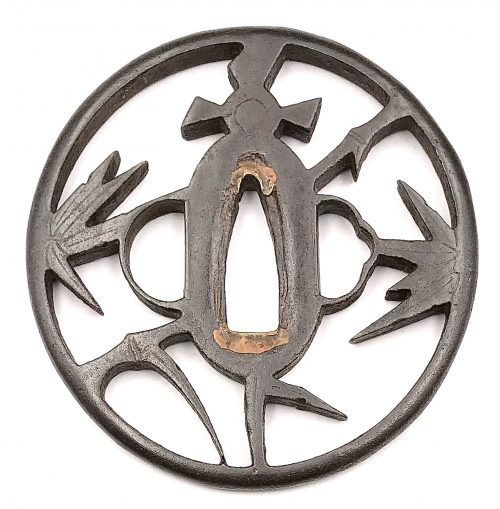
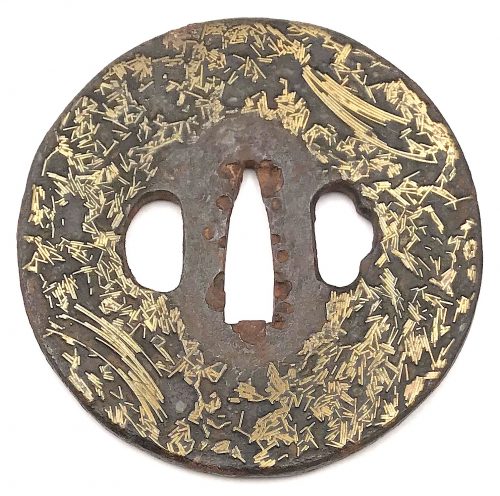
Iron tsuba of six-lobed (mutsu-mokkō-gata) form, with six wild boar's eye shape (
inome) openings (
sukashi).
Hitsu-ana and the entire perimeter of tsuba have typical for this school raised rim. Lobes are decorated with landscape motifs in low relief carving (
sukidashi-bori). On the obverse: A hut under a full moon, Shinto shrine gates (
torii) with pines and a full moon, rocks, a large pine tree, and a temple (
pagoda) surrounded by rocks and waves. On the reverse: waves, fishing boat, wild gees in flight under full moon, maple, hexagon (tortoiseshell,
kikko) with a dot inside and a dot outside (inclusion/exclusion symbol), and chrysanthemum (the last two may be family crests, mon).
Kamakura-bori school. Late
Muromachi period (1514-1573).
Height: 64.2 mm, width: 74.3 mm, Thickness at
seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, at rim 2.6 mm. Weight: 62.8 g (light).
NBTHK old green certificate №561: Tokubetsu Kicho - "Extraordinary Work".
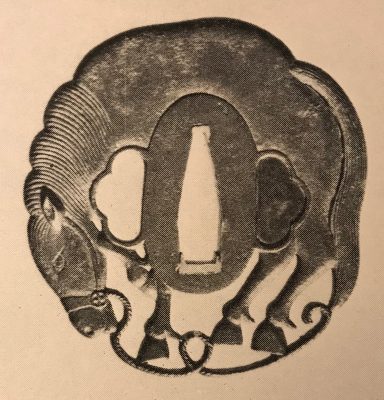
A look-a-like tsuba can be found at the Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17, though his tsuba is more massive (80 x 84 x 4 mm).

Compton Collection, part II, pp. 14-15, №17: Kamakura-bori tsuba, ca. 1450.
NBTHK paper says that the motif is
Hakkei (八景), i.e. "Eight Views," so several interpretations are possible (the original Chinese ones,
Omi Hakkei, etc.). However, most likely it is the 'Eight views of Omi' (近江八景 - 'Omi Hakkei'). Why the artist selected a 6-lobed form for depicting 8 views remains unclear, and thus we are in our right to raise the question whether the motif is indeed
Hakkei.
The term Omi hakkei (eight views of Omi) refers to painting or print sets which illustrate life on the shores of Lake Biwa in Omi (now Shiga Prefecture). The model for such paintings came from China, where, from the eleventh century onward, painters had produced eight views of the Hsiao and Hsiang lake areas of Hunan Province. The themes, which follow the original Chinese models, are: geese descending to land, returning fishing boats, clearing rain, a snow-covered evening landscape, the autumn moon, night rain, a temple bell at evening, and the glow of sunset. Japanese artists have also used the eight-theme approach for other parts of country - including cities - and applied it to subject matter other than landscapes. [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, page 308-9]. Japan Encyclopedia by Louis Frédéric also mentions Omi Hakkei as "Eight landscapes of Omi", and states that this theme was often cited in poetry after 1500. It is likely that the tsuba in focus is designed under the influence of the theme popularity in the 16th century. The theme was effectively exploited by prominent ukiyo-e artists Suzuki Harunobu and Utagawa Hiroshige in the 18th and 19th century, respectively. These are the eight scenes of the theme (see
Wikipedia):
- Returning sails at Yabase (矢橋の帰帆) - Yabase. Yabase is an old harbour on the east side of the lake. Near the Tokaido, it was used for a shortcut to Otsu by boat.
- Evening glow at Seta (勢多(瀬田)の夕照) - The Chinese Bridge at Seta. The long bridge across the Seta was used by the Tokaido. In the background the "Fuji of Omi", the Mikamiyama. It is just above 400 m, but indeed well visible.
- Autumn moon at Ishiyama (石山の秋月) - Ishiyama Temple. The Ishiyamadera was located on a hillside next to the Seta River. It got his name form the strange rocks on which it is built, partly on supporting beams. A hut at the upper end of the site allows a view of the lake, and the moon.
- Clear breeze at Awazu (粟津の晴嵐) - Awazuhara. Awazu is well known for its pine wood, Awazu-ga-hara.
- Evening bell at Miidera (三井晩鐘) - Mii-dera. Miidera temple was built in the 8th century. Its famous bell is one of the "Three bells of Japan", the other two being those at Byoodo-in, Uji and at Jingoji, Kyoto.
- Evening rain at Karasaki (唐崎の夜雨) - Karasaki Shrine. Karasaki is a small cape with a single large pine tree, a hitsu-matsu.
- Wild geese returning home at Katata (堅田の落雁) - Ukimido. Alighting geese cannot be seen always, however the little temple near Katata in the square hōkyō-style, detached from the lakeside, connected by a bridge. The first part of the name uki is the same as in Ukiyo-e, meaning floating. Midō means temple.
- Evening snow at Hira (比良の暮雪) - Hira Mountains. The Hira mountains on the west side of the lake experience the hard winter, when the winter monsoon brings much snow from the continent.
In any case, as a conservative, I say that it is a landscape motif and a late Muromachi period work, rather than Omi hakkei motif and a mid-Muromachi work.
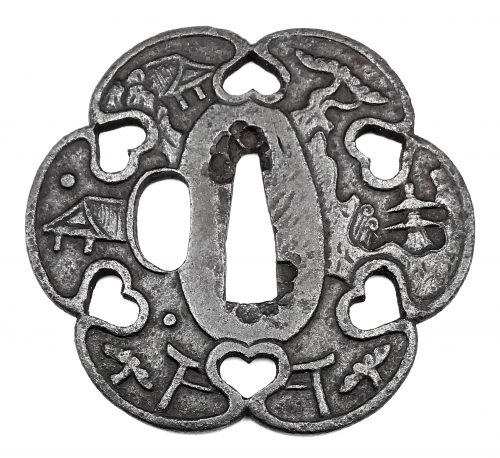
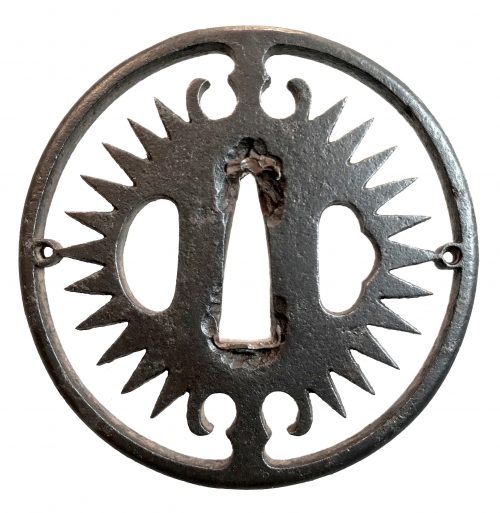
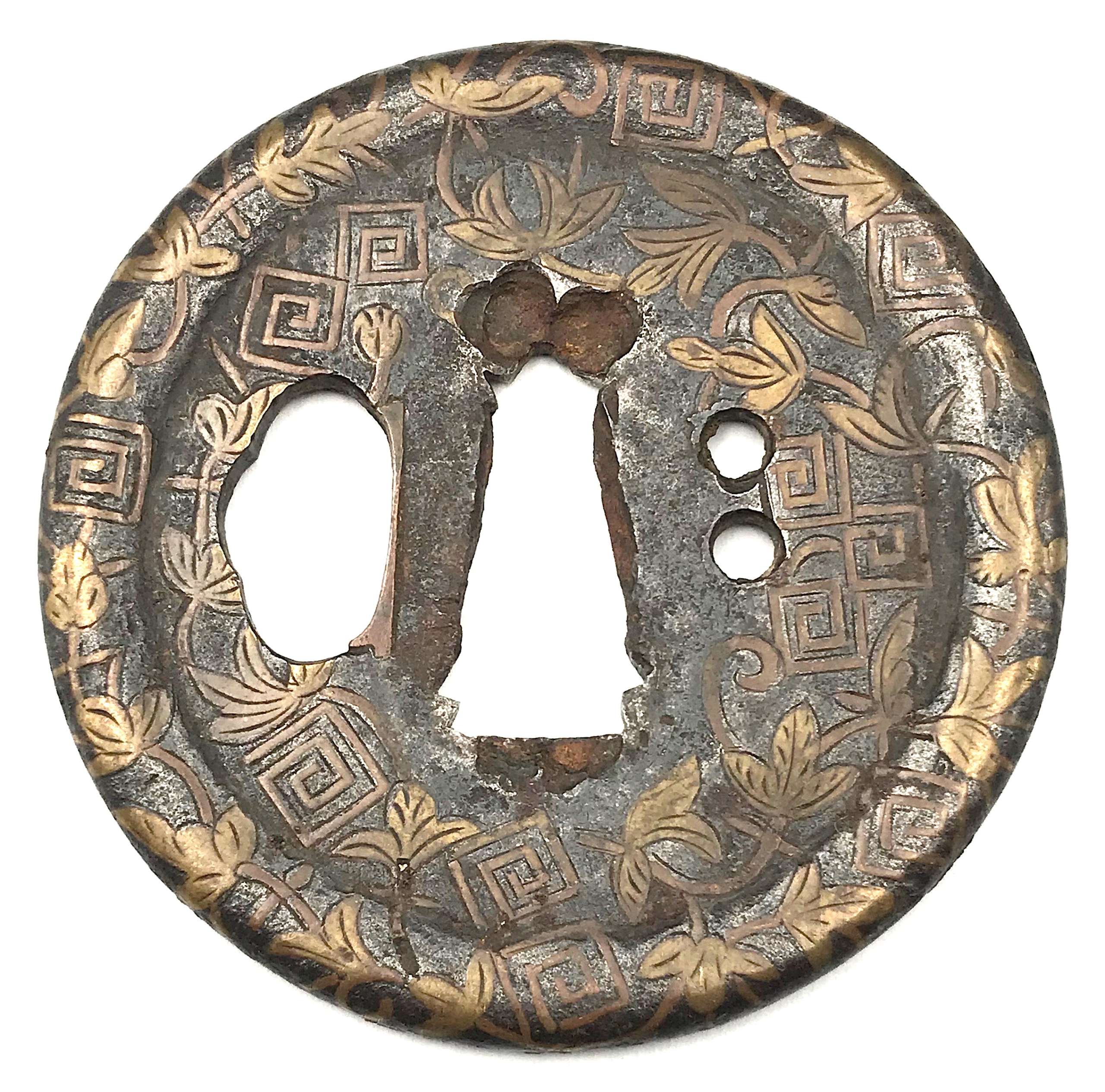
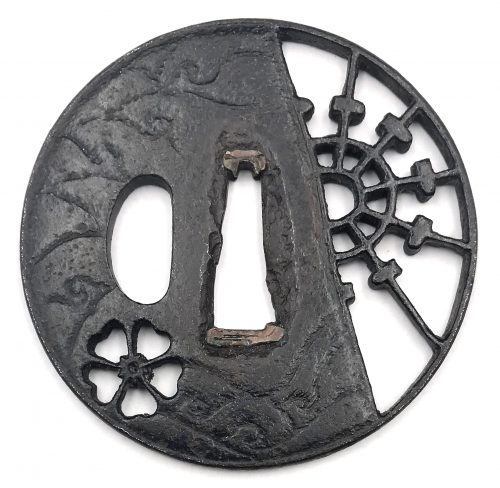
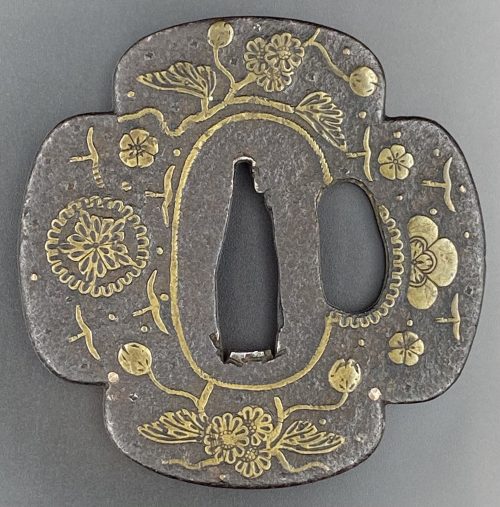
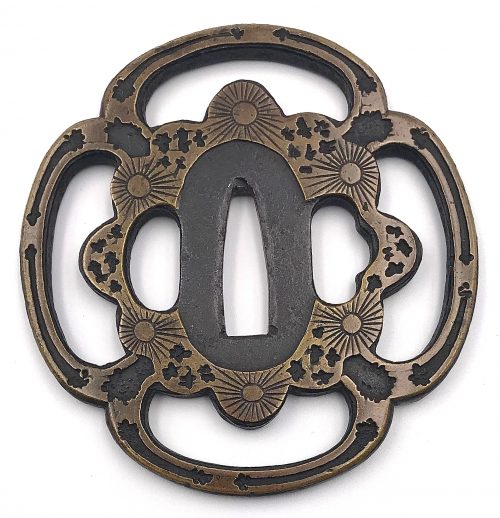
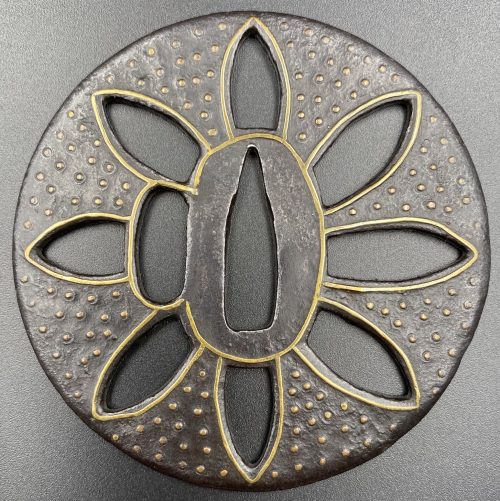
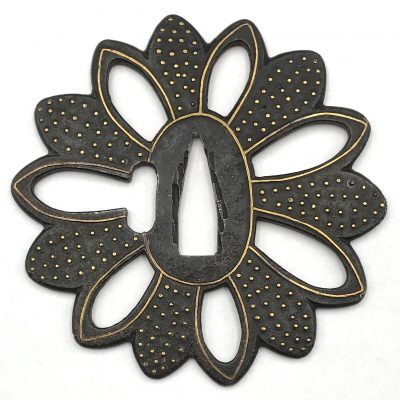
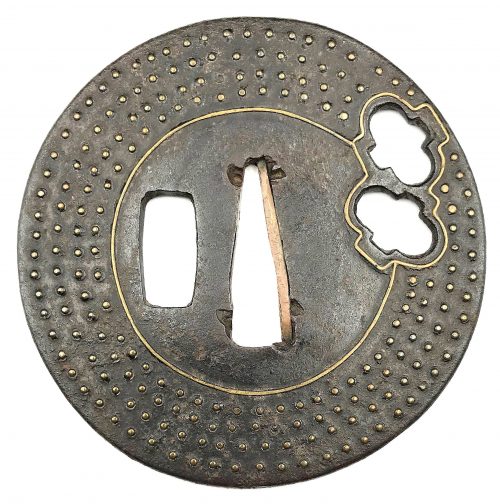



























 English translation of the book indicated above Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1 by Harry Afu Watson, AFU Research Enterprises, Inc., 1993. Tsuba in question illustrated on page 14 and described as follows: " Tsuba mumei Ōnin. Tetsu ji maru gata ko-sukashi tsuchime shitate shinchū suemon ten zogan maru mimi. Brass suemon". My question remains: why such a text is called 'translation' while it looks more like transliteration of romanization?
English translation of the book indicated above Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1 by Harry Afu Watson, AFU Research Enterprises, Inc., 1993. Tsuba in question illustrated on page 14 and described as follows: " Tsuba mumei Ōnin. Tetsu ji maru gata ko-sukashi tsuchime shitate shinchū suemon ten zogan maru mimi. Brass suemon". My question remains: why such a text is called 'translation' while it looks more like transliteration of romanization?