-
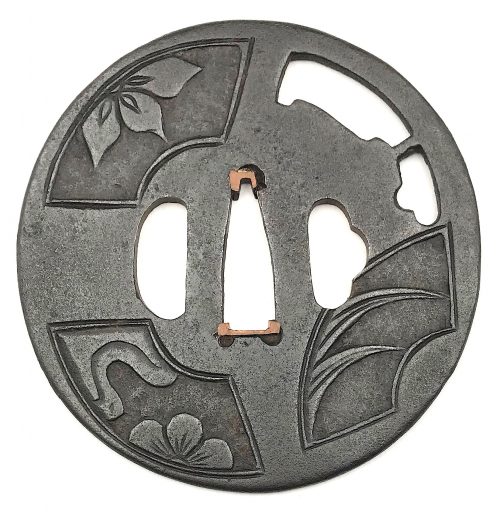 Iron tsuba of round form with design of hatchet executed in openwork (sukashi) and three fan panels motif on both sides carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori). Designs on the fan panels - face: bellflower, plum blossom in mist, grass leaves; - back: clouds, grass, and half plum blossom in mist. Copper sekigane. Koga-hitsu-ana probably cut out on a later date. Kamakura or kamakura-bori school. Edo period. Height: 83.8 mm, Width: 82.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm. NBTHK certificate № 4005500: Hozon (worthy of preservation).
Iron tsuba of round form with design of hatchet executed in openwork (sukashi) and three fan panels motif on both sides carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori). Designs on the fan panels - face: bellflower, plum blossom in mist, grass leaves; - back: clouds, grass, and half plum blossom in mist. Copper sekigane. Koga-hitsu-ana probably cut out on a later date. Kamakura or kamakura-bori school. Edo period. Height: 83.8 mm, Width: 82.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm. NBTHK certificate № 4005500: Hozon (worthy of preservation). -
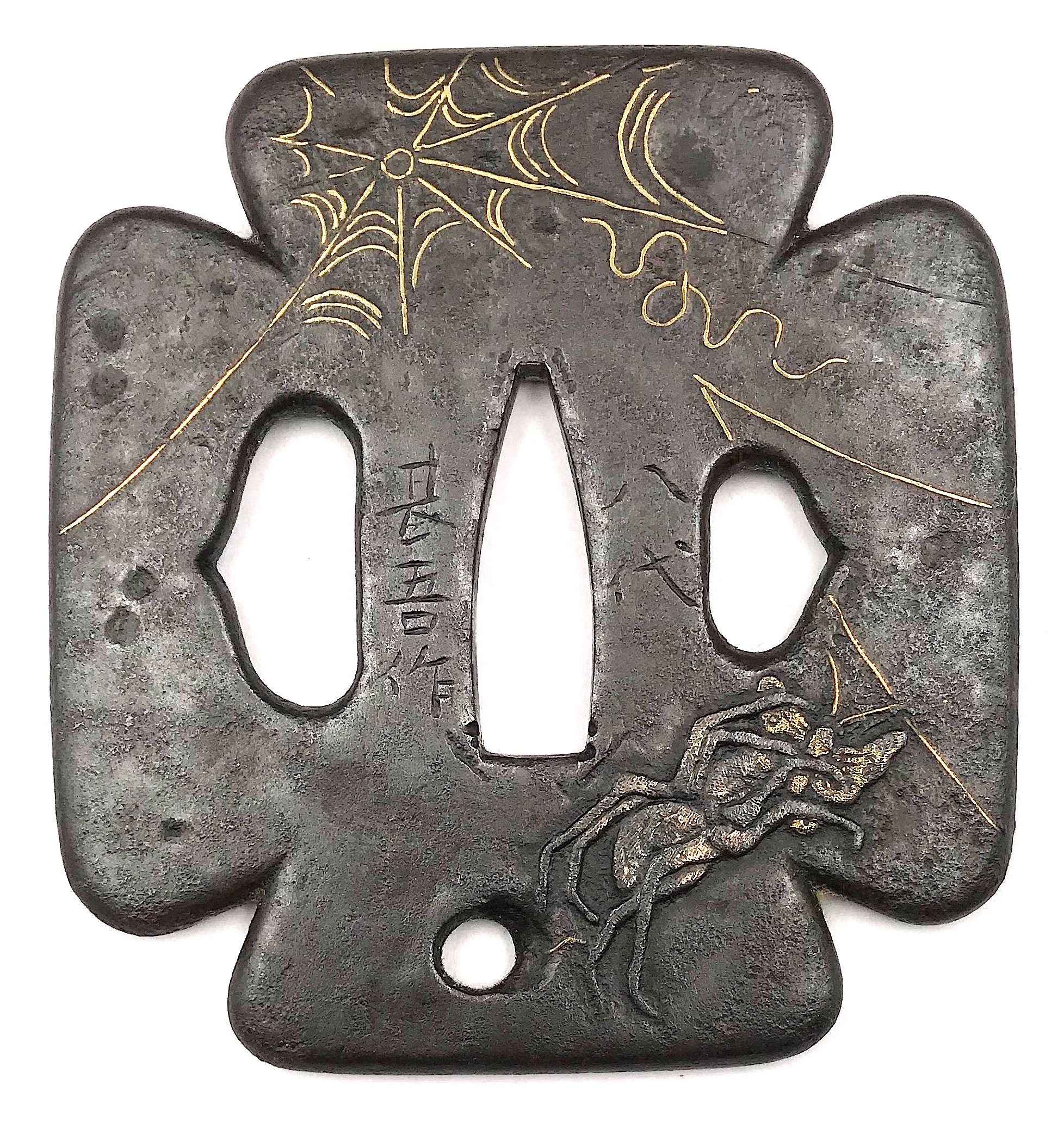

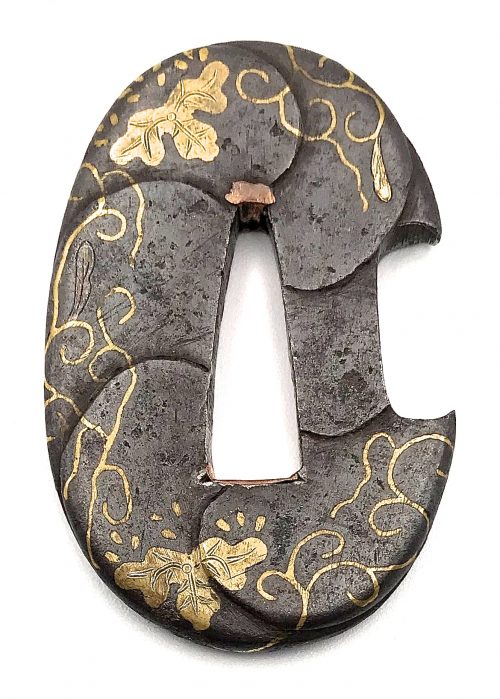
Very fine iron plate well hammered and turned, tapering and rolling to the rounded edge. Tsuba of a cross-form mokko shape (juji-mokko-gata) decorated with spider web inlaid in gold on both sides. The face is carved with a silver-damascened spider holding a gold-damascened butterfly (nunome-zōgan). Kozuka and kogai hitsu-ana of inome (boar's eye) form. The udenuki ana may be of purely decorative purpose.
Signed: Yatsushiro [八代] Jingo Saku [甚吾作], a signature of Chisokutei Amatsune, one of the last Jingo masters.
Late Edo period, Tenpō era, 1830-1844.Size: Height: 77.5 mm; Width: 72.8 mm; Thickness: 4.1 mm; Weight: 141 g.
In a custom wooden box.
Here is what Markus Sesko wrights in his book The Japanese toso-kinko Schools, 2012, on page 374:An artist who worked in the style of the Shimizu-Jingo school was Chisokutei Amatsune (知足亭天常). He was actually a samurai from Yatsushiro who made tsuba as a sideline. An extant old hakogaki of one of his pieces mentions that he died in Edo in the sixth month of An'ei eight (1779) at the age of 73. But the era of An'ei is probably wrong because Chikokutei (sic) is today dated by most experts around Tenpō (1830-1844). His relationships with the Shimizu school or under which Jingo master he had studied are unknown. From the point of view of production time and the finishing of nakago-ana, he is rather associated with the 5th and last gen. Shigenaga who died in the seventh year of Kaei (1854). A peculiarity of Chisokutei was that he signed his Jingo copies with "Yatsushiro Jingo Saku" ([八代甚吾作) but added the small syllable "chi" (チ) or the character "Chi" (知) for "Chisokutei" to identify them as copies.
No longer available. -
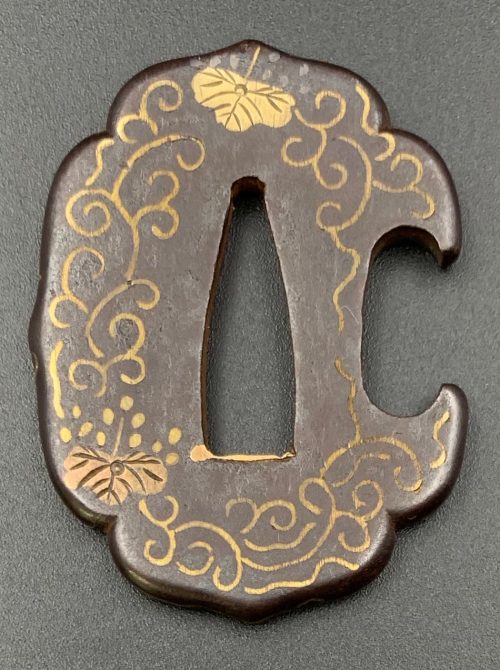

Small iron tsuba (tantō size) of aoi form with the design of paulownia leaves and blossoms in copper and brass flat inlay (hira-zōgan). Brass sekigane. Open kozuka hitsu-ana.
Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 53.4 x 40.7 x 4.4 mm; weight: 47.4 g
-
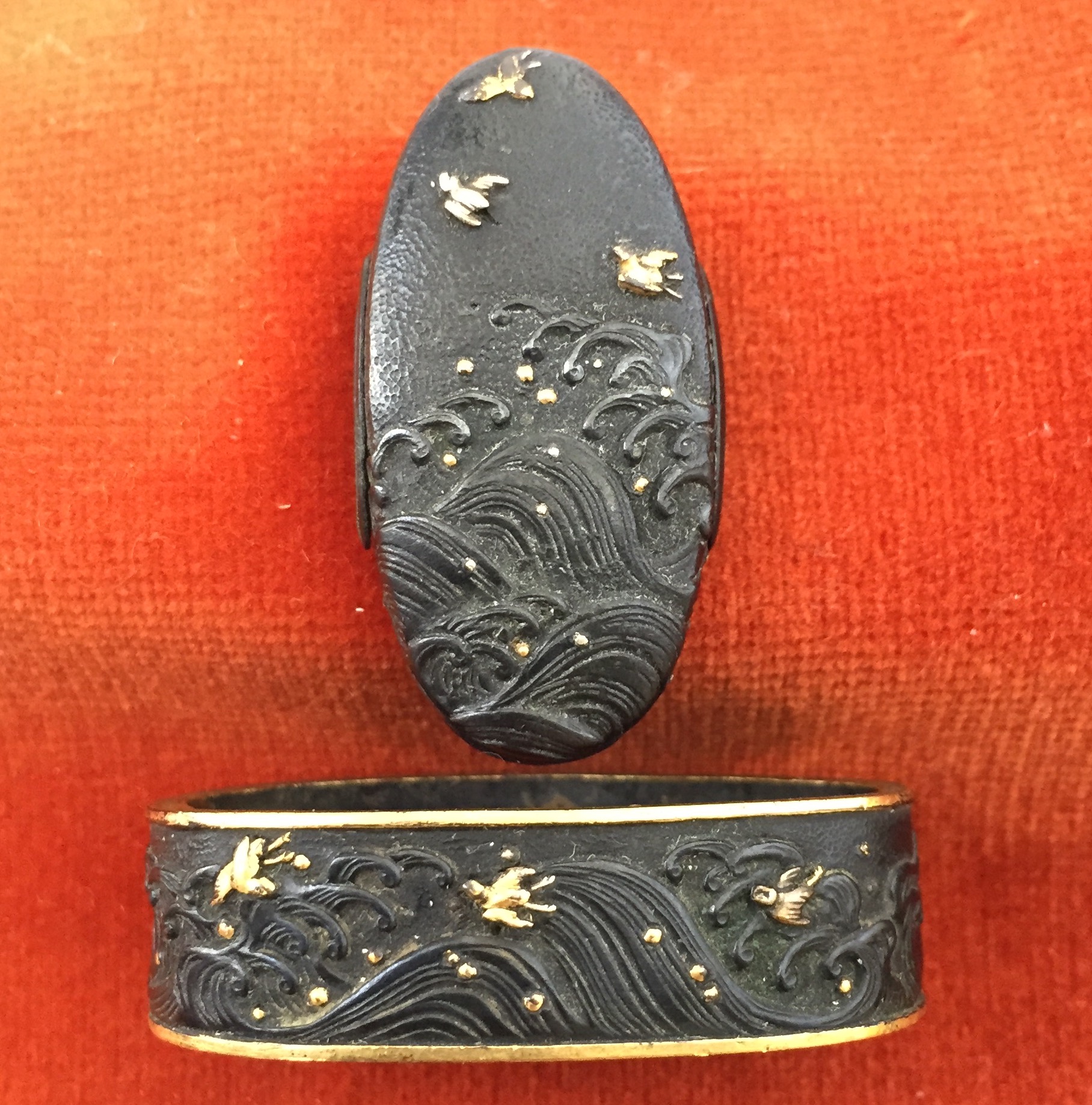 Fuchi: 37 x 21 x 11 mm; Weight: 13 g Kashira: 34 x 16 x 6 mm ; Weight: 10 g Material : Shakudo; Gold. Signature: Unsigned Technique: Sunameji Sukibori Zogan Decoration: Nami Chidori zu (wave & plover)
Fuchi: 37 x 21 x 11 mm; Weight: 13 g Kashira: 34 x 16 x 6 mm ; Weight: 10 g Material : Shakudo; Gold. Signature: Unsigned Technique: Sunameji Sukibori Zogan Decoration: Nami Chidori zu (wave & plover) -
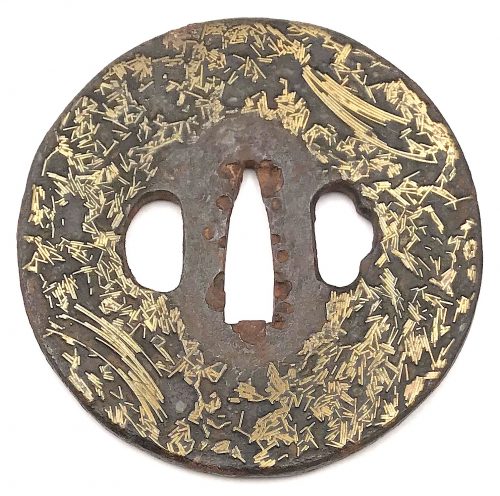 Gomoku-zōgan tsuba. Iron, inlaid with brass scrap (gomoku-zōgan), and polished. Height: 75.3 mm; Width 74.9 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. Weight 130.2 g. Edo, 18th century. Gary D. Murtha dedicates 10 pages to this type of tsuba: "...they were made by soldering brass overlay scraps to the iron plate". Actual gomoku-zōgan tsuba are seldom found in collections most likely because they have little if any artistic attributes. In addition, many have rough surfaces making them questionable for use on a sword. It is said that many of these were produced in Yokohama for export to the West during the late Edo period". G. D. Murtha then describes the technique of making gomoku-zōgan in every detail, and states that "The brass pieces are said to represent 'fallen pine needles', a description most likely created to add aesthetic value to help market the tsuba" [see:Gary D. Murtha. Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro. GDM Publications, 2016; pp. 160-161].
Gomoku-zōgan tsuba. Iron, inlaid with brass scrap (gomoku-zōgan), and polished. Height: 75.3 mm; Width 74.9 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. Weight 130.2 g. Edo, 18th century. Gary D. Murtha dedicates 10 pages to this type of tsuba: "...they were made by soldering brass overlay scraps to the iron plate". Actual gomoku-zōgan tsuba are seldom found in collections most likely because they have little if any artistic attributes. In addition, many have rough surfaces making them questionable for use on a sword. It is said that many of these were produced in Yokohama for export to the West during the late Edo period". G. D. Murtha then describes the technique of making gomoku-zōgan in every detail, and states that "The brass pieces are said to represent 'fallen pine needles', a description most likely created to add aesthetic value to help market the tsuba" [see:Gary D. Murtha. Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro. GDM Publications, 2016; pp. 160-161]. -
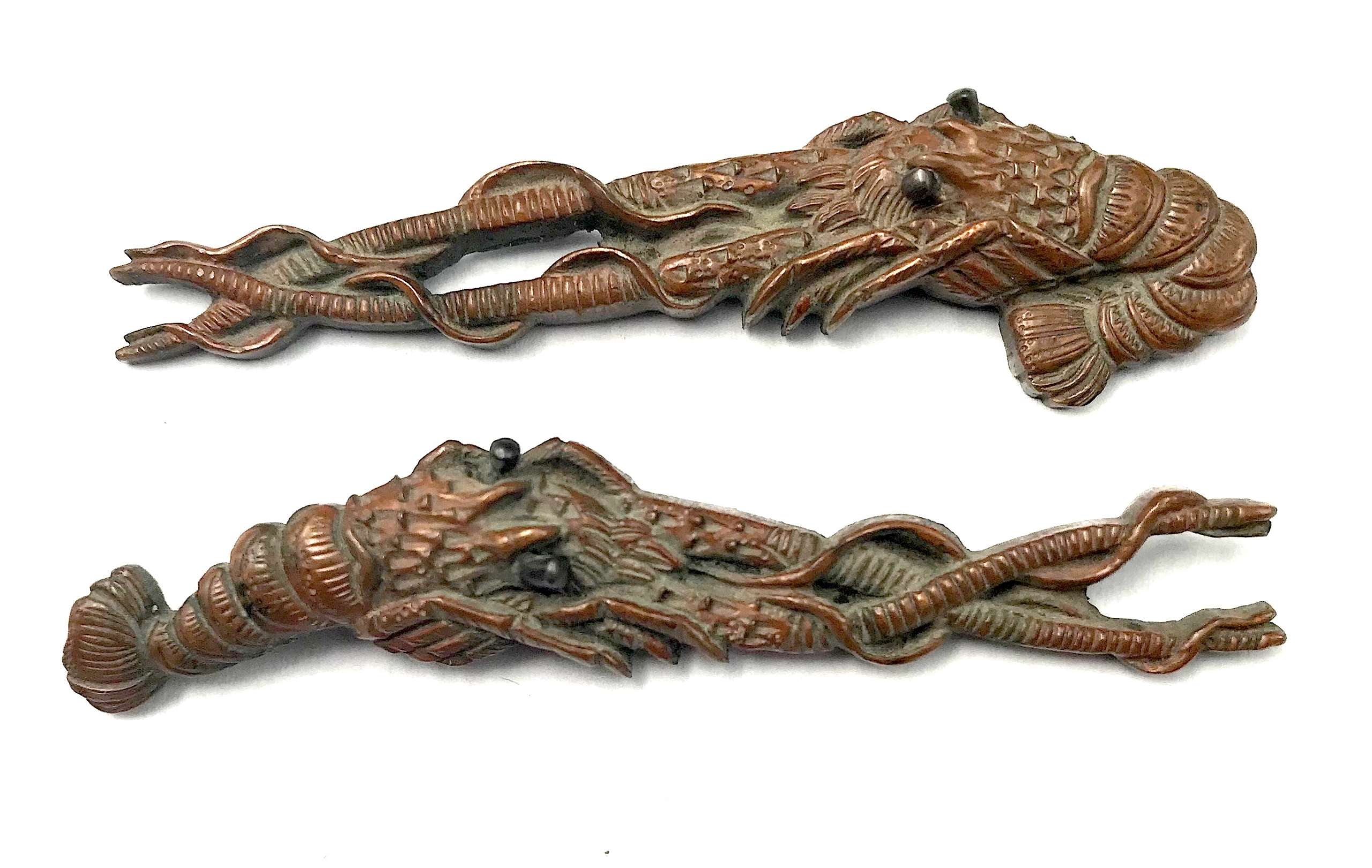 A pair of copper menuki in the form of a shrimp (lobster, crawfish, ebi) with eyes inlaid in shakudō.
A pair of copper menuki in the form of a shrimp (lobster, crawfish, ebi) with eyes inlaid in shakudō.Length: 58.2 mm.
-
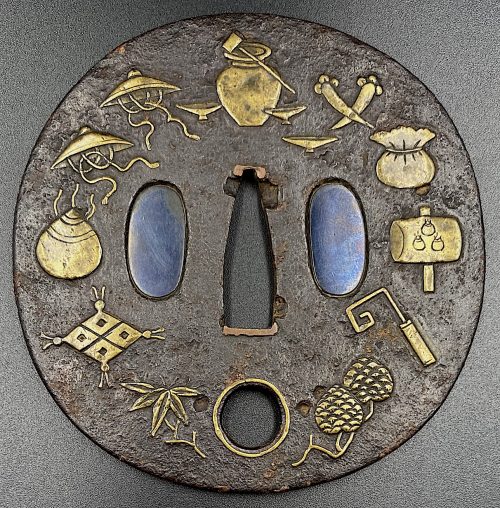 Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):
Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):- Sake set [shuki, 酒器], namely flask, ladle, and cups
- Cloves [choji, 丁子]
- Purse of inexhaustible reaches [kinchaku, 巾着]
- Magic mallet [kozuchi, 小槌]
- Key to the storehouse of the Gods [kagi, 鍵]
- Rhombus, or Lozenge (hosho, 方勝), with the second ideograph meaning victory.
- Sacred (or wish-granting) gem, or jewel [hōju, 宝珠]
- Hats of invisibility [kakuregasa, 隠れ笠]
-
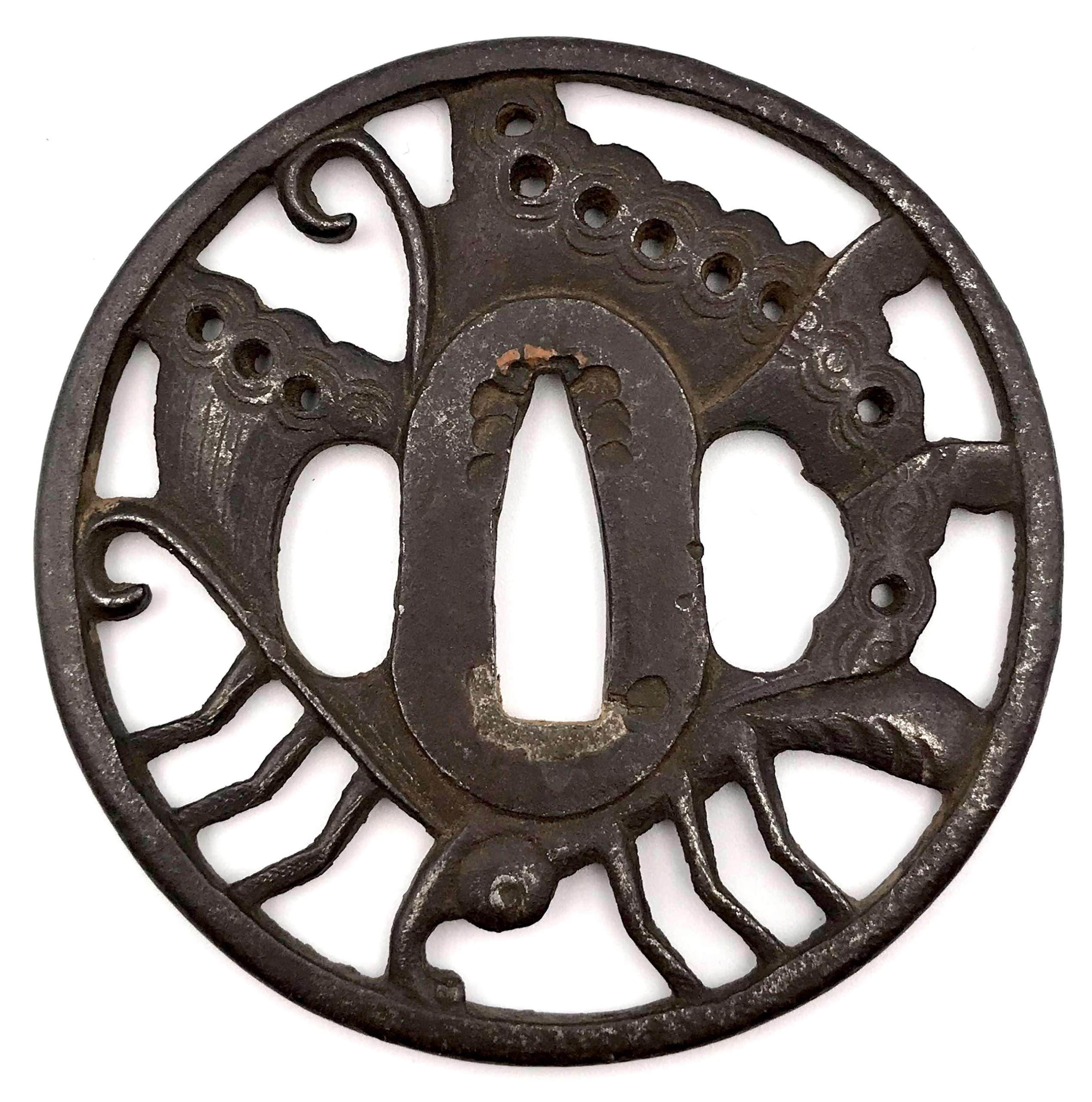
 Iron tsuba of oval form with design of iris and plank bridge (yatsubashi) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded cornered rim. Unsigned. Attributed to Jingo - 3rd generation Shimizu, 2nd generation Jingo (1691-1777) [M. Sesko, Genealogy..., p. 94]. Edo period: Late 18th century (Hohreki / Meiwa era). Height: 69.5 mm. Width: 65.2 mm. Rim thickness: 4.6 mm. Center thickness: 4.8 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 251: "Shimizu. Third generation Jingo (died at 87 years of age in the sixth year of An-ei, 1777). The eight-section bridge with irises are arranged to create the design of 'yatsubashi'. The features are unique for the Shimizu school and show no influence of the Hirita, Nishigaki or Hayashi schools". The design visually resembles a butterfly. As described in Family Crests of Japan by Stone Bridge Press [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007], and also in Japanese Family Crests by Yuzuru Okada [Yuzuru Okada. Japanese Family Crests // Series: Tourist Library: 37. Board of tourist industry; Japanese Government Railways, - 1941], there is a special technique used in construction of family crests, called 'reshaping' by the former and 'reconstruction' by the latter: "reconstruction is realized when a motive has its general shape composed of the detail of entirely different motive as, for instance, the crest of a butterfly formed of pine-needles. [...] The fanciful and ingenious forms evolved in this way may be represented by the kasiwa-giri or 'oak-leaf-paulownia', the ogi-bisi or 'fan-lozenge', the matuba-zuru or 'pine-needle-crane', the omodaka-kotyo or 'water-plantain-butterfly', etc." In our case we can call the motif yatsubashi-chocho or 'Iris-and-Bridge—Butterfly'.
Iron tsuba of oval form with design of iris and plank bridge (yatsubashi) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded cornered rim. Unsigned. Attributed to Jingo - 3rd generation Shimizu, 2nd generation Jingo (1691-1777) [M. Sesko, Genealogy..., p. 94]. Edo period: Late 18th century (Hohreki / Meiwa era). Height: 69.5 mm. Width: 65.2 mm. Rim thickness: 4.6 mm. Center thickness: 4.8 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 251: "Shimizu. Third generation Jingo (died at 87 years of age in the sixth year of An-ei, 1777). The eight-section bridge with irises are arranged to create the design of 'yatsubashi'. The features are unique for the Shimizu school and show no influence of the Hirita, Nishigaki or Hayashi schools". The design visually resembles a butterfly. As described in Family Crests of Japan by Stone Bridge Press [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007], and also in Japanese Family Crests by Yuzuru Okada [Yuzuru Okada. Japanese Family Crests // Series: Tourist Library: 37. Board of tourist industry; Japanese Government Railways, - 1941], there is a special technique used in construction of family crests, called 'reshaping' by the former and 'reconstruction' by the latter: "reconstruction is realized when a motive has its general shape composed of the detail of entirely different motive as, for instance, the crest of a butterfly formed of pine-needles. [...] The fanciful and ingenious forms evolved in this way may be represented by the kasiwa-giri or 'oak-leaf-paulownia', the ogi-bisi or 'fan-lozenge', the matuba-zuru or 'pine-needle-crane', the omodaka-kotyo or 'water-plantain-butterfly', etc." In our case we can call the motif yatsubashi-chocho or 'Iris-and-Bridge—Butterfly'. -
 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of a butterfly in openwork (sukashi) with details carved in kebori. Eyes inlaid in brass (one inlay is missing). Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 80.4 x 80.6 x 4.4 mm References At Haynes Catalog #6, p. 18-19, Lot 30: "Famous Ikeda butterfly design" (Ikeda family of Inaba and Okayama, and at least 7 other families). Ca. 1700. Shōami of Kyoto, no doubt. Ht 8.2 cm, Th. 5 mm. ["Important tsuba, menuki, bokuto, woodblock prints, koshirae, sword pistol and kana mono". San Francisco, June 1-26, 1983. Catalog #6. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd.]Similar tsuba at Haynes Catalog #9, p.71, lot 143: the classic Shoami tsuba of the mon of the Ikeda family. This example, as most, seems to be made by the same hand as the others. See Haynes sale number 6, lot 30, for an identical example. The eye is brass. From an old French collection. Ht. 7.9 cm., Th. 5 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of a butterfly in openwork (sukashi) with details carved in kebori. Eyes inlaid in brass (one inlay is missing). Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 80.4 x 80.6 x 4.4 mm References At Haynes Catalog #6, p. 18-19, Lot 30: "Famous Ikeda butterfly design" (Ikeda family of Inaba and Okayama, and at least 7 other families). Ca. 1700. Shōami of Kyoto, no doubt. Ht 8.2 cm, Th. 5 mm. ["Important tsuba, menuki, bokuto, woodblock prints, koshirae, sword pistol and kana mono". San Francisco, June 1-26, 1983. Catalog #6. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd.]Similar tsuba at Haynes Catalog #9, p.71, lot 143: the classic Shoami tsuba of the mon of the Ikeda family. This example, as most, seems to be made by the same hand as the others. See Haynes sale number 6, lot 30, for an identical example. The eye is brass. From an old French collection. Ht. 7.9 cm., Th. 5 mm.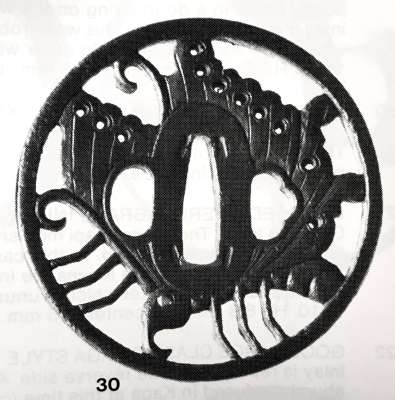
Haynes Catalog #6, lot 30.
Similar tsuba in the Randolph B. Caldwell Collection, 1994, page 24, №13: "A circular iron tsuba pierced in positive sukashi with a butterfly within an angular rim, details engraved. The eye inlaid in brass [in my specimen the inlay is missing on the omote side]. Unsigned. Bizen Shōami, Momoyama period. Dimensions: 8.0 x 8.2 x 0.5 cm. Similar example: Durand-Ruel, collection Ch. Gilloz, number 1302. [SV: that's possibly the 'old French collection' of Robert Haynes.]
Haynes Catalog #9, lot 143.
If we accept Haynes' theory regarding the genealogy and history of Bizen Shōami family, Momoyama period attribution would seem unlikely. I am leaning towards the early to mid 17th century.
Caldwell Collection, #13.
-
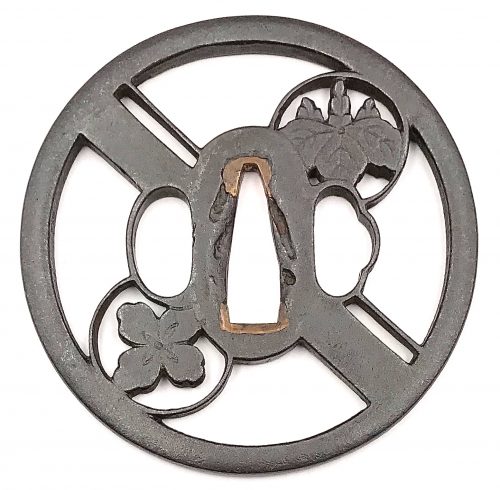 Iron tsuba of round form with design of double crossbar and two family crests (hikiryo-ni-kamon) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Owari school. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun / Enppo era). Height: 80.9 mm. Width: 80.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.0 mm. Center thickness: 4.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 172: "A paulownia and a clover are diagonally opposite two crossbars. This expressive design suggests a Higo origin, but the iron and the finish are certainly of the Owari school. Work of this nature may have been influenced by Hayashi Matashichi (1613-1699)."
Iron tsuba of round form with design of double crossbar and two family crests (hikiryo-ni-kamon) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Owari school. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun / Enppo era). Height: 80.9 mm. Width: 80.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.0 mm. Center thickness: 4.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 172: "A paulownia and a clover are diagonally opposite two crossbars. This expressive design suggests a Higo origin, but the iron and the finish are certainly of the Owari school. Work of this nature may have been influenced by Hayashi Matashichi (1613-1699)." -
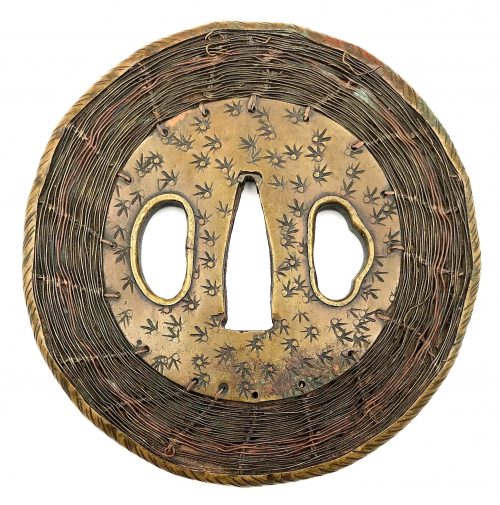 Shingen school (or style) tsuba of round form with iron core and web, covered with a thin brass plate decorated with star-shaped punch marks. The rim of tsuba is a brass nawame-fukurin. Between the central brass plate and the rim there is woven wire of brass and copper in a basketweave pattern. Both hitsu-ana have raised rim. Traces of oxidation. Unsigned. Edo period, 18th century. Size: Height: 88.4 mm, Width: 86.6 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.6 mm. Weight: 132.4 g. Robert E. Haynes in his "Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010" on p. 117 says: "Brass outer plate of round shape. This tsuba has an iron core tsuba of spoke form as made by Saotome school, ca. 1500. There are brass plates on either side connected to the rim by woven brass and shakudō wire. The wire has been hand drawn, which is very difficult. The hitsuana are brass lined and the rim has a brass cover. This type of tsuba is referred to as a Shingen tsuba. This is a reference to Takeda Shingen Harunobu (1521-1573), the great and famous daimyō." For reference see the MFA collection. A look-a-like tsuba is illustrated in Compton Collection, vol. 2, p. 26-27, №52:More details and examples can be found at: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Shingen school (or style) tsuba of round form with iron core and web, covered with a thin brass plate decorated with star-shaped punch marks. The rim of tsuba is a brass nawame-fukurin. Between the central brass plate and the rim there is woven wire of brass and copper in a basketweave pattern. Both hitsu-ana have raised rim. Traces of oxidation. Unsigned. Edo period, 18th century. Size: Height: 88.4 mm, Width: 86.6 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.6 mm. Weight: 132.4 g. Robert E. Haynes in his "Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010" on p. 117 says: "Brass outer plate of round shape. This tsuba has an iron core tsuba of spoke form as made by Saotome school, ca. 1500. There are brass plates on either side connected to the rim by woven brass and shakudō wire. The wire has been hand drawn, which is very difficult. The hitsuana are brass lined and the rim has a brass cover. This type of tsuba is referred to as a Shingen tsuba. This is a reference to Takeda Shingen Harunobu (1521-1573), the great and famous daimyō." For reference see the MFA collection. A look-a-like tsuba is illustrated in Compton Collection, vol. 2, p. 26-27, №52:More details and examples can be found at: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Compton Collection, vol. 2, p. 26-27, №52.
-
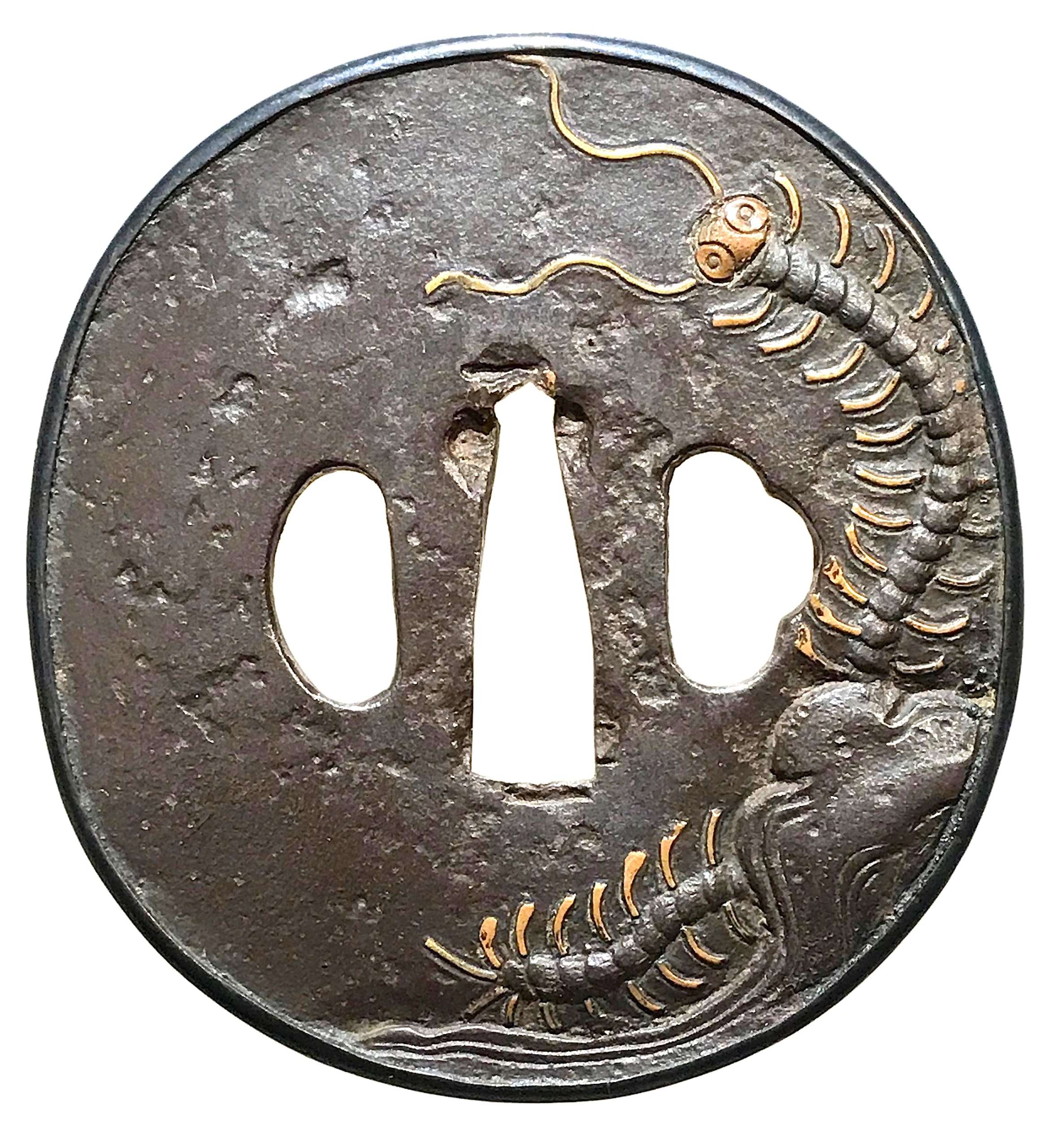
Iron tsuba of oval form with a shakudō fukurin and rough surface decorated by low relief carving and brass inlay with a centipede emerging from under the rock on both sides.
Edo period.Size: 78.9 x 73.6 x 3.8 mm
Unsigned. However, this tsuba may be (though with reservation) attributed to Misumi Kōji school. There is some information regarding this master(s) in Tsuba. An aesthetic study by Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes (from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997) on pages 163-4, though I was not able to locate the tsuba in the original publication. Possibly, this fragment of the book was added by Robert Haynes. Markus Sesko speculates about Misumi in his The Japanese toso-kinko Schools.// Lulu Inc., 2012 on pages 374-5: "Misumi Kōjo Tsuba. Iron plate, elliptical shape, shakudō takabori suemon, yamagane fukurin. Centipede." But of course, visual similarity does not prove anything. I was not able to find any traces of signature or a triangle on the seppa-dai.
Misumi Kōji Tsuba on p. 163.
-

Small iron tsuba (tantō size) of oval form carved with imitation of six overlapping plates, decorated with paulownia blossoms, leaves, and tendrils in brass and copper hira-zōgan. Copper sekigane. Open kozuka hitsu-ana.
Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 50.5 x 34.0 x 4.9 mm.
-
 Signature: Unsigned
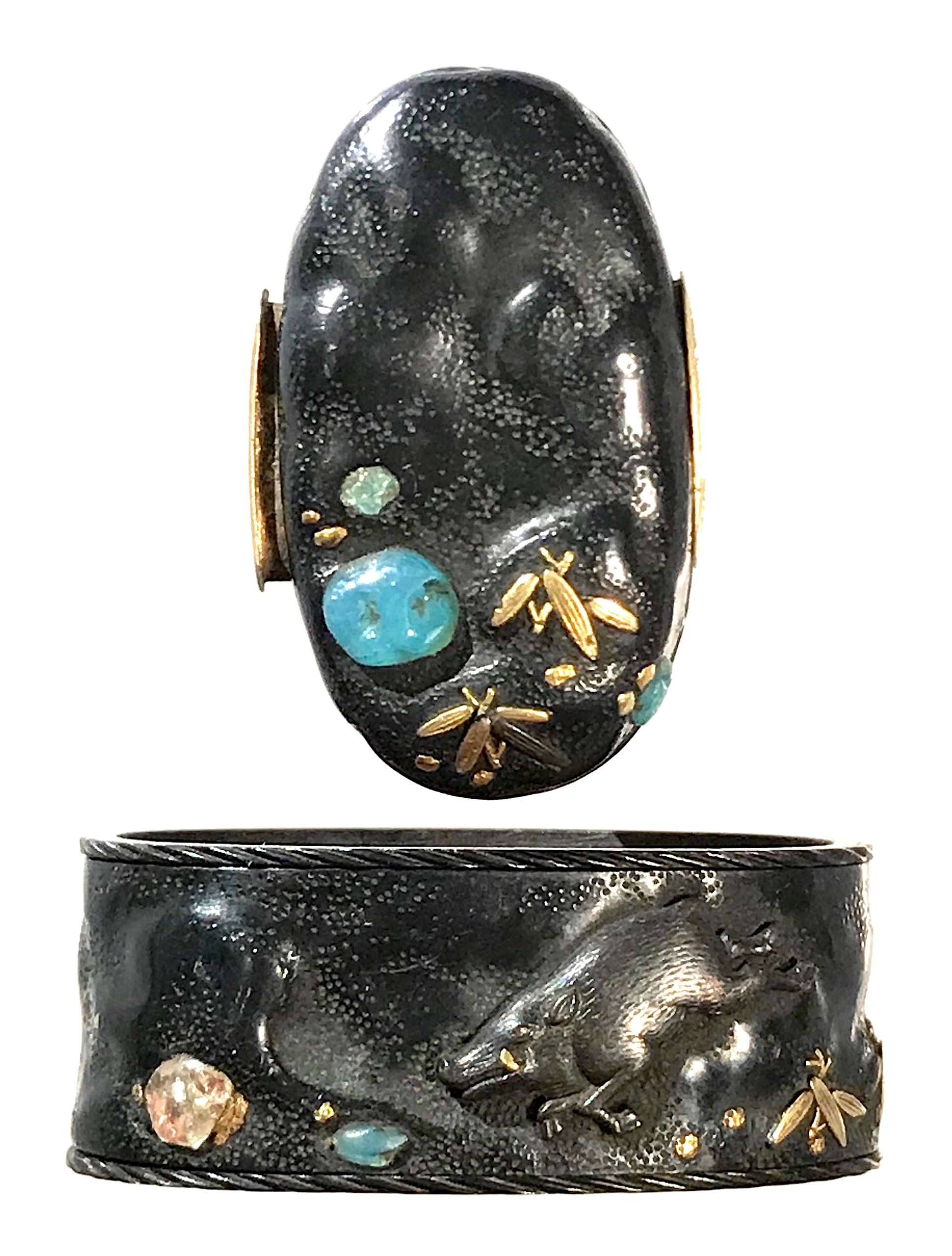
Signature: UnsignedFuchi-kashira with rock and boar (iwa ni inoshishi zu) motif. Inlay of precious stones or colour glass. Shakudō, gold, gemstones. Technique: Sukibori zogan kiniroe.
Fuchi: 36 x 21 x 14 mm; Weight: 22 g; Kashira: 32 x 17 x 5 mm; Weight: 8 g; Material : Shakudō; Gold; Gemstones (Chalcedony and Rose Quartz). Possibly, Owari school. -
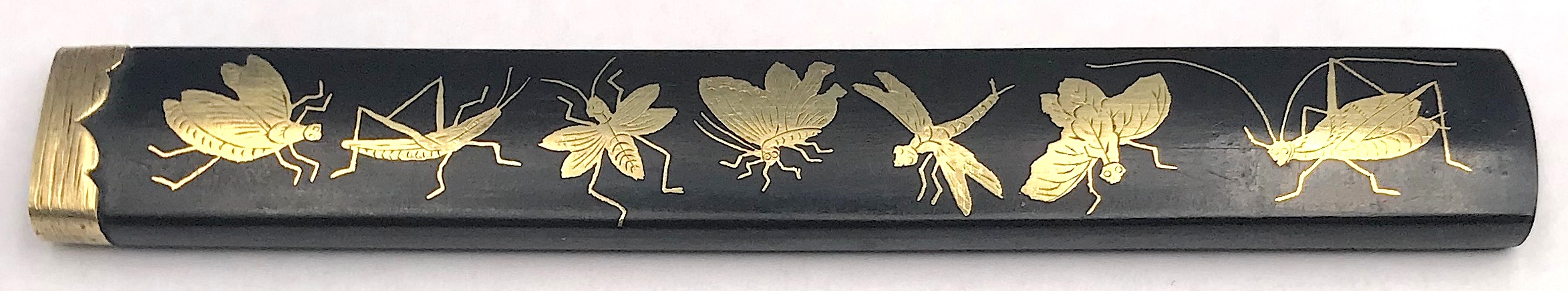 Kozuka with seven insects (fly, grasshopper, bee, butterfly, dragonfly, firefly, and cricket) and grass with dewdrops motif. Shakudō, flush gold inlay (hira-zōgan). 95.2 (H) x 13.7 mm (W). Mid Edo period (Late 17th - early 18th century, Genroku era 1688-1703). Unsigned. Kaga school. A look-a-like kozuka (with five insects) is illustrated at Japanese Sword Fittings. A descriptive catalogue of the Collection of G.H. Naunton, Esq., completed and illustrated by Henri L. Joly, - 1912 on plate XXIX, №691 [LIB-1389 in this Collection] with the following description at page 54: "Shakudō, inlaid with butterfly, dragon-fly, grasshopper, locust and another insect, gold."
Kozuka with seven insects (fly, grasshopper, bee, butterfly, dragonfly, firefly, and cricket) and grass with dewdrops motif. Shakudō, flush gold inlay (hira-zōgan). 95.2 (H) x 13.7 mm (W). Mid Edo period (Late 17th - early 18th century, Genroku era 1688-1703). Unsigned. Kaga school. A look-a-like kozuka (with five insects) is illustrated at Japanese Sword Fittings. A descriptive catalogue of the Collection of G.H. Naunton, Esq., completed and illustrated by Henri L. Joly, - 1912 on plate XXIX, №691 [LIB-1389 in this Collection] with the following description at page 54: "Shakudō, inlaid with butterfly, dragon-fly, grasshopper, locust and another insect, gold." See also tsuba TSU-0211 in this collection:
See also tsuba TSU-0211 in this collection:


-
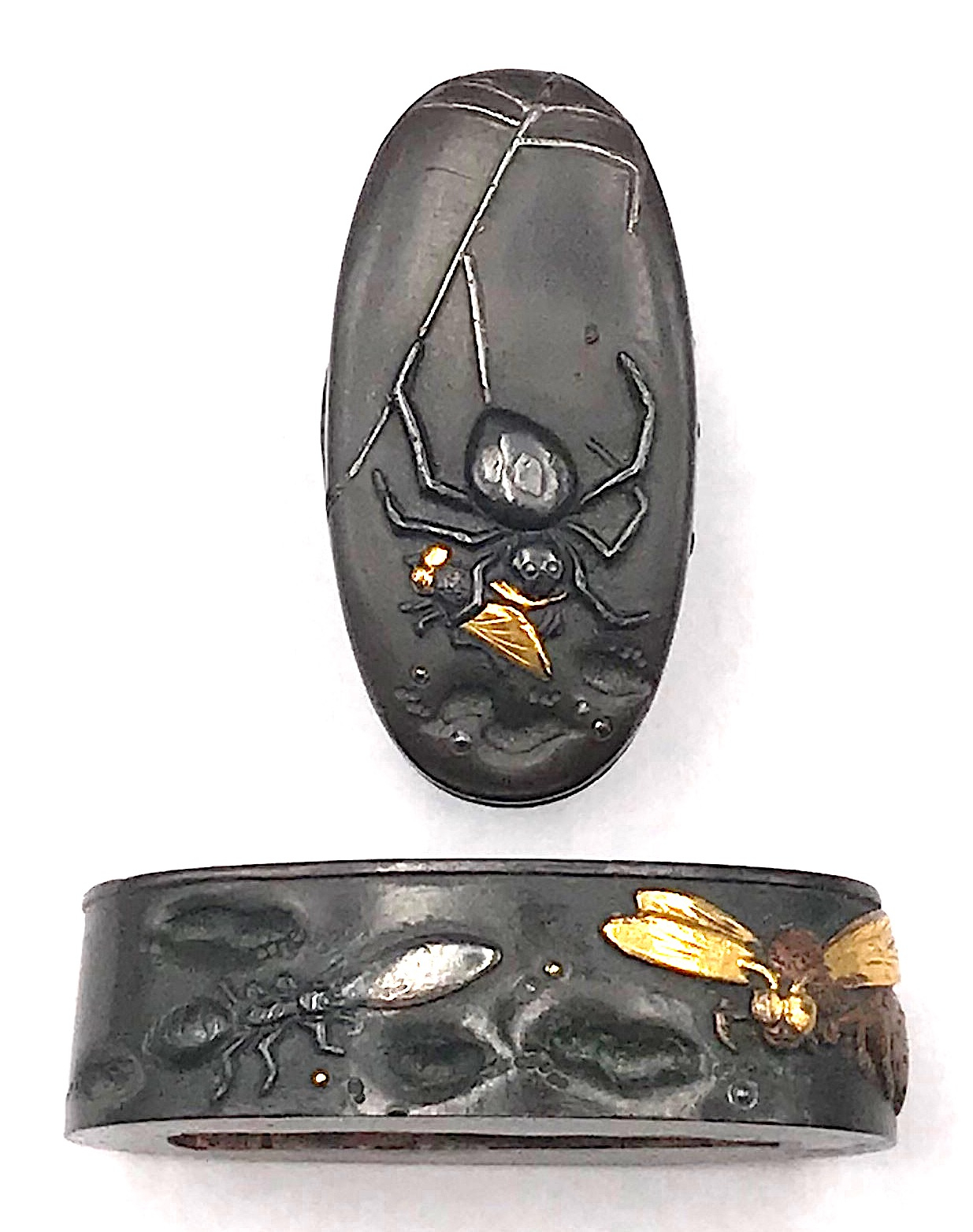

Fuchi-kashira made of Shibuichi carved and inlaid with shakudō, gold, silver, and copper with the design of spider holding a fly on the fuchi, and other insects (ant-lion, wasp, and ant) on the kashira.
Fuchi: 35.1 mm. Kashira: 38.7 mm. Main material: Shibuichi. Other metals: shakudō, gold, silver, and copper. Decorative technique: iroe taka-zōgan. -
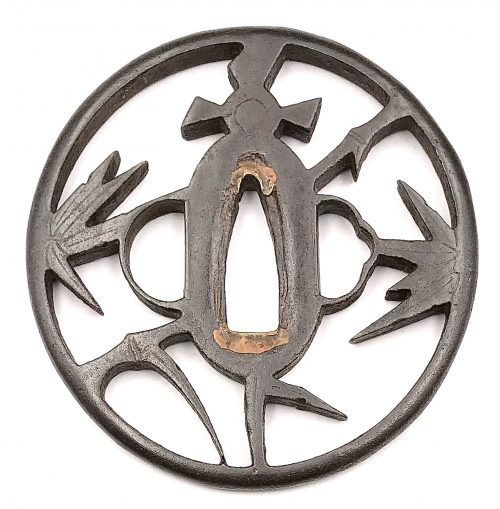 Iron tsuba with design of bamboo and sparrow (take-ni-suzume) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane. Akasaka school. Unsigned. Attributed to second generation Tadamasa Shōzaemon (died in in the fifth year of Enppo, 1677). Early Edo period: 17th century (Kan-ei / Kanbun era). Height: 79.0 mm. Width: 77.5 mm. Rim thickness: 5.5 mm. Center thickness: 6.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 222: "It is believed that sparrows nest in a bamboo grove". According to Merrily Baird [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001], "a bamboo grove is said to be emblematic of security as the bamboo is resilient even in the face of high winds and heavy rains. [...] The association of the sparrow (suzume) with bamboo is an old one found in Japanese poetry, paining, and design. The bird is said to be obsessed with its honor, especially the repaying of debts".
Iron tsuba with design of bamboo and sparrow (take-ni-suzume) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane. Akasaka school. Unsigned. Attributed to second generation Tadamasa Shōzaemon (died in in the fifth year of Enppo, 1677). Early Edo period: 17th century (Kan-ei / Kanbun era). Height: 79.0 mm. Width: 77.5 mm. Rim thickness: 5.5 mm. Center thickness: 6.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 222: "It is believed that sparrows nest in a bamboo grove". According to Merrily Baird [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001], "a bamboo grove is said to be emblematic of security as the bamboo is resilient even in the face of high winds and heavy rains. [...] The association of the sparrow (suzume) with bamboo is an old one found in Japanese poetry, paining, and design. The bird is said to be obsessed with its honor, especially the repaying of debts". -
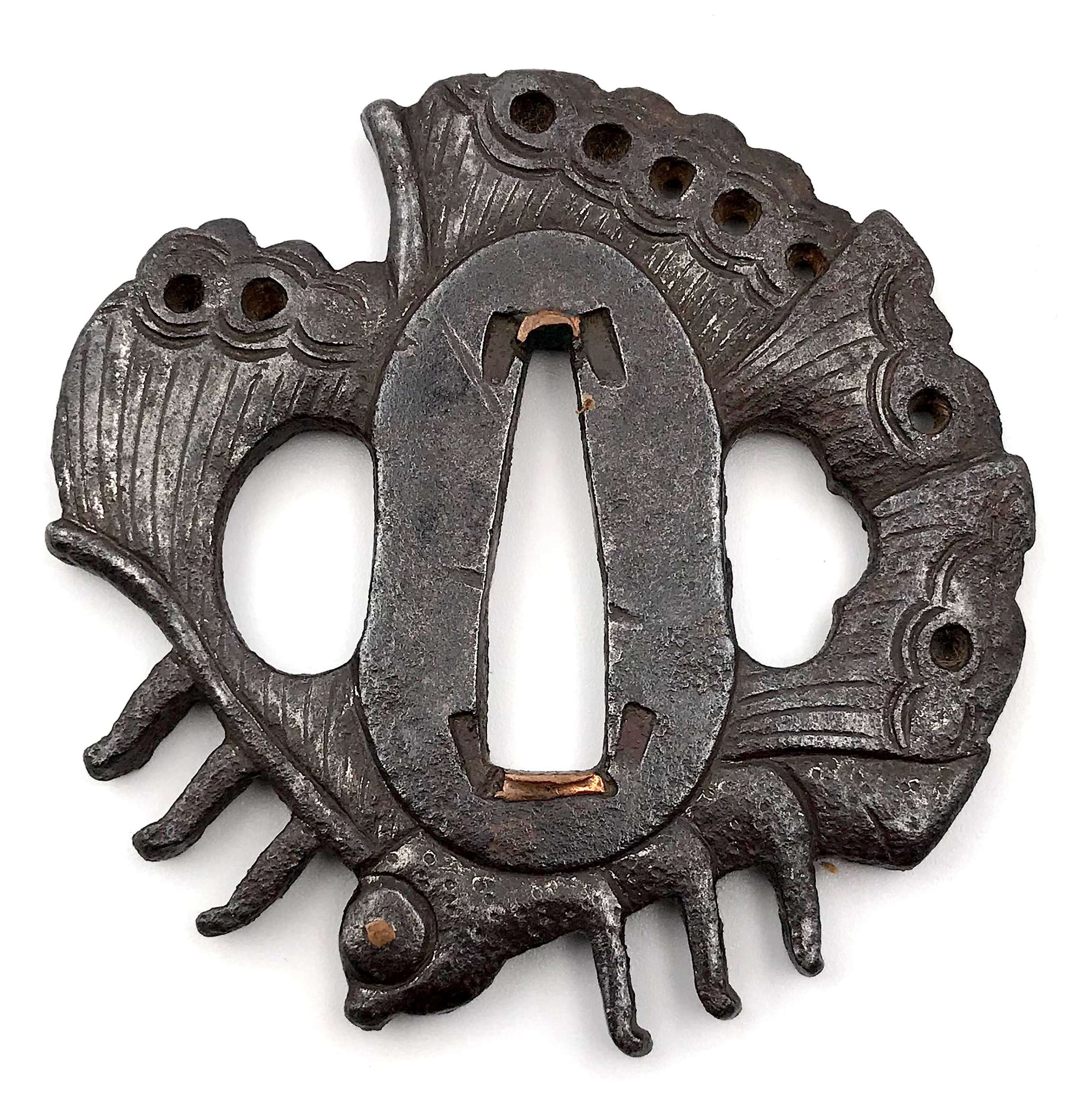 This tsuba is a cut from a typical Bizen Shōami butterfly tsuba (see TSU-0100 in this collection), which normally would have had a circular rim around the butterfly. In this particular example of altered guard we have both eyes of the insect (inlaid in brass or copper) intact. The kebori carving is more pronounced than in TSU-0100 example. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 64.7 x 63.7 x 5.2 mm References: see TSU-0100.
This tsuba is a cut from a typical Bizen Shōami butterfly tsuba (see TSU-0100 in this collection), which normally would have had a circular rim around the butterfly. In this particular example of altered guard we have both eyes of the insect (inlaid in brass or copper) intact. The kebori carving is more pronounced than in TSU-0100 example. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 64.7 x 63.7 x 5.2 mm References: see TSU-0100. -
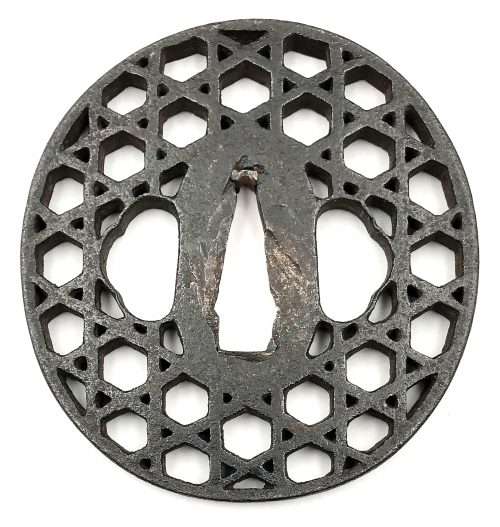

Iron tsuba of oval form decorated with design of jakago (bamboo lattice work) in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane.
Unsigned. Edo period.
Size: 73.7 x 70.3 x 5.6 mm.Note regarding design: though some might think that this piece belonged to a member of the lost tribe of Israel, it did not. Jakago baskets were made of bamboo, filled with rocks and used to catch crabs (besides other uses).

Jeanne Allen. Designer's Guide to Samurai Patterns. Chronicle Books, San Francisco, 1990; p.51, №57.
-
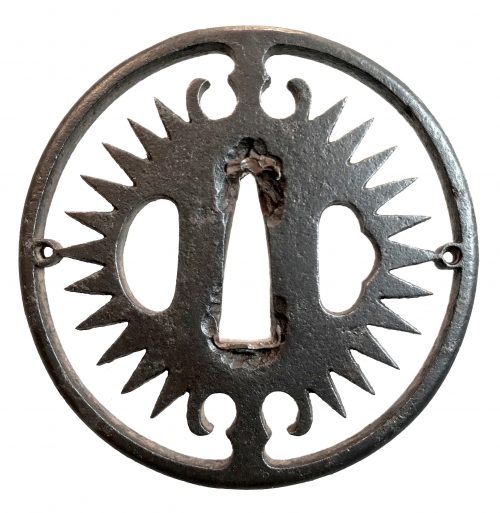 Iron tsuba of round form with design of slanting rays of light (shakoh) or clock gear (tokei) in openwork (sukashi). Commonly considered a Christian / Jesuit motif. Copper sekigane. According to seller, Owari School. Haynes writes that most tsuba of this design are Owari (Tsuba. Aesthetic Study). Unsigned. Edo period. According to F. Geyer, diamond-shaped vertical posts and long rays suggest that this tsuba was probably made between 1605 and 1630.
Iron tsuba of round form with design of slanting rays of light (shakoh) or clock gear (tokei) in openwork (sukashi). Commonly considered a Christian / Jesuit motif. Copper sekigane. According to seller, Owari School. Haynes writes that most tsuba of this design are Owari (Tsuba. Aesthetic Study). Unsigned. Edo period. According to F. Geyer, diamond-shaped vertical posts and long rays suggest that this tsuba was probably made between 1605 and 1630.Size: 76.9 x 76.0 x 5.4 mm
For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91. -
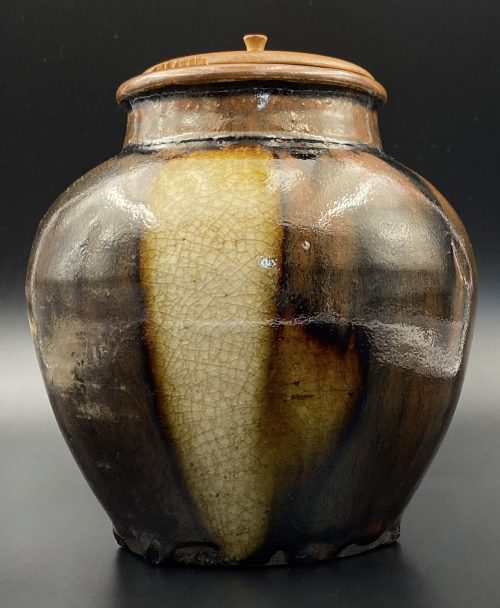 Seller's description: "pottery jar presenting a circular, concave base, an apple-form body, a cylindrical neck, and an annular flared rim. Boasting a lustrous burnish, the gorgeous vessel displays three narrow vertical panels in a hue of cream over mottled shades of chocolate brown and mocha on its body and a caramel-coloured neck and rim. The discoid lid features a lovely natural woodgrain surface incised with three decorative concentric circles around a petite knob-like handle. Note the beautiful globules of glaze that decorate the periphery of the base! This type of vessel is known as Seto ware." Size: Dia: 13 cm, H: 14 cm.
Seller's description: "pottery jar presenting a circular, concave base, an apple-form body, a cylindrical neck, and an annular flared rim. Boasting a lustrous burnish, the gorgeous vessel displays three narrow vertical panels in a hue of cream over mottled shades of chocolate brown and mocha on its body and a caramel-coloured neck and rim. The discoid lid features a lovely natural woodgrain surface incised with three decorative concentric circles around a petite knob-like handle. Note the beautiful globules of glaze that decorate the periphery of the base! This type of vessel is known as Seto ware." Size: Dia: 13 cm, H: 14 cm. -
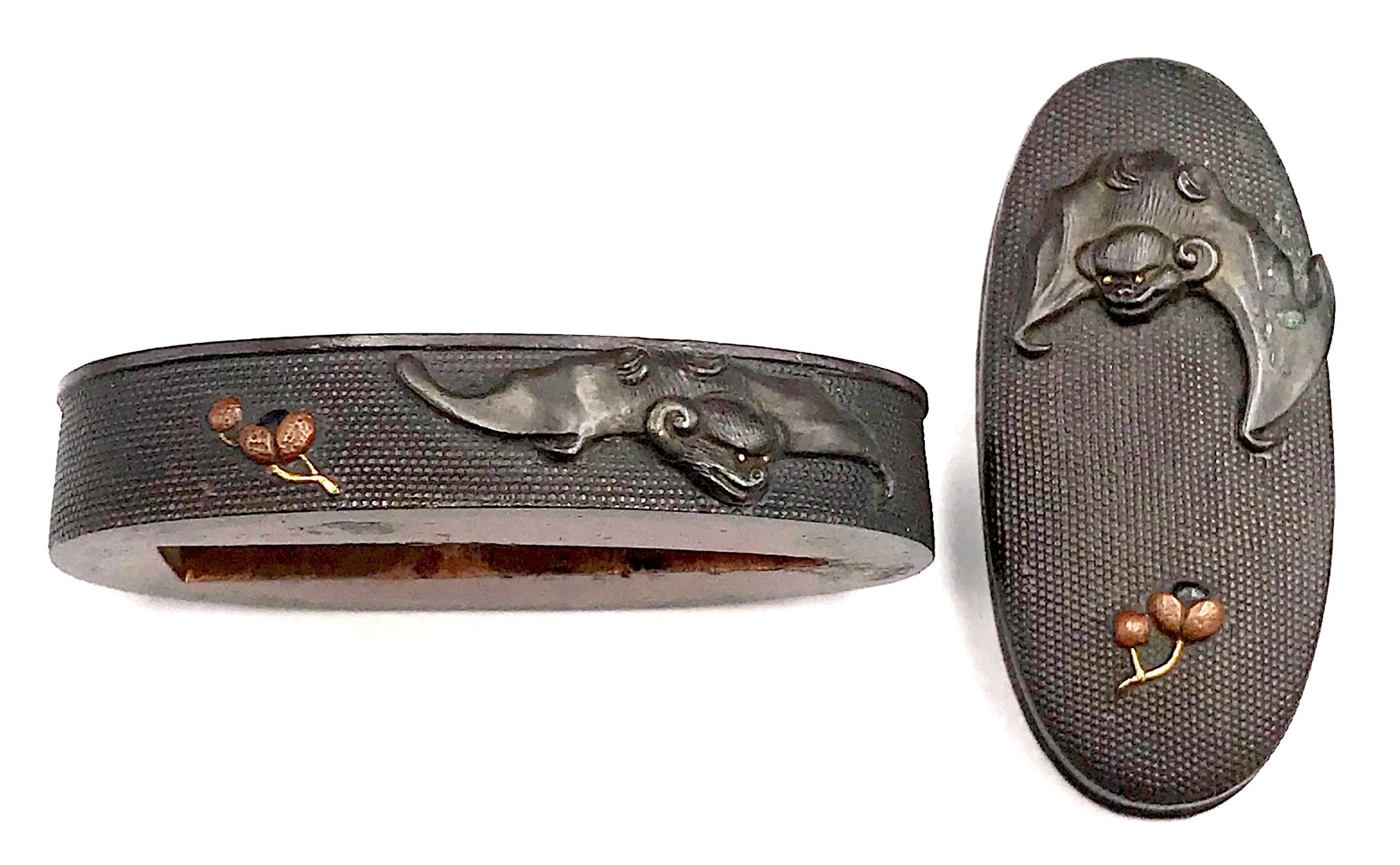

Fuchi-kashira made of shakudō carved and inlaid with gold and red copper with the design of a bat and a fruit (persimmon?). Nanako surface.
Fuchi: 37 x 19 x 7 mm. Kashira: 34 x 16 x 5 mm. Main material: shakudō. Other metals: gold and copper. Surface treatment: nanako-ji. -
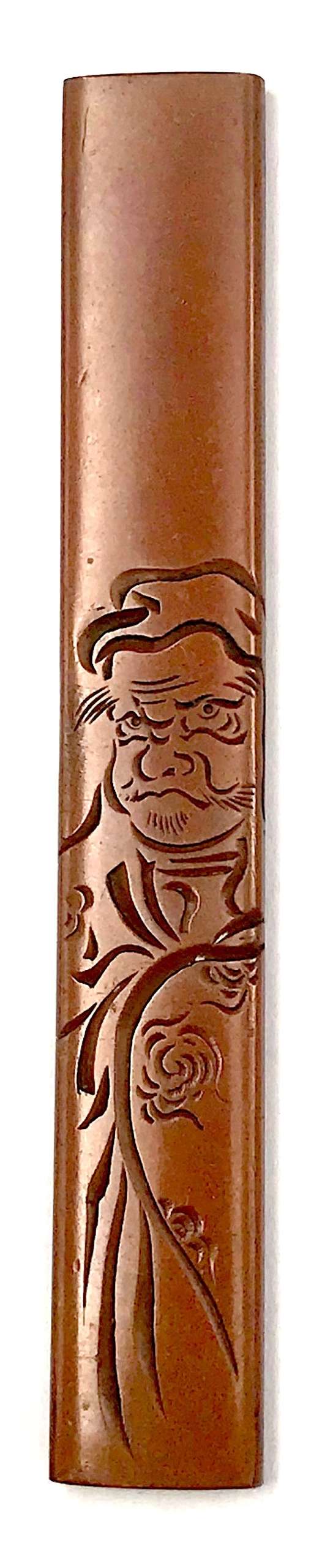 Kozuka made of pure copper with Daruma motif. The engraving technique is known as katakibori ("half-cut carving"). Signed on the back: Yasuchika. Size: 96.5 (H) x 14.5 mm (W). Edo period (Late 18th century). The technique of Katakiribori was developed by Yokoya school of artisans. Detailed account of Yasuchika family of kodōgo carvers is given at Japanese Sword Fittings from the Alexander G. Mosle Collection; Sebastian Izzard LLC, 2004 on page 64. The article ends with the following statement: "Given the popularity of his style and his many students, it is not surprising that a number of works bearing Yasuchika's signature are today disputed." S. Izzard attributes Yasuchika masters to Nara school. Yasuchika-signed kozuka in Important Japanese Swords and Sword Furniture and Works of Art [November 5, 1980, sales "Kotetsu". New York, Christie, Manson & Woods International Inc., 1980, pp.92-93, lot 172 and 173] are stylistically very different to our example. A shibuichi katakiribori kozuka, bearing the signature of Yashuchika, is illustrated at The Hartman Collection of Japanese Metalwork [sold at auction by Christie, Manson & Woods Ltd. June 30 and July 1, London, 1976] on page 82, lot 291. It depicts Daikoku and stylistically similar to ours. The description on page 83 says: "signed Yasuchika, and inscribed "drawn by Hanabusa Itcho" (Yasuchika IV, school of Iawamoto konkan, circa 1800)". A detailed account of Yasuchika signatures is presented at Masterpiece tsuba and kodogu from the Hans Conried and Alexander G. Mosle collections. Important woodblock prints by Utamaro, Hokusai, Hiroshige, Yoshida and other masters. San Francisco, September 1-25, 1983. Catalog #7. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd., pp. 141-174. The example that looks like ours is on page 146:
Kozuka made of pure copper with Daruma motif. The engraving technique is known as katakibori ("half-cut carving"). Signed on the back: Yasuchika. Size: 96.5 (H) x 14.5 mm (W). Edo period (Late 18th century). The technique of Katakiribori was developed by Yokoya school of artisans. Detailed account of Yasuchika family of kodōgo carvers is given at Japanese Sword Fittings from the Alexander G. Mosle Collection; Sebastian Izzard LLC, 2004 on page 64. The article ends with the following statement: "Given the popularity of his style and his many students, it is not surprising that a number of works bearing Yasuchika's signature are today disputed." S. Izzard attributes Yasuchika masters to Nara school. Yasuchika-signed kozuka in Important Japanese Swords and Sword Furniture and Works of Art [November 5, 1980, sales "Kotetsu". New York, Christie, Manson & Woods International Inc., 1980, pp.92-93, lot 172 and 173] are stylistically very different to our example. A shibuichi katakiribori kozuka, bearing the signature of Yashuchika, is illustrated at The Hartman Collection of Japanese Metalwork [sold at auction by Christie, Manson & Woods Ltd. June 30 and July 1, London, 1976] on page 82, lot 291. It depicts Daikoku and stylistically similar to ours. The description on page 83 says: "signed Yasuchika, and inscribed "drawn by Hanabusa Itcho" (Yasuchika IV, school of Iawamoto konkan, circa 1800)". A detailed account of Yasuchika signatures is presented at Masterpiece tsuba and kodogu from the Hans Conried and Alexander G. Mosle collections. Important woodblock prints by Utamaro, Hokusai, Hiroshige, Yoshida and other masters. San Francisco, September 1-25, 1983. Catalog #7. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd., pp. 141-174. The example that looks like ours is on page 146:
 Though we have to admit that the example from Catalog #7 by Robert E. Haynes looks much stronger.
Though we have to admit that the example from Catalog #7 by Robert E. Haynes looks much stronger.
-
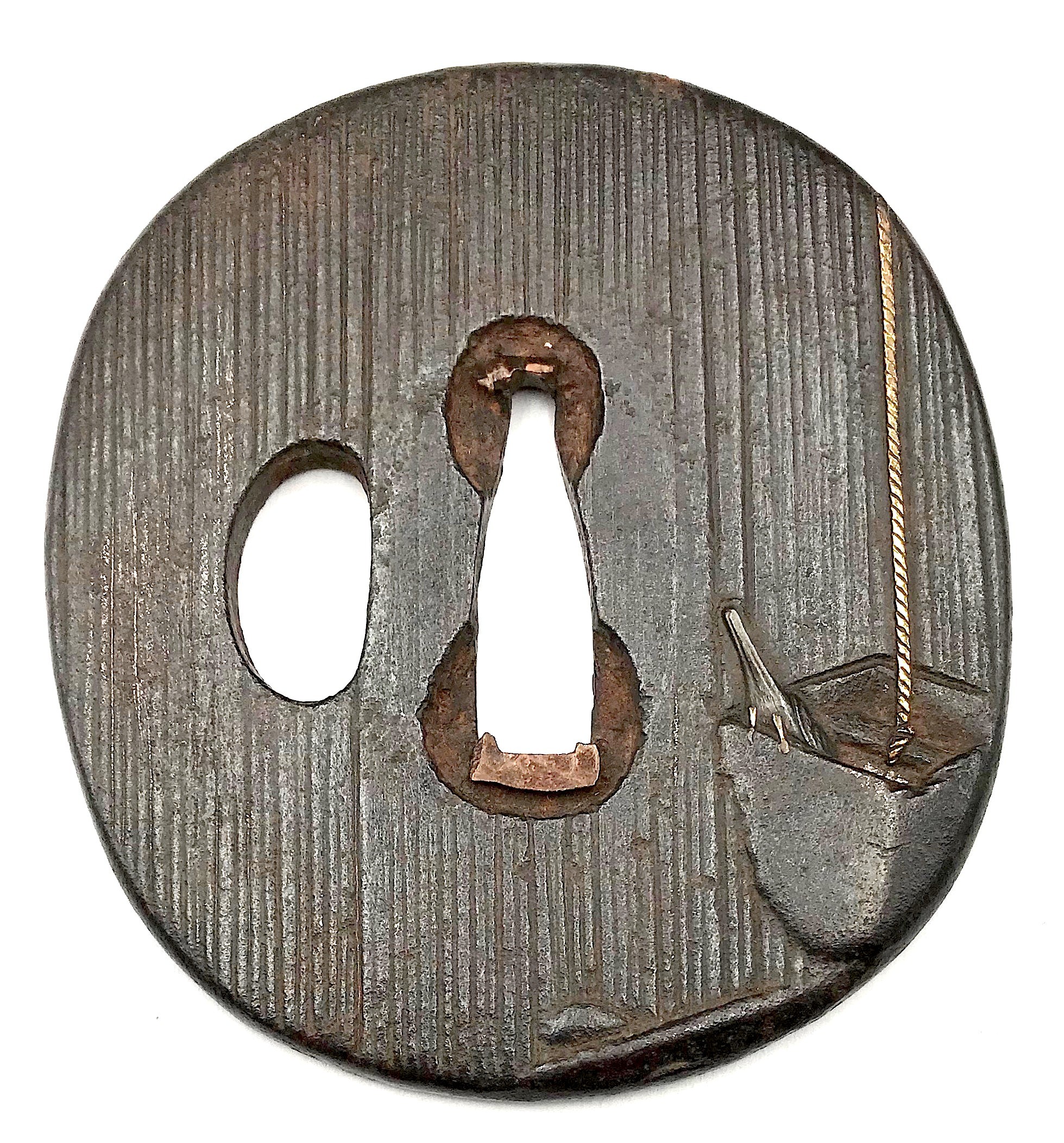

Iron tsuba of elongated round form with brown (chocolate) patina. The surface is carved with file strokes (sujikai-yasurime) to imitate heavy rain. The design of a bird drinking water from a bucket hanging on a rope is carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori); the rope is inlaid in gold. The well structure on the reverse, carved in low relief. Nakago-ana is enlarged and plugged with copper sekigane. Unsigned.
Edo period.Size: Height: 75.1 mm; Width: 68.3 mm; Thickness: 4.6 mm; Weight: 134 g.
Unsigned.
SOLD -
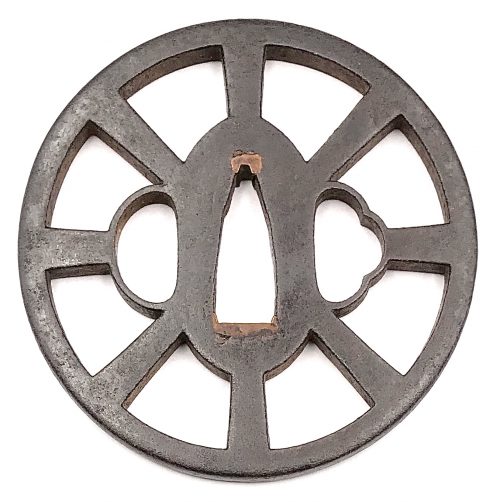 Iron tsuba of round form with design of wheel (kuruma) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Yagyu school. Signed of the face: Fukui Tsuguzaemon. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun/Enppo era). Height: 76.7 mm. Width: 76.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.2 mm. Center thickness: 5.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 203: "This design of spoke wheel relates to the 'circular principle' found in the Yagyu philosophy. Although it is very faint, Fukui Tsuguzaemon's signature is visible. Without a signature and based on appearance alone, it would undoubtable attributed to a later period".
Iron tsuba of round form with design of wheel (kuruma) in openwork (sukashi). Squared rim. Copper sekigane. Yagyu school. Signed of the face: Fukui Tsuguzaemon. Early Edo period: Late 17th century (Kanbun/Enppo era). Height: 76.7 mm. Width: 76.8 mm. Rim thickness: 5.2 mm. Center thickness: 5.6 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 203: "This design of spoke wheel relates to the 'circular principle' found in the Yagyu philosophy. Although it is very faint, Fukui Tsuguzaemon's signature is visible. Without a signature and based on appearance alone, it would undoubtable attributed to a later period".Merrily Baird in her book "Symbols of Japan" [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001] provides the following explanation of the Wheel-of-the-Law symbol: "The Wheel-of-the-Law or Golden Wheel (rimbo, kinrin) has its origins in India, where it is known as chakra. [...] In Buddhist practice, it has been represented with eight spokes, reflecting the eight-fold path to overcoming worldly desire, and it signifies that all illusions will be crushed by the faith's enlightenment. [...] The Wheel-of-the-Law is an attribute of such deities as Senju Kannon, the Thousand-Armed Kannon, and Dainichi Nyorai, the all-illuminating solar figure who is the principal deity for Shingon Buddhism. From the Edo period on, the wheel also has been used in a secular manner", e.g. on family crests.
-
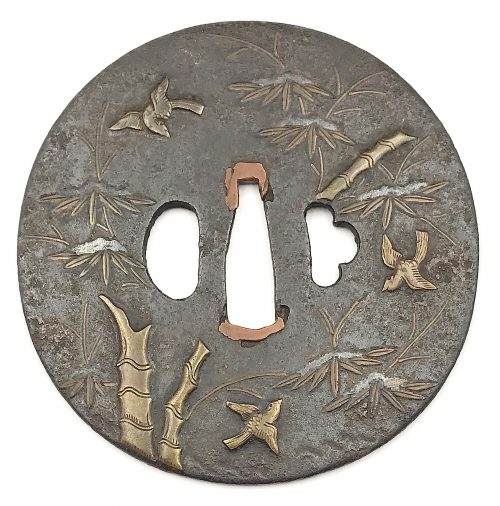 Iron tsuba decorated with sparrows and bamboo inlaid and chiseled in yellow brass, with snow lying on bamboo leaves inlaid in silver-ish shibuichi. Copper sekigane. The kogai-hitsu-ana probably cut out at a later date. Heianjō school. Unsigned. Height: 86.0 mm, Width: 85.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.9 mm. Momoyama or early Edo period, first half of the 17th century. Merrily Baird, Symbols..., page 118: "The association of the sparrow (suzume) with both bamboo and rice heads is an old one found in Japanese poetry, paining, and design."
Iron tsuba decorated with sparrows and bamboo inlaid and chiseled in yellow brass, with snow lying on bamboo leaves inlaid in silver-ish shibuichi. Copper sekigane. The kogai-hitsu-ana probably cut out at a later date. Heianjō school. Unsigned. Height: 86.0 mm, Width: 85.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.9 mm. Momoyama or early Edo period, first half of the 17th century. Merrily Baird, Symbols..., page 118: "The association of the sparrow (suzume) with both bamboo and rice heads is an old one found in Japanese poetry, paining, and design." -
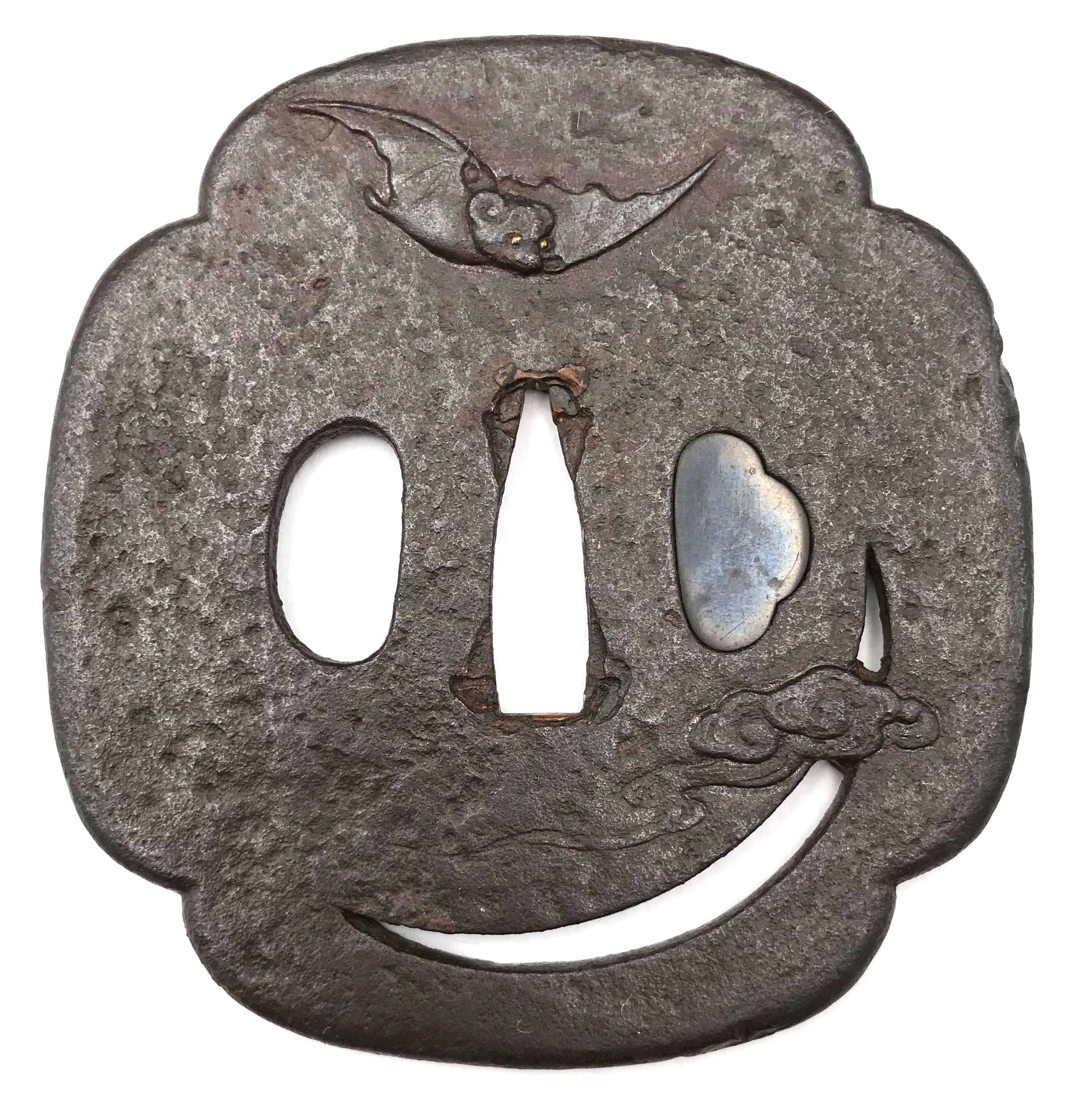

Iron tsuba of mokko form with rough surface decorated in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori) and openwork (sukashi) with a flying bat, a crescent moon, and a cloud over the moon. Bat's eyes inlaid with gold. Crescent moon and cloud on the reverse. Copper sekigane. Kogai hitsu-ana plugged with shakudō.
Unsigned.
Edo period.Size: Height: 83.7 mm; Width: 80.3 mm; Thickness: 2.9 mm; Weight: 141 g.
-
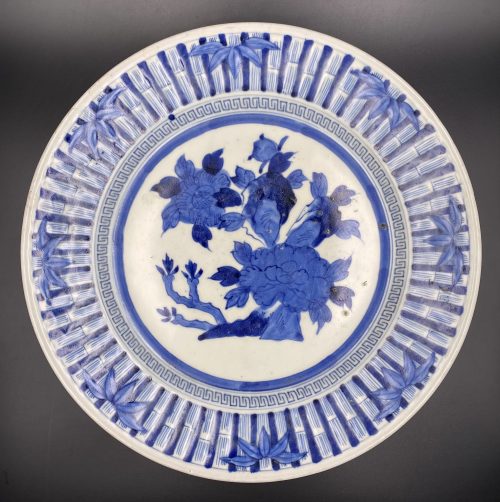 Underglaze cobalt blue and white porcelain plate decorated with a bamboo border, key fret above the blue ring, and a bush of chrysanthemums in the centre. The bottom is decorated with stylized clouds and flowers, a border of lotus petals and signed with a general mark in the centre. Diameter: 29.5 cm; Height: 3.5 cm.
Underglaze cobalt blue and white porcelain plate decorated with a bamboo border, key fret above the blue ring, and a bush of chrysanthemums in the centre. The bottom is decorated with stylized clouds and flowers, a border of lotus petals and signed with a general mark in the centre. Diameter: 29.5 cm; Height: 3.5 cm. -
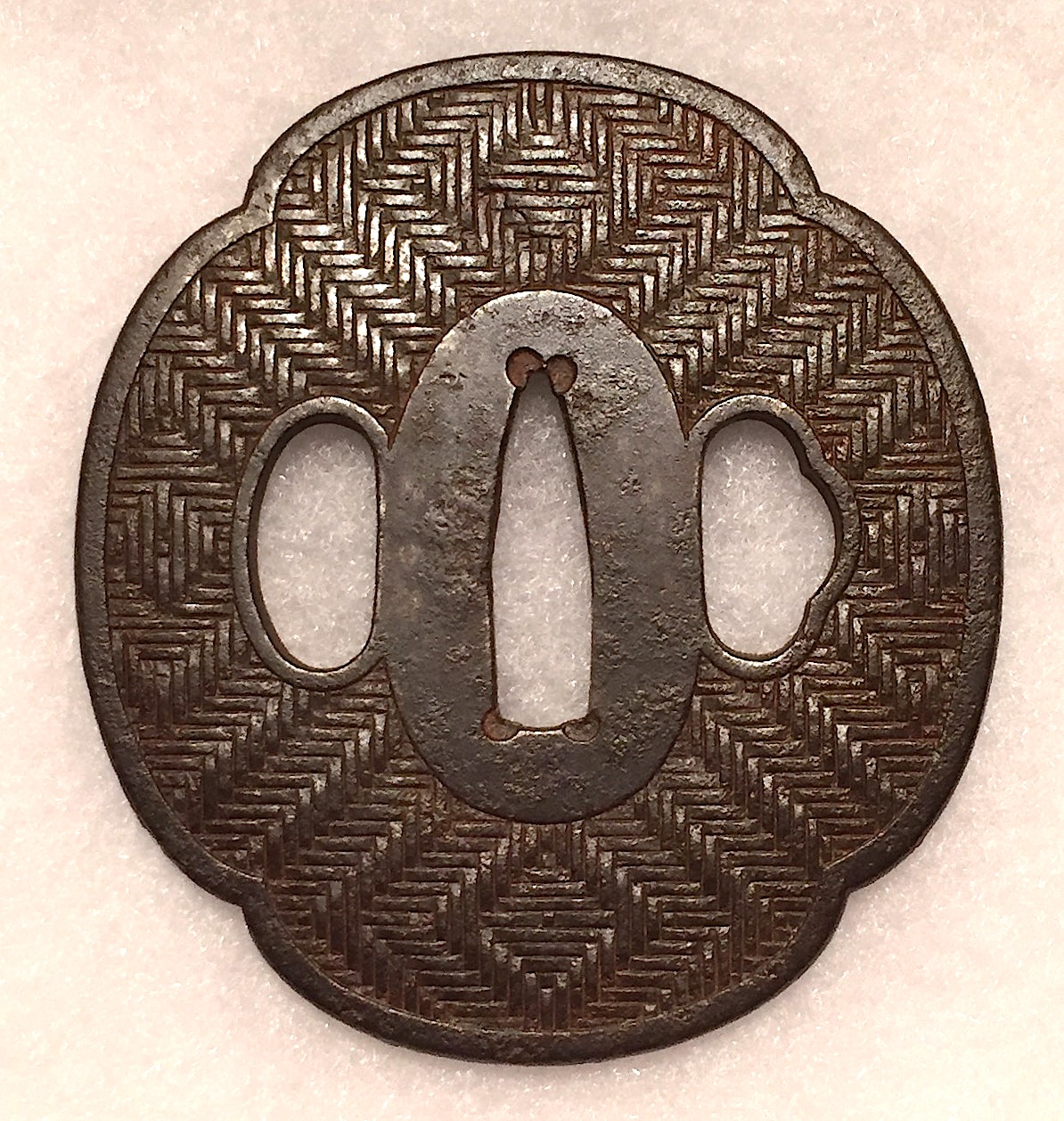 Iron tsuba with brown patina in mokkō-gata form with woven design. Size: 72 x 67 x 5 mm.
Iron tsuba with brown patina in mokkō-gata form with woven design. Size: 72 x 67 x 5 mm. -
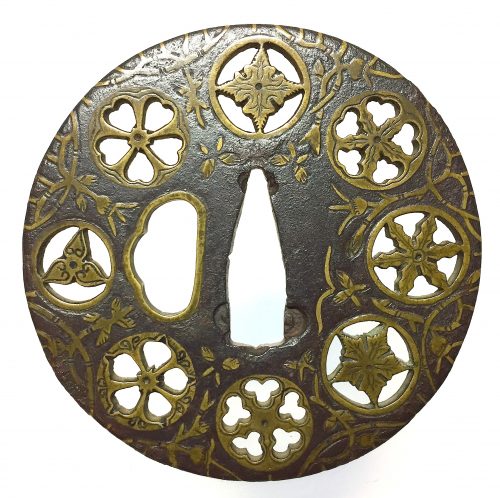 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm -
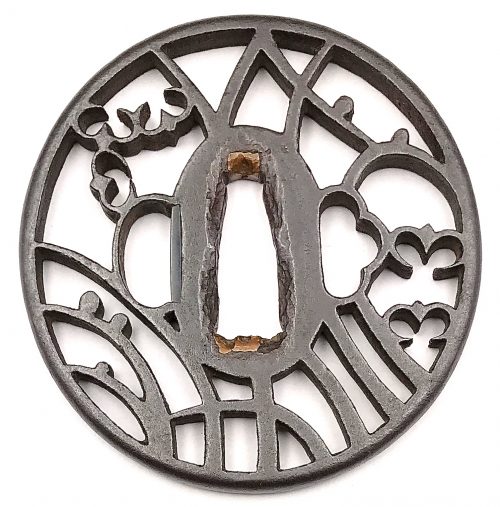 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form with design of wild geese and drops on pampas grass (masashino) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane. Owari school. Early Edo period: early 17th century (Kan-ei era). Height: 78.8 mm. Width: 76.3 mm. Rim thickness: 6.1 mm. Center thickness: 6.4 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 169. A description of musashino symbolism can be found at Symbols of Japan by Merrily Baird [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001]: Musashino - "the plain of Musashi - a large expanse in the Tokyo area, was celebrated in poetry for the grasses that grew there before the recent era of industrialization... The use of Musashino themes was particularly common in the Momoyama and Edo periods". Pampas grass with dew drops and wild geese in flight collectively provide strong autumnal connotation.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form with design of wild geese and drops on pampas grass (masashino) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane. Owari school. Early Edo period: early 17th century (Kan-ei era). Height: 78.8 mm. Width: 76.3 mm. Rim thickness: 6.1 mm. Center thickness: 6.4 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 169. A description of musashino symbolism can be found at Symbols of Japan by Merrily Baird [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001]: Musashino - "the plain of Musashi - a large expanse in the Tokyo area, was celebrated in poetry for the grasses that grew there before the recent era of industrialization... The use of Musashino themes was particularly common in the Momoyama and Edo periods". Pampas grass with dew drops and wild geese in flight collectively provide strong autumnal connotation. -
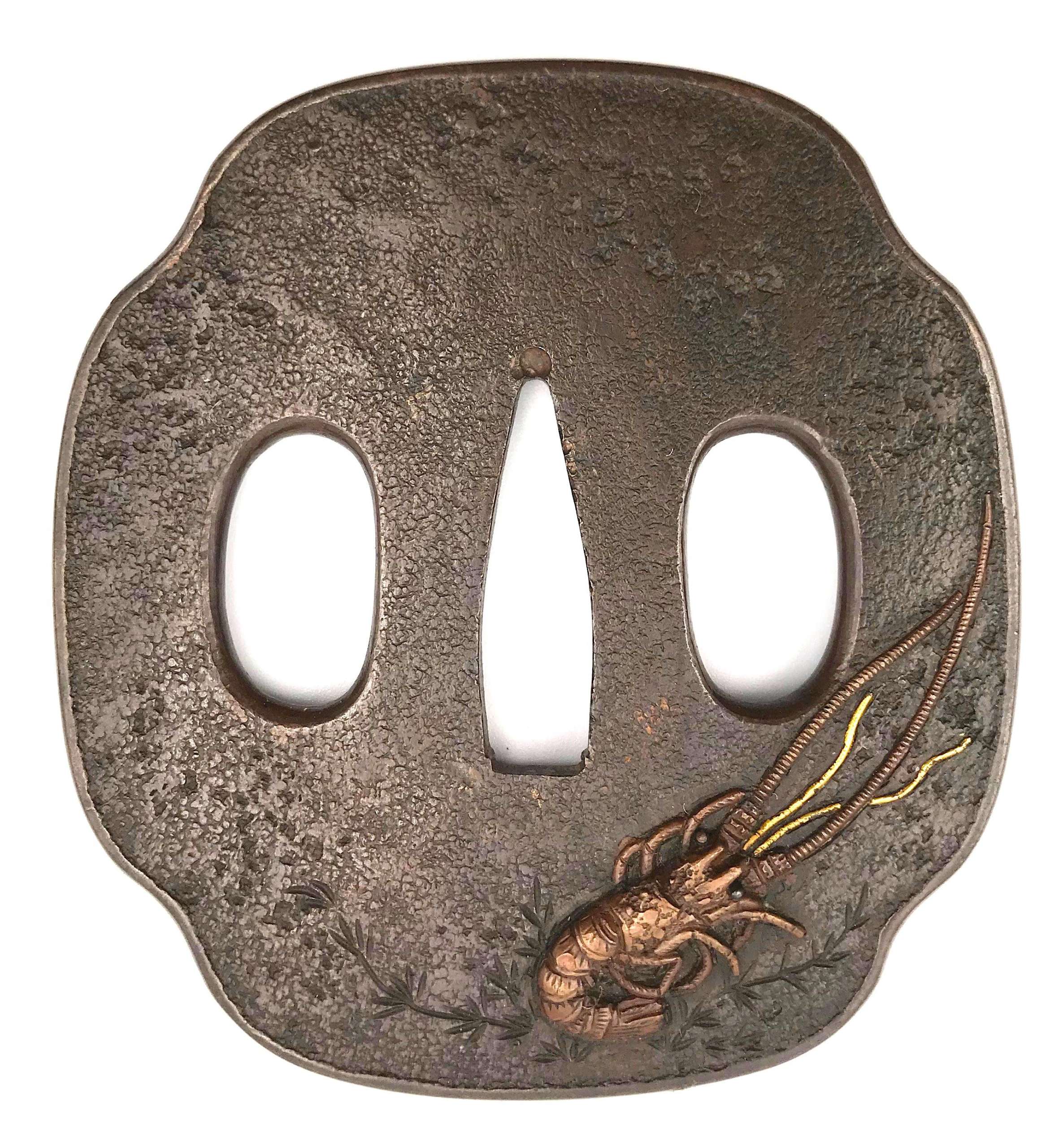

Bronze tsuba of mokkō form with narrow slightly raised rim carved in kebori with the sea weed and inlaid with a lobster (ebi) made of copper on the face and two sea shells made of shakudo on the back. Lobster's antennae inlaid in gold, and eyes inlaid in shakudo. Ishime-ji treated surface.
Unsigned.
Late Edo period (mid-19th century). Dimensions: 76.3 x 71.1 x 3.7 mm -
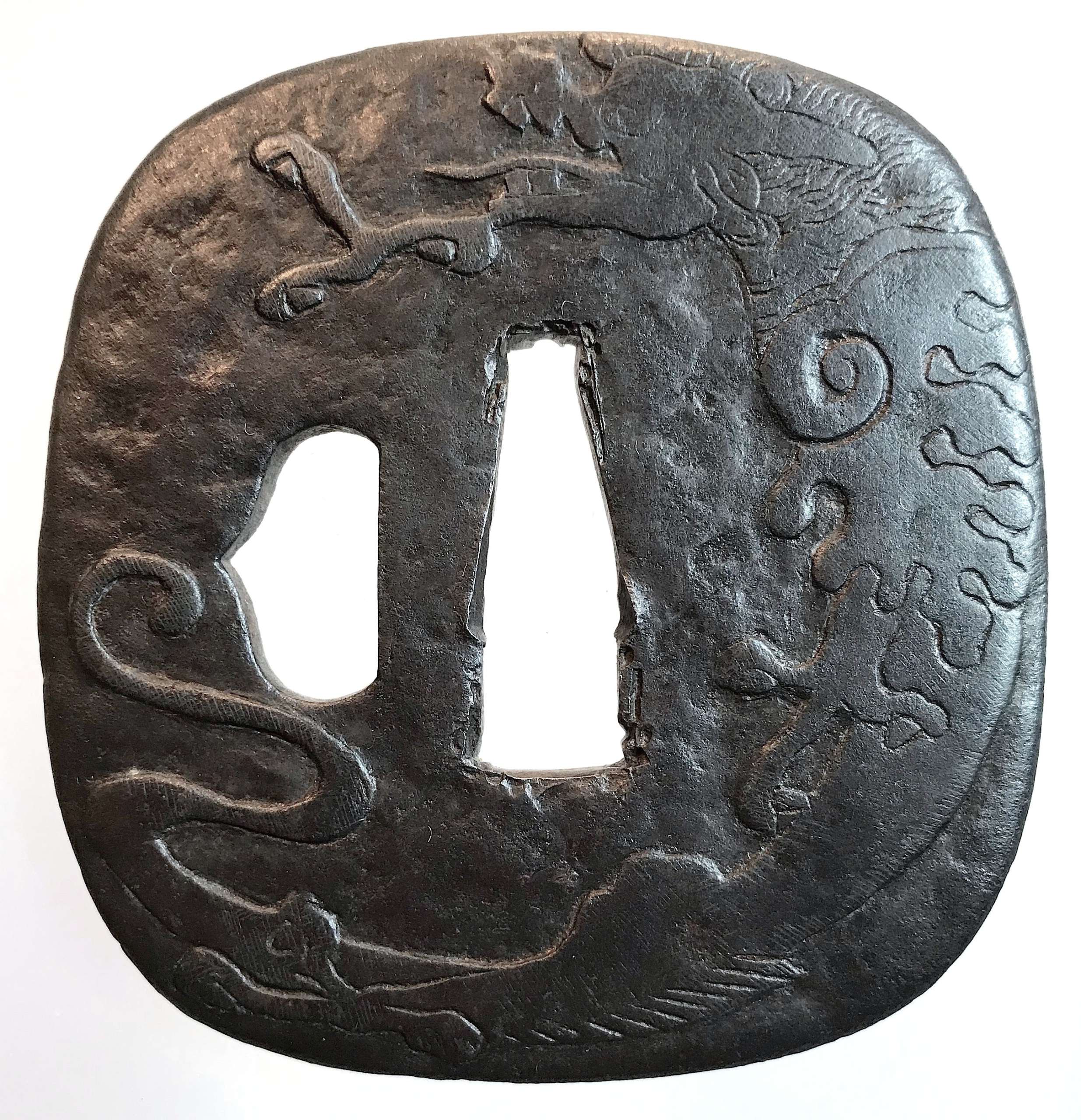 Shimizu-Jingo tsuba with a dragon and vajra (on reverse) motif. Unsigned. Possibly, 3rd or 4th master of Shimizu-Jingo family in Higo province. Iron. Low relief carving. Edo period, 1700's. Height: 75.4 mm, Width: 72.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm
Shimizu-Jingo tsuba with a dragon and vajra (on reverse) motif. Unsigned. Possibly, 3rd or 4th master of Shimizu-Jingo family in Higo province. Iron. Low relief carving. Edo period, 1700's. Height: 75.4 mm, Width: 72.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm -
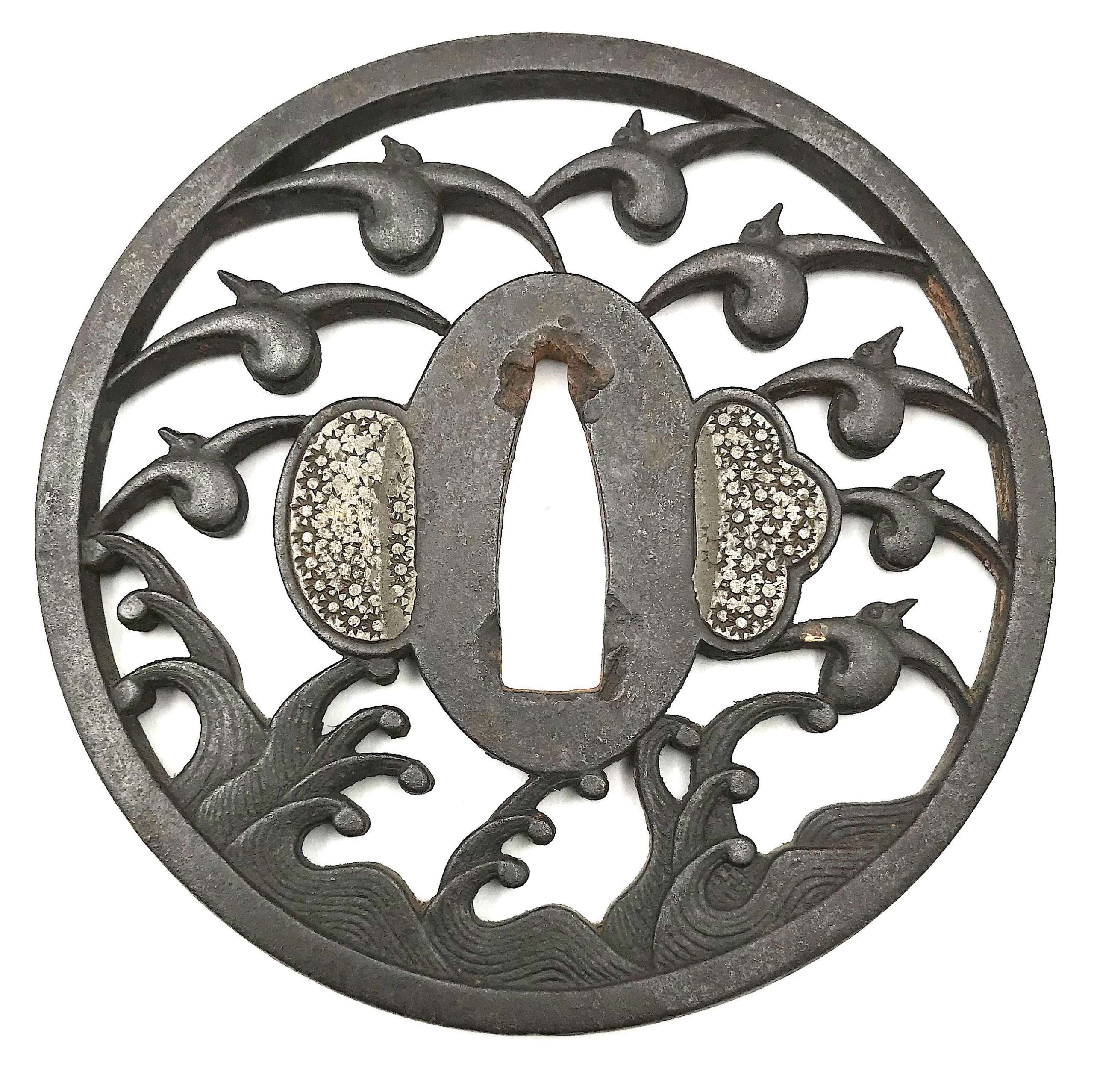

Iron tsuba of circular form with the knotted geese (kari) flying over the rough waves pierced (sukashi) and carved in low relief (nikubori). Hitsu-ana plugged with soft metal. Hitsu-ana plugged with soft metal (tin or lead).
Signed: Echizen koku jū Myochin Katsuharu saku.
Edo period.Size: Height: 80.7 mm; Width: 81.0 mm; Thickness: 4.5 mm; Weight: 110 g.
Two tsuba of this master can be found at Georg Oeder Collection (Japanische Stichblätter und Schwertzieraten. Sammlung Georg Oeder Düsseldorf. Beschreibendes Verzeichnis von P. Vautier. Herausgegeben von Otto Kümmel.Oesterheld & Co / Verlag / Berlin, Oesterheld, 1915; LIB-1465 in this collection) under №№ 172 and 173, page 21, though no illustrations. SOLD. -
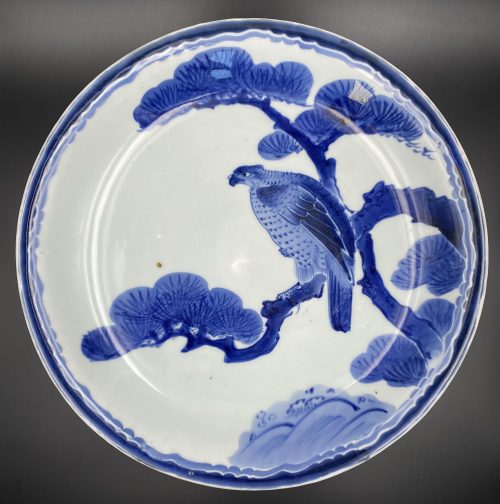 Underglaze cobalt blue and white porcelain plate decorated with a falcon on a pine tree and rough waves beneath; rim with a stylized wave design; seven spur marks on the reverse. Diameter: 31 cm; Height: 5 cm; Diameter of the foot: 18 cm.
Underglaze cobalt blue and white porcelain plate decorated with a falcon on a pine tree and rough waves beneath; rim with a stylized wave design; seven spur marks on the reverse. Diameter: 31 cm; Height: 5 cm; Diameter of the foot: 18 cm. -
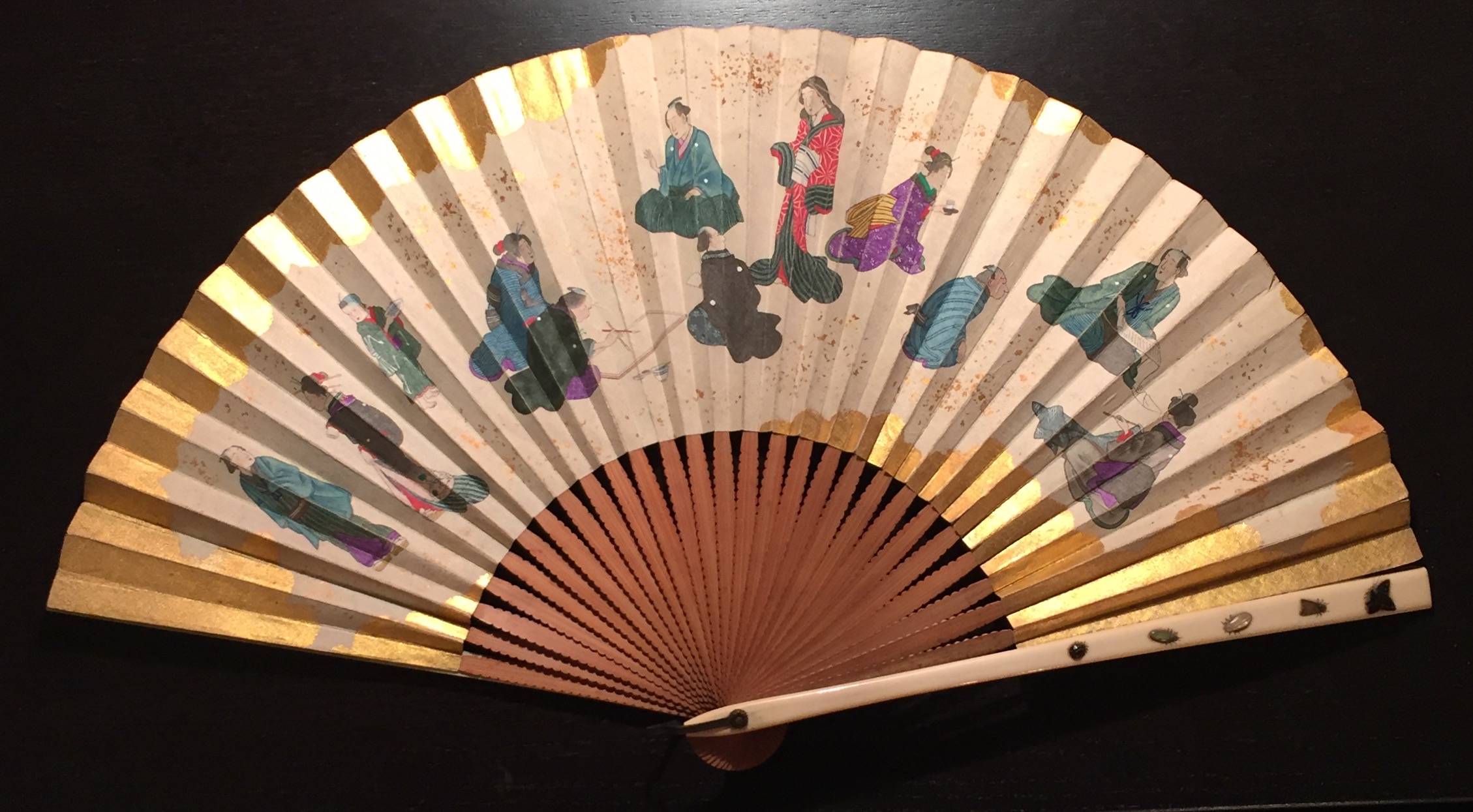 Late 19th-century (1850-1870) Japanese export fan. This fan has a double leaf painted with a different design on either side. Ivory encrusted with gemstones and other materials. Subject matter such as women wearing kimono is also more typical of export than domestic products (V&A). Autumn theme on the reverse.
Late 19th-century (1850-1870) Japanese export fan. This fan has a double leaf painted with a different design on either side. Ivory encrusted with gemstones and other materials. Subject matter such as women wearing kimono is also more typical of export than domestic products (V&A). Autumn theme on the reverse.


