Size: 77.7 x 76.1 x 6.7 mm.
For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba" by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91.-
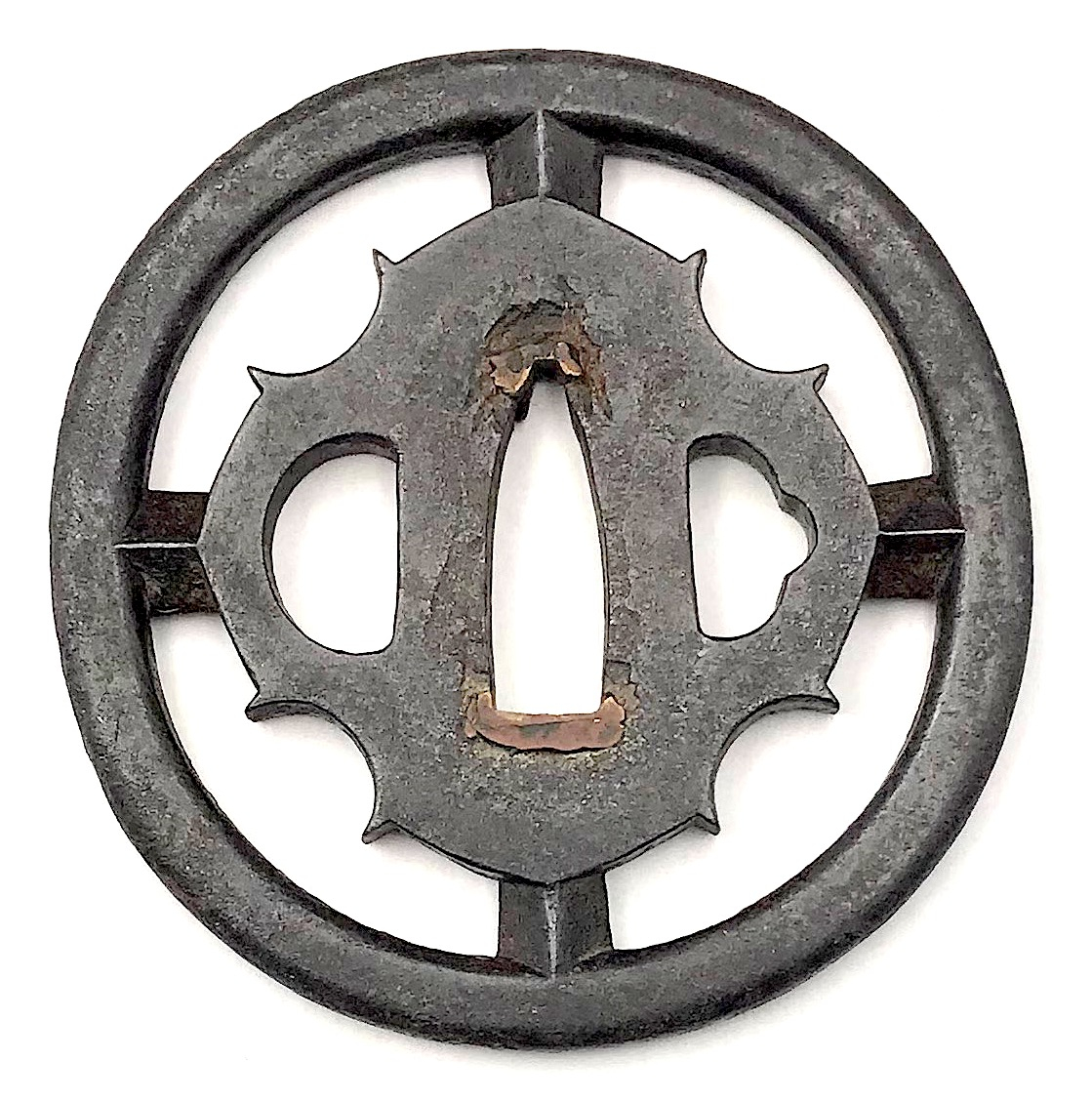 Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Edo period.
Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Edo period. -
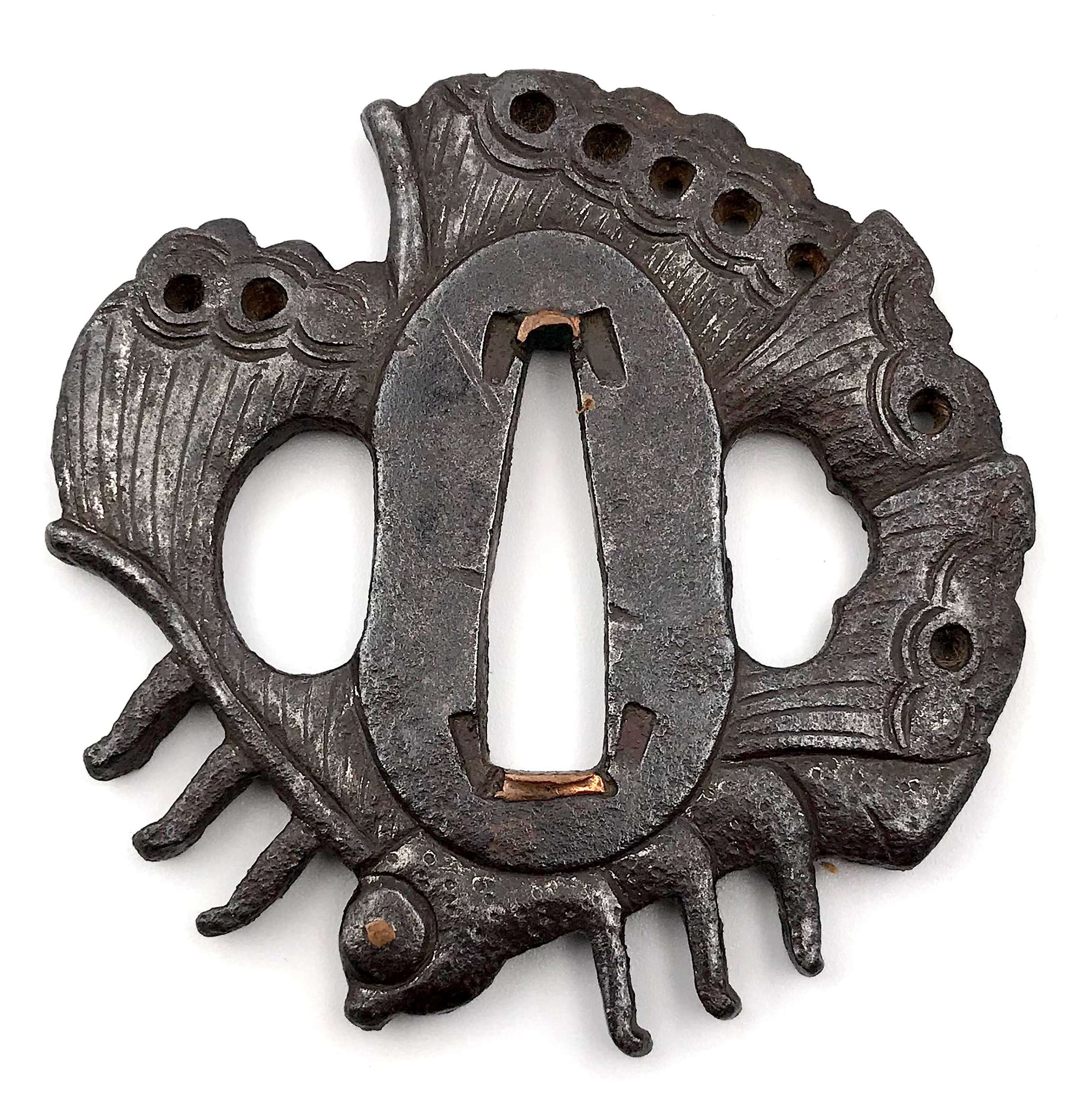
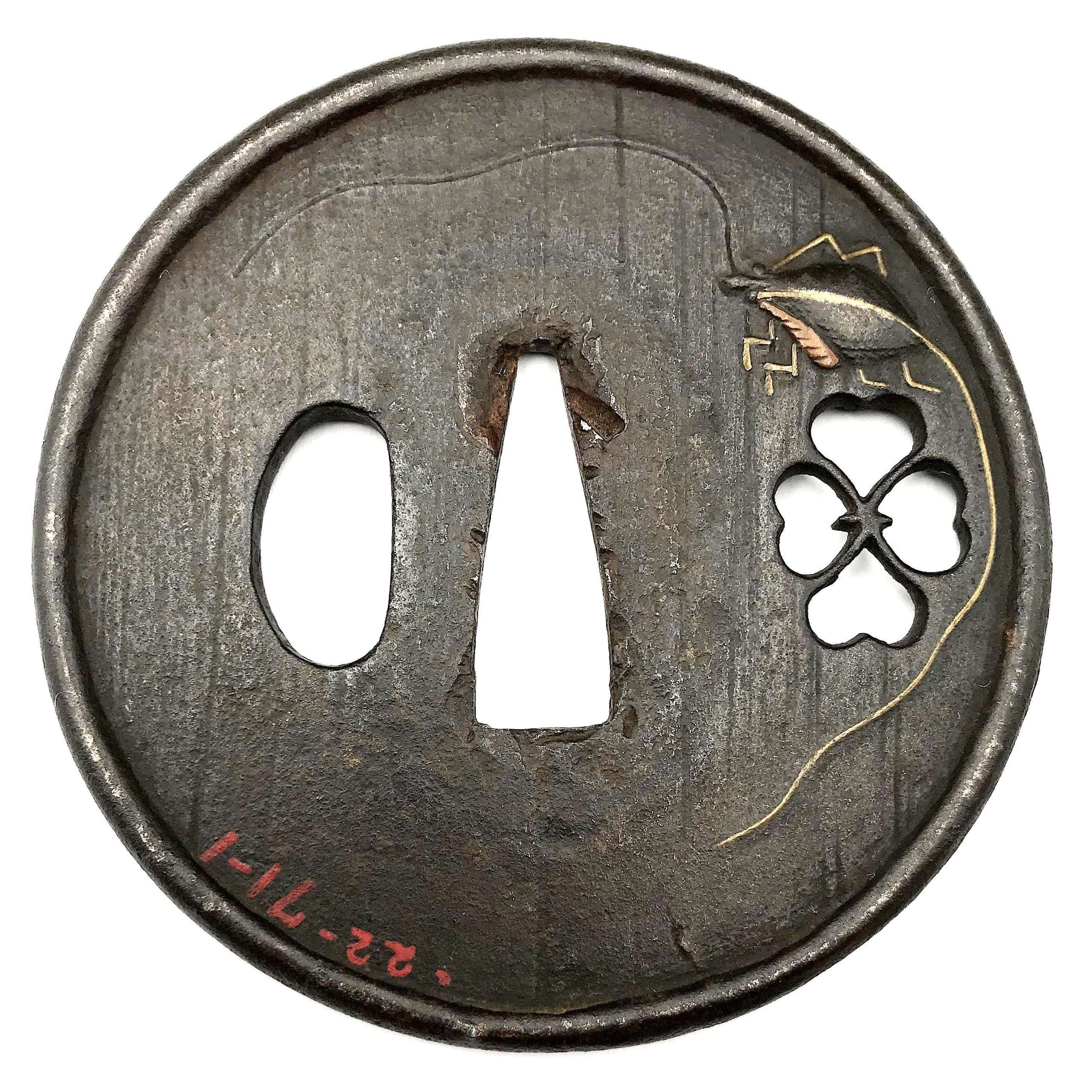 Iron tsuba of round form with a Marsilea (water clover, paddy plant, denjiso) in openwork (sukashi) and a cricket carved in low relief (katakiribori) with extremities and one antenna inlaid with brass; the other antenna is carved in kebori (which antenna is inlaid and which is carved alternates on the face and on the reverse). The plate decorated with vertical file stroke ornamentation (tate-yasurime). Raised dam-shaped rim (dote-mimi). Inscription from a previous collector in red oil paint: 22-71-1. Edo period, possibly 17th century. Katchushi school.
Iron tsuba of round form with a Marsilea (water clover, paddy plant, denjiso) in openwork (sukashi) and a cricket carved in low relief (katakiribori) with extremities and one antenna inlaid with brass; the other antenna is carved in kebori (which antenna is inlaid and which is carved alternates on the face and on the reverse). The plate decorated with vertical file stroke ornamentation (tate-yasurime). Raised dam-shaped rim (dote-mimi). Inscription from a previous collector in red oil paint: 22-71-1. Edo period, possibly 17th century. Katchushi school.Size: 75.0 x 74.4 x 3.6 (center), 5.0 (rim) mm.
The plant Marsilea (paddy plant, denjiso), common names include water clover and four-leaf clover because the long-stalked leaves have four clover-like lobes and are either held above water or submerged. In The elements of Japanese design by John W. Dower, this motif is listed under the numbers 634-35 Paddy Plant (denjiso). Obviously, as a four-leaf clover it is an auspicious symbol. The four leaves radiate out as the shape of the kanji 田 (romaji 'ta'), which means 'rice paddy'. This symbol may be used as a family crest (mon), and this would be the most probable explanation of the sukashi on this tsuba. -
 Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Edo period.
Iron tsuba of round form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Edo period.Size: 83.4 x 83.1 x 4.4 mm
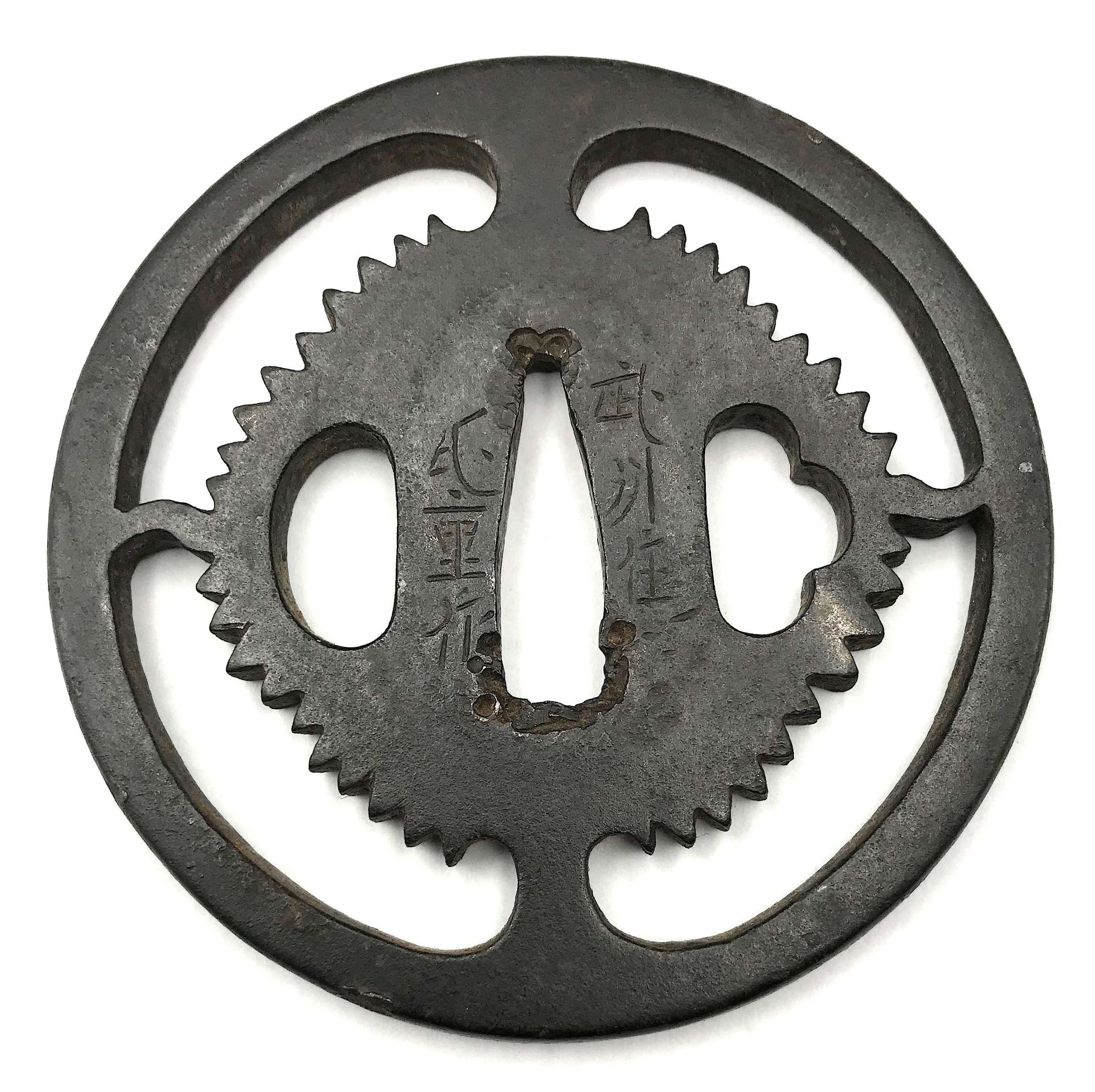
Signed Bushū-jū Ujishige saku (武州住氏重作) [Markus Sesko]. Ujishige (died 1677), 3rd generation of the Katsuki-Gondayu line; 1st gen. Ujiie came from Kyoto to Kaga to work for the Maeda family. There was another Ujishige, 4th generation Kaneko (?), who died in 1867 [M. Sesko, Genealogies...], but this tsuba looks a bit earlier than that. This particular Ujishige states in his signature that he is from Bushū, or Musashi Province, modern Tokyo Metropolis. He might have moved from Bushū to Kaga, of course. There is no artist with the name Ujishige in Bushū-Ito School anyway.
For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91. -
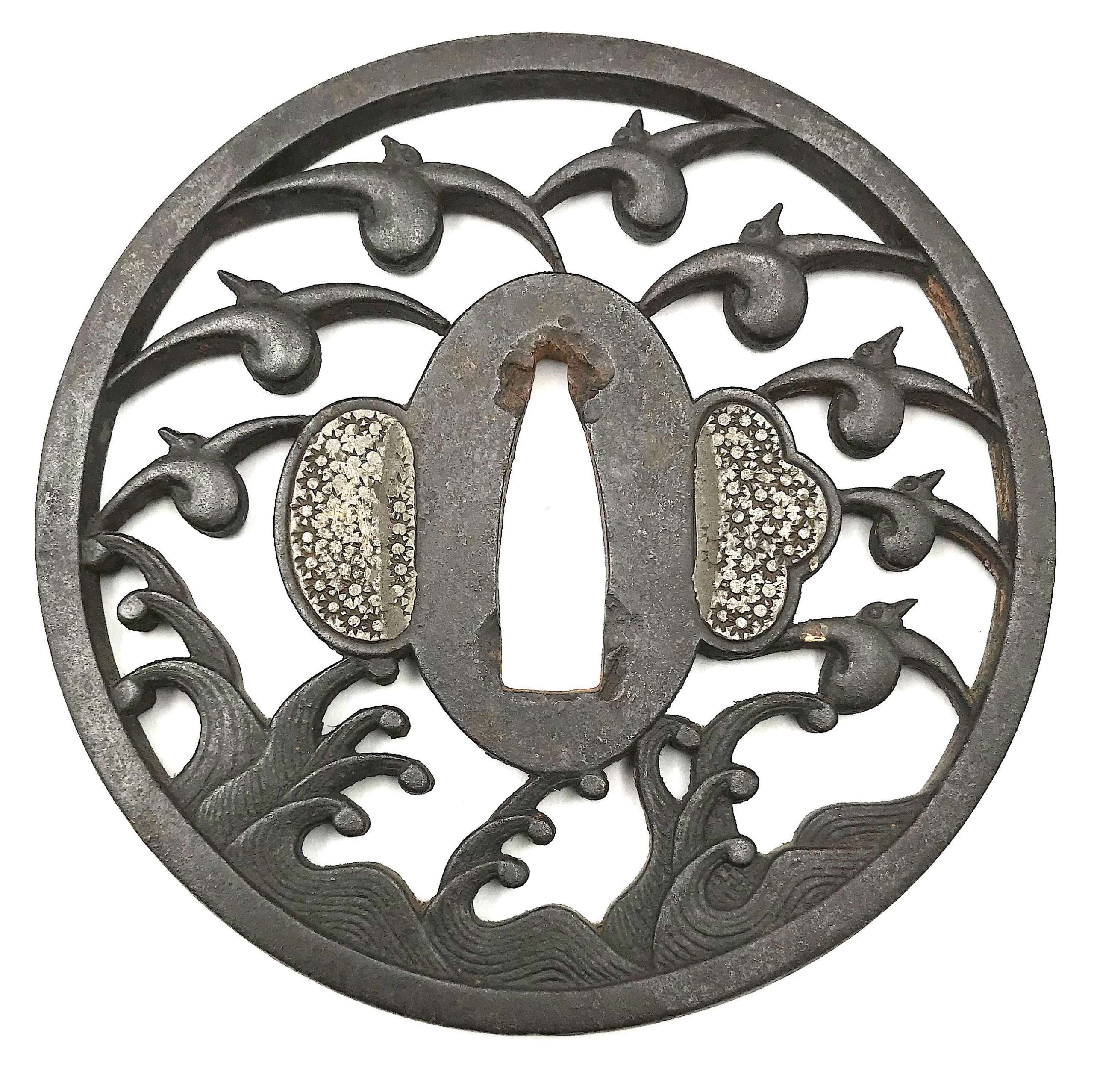

Iron tsuba of circular form with the knotted geese (kari) flying over the rough waves pierced (sukashi) and carved in low relief (nikubori). Hitsu-ana plugged with soft metal. Hitsu-ana plugged with soft metal (tin or lead).
Signed: Echizen koku jū Myochin Katsuharu saku.
Edo period.Size: Height: 80.7 mm; Width: 81.0 mm; Thickness: 4.5 mm; Weight: 110 g.
Two tsuba of this master can be found at Georg Oeder Collection (Japanische Stichblätter und Schwertzieraten. Sammlung Georg Oeder Düsseldorf. Beschreibendes Verzeichnis von P. Vautier. Herausgegeben von Otto Kümmel.Oesterheld & Co / Verlag / Berlin, Oesterheld, 1915; LIB-1465 in this collection) under №№ 172 and 173, page 21, though no illustrations. SOLD. -
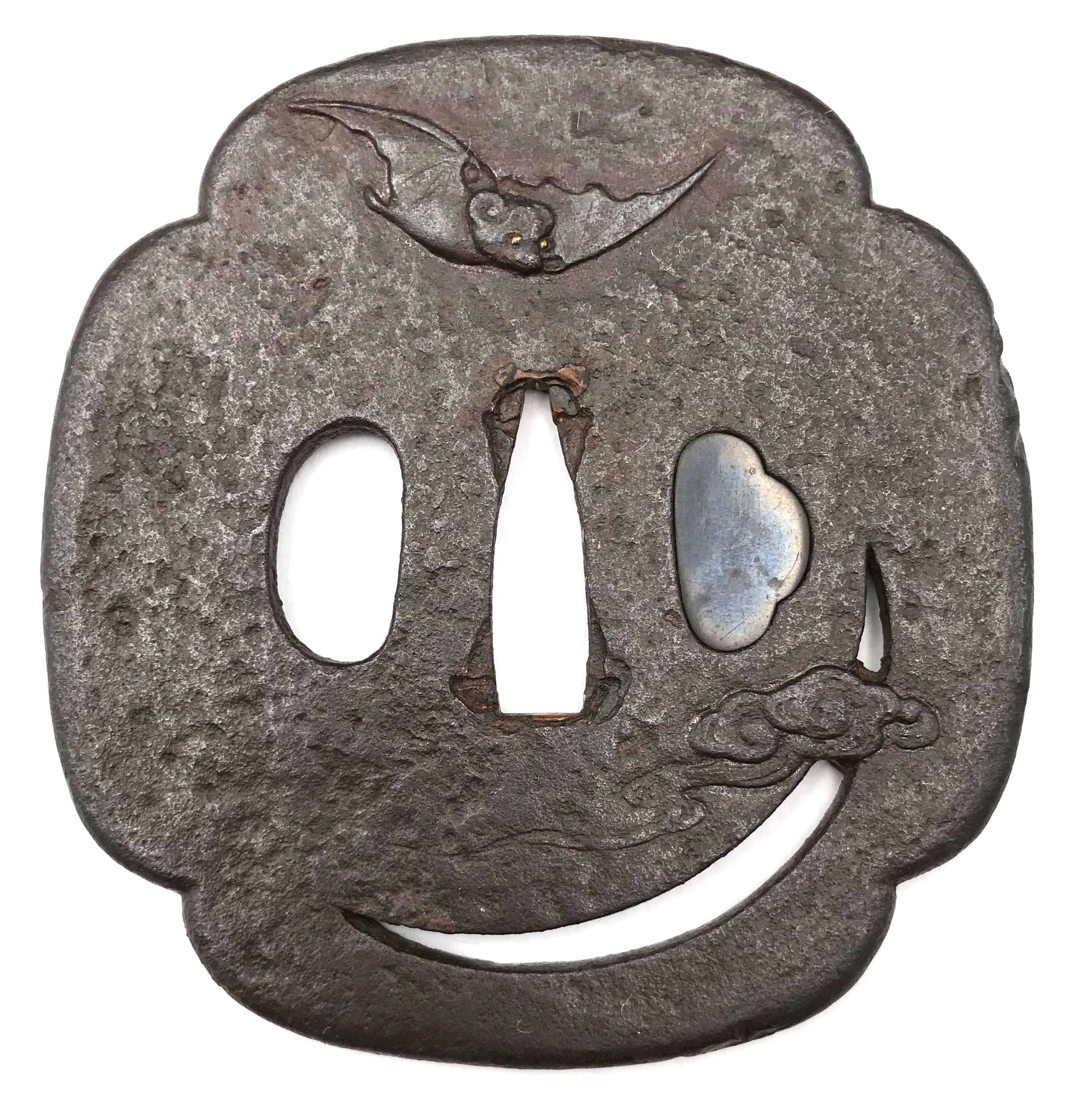

Iron tsuba of mokko form with rough surface decorated in low relief carving (sukidashi-bori) and openwork (sukashi) with a flying bat, a crescent moon, and a cloud over the moon. Bat's eyes inlaid with gold. Crescent moon and cloud on the reverse. Copper sekigane. Kogai hitsu-ana plugged with shakudō.
Unsigned.
Edo period.Size: Height: 83.7 mm; Width: 80.3 mm; Thickness: 2.9 mm; Weight: 141 g.
-
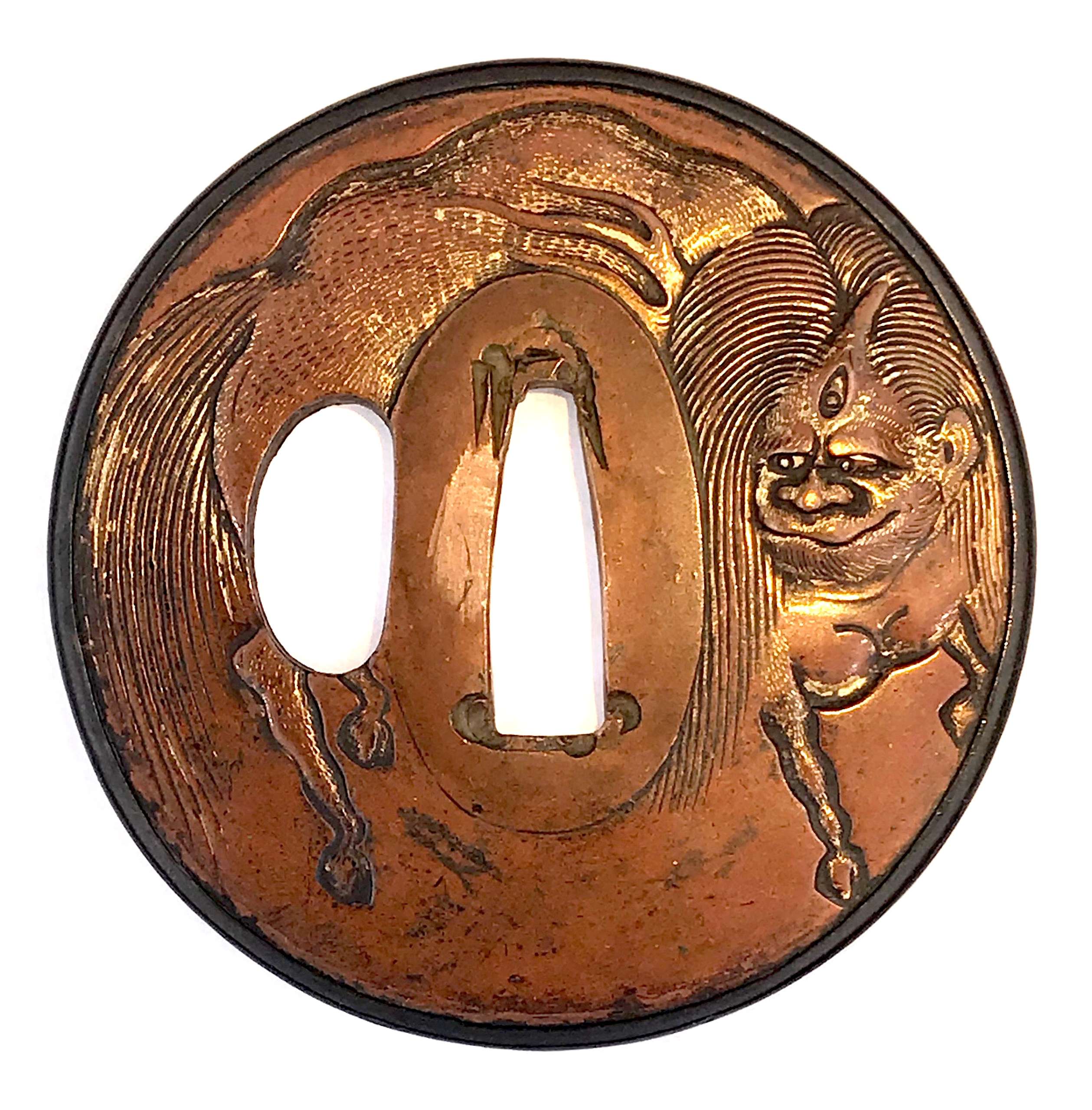

Copper tsuba of slightly elongated round form carved in low relief (usuniku-bori, katakiri bori) with the design of a mythical creature: a horse, however, with divided hoofs, with anthropomorphic (human-like) face though with a vertically positioned third eye on the forehead, and a corn. Certain elements of the image accentuated with gold iroe. On the back: flowers and grasses carved in katakiribori technique. Shakudō fukurin.
Edo period.
Dimensions: 70.7 x 70.2 x 3.7 mm In a custom wooden box. -
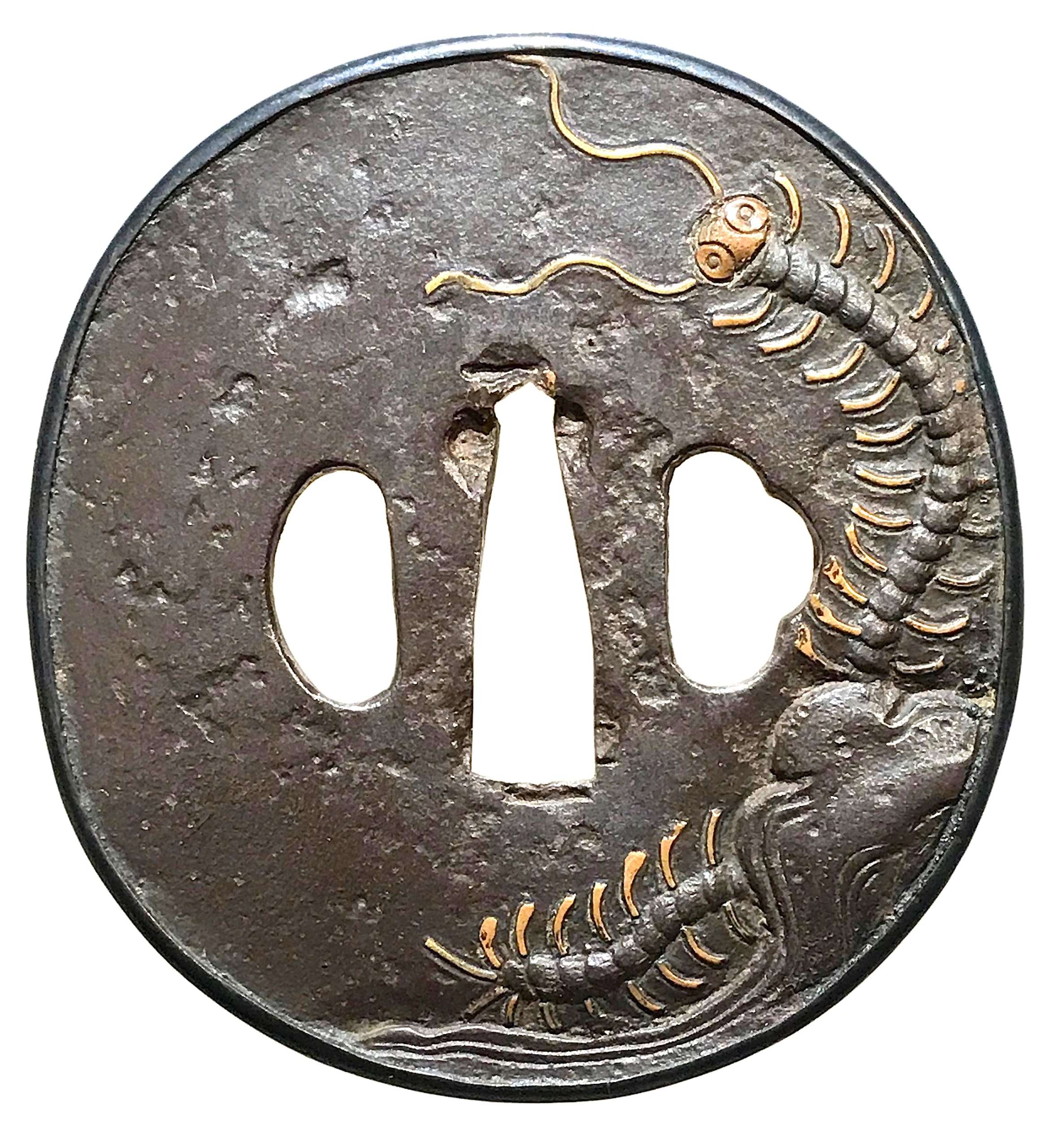
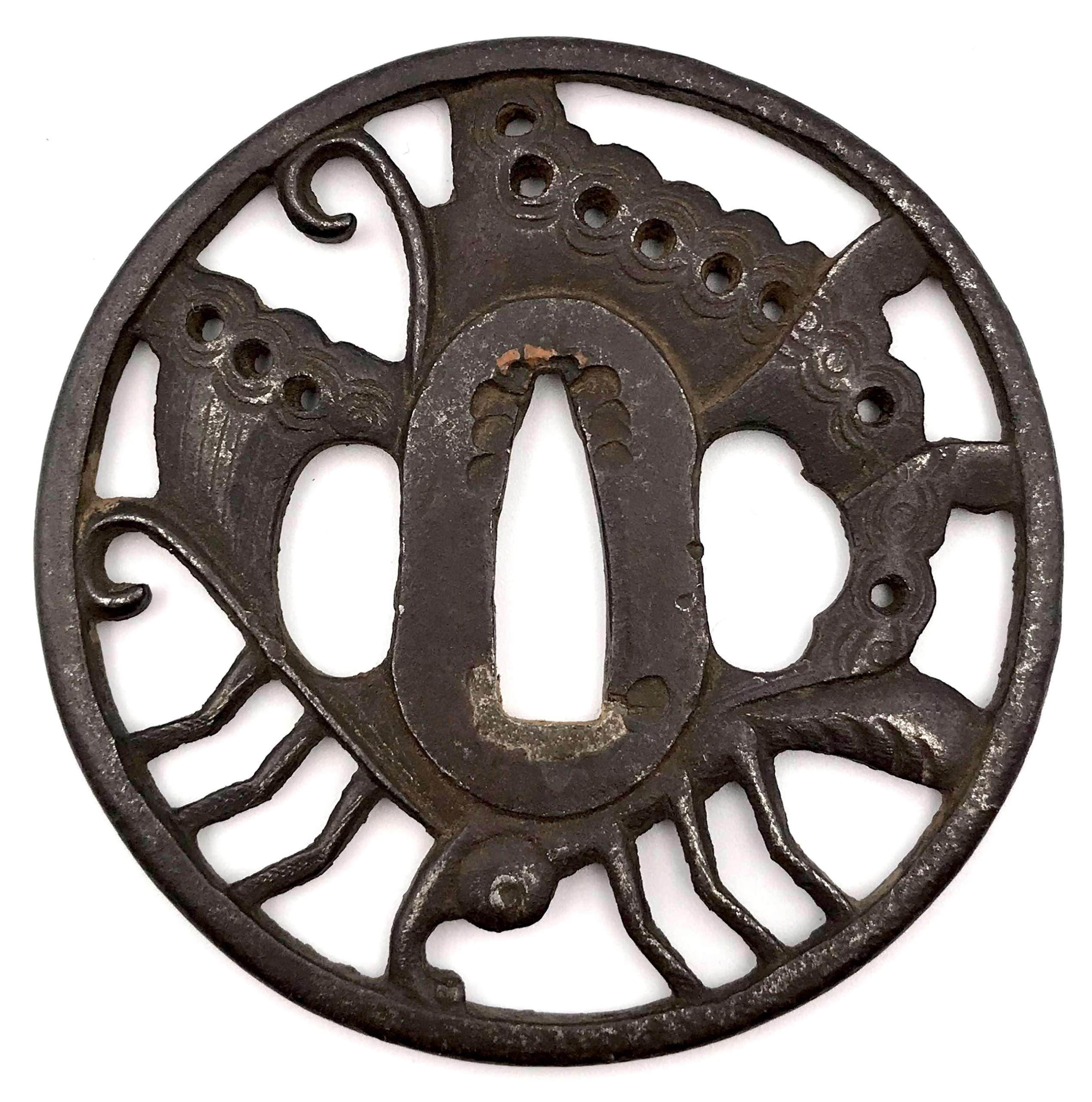
Iron tsuba of oval form with a shakudō fukurin and rough surface decorated by low relief carving and brass inlay with a centipede emerging from under the rock on both sides.
Edo period.Size: 78.9 x 73.6 x 3.8 mm
Unsigned. However, this tsuba may be (though with reservation) attributed to Misumi Kōji school. There is some information regarding this master(s) in Tsuba. An aesthetic study by Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes (from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997) on pages 163-4, though I was not able to locate the tsuba in the original publication. Possibly, this fragment of the book was added by Robert Haynes. Markus Sesko speculates about Misumi in his The Japanese toso-kinko Schools.// Lulu Inc., 2012 on pages 374-5: "Misumi Kōjo Tsuba. Iron plate, elliptical shape, shakudō takabori suemon, yamagane fukurin. Centipede." But of course, visual similarity does not prove anything. I was not able to find any traces of signature or a triangle on the seppa-dai.
Misumi Kōji Tsuba on p. 163.
-
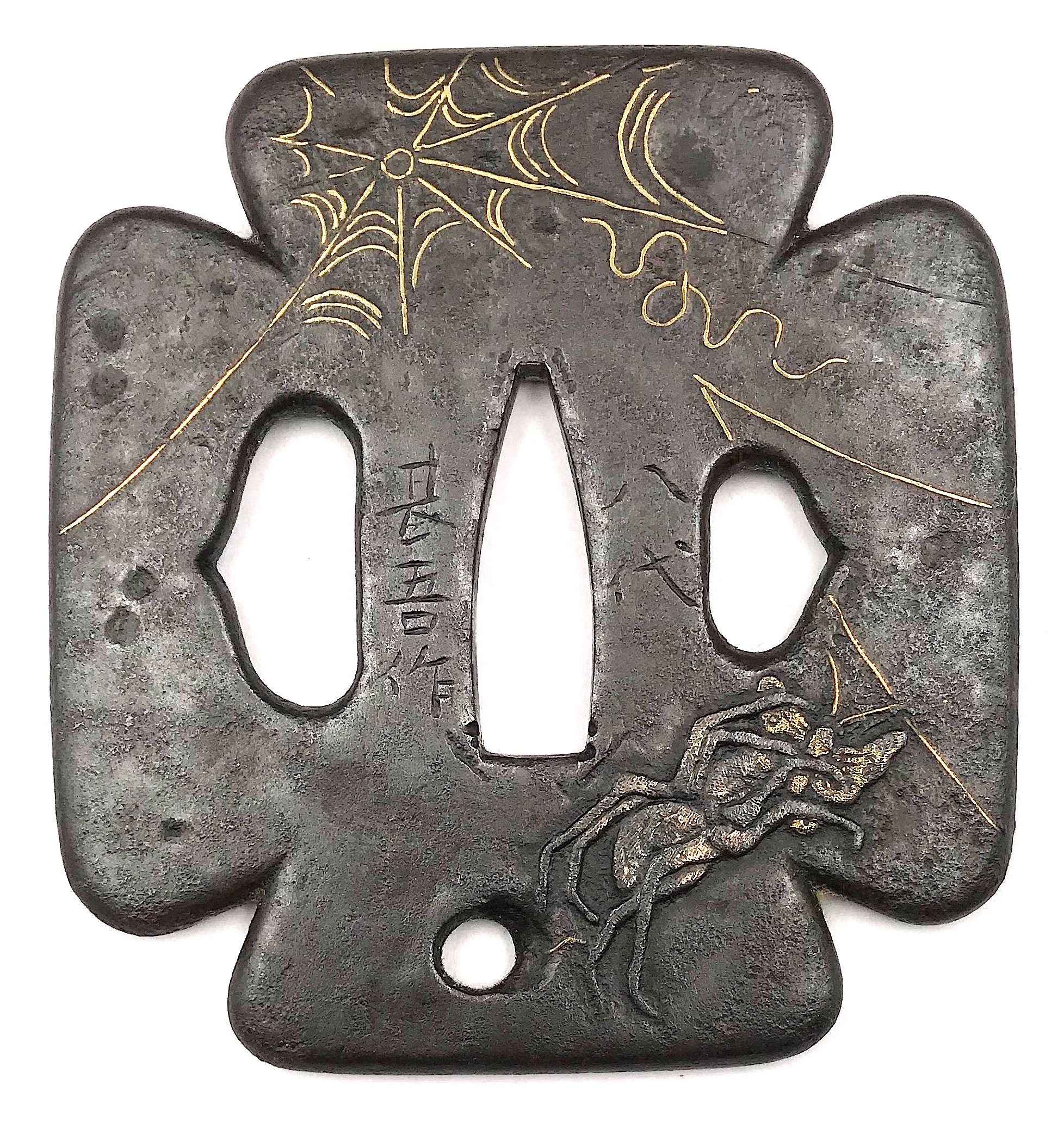

Very fine iron plate well hammered and turned, tapering and rolling to the rounded edge. Tsuba of a cross-form mokko shape (juji-mokko-gata) decorated with spider web inlaid in gold on both sides. The face is carved with a silver-damascened spider holding a gold-damascened butterfly (nunome-zōgan). Kozuka and kogai hitsu-ana of inome (boar's eye) form. The udenuki ana may be of purely decorative purpose.
Signed: Yatsushiro [八代] Jingo Saku [甚吾作], a signature of Chisokutei Amatsune, one of the last Jingo masters.
Late Edo period, Tenpō era, 1830-1844.Size: Height: 77.5 mm; Width: 72.8 mm; Thickness: 4.1 mm; Weight: 141 g.
In a custom wooden box.
Here is what Markus Sesko wrights in his book The Japanese toso-kinko Schools, 2012, on page 374:An artist who worked in the style of the Shimizu-Jingo school was Chisokutei Amatsune (知足亭天常). He was actually a samurai from Yatsushiro who made tsuba as a sideline. An extant old hakogaki of one of his pieces mentions that he died in Edo in the sixth month of An'ei eight (1779) at the age of 73. But the era of An'ei is probably wrong because Chikokutei (sic) is today dated by most experts around Tenpō (1830-1844). His relationships with the Shimizu school or under which Jingo master he had studied are unknown. From the point of view of production time and the finishing of nakago-ana, he is rather associated with the 5th and last gen. Shigenaga who died in the seventh year of Kaei (1854). A peculiarity of Chisokutei was that he signed his Jingo copies with "Yatsushiro Jingo Saku" ([八代甚吾作) but added the small syllable "chi" (チ) or the character "Chi" (知) for "Chisokutei" to identify them as copies.
No longer available. -
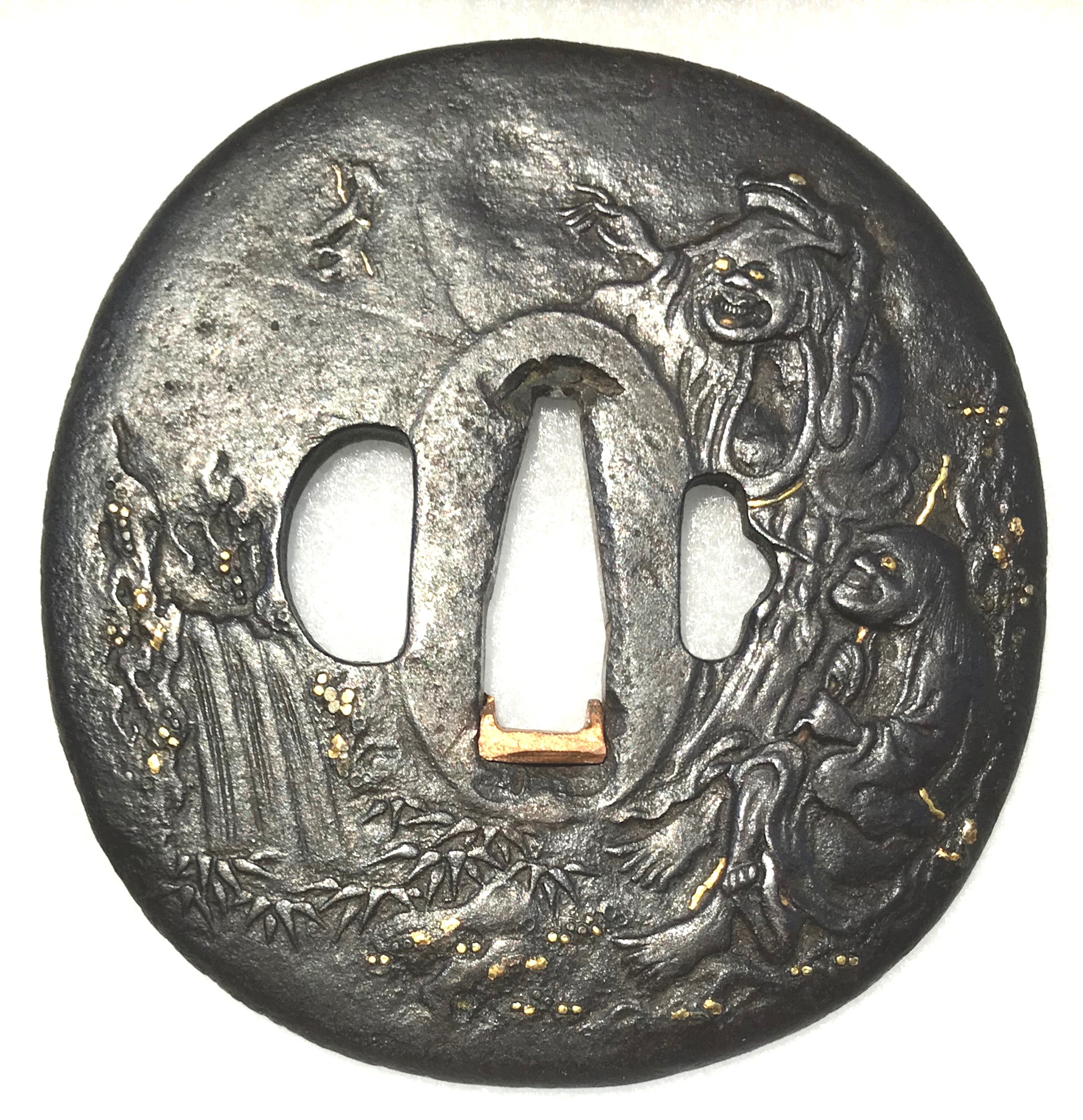

Iron tsuba of oval form with the design of two immortals (Gama Sennin with the toad upon his head and Tekkai Sennin with his iron crutch) beside a waterfall carved in low relief with a high relief effect (takabori) and with details inlaid in gold. A waterfall carved on the reverse. Nakago-ana is plugged with copper sekigane. Unsigned. Allegedly, Mito School.
Edo period, ca. 1700.
Size: Height: 87.0 mm; Width: 82.8 mm; Thickness: 4.4 mm; Weight: 179 g.
No longer available. -
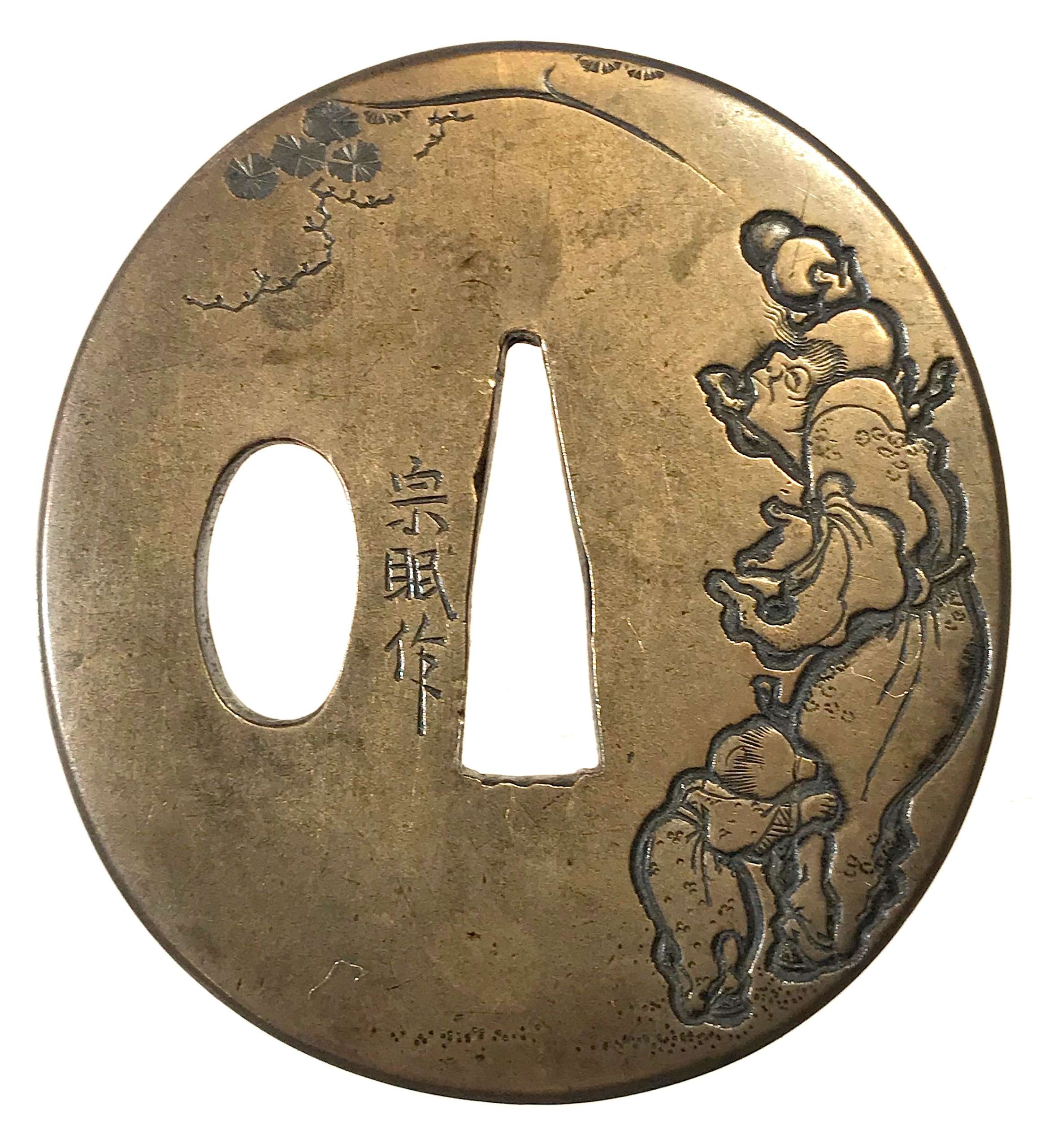

Sentoku tsuba of oval form with Sennin (Chinese immortal) motif carved in low relief (katakiribori). The Sennin is depicted with a double gourd in his right hand and a child beside his left hip. A pine tree carved on the reverse.
Signed: Sōmin saku (宗眠作) [M.Sesko]. Yokoya School (see The Japanese toso-kinko Schools by Markus Sesko, pp. 133-8).
Edo period (second half of the 18th century). Dimensions: Height: 61.6 mm; Width: 56.4 mm; Thickness: 4.2 mm; Weight: 85 g. -
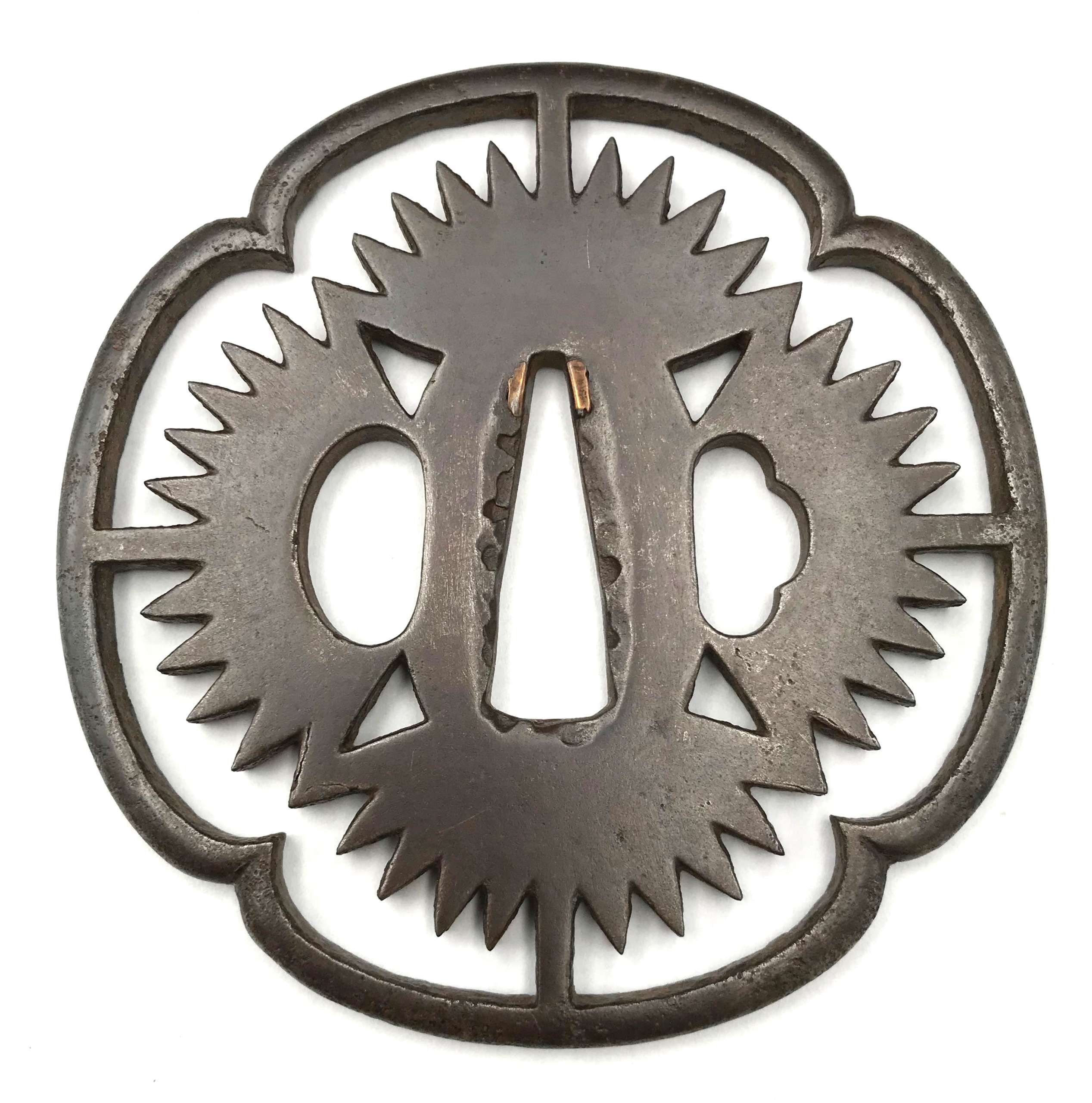 Iron tsuba of mokko form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Owari school. Edo period.
Iron tsuba of mokko form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Owari school. Edo period.Size: 83.4 x 83.1 x 4.4 mm
NTHK certified KANTEISHO ("Important Work"). In a custom wooden box. For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91. -
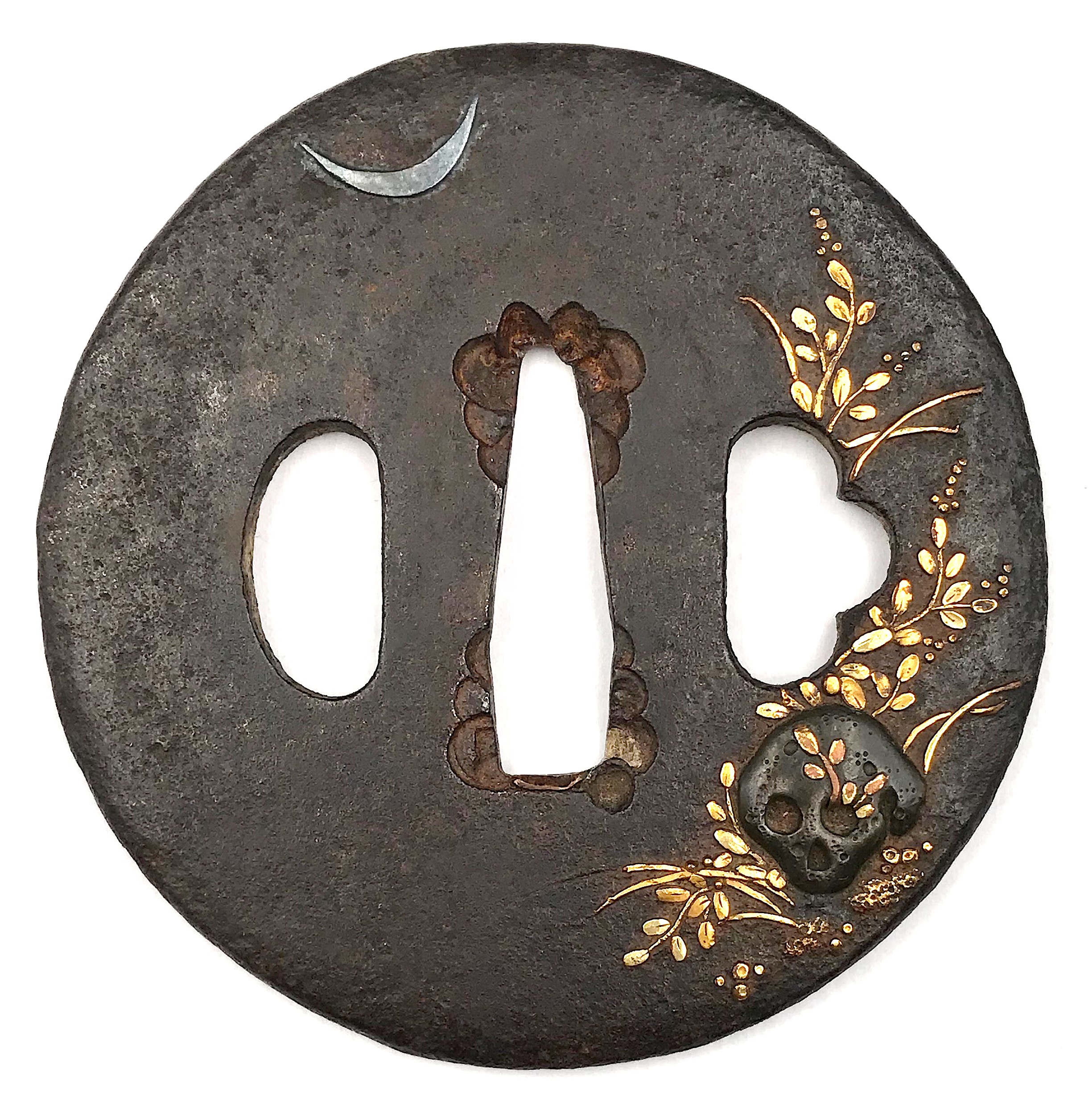 An iron tsuba of round shape inlaid with shakudō, gold, and silver with a motif of a weather-beaten (nozarashi) skull and grasses growing beside as well as through the eye-pit, and a crescent moon above the scene. Grasses on the reverse. Unsigned. Dimensions: 71.7 x 70.6 x 4.2 mm Reference: Skull, bones and grave markers SOLD
An iron tsuba of round shape inlaid with shakudō, gold, and silver with a motif of a weather-beaten (nozarashi) skull and grasses growing beside as well as through the eye-pit, and a crescent moon above the scene. Grasses on the reverse. Unsigned. Dimensions: 71.7 x 70.6 x 4.2 mm Reference: Skull, bones and grave markers SOLD -
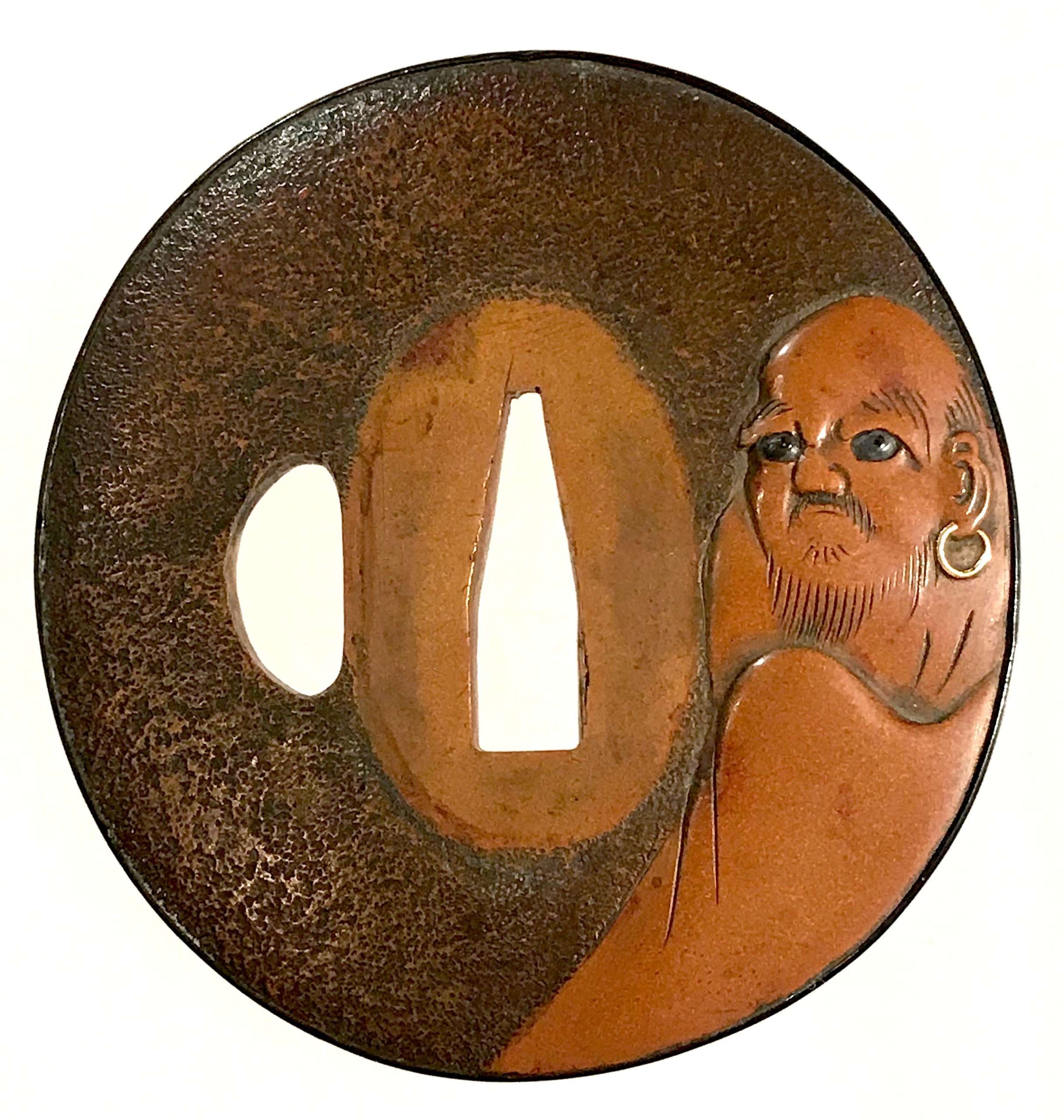

A copper tsuba with ishime-ji ground carved and polished (migaki-ji) with sitting Daruma; his eyes are inlaid with shakudo and he has a golden earring. The reverse carved with four characters: 廓 然 無 性 (Kakunen-mushō). It is a Zen proverb that goes back to Bodhidharma (Daruma), meaning "boundless expanse and nothing that can be called holy." [Markus Sesko translation]. Shakudo fukurin.
Unsigned.
Edo period (circa 1800). Dimensions: 68.2 x 65.5 x 4.8 (center) x 3.2 (rim) mm -
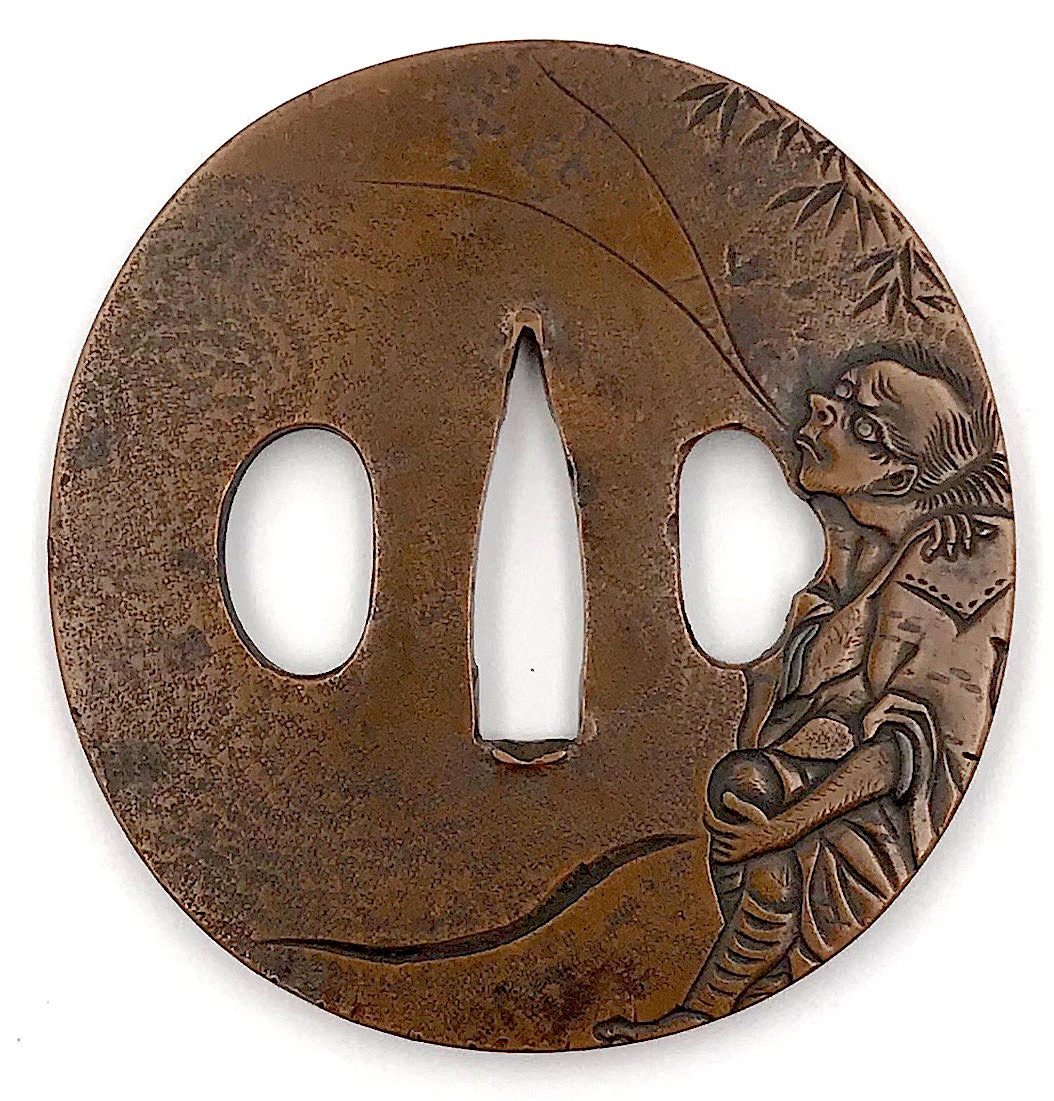

Copper tsuba of oval form carved in kebori and katakiribori with Tekkai Sennin sitting under bamboo on the face and with a pine tree on the back. Ishime-ji treated surface.
Signed on the reverse: Jōi (乗 意).
Edo period (First half of 18th century). Dimensions: 69.6 x 66.5 x 4.5 mm Sugiura Jōi (杉 浦 乗 意) was a master of Nara School in Edo; he was a student of Toshinaga [M. Sesko, 'Genealogies', p. 32]. "Sugiura Jōi (1701-1761) made many fuchigashira and kozuka, tsuba are rather rare." [M. Sesko, The Japanese toso-kinko Schools]. -
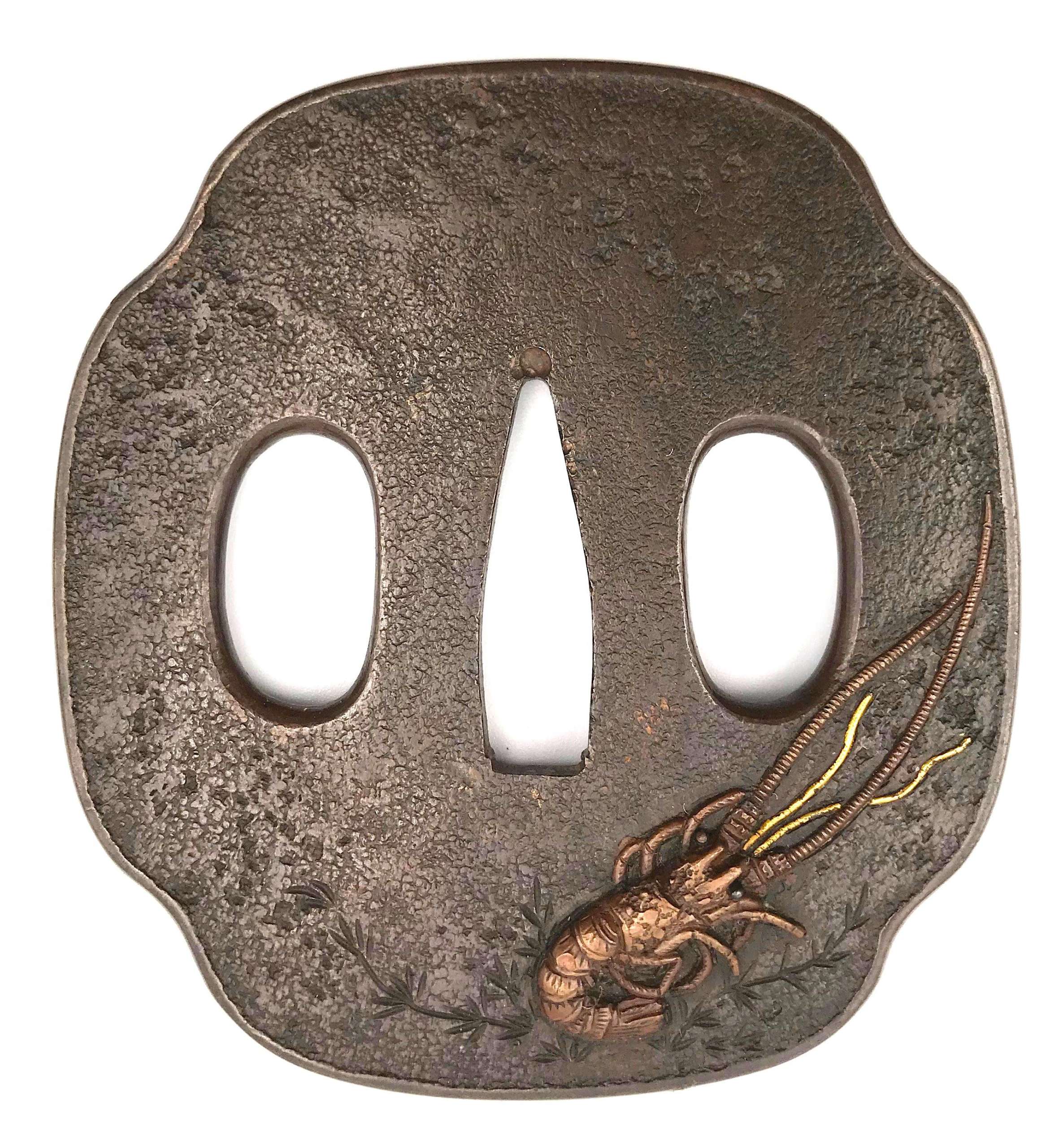

Bronze tsuba of mokkō form with narrow slightly raised rim carved in kebori with the sea weed and inlaid with a lobster (ebi) made of copper on the face and two sea shells made of shakudo on the back. Lobster's antennae inlaid in gold, and eyes inlaid in shakudo. Ishime-ji treated surface.
Unsigned.
Late Edo period (mid-19th century). Dimensions: 76.3 x 71.1 x 3.7 mm -
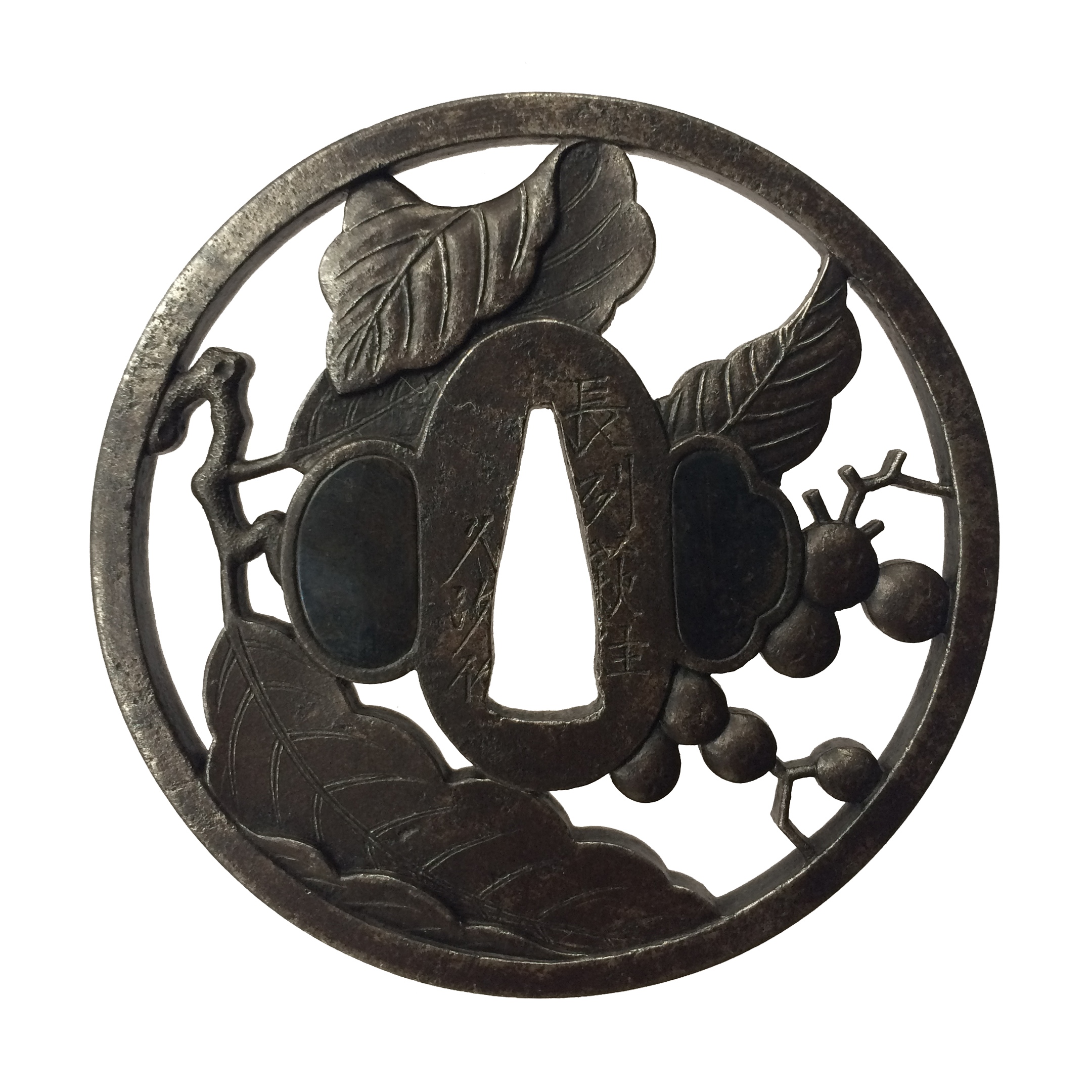

Iron tsuba of circular form with a branch of loquat (biwa) pierced in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi) and carved in marubori technique (marubori-sukashi). Kozuka and kogai hitsu-ana are plugged with shakudo.
Signature: Choshu Kawaji ju Hisatsugu saku. Chōshū school in Nagato province.
According to M. Sesko 'Genealogies' Hisatsugu was a 4th generation Kawaji School master from Chōshū (present day Nagato), with the name Gonbei, formerly Toramatsu, adopted son of Tomohisa (1687-1743) [page 117]. For Tomohisa work see TSU-0104 in this collection. -
 This tsuba is a cut from a typical Bizen Shōami butterfly tsuba (see TSU-0100 in this collection), which normally would have had a circular rim around the butterfly. In this particular example of altered guard we have both eyes of the insect (inlaid in brass or copper) intact. The kebori carving is more pronounced than in TSU-0100 example. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 64.7 x 63.7 x 5.2 mm References: see TSU-0100.
This tsuba is a cut from a typical Bizen Shōami butterfly tsuba (see TSU-0100 in this collection), which normally would have had a circular rim around the butterfly. In this particular example of altered guard we have both eyes of the insect (inlaid in brass or copper) intact. The kebori carving is more pronounced than in TSU-0100 example. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 64.7 x 63.7 x 5.2 mm References: see TSU-0100. -
 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of a butterfly in openwork (sukashi) with details carved in kebori. Eyes inlaid in brass (one inlay is missing). Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 80.4 x 80.6 x 4.4 mm References At Haynes Catalog #6, p. 18-19, Lot 30: "Famous Ikeda butterfly design" (Ikeda family of Inaba and Okayama, and at least 7 other families). Ca. 1700. Shōami of Kyoto, no doubt. Ht 8.2 cm, Th. 5 mm. ["Important tsuba, menuki, bokuto, woodblock prints, koshirae, sword pistol and kana mono". San Francisco, June 1-26, 1983. Catalog #6. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd.]Similar tsuba at Haynes Catalog #9, p.71, lot 143: the classic Shoami tsuba of the mon of the Ikeda family. This example, as most, seems to be made by the same hand as the others. See Haynes sale number 6, lot 30, for an identical example. The eye is brass. From an old French collection. Ht. 7.9 cm., Th. 5 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of a butterfly in openwork (sukashi) with details carved in kebori. Eyes inlaid in brass (one inlay is missing). Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 80.4 x 80.6 x 4.4 mm References At Haynes Catalog #6, p. 18-19, Lot 30: "Famous Ikeda butterfly design" (Ikeda family of Inaba and Okayama, and at least 7 other families). Ca. 1700. Shōami of Kyoto, no doubt. Ht 8.2 cm, Th. 5 mm. ["Important tsuba, menuki, bokuto, woodblock prints, koshirae, sword pistol and kana mono". San Francisco, June 1-26, 1983. Catalog #6. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd.]Similar tsuba at Haynes Catalog #9, p.71, lot 143: the classic Shoami tsuba of the mon of the Ikeda family. This example, as most, seems to be made by the same hand as the others. See Haynes sale number 6, lot 30, for an identical example. The eye is brass. From an old French collection. Ht. 7.9 cm., Th. 5 mm.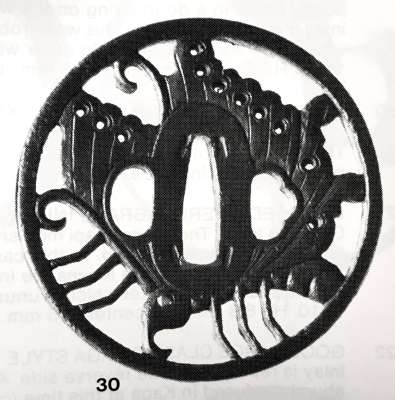
Haynes Catalog #6, lot 30.
Similar tsuba in the Randolph B. Caldwell Collection, 1994, page 24, №13: "A circular iron tsuba pierced in positive sukashi with a butterfly within an angular rim, details engraved. The eye inlaid in brass [in my specimen the inlay is missing on the omote side]. Unsigned. Bizen Shōami, Momoyama period. Dimensions: 8.0 x 8.2 x 0.5 cm. Similar example: Durand-Ruel, collection Ch. Gilloz, number 1302. [SV: that's possibly the 'old French collection' of Robert Haynes.]
Haynes Catalog #9, lot 143.
If we accept Haynes' theory regarding the genealogy and history of Bizen Shōami family, Momoyama period attribution would seem unlikely. I am leaning towards the early to mid 17th century.
Caldwell Collection, #13.
-
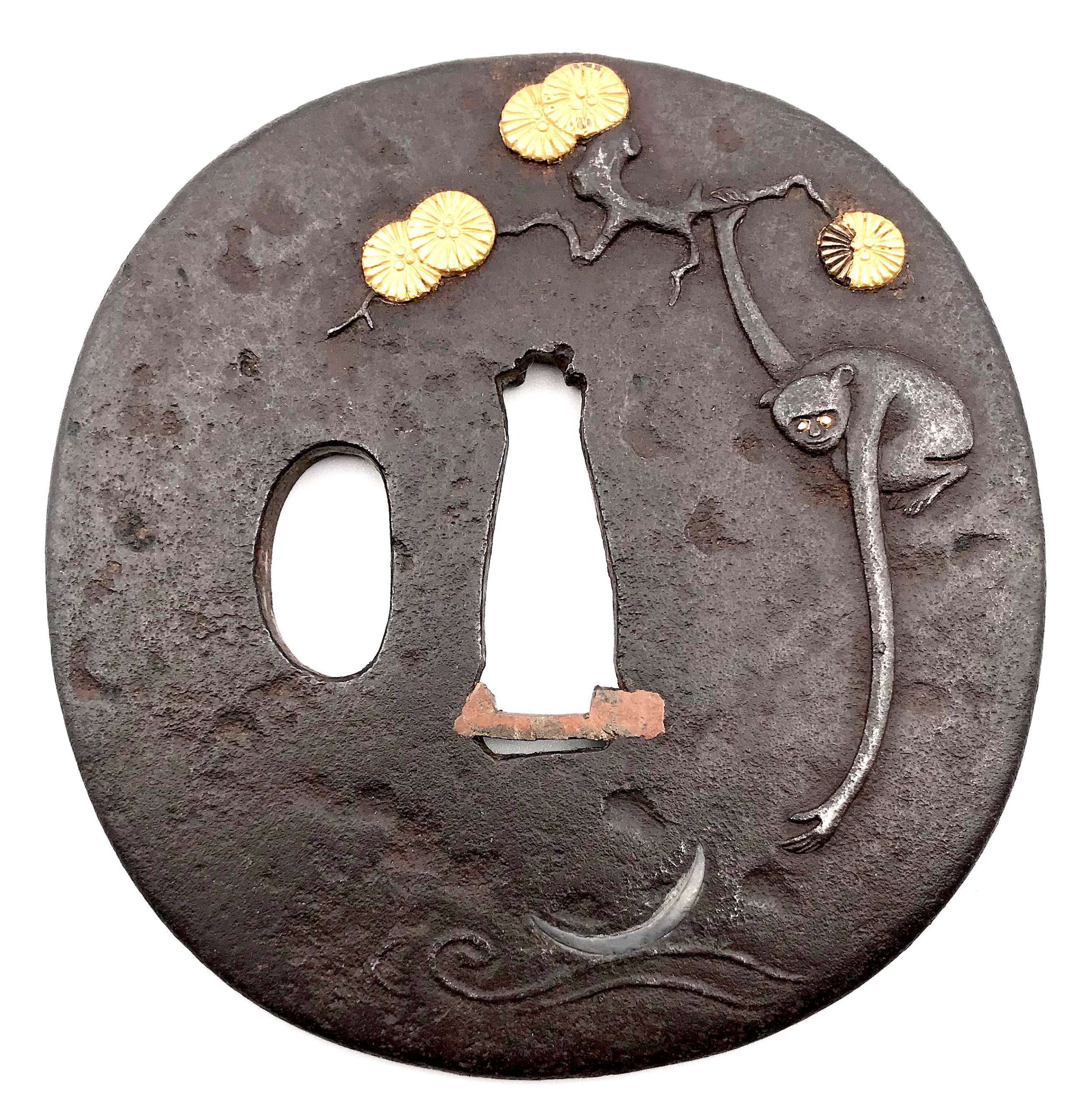 [SOLD]
[SOLD]Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form carved and inlaid in gold and shibuichi with a long-armed monkey hanging from a pine tree branch reaching for the reflection of a crescent moon in the stream. A pine tree carved with details inlaid in gold on the reverse. The design seems to be inspired by Kaneie work (Compton III, p. 10, №6a; Tsuba no bi, 1947, p. 33, №56).
Dimensions: 76.8 x 74.2 x 3.6 mm. Mid-Edo period. Unsigned.
Compton III, p. 10, №6a

Tsuba no bi, 1947, p. 33, №56.
-
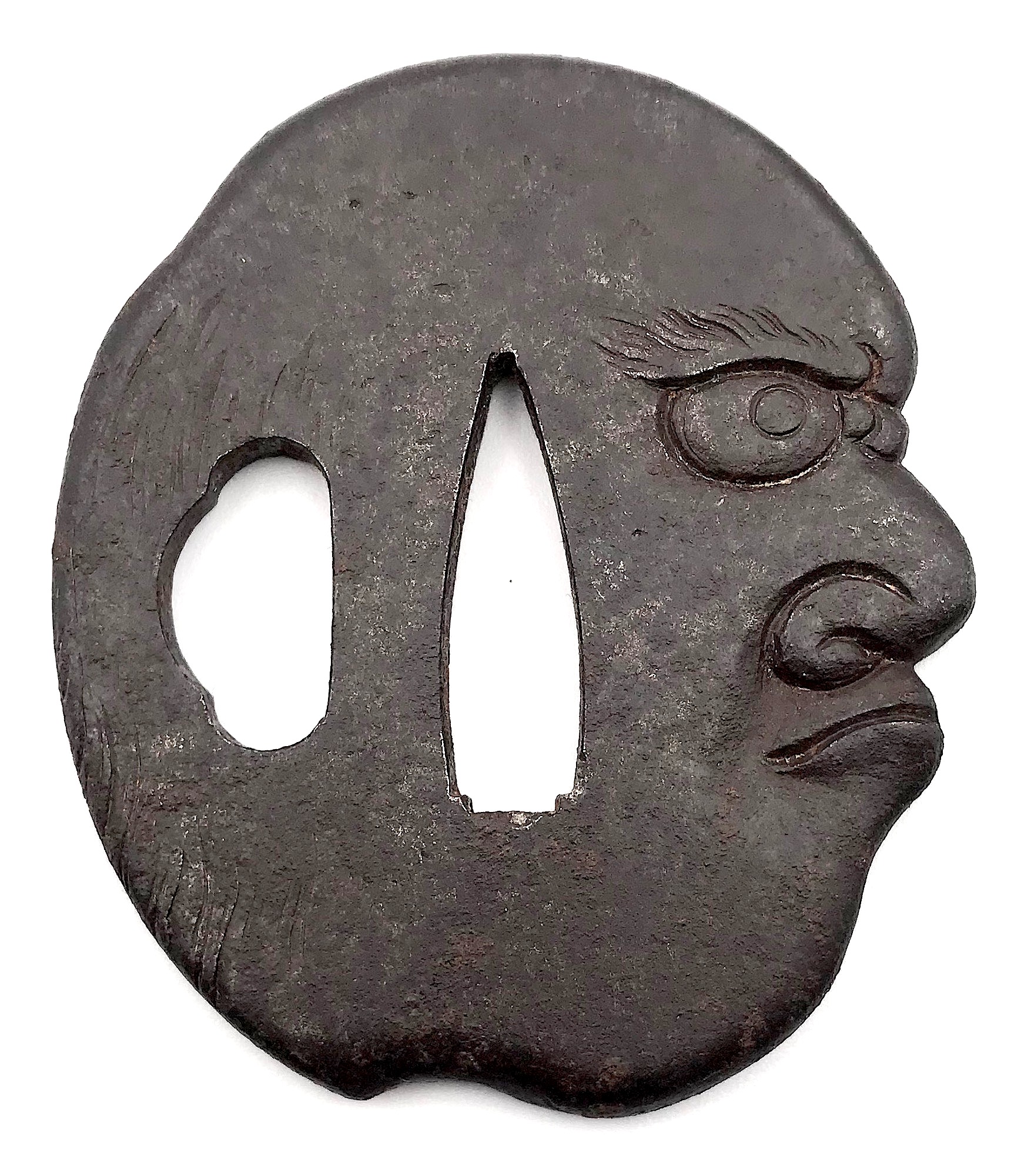 An iron tsuba in the shape of a bold or shaved human head in full round. Unsigned. Dimensions: 62.5 x 53.4 x 4.4 mm Iron, in the shape of a Ni O (Nio) head, in full round, the back flat chased as a pine forest. Signed : Miōchin Masatsugu in sosho. №38 in The Naunton Collection, 1912. There are a few tsuba of such design known. SOLDIron, a severed head. Signed: Takeaki of Kwaiyō. Ex Hawkshaw Collection [Plate VII]. Below written: Takurio, Suruga, 1118; Tamagawa, p. ; Tanaka, p. 168; Tanetora, 1894. №2729 in The Naunton Collection, 1912.
An iron tsuba in the shape of a bold or shaved human head in full round. Unsigned. Dimensions: 62.5 x 53.4 x 4.4 mm Iron, in the shape of a Ni O (Nio) head, in full round, the back flat chased as a pine forest. Signed : Miōchin Masatsugu in sosho. №38 in The Naunton Collection, 1912. There are a few tsuba of such design known. SOLDIron, a severed head. Signed: Takeaki of Kwaiyō. Ex Hawkshaw Collection [Plate VII]. Below written: Takurio, Suruga, 1118; Tamagawa, p. ; Tanaka, p. 168; Tanetora, 1894. №2729 in The Naunton Collection, 1912.
№38 Naunton Collection, 1912.
Reference to Hawkshaw Collection [Plate VII] happened to be not exact; it is Plate VIII, №236. It is clearly not the Hawkshaw piece (different facial expression, signle hitsu-ana, no plug. Description at Hawkshaw, 1910, reads: Iron, in the shape of a man's head, severed at the neck, the forehead in three wrinkles, the mouth hard-set and drooping, the eyes open, inlaid brass with shakudo pupils. Signed: Shoami; dated second year of Shoho, first month [SV: December 1644 through February 1648].
№2729 Naunton Collection, 1912.

№236 Hawkshaw Collection, 1910.
-
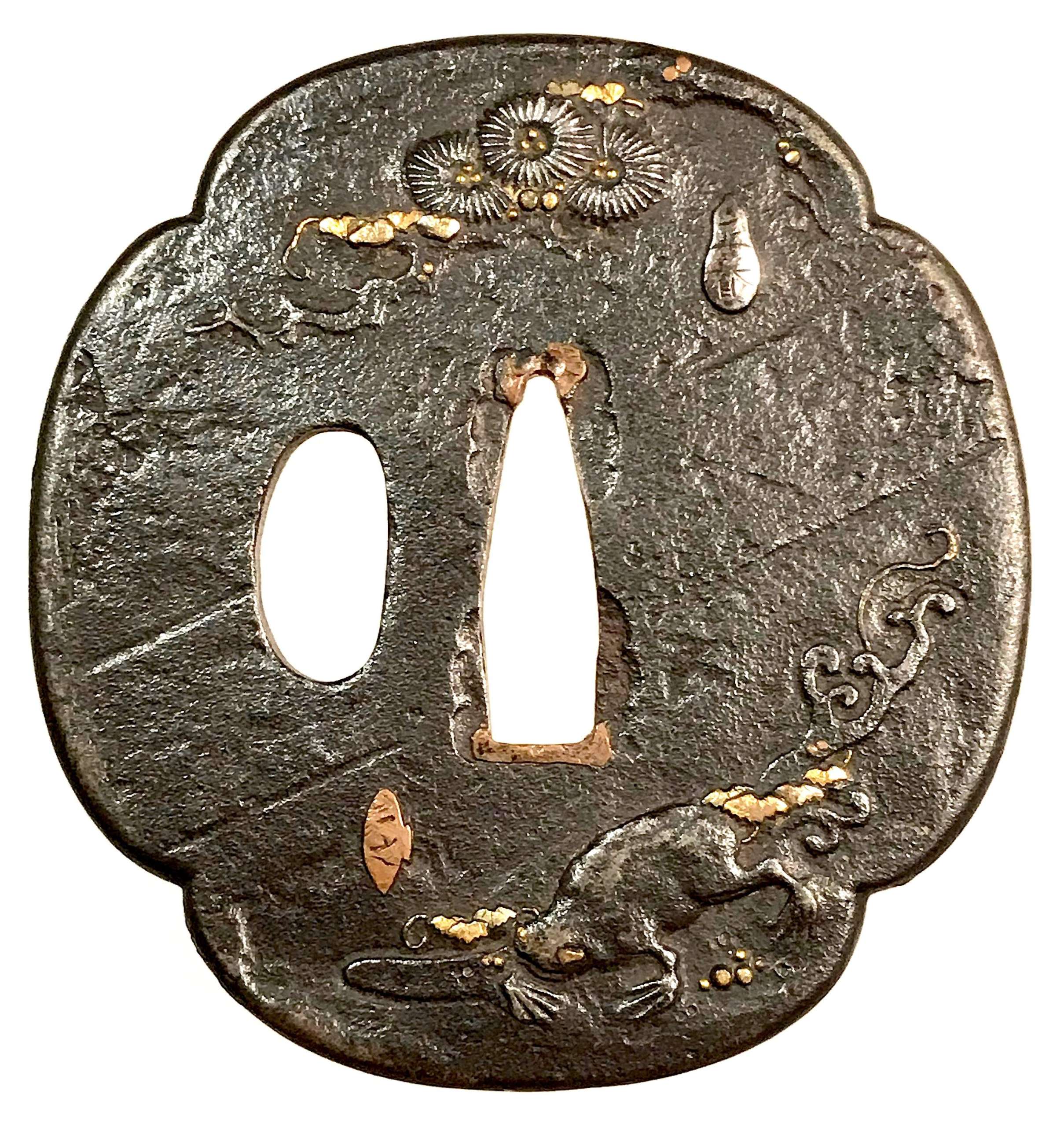

Iron tsuba of mokkō-form with a pine and a frog on the face and a snail on the back, carved and inlaid with gold. Each figurative element of the design is signed on three inlaid cartouches: Masaharu (正春), Kazuyuki (一之), and Yoshikazu (良一) [read by Markus Sesko]. Snake, snail, and frog together make a design called "SANSUKUMI" - Three Cringing Ones [Merrily Baird]. The snail can poison the snake, the frog eats the snail, and the snake eats the frog. It's unclear whether the pine replaces the snake on this tsuba, or the snake is hiding in the pine? Anyway, the frog and the snail are clearly represented. "Maybe we have here a joint work with Masaharu (the silver cartouche next to the pine) being the master and making the plate and Kazuyuki and Yoshikazu as his students carving out the frog and the snail respectively". Copper sekigane.
Dimensions: 70.9 x 67.2 x 3.0 mm. Edo period (18th century).Markus Sesko writes: "I agree, the frog and the snail most likely allude to the san-sukumi motif. It is possible that we have here an artist's choice to deliberately leave out the snake, maybe he thought that the motif is already obvious and there is no need to add a snake to make it clear that the tsuba shows the san-sukumi motif." [Markus Sesko].
Kazuyuki (一之): adopted son of Kumagai Yoshiyuki, student of Ichijō (Gotō-Ichijō Scool) [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 19.] Masaharu (正春): Kasuya fam., student of Masamichi (1707-1757) who was the 4th generation Nomura School master in Edo. [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 49.] -
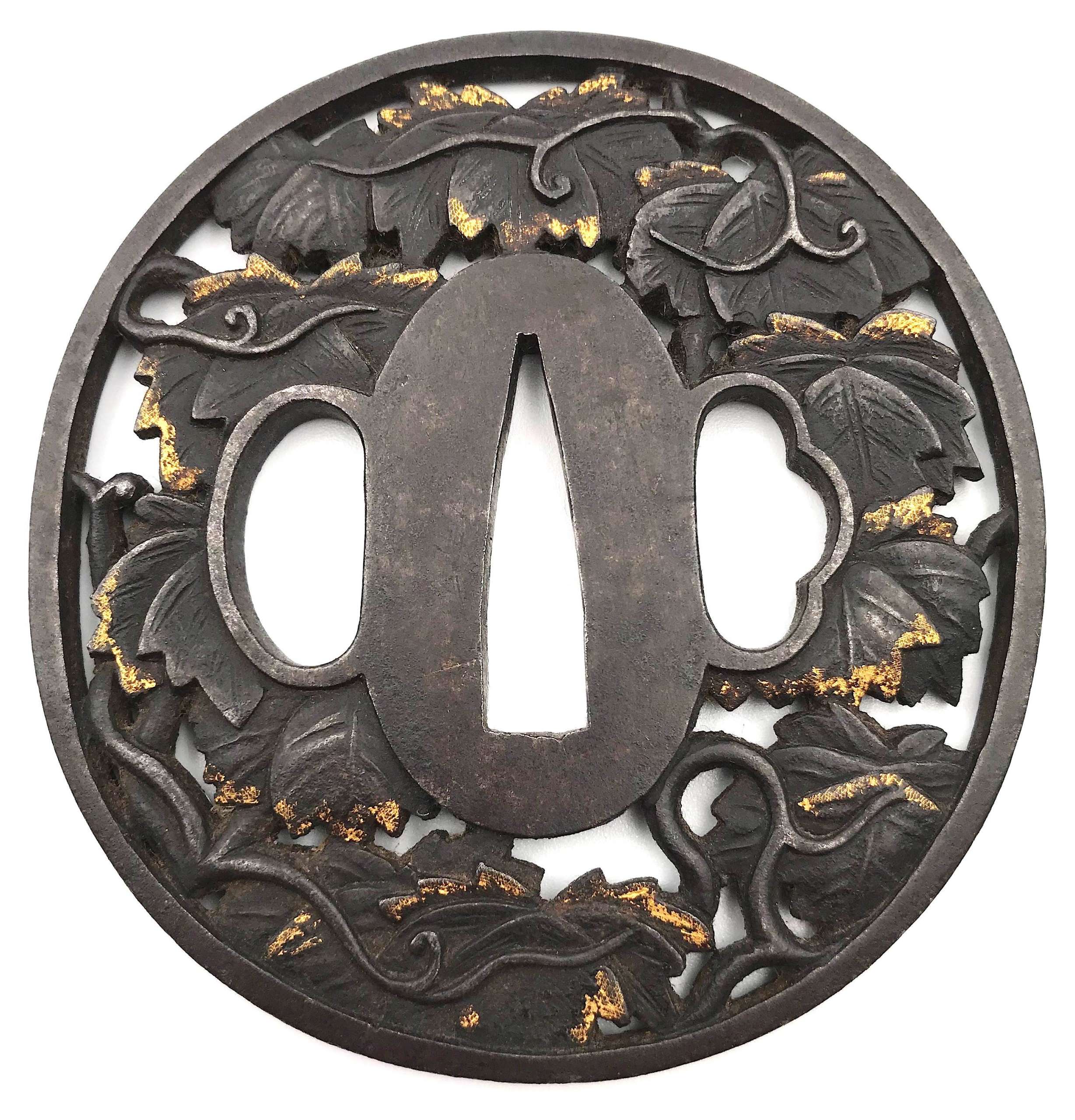

An iron tsuba of slightly vertically elongated circular form carved and pierced with a mass of ivy (tsuta) leaves and tendrils, details damascened with gold in nunome-zōgan technique. Hitsu-ana with raised rim.
Unsigned.
Chōshū school.Height: 72.0 mm; width: 69.0 mm; thickness: 4.7 mm; Weight: 92 g.
According to John W. Dower, "ivy bears fairly close resemblance to both maple leaf and grape leaf". However, I consider this tsuba decorated with ivy leaves for several reasons, such as the lack of racemations in the presence of tendrils. -
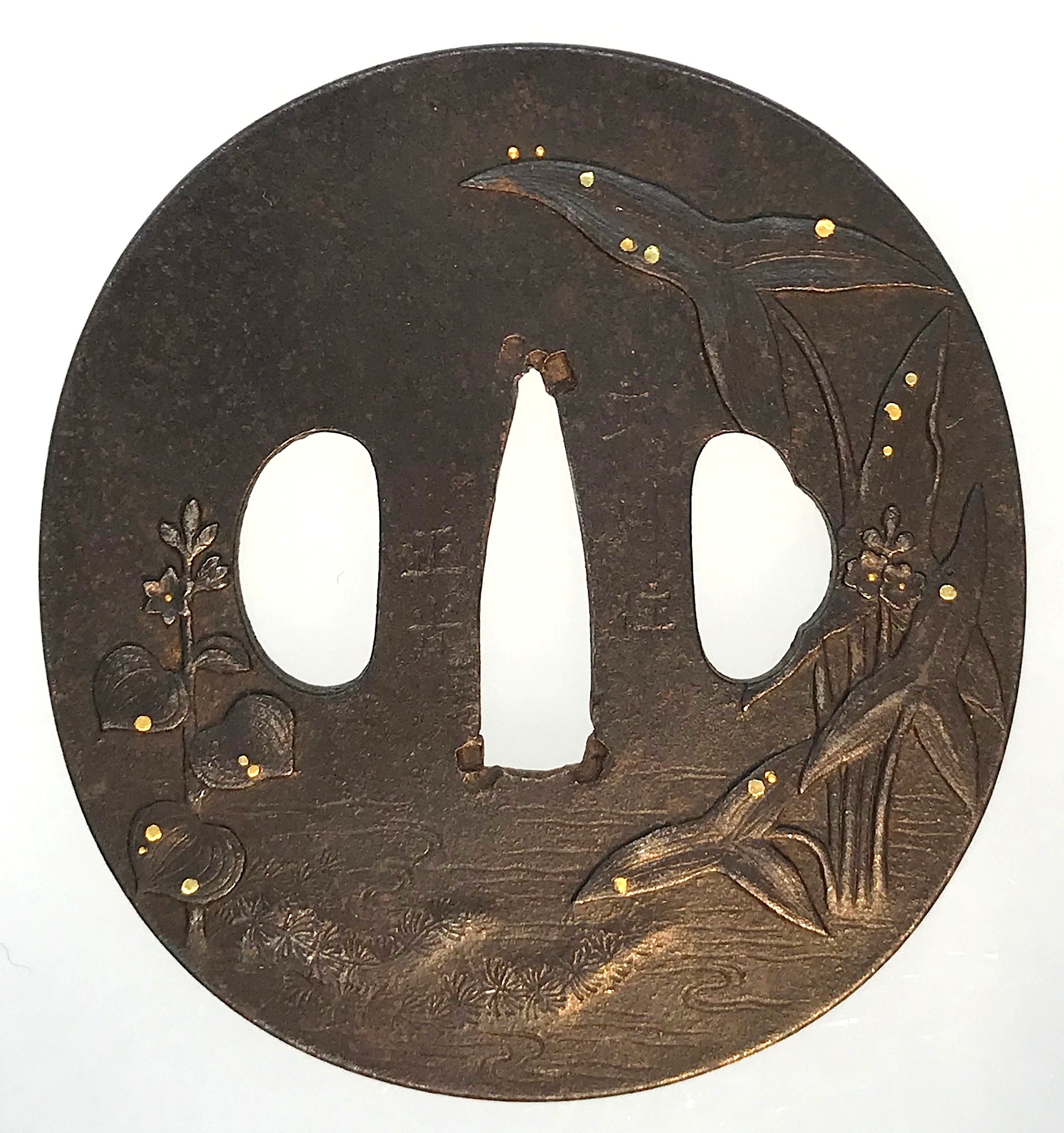

An iron tsuba of oval form decorated with a water plantain (omodaka) carved in low relief and water drops inlaid in gold.
Signed: Bushū jū Masamitsu.
Bushū-Itō school.Height: 71.8; Width: 67.3; Thickness: 3.6; Weight: 96 g.
Mid to late Edo period; 18th-19th century.
There were several tsuba artists with the name of Masamitsu. The one who worked with iron and spelled [正光] is mentioned at Markus Sesko's 'Genealogies' on page 106 in Akasaka School of Edo section as Masamitsu Gorōbei , student of Tadatoki, 4th generation Akasaka master. The name is not mentioned at Torigoye/Haynes 'Tsuba. An Aesthetic Study' in the list of Bushū-Itō family masters on page 181. -
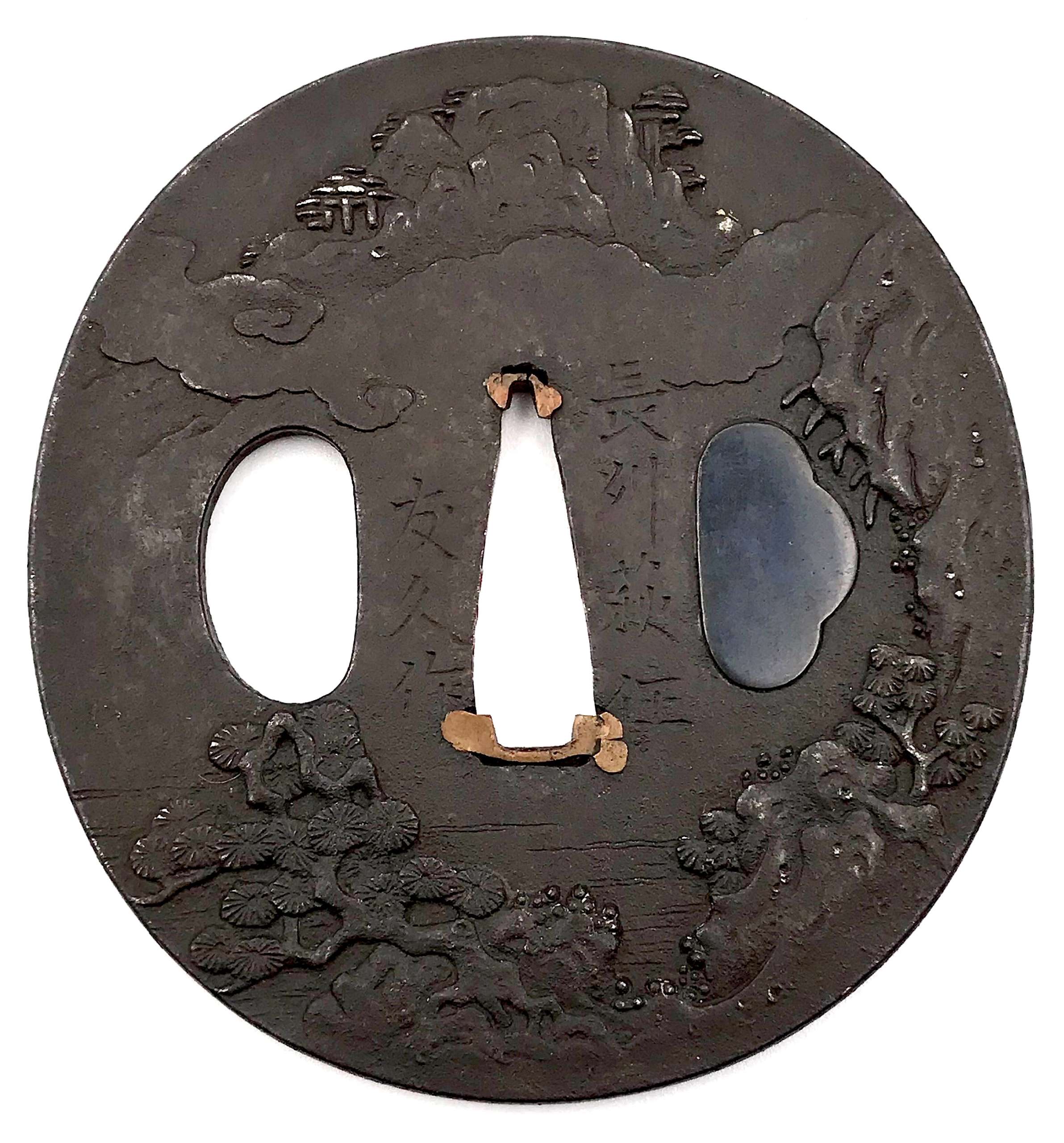

Iron tsuba of oval form carved with a landscape motif. Kogai-hitsu-ana plugged with shakudo. Sekigane of copper.
Signed: Chōshū Hagi-jū Tomohisa saku (長州萩住友久作).
Tomohisa, adopted son of Rokurō'emon, was 3rd generation master of Kawaji School from Hagi in Nagato (Chōshū), lived 1687-1743 [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 117].
Edo period, circa 1700. Dimensions: 71.1 x 66.8 x 2.9 mm For his adopted son Hisatsugu work see TSU-0103 in this collection. -
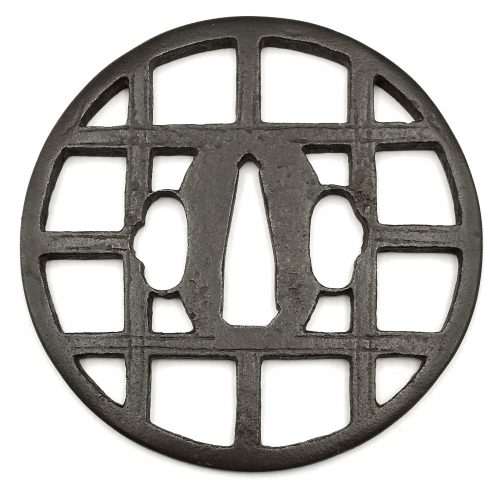 Iron tsuba of round form with design of lattice (kōshi-mon, 格子文) cut in openwork (sukashi), with low relief shallow linear carving along the bars. Well forged plate with brown-ish hue. To the right of nakago-ana there is a clear inscription of the character Shō (正), which is explained by Markus Sesko is follows: "The Shinsa obviously recognized more from the signature when having the tsuba in hand, i.e. they were confident to say it is signed "Shōami" but the rest is illegible (ika-fumei, 以下不明). That is, if they were just able to read the first character SHŌ (正) and saw that there were two more, most likely A (阿) and MI (弥), they would have put those character in boxes on the paper. Boxes around characters namely means that the character is not 100% legible but it can be assumed what it is." Momoyama or early Edo period. Dimensions: 85.9 mm diameter, 3.6 mm thickness at seppa-dai. Weight: 79 g. NBTHK certificate № 425069 with attestation: Hozon - "Worthy of preservation". A similar tsuba is presented at Japanese Sword Fittings from the R. B. Caldwell Collection. Sale LN4188 "HIGO". Sotheby's, 30th March 1994, №15. The description says: "A rare early Kamakura-bori tsuba. Nambokucho period (late 14th century). Of circular form, the dark plate carved and pierced with a gate design, the struts with double engraved lines. Unsigned. 8.5 cm." The lot was sold for 1,840 GBP.We have two possible explanations of the discrepancy between Sotheby's and Shinsa/Sesko attribution: 1) either Sotheby's or Shinsa/Sesko were wrong in their attribution or 2) these are two different pieces, one - Kamakura-bori from the 14th century and another - Shōami from 16th/17th century. Anyway, I would consider my piece as a Shōami tsuba of Momoyama - early Edo period, just for the sake of modesty.
Iron tsuba of round form with design of lattice (kōshi-mon, 格子文) cut in openwork (sukashi), with low relief shallow linear carving along the bars. Well forged plate with brown-ish hue. To the right of nakago-ana there is a clear inscription of the character Shō (正), which is explained by Markus Sesko is follows: "The Shinsa obviously recognized more from the signature when having the tsuba in hand, i.e. they were confident to say it is signed "Shōami" but the rest is illegible (ika-fumei, 以下不明). That is, if they were just able to read the first character SHŌ (正) and saw that there were two more, most likely A (阿) and MI (弥), they would have put those character in boxes on the paper. Boxes around characters namely means that the character is not 100% legible but it can be assumed what it is." Momoyama or early Edo period. Dimensions: 85.9 mm diameter, 3.6 mm thickness at seppa-dai. Weight: 79 g. NBTHK certificate № 425069 with attestation: Hozon - "Worthy of preservation". A similar tsuba is presented at Japanese Sword Fittings from the R. B. Caldwell Collection. Sale LN4188 "HIGO". Sotheby's, 30th March 1994, №15. The description says: "A rare early Kamakura-bori tsuba. Nambokucho period (late 14th century). Of circular form, the dark plate carved and pierced with a gate design, the struts with double engraved lines. Unsigned. 8.5 cm." The lot was sold for 1,840 GBP.We have two possible explanations of the discrepancy between Sotheby's and Shinsa/Sesko attribution: 1) either Sotheby's or Shinsa/Sesko were wrong in their attribution or 2) these are two different pieces, one - Kamakura-bori from the 14th century and another - Shōami from 16th/17th century. Anyway, I would consider my piece as a Shōami tsuba of Momoyama - early Edo period, just for the sake of modesty.
Caldwell Collection. Sotheby's 1994, №15.
-
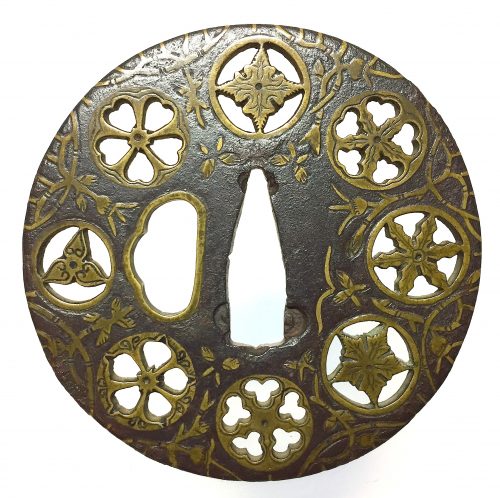 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm -
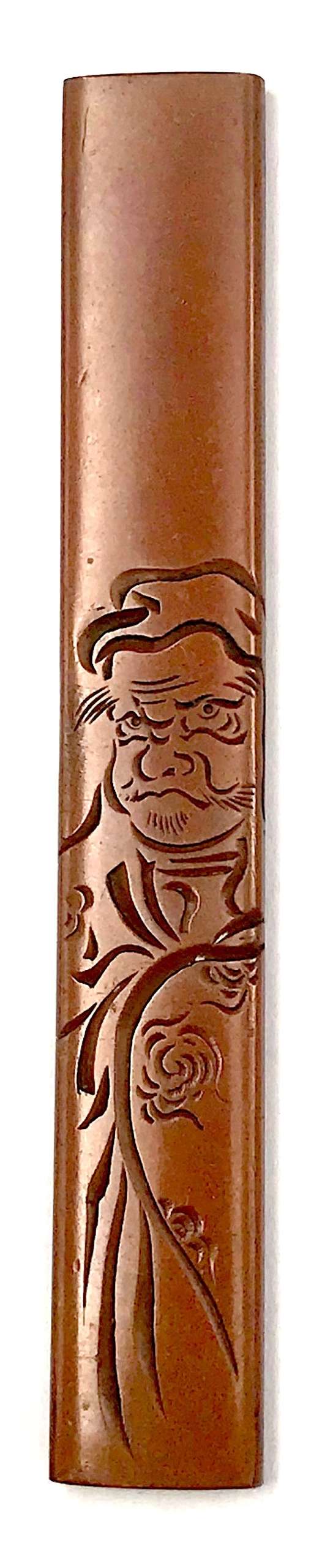 Kozuka made of pure copper with Daruma motif. The engraving technique is known as katakibori ("half-cut carving"). Signed on the back: Yasuchika. Size: 96.5 (H) x 14.5 mm (W). Edo period (Late 18th century). The technique of Katakiribori was developed by Yokoya school of artisans. Detailed account of Yasuchika family of kodōgo carvers is given at Japanese Sword Fittings from the Alexander G. Mosle Collection; Sebastian Izzard LLC, 2004 on page 64. The article ends with the following statement: "Given the popularity of his style and his many students, it is not surprising that a number of works bearing Yasuchika's signature are today disputed." S. Izzard attributes Yasuchika masters to Nara school. Yasuchika-signed kozuka in Important Japanese Swords and Sword Furniture and Works of Art [November 5, 1980, sales "Kotetsu". New York, Christie, Manson & Woods International Inc., 1980, pp.92-93, lot 172 and 173] are stylistically very different to our example. A shibuichi katakiribori kozuka, bearing the signature of Yashuchika, is illustrated at The Hartman Collection of Japanese Metalwork [sold at auction by Christie, Manson & Woods Ltd. June 30 and July 1, London, 1976] on page 82, lot 291. It depicts Daikoku and stylistically similar to ours. The description on page 83 says: "signed Yasuchika, and inscribed "drawn by Hanabusa Itcho" (Yasuchika IV, school of Iawamoto konkan, circa 1800)". A detailed account of Yasuchika signatures is presented at Masterpiece tsuba and kodogu from the Hans Conried and Alexander G. Mosle collections. Important woodblock prints by Utamaro, Hokusai, Hiroshige, Yoshida and other masters. San Francisco, September 1-25, 1983. Catalog #7. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd., pp. 141-174. The example that looks like ours is on page 146:
Kozuka made of pure copper with Daruma motif. The engraving technique is known as katakibori ("half-cut carving"). Signed on the back: Yasuchika. Size: 96.5 (H) x 14.5 mm (W). Edo period (Late 18th century). The technique of Katakiribori was developed by Yokoya school of artisans. Detailed account of Yasuchika family of kodōgo carvers is given at Japanese Sword Fittings from the Alexander G. Mosle Collection; Sebastian Izzard LLC, 2004 on page 64. The article ends with the following statement: "Given the popularity of his style and his many students, it is not surprising that a number of works bearing Yasuchika's signature are today disputed." S. Izzard attributes Yasuchika masters to Nara school. Yasuchika-signed kozuka in Important Japanese Swords and Sword Furniture and Works of Art [November 5, 1980, sales "Kotetsu". New York, Christie, Manson & Woods International Inc., 1980, pp.92-93, lot 172 and 173] are stylistically very different to our example. A shibuichi katakiribori kozuka, bearing the signature of Yashuchika, is illustrated at The Hartman Collection of Japanese Metalwork [sold at auction by Christie, Manson & Woods Ltd. June 30 and July 1, London, 1976] on page 82, lot 291. It depicts Daikoku and stylistically similar to ours. The description on page 83 says: "signed Yasuchika, and inscribed "drawn by Hanabusa Itcho" (Yasuchika IV, school of Iawamoto konkan, circa 1800)". A detailed account of Yasuchika signatures is presented at Masterpiece tsuba and kodogu from the Hans Conried and Alexander G. Mosle collections. Important woodblock prints by Utamaro, Hokusai, Hiroshige, Yoshida and other masters. San Francisco, September 1-25, 1983. Catalog #7. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd., pp. 141-174. The example that looks like ours is on page 146:
 Though we have to admit that the example from Catalog #7 by Robert E. Haynes looks much stronger.
Though we have to admit that the example from Catalog #7 by Robert E. Haynes looks much stronger.
-
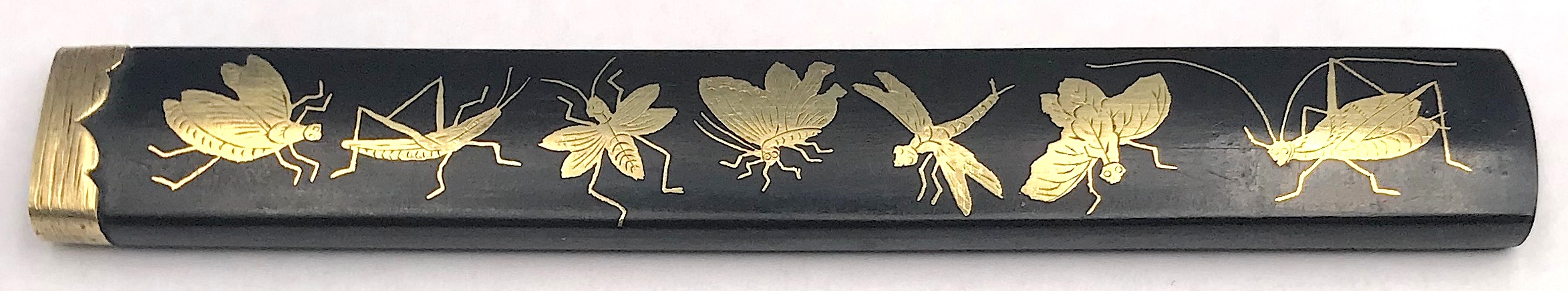 Kozuka with seven insects (fly, grasshopper, bee, butterfly, dragonfly, firefly, and cricket) and grass with dewdrops motif. Shakudō, flush gold inlay (hira-zōgan). 95.2 (H) x 13.7 mm (W). Mid Edo period (Late 17th - early 18th century, Genroku era 1688-1703). Unsigned. Kaga school. A look-a-like kozuka (with five insects) is illustrated at Japanese Sword Fittings. A descriptive catalogue of the Collection of G.H. Naunton, Esq., completed and illustrated by Henri L. Joly, - 1912 on plate XXIX, №691 [LIB-1389 in this Collection] with the following description at page 54: "Shakudō, inlaid with butterfly, dragon-fly, grasshopper, locust and another insect, gold."
Kozuka with seven insects (fly, grasshopper, bee, butterfly, dragonfly, firefly, and cricket) and grass with dewdrops motif. Shakudō, flush gold inlay (hira-zōgan). 95.2 (H) x 13.7 mm (W). Mid Edo period (Late 17th - early 18th century, Genroku era 1688-1703). Unsigned. Kaga school. A look-a-like kozuka (with five insects) is illustrated at Japanese Sword Fittings. A descriptive catalogue of the Collection of G.H. Naunton, Esq., completed and illustrated by Henri L. Joly, - 1912 on plate XXIX, №691 [LIB-1389 in this Collection] with the following description at page 54: "Shakudō, inlaid with butterfly, dragon-fly, grasshopper, locust and another insect, gold." See also tsuba TSU-0211 in this collection:
See also tsuba TSU-0211 in this collection:


-
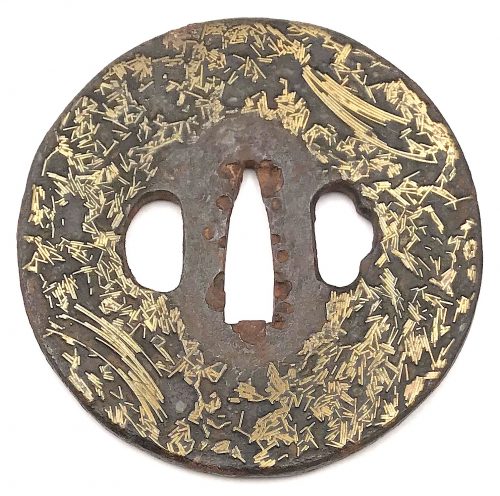 Gomoku-zōgan tsuba. Iron, inlaid with brass scrap (gomoku-zōgan), and polished. Height: 75.3 mm; Width 74.9 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. Weight 130.2 g. Edo, 18th century. Gary D. Murtha dedicates 10 pages to this type of tsuba: "...they were made by soldering brass overlay scraps to the iron plate". Actual gomoku-zōgan tsuba are seldom found in collections most likely because they have little if any artistic attributes. In addition, many have rough surfaces making them questionable for use on a sword. It is said that many of these were produced in Yokohama for export to the West during the late Edo period". G. D. Murtha then describes the technique of making gomoku-zōgan in every detail, and states that "The brass pieces are said to represent 'fallen pine needles', a description most likely created to add aesthetic value to help market the tsuba" [see:Gary D. Murtha. Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro. GDM Publications, 2016; pp. 160-161].
Gomoku-zōgan tsuba. Iron, inlaid with brass scrap (gomoku-zōgan), and polished. Height: 75.3 mm; Width 74.9 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. Weight 130.2 g. Edo, 18th century. Gary D. Murtha dedicates 10 pages to this type of tsuba: "...they were made by soldering brass overlay scraps to the iron plate". Actual gomoku-zōgan tsuba are seldom found in collections most likely because they have little if any artistic attributes. In addition, many have rough surfaces making them questionable for use on a sword. It is said that many of these were produced in Yokohama for export to the West during the late Edo period". G. D. Murtha then describes the technique of making gomoku-zōgan in every detail, and states that "The brass pieces are said to represent 'fallen pine needles', a description most likely created to add aesthetic value to help market the tsuba" [see:Gary D. Murtha. Japanese sword guards. Onin - Heianjo - Yoshiro. GDM Publications, 2016; pp. 160-161]. -
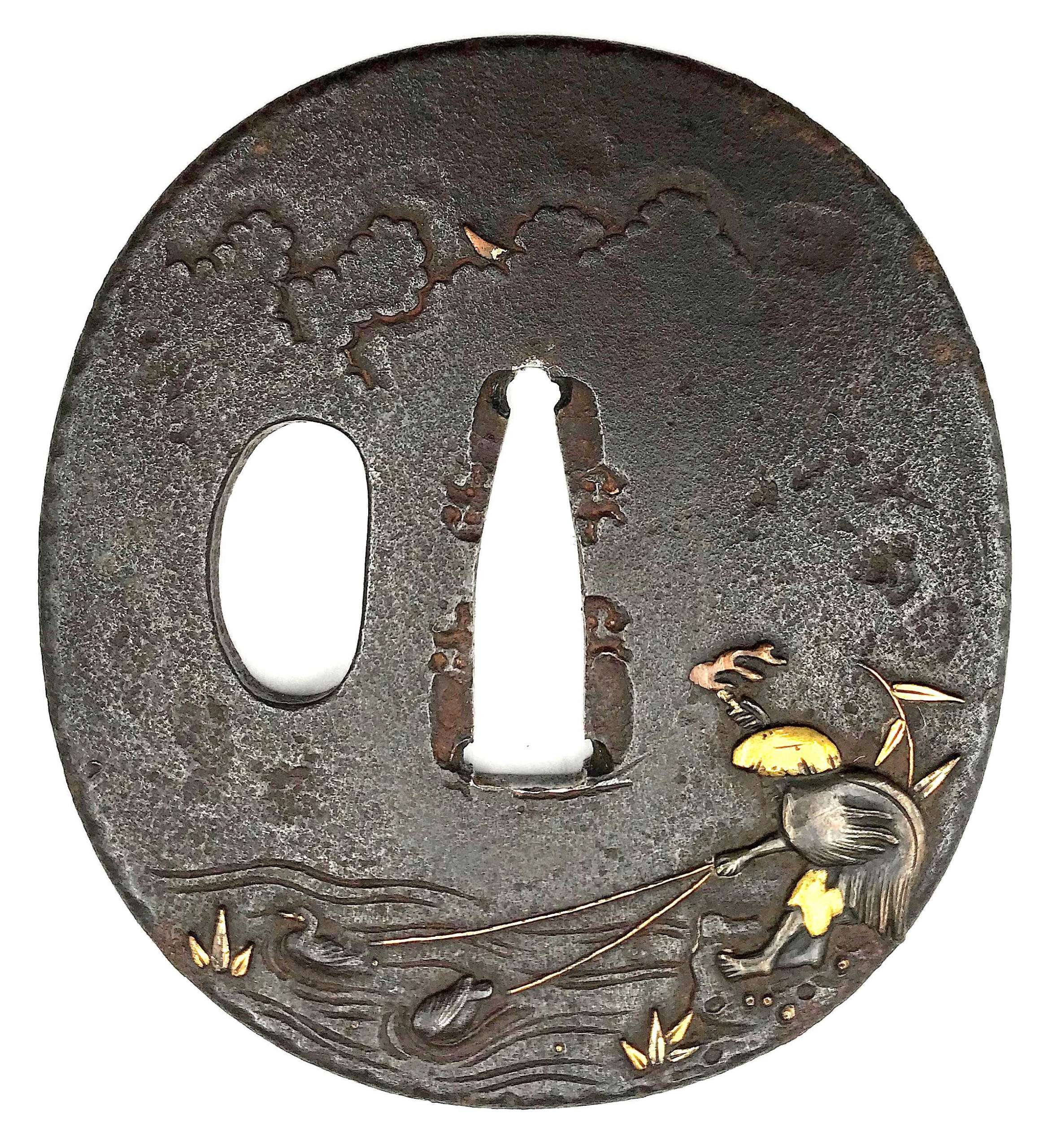 Iron tsuba of oval form carved and inlaid in gold and copper with cormorant fisherman in disguise. Unsigned. Dimensions: 67.7 mm x 61.5 mm x 3.8 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th century. "Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. [...] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one's master and keen eyesight." - from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also TSU-0212 and TSU-0096
Iron tsuba of oval form carved and inlaid in gold and copper with cormorant fisherman in disguise. Unsigned. Dimensions: 67.7 mm x 61.5 mm x 3.8 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th century. "Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. [...] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one's master and keen eyesight." - from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also TSU-0212 and TSU-0096 -
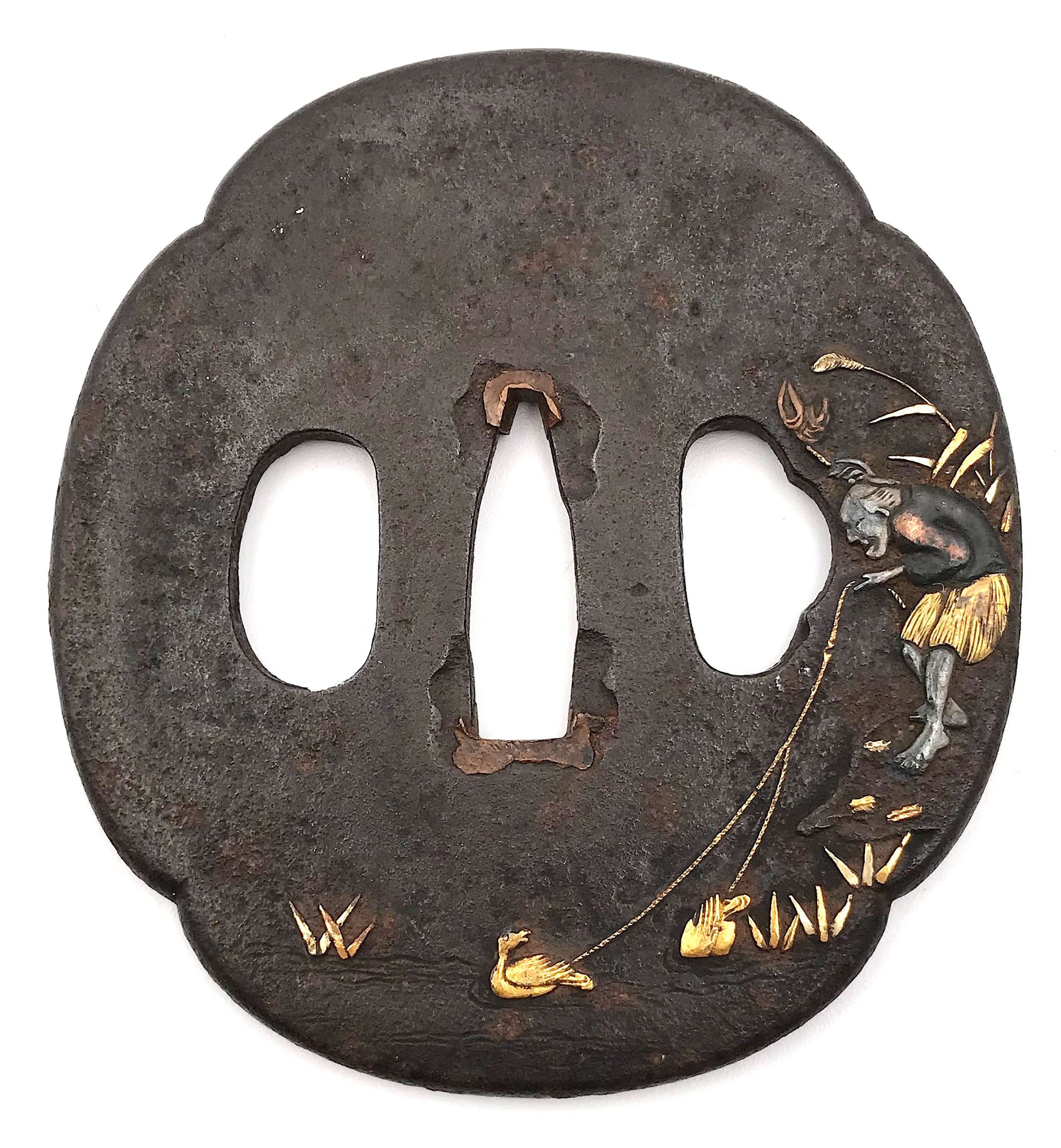 Mokkō form iron tsuba carved in relief and inlaid with soft metals (copper, gold, silver) with the design of a cormorant fisherman on the face and a boat on the reverse. Unsigned. Dimensions: 77 mm x 69 mm x 3.0 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th or 19th century. "Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. [...] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one's master and keen eyesight." - from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also in this collection TSU-0212 and TSU-0241.
Mokkō form iron tsuba carved in relief and inlaid with soft metals (copper, gold, silver) with the design of a cormorant fisherman on the face and a boat on the reverse. Unsigned. Dimensions: 77 mm x 69 mm x 3.0 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th or 19th century. "Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. [...] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one's master and keen eyesight." - from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also in this collection TSU-0212 and TSU-0241. -
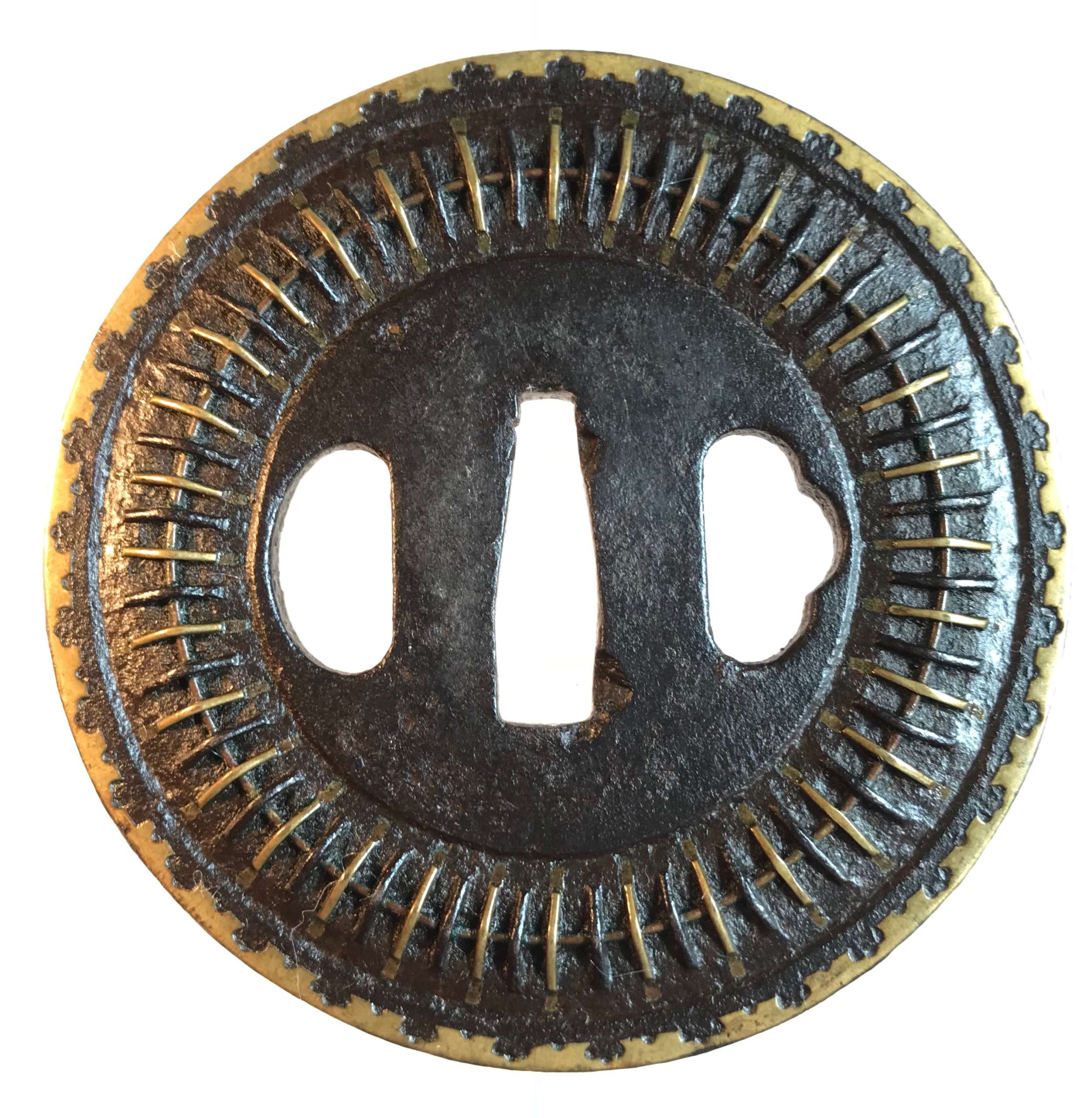 Mukade-zōgan tsuba with two types of wires. Iron, inlaid with brass and iron wire fastened to the surface with metal staples (mukade-zōgan); Brass inlay around the rim. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] Height: 85.8 mm; Width 86.2 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.3 mm. Weight 177.6 g. Early Edo, 17th century. http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Mukade-zōgan tsuba with two types of wires. Iron, inlaid with brass and iron wire fastened to the surface with metal staples (mukade-zōgan); Brass inlay around the rim. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] Height: 85.8 mm; Width 86.2 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.3 mm. Weight 177.6 g. Early Edo, 17th century. http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ -
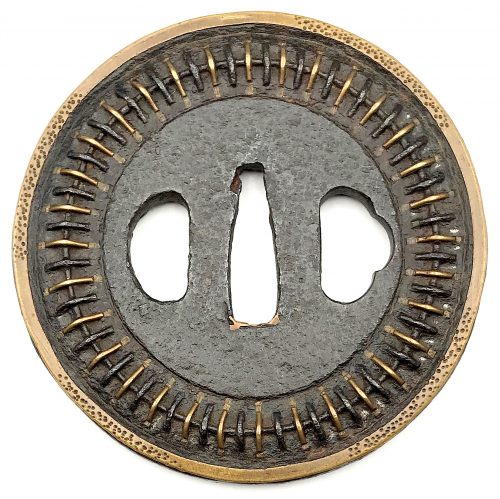 Iron tsuba of round form with circular iron wire fastened to the surface with iron and brass staples (mukade-zōgan); brass ring about 2.5 mm wide along the rim with chisel marks. Design repeats on the reverse. Copper sekigane. Early Edo, 17th century. Size: Height: 83.3 mm; width 83.9 mm; thickness at seppa-dai: 4.5 mm. Weight 173.6 g. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] See also: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ SOLD
Iron tsuba of round form with circular iron wire fastened to the surface with iron and brass staples (mukade-zōgan); brass ring about 2.5 mm wide along the rim with chisel marks. Design repeats on the reverse. Copper sekigane. Early Edo, 17th century. Size: Height: 83.3 mm; width 83.9 mm; thickness at seppa-dai: 4.5 mm. Weight 173.6 g. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] See also: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ SOLD -
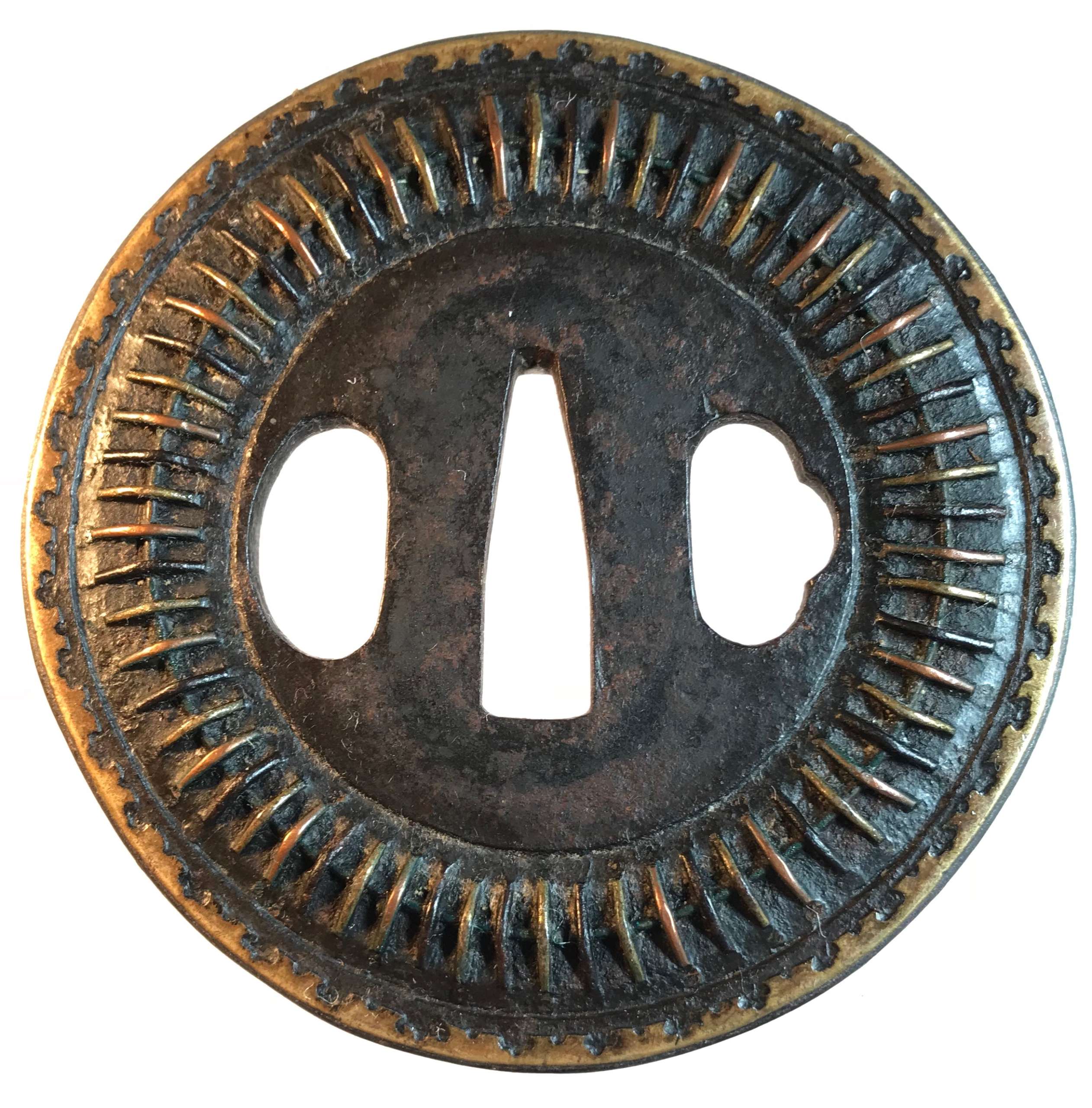 Iron tsuba of round form inlaid with brass, copper, and shakudō wire fastened to the surface with metal staples (mukade-zōgan); Scalloped brass inlay around the rim. Early Edo, 17th century. Height: 84.8 mm; Width 84.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.7 mm. Weight 161.6 g. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] See also: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Iron tsuba of round form inlaid with brass, copper, and shakudō wire fastened to the surface with metal staples (mukade-zōgan); Scalloped brass inlay around the rim. Early Edo, 17th century. Height: 84.8 mm; Width 84.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.7 mm. Weight 161.6 g. Design is thought to resemble a centipede. "Centipede-like inlay (mukade zogan) of alternating iron and brass staples produce an appearance that was particularly favored by Takeda Shingen (1521-1573), one of the most powerful warlords of his time. The centipede is sacred to Bishamon (God of War) and especially propitious for a warrior. Shingen type, 16th century.” [The Peabody Museum collection of Japanese sword guards with selected pieces of sword furniture, by John D. Hamilton. Photographs by Mark Sexton. Salem, MA, 1975.] See also: http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ -
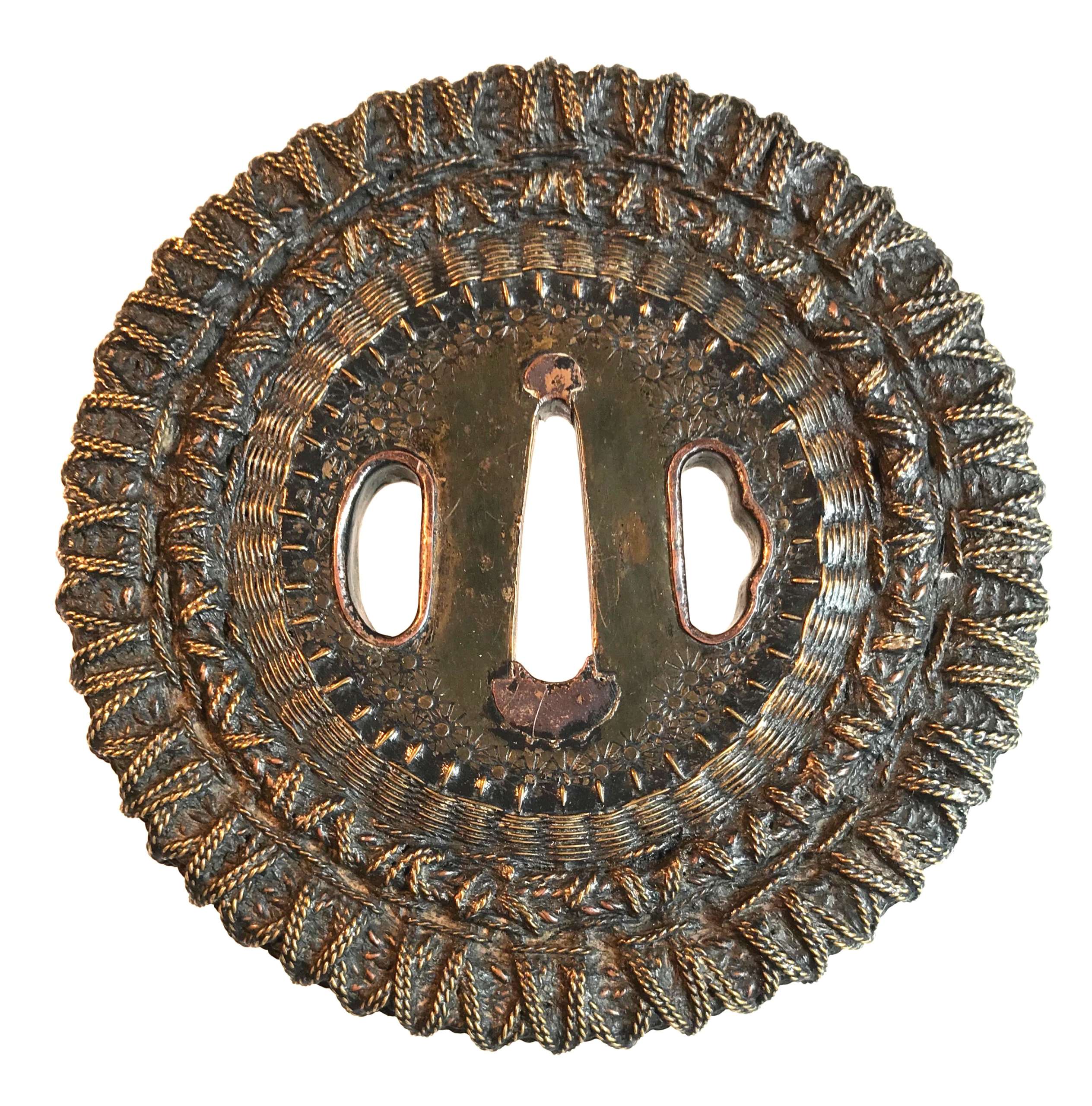 Shingen school (or style) tsuba of round form with an iron core of spoked-wheel shape, with its centre covered with a copper plate decorated with star-shaped punch marks. From this copper plate outward, the body is formed by brass and copper wire (flat and twisted) in a weave pattern. Both hitsu-ana are outlined in brass with a raised rim. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Edo period, 18th century. SOLD Height: 98.0 mm, Width: 97.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 6.0 mm. Weight: 290 g. NBTHK certificate №436696: 'Hozon' attestation. Citing "JAPANESE SWORD-MOUNTS IN THE COLLECTIONS OF FIELD MUSEUM" by Helen C. Gunsaulus, Assistant Curator of Japanese Ethnology. 61 plates. Berthold Laufer, Curator of Anthropology. Field Museum of Natural History, Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p.45: "An unusual group of tsuba popular in the late sixteenth century and afterwards is made up of those guards known as Shingen tsuba, a name which was derived from a sixteenth-century warrior, Takeda Shingen (Takeda Harunobu, 1521-73), who is said to have preferred this style of guard, as it combined strength and lightness. Under the category of "Shingen", four different types abd generally listed, though a fifth appears in the drawings in the Boston Catalogue of Okabe Kakuya "Japanese Sword Guards" (p. 21). It is square, that form which is said to have been used in Ashikaga days for scaling walls, the sword having been set up as a step. [...] The following descriptions include, however, the Shingen tsuba usually met with.
Shingen school (or style) tsuba of round form with an iron core of spoked-wheel shape, with its centre covered with a copper plate decorated with star-shaped punch marks. From this copper plate outward, the body is formed by brass and copper wire (flat and twisted) in a weave pattern. Both hitsu-ana are outlined in brass with a raised rim. Copper sekigane. Unsigned. Edo period, 18th century. SOLD Height: 98.0 mm, Width: 97.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 6.0 mm. Weight: 290 g. NBTHK certificate №436696: 'Hozon' attestation. Citing "JAPANESE SWORD-MOUNTS IN THE COLLECTIONS OF FIELD MUSEUM" by Helen C. Gunsaulus, Assistant Curator of Japanese Ethnology. 61 plates. Berthold Laufer, Curator of Anthropology. Field Museum of Natural History, Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p.45: "An unusual group of tsuba popular in the late sixteenth century and afterwards is made up of those guards known as Shingen tsuba, a name which was derived from a sixteenth-century warrior, Takeda Shingen (Takeda Harunobu, 1521-73), who is said to have preferred this style of guard, as it combined strength and lightness. Under the category of "Shingen", four different types abd generally listed, though a fifth appears in the drawings in the Boston Catalogue of Okabe Kakuya "Japanese Sword Guards" (p. 21). It is square, that form which is said to have been used in Ashikaga days for scaling walls, the sword having been set up as a step. [...] The following descriptions include, however, the Shingen tsuba usually met with.- So-called Mukade ("centipede") tsuba are made of iron in which a centepede is inlaid in brass or copper wire. Mukade tsuba of Myōchin and Umetada warkmanship have been found with the inscription, "Made to the taste of Takeda Shingen".
- There are those of solid iron, with need centers of brass, to the edges of which is affixed a weaving of brass and copper wires which is bound to the foundation disk by a rim, usually decorated simply.
- Another type is of solid iron, bored at intervals and laced with braided or twisted wires of copper and brass.
- The fourth type is a chrysanthemoid form, chiselled in open work and laced or woven tightly with copper and brass wire."

Compton Collection, Part II, p.p. 26-27, №54.
-
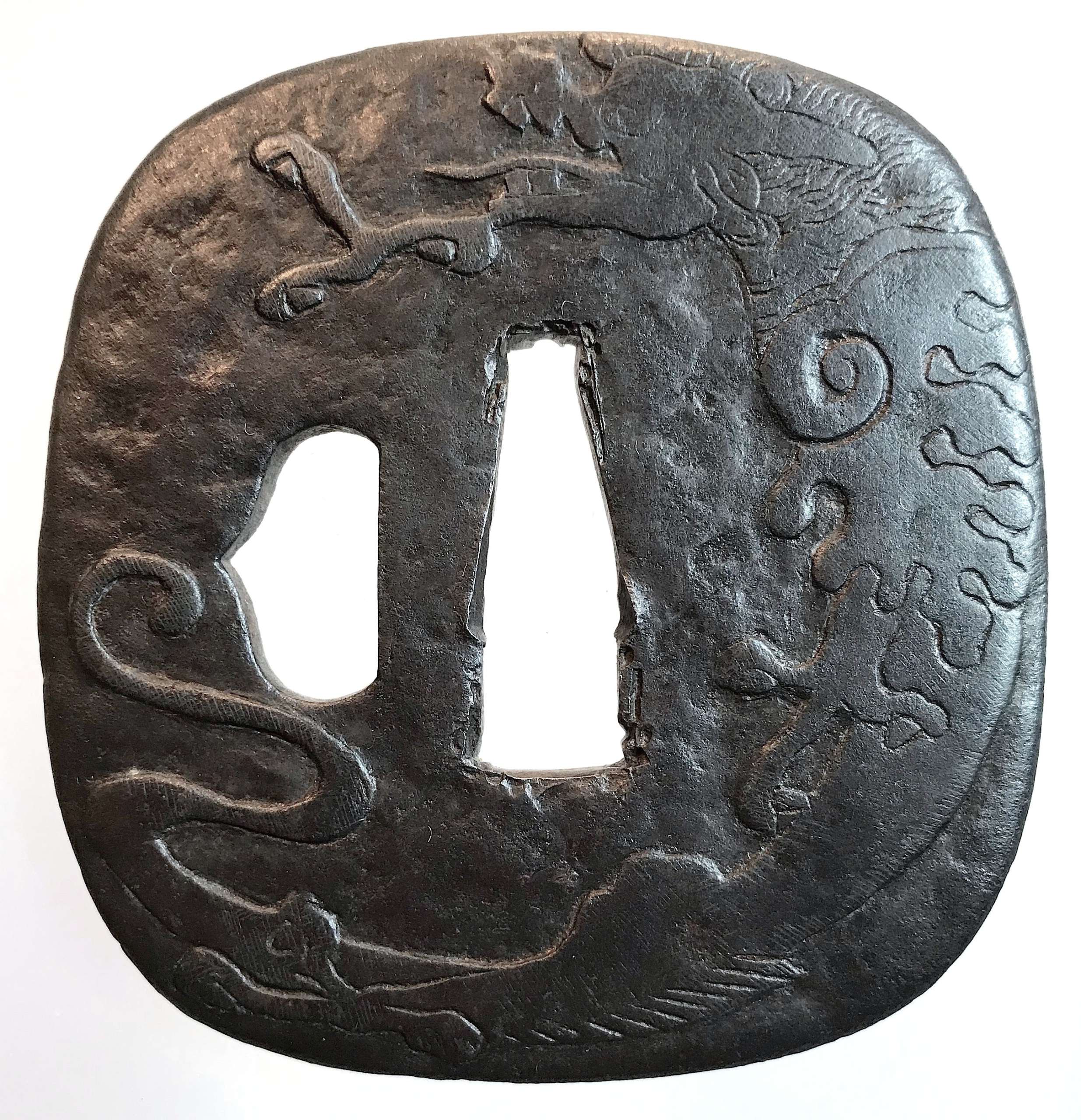 Shimizu-Jingo tsuba with a dragon and vajra (on reverse) motif. Unsigned. Possibly, 3rd or 4th master of Shimizu-Jingo family in Higo province. Iron. Low relief carving. Edo period, 1700's. Height: 75.4 mm, Width: 72.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm
Shimizu-Jingo tsuba with a dragon and vajra (on reverse) motif. Unsigned. Possibly, 3rd or 4th master of Shimizu-Jingo family in Higo province. Iron. Low relief carving. Edo period, 1700's. Height: 75.4 mm, Width: 72.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm


