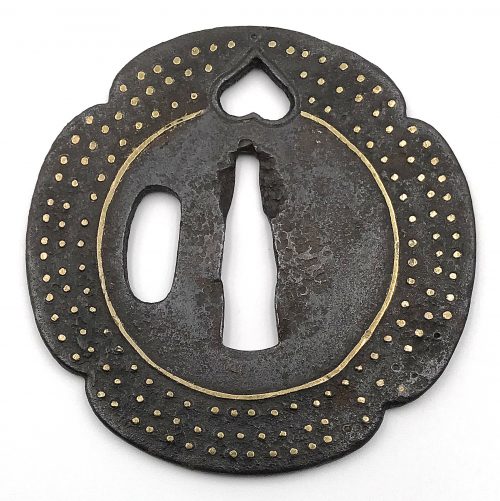
Iron tsuba of mokkō form decorated with inome (wild boar's eye) in openwork (sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate decorated with 3 concentric circular rows of brass dots in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire (sen-zōgan). Some dots and the outline of inome on the face are missing.
Ōnin school. Unsigned. Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century. Dimensions: 72.1 x 71.3 x 2.3 mm.-

-
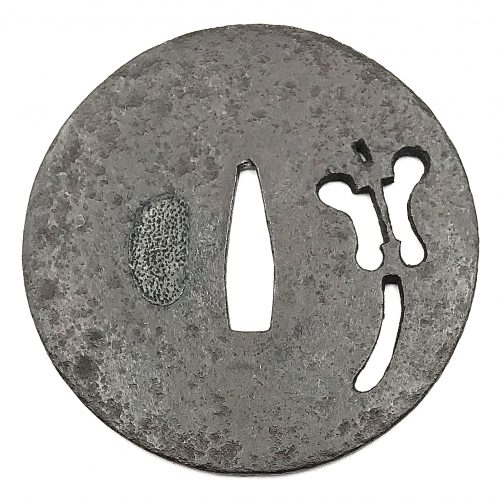 Iron tsuba of round form with design of military commander's fan (gunbai) in openwork (sukashi). Square rim. Hitsu-ana plugged with lead or tin. Ko-tosho school. Mid Muromachi period. Late 15th century: Entoku era [1489-92] / Meio era [1489-1501]. Height: 80.3 mm, Width: 81.5 mm, Rim thickness: 3.0 mm. Centre thickness: 3.5 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, №23 in Japanese Sword Guard Masterpieces from the Sasano Collection, 1994: Ko-tosho. Sukashi design: Military commander's fan (gunbai). Mid Muromachi period. Late 15th century (Entoku / Meio era). The military commander's fan (gunbai) was cherished by samurai warriors. This tsuba is relatively thick, with the large fan nicely positioned on the plate.
Iron tsuba of round form with design of military commander's fan (gunbai) in openwork (sukashi). Square rim. Hitsu-ana plugged with lead or tin. Ko-tosho school. Mid Muromachi period. Late 15th century: Entoku era [1489-92] / Meio era [1489-1501]. Height: 80.3 mm, Width: 81.5 mm, Rim thickness: 3.0 mm. Centre thickness: 3.5 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, №23 in Japanese Sword Guard Masterpieces from the Sasano Collection, 1994: Ko-tosho. Sukashi design: Military commander's fan (gunbai). Mid Muromachi period. Late 15th century (Entoku / Meio era). The military commander's fan (gunbai) was cherished by samurai warriors. This tsuba is relatively thick, with the large fan nicely positioned on the plate. -
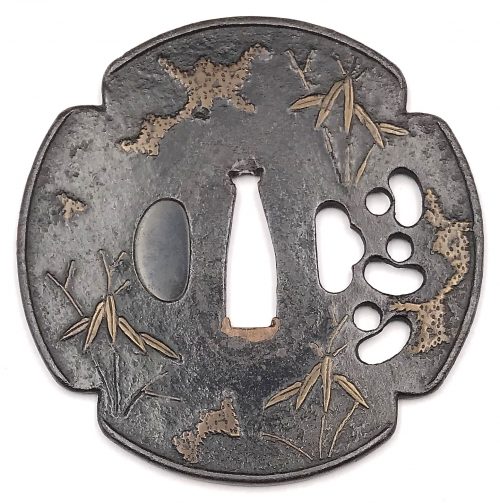 Iron tsuba of four-lobbed mokkō form (possibly it was circular and then altered to produce the mokkō) with slightly raised rim decorated with three kukurizaru ('tied up monkey' toy) in openwork (sukashi) next to kogai-hitsu-ana; inlaid in red-ish copper (suaka) with the design of bamboo stems and leaves, and shapeless masses which most probably represent snow. Kozuka-hitsu-ana plugged with shakudo. Probably original kogai-hitsu-ana. Copper sekigane. Surface still covered with lacquer (urushi). Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Size: 86.1 x 85.8 x 2.6 mm NBTHK Certificate №4002543: Hozon - "Worthy of preservation" (Attribution: Mumei Heianjō Zōgan)
Iron tsuba of four-lobbed mokkō form (possibly it was circular and then altered to produce the mokkō) with slightly raised rim decorated with three kukurizaru ('tied up monkey' toy) in openwork (sukashi) next to kogai-hitsu-ana; inlaid in red-ish copper (suaka) with the design of bamboo stems and leaves, and shapeless masses which most probably represent snow. Kozuka-hitsu-ana plugged with shakudo. Probably original kogai-hitsu-ana. Copper sekigane. Surface still covered with lacquer (urushi). Late Muromachi period (1514-1573). Size: 86.1 x 85.8 x 2.6 mm NBTHK Certificate №4002543: Hozon - "Worthy of preservation" (Attribution: Mumei Heianjō Zōgan) -
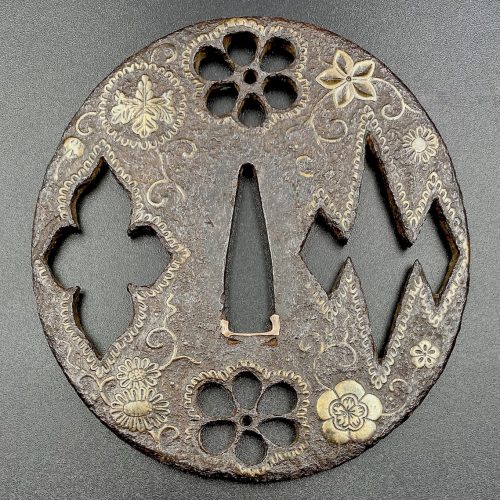 Iron tsuba of a round form (maru-gata) pierced (sukashi) with two six-petal flowers at 6 and 12 o’clock and modified lozenges at 3 and 9 o’clock, and inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils and flowers (chrysanthemum, cherry blossom, Chinese bellflower, paulownia); openings outlined with scalloped brass wire. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer on the surface. Nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Some elements of inlay missing. The rim with conspicuous tekkotsu, quite worn. Measurements: Height 92.0 mm; Width 86.3 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 3.2 mm, at rim 4.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier.
Iron tsuba of a round form (maru-gata) pierced (sukashi) with two six-petal flowers at 6 and 12 o’clock and modified lozenges at 3 and 9 o’clock, and inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) with tendrils and flowers (chrysanthemum, cherry blossom, Chinese bellflower, paulownia); openings outlined with scalloped brass wire. The plate is slightly concave with traces of lacquer on the surface. Nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Some elements of inlay missing. The rim with conspicuous tekkotsu, quite worn. Measurements: Height 92.0 mm; Width 86.3 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 3.2 mm, at rim 4.2 mm. Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) or earlier. -
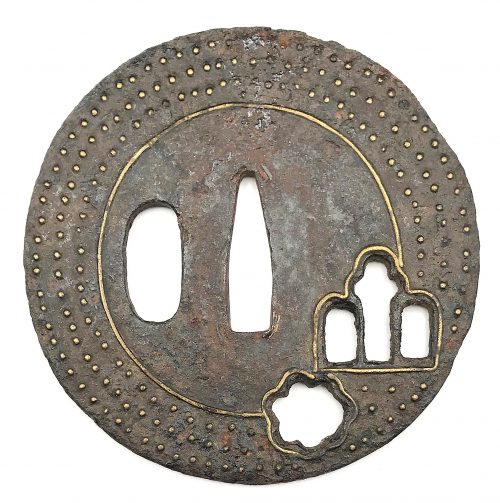 Iron tsuba of round form with design of iris and snowflake in openwork (ko-sukashi or small cut-outs) outlined with brass wire. Three concentric rows of brass dots (ten-zōgan), with a brass circular line inside the innermost row of dots (missing on the back). Hitsu-ana is not outlined with brass wire, which let us suppose that it was cut out at a later date. Iron and brass. Ko-sukashi and ten-zōgan technique. Mid Muromachi period (1454-1513). Height: 74.0 mm, Width: 73.6 mm, Thickness: 3.0 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form with design of iris and snowflake in openwork (ko-sukashi or small cut-outs) outlined with brass wire. Three concentric rows of brass dots (ten-zōgan), with a brass circular line inside the innermost row of dots (missing on the back). Hitsu-ana is not outlined with brass wire, which let us suppose that it was cut out at a later date. Iron and brass. Ko-sukashi and ten-zōgan technique. Mid Muromachi period (1454-1513). Height: 74.0 mm, Width: 73.6 mm, Thickness: 3.0 mm.NBTHK certification of 1968: "Kicho". Condition is relatively poor: rust, missing inlay, scratches.
While representation of the snowflake is rather standard, the meaning of the other cut-out design was initially less clear. Similar symbol was found at (1) "Kokusai Tosogu Kai, International Convention & Exhibition, September 24-25, 2005, The Frazier Historical Arms Museum, Louisville, Kentucky, USA"; on page 21 there is a photograph J-6 of a ko-tosho tsuba with "iris theme openwork"; (2) Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections. Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997; page 11, lot 6 - a ko-katchushi tsuba of early Muromachi period fith "simple design of stylized iris". In both sources the symbol is explained as 'iris" (kakitsubata).
Freeman and Sharpe collections. Sotheby's, 1997.

Kokusai Tosogu Kai, September 24-25, 2005.
-
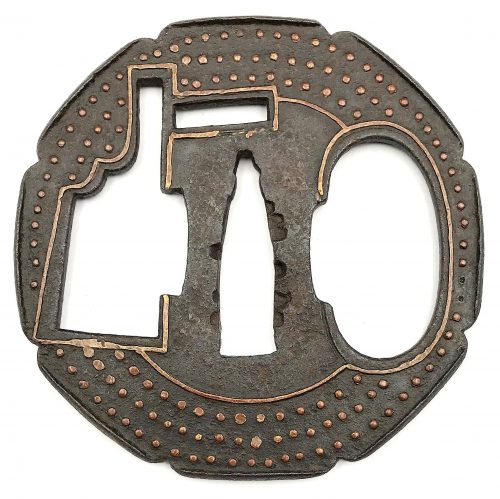 Iron tsuba of octafoil form with design of rudder (kaji) and lake in openwork (sukashi) outlined with brass wire. Thin plate also decorated with three concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. Cut-outs for kozuka and kogai probably added later. Slightly raised rim between the indentations (suki-nokoshi-mimi). The inlaid metal of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, not brass. Sekigane, visible on the NBTHK paper photo, are missing, possibly removed by a previous owner. Muromachi period. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Dimensions: 81.2 mm x 81.8 mm x 2.7 mm. Weight: 79.0 g. Large nakago-ana: 34 mm high and 10 mm wide. NBTHK certificate №455786: Hozon. Note regarding design: it was quite hard to interpret the big oval opening. The first suggestion was 'sea cucubmer', and it was based on a design published by Kazutaro Torigoye [Kodogu and tsuba. International collections not published in my books (Toso Soran), 1978] on page 202: Katchūshi tsuba: Sea cucumber and butterfly. Look and judge yourself:The second suggestion - 'lake' - came from [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014], page 14 №5:
Iron tsuba of octafoil form with design of rudder (kaji) and lake in openwork (sukashi) outlined with brass wire. Thin plate also decorated with three concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. Cut-outs for kozuka and kogai probably added later. Slightly raised rim between the indentations (suki-nokoshi-mimi). The inlaid metal of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, not brass. Sekigane, visible on the NBTHK paper photo, are missing, possibly removed by a previous owner. Muromachi period. Ōnin school. Unsigned. Dimensions: 81.2 mm x 81.8 mm x 2.7 mm. Weight: 79.0 g. Large nakago-ana: 34 mm high and 10 mm wide. NBTHK certificate №455786: Hozon. Note regarding design: it was quite hard to interpret the big oval opening. The first suggestion was 'sea cucubmer', and it was based on a design published by Kazutaro Torigoye [Kodogu and tsuba. International collections not published in my books (Toso Soran), 1978] on page 202: Katchūshi tsuba: Sea cucumber and butterfly. Look and judge yourself:The second suggestion - 'lake' - came from [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014], page 14 №5:
Torigoye: sea cucumber and butterfly.
Opening on my tsuba looks more like the 'lake'. Also, rudder and lake make more sense than rudder and sea cucumber. At least to me...
Ko-Katchūshi tsuba: Lake and pine.
-
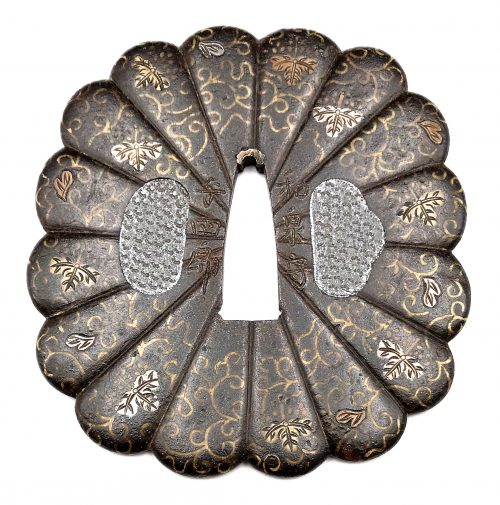 The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:
The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:"Early signed example of the work of Koike Naomasa. The kiku shape iron plate is well finished. The flush inlay is brass, for the scroll work on both sides, with the leaves and kiri mon in brass, copper and silver with strong detail carving. Some of the inlay goes almost over the edge, which is goishi gata. The large hitsuana are plugged in lead with starburst kokuin surface design. [...]The face is signed in deep bold kanji: Koike Naomasa; the back is signed: Izumi no Kami, on the right and Yoshiro on the left. There are one or two small pieces of inlay missing. Sold by Sotheby London, Oct. 27, 1981, lot 368. Height = 86 mm, thickness (seppa-dai) = 3.75 mm, (edge) = 4 mm."
Another similar example presented at: "Tsuba" by Günter Heckmann, 1995, №T55 — "Designation: Koike Naomasa. Mid Edo, end of the 17th century. Iron, hira-zogan in brass, copper, silver and shakudo, katakiri-bori. Tendrils and leaves. 87.0 x 78.0 x 4.0 mm." Reference: Japanische Schwertzierate by Lumir Jisl, 1967, page. 13. [SV: Actually, his tsuba is signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back; and Koike Naomasa on the front, exactly as Robert Haynes's tsuba. Dating this tsuba Mid-Edo, 17th century may be considered a misattribution]. More details regarding the Yoshirō tsuba. -
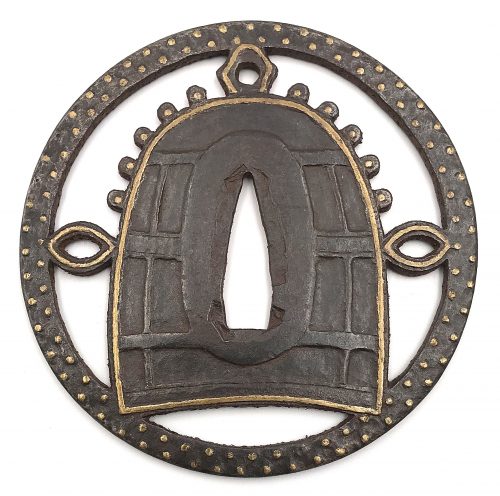

Iron tsuba of round form with brown patina decorated with the design of a Buddhist temple bell (tsurigane) in openwork (sukashi), with details outlined in brass wire (sen-zōgan), the outer ring decorated with two rows of brass dots (ten-zōgan), and the bell details carved in sukidashi-bori as on kamakura-bori pieces.
Ōnin school. Unsigned. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Dimensions: 88.8 x 88.3 x 3.0 mm. As per Merrily Baird, two legends are usually associated with the image of tsurigane, a large, suspended Buddhist bell: one is that of Dojo Temple (Dojo-ji), and the other is of Benkei stealing the tsurigane of Miidera Temple. Interestingly, this type of bell (tsurigane) is not described as a family crest (mon), while suzu and hansho bells are. -
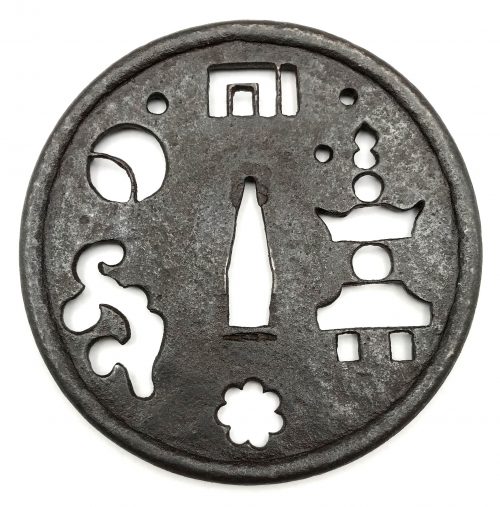 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of moon, stars, cloud, snowflake, gorintō, and Genji-mon in negative openwork (in-sukashi). Raised tubular rim (dote-mimi). Deep black patina, traces of lacquer. Naka-daka type of plate (thicker in center, getting thiner towards the rim). Visible gap between the rim and the plate. Dimensions: Height: 91.7 mm; Width: 90.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.5 mm, plate before rim: 2.2 mm, of the rim: 5.6 mm. At least Mid Muromachi period, 15th century, but possibly earlier. In 'Silver Book', commenting tsuba №34 Sasano writes: "The technique used to create the rim is the same used for the peak (koshimaki) of helmets (kabuto) during the Kamakura and Nanbokucho periods." On the other hand, the abundance of sukashi elements points towards later times, perhaps late Muromachi or even Momoyama period. "Gorintō is a grave stone composed of five pieces, piled on one the other, representing, from the bottom upward, earth, water, fire, wind, and heaven, respectively" [Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1. AFU, 1993, p. 6. / LIB-1554]. A romantic description of the piece may look like this: The air is scented (incense symbol); it's a graveyard, marked by gorintō; a winter (snowflake) evening or night (moon, stars); mist is rising from a ravine towards moon. I did not manage to find a katchūshi piece of this design, only a few Kamakura-bori tsuba:
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of moon, stars, cloud, snowflake, gorintō, and Genji-mon in negative openwork (in-sukashi). Raised tubular rim (dote-mimi). Deep black patina, traces of lacquer. Naka-daka type of plate (thicker in center, getting thiner towards the rim). Visible gap between the rim and the plate. Dimensions: Height: 91.7 mm; Width: 90.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.5 mm, plate before rim: 2.2 mm, of the rim: 5.6 mm. At least Mid Muromachi period, 15th century, but possibly earlier. In 'Silver Book', commenting tsuba №34 Sasano writes: "The technique used to create the rim is the same used for the peak (koshimaki) of helmets (kabuto) during the Kamakura and Nanbokucho periods." On the other hand, the abundance of sukashi elements points towards later times, perhaps late Muromachi or even Momoyama period. "Gorintō is a grave stone composed of five pieces, piled on one the other, representing, from the bottom upward, earth, water, fire, wind, and heaven, respectively" [Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1. AFU, 1993, p. 6. / LIB-1554]. A romantic description of the piece may look like this: The air is scented (incense symbol); it's a graveyard, marked by gorintō; a winter (snowflake) evening or night (moon, stars); mist is rising from a ravine towards moon. I did not manage to find a katchūshi piece of this design, only a few Kamakura-bori tsuba:
100 selected tsuba from European collections. Catalogue by Robert Haynes and Robert Burawoy, 1984, page 16, №5.
While the upper tsuba is dated end of Muromachi, the lower is attributed to the 17th century - Momoyama or early Edo period, though the author put this attribution under question. Deciphering of the strangely shaped opening to the left of nakago-ana is sometimes "a conventional scroll", and sometimes - a fern or bracken. I think mine is a cloud or mist, but I don't have any material evidence proving this understanding and came to conclusion by context only. It may easily be a dinosaurs playing ball. The fact that this thing always accompanies the Genji-mon, or incense symbol, it may be a scent itself.
Japanese Sword Fittings. Collection of G.H. Naunton, Esq., by Henri L. Joly, - 1912; №9.
-
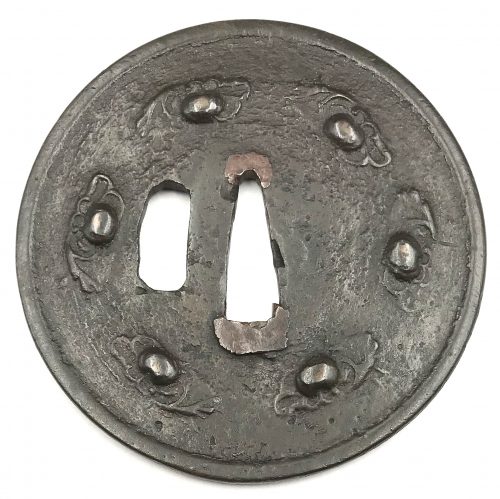 Circular form tsuba made by a mirror-maker, i.e. kagamishi. Cast yamagane plate with design of six persimmons on their peduncles surrounded by leaves. Slightly raised rounded square rim. Hitsu-ana is brutally cut later in time. Copper sekigane. Early Muromachi period (1393-1457) or earlier. The inscription on the box reads: "Kamakura or Muromachi Period. Yamagane Tsuba". Dimensions: 81.9 x 81.6 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.8 - 3.0 mm, rim 3.4 mm.
Circular form tsuba made by a mirror-maker, i.e. kagamishi. Cast yamagane plate with design of six persimmons on their peduncles surrounded by leaves. Slightly raised rounded square rim. Hitsu-ana is brutally cut later in time. Copper sekigane. Early Muromachi period (1393-1457) or earlier. The inscription on the box reads: "Kamakura or Muromachi Period. Yamagane Tsuba". Dimensions: 81.9 x 81.6 mm; thickness at seppa-dai 2.8 - 3.0 mm, rim 3.4 mm. -
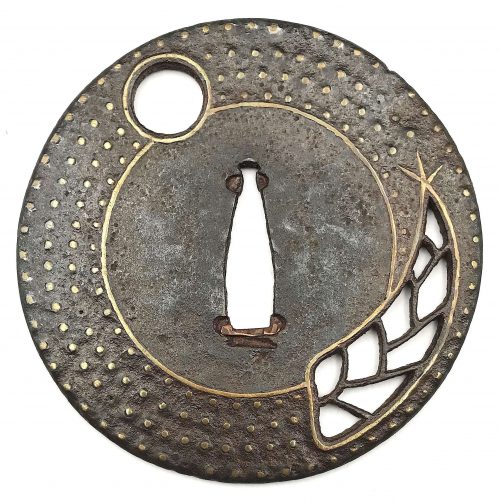 Ōnin shinchū ten-zōgan tsuba. Iron tsuba of round form decorated with full moon and bamboo shoot (takenoko) motif executed in openwork (sukashi) and inlaid with four concentric rows of brass dots (ten-zōgan). The innermost row of dots as well as the sukashi openings outlined with the inlaid linear brass wire. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Diameter: 82.0 mm; Thickness: 2.8 mm Cited from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 72: "In Japanese art, the appearance of bamboo shoots is often without symbolic meaning. In other cases, however, the shoots are emblematic of Moso (Chinese: Meng Tsung/Meng Zong), a paragon of filial piety who dug through snow to find shoots for his mother. ... especially in miniature art forms, let bamboo shoots alone speak for the full story." The full story is this (See THE TWENTY-FOUR PARAGONS OF FILIAL PIETY [ERSHISI XIAO]):
Ōnin shinchū ten-zōgan tsuba. Iron tsuba of round form decorated with full moon and bamboo shoot (takenoko) motif executed in openwork (sukashi) and inlaid with four concentric rows of brass dots (ten-zōgan). The innermost row of dots as well as the sukashi openings outlined with the inlaid linear brass wire. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Diameter: 82.0 mm; Thickness: 2.8 mm Cited from Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 72: "In Japanese art, the appearance of bamboo shoots is often without symbolic meaning. In other cases, however, the shoots are emblematic of Moso (Chinese: Meng Tsung/Meng Zong), a paragon of filial piety who dug through snow to find shoots for his mother. ... especially in miniature art forms, let bamboo shoots alone speak for the full story." The full story is this (See THE TWENTY-FOUR PARAGONS OF FILIAL PIETY [ERSHISI XIAO]):Tears That Brought Bamboo-shoots From the Frozen Earth: Meng Zong Meng Zong lived during the Three Kingdoms Period of China's past. His father died when he was young, and he and his mother struggled to survive. One winter his mother was stricken with a serious illness, and craved some bamboo-shoot broth as medicine. But in the depths of winter, with snow and ice blanketing the ground, where was anyone to find fresh bamboo shoots, shoots that emerge only in the warm months? Nonetheless, Meng Zong, to avoid disappointing his mother, bravely fetched his shovel and went out into the white landscape in search of bamboo shoots. In the thicket he found only frosted leaves and green stalks coated with snowflakes and ice. Look as he might, there were simply no fresh shoots growing in the winter. The thought of his poor mother lying sick on her bed, waiting for bamboo-broth medicine, made his heartache. Uncontrollably, tears began to fall in rivers to the ground beneath the tall, emerald canes. Even now, as his tears flowed down, he kept a light of faith in his heart. If he was truly sincere in his search, perhaps.... Just then Meng Zong nearly tripped and fell over a sharply protruding lump of earth. He quickly knelt down and knocked aside the dirt with his trembling fingers. How uncanny! Underneath his frozen hands he discovered a bed of fresh, tender bamboo shoots! Overjoyed, he gathered up a coatful and carried them back home. The broth that he quickly set stewing in the pot soon cured his mother's illness. The neighbors, hearing the story, exclaimed that it was the strength of his sincere, unselfish, filial resolve that inspired heaven and earth to respond, and to bring up, out of season, the fresh shoots that cured his mother's disease. Before Meng Zong's prayers generated this miracle, it was normally considered impossible for bamboo shoots to grow in the winter. After the nmiracle took place, however, people were able to gather and to eat bamboo shoots all year round. The winter variety that existed hereafter became known as "winter shoots." The villagers were deeply influenced by Meng Zong's courage and devotion. They renamed the spot where the event took place, "Meng Zong's Bamboo Grove". We can now enjoy bamboo sprouts during the winter as well, and as we do so, it is fitting to recollect Meng Zong's outstanding example of filial respect, and reflect on our conduct as sons and daughter of our parents. A verse in his honor says, His teardrops transformed winter at the roots; Up from the ice crept tender bamboo shoots. Instantly, the winter-sprouts matured; Heaven's will: a happy, peaceful world.
-
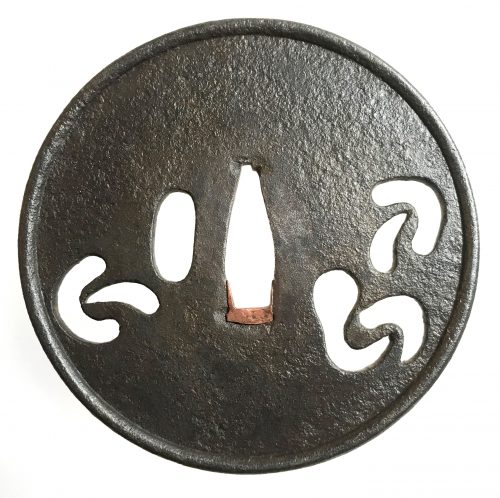 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of pine tree mushrooms (matsutake) in openwork (sukashi). Hitsu-ana of elongated oval form. Raised rim (mimi) with iron bones (tekkotsu). Copper sekigane. Size: 84.5 mm x 85.1 mm; thickness: 3.0 mm (center), 5.6 mm (rim). Mid Muromachi period, 15th century. The shape and width of the rim, as well as the shape of the hitsu-ana, argue for earlier Muromachi. Tsuba is slightly wider than high, that might suggest middle of Muromachi age. According to Robert Haynes, circa 1450-1500.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of pine tree mushrooms (matsutake) in openwork (sukashi). Hitsu-ana of elongated oval form. Raised rim (mimi) with iron bones (tekkotsu). Copper sekigane. Size: 84.5 mm x 85.1 mm; thickness: 3.0 mm (center), 5.6 mm (rim). Mid Muromachi period, 15th century. The shape and width of the rim, as well as the shape of the hitsu-ana, argue for earlier Muromachi. Tsuba is slightly wider than high, that might suggest middle of Muromachi age. According to Robert Haynes, circa 1450-1500. -
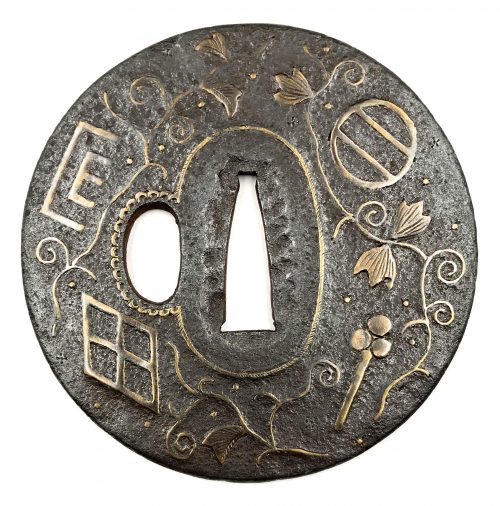 Thin iron tsuba of round form with design of family crests (mon) and arabesque (karakusa) in brass or copper inlay (suemon-zōgan) and occasional scattered brass dots or nail heads in ten-zōgan. Seppa-dai outlined with brass wire in the shape of a rope; kozuka-hitsu-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire. Rounded rim with iron bones (tekkotsu). The surface covered with lacquer (urushi). Ōnin school. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Family crests on the face: 1:30: Two lines (double stripe) encircled (maruni futatsu biki). 4:30: Stylized clove (choji). 7:30: Divided rhombus, or four lozenges incorporated in one (wari-bishi); it is also called Takeda-bishi, the family crest of warrior Takeda Shingen (among the others). 10:00: Stylized Genji-mon (Genji kō-zu) or incense symbol. On the reverse: 2:00 - "Chinese cloud" not a crest. 5:00: Bit (Kutsuwa) 7:30: Number four in a fan (ōgi-san) 10:30: Two dots in a well frame (igeta).
Thin iron tsuba of round form with design of family crests (mon) and arabesque (karakusa) in brass or copper inlay (suemon-zōgan) and occasional scattered brass dots or nail heads in ten-zōgan. Seppa-dai outlined with brass wire in the shape of a rope; kozuka-hitsu-ana outlined with scalloped brass wire. Rounded rim with iron bones (tekkotsu). The surface covered with lacquer (urushi). Ōnin school. Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Family crests on the face: 1:30: Two lines (double stripe) encircled (maruni futatsu biki). 4:30: Stylized clove (choji). 7:30: Divided rhombus, or four lozenges incorporated in one (wari-bishi); it is also called Takeda-bishi, the family crest of warrior Takeda Shingen (among the others). 10:00: Stylized Genji-mon (Genji kō-zu) or incense symbol. On the reverse: 2:00 - "Chinese cloud" not a crest. 5:00: Bit (Kutsuwa) 7:30: Number four in a fan (ōgi-san) 10:30: Two dots in a well frame (igeta). -
 Iron tsuba of round form pierced with design of paulownia (kiri) in a circle in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi), details carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori). Hitsu-ana were cut later and then both plugged with lead or pewter. Brown patina. The most unusual characteristic of this tsuba is its 'positiveness': the absolute majority of Kamakura-bori tsuba are of ko-sukashi type, i.e. with small openings, presenting the motif in negative silhouette. Kamakura-bori school. Muromachi period (ca. 1450). Size: Height: 85.1 mm, width: 84.8 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, at rim: 2.8 mm. Weight: 79.1 g. A similar tsuba is presented at Japanese Swords and Sword Fittings from the Collection of Dr. Walter Ames Compton. Part I. Christie's, New York, March 31, 1992, page 11, №3: "A Kamakura-bori tsuba. Muromachi period, ca. 1450. The round iron plate is pierced with an openwork design of a paulownia crest (kiri-mon), the surface details of which are carved in low relief. The design is repeated on the reverse. The edge is slightly raised and the rim has some iron bones. 78 mm x 77 mm x 3.5 mm. Hakogaki by Sato Kanzan, dated summer 1973."
Iron tsuba of round form pierced with design of paulownia (kiri) in a circle in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi), details carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori). Hitsu-ana were cut later and then both plugged with lead or pewter. Brown patina. The most unusual characteristic of this tsuba is its 'positiveness': the absolute majority of Kamakura-bori tsuba are of ko-sukashi type, i.e. with small openings, presenting the motif in negative silhouette. Kamakura-bori school. Muromachi period (ca. 1450). Size: Height: 85.1 mm, width: 84.8 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, at rim: 2.8 mm. Weight: 79.1 g. A similar tsuba is presented at Japanese Swords and Sword Fittings from the Collection of Dr. Walter Ames Compton. Part I. Christie's, New York, March 31, 1992, page 11, №3: "A Kamakura-bori tsuba. Muromachi period, ca. 1450. The round iron plate is pierced with an openwork design of a paulownia crest (kiri-mon), the surface details of which are carved in low relief. The design is repeated on the reverse. The edge is slightly raised and the rim has some iron bones. 78 mm x 77 mm x 3.5 mm. Hakogaki by Sato Kanzan, dated summer 1973."
Compton's Collection, Part I, p. 11, №3.
-
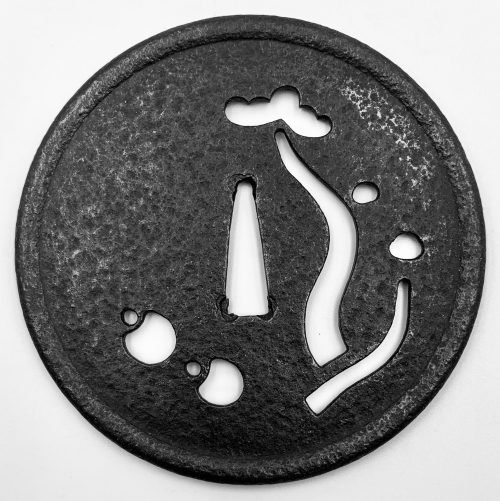

Iron tsuba of circular form with design of pine trees (matsu) and monkey toys (kukurizaru) in openwork (ko-sukashi). Ko-Katchushi school.
Raised rim (mimi) with iron bones (tekkotsu). Size: Diameter: 99.5 mm; Thickness: 2.1 mm at centre; 4.3 mm at the rim.Early Muromachi period: 15th century (Kakitsu - Bun'an era, 1441 - 1449).
-
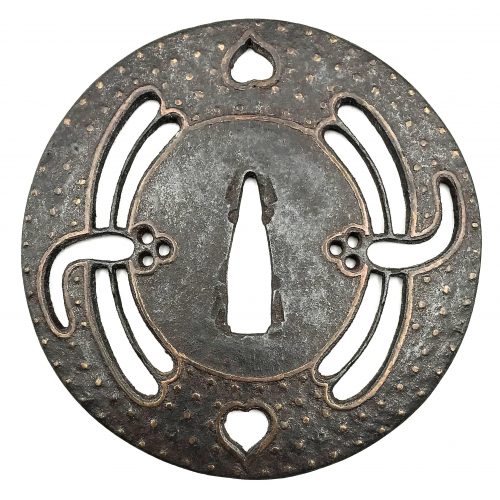 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with two boar's eyes (inome) and two dragonflies (tombo) in small openwork (ko-sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate also decorated with 2 to 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. The inlaid metal is of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, and not brass. The surface has remnants of lacquer. Ōnin school. Mid Muromachi period, middle of 15th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 90 mm, thickness: 3.2 mm. Notes regarding design: "According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13]. Two other cutouts - in the form of what in European tradition symbolizes the heart, on the top and in the bottom of tsuba disc - may have two different explanations. The most usual one, inome - "Heart-shaped pattern, which is said to go back to the shape of a wild boar's eye" [Markus Sesko. Encyclopedia of Japanese Swords. Print and publishing: Lulu Enterprises, Inc., 2014.]. This understanding is shared by Robert Haynes [Robert E. Haynes. Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010.] and elsewhere, with an exception of Okabe-Kakuya [Okabe-Kakuya. JAPANESE SWORD GUARDS. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. In cooperation with the department of Chinese and Japanese art; - 1908, p. 14], who provides the illustration of inome-shaped cut-outs with the following explanation: " The tsuba shown in Fig. 13 approaches a square form with rounded corners and is perforated with Aoi decoration. But this book was written long time ago, when people even at MFA might not know enough...
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with two boar's eyes (inome) and two dragonflies (tombo) in small openwork (ko-sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate also decorated with 2 to 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. The inlaid metal is of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, and not brass. The surface has remnants of lacquer. Ōnin school. Mid Muromachi period, middle of 15th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 90 mm, thickness: 3.2 mm. Notes regarding design: "According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13]. Two other cutouts - in the form of what in European tradition symbolizes the heart, on the top and in the bottom of tsuba disc - may have two different explanations. The most usual one, inome - "Heart-shaped pattern, which is said to go back to the shape of a wild boar's eye" [Markus Sesko. Encyclopedia of Japanese Swords. Print and publishing: Lulu Enterprises, Inc., 2014.]. This understanding is shared by Robert Haynes [Robert E. Haynes. Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010.] and elsewhere, with an exception of Okabe-Kakuya [Okabe-Kakuya. JAPANESE SWORD GUARDS. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. In cooperation with the department of Chinese and Japanese art; - 1908, p. 14], who provides the illustration of inome-shaped cut-outs with the following explanation: " The tsuba shown in Fig. 13 approaches a square form with rounded corners and is perforated with Aoi decoration. But this book was written long time ago, when people even at MFA might not know enough... The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.
The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.
 There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
 Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."
Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."
-
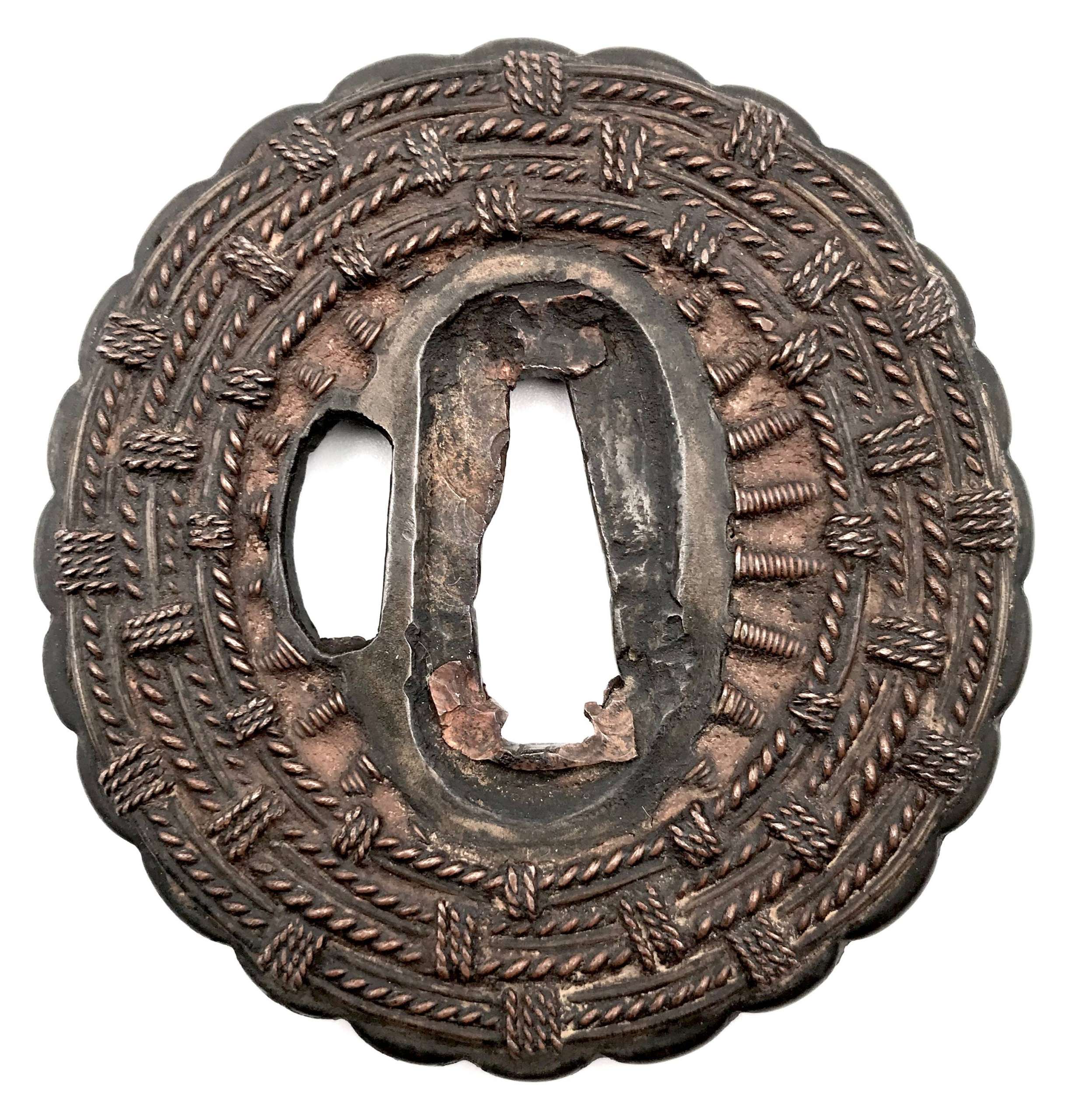 Tsuba of chrysanthemoid form (kikka-gata) with yamagane core and woven copper wire pattern. Copper sekigane. Shingen school. Height: 70.2 mm; Width 67.2 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.4-3.6 mm, overall 7.3 mm. Weight 82.7 g Inscription on the wooden box reads: "Muromachi period Mumei Zōgan Shingen Tsuba" Muromachi period, 16th century. Age attribution is based on the fact that the core is made of yamagane; later copies of Edo period are usually made of iron. This small and light tsuba was likely mounted on a combat sword, while larger and much heavier woven wire Shingen tsuba of Edo period were of purely decorative purpose. http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/
Tsuba of chrysanthemoid form (kikka-gata) with yamagane core and woven copper wire pattern. Copper sekigane. Shingen school. Height: 70.2 mm; Width 67.2 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.4-3.6 mm, overall 7.3 mm. Weight 82.7 g Inscription on the wooden box reads: "Muromachi period Mumei Zōgan Shingen Tsuba" Muromachi period, 16th century. Age attribution is based on the fact that the core is made of yamagane; later copies of Edo period are usually made of iron. This small and light tsuba was likely mounted on a combat sword, while larger and much heavier woven wire Shingen tsuba of Edo period were of purely decorative purpose. http://varshavskycollection.com/shingen-tsuba/ -
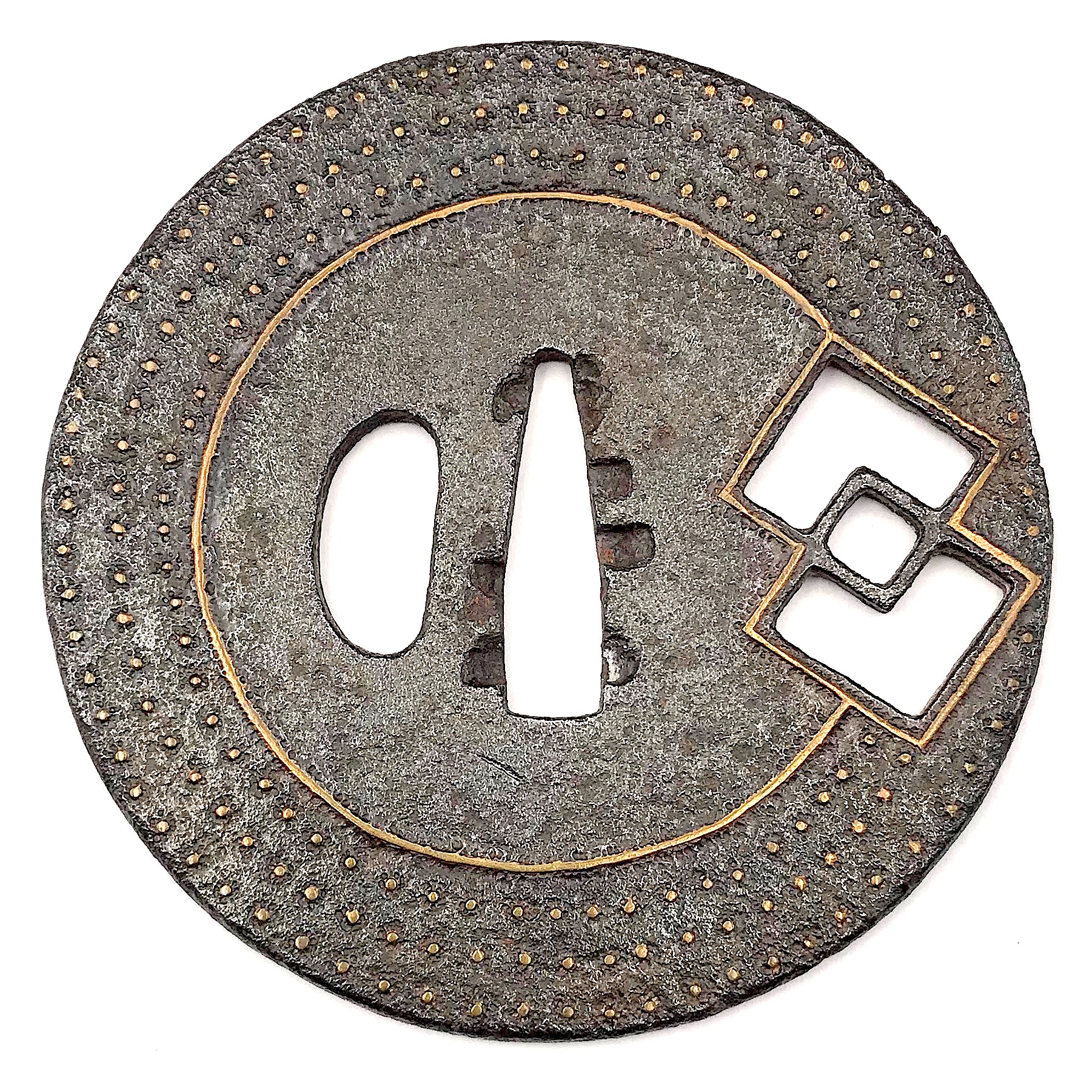 Onin Tsuba with two overlapping lozenges, or interlocked diamond shapes. Iron and brass. Sukashi and ten-zogan technique. Muromachi period. Diameter: 81.0 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm The symbol of two overlapping lozenges (or, interlocked diamond shapes), presumably a family crest (kamon) may be deciphered as chigai kuginuki (nail extraction tool => 'conquered nine castles' ) or as chigai bishi (overlapping lozenges). Similar symbol can be found at Butterfield & Butterfield. IMPORTANT JAPANESE SWORDS, SWORD FITTINGS AND ARMOR. Auction Monday, November 19th, 1979. Sale # 3063], №94 with the following explanation: " This was the mon (crest) of the Yonekura family of Kaga Prov., at Kanazawa". An interesting insight is provided by Robert E. Haynes at Important Japanese kodogu, gaiso and works of art. San Francisco, April 9-11, 1982. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd., № 36 (see photo): "This would seem to be the Yonekura family mon. They were Seiwa-Genji Daimyō family made noble in 1696 and resided in Kanazawa in Kaga". Would it be possible that this is a late 17th century Ōnin tsuba?
Onin Tsuba with two overlapping lozenges, or interlocked diamond shapes. Iron and brass. Sukashi and ten-zogan technique. Muromachi period. Diameter: 81.0 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm The symbol of two overlapping lozenges (or, interlocked diamond shapes), presumably a family crest (kamon) may be deciphered as chigai kuginuki (nail extraction tool => 'conquered nine castles' ) or as chigai bishi (overlapping lozenges). Similar symbol can be found at Butterfield & Butterfield. IMPORTANT JAPANESE SWORDS, SWORD FITTINGS AND ARMOR. Auction Monday, November 19th, 1979. Sale # 3063], №94 with the following explanation: " This was the mon (crest) of the Yonekura family of Kaga Prov., at Kanazawa". An interesting insight is provided by Robert E. Haynes at Important Japanese kodogu, gaiso and works of art. San Francisco, April 9-11, 1982. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd., № 36 (see photo): "This would seem to be the Yonekura family mon. They were Seiwa-Genji Daimyō family made noble in 1696 and resided in Kanazawa in Kaga". Would it be possible that this is a late 17th century Ōnin tsuba?
Robert E. Haynes Catalog of April 9-11, 1982, № 36.


