-
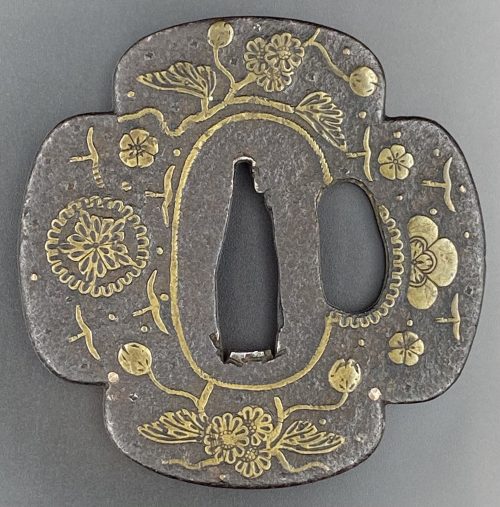 Iron tsuba of quatrefoil form (mokka-gata) adorned with the design of stars, wild geese, blossoms, leaves and tendrils realized in the brass inlay. The inlay technique includes suemon-zōgan and ten-zōgan. A smaller opening (kozuka hitsu-ana) surrounded by a scalloped brass border. The seppa-dai bordered with linear inlay. A few dots of inlay on both sides are missing. Measurements: height 71 mm, width 70 mm, thickness at centre 2.7 cm Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573)
Iron tsuba of quatrefoil form (mokka-gata) adorned with the design of stars, wild geese, blossoms, leaves and tendrils realized in the brass inlay. The inlay technique includes suemon-zōgan and ten-zōgan. A smaller opening (kozuka hitsu-ana) surrounded by a scalloped brass border. The seppa-dai bordered with linear inlay. A few dots of inlay on both sides are missing. Measurements: height 71 mm, width 70 mm, thickness at centre 2.7 cm Time: Late Muromachi (1514 – 1573) -
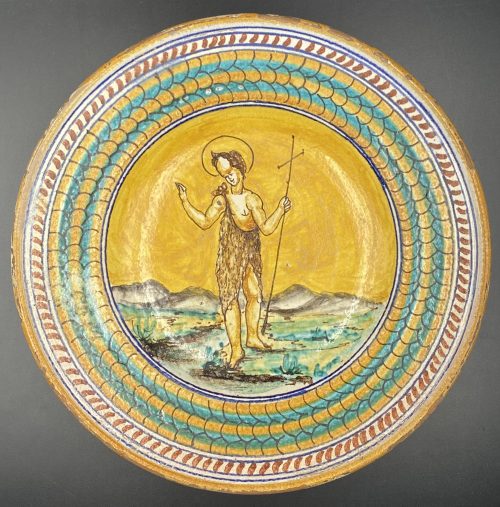 Tin-glazed earthenware polychrome plate of round form, decorated with a figure of John the Baptist wearing clothes of camel's hair with a tall cross in his left hand and with a halo over his head, walking in a desert with hills on the background. The lip is decorated with circles and scales, base with concentric circles. Diameter: 23 cm; Height: 4 cm.
Tin-glazed earthenware polychrome plate of round form, decorated with a figure of John the Baptist wearing clothes of camel's hair with a tall cross in his left hand and with a halo over his head, walking in a desert with hills on the background. The lip is decorated with circles and scales, base with concentric circles. Diameter: 23 cm; Height: 4 cm. -
 Jizai okimono bronze articulated model of a crab. Japan, Meiji period(1868-1912). Size: Body: 6.5 x 6 cm. Total: 23 x 11 cm. Weight: 762 g
Jizai okimono bronze articulated model of a crab. Japan, Meiji period(1868-1912). Size: Body: 6.5 x 6 cm. Total: 23 x 11 cm. Weight: 762 g -
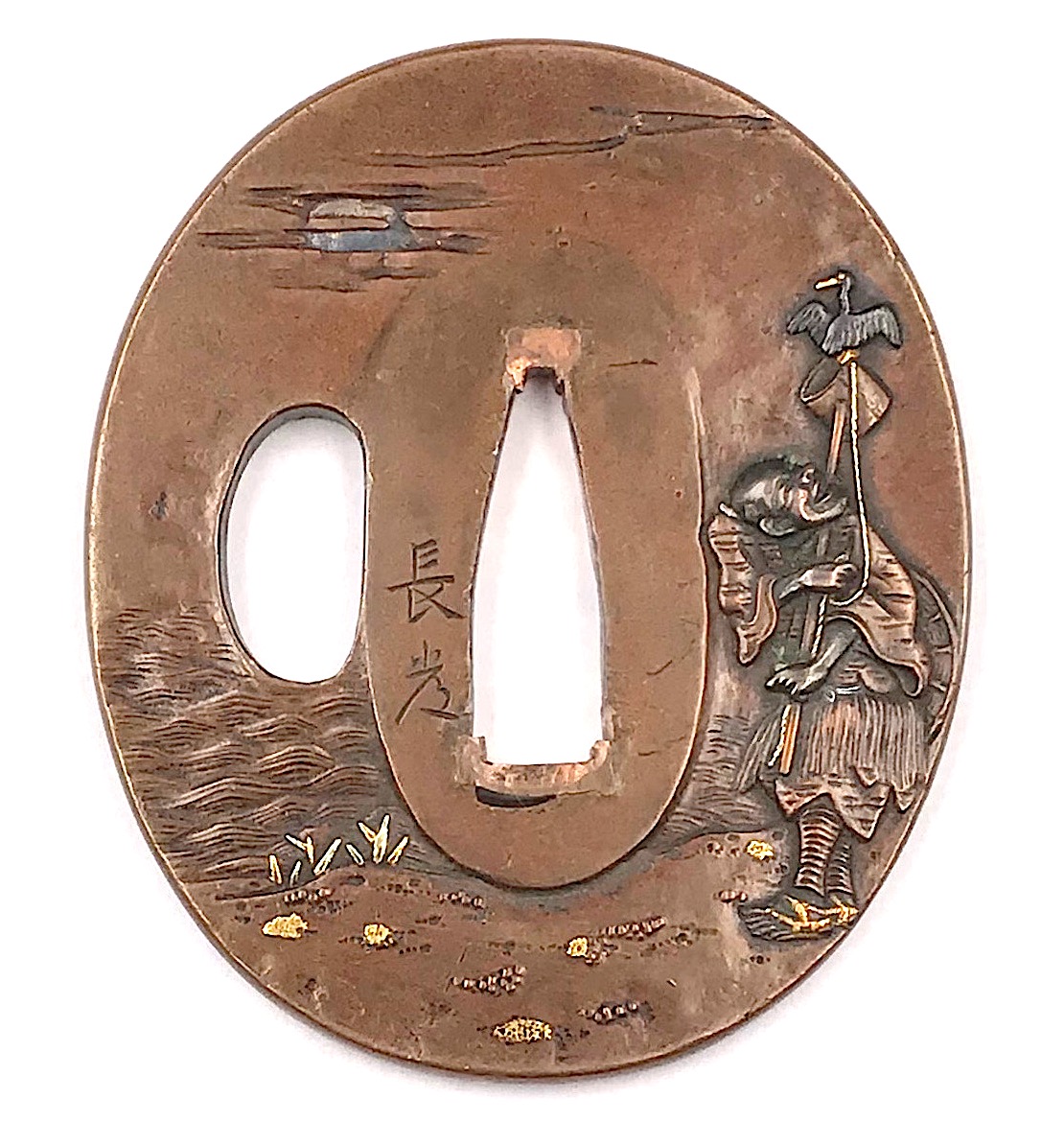 Copper (suaka) tsuba of oval form carved in relief, pierced and inlaid with soft metals (gold, shakudō, shibuichi or silver) with a cormorant fisherman (ushō) and moon motif on the face and a boat among the bank reeds on the reverse. Signed: Nagatsune. Box inscription: Tsuba with cormorant fishing, made by Nagatsune. Dimensions: 62.7 mm x 53.2 mm x 4.2 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th century. Nagatsune (1721-1787), 1st generation master of Inchinomiya School in Kyoto, adopted son of the gilder Nagayoshi, student of Yasui Takanaga [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', p. 26]. Detailed account of the school is given at The Japanese toso-kinko Schools.// Lulu Inc., 2012 by Markus Sesko, pp. 104-108. Nagatsune's biographical sketch can be found there on pp. 104-106. "What Sōminis in the East (Edo), Nagatsune is in the West (Kyōto)." “Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. […] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one’s master and keen eyesight.” – from Merrily Baird 'Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design.' //Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also in this collection: TSU-241 and TSU-0096
Copper (suaka) tsuba of oval form carved in relief, pierced and inlaid with soft metals (gold, shakudō, shibuichi or silver) with a cormorant fisherman (ushō) and moon motif on the face and a boat among the bank reeds on the reverse. Signed: Nagatsune. Box inscription: Tsuba with cormorant fishing, made by Nagatsune. Dimensions: 62.7 mm x 53.2 mm x 4.2 mm (at seppa-dai) Edo period: 18th century. Nagatsune (1721-1787), 1st generation master of Inchinomiya School in Kyoto, adopted son of the gilder Nagayoshi, student of Yasui Takanaga [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', p. 26]. Detailed account of the school is given at The Japanese toso-kinko Schools.// Lulu Inc., 2012 by Markus Sesko, pp. 104-108. Nagatsune's biographical sketch can be found there on pp. 104-106. "What Sōminis in the East (Edo), Nagatsune is in the West (Kyōto)." “Since Nara period, Japanese fishermen in small boats have used cormorants (u) to catch river fish at night, binding the necks of the birds so that the fish are not swallowed. […] The bird and the work it performs are symbols of selfless devotion to one’s master and keen eyesight.” – from Merrily Baird 'Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design.' //Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001; p. 104. See also in this collection: TSU-241 and TSU-0096The design was popular among the tsuba makers. We find one in the Alexander G. Moslé collection [Japanese Sword Fittings from the Alexander G. Moslé Collection; Sebastian Izzard LLC, 2004, page 90, №123] signed Nagatsune with kaō: Tsuba with cormorant fisherman, moon, and boat. Squared-oval shibuichi plate, slightly raised rim, engraved, pierced, and inlaid with soft metals in relief. 6.7 x 5.8 cm.

Alexander G. Moslé collection №123.
Another reference: Lundgren Collection, 1990, page 86 №207: Sword guard with design of ushō (person who fishes with cormorants). Signed by Nagatsune. Ichinomiya school. 6.45 x 5.95 x 0.40 cm. Polished shibuichi taka-bori relief, gold and silver inlay. Edo period, 18th century.

Lundgren Collection №207:
-
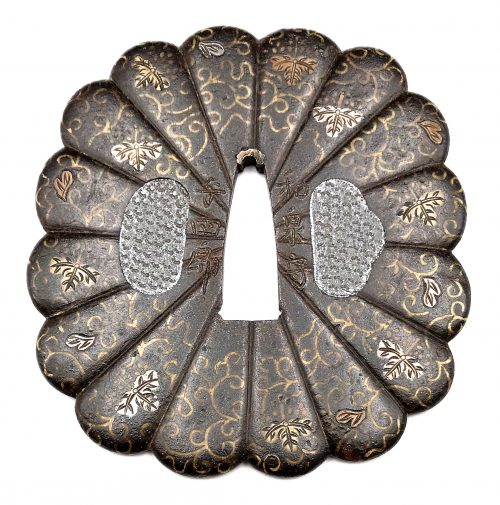 The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:
The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:"Early signed example of the work of Koike Naomasa. The kiku shape iron plate is well finished. The flush inlay is brass, for the scroll work on both sides, with the leaves and kiri mon in brass, copper and silver with strong detail carving. Some of the inlay goes almost over the edge, which is goishi gata. The large hitsuana are plugged in lead with starburst kokuin surface design. [...]The face is signed in deep bold kanji: Koike Naomasa; the back is signed: Izumi no Kami, on the right and Yoshiro on the left. There are one or two small pieces of inlay missing. Sold by Sotheby London, Oct. 27, 1981, lot 368. Height = 86 mm, thickness (seppa-dai) = 3.75 mm, (edge) = 4 mm."
Another similar example presented at: "Tsuba" by Günter Heckmann, 1995, №T55 — "Designation: Koike Naomasa. Mid Edo, end of the 17th century. Iron, hira-zogan in brass, copper, silver and shakudo, katakiri-bori. Tendrils and leaves. 87.0 x 78.0 x 4.0 mm." Reference: Japanische Schwertzierate by Lumir Jisl, 1967, page. 13. [SV: Actually, his tsuba is signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back; and Koike Naomasa on the front, exactly as Robert Haynes's tsuba. Dating this tsuba Mid-Edo, 17th century may be considered a misattribution]. More details regarding the Yoshirō tsuba. -
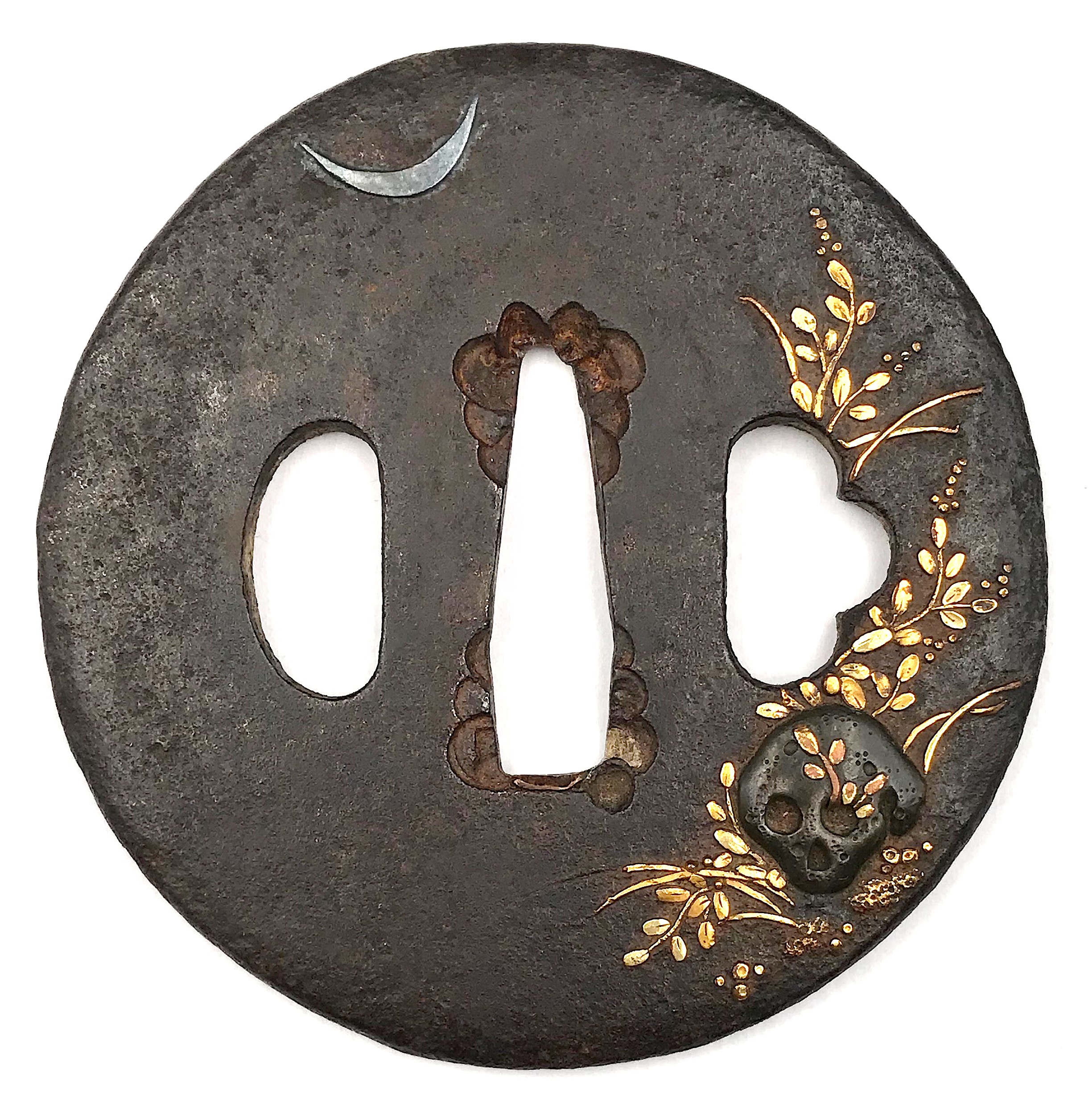 An iron tsuba of round shape inlaid with shakudō, gold, and silver with a motif of a weather-beaten (nozarashi) skull and grasses growing beside as well as through the eye-pit, and a crescent moon above the scene. Grasses on the reverse. Unsigned. Dimensions: 71.7 x 70.6 x 4.2 mm Reference: Skull, bones and grave markers SOLD
An iron tsuba of round shape inlaid with shakudō, gold, and silver with a motif of a weather-beaten (nozarashi) skull and grasses growing beside as well as through the eye-pit, and a crescent moon above the scene. Grasses on the reverse. Unsigned. Dimensions: 71.7 x 70.6 x 4.2 mm Reference: Skull, bones and grave markers SOLD -
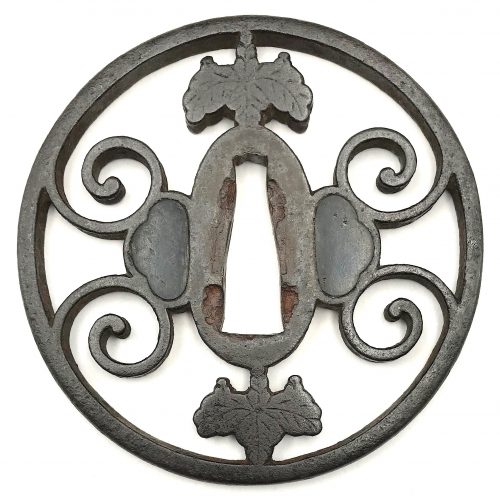

Iron tsuba of round form decorated with a design of bracken scrolls and paulownia leaves and blossoms (kiri-mon) in openwork (sukashi). Details carved in kebori. Squared rim with iron bones (tekkotsu). Hitsu-ana plugged with shakudō.
Size: 83.6 x 82.9 x 5.4 (center), 5.1 (rim) mm.
Unsigned.
Muromachi period, ca. 16th century.
-
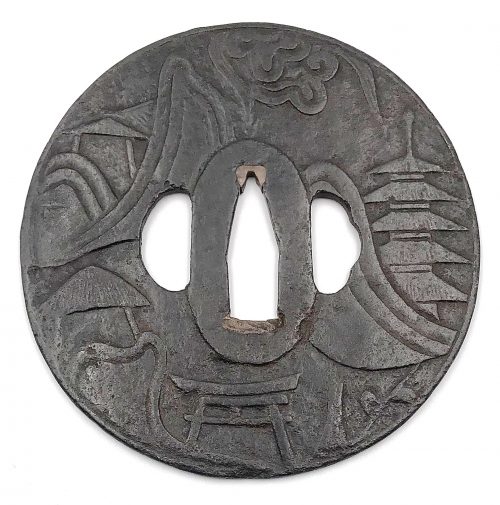

Thin iron plate of round form and black color carved in sukidashi-bori with design of rocks, waves, clouds, temple gates (torii), mountain pavilion and 5-storey pagoda on both sides, alluding to Todai-ji temple in Nara. Hitsu-ana pierced later. Very narrow very slightly raised rim. Copper sekigane.
Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Dimensions: 88.7 x 88.0 x 2.4 mm (seppa-dai), 1.8 mm (base plate).Reference: “Art of the Samurai” on page 232, №140: ”Kamakura tsuba with Sangatsu-do tower and bridge. Muromachi period, 16th century. 83 mm x 80 mm. Unsigned. Tokyo National Museum. The mountain pavilion and bridge carved in sunken relief on the iron tsuba – both part of Tōdai-ji, a temple in Nara – are detailed in fine kebori (line) engraving. As a result of the chiseling used to create the relief, the ground of the piece is relatively thin".
-
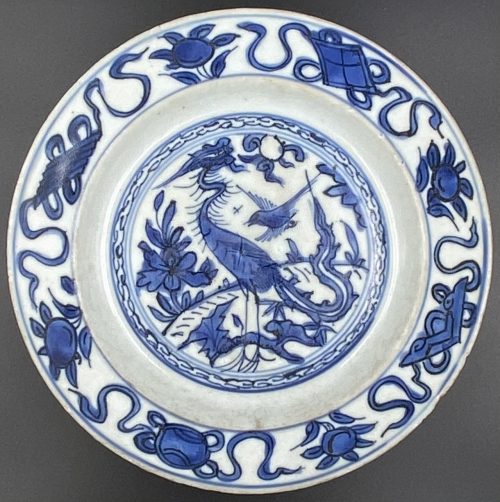 Plate with crane, bird, plants, and four treasures. Porcelain with underglaze blue decoration and illegible factory mark to the bottom. Ming Dynasty [大明] (1368 – 1644); Wanli Era (1572 – 1620); Late 16th – Early 17th century. Diameter: 19.5 cm; Height: 3 cm
Plate with crane, bird, plants, and four treasures. Porcelain with underglaze blue decoration and illegible factory mark to the bottom. Ming Dynasty [大明] (1368 – 1644); Wanli Era (1572 – 1620); Late 16th – Early 17th century. Diameter: 19.5 cm; Height: 3 cm -
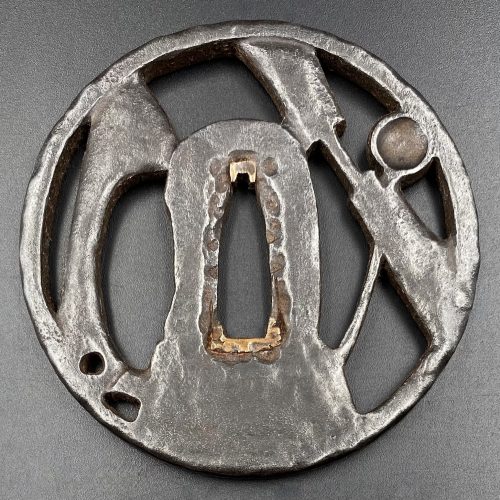 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with a ladle, pestle, mortar, and rice sickle in positive silhouette openwork (nikubori-ji-sukashi). Slightly rounded rim with iron bones (tekkotsu). Seppa-dai plugged with copper fittings (sekigane). Silver patina. The design resembles mochi-making utensils; mochi (rice cake) symbolizes longevity. Kanayama school, c. 1590 (Momoyama period). Note: unusually large size for a Kanayama tsuba: diameter 79.5 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 5.5 mm, at rim: 6.0 mm. Concerning the design: While the ladle and pestle are clear, the mortar (under the seppa-dai), and the sickle (to the left) require certain imagination.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with a ladle, pestle, mortar, and rice sickle in positive silhouette openwork (nikubori-ji-sukashi). Slightly rounded rim with iron bones (tekkotsu). Seppa-dai plugged with copper fittings (sekigane). Silver patina. The design resembles mochi-making utensils; mochi (rice cake) symbolizes longevity. Kanayama school, c. 1590 (Momoyama period). Note: unusually large size for a Kanayama tsuba: diameter 79.5 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 5.5 mm, at rim: 6.0 mm. Concerning the design: While the ladle and pestle are clear, the mortar (under the seppa-dai), and the sickle (to the left) require certain imagination. -
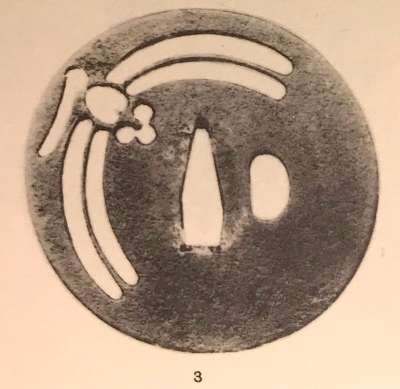
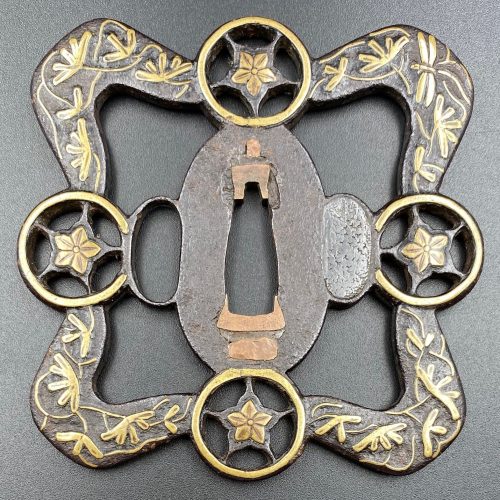 Iron tsuba of a spindle shape (tate-itomaki-gata) pierced and inlaid in brass suemon-zōgan with bellflowers, vines and foliage, and a dragonfly in the upper right corner, on both sides. One of the hitsu-ana plugged with grey metal (led or pewter), nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. The shape of the tsuba may be interpreted as four saddles connected to each other by horse bits. Such a design of sukashi and zōgan is usually attributed to Kaga Yoshirō branch of Heianjo school, active in the second half of the 17th century (c. 1650-1700). Size: 95.9 mm diagonal; 4.1 mm thickness. Tokubetsu Kicho certificate № 332 issued by NBTHK on October 12, 1965.
Iron tsuba of a spindle shape (tate-itomaki-gata) pierced and inlaid in brass suemon-zōgan with bellflowers, vines and foliage, and a dragonfly in the upper right corner, on both sides. One of the hitsu-ana plugged with grey metal (led or pewter), nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. The shape of the tsuba may be interpreted as four saddles connected to each other by horse bits. Such a design of sukashi and zōgan is usually attributed to Kaga Yoshirō branch of Heianjo school, active in the second half of the 17th century (c. 1650-1700). Size: 95.9 mm diagonal; 4.1 mm thickness. Tokubetsu Kicho certificate № 332 issued by NBTHK on October 12, 1965. -
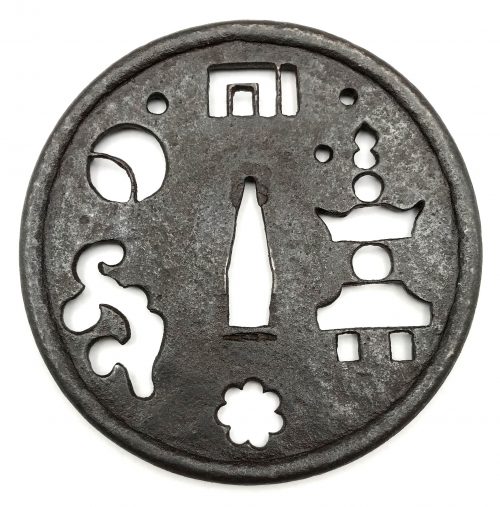 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of moon, stars, cloud, snowflake, gorintō, and Genji-mon in negative openwork (in-sukashi). Raised tubular rim (dote-mimi). Deep black patina, traces of lacquer. Naka-daka type of plate (thicker in center, getting thiner towards the rim). Visible gap between the rim and the plate. Dimensions: Height: 91.7 mm; Width: 90.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.5 mm, plate before rim: 2.2 mm, of the rim: 5.6 mm. At least Mid Muromachi period, 15th century, but possibly earlier. In 'Silver Book', commenting tsuba №34 Sasano writes: "The technique used to create the rim is the same used for the peak (koshimaki) of helmets (kabuto) during the Kamakura and Nanbokucho periods." On the other hand, the abundance of sukashi elements points towards later times, perhaps late Muromachi or even Momoyama period. "Gorintō is a grave stone composed of five pieces, piled on one the other, representing, from the bottom upward, earth, water, fire, wind, and heaven, respectively" [Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1. AFU, 1993, p. 6. / LIB-1554]. A romantic description of the piece may look like this: The air is scented (incense symbol); it's a graveyard, marked by gorintō; a winter (snowflake) evening or night (moon, stars); mist is rising from a ravine towards moon. I did not manage to find a katchūshi piece of this design, only a few Kamakura-bori tsuba:
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of moon, stars, cloud, snowflake, gorintō, and Genji-mon in negative openwork (in-sukashi). Raised tubular rim (dote-mimi). Deep black patina, traces of lacquer. Naka-daka type of plate (thicker in center, getting thiner towards the rim). Visible gap between the rim and the plate. Dimensions: Height: 91.7 mm; Width: 90.8 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.5 mm, plate before rim: 2.2 mm, of the rim: 5.6 mm. At least Mid Muromachi period, 15th century, but possibly earlier. In 'Silver Book', commenting tsuba №34 Sasano writes: "The technique used to create the rim is the same used for the peak (koshimaki) of helmets (kabuto) during the Kamakura and Nanbokucho periods." On the other hand, the abundance of sukashi elements points towards later times, perhaps late Muromachi or even Momoyama period. "Gorintō is a grave stone composed of five pieces, piled on one the other, representing, from the bottom upward, earth, water, fire, wind, and heaven, respectively" [Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1. AFU, 1993, p. 6. / LIB-1554]. A romantic description of the piece may look like this: The air is scented (incense symbol); it's a graveyard, marked by gorintō; a winter (snowflake) evening or night (moon, stars); mist is rising from a ravine towards moon. I did not manage to find a katchūshi piece of this design, only a few Kamakura-bori tsuba:
100 selected tsuba from European collections. Catalogue by Robert Haynes and Robert Burawoy, 1984, page 16, №5.
While the upper tsuba is dated end of Muromachi, the lower is attributed to the 17th century - Momoyama or early Edo period, though the author put this attribution under question. Deciphering of the strangely shaped opening to the left of nakago-ana is sometimes "a conventional scroll", and sometimes - a fern or bracken. I think mine is a cloud or mist, but I don't have any material evidence proving this understanding and came to conclusion by context only. It may easily be a dinosaurs playing ball. The fact that this thing always accompanies the Genji-mon, or incense symbol, it may be a scent itself.
Japanese Sword Fittings. Collection of G.H. Naunton, Esq., by Henri L. Joly, - 1912; №9.
-
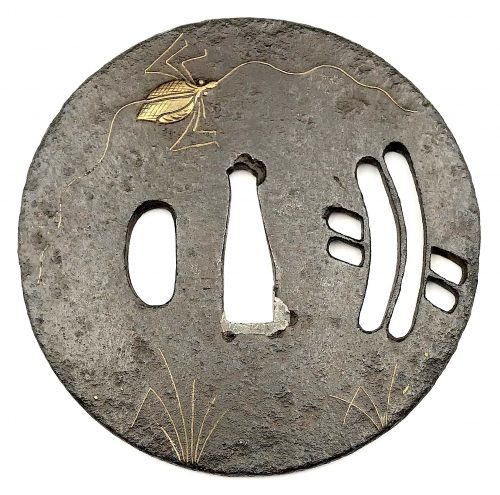 Iron tsuba with design of a cricket and grass inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) and a bridge over a stream in openwork (sukashi) on both sides. Inlay of distant part of the cricket's antenna is missing. Heianjō School. Momoyama period. Diameter: 79.5 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.3 mm NBTHK # 4002100.
Iron tsuba with design of a cricket and grass inlaid in brass (suemon-zōgan) and a bridge over a stream in openwork (sukashi) on both sides. Inlay of distant part of the cricket's antenna is missing. Heianjō School. Momoyama period. Diameter: 79.5 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.3 mm NBTHK # 4002100. -
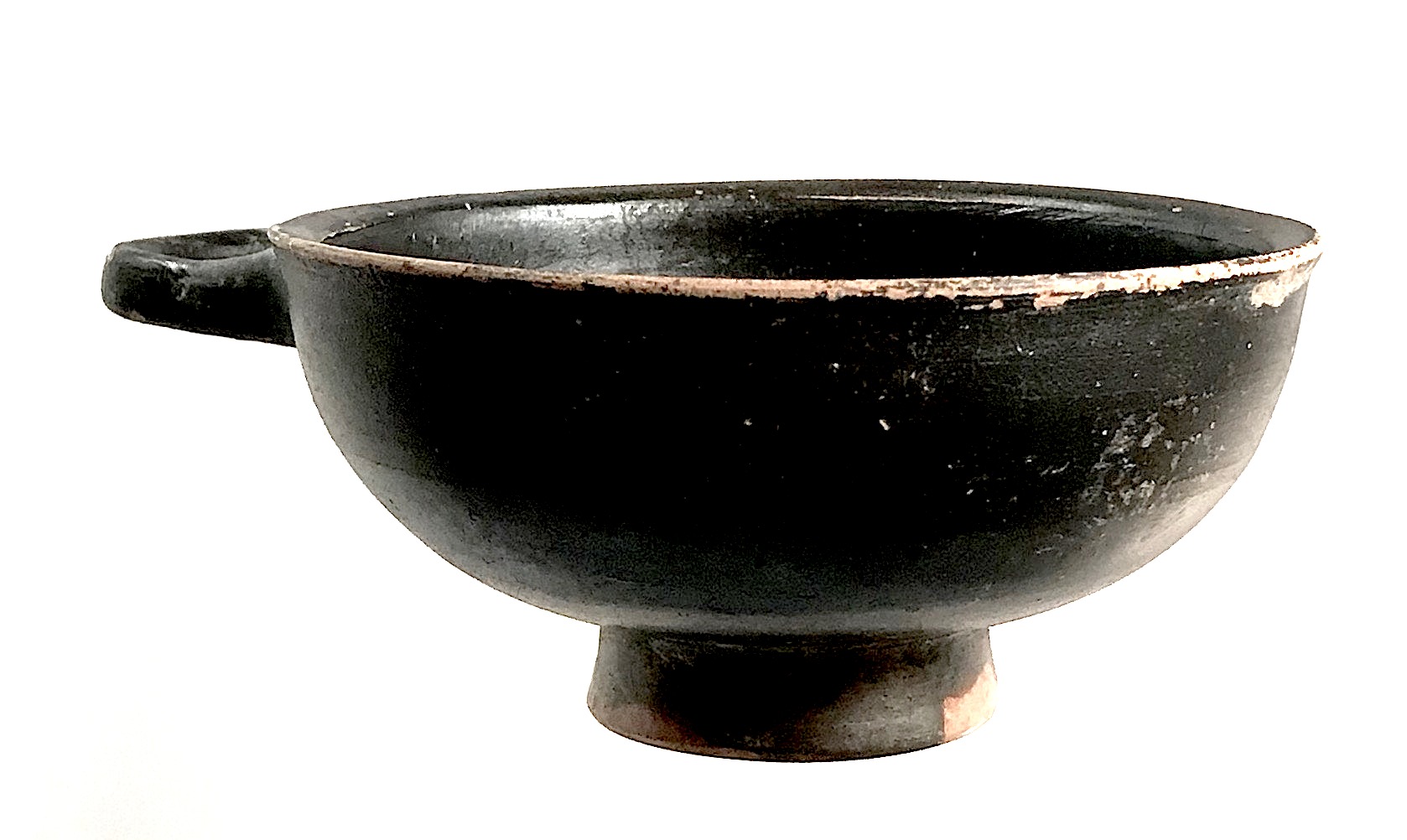 Ancient Greek glazed terracotta kylix (cup with a shallow bowl and a stem), ca. 350 BC. Dimensions: 14.4 x 11 cm The primary use for the kylix was drinking wine (usually mixed with water, and sometimes other flavourings) at a symposium or male "drinking party" in the ancient Greek world, so they are often decorated with scenes of a humorous, light-hearted, or sexual nature that would only become visible when the cup was drained.
Ancient Greek glazed terracotta kylix (cup with a shallow bowl and a stem), ca. 350 BC. Dimensions: 14.4 x 11 cm The primary use for the kylix was drinking wine (usually mixed with water, and sometimes other flavourings) at a symposium or male "drinking party" in the ancient Greek world, so they are often decorated with scenes of a humorous, light-hearted, or sexual nature that would only become visible when the cup was drained. -
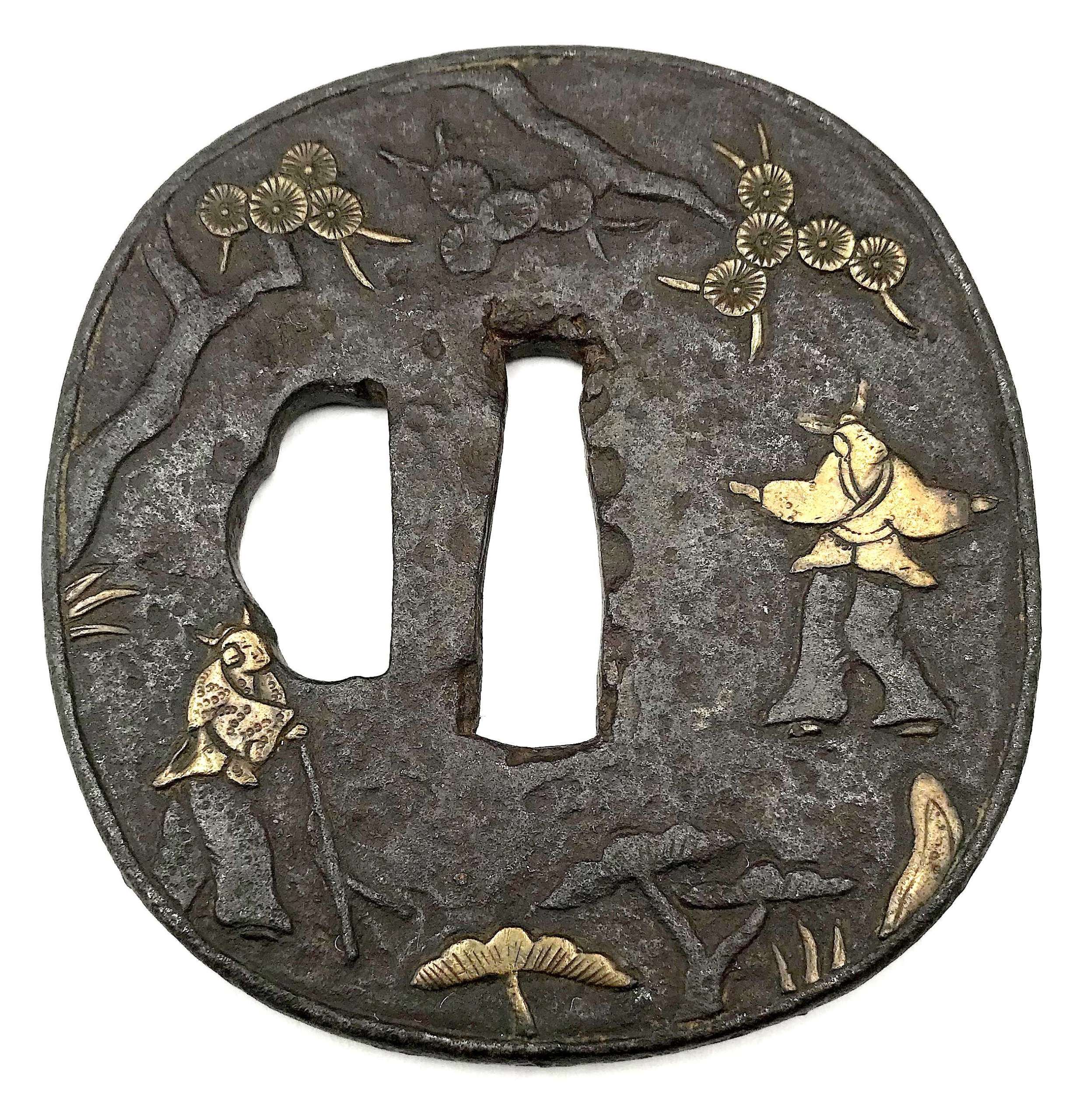 Relatively thick iron tsuba of rounded square form with slightly elevated rim decorated in carving (sukidashi-bori) and yellow brass (shinchū) inlay (suemon-zōgan) with legendary creatures (humans with cow heads) in a pine tree forrest on the face, and a horned man with a stick hunting a rabbit in the woods on the reverse. Large hitsu-ana possibly cut off later on. In the beginning of the 20th century such tsuba were usually attributed to Fushimi-Kaga school. This one may be attributed to either Ōnin or to Heianjō. The latter seems most plosible because of the thick web and dull patina. The technique may also be called "shinchū-zōgan". Momoyama or early Edo period. Unsigned. Dimensions: 72.3 x 68.4 x 4.1 mm
Relatively thick iron tsuba of rounded square form with slightly elevated rim decorated in carving (sukidashi-bori) and yellow brass (shinchū) inlay (suemon-zōgan) with legendary creatures (humans with cow heads) in a pine tree forrest on the face, and a horned man with a stick hunting a rabbit in the woods on the reverse. Large hitsu-ana possibly cut off later on. In the beginning of the 20th century such tsuba were usually attributed to Fushimi-Kaga school. This one may be attributed to either Ōnin or to Heianjō. The latter seems most plosible because of the thick web and dull patina. The technique may also be called "shinchū-zōgan". Momoyama or early Edo period. Unsigned. Dimensions: 72.3 x 68.4 x 4.1 mm -
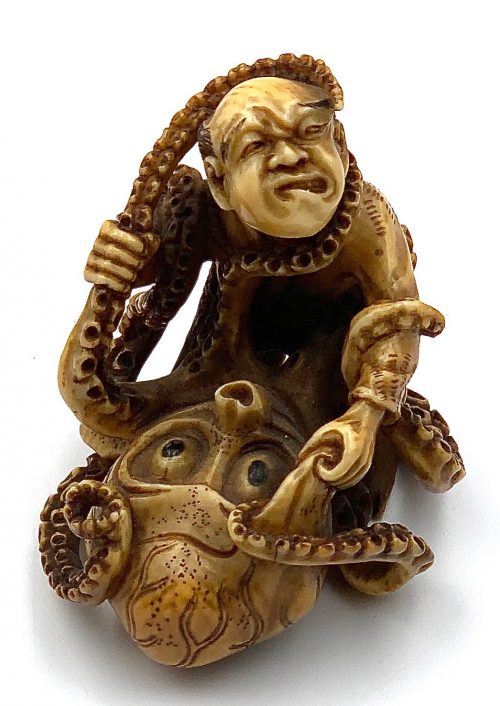

Ivory netsuke with a design of a man (possibly - Ariōmaru) wrestling a giant octopus.
Circa 1850. Dimensions: 45.5 x 48.3 x 37.8 mmUnsigned.
-
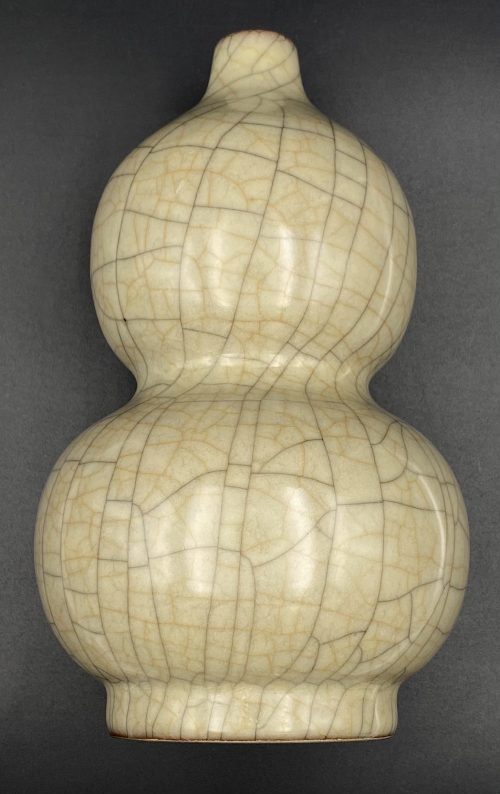 A footed double-gourd porcelain bottle with iron and gold coloured crackle on grey background. China, the Qianlong period (1711 – 1799) of the Qing Dynasty (1644 – 1912). Diameter: 12 cm; Height: 21 cm.
A footed double-gourd porcelain bottle with iron and gold coloured crackle on grey background. China, the Qianlong period (1711 – 1799) of the Qing Dynasty (1644 – 1912). Diameter: 12 cm; Height: 21 cm. -
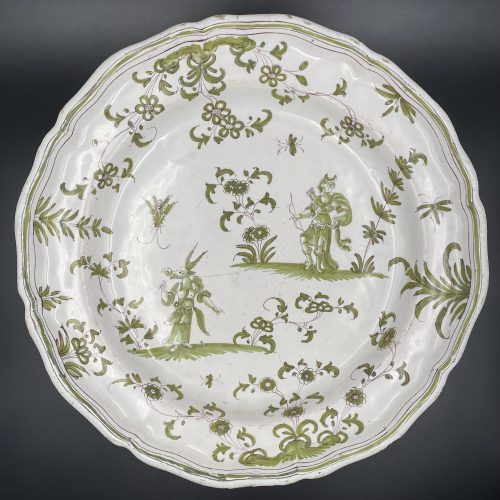 Moustiers faience plate: tin-glazed earthenware plate with a scalloped rim, with green monochrome grotesque decoration of a whimsical creature and a female archer, surrounded by flowering vegetation and insects. Marked "X" on the bottom. "Joseph Fouque/Jean-Francois Pelloquin, started in 1749, used an"X" in its pottery mark". Diameter: 31 cm; Height: 4 cm.
Moustiers faience plate: tin-glazed earthenware plate with a scalloped rim, with green monochrome grotesque decoration of a whimsical creature and a female archer, surrounded by flowering vegetation and insects. Marked "X" on the bottom. "Joseph Fouque/Jean-Francois Pelloquin, started in 1749, used an"X" in its pottery mark". Diameter: 31 cm; Height: 4 cm. -
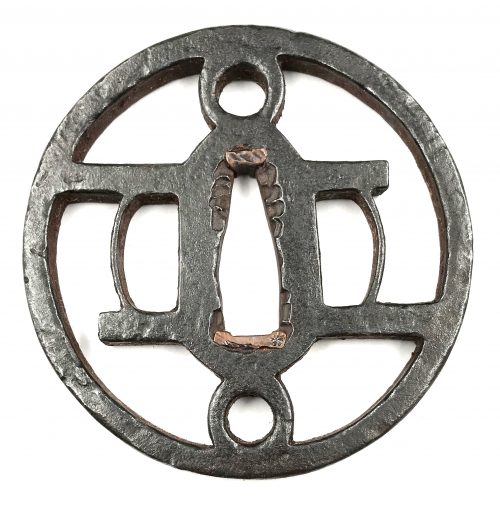 Iron tsuba of round form with design of two parallel crossbars and two rings in openwork (sukashi). Rounded square rim. Moderate iron bones (tekkotsu) allover. Copper sekigane. Kanayama school. Momoyama period (or late Muromachi). Size: 74.5 x 74.0 x 5.5 mm. The rings possibly represent the sun and the moon, or the stars. The parallel crossbars may represent the "two stripes" (futatsu biki) family crest (incl. Ashikaga family).
Iron tsuba of round form with design of two parallel crossbars and two rings in openwork (sukashi). Rounded square rim. Moderate iron bones (tekkotsu) allover. Copper sekigane. Kanayama school. Momoyama period (or late Muromachi). Size: 74.5 x 74.0 x 5.5 mm. The rings possibly represent the sun and the moon, or the stars. The parallel crossbars may represent the "two stripes" (futatsu biki) family crest (incl. Ashikaga family). -
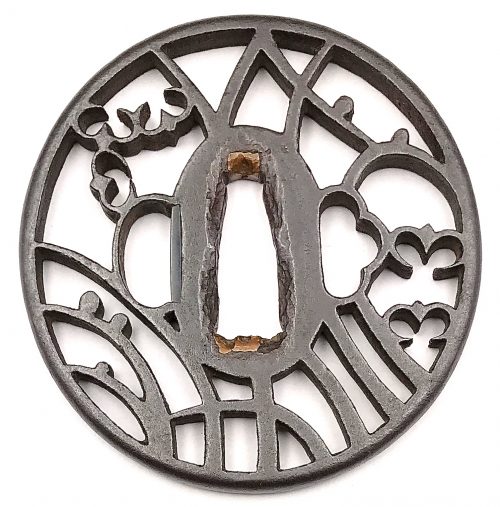 Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form with design of wild geese and drops on pampas grass (masashino) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane. Owari school. Early Edo period: early 17th century (Kan-ei era). Height: 78.8 mm. Width: 76.3 mm. Rim thickness: 6.1 mm. Center thickness: 6.4 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 169. A description of musashino symbolism can be found at Symbols of Japan by Merrily Baird [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001]: Musashino - "the plain of Musashi - a large expanse in the Tokyo area, was celebrated in poetry for the grasses that grew there before the recent era of industrialization... The use of Musashino themes was particularly common in the Momoyama and Edo periods". Pampas grass with dew drops and wild geese in flight collectively provide strong autumnal connotation.
Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form with design of wild geese and drops on pampas grass (masashino) in openwork (sukashi). Rounded rim. Copper sekigane. Owari school. Early Edo period: early 17th century (Kan-ei era). Height: 78.8 mm. Width: 76.3 mm. Rim thickness: 6.1 mm. Center thickness: 6.4 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 169. A description of musashino symbolism can be found at Symbols of Japan by Merrily Baird [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001]: Musashino - "the plain of Musashi - a large expanse in the Tokyo area, was celebrated in poetry for the grasses that grew there before the recent era of industrialization... The use of Musashino themes was particularly common in the Momoyama and Edo periods". Pampas grass with dew drops and wild geese in flight collectively provide strong autumnal connotation. -
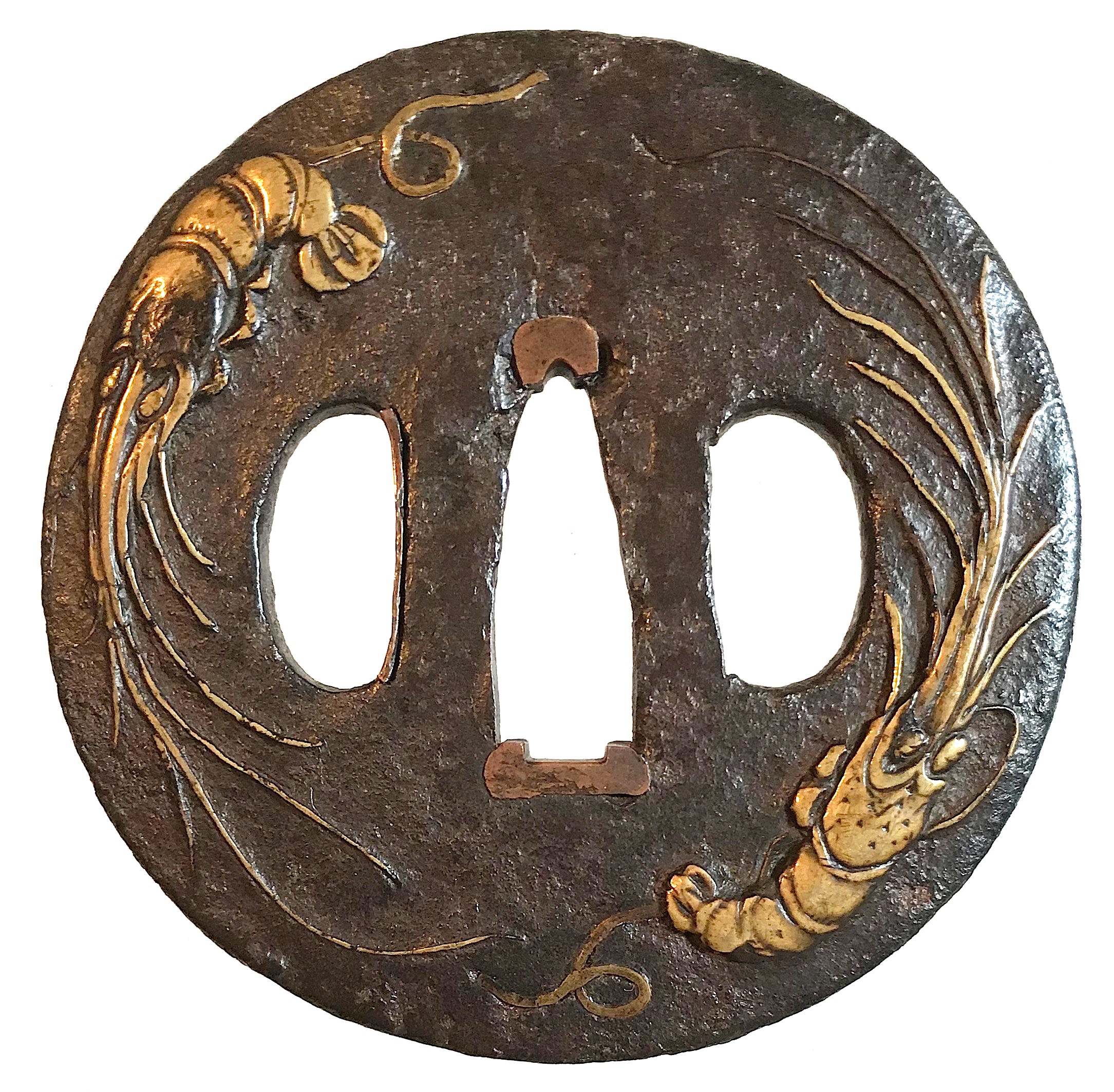 Iron tsuba of round form with two ebi (lobster) on omote (obverse side) and shika (deer) among scattered momiji (maple leaves) on ura (reverse side) motif in brass takabori (high relief) suemon-zōgan. Traces of lacquer. Unsigned. Late Muromachi / Momoyama period (late 16th / Early 17th century). Dimensions: 69.0.6 mm (H) x 69.6 mm (W) x 3.4 mm (T, seppa-dai). Weight: 92.6 g. Illustrated at: The Lundgren Collection of Japanese Swords, Sword Fittings and A Group of Miochin School Metalwork. Christie's Auction: Tuesday, 18 November 1997, London. Sales "GOTO-5881". Christie's, 1997. - #2 at page 7. Provenance: The second John Harding; The Lundgren Collection. Description at Christie's: "The iron plate depicting two lobsters in takabory and brass takazogan, the reverse similarly decorated with deer among scattered maple leaves, square mimi, late Muromachi / early Momoyama period (late 16th/early 17th century) Diameter 68 mm, mimi thickness 4 mm. Provenance: The second John Harding." Also at: JAPANESE SWORD-FITTINGS & METALWORK IN THE LUNDGREN COLLECTION. Published by Otsuka Kogeisha, Tokyo 1992. № 134. Description on page 173: Sword guard with design of shrimps in inlay (scarlet [sic] maple leaves and deer on the reverse side). Unsigned. Heianjō inlay school. Vertical 6.85 cm, horizontal 6.90 cm, Th. of rim 0.40 cm. Iron. Taka-bori relief and brass inlay. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. According to Merrily Baird, maple leaves, especially if paired with the deer, allude to autumnal tradition of Japanese aristocracy of viewing the seasonal changes of color in the Nara area. The lobster is typical Japanese ebi, - it lacks prominent claws, and has a spiny shell. As a symbol of longevity and good fortune, lobster is a staple of New Year's decoration.
Iron tsuba of round form with two ebi (lobster) on omote (obverse side) and shika (deer) among scattered momiji (maple leaves) on ura (reverse side) motif in brass takabori (high relief) suemon-zōgan. Traces of lacquer. Unsigned. Late Muromachi / Momoyama period (late 16th / Early 17th century). Dimensions: 69.0.6 mm (H) x 69.6 mm (W) x 3.4 mm (T, seppa-dai). Weight: 92.6 g. Illustrated at: The Lundgren Collection of Japanese Swords, Sword Fittings and A Group of Miochin School Metalwork. Christie's Auction: Tuesday, 18 November 1997, London. Sales "GOTO-5881". Christie's, 1997. - #2 at page 7. Provenance: The second John Harding; The Lundgren Collection. Description at Christie's: "The iron plate depicting two lobsters in takabory and brass takazogan, the reverse similarly decorated with deer among scattered maple leaves, square mimi, late Muromachi / early Momoyama period (late 16th/early 17th century) Diameter 68 mm, mimi thickness 4 mm. Provenance: The second John Harding." Also at: JAPANESE SWORD-FITTINGS & METALWORK IN THE LUNDGREN COLLECTION. Published by Otsuka Kogeisha, Tokyo 1992. № 134. Description on page 173: Sword guard with design of shrimps in inlay (scarlet [sic] maple leaves and deer on the reverse side). Unsigned. Heianjō inlay school. Vertical 6.85 cm, horizontal 6.90 cm, Th. of rim 0.40 cm. Iron. Taka-bori relief and brass inlay. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. According to Merrily Baird, maple leaves, especially if paired with the deer, allude to autumnal tradition of Japanese aristocracy of viewing the seasonal changes of color in the Nara area. The lobster is typical Japanese ebi, - it lacks prominent claws, and has a spiny shell. As a symbol of longevity and good fortune, lobster is a staple of New Year's decoration. -
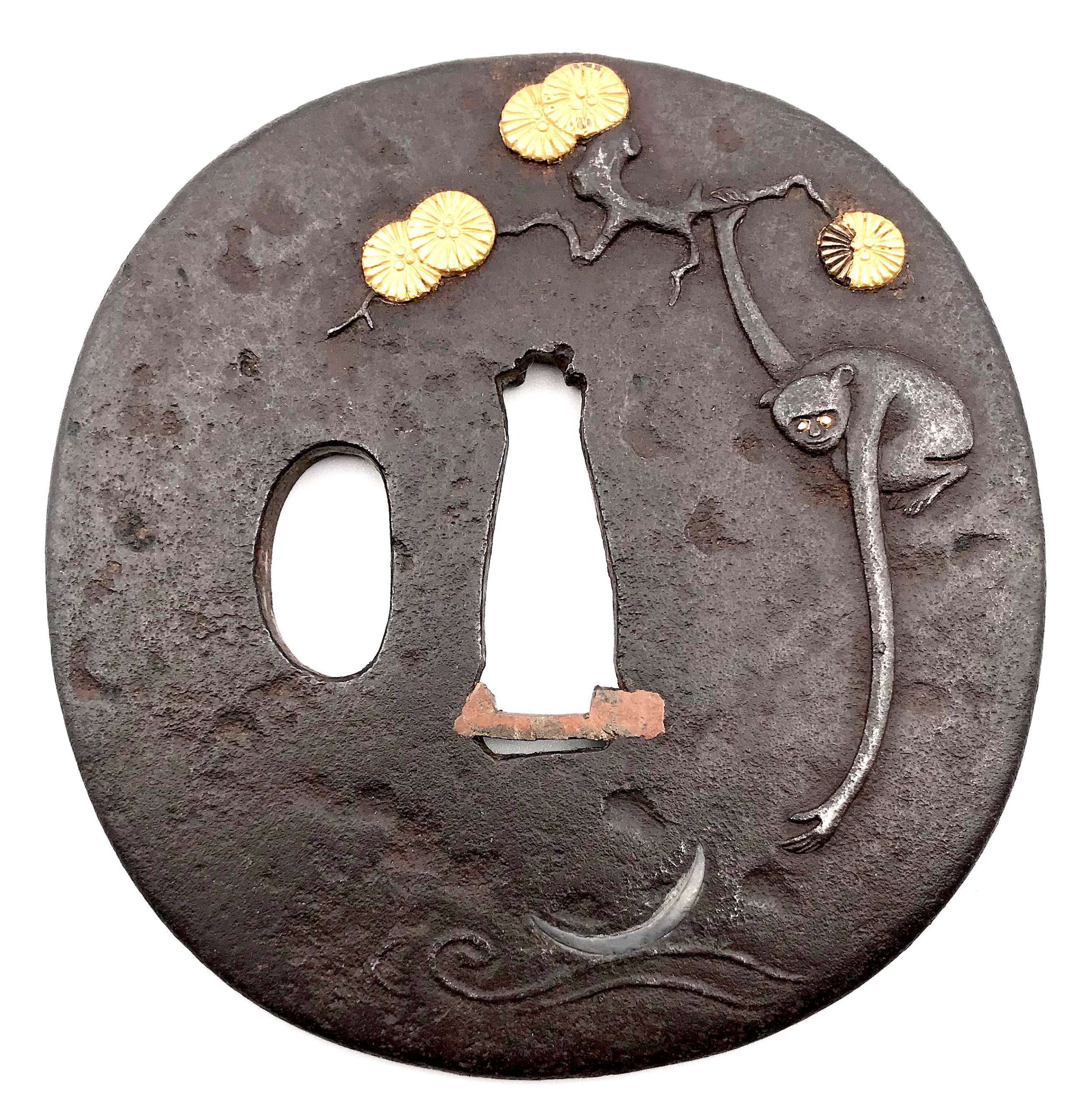 [SOLD]
[SOLD]Iron tsuba of slightly elongated round form carved and inlaid in gold and shibuichi with a long-armed monkey hanging from a pine tree branch reaching for the reflection of a crescent moon in the stream. A pine tree carved with details inlaid in gold on the reverse. The design seems to be inspired by Kaneie work (Compton III, p. 10, №6a; Tsuba no bi, 1947, p. 33, №56).
Dimensions: 76.8 x 74.2 x 3.6 mm. Mid-Edo period. Unsigned.
Compton III, p. 10, №6a

Tsuba no bi, 1947, p. 33, №56.
-
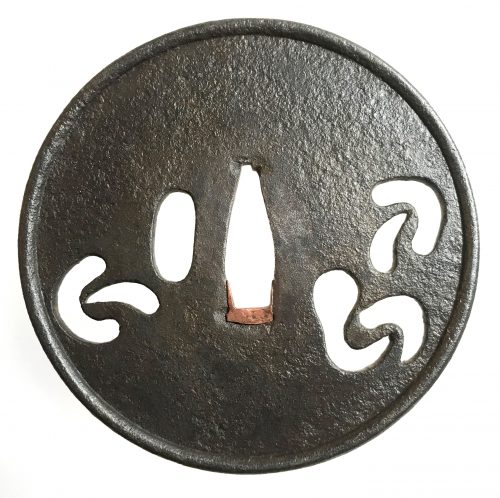
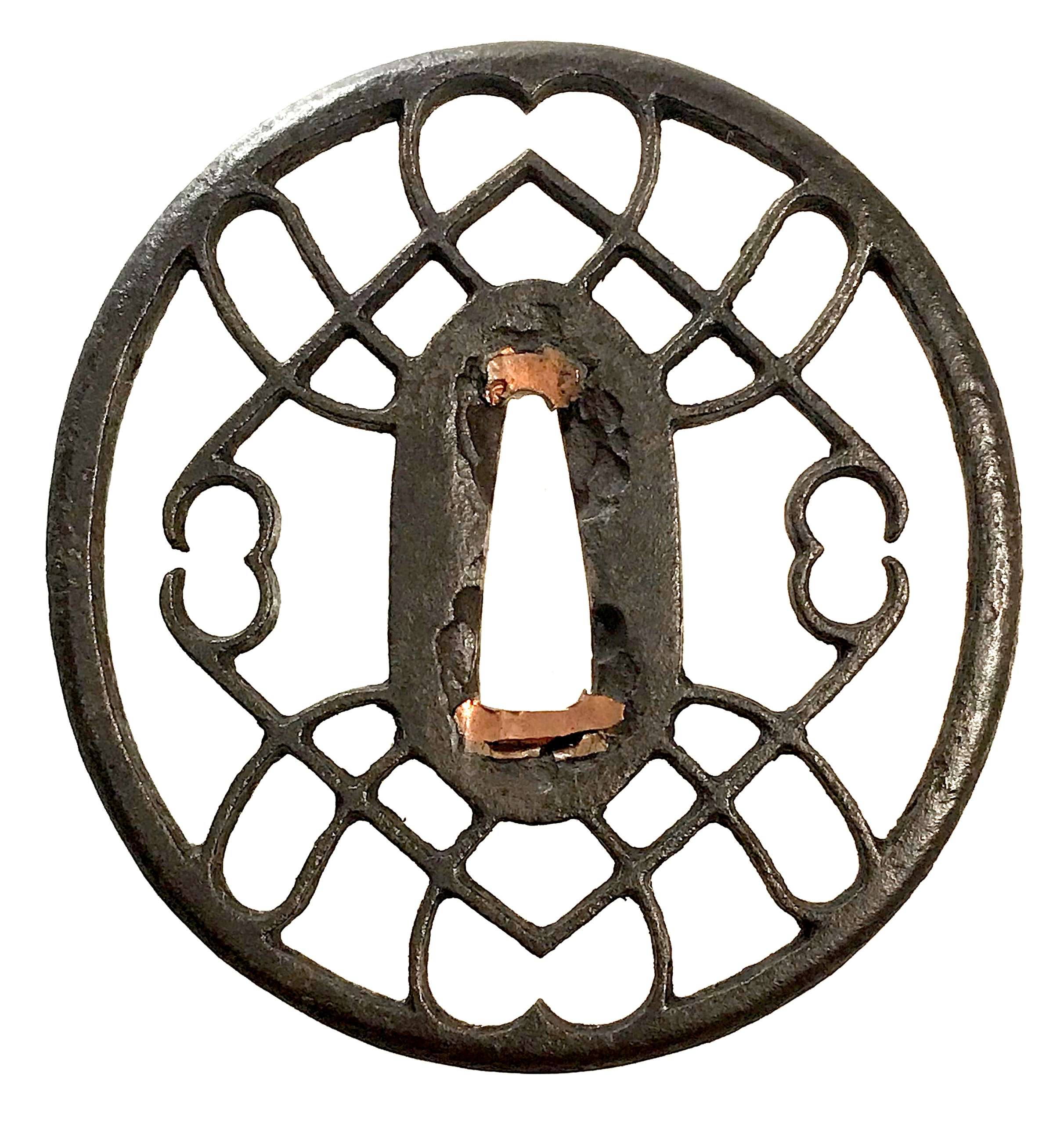 Iron tsuba of oval form with the motif of horse trappings in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Iron bones (tekkotsu) on the rim.
Iron tsuba of oval form with the motif of horse trappings in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Iron bones (tekkotsu) on the rim.Size: 80.4 x 75.8 x 5.2 mm
NBTHK Certificate №454567, allegedly saying that it is Akasaka School, Muromachi period. A look-a-like tsuba in Robert. E. Haynes Catalog #7, 1983 on page 57 under №48 is described as follows: "A masterpiece second period Owari sukashi tsuba. The plate is of beautiful color and quality almost like velvet. The design is very hard to discern, it might be the horse trappings, or even a moon. The style and type of Owari tsuba shows the great tradition of the Momoyama period and why it was the renaissance in time, as well as the arts produced, through the long history of all Japanese art. Ca. 1580. Ht. 7.7 cm, Th. (center) 5.5 mm, (edge) 5.25 to 5.75 mm."I believe we can safely attribute this tsuba to Owari School, c. 1580.
Robert. E. Haynes Catalog #7, 1983, p. 57, №48.
-

Pro-tech Walter Brend custom switchblade knife with solid 416 stainless steel frame, amber jigged bone inlays, mirror polished 154-CM blade.
Size: 94 mm (closed); 168 mm (opned); 74 mm blade)
-
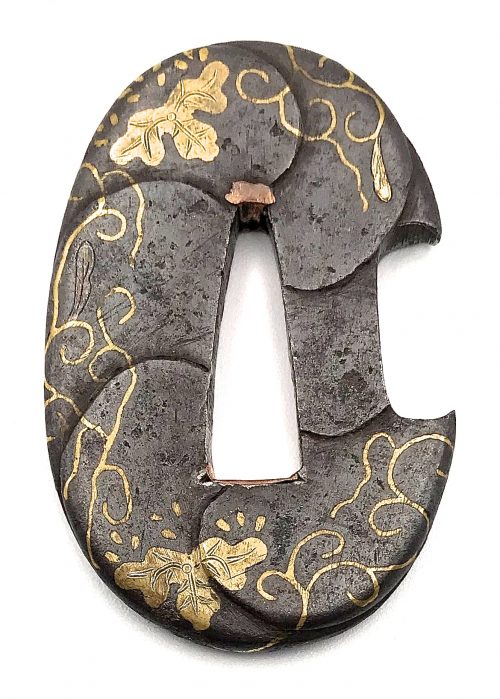

Small iron tsuba (tantō size) of oval form carved with imitation of six overlapping plates, decorated with paulownia blossoms, leaves, and tendrils in brass and copper hira-zōgan. Copper sekigane. Open kozuka hitsu-ana.
Early Edo period, 17th century.
Size: 50.5 x 34.0 x 4.9 mm.
-
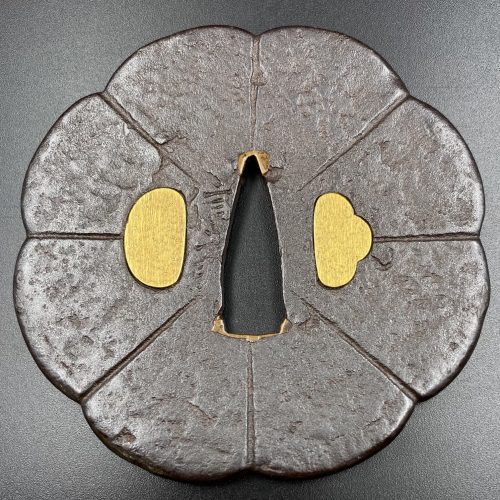

Iron tsuba in a form of an eight-petalled blossom (lotus) form, petals separated by linear low-relief carving, both hitsu-ana filled with gold plugs, the surface decorated with tsuchime-ji, rich grey-brownish patina, niku from 4 mm in the centre to 6 mm at the rim. Strong (futoji-mei) Nobuie [信家] signature to the left of nakago-ana. Attributed to the 2nd generation of Nobuie masters (Nidai Nobuie).
Size: outer diameter 84 mm, thickness at centre: 4 mm, at rim: 6 mm. Wight: 167 g.Signed: Nobuie [信家]
Probably the work of Nidai Nobuie (c. 1600).
The gold plugs are likely a later work. -
 Tin-glazed earthenware salt cellars decorated with winged creatures and grotesque paintings. Restored, losses. Size: 16 x 16 cm; Height: 2.5 cm. Attributed to Deruta, Italy, c. 1600.
Tin-glazed earthenware salt cellars decorated with winged creatures and grotesque paintings. Restored, losses. Size: 16 x 16 cm; Height: 2.5 cm. Attributed to Deruta, Italy, c. 1600. -
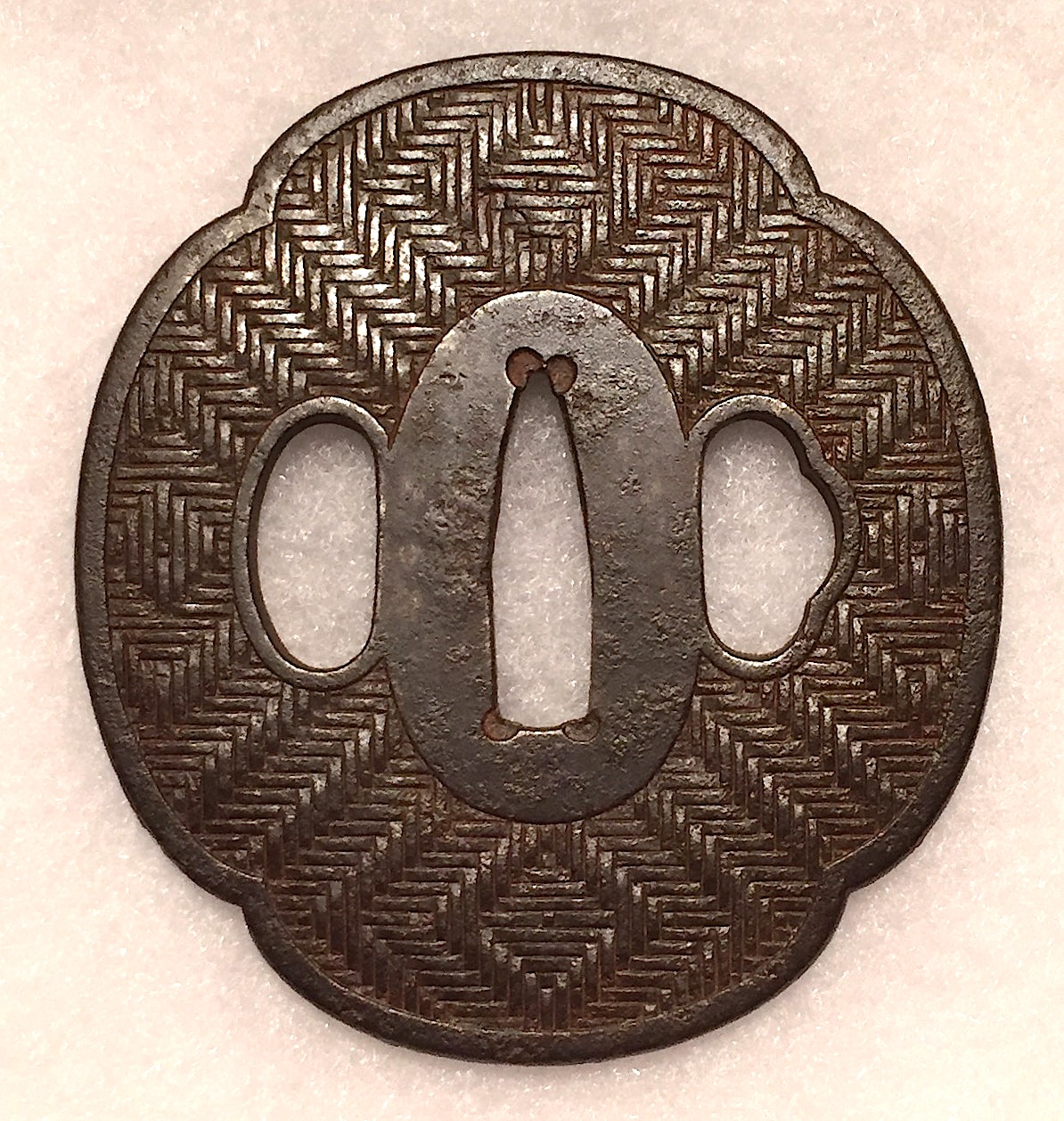 Iron tsuba with brown patina in mokkō-gata form with woven design. Size: 72 x 67 x 5 mm.
Iron tsuba with brown patina in mokkō-gata form with woven design. Size: 72 x 67 x 5 mm. -
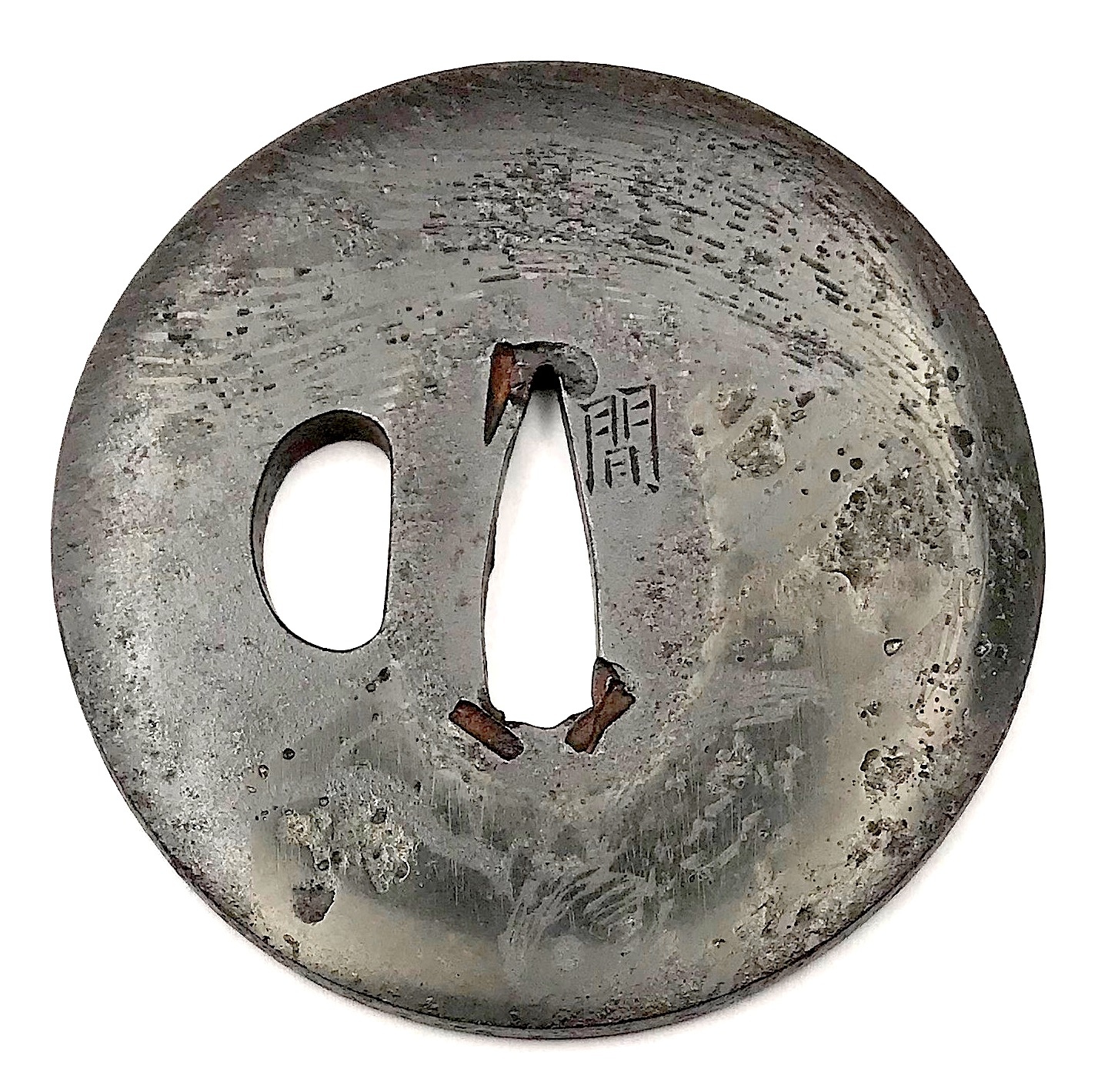 Iron tsuba of round form (width > height) decorated with a squirrel (on the face) and bamboo (on the reverse) motif in sahari flat inlay (hira-zōgan). Signed: Hazama (間) Size: 75.1mm x 75.9mm, thickness of seppa-dai 5.4mm. Early 18th century, mid Edo. Haynes/Torigoye: "There is another name for Hazama tsuba: the Kameyama school. In the period from Hōei to Kyōhō (1704-36) at Kameyama, in the province of Ise, the Kunitomo family made this style of tsuba" [...] The two artists who are best known for the sahari style of inlaid tsuba are Sadahide and Masahide" [...] The signature Hazama should be considered as that of Masahide". Sahari inlay is the distinctive characteristics of Hazama school. Sahari is an alloy of copper, tin, lead, zinc and silver. Hazama tsuba was carved patterns at first, then poured heated into the carvings on iron ground. Because it is an alloy, sahari shows different colors in each tsuba. According to Merrily Baird [Symbols, p. 163], "squirrels (risu) ... have no symbolic importance". NBTHK certificate №448388.
Iron tsuba of round form (width > height) decorated with a squirrel (on the face) and bamboo (on the reverse) motif in sahari flat inlay (hira-zōgan). Signed: Hazama (間) Size: 75.1mm x 75.9mm, thickness of seppa-dai 5.4mm. Early 18th century, mid Edo. Haynes/Torigoye: "There is another name for Hazama tsuba: the Kameyama school. In the period from Hōei to Kyōhō (1704-36) at Kameyama, in the province of Ise, the Kunitomo family made this style of tsuba" [...] The two artists who are best known for the sahari style of inlaid tsuba are Sadahide and Masahide" [...] The signature Hazama should be considered as that of Masahide". Sahari inlay is the distinctive characteristics of Hazama school. Sahari is an alloy of copper, tin, lead, zinc and silver. Hazama tsuba was carved patterns at first, then poured heated into the carvings on iron ground. Because it is an alloy, sahari shows different colors in each tsuba. According to Merrily Baird [Symbols, p. 163], "squirrels (risu) ... have no symbolic importance". NBTHK certificate №448388. -
 Iron tsuba of round form pierced with design of paulownia (kiri) in a circle in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi), details carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori). Hitsu-ana were cut later and then both plugged with lead or pewter. Brown patina. The most unusual characteristic of this tsuba is its 'positiveness': the absolute majority of Kamakura-bori tsuba are of ko-sukashi type, i.e. with small openings, presenting the motif in negative silhouette. Kamakura-bori school. Muromachi period (ca. 1450). Size: Height: 85.1 mm, width: 84.8 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, at rim: 2.8 mm. Weight: 79.1 g. A similar tsuba is presented at Japanese Swords and Sword Fittings from the Collection of Dr. Walter Ames Compton. Part I. Christie's, New York, March 31, 1992, page 11, №3: "A Kamakura-bori tsuba. Muromachi period, ca. 1450. The round iron plate is pierced with an openwork design of a paulownia crest (kiri-mon), the surface details of which are carved in low relief. The design is repeated on the reverse. The edge is slightly raised and the rim has some iron bones. 78 mm x 77 mm x 3.5 mm. Hakogaki by Sato Kanzan, dated summer 1973."
Iron tsuba of round form pierced with design of paulownia (kiri) in a circle in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi), details carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori). Hitsu-ana were cut later and then both plugged with lead or pewter. Brown patina. The most unusual characteristic of this tsuba is its 'positiveness': the absolute majority of Kamakura-bori tsuba are of ko-sukashi type, i.e. with small openings, presenting the motif in negative silhouette. Kamakura-bori school. Muromachi period (ca. 1450). Size: Height: 85.1 mm, width: 84.8 mm, thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm, at rim: 2.8 mm. Weight: 79.1 g. A similar tsuba is presented at Japanese Swords and Sword Fittings from the Collection of Dr. Walter Ames Compton. Part I. Christie's, New York, March 31, 1992, page 11, №3: "A Kamakura-bori tsuba. Muromachi period, ca. 1450. The round iron plate is pierced with an openwork design of a paulownia crest (kiri-mon), the surface details of which are carved in low relief. The design is repeated on the reverse. The edge is slightly raised and the rim has some iron bones. 78 mm x 77 mm x 3.5 mm. Hakogaki by Sato Kanzan, dated summer 1973."
Compton's Collection, Part I, p. 11, №3.
-
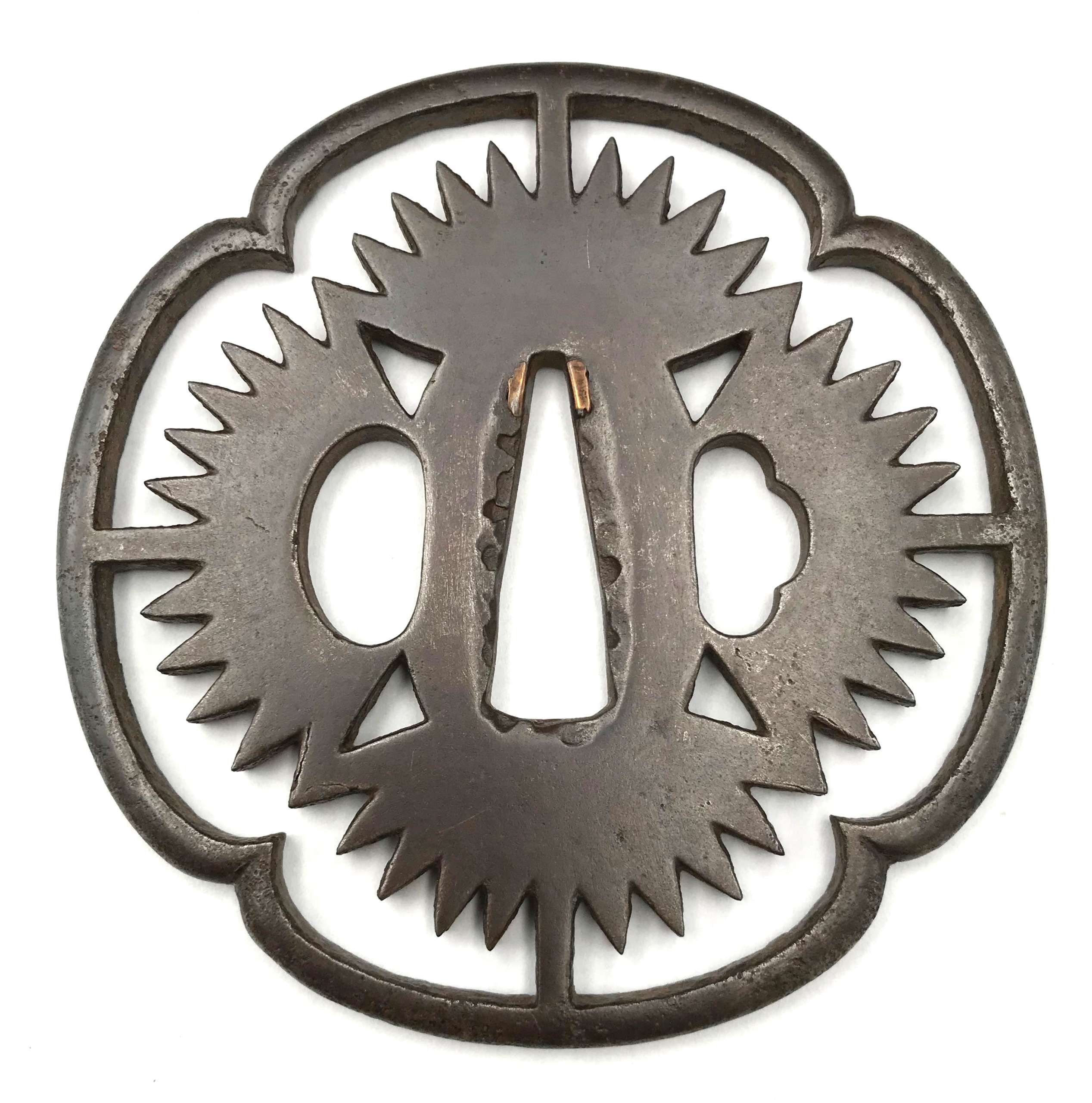 Iron tsuba of mokko form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Owari school. Edo period.
Iron tsuba of mokko form with slanting rays of light (shakoh) Christian motif (Jesuit's IHS symbol) in openwork (sukashi). Traditional description of this kind of design is called "tokei", or "clock gear". Owari school. Edo period.Size: 83.4 x 83.1 x 4.4 mm
NTHK certified KANTEISHO ("Important Work"). In a custom wooden box. For information regarding shakoh tsuba see article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91. -
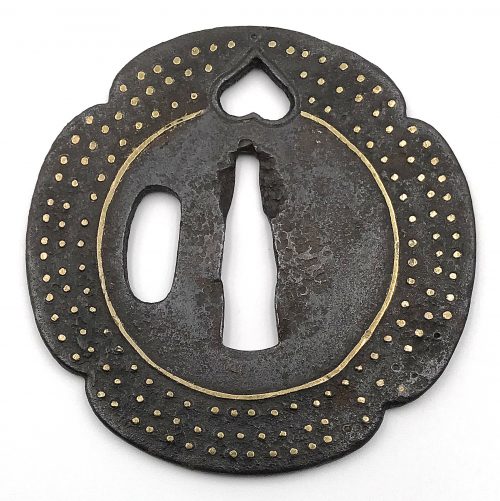

Iron tsuba of mokkō form decorated with inome (wild boar's eye) in openwork (sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate decorated with 3 concentric circular rows of brass dots in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire (sen-zōgan). Some dots and the outline of inome on the face are missing.
Ōnin school. Unsigned. Mid Muromachi period, middle of the 15th century. Dimensions: 72.1 x 71.3 x 2.3 mm. -
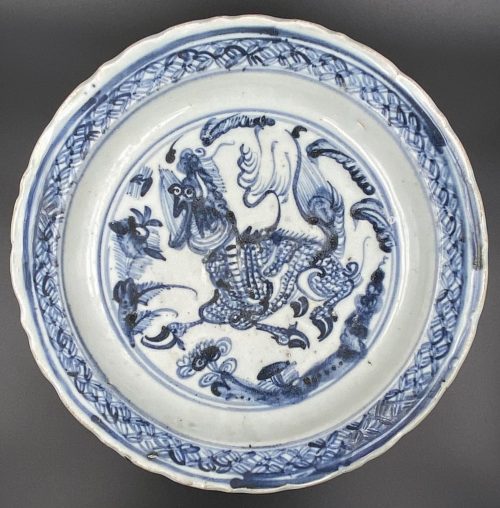 Footed plate with scalloped rim, centre decorated with running yak or another even-toed animal among flowers, jewel diaper pattern to the inner lip; foliage motif to the outside is bordered with foliage above and lotus leaves below. Porcelain with underglaze blue decoration. Ming Dynasty [大明] (1368 – 1644); Wanli Era (1572 – 1620); Late 16th – Early 17th century. Diameter: 25.5 cm; Height: 4.2 cm
Footed plate with scalloped rim, centre decorated with running yak or another even-toed animal among flowers, jewel diaper pattern to the inner lip; foliage motif to the outside is bordered with foliage above and lotus leaves below. Porcelain with underglaze blue decoration. Ming Dynasty [大明] (1368 – 1644); Wanli Era (1572 – 1620); Late 16th – Early 17th century. Diameter: 25.5 cm; Height: 4.2 cm -
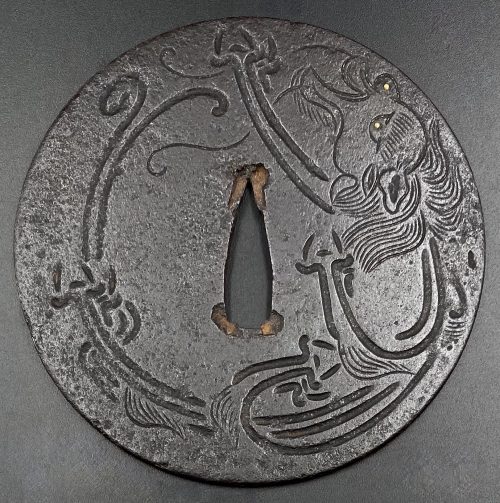 Iron tsuba of round form, on both sides decorated in low relief (kebori) with a dragon, eyes inlaid in brass. NBTHK: Hozon, № 4011013. Kamakura-bori type of tsuba. Med-Muromachi period, c. 1450. Diameter: 90 mm; Thickness (centre): 3.3 cm, Thickness (rim): 2.4 cm Reference: Japanese Swords and Sword Fittings from the Collection of Dr Walter Ames Compton (Part I). — NY: Christie's, 1992, p. 10, №2. Obviously, Compton's tsuba has an altered nakago-ana and placed on the photo upside down. Compton's tsuba has a raised mimi, while mine does not.
Iron tsuba of round form, on both sides decorated in low relief (kebori) with a dragon, eyes inlaid in brass. NBTHK: Hozon, № 4011013. Kamakura-bori type of tsuba. Med-Muromachi period, c. 1450. Diameter: 90 mm; Thickness (centre): 3.3 cm, Thickness (rim): 2.4 cm Reference: Japanese Swords and Sword Fittings from the Collection of Dr Walter Ames Compton (Part I). — NY: Christie's, 1992, p. 10, №2. Obviously, Compton's tsuba has an altered nakago-ana and placed on the photo upside down. Compton's tsuba has a raised mimi, while mine does not.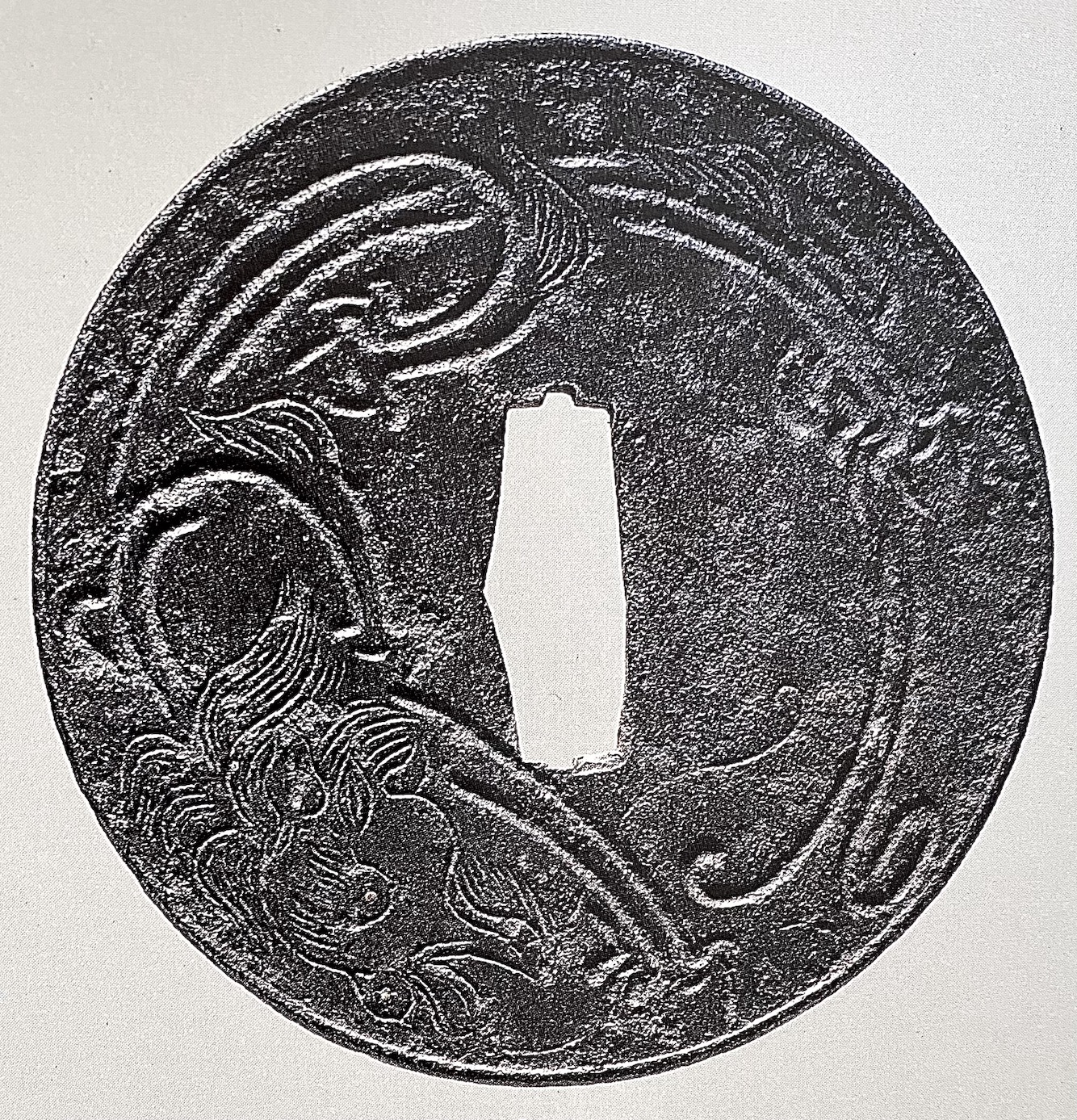
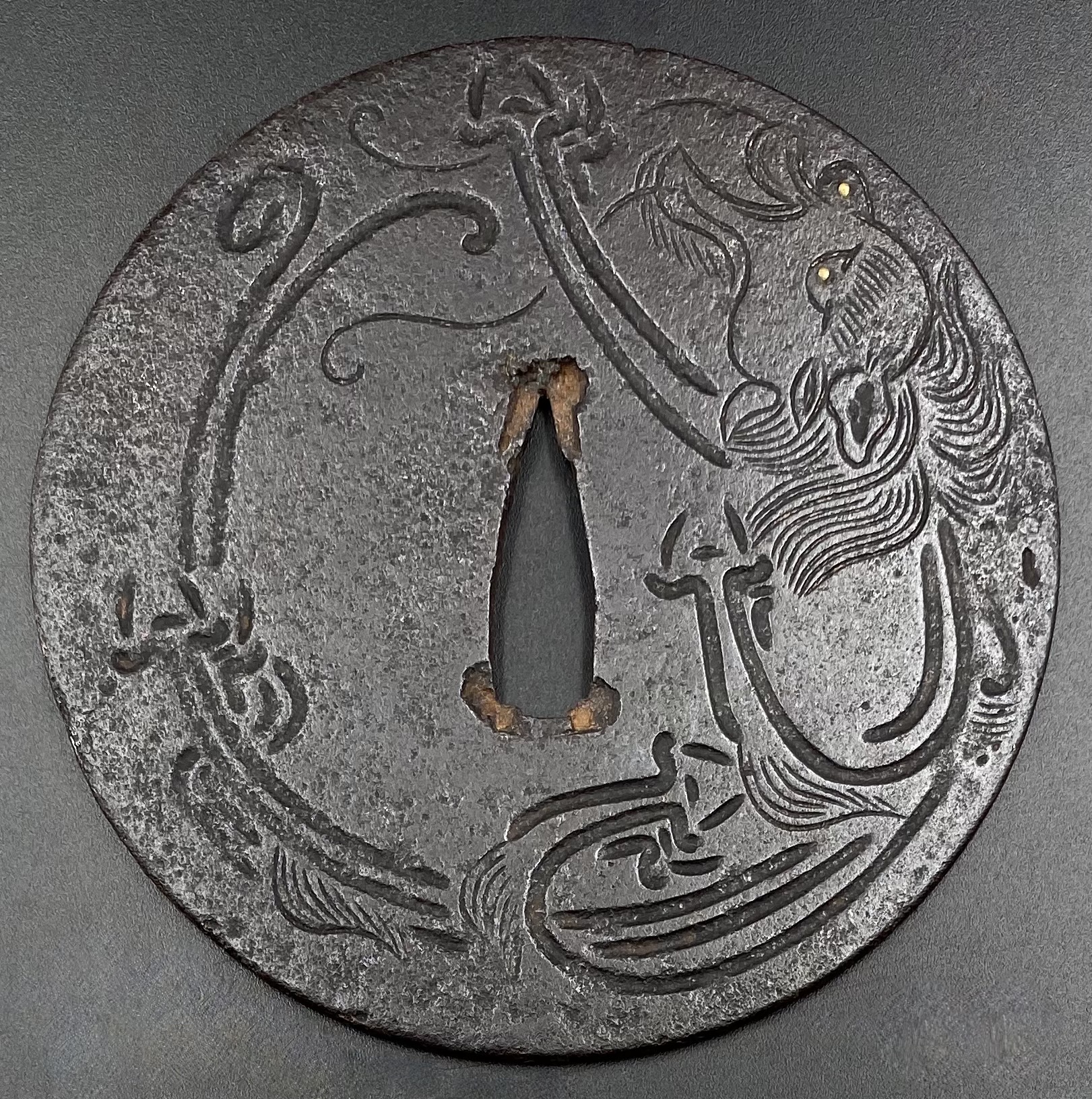 Two other examples of the same design may be found at: (1) Christie, Manson & Woods auction sales “Kotetsu”, 1980, page 12, №10 and (2) Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections №36, pp. 18-19. Both have raised mimi, the latter classified as Katchushi tsuba.
More about Kamakura-bori tsuba here.
Two other examples of the same design may be found at: (1) Christie, Manson & Woods auction sales “Kotetsu”, 1980, page 12, №10 and (2) Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections №36, pp. 18-19. Both have raised mimi, the latter classified as Katchushi tsuba.
More about Kamakura-bori tsuba here.
-
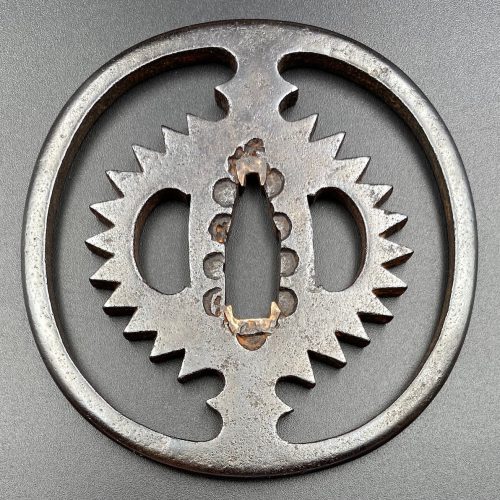 Iron tsuba of round form pierced with the design of slanting rays of light (Christian motif, Jesuit’s IHS symbol) in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi). This design is often called “tokei” [時計], or “clock gear”. Nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. Rounded rim. Unsigned. Higo school. Early Edo period, mid-17th century (1632-1650).
Iron tsuba of round form pierced with the design of slanting rays of light (Christian motif, Jesuit’s IHS symbol) in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi). This design is often called “tokei” [時計], or “clock gear”. Nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. Rounded rim. Unsigned. Higo school. Early Edo period, mid-17th century (1632-1650).Size: 78.3 x 77.0 x 5.3 mm
For information regarding this type of tsuba see the article 'Kirishitan Ikenie Tsuba by Fred Geyer at Kokusai Tosogu Kai; The 2nd International Convention & Exhibition, October 18-23, 2006, pp. 84-91. School and age attribution thanks to Bruce Kirkpatrick. . 
IHS emblem of the Jesuits
-
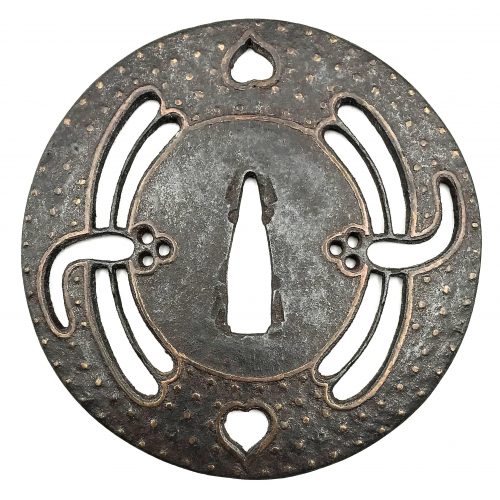 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with two boar's eyes (inome) and two dragonflies (tombo) in small openwork (ko-sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate also decorated with 2 to 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. The inlaid metal is of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, and not brass. The surface has remnants of lacquer. Ōnin school. Mid Muromachi period, middle of 15th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 90 mm, thickness: 3.2 mm. Notes regarding design: "According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13]. Two other cutouts - in the form of what in European tradition symbolizes the heart, on the top and in the bottom of tsuba disc - may have two different explanations. The most usual one, inome - "Heart-shaped pattern, which is said to go back to the shape of a wild boar's eye" [Markus Sesko. Encyclopedia of Japanese Swords. Print and publishing: Lulu Enterprises, Inc., 2014.]. This understanding is shared by Robert Haynes [Robert E. Haynes. Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010.] and elsewhere, with an exception of Okabe-Kakuya [Okabe-Kakuya. JAPANESE SWORD GUARDS. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. In cooperation with the department of Chinese and Japanese art; - 1908, p. 14], who provides the illustration of inome-shaped cut-outs with the following explanation: " The tsuba shown in Fig. 13 approaches a square form with rounded corners and is perforated with Aoi decoration. But this book was written long time ago, when people even at MFA might not know enough...
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with two boar's eyes (inome) and two dragonflies (tombo) in small openwork (ko-sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate also decorated with 2 to 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. The inlaid metal is of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, and not brass. The surface has remnants of lacquer. Ōnin school. Mid Muromachi period, middle of 15th century. Dimensions: Diameter: 90 mm, thickness: 3.2 mm. Notes regarding design: "According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13]. Two other cutouts - in the form of what in European tradition symbolizes the heart, on the top and in the bottom of tsuba disc - may have two different explanations. The most usual one, inome - "Heart-shaped pattern, which is said to go back to the shape of a wild boar's eye" [Markus Sesko. Encyclopedia of Japanese Swords. Print and publishing: Lulu Enterprises, Inc., 2014.]. This understanding is shared by Robert Haynes [Robert E. Haynes. Study Collection of Japanese Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010.] and elsewhere, with an exception of Okabe-Kakuya [Okabe-Kakuya. JAPANESE SWORD GUARDS. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. In cooperation with the department of Chinese and Japanese art; - 1908, p. 14], who provides the illustration of inome-shaped cut-outs with the following explanation: " The tsuba shown in Fig. 13 approaches a square form with rounded corners and is perforated with Aoi decoration. But this book was written long time ago, when people even at MFA might not know enough... The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.
The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.
 There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
 Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."
Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."
-
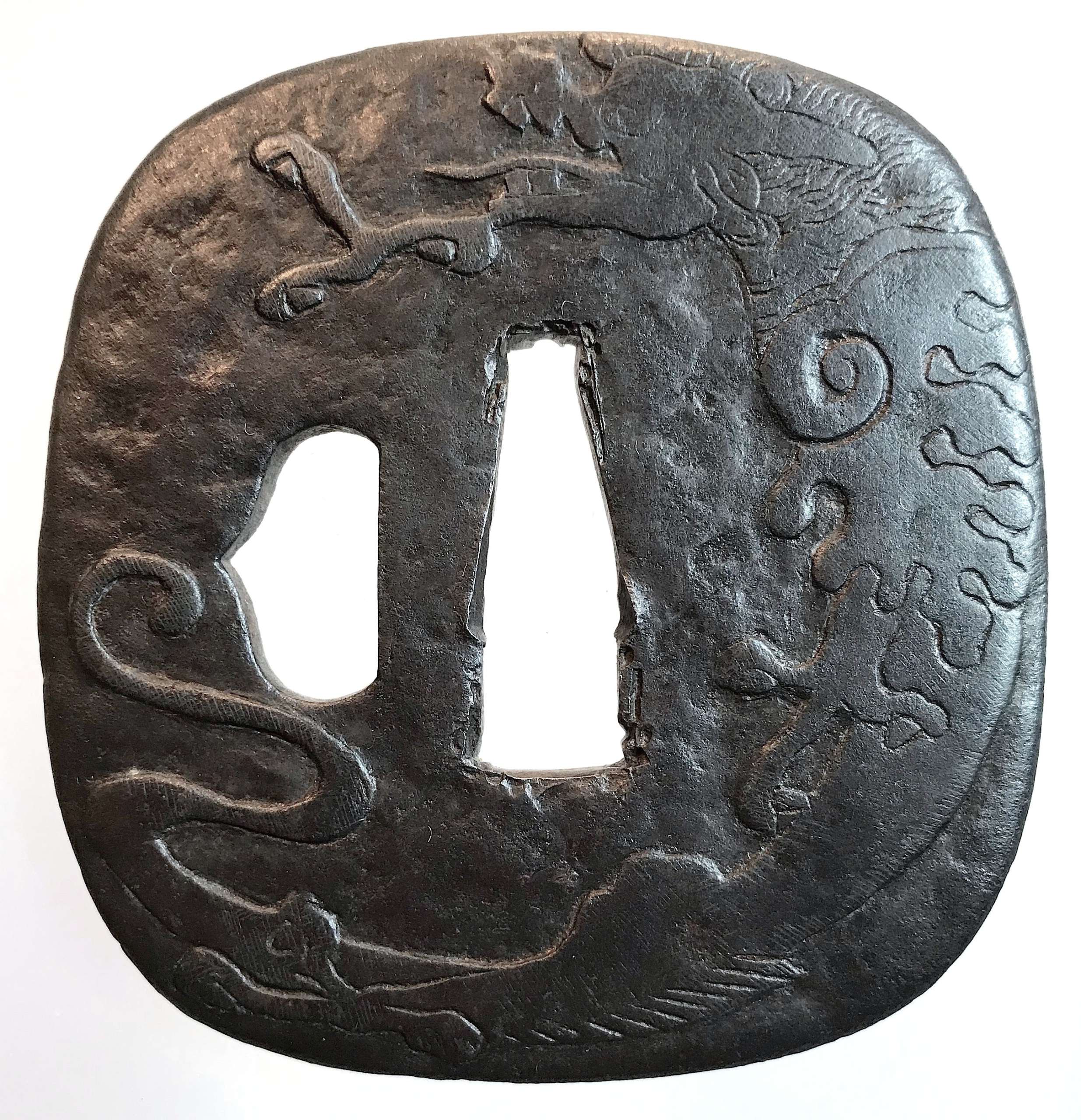 Shimizu-Jingo tsuba with a dragon and vajra (on reverse) motif. Unsigned. Possibly, 3rd or 4th master of Shimizu-Jingo family in Higo province. Iron. Low relief carving. Edo period, 1700's. Height: 75.4 mm, Width: 72.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm
Shimizu-Jingo tsuba with a dragon and vajra (on reverse) motif. Unsigned. Possibly, 3rd or 4th master of Shimizu-Jingo family in Higo province. Iron. Low relief carving. Edo period, 1700's. Height: 75.4 mm, Width: 72.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 4.0 mm -
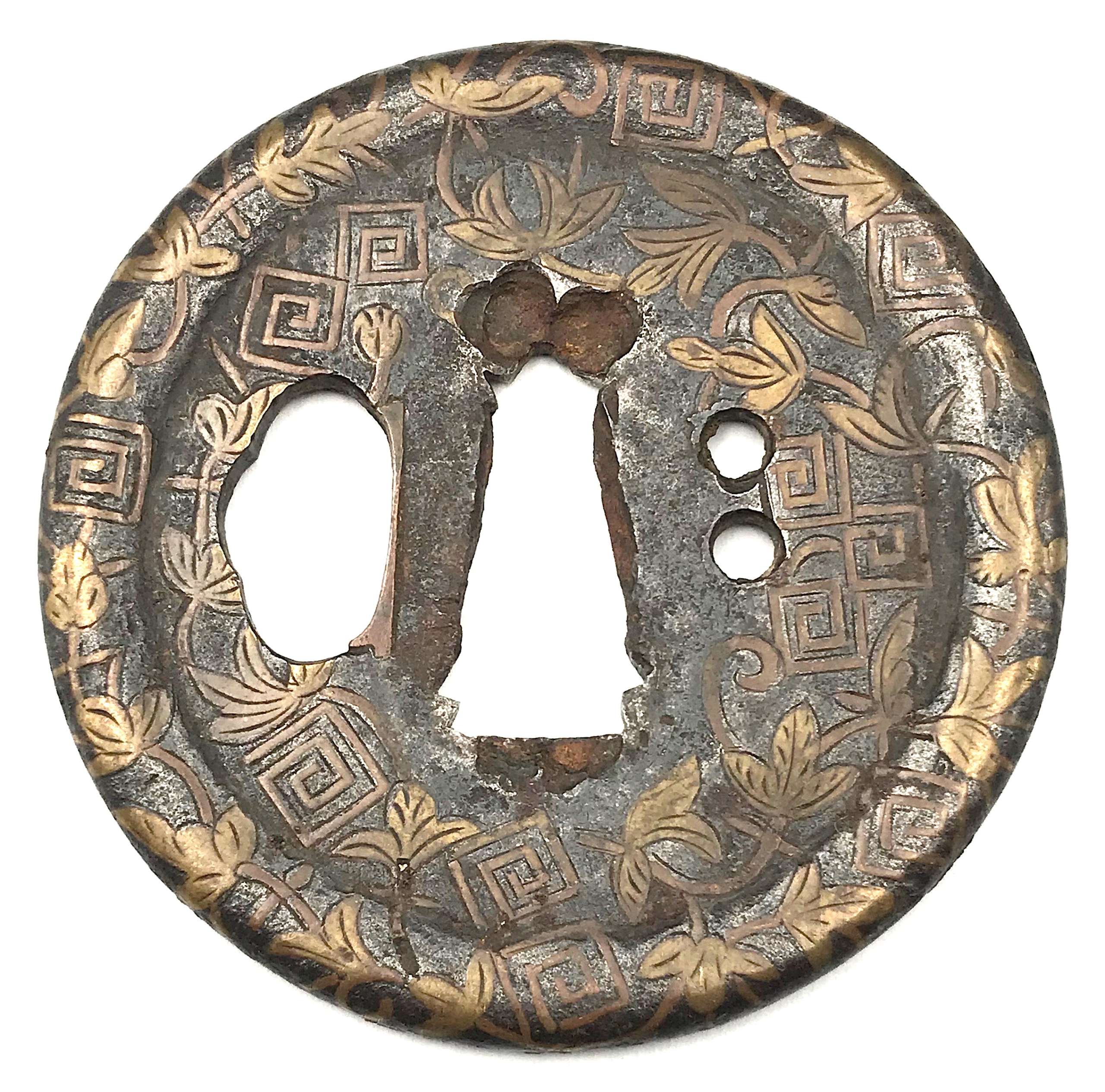

Iron tsuba of round form with dam-shaped rim (dote-mimi) pierced with hitsu-ana and two udenuki-ana (probably cut later on) decorated in flat inlay (hira-zōgan) with vines and symbols of thunder or lightning (possibly - family crest, mon). Hitsu-ana and nakago-ana with copper sekigane.
Ōnin or Heianjō school, or, possibly Kaga or Umetada school. Momoyama period or earlier (Muromachi), 16th century. Unsigned.Size: 64.5 x 63.8 x 2.2 (center), 4.2 (rim) mm.
Provenance: Lundgren Collection: [Japanese sword-fittings and metalwork in the Lundgren Collection. Published by Otsuka Kogeisha Co., Ltd., Tokyo 1992], №31; The Lundgren Collection of Japanese Swords, Sword Fittings and A Group of Miochin School Metalwork. Christie's Auction: Tuesday, 18 November 1997, London. Sales "GOTO-5881". Christie's, 1997, №2. Lundgren's description at Christie's: Heianjo tsuba. Unsigned. The circular plate decorated in brass hirazogan with flowers, plants and symbols of thunder, dote mimi and udenuki ana, late Muromachi period (16th century). Tokyo 1992 description: Sword guard with design of flowering plants and frets in inlay. Unsigned. Heianjo inlay school. 6.35 x 6.3 cm, thickness of rim 0.40 cm. Iron. Flat brass inlay. Muromachi-Momoyama Period, 16th century. Provenance: The Second John Harding. A somewhat look-a-like pieces can be found in various catalogues. The one in Naunton Collection, №172, is signed: Umetada of Yamashiro: "Iron, small, almost circular, with raised oval rim, inlaid all over with leaves and scrolls in brass hirazōgan." -
 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of pine tree mushrooms (matsutake) in openwork (sukashi). Hitsu-ana of elongated oval form. Raised rim (mimi) with iron bones (tekkotsu). Copper sekigane. Size: 84.5 mm x 85.1 mm; thickness: 3.0 mm (center), 5.6 mm (rim). Mid Muromachi period, 15th century. The shape and width of the rim, as well as the shape of the hitsu-ana, argue for earlier Muromachi. Tsuba is slightly wider than high, that might suggest middle of Muromachi age. According to Robert Haynes, circa 1450-1500.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with design of pine tree mushrooms (matsutake) in openwork (sukashi). Hitsu-ana of elongated oval form. Raised rim (mimi) with iron bones (tekkotsu). Copper sekigane. Size: 84.5 mm x 85.1 mm; thickness: 3.0 mm (center), 5.6 mm (rim). Mid Muromachi period, 15th century. The shape and width of the rim, as well as the shape of the hitsu-ana, argue for earlier Muromachi. Tsuba is slightly wider than high, that might suggest middle of Muromachi age. According to Robert Haynes, circa 1450-1500. -
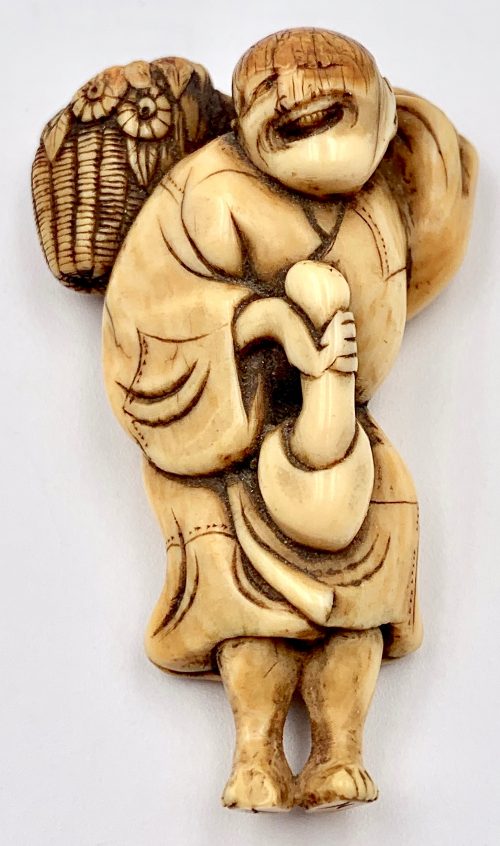

Netsuke with a design of a laughing peasant carrying a basket and holding a giant mushroom in his right hand.
18th century Dimensions: 55.7 mm tallUnsigned. According to Merrily Baird (Symbols of Japan, page. 93): ...Theis prominent use in the symbol-rich netsuke art form, however, reflects more their sexual symbolism than either their dietary appeal or interesting shapes. Mushrooms in Japan are generally a symbol of fertility, with some flat varieties, like shiitake, being associated with females. In contrast, the matsutake mushroom (Armillaria edodes) is a phallic symbol, as befits its thick, spearlike stem and the fact that it is consumed before cap opens.

Female Daruma Riding a Mushroom. Ippitsusai Bunchô. MFA impressions: 11.18513, 21.4758
-
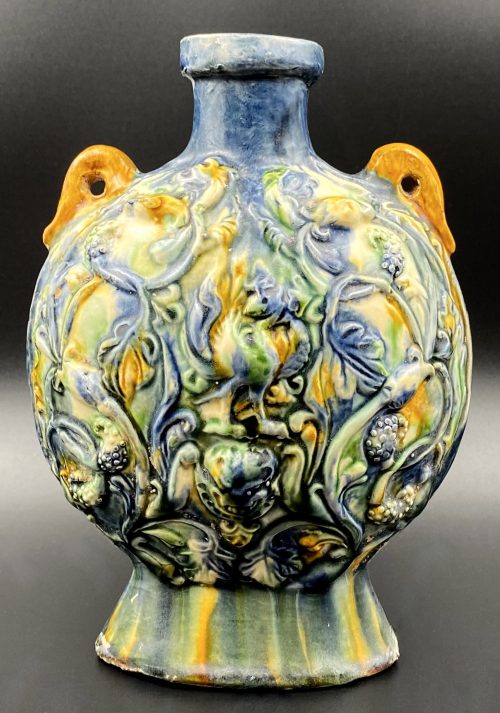 A vessel of flattened ovoid form supported on a tall splayed foot and surmounted by a short neck with the galleried rim. The shoulders set with a pair of loop handles, the body moulded on both sides with a Phenix surrounded with meandering floral and foliate scrolls. Covered with irregular splashes of green, amber, cream, and blue glazes, dripping down the foot. Foot bottom unglazed (beige body). China, the Tang dynasty [唐朝] (618 – 907). Height: 18.5 cm; Width: 13 cm
A vessel of flattened ovoid form supported on a tall splayed foot and surmounted by a short neck with the galleried rim. The shoulders set with a pair of loop handles, the body moulded on both sides with a Phenix surrounded with meandering floral and foliate scrolls. Covered with irregular splashes of green, amber, cream, and blue glazes, dripping down the foot. Foot bottom unglazed (beige body). China, the Tang dynasty [唐朝] (618 – 907). Height: 18.5 cm; Width: 13 cm -
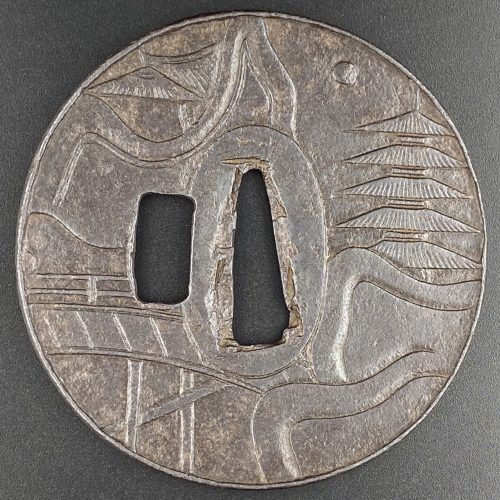

The thin iron plate of round form and black colour carved in sukidashi-bori with the design of rocks, waves, bridge, mountain pavilion and 5-storey pagoda under the moon, on both sides, alluding to Todai-ji temple in Nara. Slightly rounded rectangular hitsu-ana probably pierced later. Very narrow raised rim as usual in katsushi tsuba. In a modern wooden box.
Late Muromachi period, 16th century. Dimensions: 81.1 x 79.5 x 3. mm (seppa-dai), 2.2 mm (base plate), 4.4. (rim).Reference: “Art of the Samurai” on page 232, №140: ”Kamakura tsuba with Sangatsu-do tower and bridge. Muromachi period, 16th century. 83 mm x 80 mm. Unsigned. Tokyo National Museum. The mountain pavilion and bridge carved in sunken relief on the iron tsuba – both part of Tōdai-ji, a temple in Nara – are detailed in fine kebori (line) engraving. As a result of the chiselling used to create the relief, the ground of the piece is relatively thin”. Also page 41 in Tsuba Kanshoki. Kazutaro Torogoye, 1975 [LIB-1480.2018].
This tsuba is very much similar to TSU-0384. -
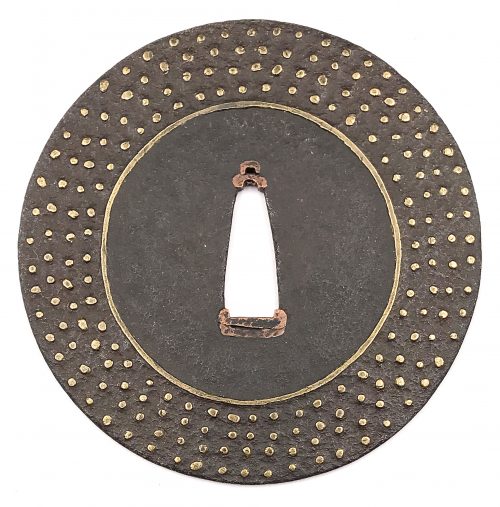 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with inlay of four concentric rows of brass dots or nail heads (ten-zōgan) and a circular brass wire inlay inside the innermost row of dots. Copper sekigane. Muromachi period, 15th or 16th century. Unsigned. Ōnin school. Size: 87.9 x 87.8 x 2.2 mm. Ōnin school got its name from the Ōnin War (応仁の乱 - Ōnin no Ran) - a civil war that lasted 10 years (1467–1477) during the Muromachi period in Japan.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with inlay of four concentric rows of brass dots or nail heads (ten-zōgan) and a circular brass wire inlay inside the innermost row of dots. Copper sekigane. Muromachi period, 15th or 16th century. Unsigned. Ōnin school. Size: 87.9 x 87.8 x 2.2 mm. Ōnin school got its name from the Ōnin War (応仁の乱 - Ōnin no Ran) - a civil war that lasted 10 years (1467–1477) during the Muromachi period in Japan. -
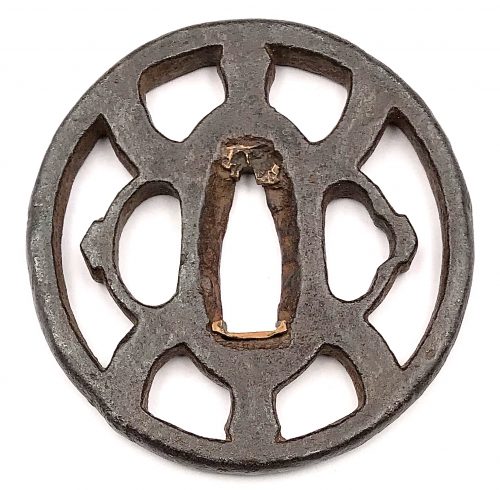 Iron tsuba of round form with design of the Chinese character for cinnabar (shu-no-ji) in openwork (sukashi). Round-cornered rim. Copper sekigane. Kanayama school. Early Edo period: Early 17th century (Kan-ei era). Height: 70.0 mm. Width: 69.6 mm. Rim thickness: 6.8 mm. Center thickness: 5.8 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 139: "Many areas have a coarse texture and strong tekkotsu, with the thickness of the metal graduating from the rim to the seppa-dai. The combined color of the iron and motif date this work to the early Edo period".
Iron tsuba of round form with design of the Chinese character for cinnabar (shu-no-ji) in openwork (sukashi). Round-cornered rim. Copper sekigane. Kanayama school. Early Edo period: Early 17th century (Kan-ei era). Height: 70.0 mm. Width: 69.6 mm. Rim thickness: 6.8 mm. Center thickness: 5.8 mm. Provenance: Sasano Masayuki Collection, № 139: "Many areas have a coarse texture and strong tekkotsu, with the thickness of the metal graduating from the rim to the seppa-dai. The combined color of the iron and motif date this work to the early Edo period". -
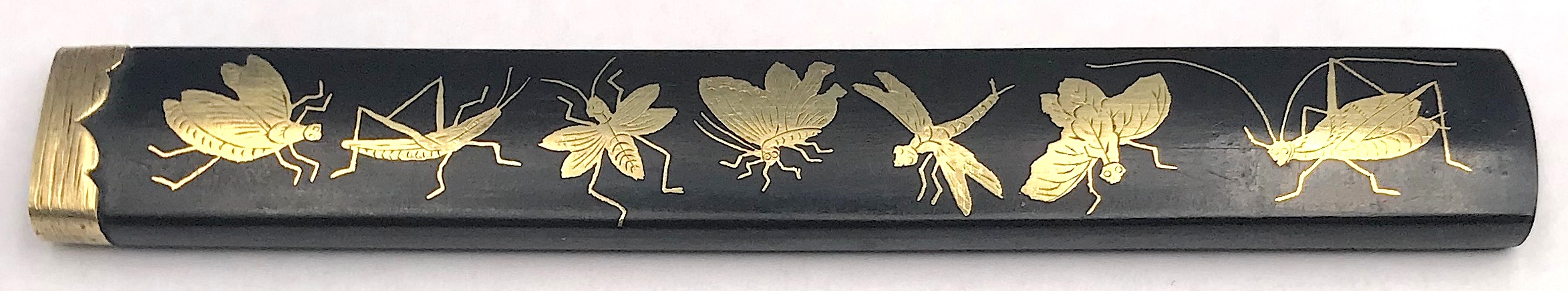 Kozuka with seven insects (fly, grasshopper, bee, butterfly, dragonfly, firefly, and cricket) and grass with dewdrops motif. Shakudō, flush gold inlay (hira-zōgan). 95.2 (H) x 13.7 mm (W). Mid Edo period (Late 17th - early 18th century, Genroku era 1688-1703). Unsigned. Kaga school. A look-a-like kozuka (with five insects) is illustrated at Japanese Sword Fittings. A descriptive catalogue of the Collection of G.H. Naunton, Esq., completed and illustrated by Henri L. Joly, - 1912 on plate XXIX, №691 [LIB-1389 in this Collection] with the following description at page 54: "Shakudō, inlaid with butterfly, dragon-fly, grasshopper, locust and another insect, gold."
Kozuka with seven insects (fly, grasshopper, bee, butterfly, dragonfly, firefly, and cricket) and grass with dewdrops motif. Shakudō, flush gold inlay (hira-zōgan). 95.2 (H) x 13.7 mm (W). Mid Edo period (Late 17th - early 18th century, Genroku era 1688-1703). Unsigned. Kaga school. A look-a-like kozuka (with five insects) is illustrated at Japanese Sword Fittings. A descriptive catalogue of the Collection of G.H. Naunton, Esq., completed and illustrated by Henri L. Joly, - 1912 on plate XXIX, №691 [LIB-1389 in this Collection] with the following description at page 54: "Shakudō, inlaid with butterfly, dragon-fly, grasshopper, locust and another insect, gold." See also tsuba TSU-0211 in this collection:
See also tsuba TSU-0211 in this collection:


-
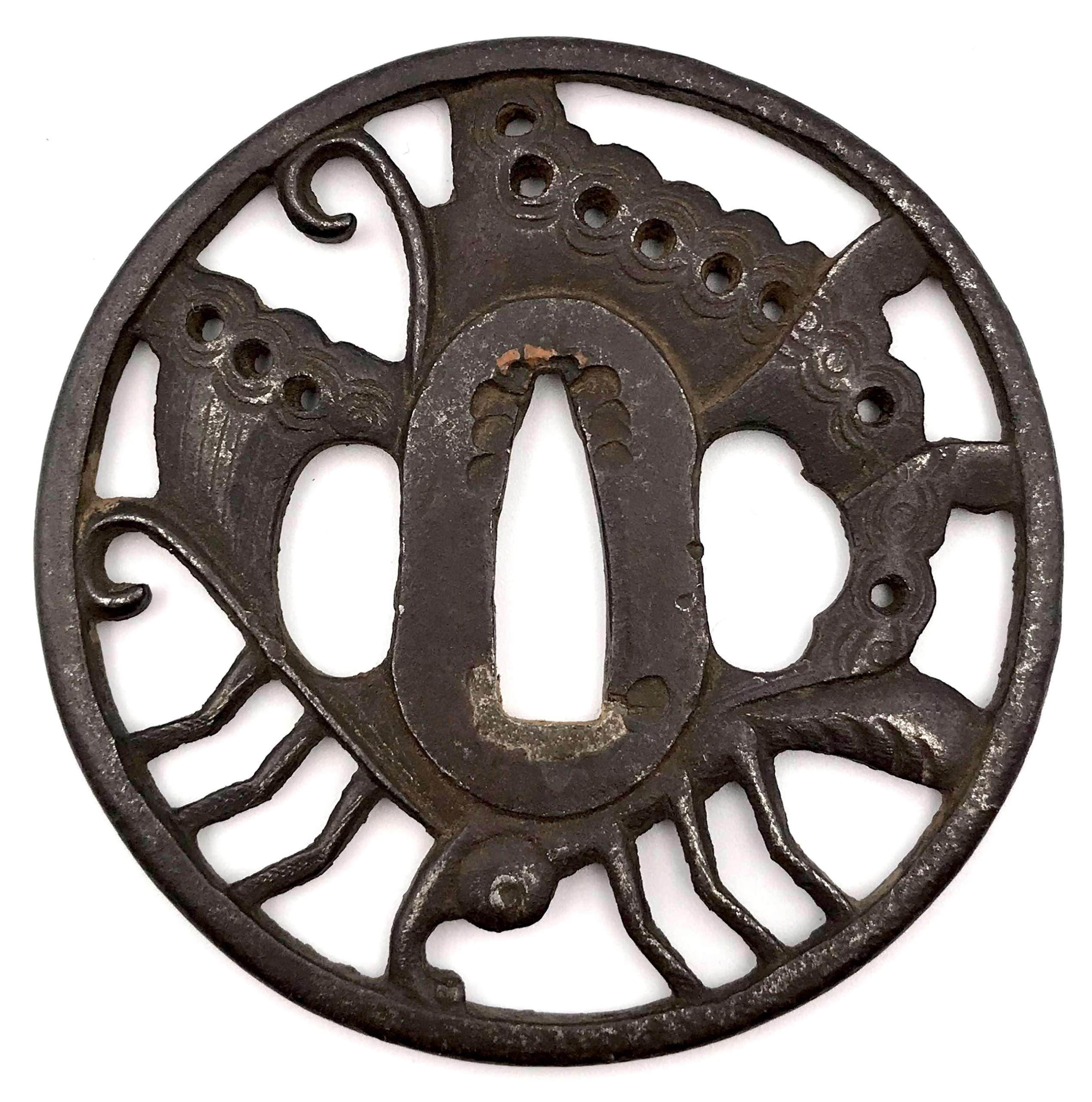 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of a butterfly in openwork (sukashi) with details carved in kebori. Eyes inlaid in brass (one inlay is missing). Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 80.4 x 80.6 x 4.4 mm References At Haynes Catalog #6, p. 18-19, Lot 30: "Famous Ikeda butterfly design" (Ikeda family of Inaba and Okayama, and at least 7 other families). Ca. 1700. Shōami of Kyoto, no doubt. Ht 8.2 cm, Th. 5 mm. ["Important tsuba, menuki, bokuto, woodblock prints, koshirae, sword pistol and kana mono". San Francisco, June 1-26, 1983. Catalog #6. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd.]Similar tsuba at Haynes Catalog #9, p.71, lot 143: the classic Shoami tsuba of the mon of the Ikeda family. This example, as most, seems to be made by the same hand as the others. See Haynes sale number 6, lot 30, for an identical example. The eye is brass. From an old French collection. Ht. 7.9 cm., Th. 5 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with the design of a butterfly in openwork (sukashi) with details carved in kebori. Eyes inlaid in brass (one inlay is missing). Unsigned. Attributed to Bizen Shōami school, early Edo period (17th century). Dimensions: 80.4 x 80.6 x 4.4 mm References At Haynes Catalog #6, p. 18-19, Lot 30: "Famous Ikeda butterfly design" (Ikeda family of Inaba and Okayama, and at least 7 other families). Ca. 1700. Shōami of Kyoto, no doubt. Ht 8.2 cm, Th. 5 mm. ["Important tsuba, menuki, bokuto, woodblock prints, koshirae, sword pistol and kana mono". San Francisco, June 1-26, 1983. Catalog #6. Robert E. Haynes, Ltd.]Similar tsuba at Haynes Catalog #9, p.71, lot 143: the classic Shoami tsuba of the mon of the Ikeda family. This example, as most, seems to be made by the same hand as the others. See Haynes sale number 6, lot 30, for an identical example. The eye is brass. From an old French collection. Ht. 7.9 cm., Th. 5 mm.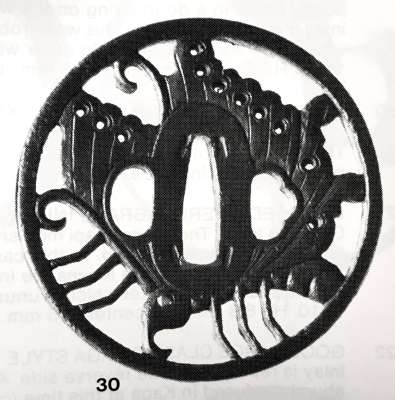
Haynes Catalog #6, lot 30.
Similar tsuba in the Randolph B. Caldwell Collection, 1994, page 24, №13: "A circular iron tsuba pierced in positive sukashi with a butterfly within an angular rim, details engraved. The eye inlaid in brass [in my specimen the inlay is missing on the omote side]. Unsigned. Bizen Shōami, Momoyama period. Dimensions: 8.0 x 8.2 x 0.5 cm. Similar example: Durand-Ruel, collection Ch. Gilloz, number 1302. [SV: that's possibly the 'old French collection' of Robert Haynes.]
Haynes Catalog #9, lot 143.
If we accept Haynes' theory regarding the genealogy and history of Bizen Shōami family, Momoyama period attribution would seem unlikely. I am leaning towards the early to mid 17th century.
Caldwell Collection, #13.
-
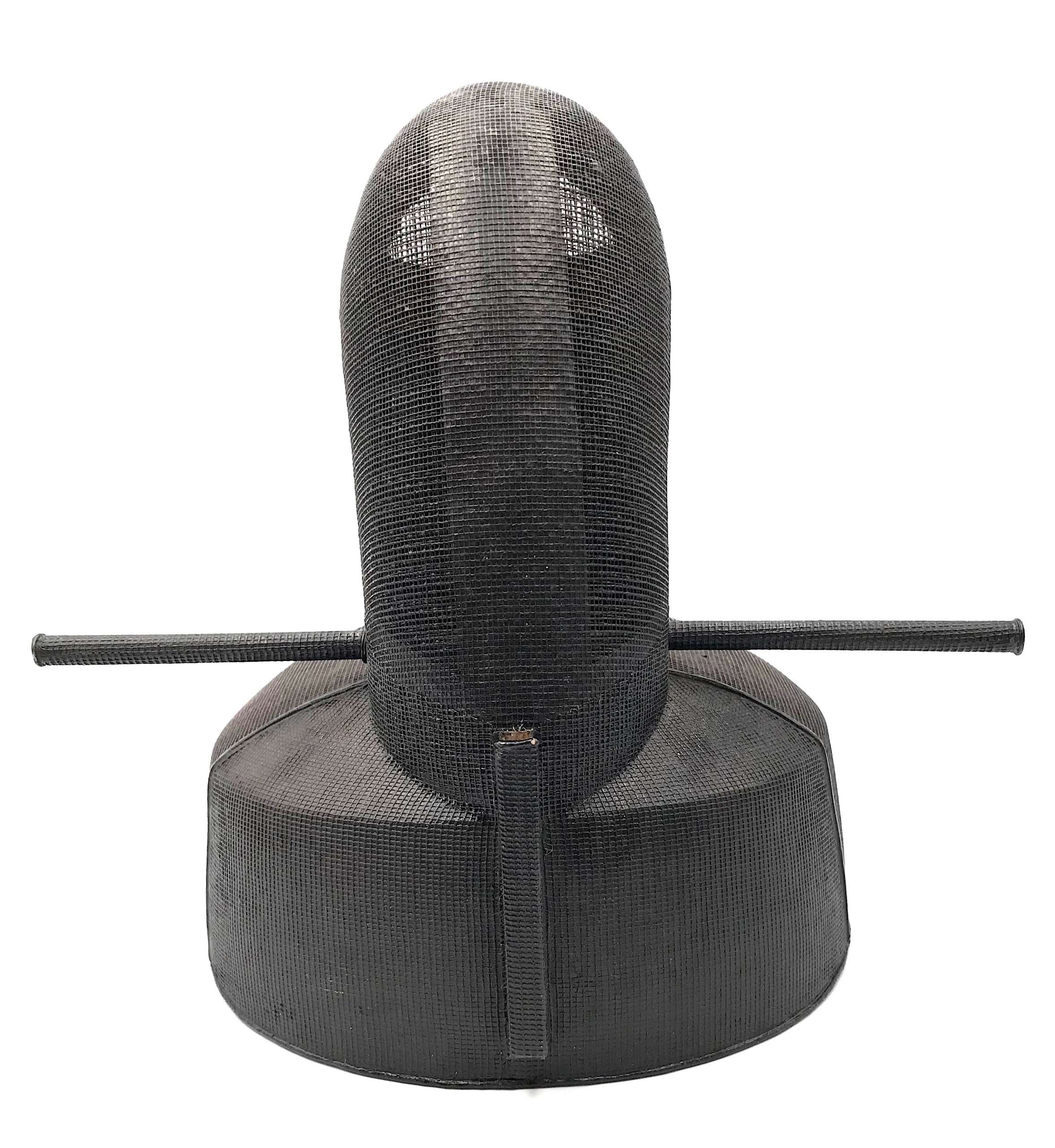 Kanmuri - a classic court cap, made of lacquered wood and paper. It is traditionally made by creating a skeleton, or harinuki, of paper on a wooden form. The outside of the hari-nuki is lacquered so as to keep its shape, and then the body of ra silk is layed on top. The entire thing is lacquered stiff.
Kanmuri - a classic court cap, made of lacquered wood and paper. It is traditionally made by creating a skeleton, or harinuki, of paper on a wooden form. The outside of the hari-nuki is lacquered so as to keep its shape, and then the body of ra silk is layed on top. The entire thing is lacquered stiff.Size: Height:20cm; Width: 21cm; Depth: 20cm.
Probably Taishō period (1912-1926), or later. Certain information is provided at http://www.sengokudaimyo.com/garb/garb.html In a wooden box without inscriptions. -

Classical picklock Italian stiletto switchblade knife with bolster release, fixed guard, Brazilian horn handle.
Size: 112 mm (closed); 240 mm (opened); 90 mm blade.
Tang is etched with: Latama, Italy. SOLD -
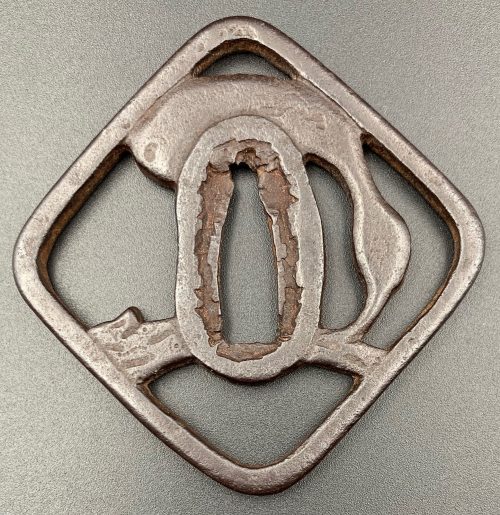

Iron tsuba of diamond form with rounded corners with the design of a double gourd on a branch in openwork. Dark brown patina. Ko-Shōami school. Custom kiri-wood box with hakogaki of Sasano Masayuki.
Momoyama Period (1574-1603)
Size: 77.1 x 75.7 x 4.6 mm; weight: 75.3 g.
Provenance: Sasano Masayuki[Translated by Markus Sesko]Hakogaki lid outside: 古正阿弥鐔 Ko-Shōami tsuba Hakogaki lid inside:Hyōtan-sukashi Mumei, Momoyama-ki saku Tetsu, ji-sukashi Koboku-aware no kasaku Heisei ninen Soshinkan Minazuki Openwork design of gourd Unsigned, Momoyama era work Iron, large openwork Masterwork full of classical charm. June of 1990, Soshinkan [pen name of Sasano Masayuki]瓢簞透 無銘 桃山期作 鉄地透
古撲惻之佳作 平成二年 素心鑑 水無月
-
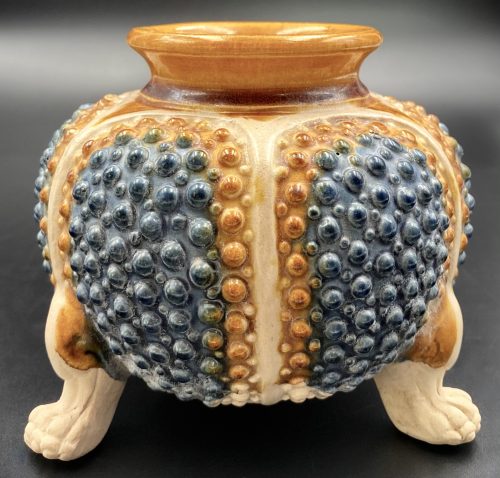 Small six-lobed sancai (blue, amber, and cream) earthenware tripod censer with amber lead glaze mouth, an outer surface of the body decorated in a form of toad skin, the centre of the bottom unglazed, standing on unglazed beast's paws. China, the Tang dynasty [唐朝] (618 – 907). Diameter: 10.2 cm; Height: 9.2 cm.
Small six-lobed sancai (blue, amber, and cream) earthenware tripod censer with amber lead glaze mouth, an outer surface of the body decorated in a form of toad skin, the centre of the bottom unglazed, standing on unglazed beast's paws. China, the Tang dynasty [唐朝] (618 – 907). Diameter: 10.2 cm; Height: 9.2 cm. -
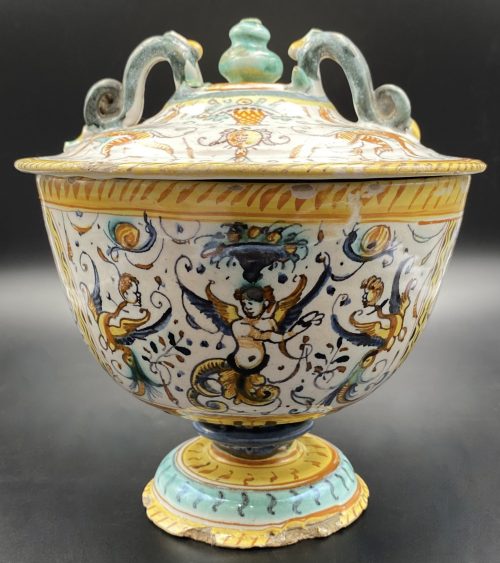 Tin-glazed earthenware footed lidded cup decorated with winged creatures and grotesque paintings, Bachus and Cupid inside. Minor losses Diameter: 16 cm; Height: 18 cm. Attributed to Deruta, Italy, c. 1600.
Tin-glazed earthenware footed lidded cup decorated with winged creatures and grotesque paintings, Bachus and Cupid inside. Minor losses Diameter: 16 cm; Height: 18 cm. Attributed to Deruta, Italy, c. 1600. -
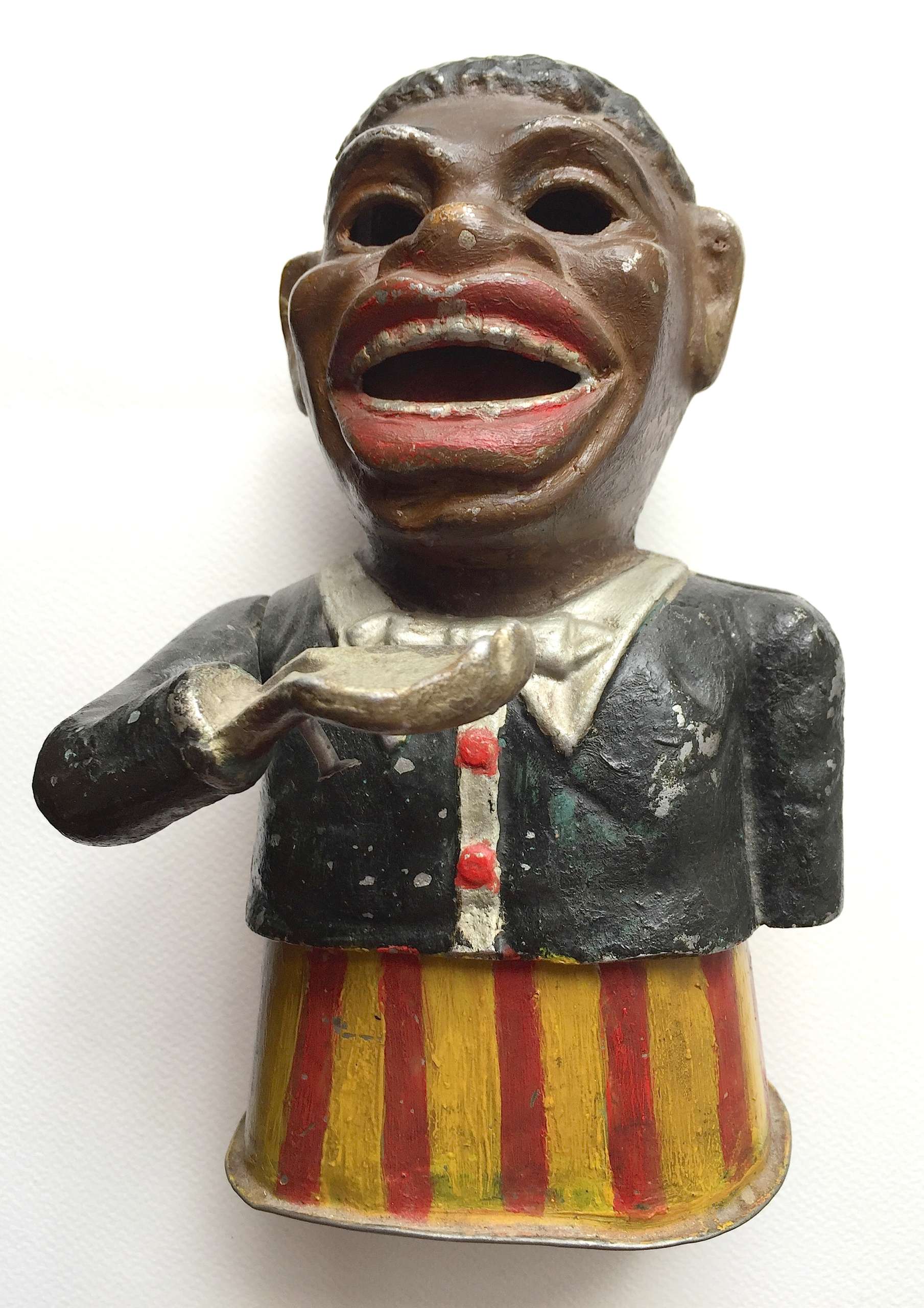 A cast iron painted 19th century style money box in the form of a negro, the arm articulated to insert coins.
A cast iron painted 19th century style money box in the form of a negro, the arm articulated to insert coins. -
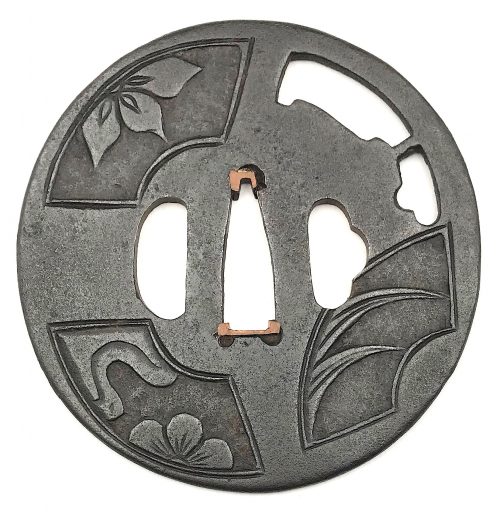 Iron tsuba of round form with design of hatchet executed in openwork (sukashi) and three fan panels motif on both sides carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori). Designs on the fan panels - face: bellflower, plum blossom in mist, grass leaves; - back: clouds, grass, and half plum blossom in mist. Copper sekigane. Koga-hitsu-ana probably cut out on a later date. Kamakura or kamakura-bori school. Edo period. Height: 83.8 mm, Width: 82.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm. NBTHK certificate № 4005500: Hozon (worthy of preservation).
Iron tsuba of round form with design of hatchet executed in openwork (sukashi) and three fan panels motif on both sides carved in low relief (sukidashi-bori). Designs on the fan panels - face: bellflower, plum blossom in mist, grass leaves; - back: clouds, grass, and half plum blossom in mist. Copper sekigane. Koga-hitsu-ana probably cut out on a later date. Kamakura or kamakura-bori school. Edo period. Height: 83.8 mm, Width: 82.2 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.2 mm. NBTHK certificate № 4005500: Hozon (worthy of preservation). -
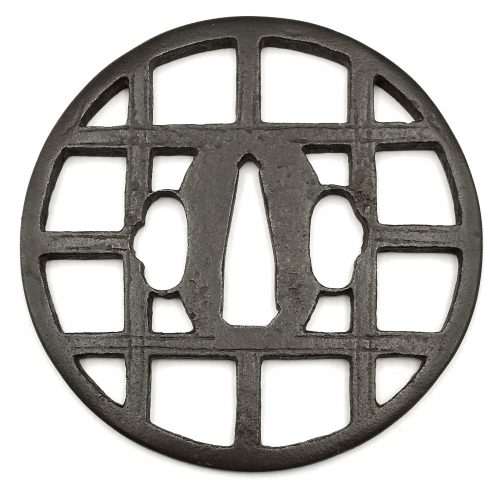 Iron tsuba of round form with design of lattice (kōshi-mon, 格子文) cut in openwork (sukashi), with low relief shallow linear carving along the bars. Well forged plate with brown-ish hue. To the right of nakago-ana there is a clear inscription of the character Shō (正), which is explained by Markus Sesko is follows: "The Shinsa obviously recognized more from the signature when having the tsuba in hand, i.e. they were confident to say it is signed "Shōami" but the rest is illegible (ika-fumei, 以下不明). That is, if they were just able to read the first character SHŌ (正) and saw that there were two more, most likely A (阿) and MI (弥), they would have put those character in boxes on the paper. Boxes around characters namely means that the character is not 100% legible but it can be assumed what it is." Momoyama or early Edo period. Dimensions: 85.9 mm diameter, 3.6 mm thickness at seppa-dai. Weight: 79 g. NBTHK certificate № 425069 with attestation: Hozon - "Worthy of preservation". A similar tsuba is presented at Japanese Sword Fittings from the R. B. Caldwell Collection. Sale LN4188 "HIGO". Sotheby's, 30th March 1994, №15. The description says: "A rare early Kamakura-bori tsuba. Nambokucho period (late 14th century). Of circular form, the dark plate carved and pierced with a gate design, the struts with double engraved lines. Unsigned. 8.5 cm." The lot was sold for 1,840 GBP.We have two possible explanations of the discrepancy between Sotheby's and Shinsa/Sesko attribution: 1) either Sotheby's or Shinsa/Sesko were wrong in their attribution or 2) these are two different pieces, one - Kamakura-bori from the 14th century and another - Shōami from 16th/17th century. Anyway, I would consider my piece as a Shōami tsuba of Momoyama - early Edo period, just for the sake of modesty.
Iron tsuba of round form with design of lattice (kōshi-mon, 格子文) cut in openwork (sukashi), with low relief shallow linear carving along the bars. Well forged plate with brown-ish hue. To the right of nakago-ana there is a clear inscription of the character Shō (正), which is explained by Markus Sesko is follows: "The Shinsa obviously recognized more from the signature when having the tsuba in hand, i.e. they were confident to say it is signed "Shōami" but the rest is illegible (ika-fumei, 以下不明). That is, if they were just able to read the first character SHŌ (正) and saw that there were two more, most likely A (阿) and MI (弥), they would have put those character in boxes on the paper. Boxes around characters namely means that the character is not 100% legible but it can be assumed what it is." Momoyama or early Edo period. Dimensions: 85.9 mm diameter, 3.6 mm thickness at seppa-dai. Weight: 79 g. NBTHK certificate № 425069 with attestation: Hozon - "Worthy of preservation". A similar tsuba is presented at Japanese Sword Fittings from the R. B. Caldwell Collection. Sale LN4188 "HIGO". Sotheby's, 30th March 1994, №15. The description says: "A rare early Kamakura-bori tsuba. Nambokucho period (late 14th century). Of circular form, the dark plate carved and pierced with a gate design, the struts with double engraved lines. Unsigned. 8.5 cm." The lot was sold for 1,840 GBP.We have two possible explanations of the discrepancy between Sotheby's and Shinsa/Sesko attribution: 1) either Sotheby's or Shinsa/Sesko were wrong in their attribution or 2) these are two different pieces, one - Kamakura-bori from the 14th century and another - Shōami from 16th/17th century. Anyway, I would consider my piece as a Shōami tsuba of Momoyama - early Edo period, just for the sake of modesty.
Caldwell Collection. Sotheby's 1994, №15.


