-
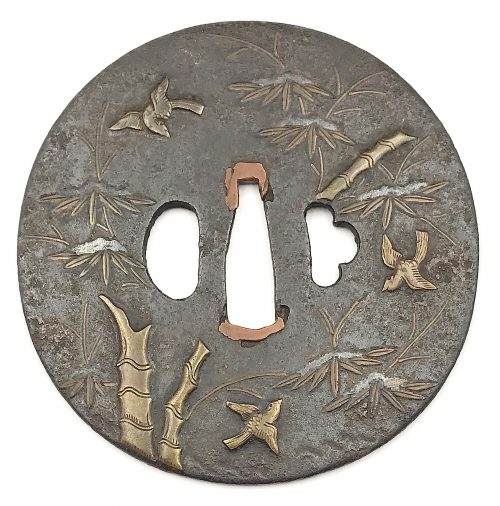 Iron tsuba decorated with sparrows and bamboo inlaid and chiseled in yellow brass, with snow lying on bamboo leaves inlaid in silver-ish shibuichi. Copper sekigane. The kogai-hitsu-ana probably cut out at a later date. Heianjō school. Unsigned. Height: 86.0 mm, Width: 85.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.9 mm. Momoyama or early Edo period, first half of the 17th century. Merrily Baird, Symbols..., page 118: "The association of the sparrow (suzume) with both bamboo and rice heads is an old one found in Japanese poetry, paining, and design."
Iron tsuba decorated with sparrows and bamboo inlaid and chiseled in yellow brass, with snow lying on bamboo leaves inlaid in silver-ish shibuichi. Copper sekigane. The kogai-hitsu-ana probably cut out at a later date. Heianjō school. Unsigned. Height: 86.0 mm, Width: 85.4 mm, Thickness at seppa-dai: 2.9 mm. Momoyama or early Edo period, first half of the 17th century. Merrily Baird, Symbols..., page 118: "The association of the sparrow (suzume) with both bamboo and rice heads is an old one found in Japanese poetry, paining, and design." -
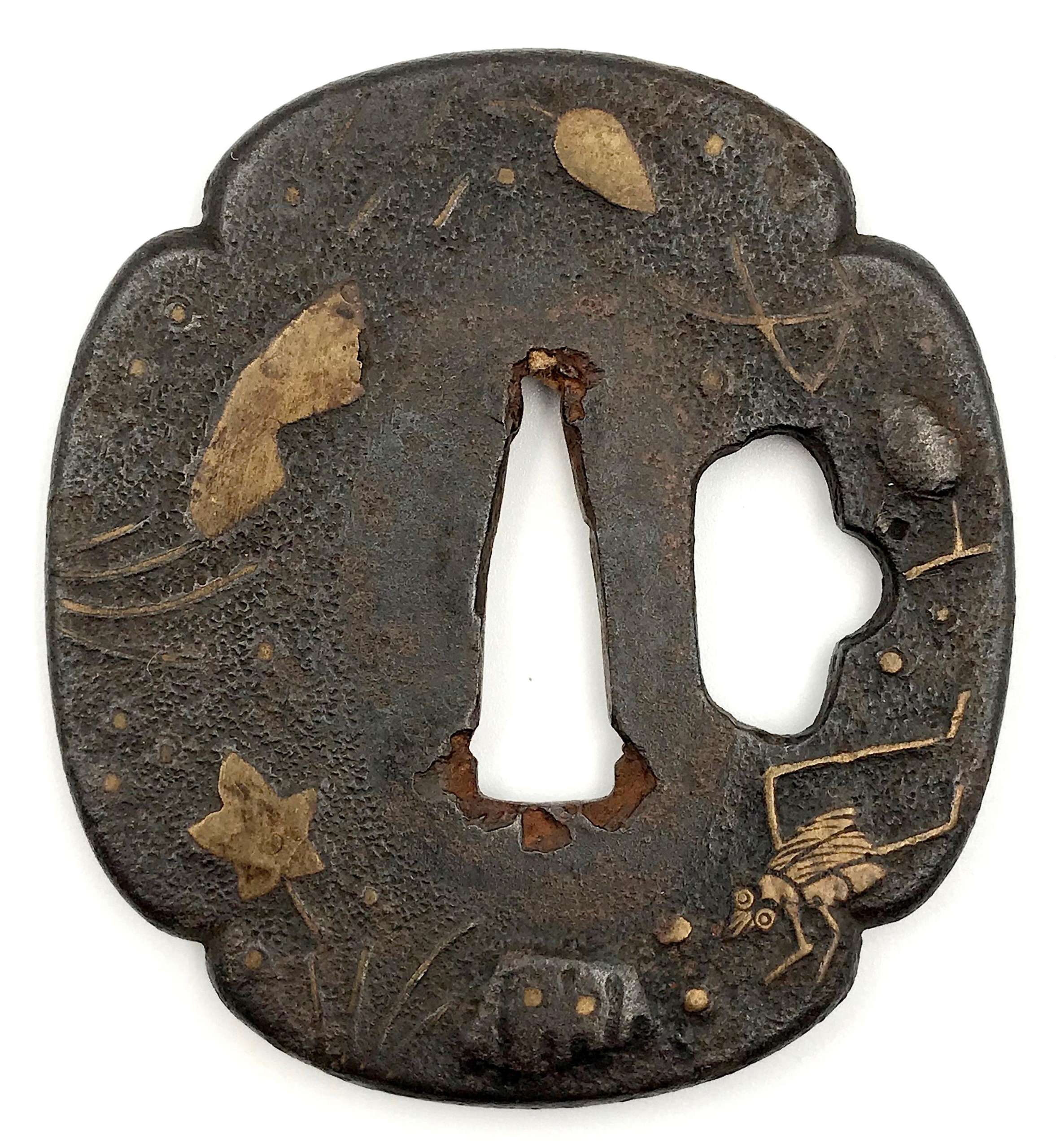 Iron tsuba of four-lobbed mokkō form decorated in brass and shakudō inlay on the face with design of rotten skull, fly, maple leaf, pine cones and needles, and on the back with design of rotten skull, wild boar, pine cones and needles. Scattered brass dots on both sides. Hitsu-ana possibly cut off later. Surface has traces of lacquer (urushi). Momoyama period. Dimensions: 67.3 x 61.5 x 4.3 mm A similar example can be found at Tsuba Kanshoki by Kazutaro Torogoye, 1975 on p. 61: "Heianjōzōgan tsuba. No sig. Iron: Pine-cone, seeds, ants & rock, brass zōgan. Kakumimi: C. 1.5 bu. Age: Momoyama. Sup. - Early work. Interest."
Iron tsuba of four-lobbed mokkō form decorated in brass and shakudō inlay on the face with design of rotten skull, fly, maple leaf, pine cones and needles, and on the back with design of rotten skull, wild boar, pine cones and needles. Scattered brass dots on both sides. Hitsu-ana possibly cut off later. Surface has traces of lacquer (urushi). Momoyama period. Dimensions: 67.3 x 61.5 x 4.3 mm A similar example can be found at Tsuba Kanshoki by Kazutaro Torogoye, 1975 on p. 61: "Heianjōzōgan tsuba. No sig. Iron: Pine-cone, seeds, ants & rock, brass zōgan. Kakumimi: C. 1.5 bu. Age: Momoyama. Sup. - Early work. Interest."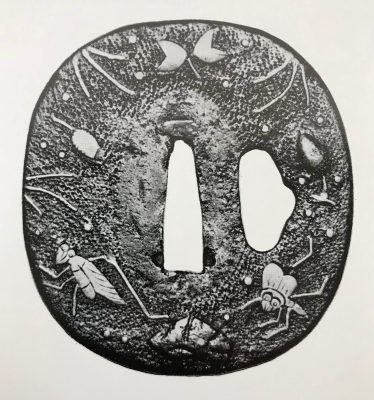
Tsuba Kanshoki, 1975, p. 61: Heianjō tsuba, Momoyama Period.
-
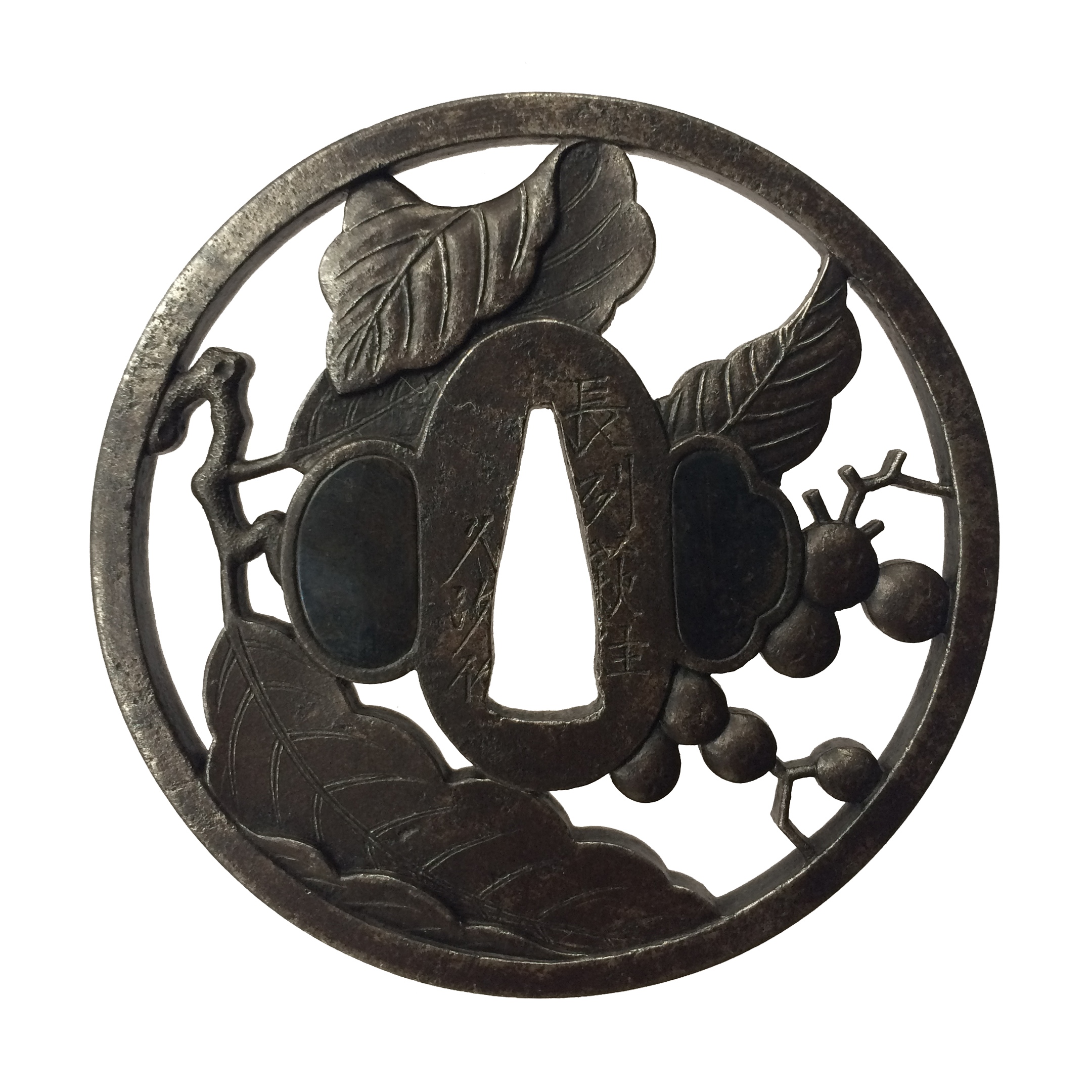

Iron tsuba of circular form with a branch of loquat (biwa) pierced in positive silhouette (ji-sukashi) and carved in marubori technique (marubori-sukashi). Kozuka and kogai hitsu-ana are plugged with shakudo.
Signature: Choshu Kawaji ju Hisatsugu saku. Chōshū school in Nagato province.
According to M. Sesko 'Genealogies' Hisatsugu was a 4th generation Kawaji School master from Chōshū (present day Nagato), with the name Gonbei, formerly Toramatsu, adopted son of Tomohisa (1687-1743) [page 117]. For Tomohisa work see TSU-0104 in this collection. -
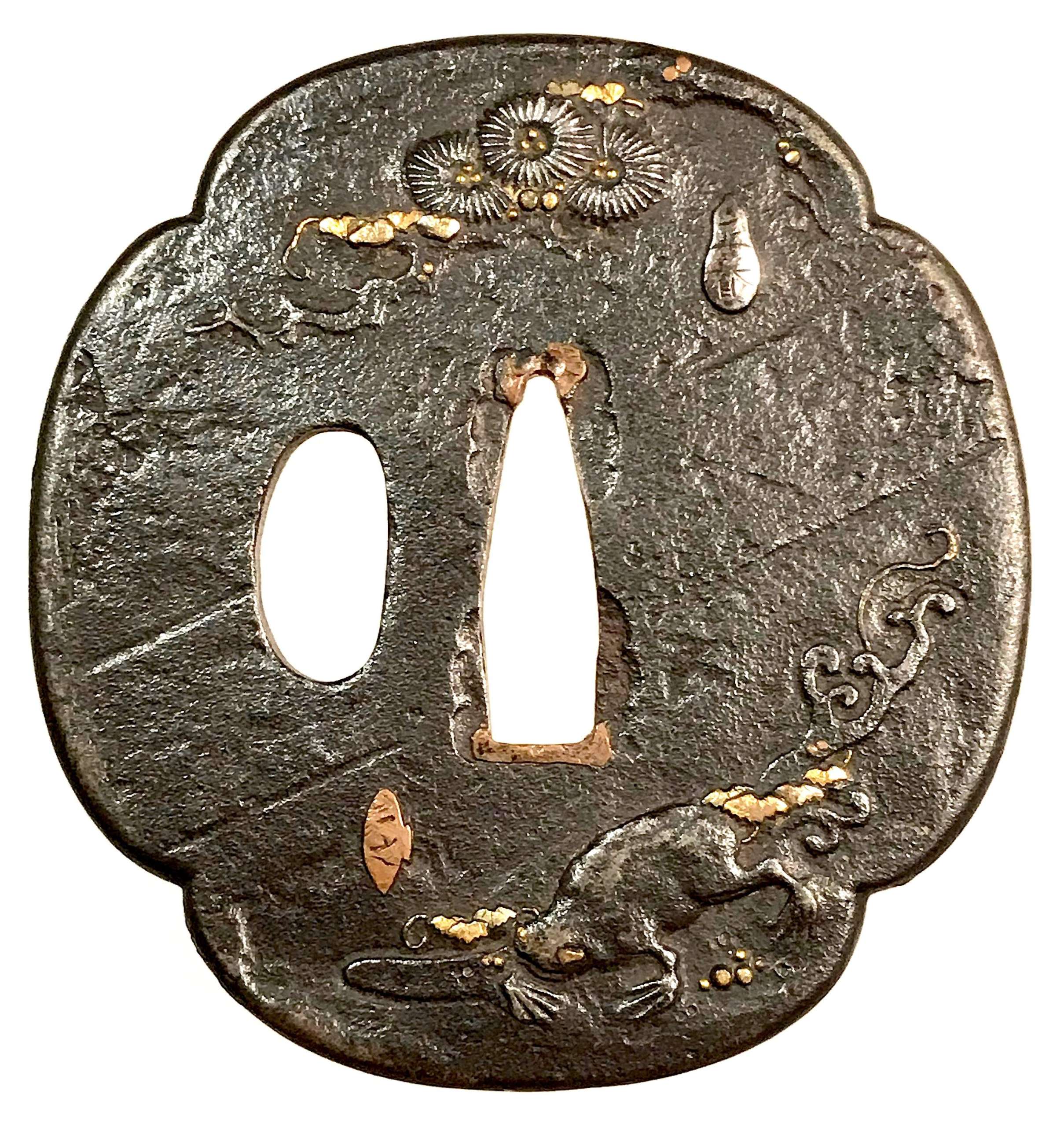

Iron tsuba of mokkō-form with a pine and a frog on the face and a snail on the back, carved and inlaid with gold. Each figurative element of the design is signed on three inlaid cartouches: Masaharu (正春), Kazuyuki (一之), and Yoshikazu (良一) [read by Markus Sesko]. Snake, snail, and frog together make a design called "SANSUKUMI" - Three Cringing Ones [Merrily Baird]. The snail can poison the snake, the frog eats the snail, and the snake eats the frog. It's unclear whether the pine replaces the snake on this tsuba, or the snake is hiding in the pine? Anyway, the frog and the snail are clearly represented. "Maybe we have here a joint work with Masaharu (the silver cartouche next to the pine) being the master and making the plate and Kazuyuki and Yoshikazu as his students carving out the frog and the snail respectively". Copper sekigane.
Dimensions: 70.9 x 67.2 x 3.0 mm. Edo period (18th century).Markus Sesko writes: "I agree, the frog and the snail most likely allude to the san-sukumi motif. It is possible that we have here an artist's choice to deliberately leave out the snake, maybe he thought that the motif is already obvious and there is no need to add a snake to make it clear that the tsuba shows the san-sukumi motif." [Markus Sesko].
Kazuyuki (一之): adopted son of Kumagai Yoshiyuki, student of Ichijō (Gotō-Ichijō Scool) [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 19.] Masaharu (正春): Kasuya fam., student of Masamichi (1707-1757) who was the 4th generation Nomura School master in Edo. [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 49.] -
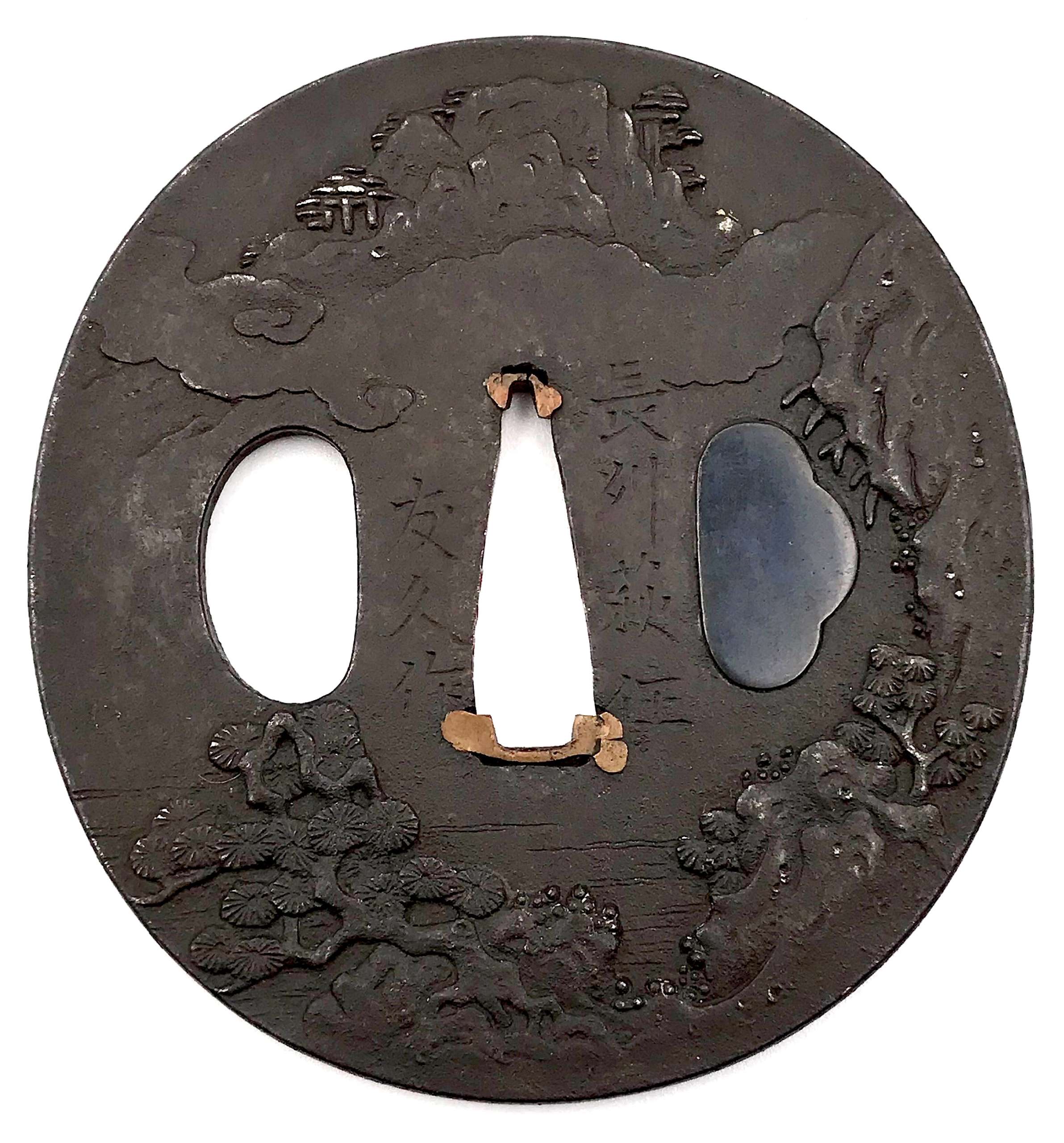

Iron tsuba of oval form carved with a landscape motif. Kogai-hitsu-ana plugged with shakudo. Sekigane of copper.
Signed: Chōshū Hagi-jū Tomohisa saku (長州萩住友久作).
Tomohisa, adopted son of Rokurō'emon, was 3rd generation master of Kawaji School from Hagi in Nagato (Chōshū), lived 1687-1743 [M. Sesko 'Genealogies', page 117].
Edo period, circa 1700. Dimensions: 71.1 x 66.8 x 2.9 mm For his adopted son Hisatsugu work see TSU-0103 in this collection. -
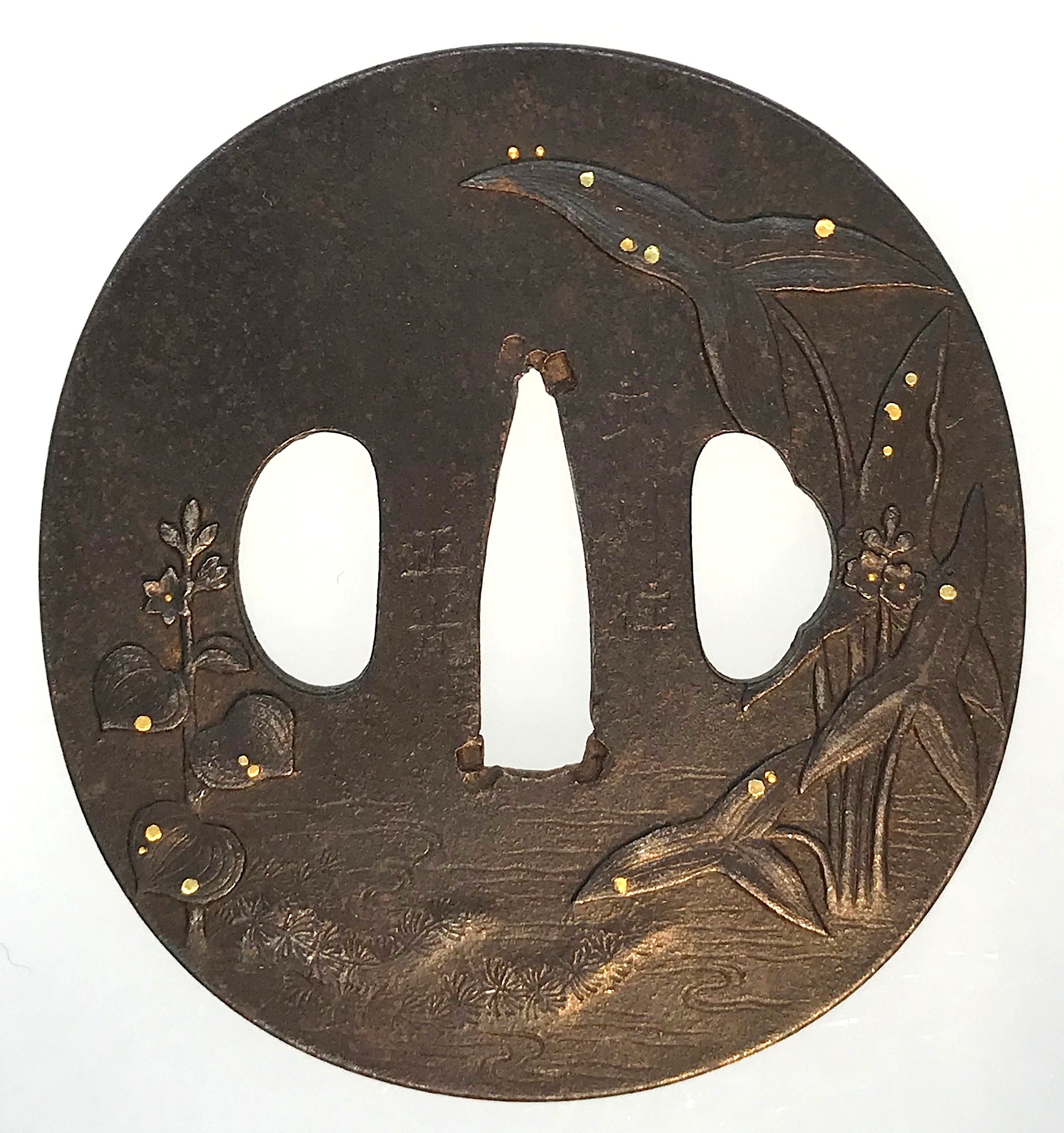

An iron tsuba of oval form decorated with a water plantain (omodaka) carved in low relief and water drops inlaid in gold.
Signed: Bushū jū Masamitsu.
Bushū-Itō school.Height: 71.8; Width: 67.3; Thickness: 3.6; Weight: 96 g.
Mid to late Edo period; 18th-19th century.
There were several tsuba artists with the name of Masamitsu. The one who worked with iron and spelled [正光] is mentioned at Markus Sesko's 'Genealogies' on page 106 in Akasaka School of Edo section as Masamitsu Gorōbei , student of Tadatoki, 4th generation Akasaka master. The name is not mentioned at Torigoye/Haynes 'Tsuba. An Aesthetic Study' in the list of Bushū-Itō family masters on page 181. -
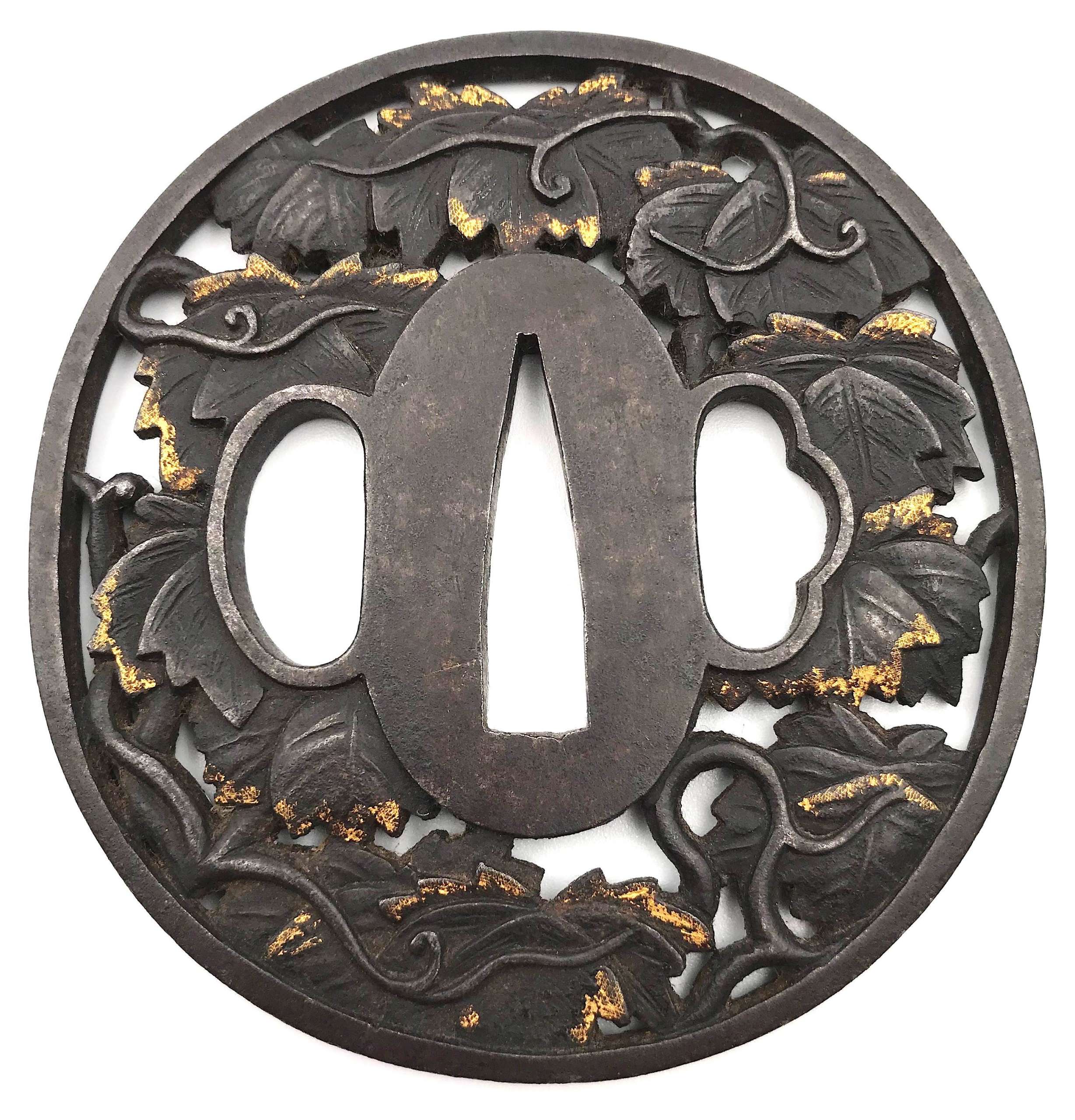

An iron tsuba of slightly vertically elongated circular form carved and pierced with a mass of ivy (tsuta) leaves and tendrils, details damascened with gold in nunome-zōgan technique. Hitsu-ana with raised rim.
Unsigned.
Chōshū school.Height: 72.0 mm; width: 69.0 mm; thickness: 4.7 mm; Weight: 92 g.
According to John W. Dower, "ivy bears fairly close resemblance to both maple leaf and grape leaf". However, I consider this tsuba decorated with ivy leaves for several reasons, such as the lack of racemations in the presence of tendrils. -
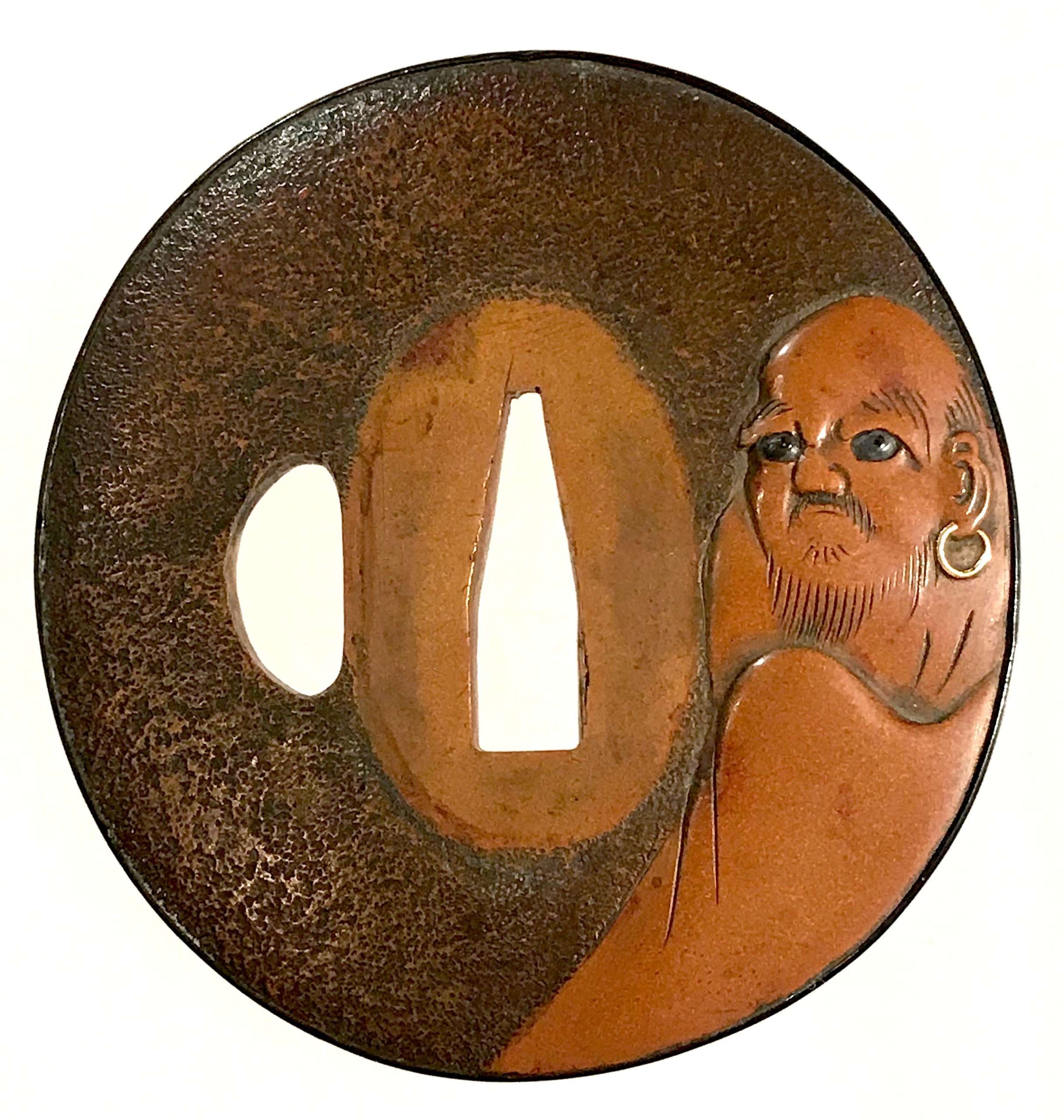

A copper tsuba with ishime-ji ground carved and polished (migaki-ji) with sitting Daruma; his eyes are inlaid with shakudo and he has a golden earring. The reverse carved with four characters: 廓 然 無 性 (Kakunen-mushō). It is a Zen proverb that goes back to Bodhidharma (Daruma), meaning "boundless expanse and nothing that can be called holy." [Markus Sesko translation]. Shakudo fukurin.
Unsigned.
Edo period (circa 1800). Dimensions: 68.2 x 65.5 x 4.8 (center) x 3.2 (rim) mm


