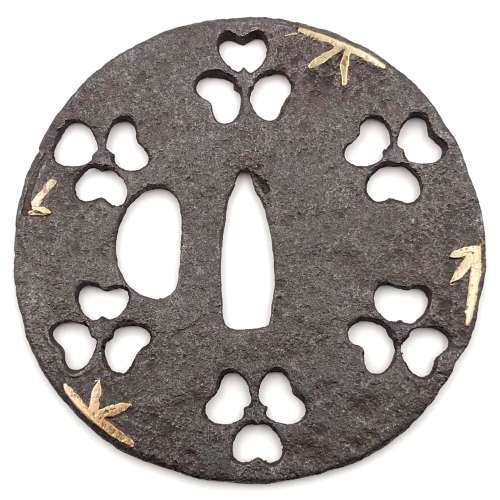
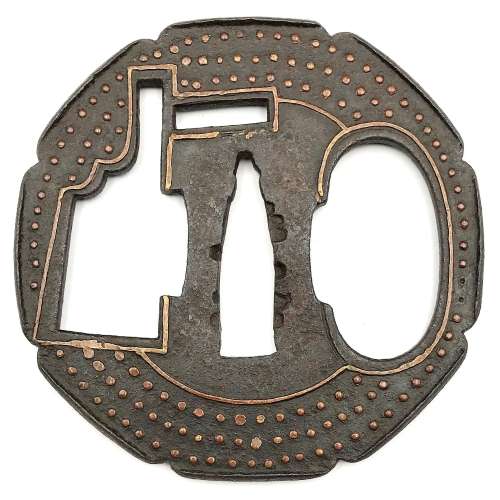
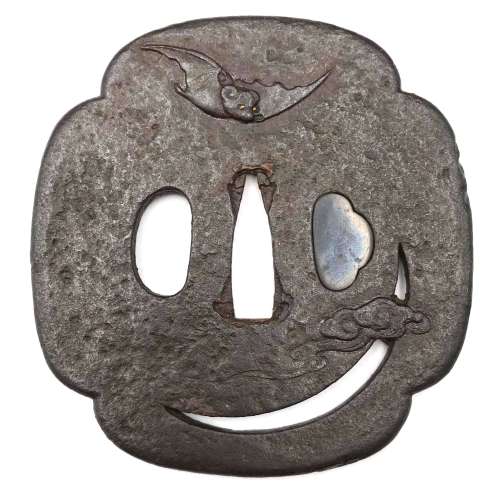
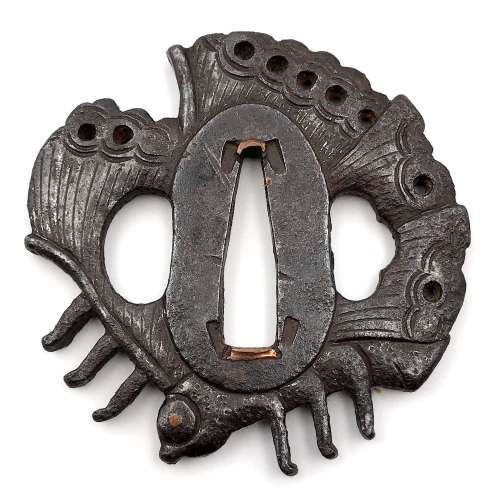
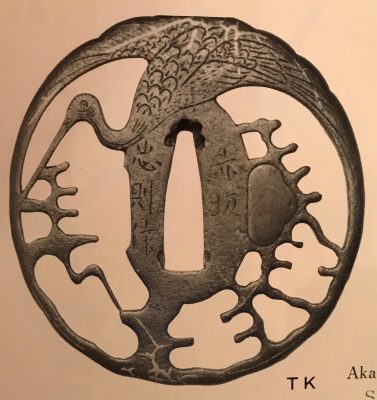
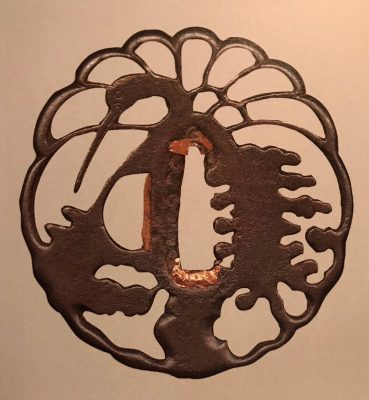
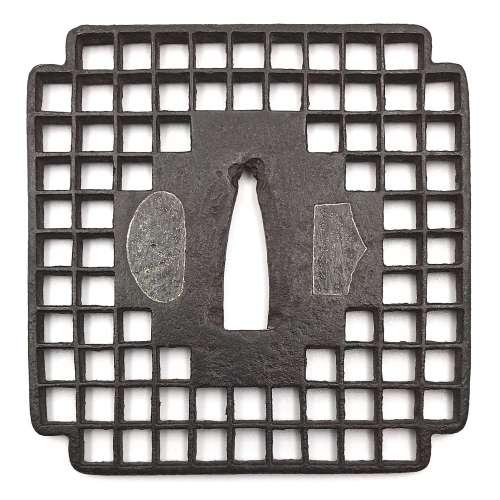
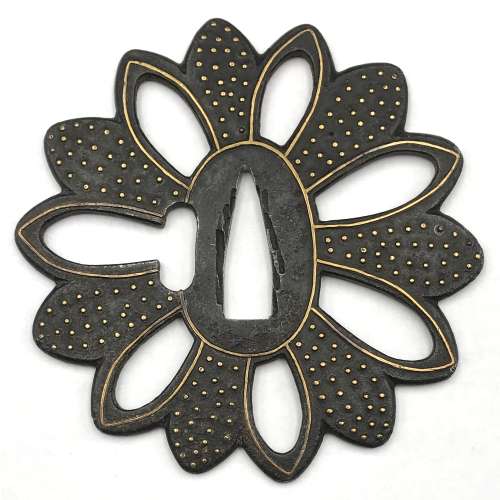
Iron tsuba of 14-petal chrysanthemoid form (
kikka-gata) with alternating solid and openwork petals, the latter outlined with brass wire (
sen-zōgan) and the former decorated with brass dots (
ten-zōgan), on both sides.
Seppa-dai is outlined with brass wire. Small
hitsu-ana probably cut later.
Late Muromachi period (Ca. 1514-1573).
Ōnin school. Unsigned.
Dimensions: 87.0 x 87.8 x 3.2 mm.
Similar tsuba in this collection:
TSU-0420.2022

Other similar specimens can be found at:
Henri L. Joly and Kumasaku Tomita,
Japanese art and handicraft, "Swords and sword fittings" section, sub-section “Inlays of Ōnin, Kyoto, Fushimi-Yoshiro, and Kaga Province”, Plate CX, #128: Iron, chrysanthemoid, thin guard with alternate petals covered with brass spots. Ōnin style. 16th century.

Japanese art and handicraft, Plate CX, #128.
, Part I, #7:
The iron plate is of flowerhead shape with each of the fourteen petals alternating between solid and openwork. The apertures are outlined in inlaid brass as is the seppa-dai and hitsu-ana. The remainder of the plate is similarly inlaid with plum flowers, birds, dots of dew, Genji mon and sambiki mon. 87 mm x 85 mm x 3.5 mm.

Compton Collection, Part I, #7.
And at
Jim Gilbert website: Onin ten zogan tsuba, mid Muromachi. Size: 7.7 cm T x 7.6 cm W x 0.3 cm. Iron plate with brass inlay. Kiku gata. The Ōnin ten zogan style is characterized by the decoration of small brass “nail heads” and wires on a thin iron plate. The iron often has a soft, granular texture and seems to be prone to rust. Unfortunately, this rust will undermine the brass inlay and result in the loss of some of the inlay. This example is in reasonably good but far from perfect condition. As is often the case, the backside is better preserved, with the wire around the seppa-dai and kozuka-ana, and all petals still intact.






 Other similar specimens can be found at:
Henri L. Joly and Kumasaku Tomita, Japanese art and handicraft, "Swords and sword fittings" section, sub-section “Inlays of Ōnin, Kyoto, Fushimi-Yoshiro, and Kaga Province”, Plate CX, #128: Iron, chrysanthemoid, thin guard with alternate petals covered with brass spots. Ōnin style. 16th century.
Other similar specimens can be found at:
Henri L. Joly and Kumasaku Tomita, Japanese art and handicraft, "Swords and sword fittings" section, sub-section “Inlays of Ōnin, Kyoto, Fushimi-Yoshiro, and Kaga Province”, Plate CX, #128: Iron, chrysanthemoid, thin guard with alternate petals covered with brass spots. Ōnin style. 16th century.