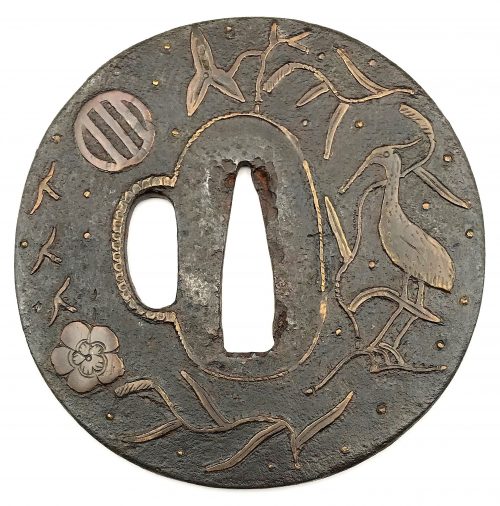
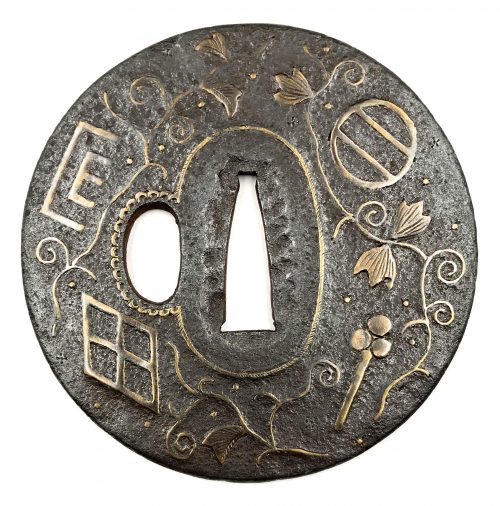
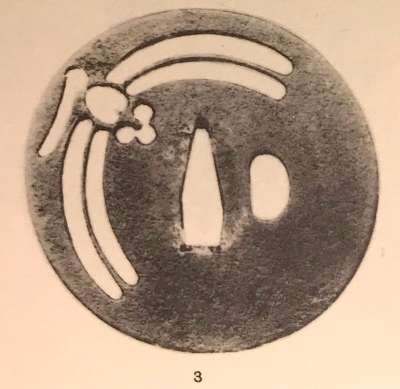
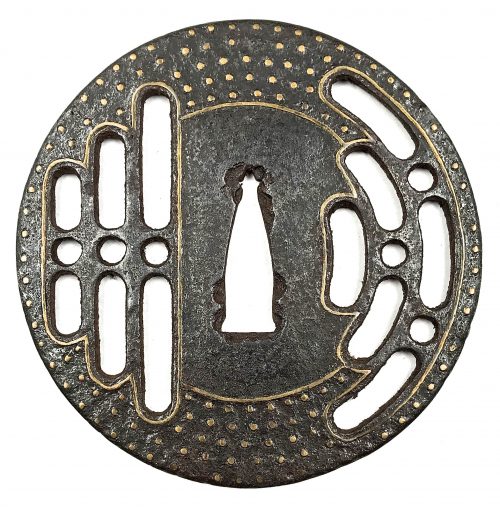
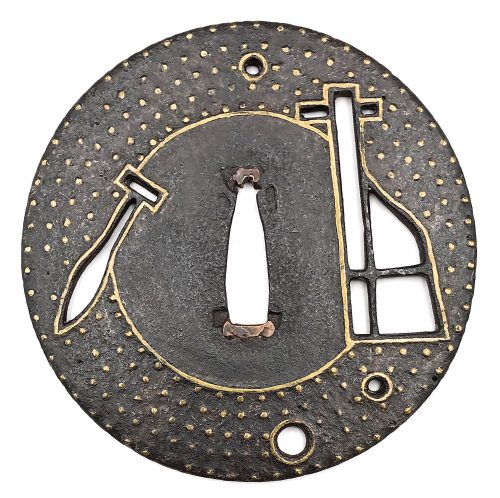
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with two boar's eyes (
inome) and two dragonflies (
tombo) in small openwork (
ko-sukashi) outlined with brass wire. The plate also decorated with 2 to 5 concentric circular rows of brass dots (nail heads) in ten-zōgan. Center of the plate outlined with the inlaid circular brass wire. The inlaid metal is of red-ish hue, so it may be copper, and not brass. The surface has remnants of lacquer.
Ōnin school.
Mid Muromachi period, middle of 15th century.
Dimensions: Diameter: 90 mm, thickness: 3.2 mm.
Notes regarding design:
"According to various sources, the dragonfly (tombo) is emblematic of martial success, as various names for the insect are homophones for words meaning "victory". The dragonfly is also auspicious because references in the Kojiki and Nihongi link it in both name and shape to the old kingdom of Yamato." [Merrily Baird. Symbols of Japan. Thematic motifs in art and design. Rizzoli international publications, Inc., 2001, p. 108]. "The dragonfly (tonbo), was also called kachimushi in earlier times, and due to the auspicious literal meaning "victory bug" of the characters of this word it became a popular theme on sword fittings." [Iron tsuba. The works of the exhibition "Kurogane no hana", The Japanese Sword Museum, 2014, p. 13].
Two other cutouts - in the form of what in European tradition symbolizes the heart, on the top and in the bottom of tsuba disc - may have two different explanations. The most usual one, inome - "Heart-shaped pattern, which is said to go back to the shape of a wild boar's eye" [Markus Sesko. Encyclopedia of Japanese Swords. Print and publishing: Lulu Enterprises, Inc., 2014.]. This understanding is shared by Robert Haynes [Robert E. Haynes. Study Collection of Japanese
Sword Fittings. Nihon Art Publishers, 2010.] and elsewhere, with an exception of Okabe-Kakuya [Okabe-Kakuya. JAPANESE SWORD GUARDS. Museum of Fine Arts, Boston. In cooperation with the department of Chinese and Japanese art; - 1908, p. 14], who provides the illustration of inome-shaped cut-outs with the following explanation: " The tsuba shown in Fig. 13 approaches a square form with rounded corners and is perforated with Aoi decoration. But this book was written long time ago, when people even at MFA might not know enough...

The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (
aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This
mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four
aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.

There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (
akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the
Kojiki and
Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name
Akitsu-shima... etc."
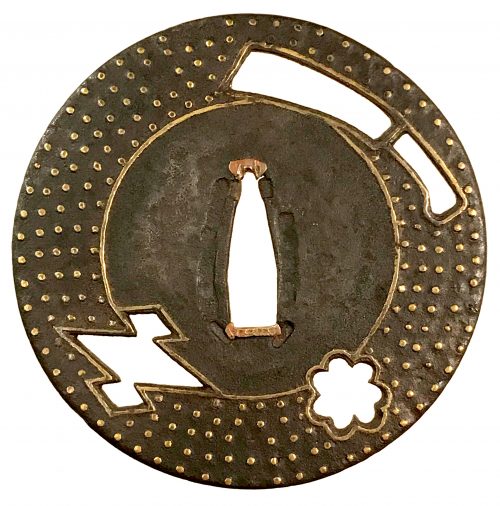










 The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.
The same interpretation of the said heart-like symbol (aoi leaf) is given at Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; p. 54: "This mokkō-formed tsuba recalls the aoi form, perforated as it is with the four aoi leaves." It is possible that the "wild boar's eye" theory was developed by later scholars.
 There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
There is also a theory, supported by Graham Gemmell, saying that: “In simple terms Onin works are decorated Ko-Katchushi tsuba. … But, not content with iron alone, they began to decorate it with what was, in the early Muromachi period, a rare and valuable metal, brass. The Onin workers cut the design into the iron, using narrow channels, cast the brass, piece by piece, and then hammered it into the iron plate as though they were putting together a jigsaw. When complete the tsuba would be black lacquered exactly as the plain iron ones had been, the brass shining dully through it in a way that fulfilled the goal of shibui or restrained elegance.” [Tosogu. Treasure of the samurai. Fine Japanese Sword Fittings from The Muromachi to The Meiji Period, by Graham Gemmell. // Sarzi-Amadè Limited, London, 1991. An exhibition held in London from 21st March to 4th April, 1991]. The following illustration from Helen C. Gunsaulus. Japanese sword-mounts in the collection of Field Museum. // Publication 216, Anthropological Series, Volume XVI; Chicago, 1923; pp. 43 supports the idea.
 Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."
Helen C. Gunsaulus' description of the dragonfly emblem is as follows: "This motive, the dragon-fly (akitsu), is generally accepted as a symbol of the kingdom of Japan, and the origin of the idea is traced to the legend recounted in the Kojiki and Nihongo of the Emperor Jimmu's view of the island from mountain top. He is said to have thought the kingdom looked like a dragon-fly touching its tail with its mouth. From this it received its name Akitsu-shima... etc."




 English translation of the book indicated above Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1 by Harry Afu Watson, AFU Research Enterprises, Inc., 1993. Tsuba in question illustrated on page 14 and described as follows: " Tsuba mumei Ōnin. Tetsu ji maru gata ko-sukashi tsuchime shitate shinchū suemon ten zogan maru mimi. Brass suemon". My question remains: why such a text is called 'translation' while it looks more like transliteration of romanization?
English translation of the book indicated above Nihon Tō Kōza, Volume VI, Part 1 by Harry Afu Watson, AFU Research Enterprises, Inc., 1993. Tsuba in question illustrated on page 14 and described as follows: " Tsuba mumei Ōnin. Tetsu ji maru gata ko-sukashi tsuchime shitate shinchū suemon ten zogan maru mimi. Brass suemon". My question remains: why such a text is called 'translation' while it looks more like transliteration of romanization? 
