Woodblock print album of thirteen prints,
ōban,
nishiki-e.
Artist: Chōkyōsai Eiri
[鳥橋斎 栄里] (Japanese, fl. c. 1789 ~ 1801 ).
Models of calligraphy (
Fumi no kiyogaki), New Year 1801. This title is taken from Chris Uhlenbeck's
Japanese Erotic Fantasies Sexual Imagery of the Edo Period. — Hotei Publishing, 2005, ISBN 90-74822-66-5):.
A detailed description of the album can be found at
The Complete Ukiyo-e Shunga №9 Eiri, 1996, ISBN 4-309-91019. Most of the edition is in Japanese, though Richard Lane writes a section in English:
Eiri: Love-letters, Love Consummated: Fumi-no-kiyogaki. The article starts with the following statement:
"Why all the fuss about Sharaku? Because he is so "mysterious"? No, not at all: because he is such a good artist. But Sharaku is not the only great yet enigmatic ukiyo-e artist and I propose to resurrect here one of his important contemporaries who has been all too long neglected: Chōkyōsai Eiri. As with many of the notable ukiyo-e masters, nothing is known of Eiri's biography. All we can say is what we learn from his extant prints and paintings: that he flourished during the second half of the Kansei Period [1789-1801]; and that he was a direct pupil of the great Eishi - who, being of eminent samurai stock, may well have attracted pupils of similar background."
Another citation from
Japanese Erotic Fantasies:
"This album is one of the boldest sets of ōban-size shunga known, The first edition contains thirteen instead of the customary twelve designs".
Here I present all thirteen prints, though the edition I bought in Kyoto in 2014 contained only twelve. The thirteenth print was purchased later in the United States (sheet №12).

№1: "...one of the most exotic scenes in all
shunga. A Dutch
kapitan is discovered coupling with a lovely Japanese courtesan, beside a large window opening upon a garden...".


№2: "...a fair young harlot is seen masturbating with a grinding-pestle - a man watches intently from under bedding." [I have two specimens of this design; the one from album is more soiled but less faded].

№3: "...the artist has effectively contrasted the lovers by depicting the man's face as seen through the geisha's gauze skirt. [...] we are impressed more by strikingly elegant composition, the dramatic coloring, rather than feeling any great urge to participate in the energetic proceedings..."

№4: "This scene is a most straightforward one, featuring the standard Missionary Position [capitalization by R. Lane].; but withal, the contrast of the young and naked, secret lover and the richly-clothed courtesan amid luxurious bedding..."

№5: "In a striking lesbian scene (which has no equivalent in Utamaro, and is, incidentally, often omitted in later editions of this album), the girl at left prepares to receive the
harikata (dildo) worn by the older girl at right (who holds a seashell containing lubricant)."

№6: "In the first appearance of a matronly heroine in this series, we find a widow - with shaven eyebrows and clipped hair - sporting with a handsome yound shop-clerk, mounting him with all her might."


№7: "... lady of samurai court: here, shown taking advantage of an official outing to temple and theatre, to rendezvous with a secret lover on a teahouse balcony." R. Lane considers this design the least successful in the series, especially in comparison with the same theme by Utamaro: "Utamaro female is almost ferocious in her lust for sexual gratification", which does not sound true to me. See Utamaro's sheet №5 from the album
Utamakura (歌まくら, Poem of the Pillow) [courtesy The British Museum without permission]:

Then, as Richard Lane states, "we are flung suddenly to the bottom rung of Edo society":

№8: "Here we find a fair
yotaka ('night-hawk', e.i. streetwalker) accommodating a lusty client in a lumberyard by the bank of the Sumida River".

№9: '... a slightly plump harlot of the lower class receives a night visit from her lover, whose naked form she tries to cover with a cloak."

№10: "...likely maidservant and lackey - are depicted in bath-room, their passions are all too obviously fired by steaming water."

№11: "...this scene of courtesan and secret lover ranks high not only in Eiri's
œuvre but also in the annals of the ukiyo-e genre itself. Both design and colouring are impeccable and, for this period, there is nothing even in the work of great Utamaro that really surpasses it." Again, a doubtful statement, however, this is Utamaro's design for the reader to judge:

The last design in my album is this:

#13: In most reference books it goes under number 13, and we will assign this number to the sheet. "The final scene of the album features naked participants, probably samurai man and wife. The print is rather subdued in tone and colour, if not in the degree of the passion displayed..."
An additional sheet, acquired separately from a reputable dealer in New York, is usually listed as №12:

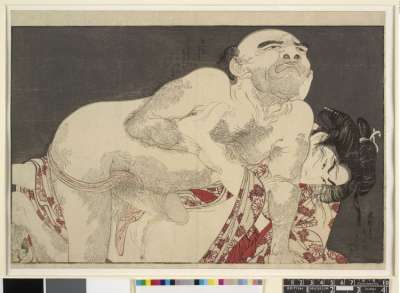
№12: "One might think that Eiri has reached his peak with the preceding plate 11 - and indeed he has, in both esthetic and erotic terms. But the album is not yet finished, and the next scene lends a needed variety to the series, a slightly comic tableau featuring a middle-aged lackey attempting to forcibly seduce a servant girl of the same domicile". Utamaro's design, that inspired Eiri is here:
All descriptions are taken from Richard Lane's article at
The Complete Ukiyo-e Shunga №9 Eiri, 1996. He concluded: "...Eiri's erotic series represents a major contribution to shunga art towards the close of ukiyo-e "Golden Age". In part inspired by Utamaro's classic album, this series withal constitutes a unified and original achievement, providing a cumulative effect of gracefully elegant yet glowing eroticism, which remains in the mind's eye long after the pictures themselves are far away."
I only would like to mention here that in several reference sources this album goes under name of
Eisho; unfortunately, this mistake is reproduced at
www.ukiyo-e.org, which miraculously shows exactly my print, but under the wrong name of the artist. The same mistake can be found at
Shunga. The art of love in Japan. Tom and Mary Anne Evans. Paddington Press Ltd., 1975. ISBN 0-8467-0066-2; plates 6.74-6.77: Chōkyōsai Eishō, c. 1800. Even the British Museum edition of 2010 gives the same erroneous attribution:
Chōkyōsai Eishō (1793-1801); they provide the following translation of title:
"Clean Draft of a Letter" [see: Shunga. Erotic art in Japan. Rosina Buckland. The British Museum Press, 2010; pp. 110-112]. To the honour of the British Museum, I must admit that they have corrected themselves in
Shunga. Sex and pleasure in Japanese art. Edited by Timothy Clark, et al. Hotei Publishing, 2013. Now, they say
Chōkyōsai Eiri (worked c. 1790s-1801); they also provide a new title:
"Neat Version of the Love Letter, or Pure Drawings of Female Beauty". I have already mentioned Richard Lane's version of title:
"Love-letters, Love Consummated", and Chris Uhlenbeck's "
Models of calligraphy". In poorly designed and printed
Shunga. Erotic figures in Japanese art. Presented by Gabriele Mandel. Translated by Alison L'Eplattenier. Crescent Books, New York, 1983, the artist is named Shokyosai Eisho (beginning of the 19th century); title provided:
"Models of Calligraphy". Correct attribution to
Chōkyōsai Eiri also can be found at
Poem of the pillow and other stories by Utamaro, Hokusai, Kuniyoshi and other artists of the floating world. Gian Carlo Calza in collaboration with Stefania Piotti. Phaidon Press, 2010; though the title is translated as "Clean Copy of Female Beauty".
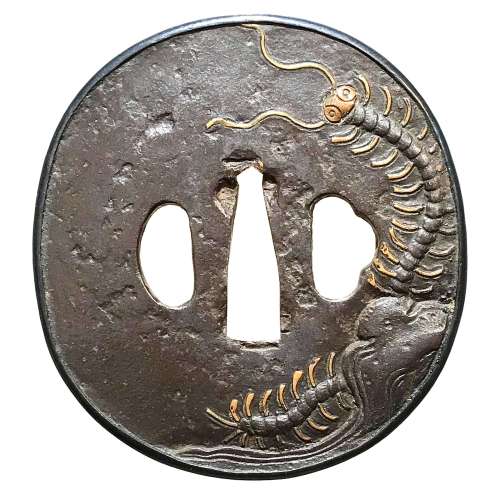
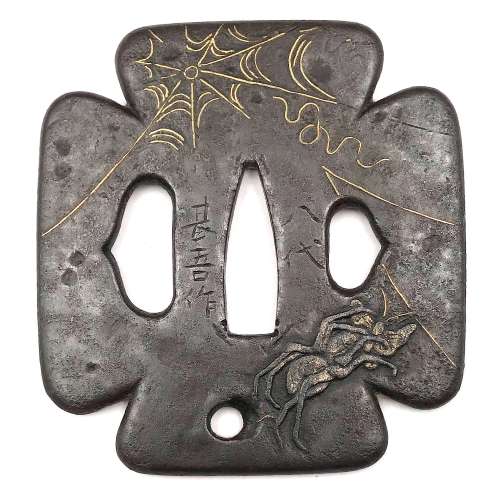
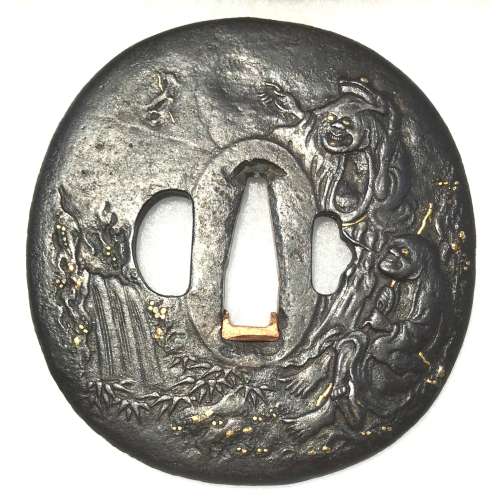
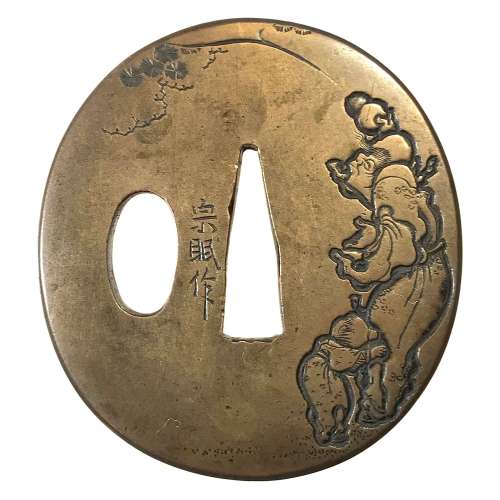
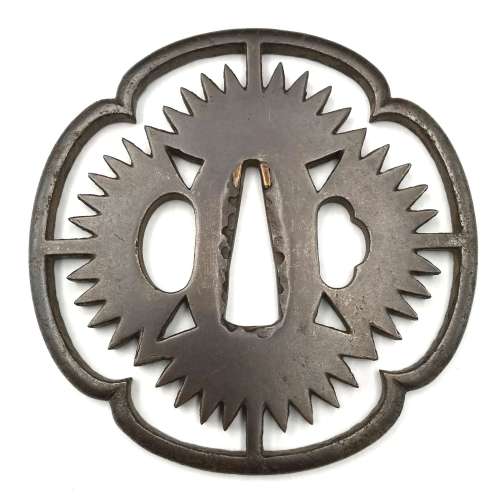
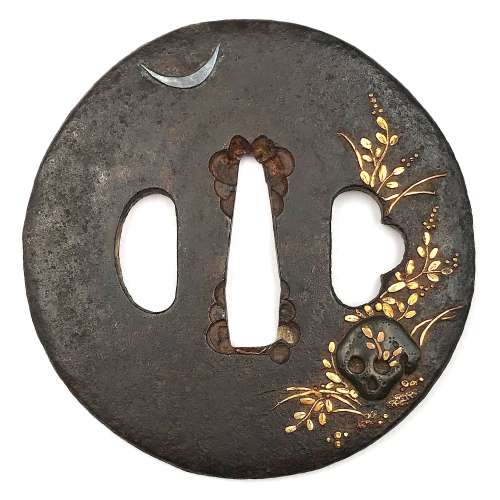
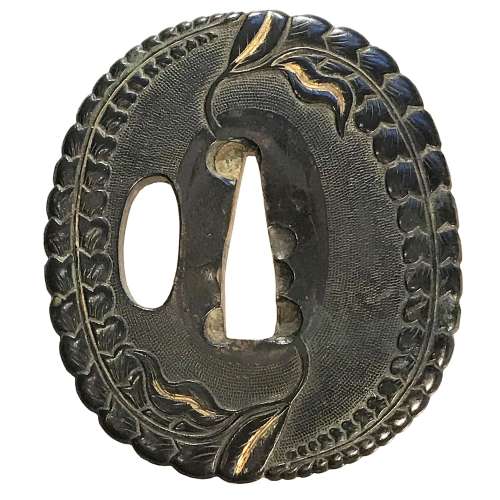
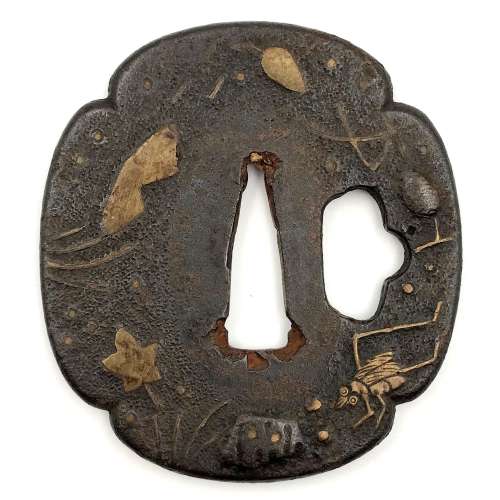
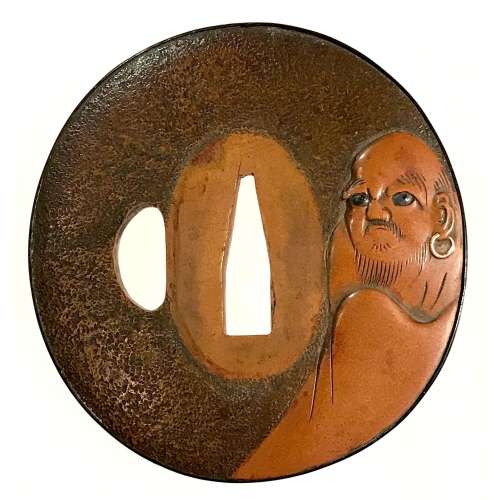
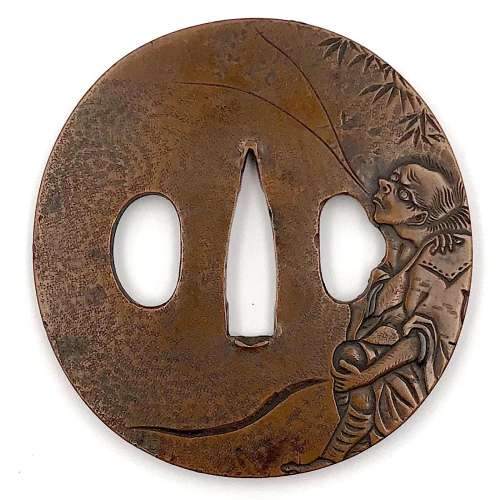
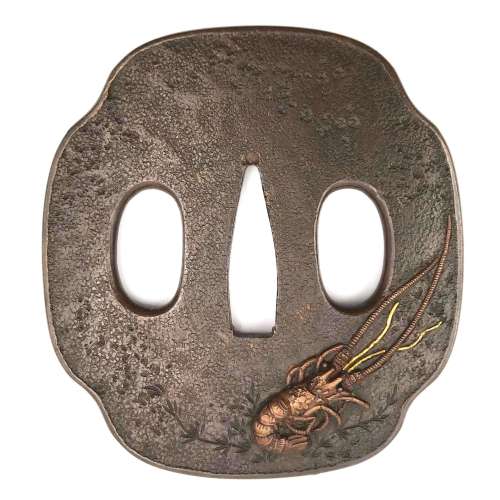
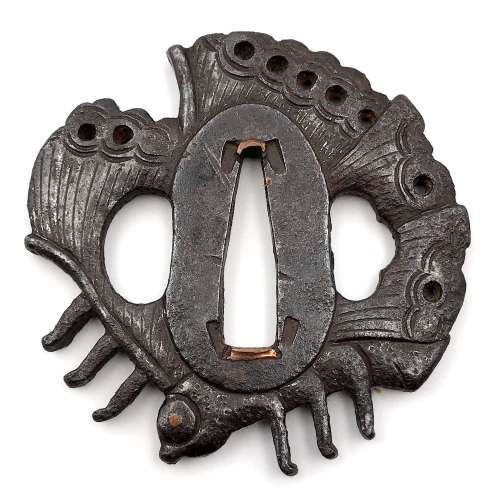
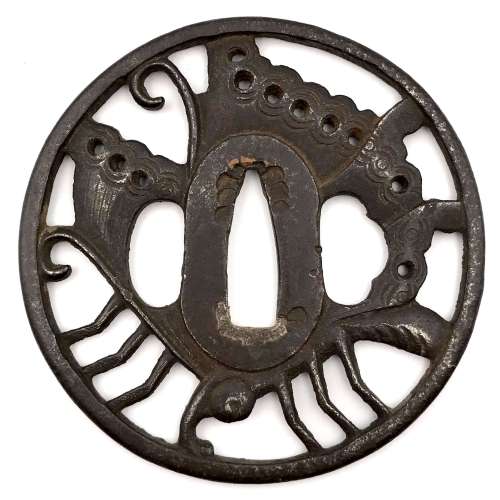
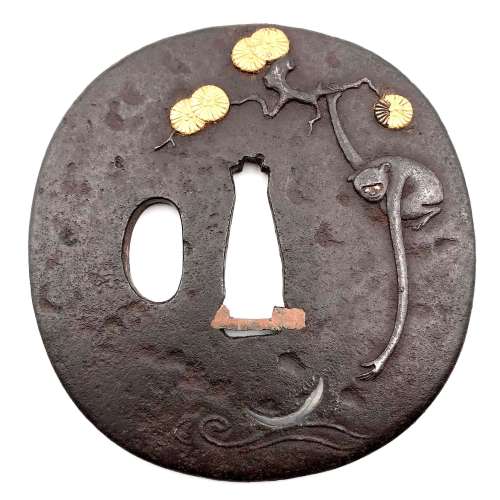
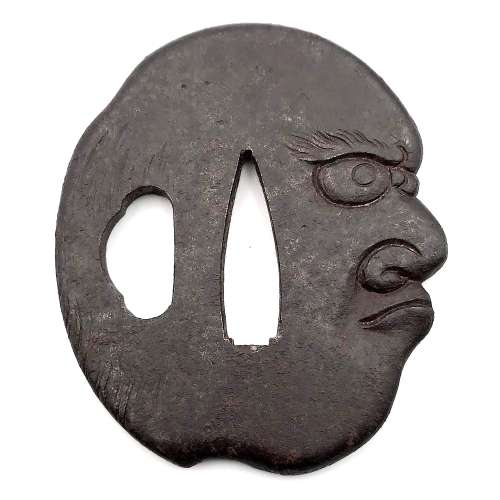
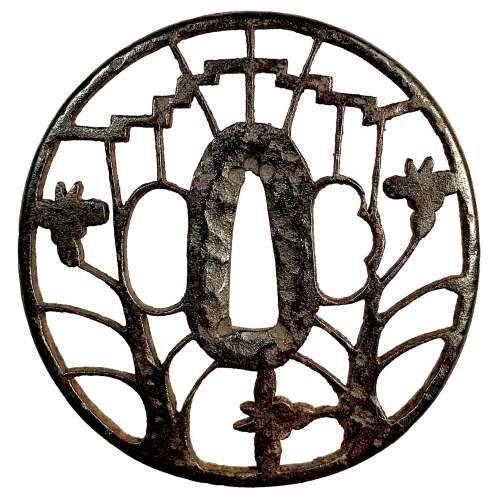
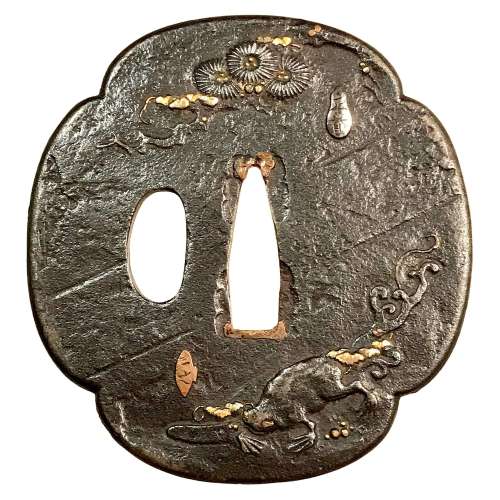
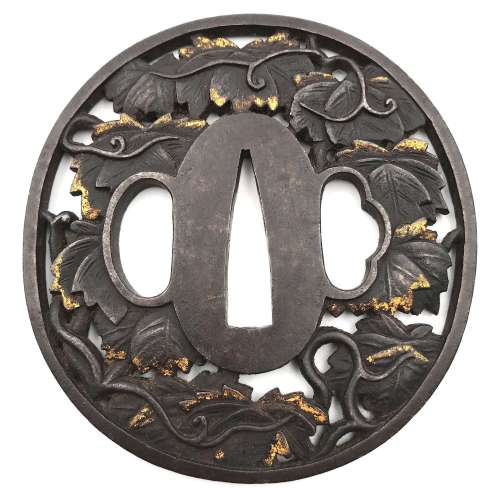
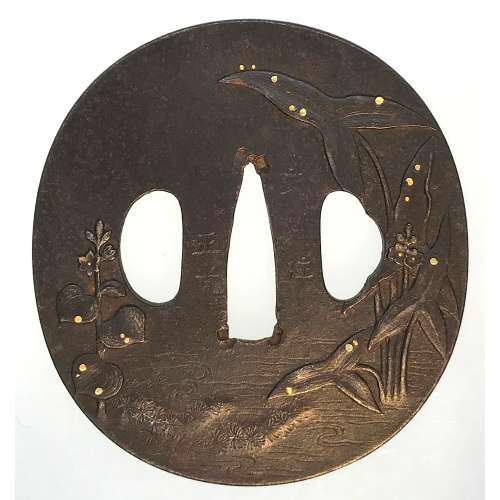
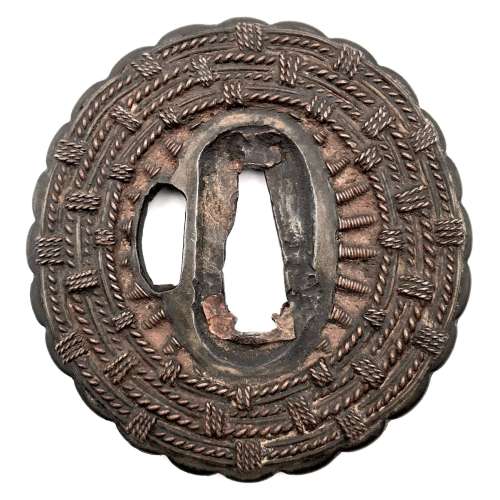
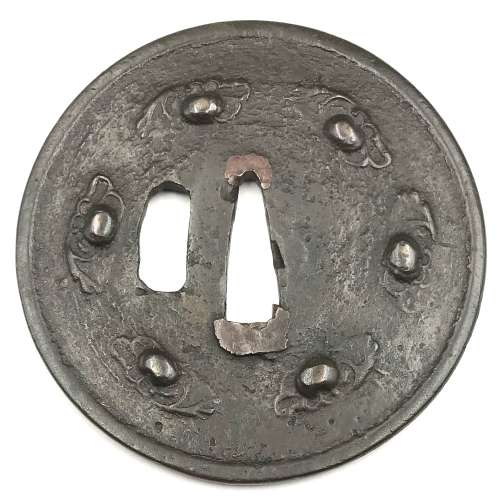
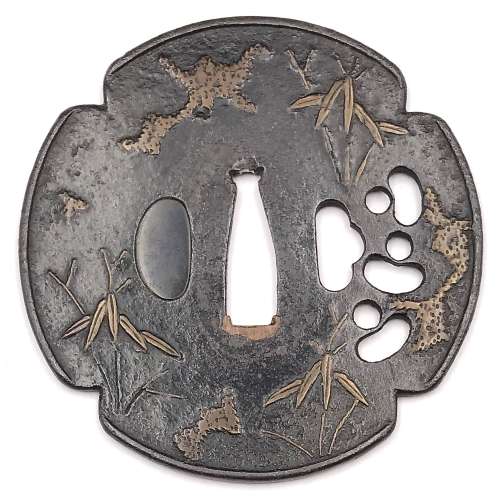
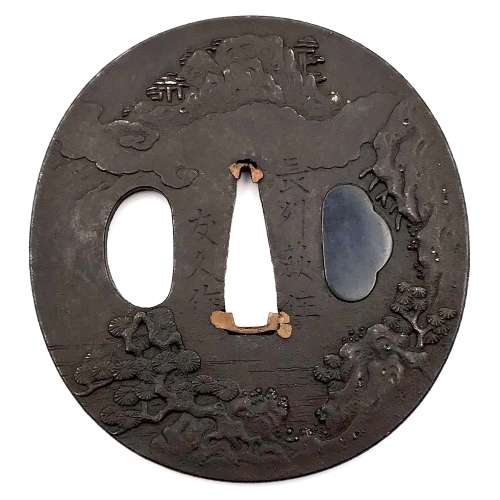
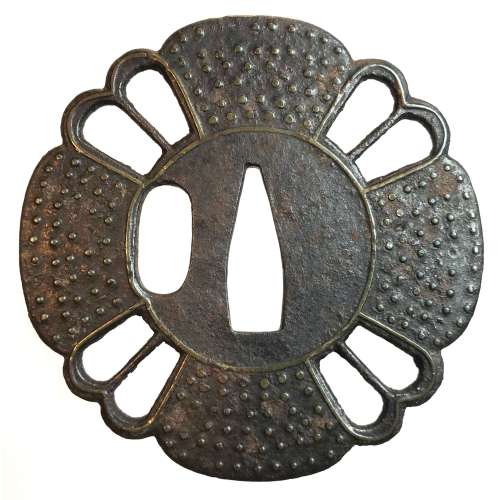
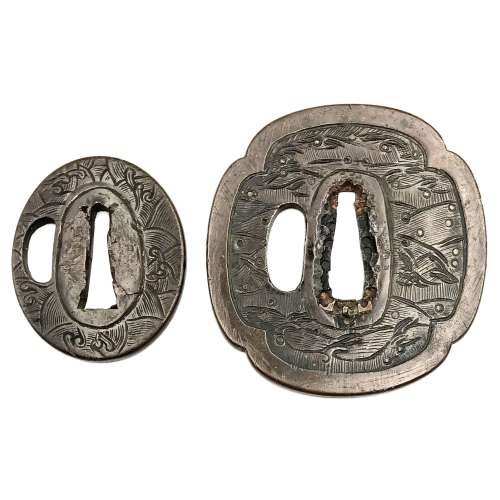
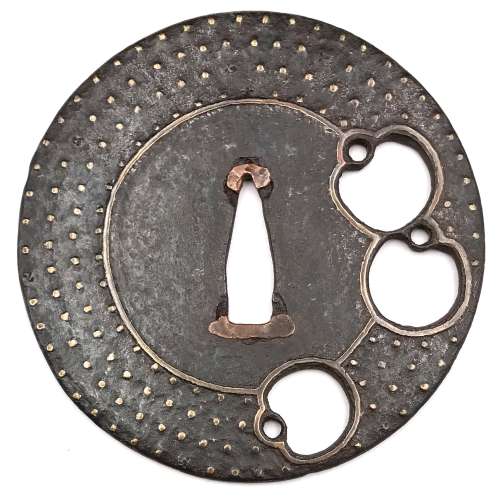
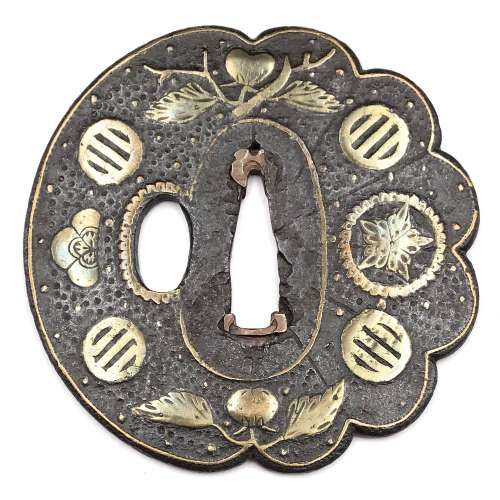
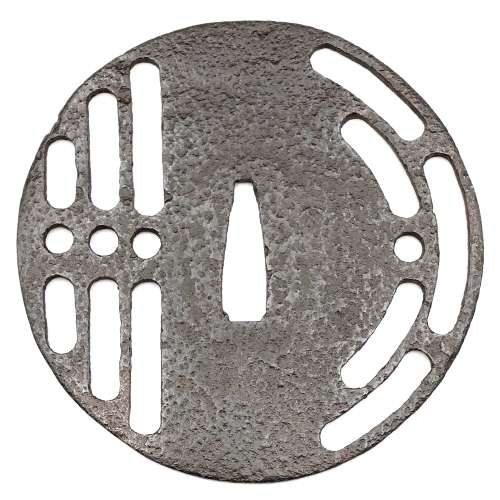
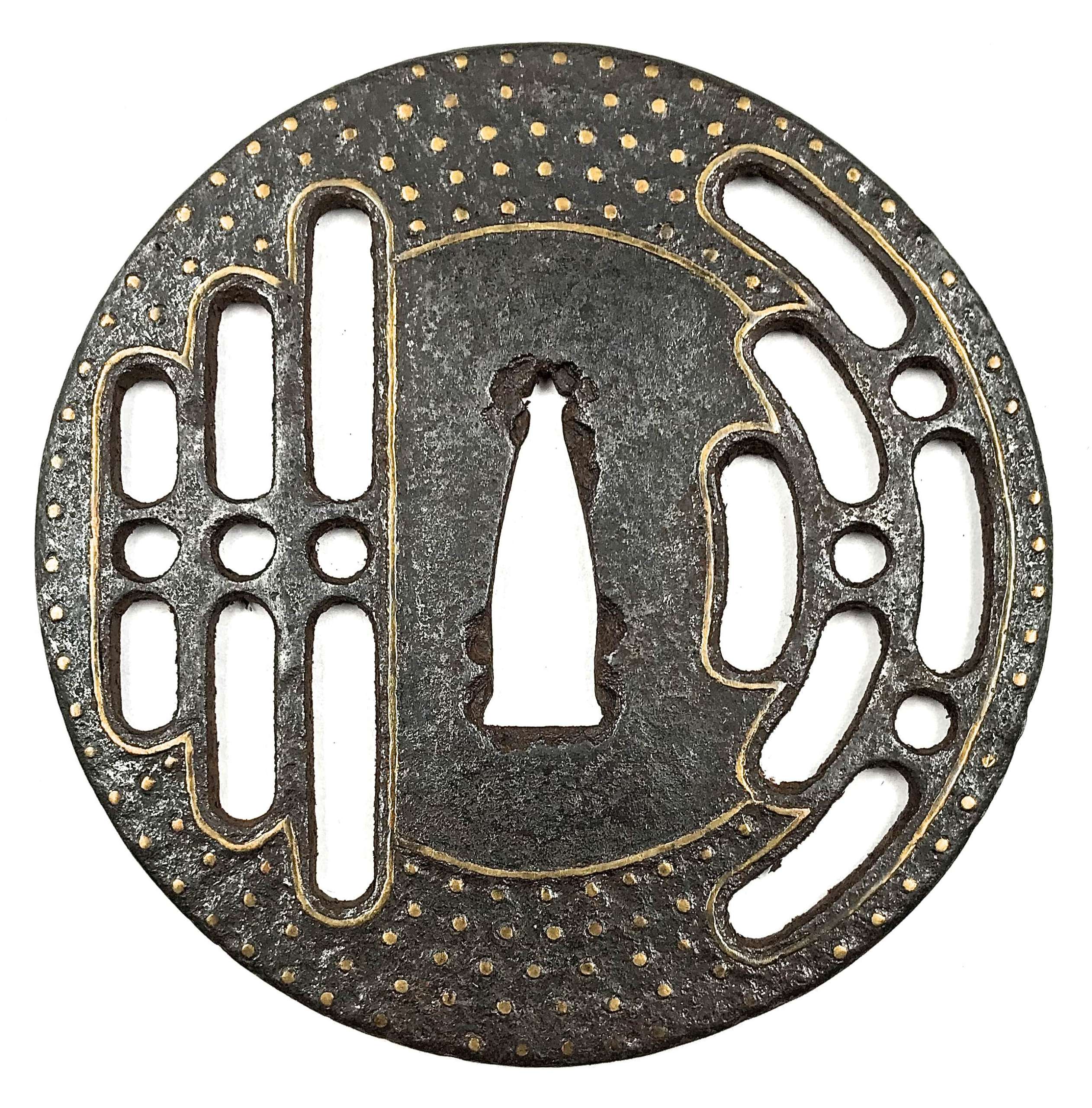











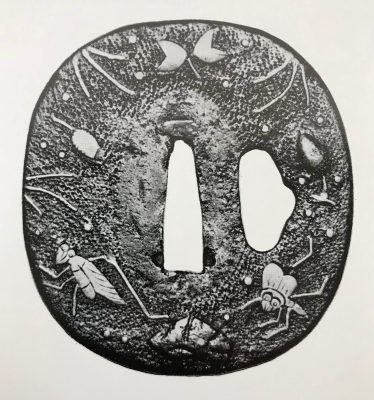






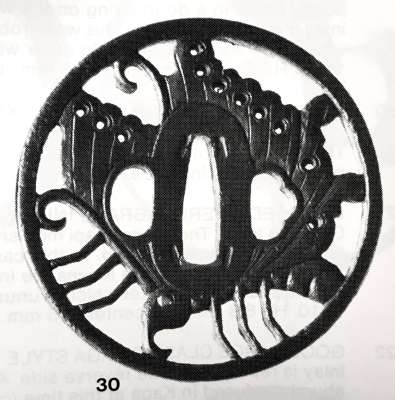




























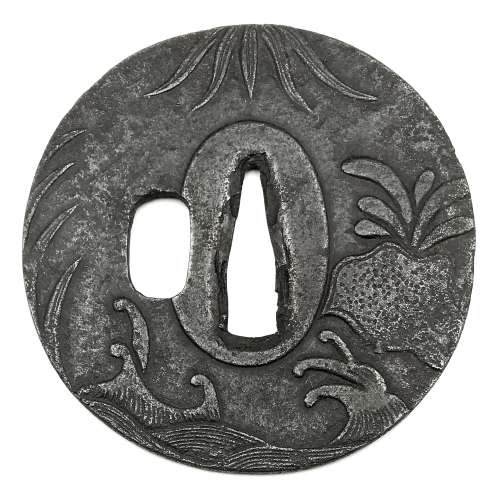
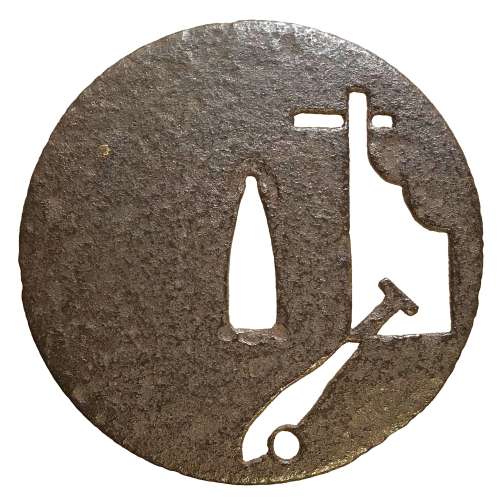
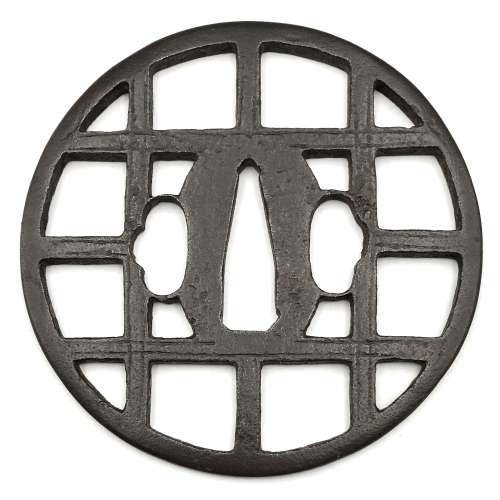
 Reference to this design can be found in LIB-1359.2017 Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections, Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997; p. 18-19, lot № 37: "A Kamakura-bori Tsuba, Momoyama Period. ...pierced with two large formalised butterflies..."
Reference to this design can be found in LIB-1359.2017 Japanese Swords and Tsuba from the Professor A. Z. Freeman and the Phyllis Sharpe Memorial collections, Sotheby's, London, Thursday 10 April 1997; p. 18-19, lot № 37: "A Kamakura-bori Tsuba, Momoyama Period. ...pierced with two large formalised butterflies..."


 As Japanese Erotic Fantasies put it: "a couple engaged in love-making, their stare fixed outside the picture plane". This is the only image of series that has a reference in available western literature, and the only one found in museum collections: Rijksmuseum Amsterdam (RP-P-1999-2001-16); reference: Fukuda (ed.) (1990), pls. 11-2.
As Japanese Erotic Fantasies put it: "a couple engaged in love-making, their stare fixed outside the picture plane". This is the only image of series that has a reference in available western literature, and the only one found in museum collections: Rijksmuseum Amsterdam (RP-P-1999-2001-16); reference: Fukuda (ed.) (1990), pls. 11-2.
 The scene of this print looks quite similar to that of the Kiyonaga's Sode no maki:
The scene of this print looks quite similar to that of the Kiyonaga's Sode no maki:
 The woman is "a young lady-in-waiting of Shogun's Court or Daimyō's Mansion, enjoying a rare outing from her tedious chores" [Richard Lane]. She is fully dressed in her outer cloak (shikake), white paper hat (agebōshi or tsunokakushi), and toed socks (tabi). A book or maybe, onkotogami (roll of tissues known as 'paper for honourable act' ) is still in the folds of her kimono. She is holding an open fan, either to cover her and her lover's faces from an unsolicited witness or to bring some fresh air to their joined lips. The pair just started their sexual intercourse.
The woman is "a young lady-in-waiting of Shogun's Court or Daimyō's Mansion, enjoying a rare outing from her tedious chores" [Richard Lane]. She is fully dressed in her outer cloak (shikake), white paper hat (agebōshi or tsunokakushi), and toed socks (tabi). A book or maybe, onkotogami (roll of tissues known as 'paper for honourable act' ) is still in the folds of her kimono. She is holding an open fan, either to cover her and her lover's faces from an unsolicited witness or to bring some fresh air to their joined lips. The pair just started their sexual intercourse.
 A scene from medieval times. A courtier in eboshi cap having sex with an aristocratic young woman with a long straight hairstyle (suihatsu).
A scene from medieval times. A courtier in eboshi cap having sex with an aristocratic young woman with a long straight hairstyle (suihatsu).
 Completely naked couple in the moment of ejaculation. Lavish garments with paulownia leaves on a yellow background counterbalance the white bodies on red bedding. The form of a woman's cheeks is telling, but I don't know about what. Maybe her advanced age?
Completely naked couple in the moment of ejaculation. Lavish garments with paulownia leaves on a yellow background counterbalance the white bodies on red bedding. The form of a woman's cheeks is telling, but I don't know about what. Maybe her advanced age?
 The pose of the couple and the overall composition are similar to that of the previous sheet. Though the lovers are dressed, and the woman's hairdo is well kept. The male looks older and the woman - younger.
The pose of the couple and the overall composition are similar to that of the previous sheet. Though the lovers are dressed, and the woman's hairdo is well kept. The male looks older and the woman - younger.
 A man takes a young maid from behind. She clenches the sleeve of her kimono in her teeth; it's either the moment of penetration (beginning of intercourse) or of her orgasm (the end of it).
A man takes a young maid from behind. She clenches the sleeve of her kimono in her teeth; it's either the moment of penetration (beginning of intercourse) or of her orgasm (the end of it).
 This seems to be a forced intercourse between a lackey with extensive bodily hair and a young maid from the same household.
This seems to be a forced intercourse between a lackey with extensive bodily hair and a young maid from the same household.
 This design is very much like the other one presented below, which is described at Japanese Erotic Fantasies on page 136 (pl. 43b) as follows: "The viewer peers through a mosquito net to see a child fast asleep, while his mother or wet-nurse moves towards her partner. On our print there is no child; instead of a sleeping baby, there is a roll of onkotogami. Fewer objects make the overall image concise, almost laconic in comparison with the Ehon hana fubuki (1802) design:
This design is very much like the other one presented below, which is described at Japanese Erotic Fantasies on page 136 (pl. 43b) as follows: "The viewer peers through a mosquito net to see a child fast asleep, while his mother or wet-nurse moves towards her partner. On our print there is no child; instead of a sleeping baby, there is a roll of onkotogami. Fewer objects make the overall image concise, almost laconic in comparison with the Ehon hana fubuki (1802) design:

 A young couple in a moment of true love. He is listening to the beating of her heart.
A young couple in a moment of true love. He is listening to the beating of her heart.
 This is a moment of true love between an old monk and a young samurai. The latter even did not take of his socks (tabi).
This is a moment of true love between an old monk and a young samurai. The latter even did not take of his socks (tabi).
 From Japanese Erotic Fantasies: "Boats played a crucial role in the workings of Yoshiwara, as they were the primary means of transport to the district. During the hot summer months, trips on pleasure boats were also a favourite pastime. Sex aboard a boat is a recurrent theme in shunga".
The last print that I am currently lacking and hunting for:
From Japanese Erotic Fantasies: "Boats played a crucial role in the workings of Yoshiwara, as they were the primary means of transport to the district. During the hot summer months, trips on pleasure boats were also a favourite pastime. Sex aboard a boat is a recurrent theme in shunga".
The last print that I am currently lacking and hunting for:
 I know where it is, but I cannot reach it... yet.
I know where it is, but I cannot reach it... yet. 
 A lookalike triptych by Kunisada can be found in
A lookalike triptych by Kunisada can be found in  Data from
Data from 













 Image from
Image from 

 №1: "...one of the most exotic scenes in all shunga. A Dutch kapitan is discovered coupling with a lovely Japanese courtesan, beside a large window opening upon a garden...".
№1: "...one of the most exotic scenes in all shunga. A Dutch kapitan is discovered coupling with a lovely Japanese courtesan, beside a large window opening upon a garden...".

 №2: "...a fair young harlot is seen masturbating with a grinding-pestle - a man watches intently from under bedding." [I have two specimens of this design; the one from album is more soiled but less faded].
№2: "...a fair young harlot is seen masturbating with a grinding-pestle - a man watches intently from under bedding." [I have two specimens of this design; the one from album is more soiled but less faded].
 №3: "...the artist has effectively contrasted the lovers by depicting the man's face as seen through the geisha's gauze skirt. [...] we are impressed more by strikingly elegant composition, the dramatic coloring, rather than feeling any great urge to participate in the energetic proceedings..."
№3: "...the artist has effectively contrasted the lovers by depicting the man's face as seen through the geisha's gauze skirt. [...] we are impressed more by strikingly elegant composition, the dramatic coloring, rather than feeling any great urge to participate in the energetic proceedings..."
 №4: "This scene is a most straightforward one, featuring the standard Missionary Position [capitalization by R. Lane].; but withal, the contrast of the young and naked, secret lover and the richly-clothed courtesan amid luxurious bedding..."
№4: "This scene is a most straightforward one, featuring the standard Missionary Position [capitalization by R. Lane].; but withal, the contrast of the young and naked, secret lover and the richly-clothed courtesan amid luxurious bedding..."
 №5: "In a striking lesbian scene (which has no equivalent in Utamaro, and is, incidentally, often omitted in later editions of this album), the girl at left prepares to receive the harikata (dildo) worn by the older girl at right (who holds a seashell containing lubricant)."
№5: "In a striking lesbian scene (which has no equivalent in Utamaro, and is, incidentally, often omitted in later editions of this album), the girl at left prepares to receive the harikata (dildo) worn by the older girl at right (who holds a seashell containing lubricant)."
 №6: "In the first appearance of a matronly heroine in this series, we find a widow - with shaven eyebrows and clipped hair - sporting with a handsome yound shop-clerk, mounting him with all her might."
№6: "In the first appearance of a matronly heroine in this series, we find a widow - with shaven eyebrows and clipped hair - sporting with a handsome yound shop-clerk, mounting him with all her might."

 №7: "... lady of samurai court: here, shown taking advantage of an official outing to temple and theatre, to rendezvous with a secret lover on a teahouse balcony." R. Lane considers this design the least successful in the series, especially in comparison with the same theme by Utamaro: "Utamaro female is almost ferocious in her lust for sexual gratification", which does not sound true to me. See Utamaro's sheet №5 from the album Utamakura (歌まくら, Poem of the Pillow) [courtesy The British Museum without permission]:
№7: "... lady of samurai court: here, shown taking advantage of an official outing to temple and theatre, to rendezvous with a secret lover on a teahouse balcony." R. Lane considers this design the least successful in the series, especially in comparison with the same theme by Utamaro: "Utamaro female is almost ferocious in her lust for sexual gratification", which does not sound true to me. See Utamaro's sheet №5 from the album Utamakura (歌まくら, Poem of the Pillow) [courtesy The British Museum without permission]:
 Then, as Richard Lane states, "we are flung suddenly to the bottom rung of Edo society":
Then, as Richard Lane states, "we are flung suddenly to the bottom rung of Edo society":
 №8: "Here we find a fair yotaka ('night-hawk', e.i. streetwalker) accommodating a lusty client in a lumberyard by the bank of the Sumida River".
№8: "Here we find a fair yotaka ('night-hawk', e.i. streetwalker) accommodating a lusty client in a lumberyard by the bank of the Sumida River".
 №9: '... a slightly plump harlot of the lower class receives a night visit from her lover, whose naked form she tries to cover with a cloak."
№9: '... a slightly plump harlot of the lower class receives a night visit from her lover, whose naked form she tries to cover with a cloak."
 №10: "...likely maidservant and lackey - are depicted in bath-room, their passions are all too obviously fired by steaming water."
№10: "...likely maidservant and lackey - are depicted in bath-room, their passions are all too obviously fired by steaming water."
 №11: "...this scene of courtesan and secret lover ranks high not only in Eiri's œuvre but also in the annals of the ukiyo-e genre itself. Both design and colouring are impeccable and, for this period, there is nothing even in the work of great Utamaro that really surpasses it." Again, a doubtful statement, however, this is Utamaro's design for the reader to judge:
№11: "...this scene of courtesan and secret lover ranks high not only in Eiri's œuvre but also in the annals of the ukiyo-e genre itself. Both design and colouring are impeccable and, for this period, there is nothing even in the work of great Utamaro that really surpasses it." Again, a doubtful statement, however, this is Utamaro's design for the reader to judge:
 The last design in my album is this:
The last design in my album is this:
 #13: In most reference books it goes under number 13, and we will assign this number to the sheet. "The final scene of the album features naked participants, probably samurai man and wife. The print is rather subdued in tone and colour, if not in the degree of the passion displayed..."
An additional sheet, acquired separately from a reputable dealer in New York, is usually listed as №12:
#13: In most reference books it goes under number 13, and we will assign this number to the sheet. "The final scene of the album features naked participants, probably samurai man and wife. The print is rather subdued in tone and colour, if not in the degree of the passion displayed..."
An additional sheet, acquired separately from a reputable dealer in New York, is usually listed as №12:
 №12: "One might think that Eiri has reached his peak with the preceding plate 11 - and indeed he has, in both esthetic and erotic terms. But the album is not yet finished, and the next scene lends a needed variety to the series, a slightly comic tableau featuring a middle-aged lackey attempting to forcibly seduce a servant girl of the same domicile". Utamaro's design, that inspired Eiri is here:
№12: "One might think that Eiri has reached his peak with the preceding plate 11 - and indeed he has, in both esthetic and erotic terms. But the album is not yet finished, and the next scene lends a needed variety to the series, a slightly comic tableau featuring a middle-aged lackey attempting to forcibly seduce a servant girl of the same domicile". Utamaro's design, that inspired Eiri is here:
 All descriptions are taken from Richard Lane's article at The Complete Ukiyo-e Shunga №9 Eiri, 1996. He concluded: "...Eiri's erotic series represents a major contribution to shunga art towards the close of ukiyo-e "Golden Age". In part inspired by Utamaro's classic album, this series withal constitutes a unified and original achievement, providing a cumulative effect of gracefully elegant yet glowing eroticism, which remains in the mind's eye long after the pictures themselves are far away."
I only would like to mention here that in several reference sources this album goes under name of Eisho; unfortunately, this mistake is reproduced at
All descriptions are taken from Richard Lane's article at The Complete Ukiyo-e Shunga №9 Eiri, 1996. He concluded: "...Eiri's erotic series represents a major contribution to shunga art towards the close of ukiyo-e "Golden Age". In part inspired by Utamaro's classic album, this series withal constitutes a unified and original achievement, providing a cumulative effect of gracefully elegant yet glowing eroticism, which remains in the mind's eye long after the pictures themselves are far away."
I only would like to mention here that in several reference sources this album goes under name of Eisho; unfortunately, this mistake is reproduced at 










