Size: 76.8 x 75.7 x 4.0 mm.
[Seller alleged that the motif is "Buddhist wheel", which seems unlikely.-
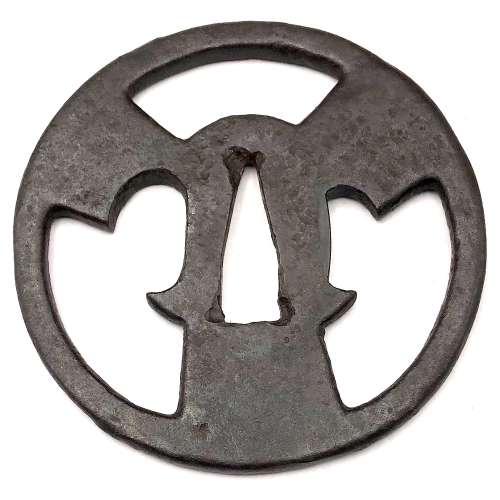 Iron tsuba of round form with three stylized folding fans motif in openwork (sukashi). Kogai-hitsu-ana with shakudō sekigane. Iron bones (tekkotsu) on the rim. Momoyama period or earlier. Possibly, Ko-Shōami school.
Iron tsuba of round form with three stylized folding fans motif in openwork (sukashi). Kogai-hitsu-ana with shakudō sekigane. Iron bones (tekkotsu) on the rim. Momoyama period or earlier. Possibly, Ko-Shōami school. -
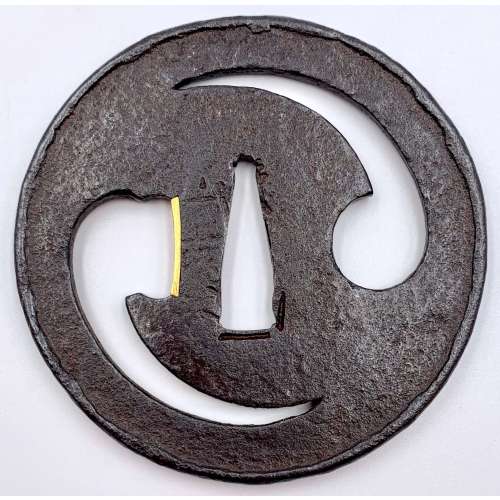

Circular tsuba (marugata ) with design of futatsu-domoe (twofold tomoe) in negative openwork (kage-sukashi), folded-over rim (uchikaeshi-mimi ). The ‘head’ of the left tomoe altered to form an opening for scabbard accessory (kata-hitsu-ana), adorned with gold ategane fitting with file marks (tate-yasurime). The hammer-blow finish of the surface (tsuchime-ji). Signed to the left of nakaga-ana: Yamakichibei (山吉兵). Attributed by Steve Waszak a the Second Generation (Nidai) master.
NBTHK paper [translated by Markus Sesko]:Tomoe-sukashi-tsuba (巴透し鐔).
KANTEI-SHO (鑑定書) - APPRAISAL No 451718
Futatsu-domoe sukashi-tsuba (二巴透鐔) ‒ Tsuba with two tomoe comma openwork design
Signed: Yamakichibei (山吉兵)
Round shape (marugata ), iron, hammerblow finish (tsuchime-ji ), negative openwork design (kage-sukashi ), folded-over rim (uchikaeshi-mimi ), one opening for scabbard accessory
(kata-hitsu-ana) (with gold ategane fitting)
According to the result of the shinsa committee of our society, we judge this work as authentic
and rank it as Hozon Tōsōgu.
February 20, 2007
[Foundation] Nihon Bijutsu Tōken Hozon Kyōkai, NBTHK (日本美術刀劍保存協會)
Diameter: 76 mm, thickness at center 3.9 mm, thickness at rim: 5.1 mm; weight: 102.5 g
Tomoe (Comma): The character 巴 (Chinese pronunciation bā). A pattern resembling the two-comma tomoe (futatsu-domoe) has been found in ancient cultures on all inhabited continents. ...aside from their military function, a ritual or fetish value, perhaps related to their testicular shape. It also has yin-yang connotation. The gold sekigane confirms the high value of the piece to the owner.
-
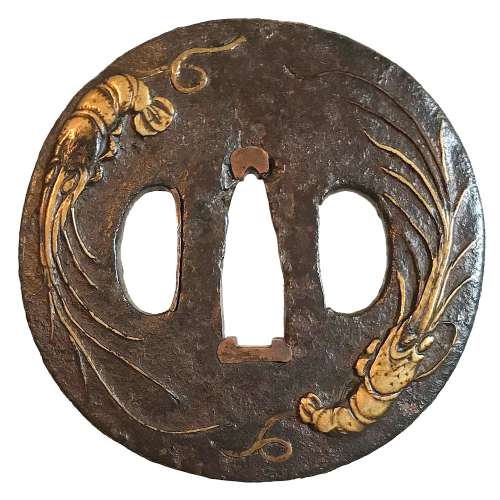 Iron tsuba of round form with two ebi (lobster) on omote (obverse side) and shika (deer) among scattered momiji (maple leaves) on ura (reverse side) motif in brass takabori (high relief) suemon-zōgan. Traces of lacquer. Unsigned. Late Muromachi / Momoyama period (late 16th / Early 17th century). Dimensions: 69.0.6 mm (H) x 69.6 mm (W) x 3.4 mm (T, seppa-dai). Weight: 92.6 g. Illustrated at: The Lundgren Collection of Japanese Swords, Sword Fittings and A Group of Miochin School Metalwork. Christie's Auction: Tuesday, 18 November 1997, London. Sales "GOTO-5881". Christie's, 1997. - #2 at page 7. Provenance: The second John Harding; The Lundgren Collection. Description at Christie's: "The iron plate depicting two lobsters in takabory and brass takazogan, the reverse similarly decorated with deer among scattered maple leaves, square mimi, late Muromachi / early Momoyama period (late 16th/early 17th century) Diameter 68 mm, mimi thickness 4 mm. Provenance: The second John Harding." Also at: JAPANESE SWORD-FITTINGS & METALWORK IN THE LUNDGREN COLLECTION. Published by Otsuka Kogeisha, Tokyo 1992. № 134. Description on page 173: Sword guard with design of shrimps in inlay (scarlet [sic] maple leaves and deer on the reverse side). Unsigned. Heianjō inlay school. Vertical 6.85 cm, horizontal 6.90 cm, Th. of rim 0.40 cm. Iron. Taka-bori relief and brass inlay. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. According to Merrily Baird, maple leaves, especially if paired with the deer, allude to autumnal tradition of Japanese aristocracy of viewing the seasonal changes of color in the Nara area. The lobster is typical Japanese ebi, - it lacks prominent claws, and has a spiny shell. As a symbol of longevity and good fortune, lobster is a staple of New Year's decoration.
Iron tsuba of round form with two ebi (lobster) on omote (obverse side) and shika (deer) among scattered momiji (maple leaves) on ura (reverse side) motif in brass takabori (high relief) suemon-zōgan. Traces of lacquer. Unsigned. Late Muromachi / Momoyama period (late 16th / Early 17th century). Dimensions: 69.0.6 mm (H) x 69.6 mm (W) x 3.4 mm (T, seppa-dai). Weight: 92.6 g. Illustrated at: The Lundgren Collection of Japanese Swords, Sword Fittings and A Group of Miochin School Metalwork. Christie's Auction: Tuesday, 18 November 1997, London. Sales "GOTO-5881". Christie's, 1997. - #2 at page 7. Provenance: The second John Harding; The Lundgren Collection. Description at Christie's: "The iron plate depicting two lobsters in takabory and brass takazogan, the reverse similarly decorated with deer among scattered maple leaves, square mimi, late Muromachi / early Momoyama period (late 16th/early 17th century) Diameter 68 mm, mimi thickness 4 mm. Provenance: The second John Harding." Also at: JAPANESE SWORD-FITTINGS & METALWORK IN THE LUNDGREN COLLECTION. Published by Otsuka Kogeisha, Tokyo 1992. № 134. Description on page 173: Sword guard with design of shrimps in inlay (scarlet [sic] maple leaves and deer on the reverse side). Unsigned. Heianjō inlay school. Vertical 6.85 cm, horizontal 6.90 cm, Th. of rim 0.40 cm. Iron. Taka-bori relief and brass inlay. Momoyama period, 16th - 17th century. According to Merrily Baird, maple leaves, especially if paired with the deer, allude to autumnal tradition of Japanese aristocracy of viewing the seasonal changes of color in the Nara area. The lobster is typical Japanese ebi, - it lacks prominent claws, and has a spiny shell. As a symbol of longevity and good fortune, lobster is a staple of New Year's decoration. -
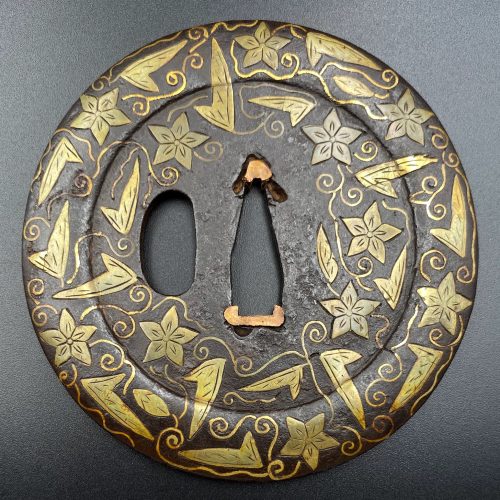 Iron tsuba of the round form (丸型, maru–gata), decorated with brass flat inlay (平象嵌, hira-zōgan) of bellflowers, leaves, and vines on both sides, inlaid brass is carved in low relief; wide rim (dote-mimi) also inlaid; the plate is pierced with hitsu-ana (probably original); nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Dimensions: Height: 84.1 mm; Width: 82.0 mm; Thickness (centre): 2.8 mm; mimi is 11.8 mm wide and 4.7 mm thick. Produced at the end of the 16th century, in the Momoyama period (1674–1703).
Iron tsuba of the round form (丸型, maru–gata), decorated with brass flat inlay (平象嵌, hira-zōgan) of bellflowers, leaves, and vines on both sides, inlaid brass is carved in low relief; wide rim (dote-mimi) also inlaid; the plate is pierced with hitsu-ana (probably original); nakago-ana plugged with copper sekigane. Dimensions: Height: 84.1 mm; Width: 82.0 mm; Thickness (centre): 2.8 mm; mimi is 11.8 mm wide and 4.7 mm thick. Produced at the end of the 16th century, in the Momoyama period (1674–1703). -
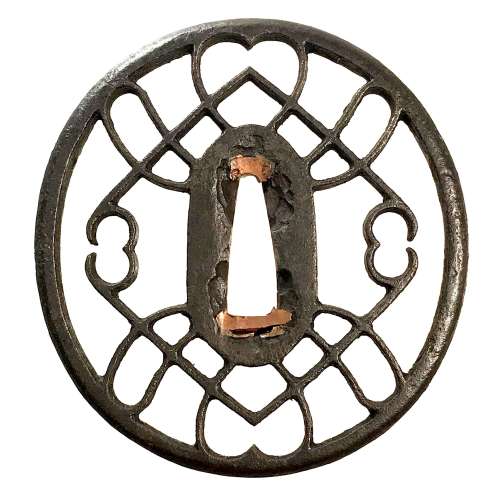 Iron tsuba of oval form with the motif of horse trappings in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Iron bones (tekkotsu) on the rim.
Iron tsuba of oval form with the motif of horse trappings in openwork (sukashi). Copper sekigane. Iron bones (tekkotsu) on the rim.Size: 80.4 x 75.8 x 5.2 mm
NBTHK Certificate №454567, allegedly saying that it is Akasaka School, Muromachi period. A look-a-like tsuba in Robert. E. Haynes Catalog #7, 1983 on page 57 under №48 is described as follows: "A masterpiece second period Owari sukashi tsuba. The plate is of beautiful color and quality almost like velvet. The design is very hard to discern, it might be the horse trappings, or even a moon. The style and type of Owari tsuba shows the great tradition of the Momoyama period and why it was the renaissance in time, as well as the arts produced, through the long history of all Japanese art. Ca. 1580. Ht. 7.7 cm, Th. (center) 5.5 mm, (edge) 5.25 to 5.75 mm."I believe we can safely attribute this tsuba to Owari School, c. 1580.
Robert. E. Haynes Catalog #7, 1983, p. 57, №48.
-

Iron tsuba of diamond form with rounded corners with the design of a double gourd on a branch in openwork. Dark brown patina. Ko-Shōami school. Custom kiri-wood box with hakogaki of Sasano Masayuki.
Momoyama Period (1574-1603)
Size: 77.1 x 75.7 x 4.6 mm; weight: 75.3 g.
Provenance: Sasano Masayuki[Translated by Markus Sesko]Hakogaki lid outside: 古正阿弥鐔 Ko-Shōami tsuba Hakogaki lid inside:Hyōtan-sukashi Mumei, Momoyama-ki saku Tetsu, ji-sukashi Koboku-aware no kasaku Heisei ninen Soshinkan Minazuki Openwork design of gourd Unsigned, Momoyama era work Iron, large openwork Masterwork full of classical charm. June of 1990, Soshinkan [pen name of Sasano Masayuki]瓢簞透 無銘 桃山期作 鉄地透
古撲惻之佳作 平成二年 素心鑑 水無月
-
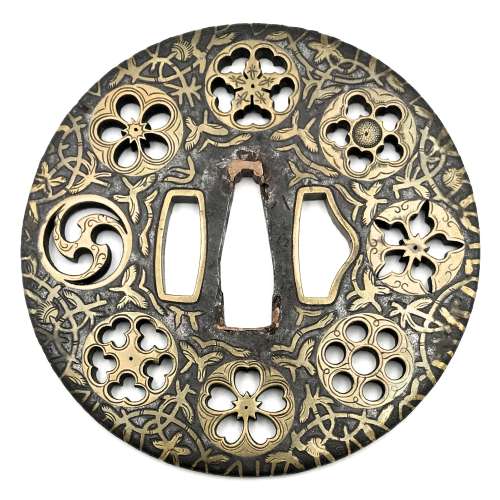 Well-forged iron plate of round shape (maru-gata) is decorated with water weeds or arabesque (karakusa) in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) all over and eight family crests (mon) of round form in cast brass with delicate linear carving (kebori) and openwork (sukashi). Crests represent: [at 9 hours] three counter-clockwise commas or swirls (tomoe); [at 10:30] plum blossom (ume); [at 12:00, 1:130, and 7:30] - stylized flower made by cutting out five suhama symblos (flower-shaped suhama); [at 3:00] bellflower (kikyō); [at 4:30] seven-star crest (shichiyō-mon); [at 6:00] cherry blossom (sakura). Brass-trimmed ryo-hitsu. Copper sekigane. Yoshirō school. Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Inscription on seppa-dai: 八幡 - Hachiman. Size: height 89.6 mm, width 89.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,0 mm. Weight 129.7 g. NBTHK certificate № 4007685, June 27, 2015: HOZON (Worthy of Preservation). As for the inscription, Nihonto Message Board blog discussion provides the following explanation of the inscription: "An expression of conviction as to being the best under the sun". On the other hand, there may be more in this confluence of symbols: the tomoe crest at 9:00 is "the kamon of Hachiman, the war god" [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007, p. 108]. The character 八 in the inscription cut stronger than the other kanji, and may be by a different hand in different time. 八 (hachi, eight): "The numeral eight was appreciated because its shape broadens toward the bottom, symbolizing eternal expansion" [ibid, p. 119]. It may be said that this tsuba is dedicated to Hachiman. Other crests (suhama, bellflower, seven-stars, plum and cherry blossoms) collectively allude to "good old times" when Fijiwara and Taira clans were in full bloom. Markus Sesko believes that the inscriptions reads: Hachiman: "the inscription is/was HACHIMAN (八幡), the God of War and a relatively popular inscription for tsuba, swords and armor." Elliott Long and Robert Haynes provide the following explanation of the inscription: "...hachi is correct and represents the name of the HACHI SHRINE. The inscription reads 'YAWATA' which is the name of the mountain in Mino Province where the HACHI Shrine is located". Details on Hachiman Shrine in Yawata (八幡市) can be found elsewhere, including Historical and geographical dictionary of Japan by Edmond Papinot. Van Ham auction house provides the following description: MON-SUKASHI TSUBA. MARUGATA. Japan. Momoyama period. Yoshiro school. Iron with inlays of brass. In hira-zogan technique with kebori engraving eight different family emblems (mon). An old inscription is dedicated to the deity Hachiman. D.4.5mm, Ø 8.3cm. Condition A/B. Supplement: Wooden box and NBTHK certificate.
Well-forged iron plate of round shape (maru-gata) is decorated with water weeds or arabesque (karakusa) in flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) all over and eight family crests (mon) of round form in cast brass with delicate linear carving (kebori) and openwork (sukashi). Crests represent: [at 9 hours] three counter-clockwise commas or swirls (tomoe); [at 10:30] plum blossom (ume); [at 12:00, 1:130, and 7:30] - stylized flower made by cutting out five suhama symblos (flower-shaped suhama); [at 3:00] bellflower (kikyō); [at 4:30] seven-star crest (shichiyō-mon); [at 6:00] cherry blossom (sakura). Brass-trimmed ryo-hitsu. Copper sekigane. Yoshirō school. Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Inscription on seppa-dai: 八幡 - Hachiman. Size: height 89.6 mm, width 89.3 mm, thickness at seppa-dai 3,0 mm. Weight 129.7 g. NBTHK certificate № 4007685, June 27, 2015: HOZON (Worthy of Preservation). As for the inscription, Nihonto Message Board blog discussion provides the following explanation of the inscription: "An expression of conviction as to being the best under the sun". On the other hand, there may be more in this confluence of symbols: the tomoe crest at 9:00 is "the kamon of Hachiman, the war god" [Family Crests of Japan; Stone Bridge Press, Berkeley, CA, 2007, p. 108]. The character 八 in the inscription cut stronger than the other kanji, and may be by a different hand in different time. 八 (hachi, eight): "The numeral eight was appreciated because its shape broadens toward the bottom, symbolizing eternal expansion" [ibid, p. 119]. It may be said that this tsuba is dedicated to Hachiman. Other crests (suhama, bellflower, seven-stars, plum and cherry blossoms) collectively allude to "good old times" when Fijiwara and Taira clans were in full bloom. Markus Sesko believes that the inscriptions reads: Hachiman: "the inscription is/was HACHIMAN (八幡), the God of War and a relatively popular inscription for tsuba, swords and armor." Elliott Long and Robert Haynes provide the following explanation of the inscription: "...hachi is correct and represents the name of the HACHI SHRINE. The inscription reads 'YAWATA' which is the name of the mountain in Mino Province where the HACHI Shrine is located". Details on Hachiman Shrine in Yawata (八幡市) can be found elsewhere, including Historical and geographical dictionary of Japan by Edmond Papinot. Van Ham auction house provides the following description: MON-SUKASHI TSUBA. MARUGATA. Japan. Momoyama period. Yoshiro school. Iron with inlays of brass. In hira-zogan technique with kebori engraving eight different family emblems (mon). An old inscription is dedicated to the deity Hachiman. D.4.5mm, Ø 8.3cm. Condition A/B. Supplement: Wooden box and NBTHK certificate. -
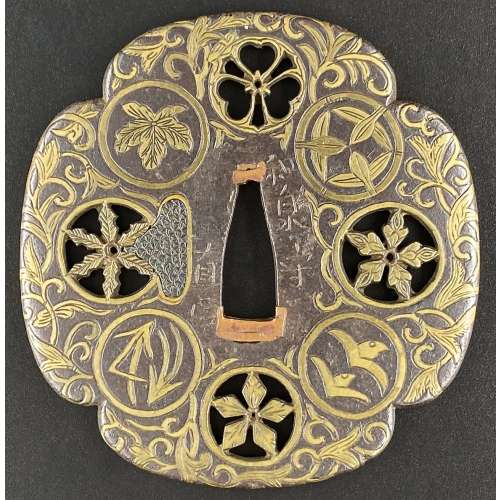 The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba.
The so-called Yoshirō-tsuba [与四郎鐔] with an iron plate of mokkō form densely decorated with floral arabesque and adorned with eight pierced, chiselled and inlaid brass roundels and signed on both sides 'Koike Yoshirō Izumi no Kami Naomasa'. Four of the roundels are pierced and have geometrical designs representing flowers (e.g. wood sorrel) or snowflakes. Four others are solid and represent family crests; on one side: Mulberry (kaji) – mon of the Matsunaga clan [松永氏], Bamboo Grass (sasa) – mon of the Takenaka clan [竹中氏]), Wild Geese (kari) – mon of the Shibata clan [新発田氏]), and Pine Needles (matsuba); on the other side: Nine Stars (kuyō) – the Hosokawa clan [細川氏], Paulownia (kiri) – the Toyotomi clan [豊臣氏]), Bamboo Leaves (take) – the Minamoto clan [源], and Seven Treasures (shippo) – Izumo Genji clan [出雲源氏]. Hitsu-ana obliterated with a nanako-treated pewter plug. Brass with rainbow patina. Artist: Koike Izumi no Kami Naomasa (Japanese, active late 16th – early 17th century). The Momoyama or early Edo period, end of the 16th to the first half of the 17th century (1574-1650). Size: 81.7 x 78.8 x 4.3 cm. Provenance: Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye. Special thanks to Markus Sesko for providing the translation of hakogaki. Hakokaki lid (outside): 小池与四郎 – Koike Yoshirō Hakokaki lid (inside): 銘曰小池与四郎 – Mei’etsu: Koike Yoshirō – Signed: Koike Yoshirō 和泉守直正 – Izumi no Kami Naomasa – Izumi no Kami Naomasa 木瓜形 鉄地 – Mokkōgata, tetsu-ji – Lobed shape, of iron 真鍮据紋象嵌 – Shinchū suemon-zōgan – with brass suemon-zōgan inlay 縦二寸七分横二寸六分 – Tate ni-sun shichi-bu, yoko ni-sun roku-bu – Height 8.2 cm, width 7.9 cm 右正真也 – Migi shōshin nari – Above described object is authentic 昭和廾九年八月十一日 – Shōwa nijūkyūnen hachigatsu jūichinichi – August 11, 1954 草堂「花押」– Sōdō + kaō – Sōdō [pen name of Torigoye Kazutarō, 鳥越一太郎] + monogram Ref.: (1) Tsuba Geijutsu-Ko by Kazutaro Torigoye, 1960; (2) Tsuba. An aesthetic study. By Kazutaro Torigoye and Robert E. Haynes from the Tsuba Geijutsu-kō of Kazataro Torigoye. Edited and published by Alan L. Harvie for the Nothern California Japanese Sword Club, 1994-1997, p. Yoshirō, 4. See also Yoshirō tsuba. -
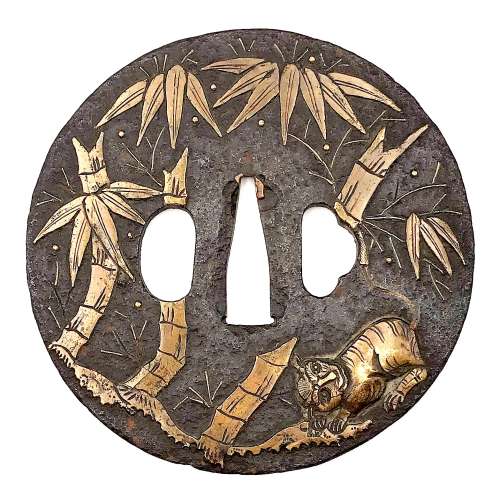 Large and thin iron tsuba of round form (width > height) decorated with the design of a tiger sheltering in bamboo in suemon-zōgan brass inlay. A fragment of tail inlay is missing. Bamboo leaves on the reverse. According to Merrily Baird [Symbols, p. 166], tiger sheltering in bamboo symbolizes "weak giving shelter to the strong". Momoyama period. Unsigned. Dimensions: 90.8 x 91.2 x 3.4 (center), 3.1 (rim) mm. Custom wooden box. NBTHK Certificate № 4001593.
Large and thin iron tsuba of round form (width > height) decorated with the design of a tiger sheltering in bamboo in suemon-zōgan brass inlay. A fragment of tail inlay is missing. Bamboo leaves on the reverse. According to Merrily Baird [Symbols, p. 166], tiger sheltering in bamboo symbolizes "weak giving shelter to the strong". Momoyama period. Unsigned. Dimensions: 90.8 x 91.2 x 3.4 (center), 3.1 (rim) mm. Custom wooden box. NBTHK Certificate № 4001593. -
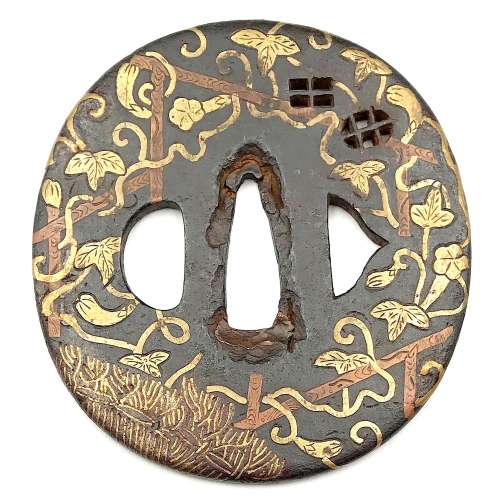 Iron tsuba of oval form with design of a gourd or aubergine vine with fruits, leaves, and blossoms climbing a trellis, and a fence in yellow brass and red copper flat inlay (hira-zōgan); inlay engraved. Two latticed windows represented by openwork (sukashi). The iron web has deep black patina. The seller attributes this tsuba to Heianjo-Namban school, whatever it means. Momoyama or early Edo period, 17th century. Kaga or Heianjō School. Unsigned. Height: 77.3, Width: 73.1, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm.
Iron tsuba of oval form with design of a gourd or aubergine vine with fruits, leaves, and blossoms climbing a trellis, and a fence in yellow brass and red copper flat inlay (hira-zōgan); inlay engraved. Two latticed windows represented by openwork (sukashi). The iron web has deep black patina. The seller attributes this tsuba to Heianjo-Namban school, whatever it means. Momoyama or early Edo period, 17th century. Kaga or Heianjō School. Unsigned. Height: 77.3, Width: 73.1, Thickness at seppa-dai: 3.6 mm. -
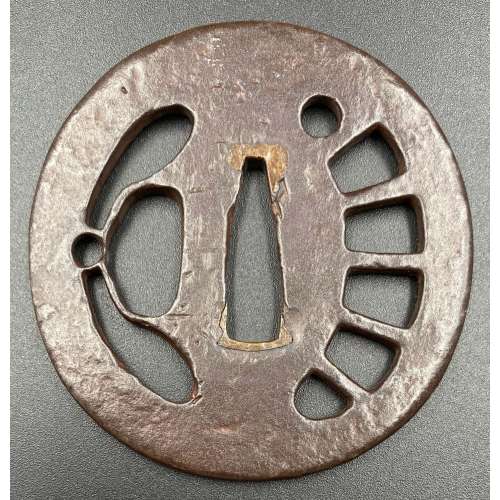

Oblong round shape (nagamaru-gata) tsuba with design of dragonfly (tombo or katsumushi) and wheel (kuruma) in negative openwork (kage-sukashi), round rim (maru-mimi ). Copper sekigane.
Okamoto Yasukazu's Owari to Mikawa no tankō, №181 characterizes the tsuba as follows: "Katsumushi, kuruma-sukashi no zu (dragonfly and wheel sukashi). Mei: Yamakichibei (Shodai). Such small tsuba are rare for the Shodai. The nakago-ana is also small so it was probably intended to be mounted on a tantō. Regardless of its size, the iron is outstanding and the workmanship shows the characteristic features of the Shodai (first generation). The kuruma-sukashi design is interpreted here in a half-moon shape and only on one side of the tsuba. Such a design is also seen on works of the Nidai (second generation)...". Signed to the left of nakaga-ana: Yamakichibei (山吉兵へ). Attributed to the First Generation (Shodai) master.
NBTHK paper (translated by Markus Sesko): The Tokubetsu-Kichō Kodōgu. Kachimushi-kuruma sukashi-tsuba (勝虫車透鐔) - Tsuba with sukashi motif of dragonfly and cartwheel. Signed: Yamakichibei (山吉兵). Iron, marugata, ko-sukashi. Issued on April 1, 1977. [Copy only] Dimensions: H: 66 mm; W: 63.2 mm; Th(center): 3.8 mm; Th(rim): 3.5 mm. Weight: 68 g. -
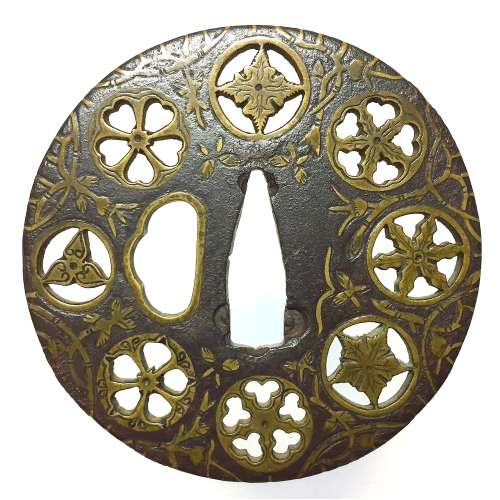 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels - circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiseled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or seaweed all over the plate. Hitsu-ana outlined in brass. Four positive silhouette roundels are 3-, 4-, 5-, and 6- pointing crests/flowers; four negative silhouette roundels are bellflower, cherry blossom, and suhama. Yoshirō school (Kaga-Yoshirō). The Momoyama or early Edo period, beginning of 17th century. Size: diameter 77 mm, thickness 3,8 mm -
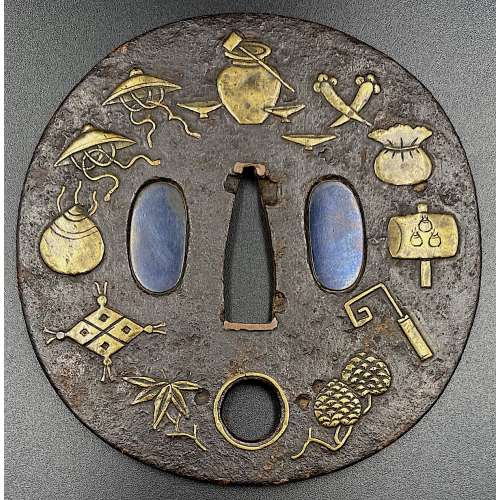 Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):
Iron tsuba of almost round form with a brass outlined circular opening (sukashi) in the bottom adorned with the Myriad Treasures [takaramono, 宝物] and winter motifs inlaid in cast brass (suemon-zōgan); hitsu-ana possibly cut later, both plugged with shakudo, nakaga-ana fitted with copper sekigane. According to Merrily Baird*) (2001), the symbolism of Myriad Treasures “is associated with the Seven Gods of Good Luck, who carry them in a sack”. Among the treasures, which are said to ensure prosperity, long life, and general good fortunes, are (reading clockwise from the top):- Sake set [shuki, 酒器], namely flask, ladle, and cups
- Cloves [choji, 丁子]
- Purse of inexhaustible reaches [kinchaku, 巾着]
- Magic mallet [kozuchi, 小槌]
- Key to the storehouse of the Gods [kagi, 鍵]
- Rhombus, or Lozenge (hosho, 方勝), with the second ideograph meaning victory.
- Sacred (or wish-granting) gem, or jewel [hōju, 宝珠]
- Hats of invisibility [kakuregasa, 隠れ笠]
-
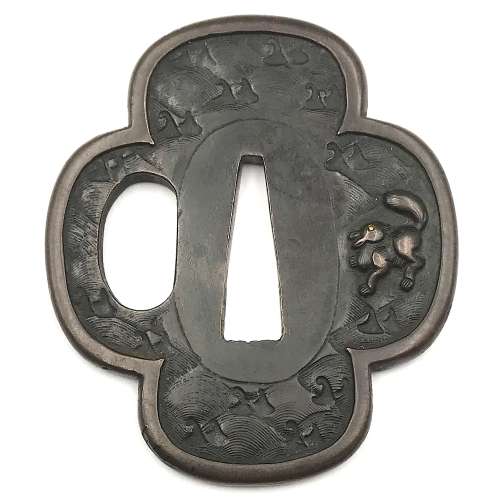 Ko-kinko ymagane cast tsuba of mokko form (kirikomi-mokkō-gata) with chiseled diaper pattern of double head waves on both sides and a rabbit cast and carved with its eye inlaid in yellow metal (gold or brass) on the face. Fukurin which holds together the sandwiched layers of metal (sanmai) is about 2.4 mm wide. A look-a-like tsub of oval form instead of mokko-gata is illustrated at Robert E. Haynes's Catalog #3,1982 on page 11, lot 15: "Rare design in style of Sanmai (three layers) / Wasei work. With yamagane core and heavy rim cover. The web plates are carved with double head Goto style waves and the face has a fox. The web plates were riveted at the seppadai. See Lot 4, page 8. Ca. 1350. Ht. 6.6 cm, th. 3 mm" [underscore mine]. Quality of photo is so poor that I decided not to provide it here. Muromachi (if we follow Robert) or Momoyama period. The Momoyama attribution is mostly based on a fact that "waves and rabbit" motif became most popular in Momoyama times. Size: 68.5 x 59.8 x 4.0 mm. NBTHK Certificate № 423120. This tsuba is listed at Yakiba website with the following passage: "Attributions as well as dating of this type of tsuba has been the subject debate over the years. There are those who believe these type of tsuba to be ko-Mino (early Mino School) tsuba, others believe them to be tachi-kanaguchi tsuba. Still others insist they are simply ko-kinko (early soft metal) tsuba. This tsuba was authenticated and determined to be "Ko-Kinko" by the NBTHK". Oval form tsuba with the same design can be found in this collection - TSU-0323.
Ko-kinko ymagane cast tsuba of mokko form (kirikomi-mokkō-gata) with chiseled diaper pattern of double head waves on both sides and a rabbit cast and carved with its eye inlaid in yellow metal (gold or brass) on the face. Fukurin which holds together the sandwiched layers of metal (sanmai) is about 2.4 mm wide. A look-a-like tsub of oval form instead of mokko-gata is illustrated at Robert E. Haynes's Catalog #3,1982 on page 11, lot 15: "Rare design in style of Sanmai (three layers) / Wasei work. With yamagane core and heavy rim cover. The web plates are carved with double head Goto style waves and the face has a fox. The web plates were riveted at the seppadai. See Lot 4, page 8. Ca. 1350. Ht. 6.6 cm, th. 3 mm" [underscore mine]. Quality of photo is so poor that I decided not to provide it here. Muromachi (if we follow Robert) or Momoyama period. The Momoyama attribution is mostly based on a fact that "waves and rabbit" motif became most popular in Momoyama times. Size: 68.5 x 59.8 x 4.0 mm. NBTHK Certificate № 423120. This tsuba is listed at Yakiba website with the following passage: "Attributions as well as dating of this type of tsuba has been the subject debate over the years. There are those who believe these type of tsuba to be ko-Mino (early Mino School) tsuba, others believe them to be tachi-kanaguchi tsuba. Still others insist they are simply ko-kinko (early soft metal) tsuba. This tsuba was authenticated and determined to be "Ko-Kinko" by the NBTHK". Oval form tsuba with the same design can be found in this collection - TSU-0323.
TSU-0323. Ko-kinko yamagane tsuba with waves and rabbit motif.
-
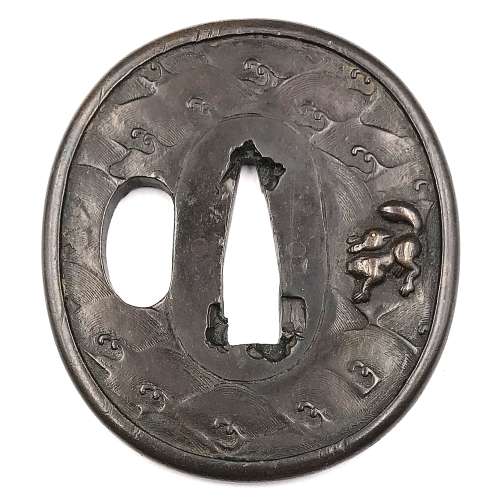 Ko-kinko ymagane cast tsuba of oval form with chiseled diaper pattern of double head waves on both sides and a rabbit cast and carved with its eye inlaid in yellow metal (gold or brass) on the face. Fukurin which holds together the sandwiched layers of metal (sanmai) is about 2.7 mm wide. Possibly, early Mino (ko-Mino) school. Size: 66.6 x 59.9 x 4.0 mm. Some connoisseurs believe that this kind of tsuba was in mass production at the time. Small animal believed to be a fox, however some attribute it to a long-tailed rabbit or a squirrel. I am leaning towards the rabbit. Similar example is found at Robert E. Haynes Catalog №3, April 9-11, 1982 on page 11, under № 15: “Rare design in style of Sanmai (three layers) / Wasei work. With yamagane core and heavy rim cover. The web plates are carved with double head Goto style waves and the face has a fox. The web plates were riveted at the seppadai. See Lot 4, page 8. Ca. 1350. Ht. 6.6 cm, th. 3 mm” [underscore mine]. Quality of photo is so poor that I decided not to provide it here. The only difference betwen my tsuba and his is that his has a square hole on the right shoulder of the seppa-dai. Early Muromachi (if we follow Robert it is even Nanbokucho, 1337-1392) or Momoyama period. The Momoyama attribution is mostly based on a fact that “waves and rabbit” motif became most popular in Momoyama times. Mokkōgata tsuba of similar design in this collection - see TSU-0282.
Ko-kinko ymagane cast tsuba of oval form with chiseled diaper pattern of double head waves on both sides and a rabbit cast and carved with its eye inlaid in yellow metal (gold or brass) on the face. Fukurin which holds together the sandwiched layers of metal (sanmai) is about 2.7 mm wide. Possibly, early Mino (ko-Mino) school. Size: 66.6 x 59.9 x 4.0 mm. Some connoisseurs believe that this kind of tsuba was in mass production at the time. Small animal believed to be a fox, however some attribute it to a long-tailed rabbit or a squirrel. I am leaning towards the rabbit. Similar example is found at Robert E. Haynes Catalog №3, April 9-11, 1982 on page 11, under № 15: “Rare design in style of Sanmai (three layers) / Wasei work. With yamagane core and heavy rim cover. The web plates are carved with double head Goto style waves and the face has a fox. The web plates were riveted at the seppadai. See Lot 4, page 8. Ca. 1350. Ht. 6.6 cm, th. 3 mm” [underscore mine]. Quality of photo is so poor that I decided not to provide it here. The only difference betwen my tsuba and his is that his has a square hole on the right shoulder of the seppa-dai. Early Muromachi (if we follow Robert it is even Nanbokucho, 1337-1392) or Momoyama period. The Momoyama attribution is mostly based on a fact that “waves and rabbit” motif became most popular in Momoyama times. Mokkōgata tsuba of similar design in this collection - see TSU-0282.
TSU-0282: Ko-kinko yamagane tsuba with waves and rabbit motif.
-
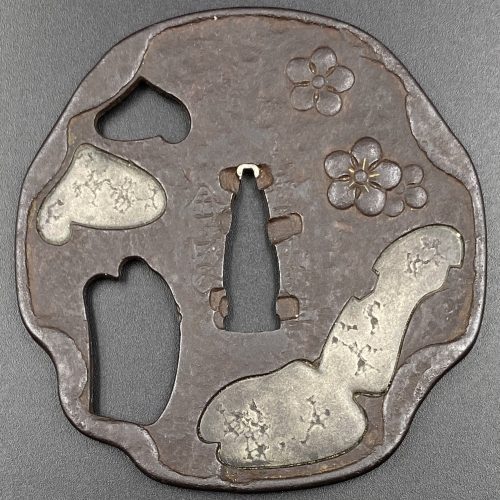

A very thin kobushi-gata form iron tsuba decorated in openwork (sukashi), some openings filled with grey metal (silver or pewter) treated in a way to resemble cracked ice, ginkgo leaf to recto and plum blossoms to verso in low-relief (takabori) and gold inlay (zōgan), and unevenly folded over rim (hineri-mimi). The overall theme of the piece is linked to the icy ponds, falling ginkgo leaves and blossoming plums in the late winter.
Size: 84 x 80 mm, thickness (center): 2 mm.Signed: Yamashiro no kuni Fushimi no ju Kaneie [Kaneie of Fushimi in Yamashiro Province] [山城國伏見住金家], with Kaō.
Probably the work of Meijin-Shodai Kaneie (c. 1580 – 1600).
The silver or pewter inlays likely a later work that may be attributed to Goto Ichijo (1791 – 1876) or one of his apprentices in the late 19th century, possibly as a tribute to the great Kaneie masters. Here is an article by Steve Waszak dedicated to Kaneie masters and this tsuba in particular.Kaneie
For many tosogu aficionados, this name reigns supreme among all tsubako across Japanese history. The first Kaneie is celebrated for many things. He is recognized as being the first ever to bring pictorial landscape subjects to a canvas so small as that of a tsuba plate. His skill in being able to render classical Chinese landscape themes while working with a material as unyielding as steel, and to do so with the sensitivity he does, is nothing short of astounding. The quality of his workmanship — especially that of his exquisitely carved motif elements and the extraordinary deftness of his tsuchime (槌目 or 鎚目, hammer-blow) utilizing such thin plates — astonishes even to this day. His sensibilities concerning the shaping of his sword guards and the presentation of the rims were no less innovative than his subject matter. He was among the very first to regularly sign his name as a tsuba smith. And it is likely that he served the great warlord Toyotomi Hideyoshi in the latter years of the 16th century. Despite the great fame and reputation of Kaneie, very little of the lives of the two men who are seen by most scholars as the “true Kaneie” tsubako of the Momoyama and earliest Edo Periods is known to us now. They were both smiths working in steel, with occasional added soft-metal inlay (usually serving to highlight features), and both made sword guards of the same style, using subject matter focused on landscapes, allusions to historical events, or religious themes. The first of these men is often referred to as “O-Shodai,” or Great First Generation, while the second is known as “Meijin-Shodai,” or Famous First Generation. While some see subsequent generations stemming from these first two men, others have the O-Shodai and the Meijin-Shodai as THE two true Kaneie and make a sharp distinction between these two smiths and any others who may share the name.The work of the O-Shodai may appear with two different mei. One of these is written “Joshu Fushimi Ju Kaneie,” while his work may also carry a mei reading “Yamashiro no Kuni Fushimi Ju Kaneie.” It is thought by some scholars that the earlier works present with the “Joshu” mei, while his later works feature the “Yamashiro” mei. However, there are only some five or six tsuba extant with the “Joshu” signature, so we should not necessarily see works with the “Yamashiro” signature as dating only to the latest years of his working life. The answers to the questions of exactly when Kaneie might have begun his life as a tsubako, or how old he was when he moved to sign his works with the “Yamashiro” mei, will probably remain shrouded in uncertainty.The association between Kaneie and Toyotomi Hideyoshi is speculative, to be sure, but the circumstantial evidence is tantalizing. The area of Fushimi is thought to have been an entirely unremarkable land prior to Hideyoshi’s building of a castle there, so it would seem unlikely that the first Kaneie would have been working in such a nondescript place, much less including the place name in his mei, before Hideyoshi’s putting it on the map, so to speak. Why emphasize such pride of place in one’s signature unless the place itself carries a certain weight? The name “Kaneie” translates roughly to “gold family,” which, given Hideyoshi’s notorious love of gold, would seem too much of a coincidence when combined with the explicit mention of Fushimi in the signatures. Combine this with the consideration of what is an equally compelling relationship between the celebrated tsubako Nobuie and Oda Nobunaga (“Nobuie” means roughly “of the family of “Nobu”), whom Hideyoshi served as a top general until Oda’s demise in 1582, and the circumstantial evidence becomes even harder to deny the plausibility of. Oda, ever the innovator, may have been the one responsible for birthing the practice of tsubako regularly signing their works. Having a superb smith like Nobuie affix the name to the tsuba as a regular practice establishes a sort of “brand name,” a brand coming with the seal of approval of Oda Nobunaga. It is more than possible that Nobunaga may have then used these valuable sword guards as rewards given to vassals and other important relations to honour them for their services to him, a practice that would have allowed Nobunaga to avoid having to use gold, guns, swords, horses, or land to do so. The awarding of a magnificent Nobuie tsuba to a deserving warrior, an appreciated ally, or a family member would bring honour to the recipient, of course, but would also honour the maker of the sword guard, and even the giver of the object. Such a way of thinking would be absolutely typical of him, and given that both Oda Nobunaga and Nobuie were men of Kiyosu in Owari in the early Momoyama Period, it does not strain credulity to imagine that the above dynamic could have occurred in just this way. If indeed it did, Toyotomi Hideyoshi is unlikely to have let this pass unnoticed. He may even have been so honoured himself! When he rose to power very shortly after Oda’s death, then, and when he reinforced and consolidated that power in the late 1580s and early 1590s, which included the building of the castle at Fushimi, perhaps he sought to emulate the Oda vision and practice of establishing a “royal tsubako.” If so, Kaneie would have been that smith.As noted, this scenario is speculative, and not a little romantic. This does not mean, however, that it is in fact not likely, for there would be a number of coincidences involved for it to be entirely false.Tsuba scholars will say that Kaneie’s skills in the making of his sword guards indicate an armour-making background. This is an interesting viewpoint, but one can’t help but wonder how many armourers were possessed of such fluent literacy in lyrical Chinese historical tales that they could then represent them as motifs on steel plates. Kaneie subjects often are in the form of Chinese landscapes and allusions, as noted, one of which — The Eight Views of the Xiao and the Xiang — was very well known as a famous subject of Chinese painting and poetry from the Song Dynasty. There exist Kaneie tsuba which depicts at least some of these “views,” and it seems unlikely that if one or more of them were to be created, not all of them would be, in a sort of “series.” The cultural and literary fluency Kaneie would seem to have had, then, may suggest a Buddhist background, and indeed, some of the subjects seen are explicitly Buddhist in nature. Perhaps his background then, somehow offering a dovetailing of metalwork and Buddhist teachings; in any event, we are all the richer for at least some of the works of Kaneie to have survived to reach us today.One of the hallmarks of Kaneie tsuba (real ones) is the extreme thinness of the plate, combined with utterly superb tsuchime expression of that plate. To be able to hammer the plate to achieve such strength of expression while the plate is so thin is seen by the Japanese as practically miraculous. A notable and important kantei point between the early masterpieces by the two “Shodai” Kaneie and the tsuba made by followers is this thinness of the plate. Another kantei point: because the plate is so thin when raised areas representing motif elements are present, they are inlaid into the plate, because trying to carve them from such a thin plate would be practically impossible: the likelihood of piercing the plate would be high, and the plate in that area, even if not pierced, would be significantly weakened by trying to manage the raising of a motif element from the plate. In real Kaneie works, then, one would expect any raised motif elements to be inlaid.Other highlights: the “Shodai” Kaneie are famous for the kobushi-gata (拳形) or “fist-shaped” design in their work, but despite this, there actually aren’t that many extant sword guards boasting this shape. Another feature for which the Kaneie are justly famous is their folding over of the lip of the rim onto the plate in a very tasteful manner, just here and there, rather than uniformly across the tsuba. However, again, this feature is actually not commonly seen, either. The combination, then, of a kobushi-gata shape with the rim folded over in just a few areas is that much rarer.Which brings us to the featured piece.Here is a Kaneie tsuba, a “Meijin-Shodai” Kaneie, which presents with a very thin plate, being between 1.5 and 2mm in thickness. The motif elements are inlaid, as we should expect. The sugata (姿, shape) is Kobushi-gata with the rim folded over in only a few places, representing a relatively infrequently encountered form, as stated. The tsuba here is fortunate not to have any added hitsu-ana, unlike many or most other Kaneie do. The sukashi elements are fascinating to consider, being difficult to determine the meaning of; however, the raised elements clearly point to a seasonal motif, with cherry and plum blossoms on the omote for Spring, and ginkgo on the ura for Fall. The inlaid metal in two of the openings — silver, shibuichi, or pewter, perhaps — is very likely a later addition, probably 19th-century, and more specifically, late-19th-century. The finishing on these inlaid portions has all the hallmarks of Goto Ichijo workmanship. Namely, the treatment of the surface of the inlay to resemble fallen snow (in the Japanese sense of things) is expressed in a very Ichijo sense of things, and, given the great importance of Kaneie tsuba, and the seasonal expression the motif of the guard has, it is plausible that the inlay is Ichijo work or that of one of his top students. In any event, this inlay complements the rest of the tsuba beautifully. The inlay also resembles the art of kintsugi (金継ぎ, golden joinery) or the Japanese practice of ceramic repair using lacquer when a piece is particularly special or important. In this way, a nod is given to Tea Culture, too, creating a wonderful blending of associations and allusions, typical of the highest Japanese aesthetic sense.At 8.4cm, the tsuba is of an excellent size and is in great condition (no rust, no deep rust pitting, no fire damage). There is, intriguingly, one small sign of battle damage at 6:00 on the guard: it would seem a sword blow cut into the tsuba at the rim, and penetrated slightly into the plate. The superb repair represented by a little stitch or two right at the rim and along a few millimetres of the plate is visible on very close inspection. The repair is old, probably nearly contemporary with when the tsuba was made. Given the high status of Kaneie in their lifetime (as tsubako for Hideyoshi, one might imagine their importance), and given the obvious high quality of this piece, it is not surprising that the finest repair efforts were put into its care.The name Kaneie justly enjoys its fame and accolades as pre-eminent among the tens of thousands of tsubako in Japanese history. We are fortunate indeed to have had a small number of the works of the early masters survive to this day. The first of their kind, and as most scholars and aficionados would wholeheartedly agree, the best of their kind, Kaneie sword guards remain among the very finest examples of the Japanese metal-working traditions. -
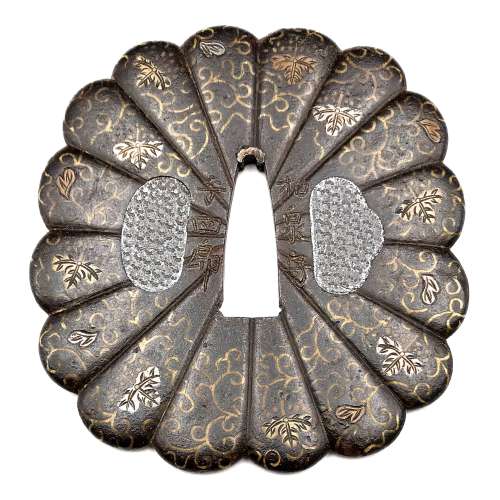 The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:
The chrysanthemoid (kiku-gata) iron plate with polished surface decorated with arabesque (karakusa) and paulownia (kiri) leaves and flowers in brass, copper and silver flush inlay (hira-zōgan) on both sides. Some of the inlay goes over the edge. Kozuka- and kogai-hitsu-ana are filled with lead plugs. Sekigane of copper. Chrysanthemum and paulownia are the symbols of imperial family. The face is signed: Izumi no Kami to the right of nakago-ana, and Yoshiro on the left; the back is signed Koike Naomasa. His signed work is considered by many experts to have been made-to-order only. The original wooden box (tomobako) with inscription (hakogaki) signed by Dr. Kazutaro Torigoye and dated Showa 39 (1964). The late Muromachi or Momoyama period, 16th century. Dimensions: 89 mm x 84 mm x 3.6 mm; Weight: 170 g. Hakogaki lid: Yoshirō kikka-gata Hakogaki lid inside: Iron, signed on the omote: Izumi no Kami – Yoshirō; on the ura: Koike Naomasa. Kikka-gata, pronounced maru-mumi, two hitsu-ana, karakusa, and kiri design in brass, silver, and suaka hira-zōgan. Height 8.5 cm, thickness 3.5 mm. Herewith I judge this work as authentic. On a lucky day in July of 1964. Torigoe Kōdō [Kazutarō] + kaō According to Robert Haynes [Catalog #7, 1983; №32, page 42-43] "This full form of the signature is seen very rarely". His example, illustrated in that catalogue, measures: height = 86 mm, thickness at seppa-dai = 3.75 mm and signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back and Koike Naomasa on the face. The further description of his specimen by Robert Haynes:"Early signed example of the work of Koike Naomasa. The kiku shape iron plate is well finished. The flush inlay is brass, for the scroll work on both sides, with the leaves and kiri mon in brass, copper and silver with strong detail carving. Some of the inlay goes almost over the edge, which is goishi gata. The large hitsuana are plugged in lead with starburst kokuin surface design. [...]The face is signed in deep bold kanji: Koike Naomasa; the back is signed: Izumi no Kami, on the right and Yoshiro on the left. There are one or two small pieces of inlay missing. Sold by Sotheby London, Oct. 27, 1981, lot 368. Height = 86 mm, thickness (seppa-dai) = 3.75 mm, (edge) = 4 mm."
Another similar example presented at: "Tsuba" by Günter Heckmann, 1995, №T55 — "Designation: Koike Naomasa. Mid Edo, end of the 17th century. Iron, hira-zogan in brass, copper, silver and shakudo, katakiri-bori. Tendrils and leaves. 87.0 x 78.0 x 4.0 mm." Reference: Japanische Schwertzierate by Lumir Jisl, 1967, page. 13. [SV: Actually, his tsuba is signed Izumi no Kami Yoshiro on the back; and Koike Naomasa on the front, exactly as Robert Haynes's tsuba. Dating this tsuba Mid-Edo, 17th century may be considered a misattribution]. More details regarding the Yoshirō tsuba. -
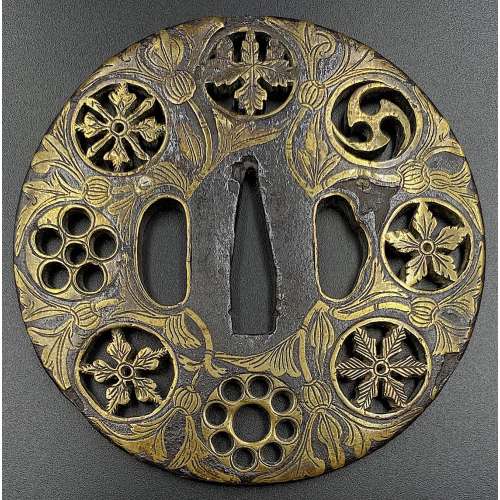 Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Iron tsuba of round form decorated with eight roundels – circular emblems of flowers and/or family crests (mon) made of cast brass, pierced and chiselled in kebori, and with flat brass inlay (hira-zōgan) of vines or leaves all over the plate. Both hitsu-ana are trimmed with brass. Nakago-ana of trapezoidal form. A distinctive character of this tsuba is a mon at 12 hours, depicting paulownia, or Kiri-mon [桐紋] – a symbol of the Toyotomi clan, led by Toyotomi Hideyoshi (豊臣 秀吉, 1537 – 1598). Kiri-mon was also used as fuku-mon (alternative family crests) for the Imperial Family and Imperial Court. Another important emblem at 6 o’clock is the Katakura clan [片倉氏, Katakura-shi] family crest. Katakura Kagetsuna (片倉 景綱, 1557 – 1615), a retainer of Date Masamune (伊達 政宗, 1567 – 1636); Kagetsuna was operational in Hideyoshi’s Odawara campaign in 1590, which ultimately ended the unification of Japan. Unsigned but may be attributed to Koike Yoshirō Naomasa or his workshop (Yoshirō, orKaga-Yoshirō school). Dimensions: Diameter: 85.5 mm; Thickness at seppa-dai: 5.0 mm.
Kiri-mon
Katakura-mon


