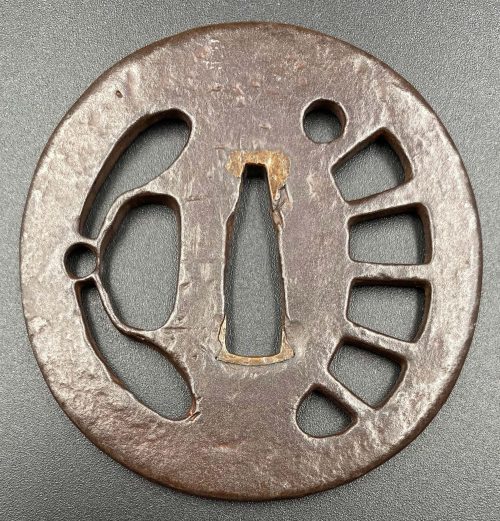
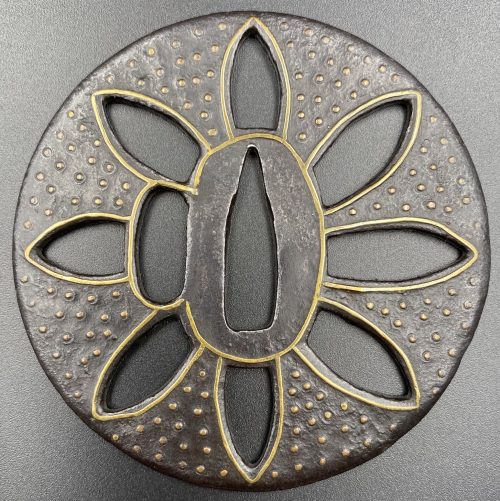
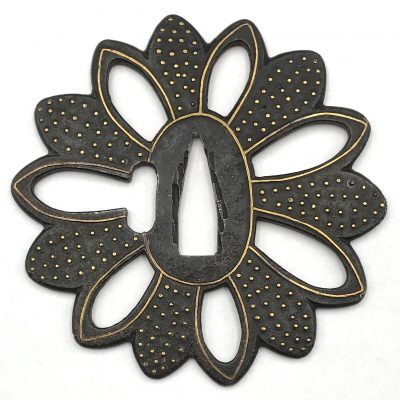
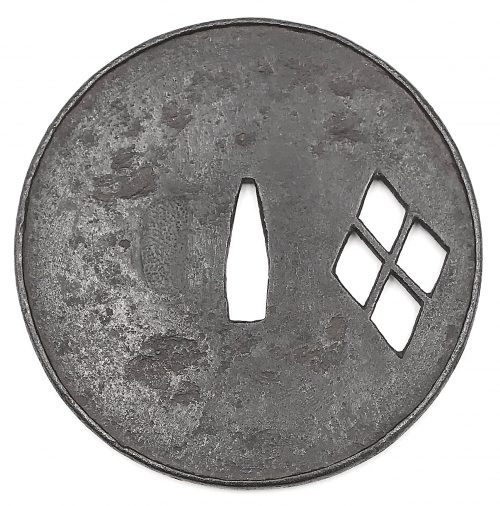
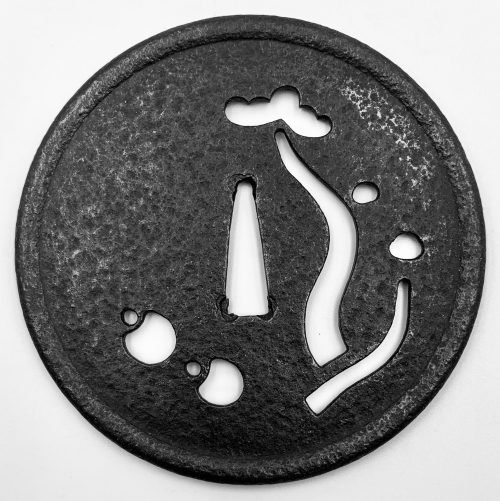
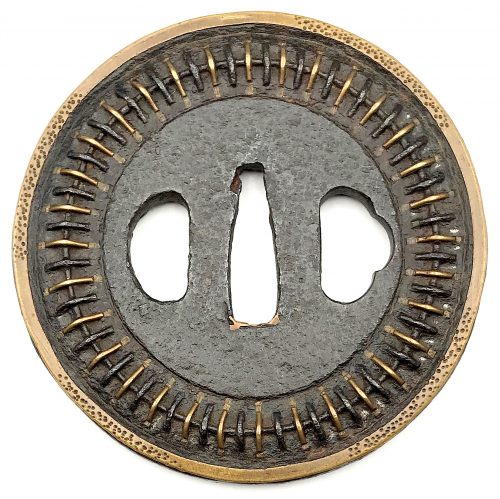
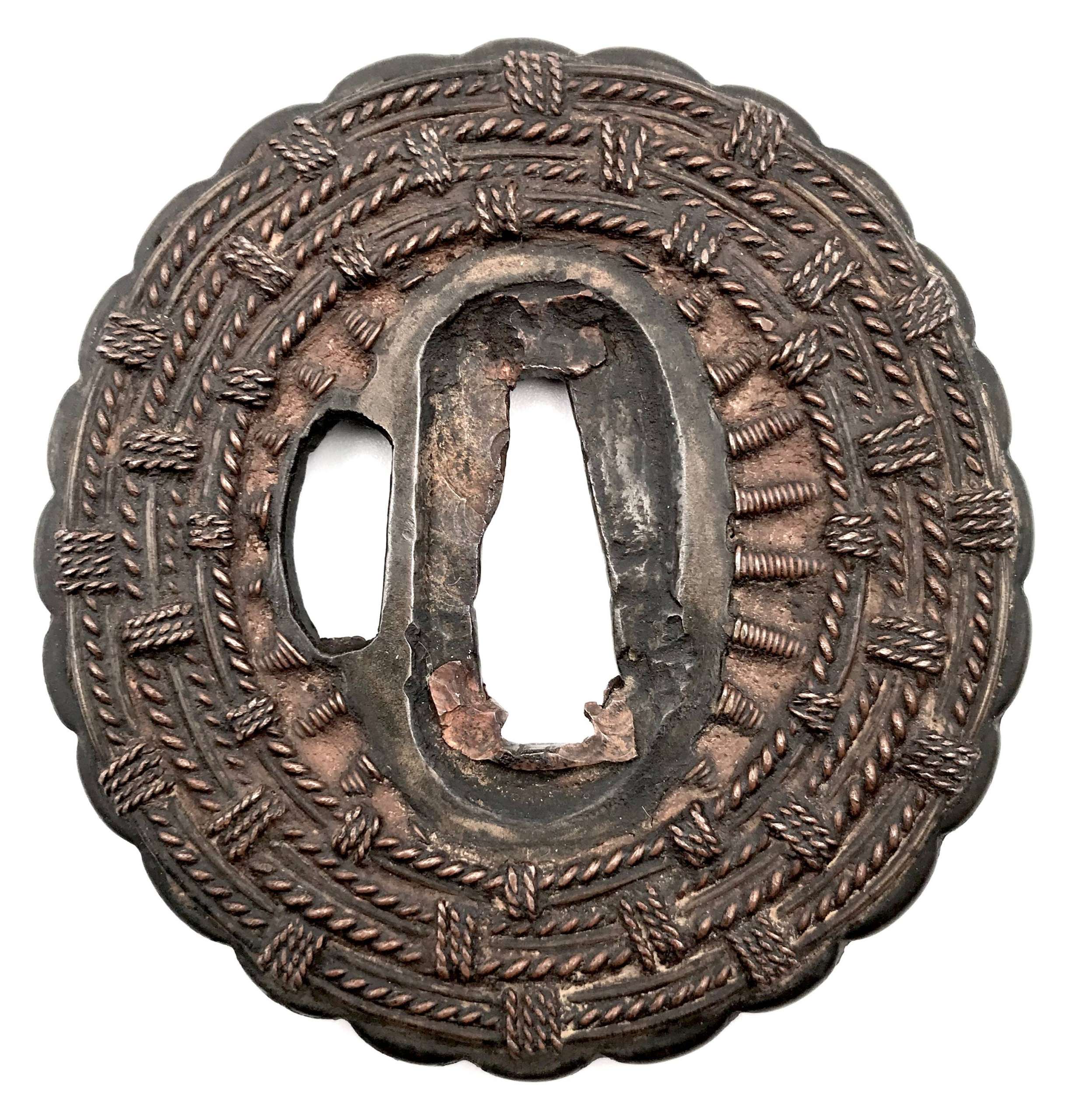
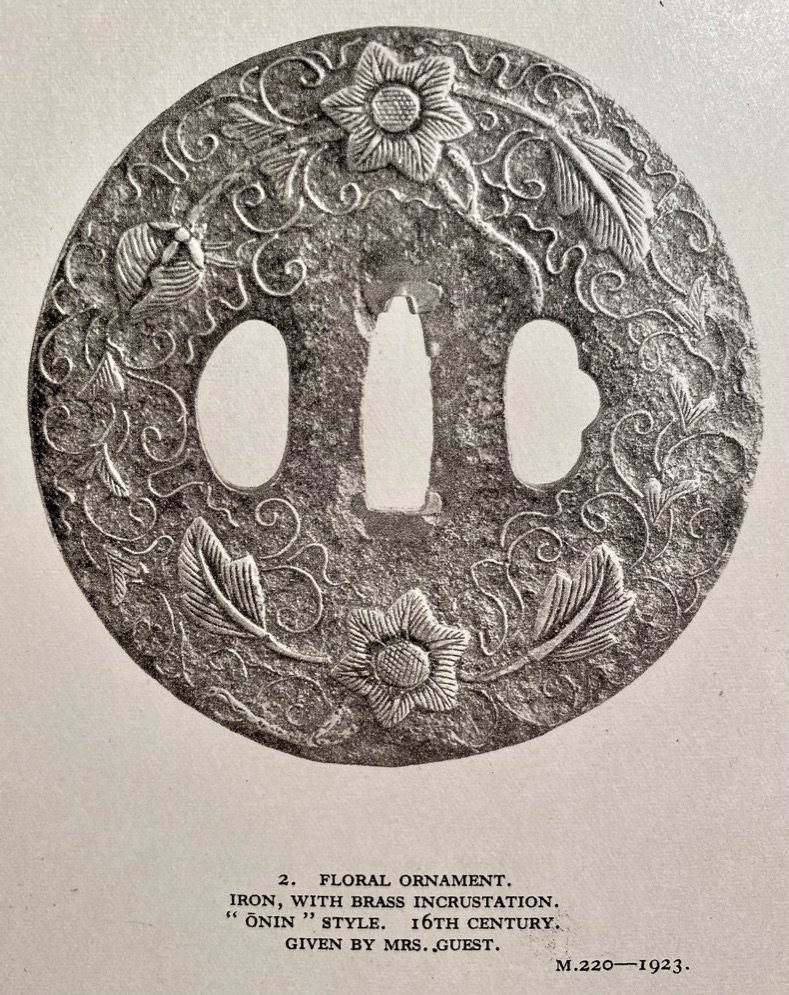
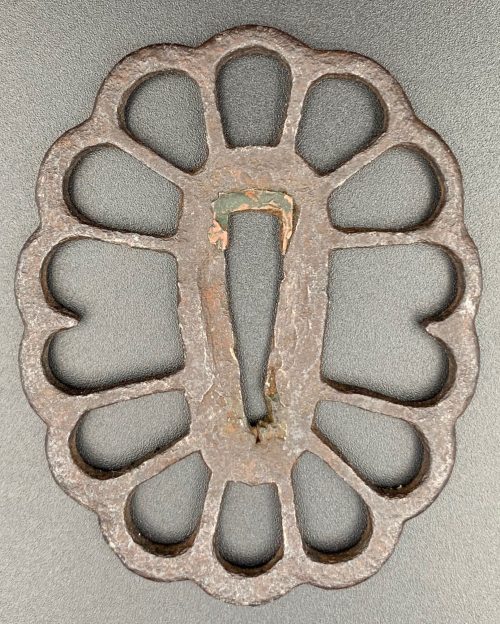
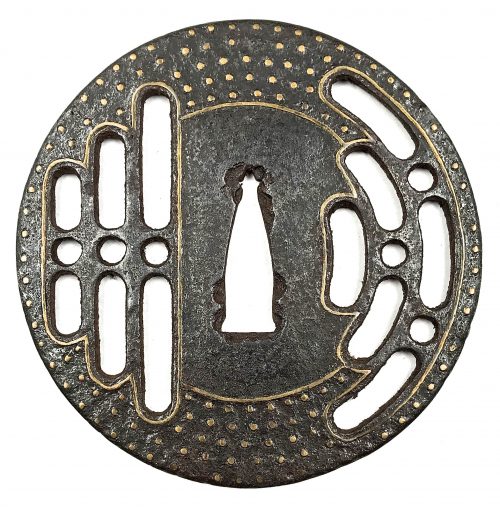
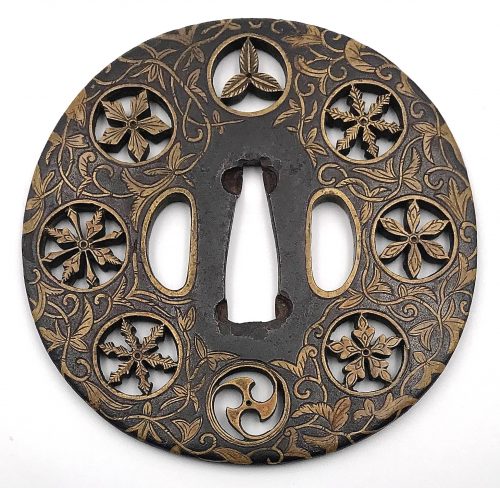
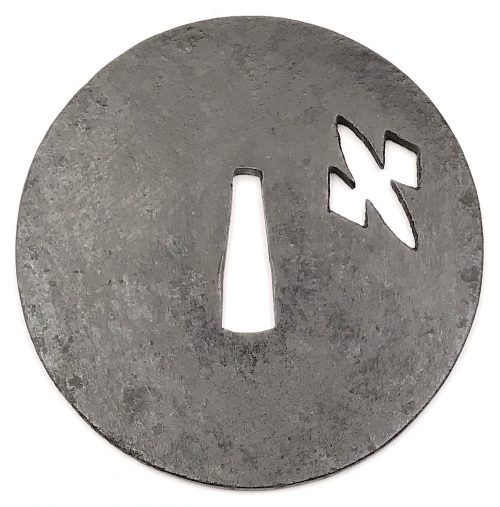
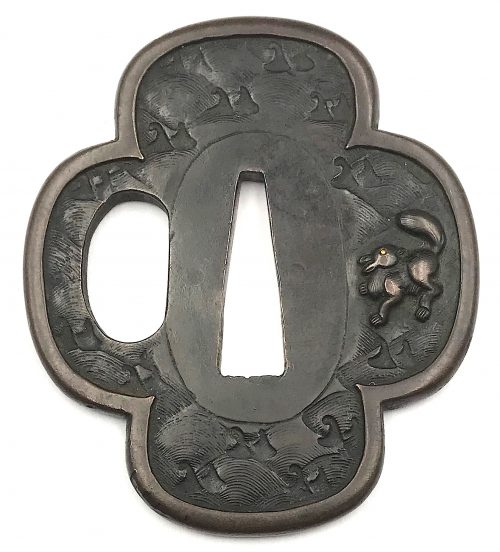
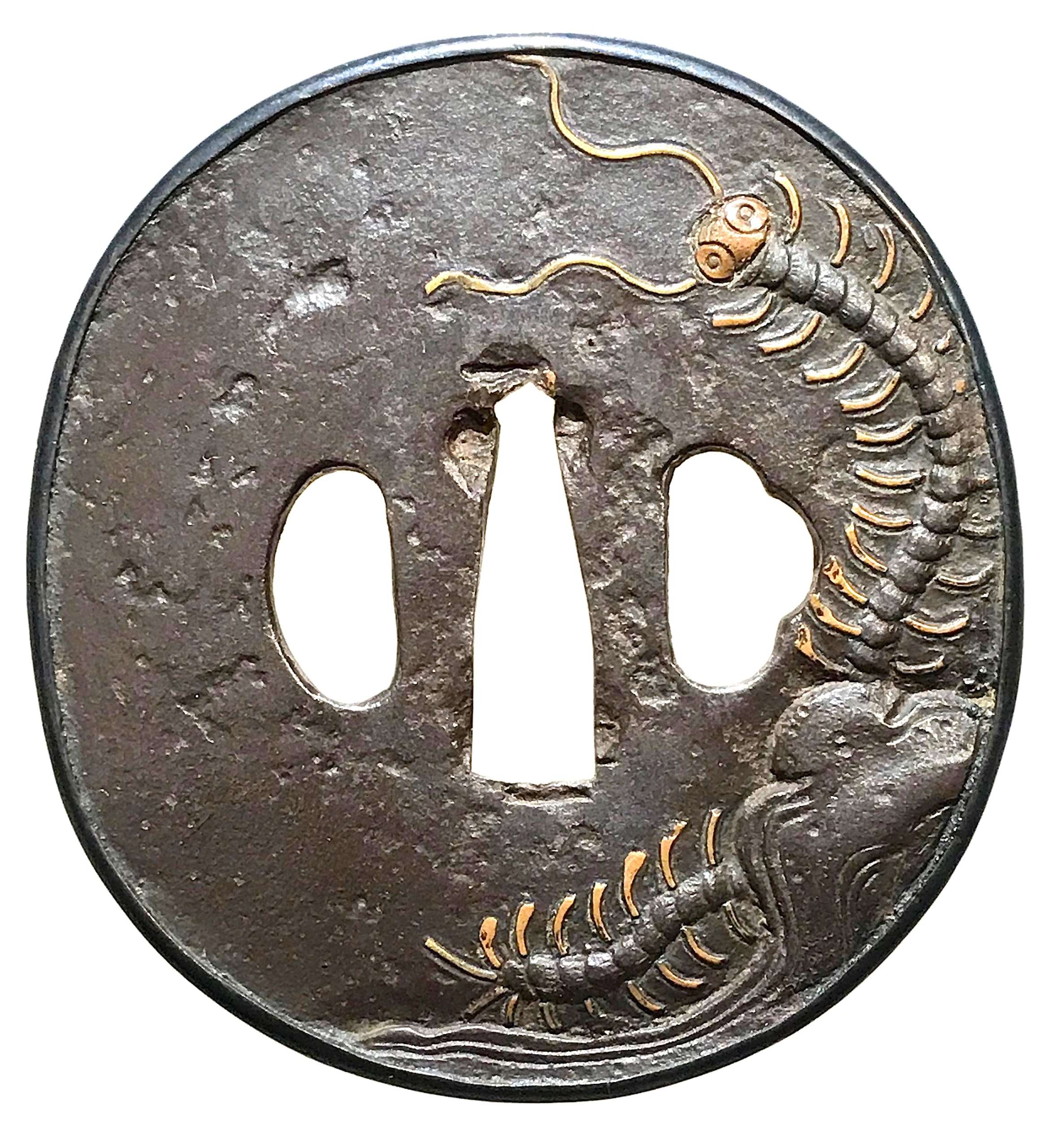
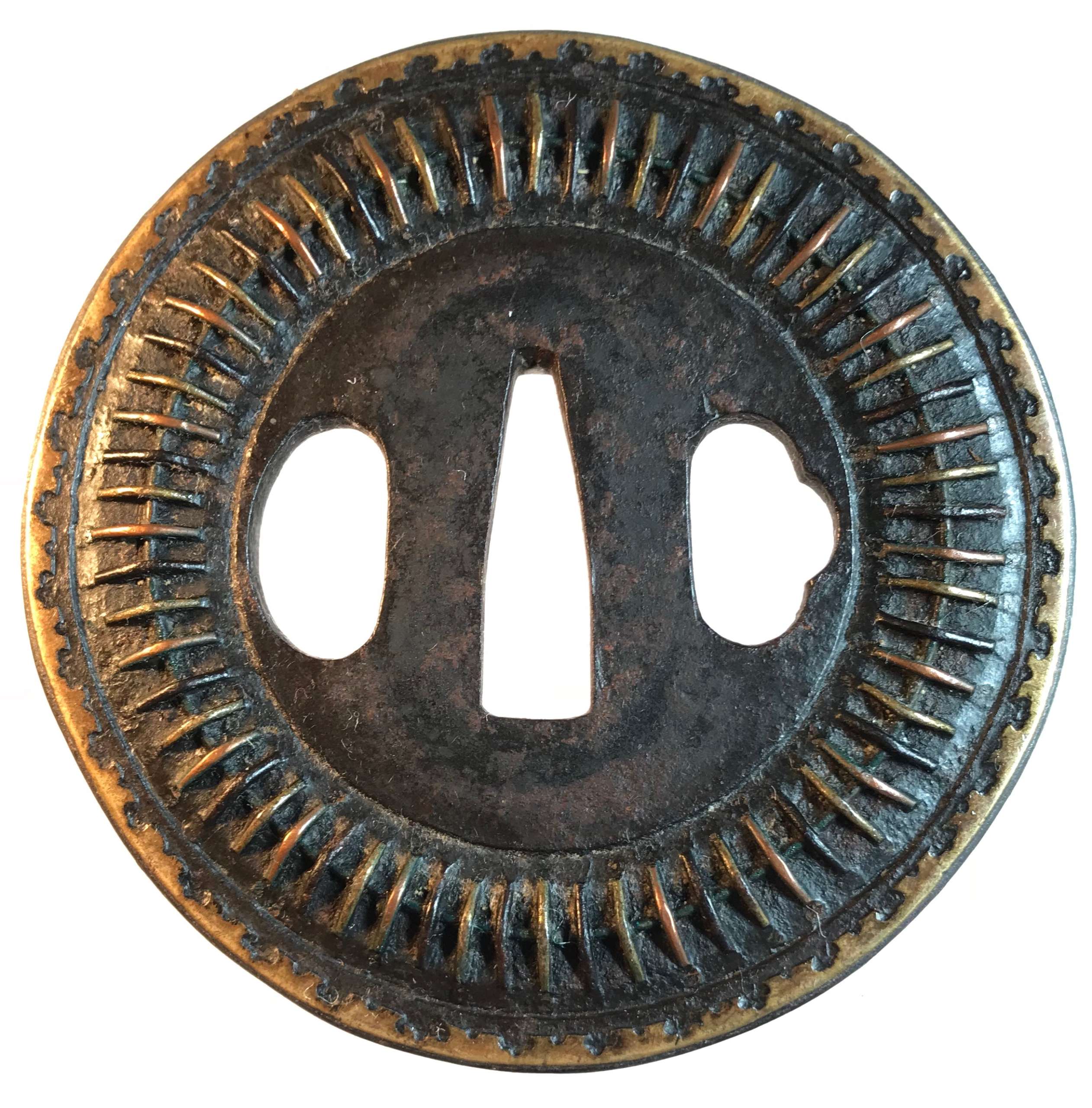
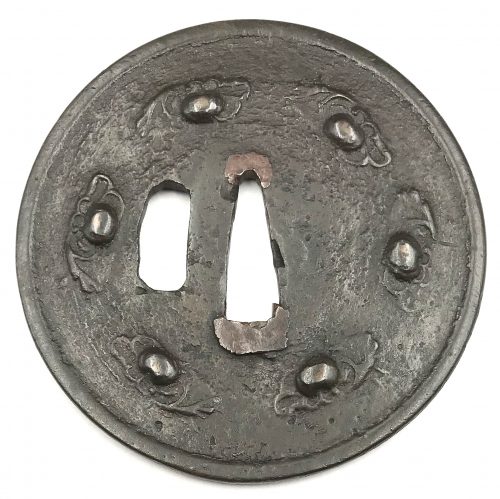
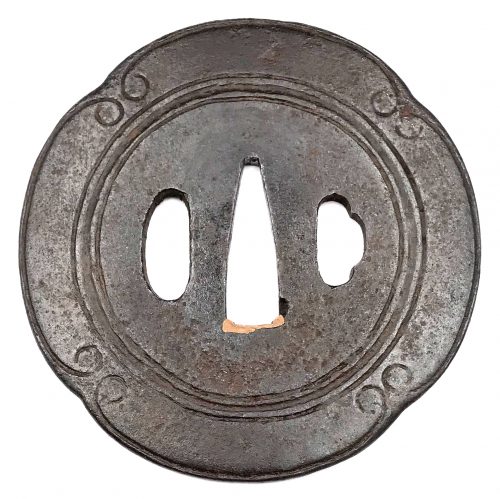
The thin, four-lobed iron plate of brownish color is carved on each side with two concentric grooves in the middle of the web, and with four thin scroll lines (handles,
kan) that follow the shape of the rim. The
hitsu-ana were added at a later date. Copper
sekigane.
Kamakura-bori school.
Muromachi period, circa 1400-1550.
Size: Height 80.4 mm, width 79.0 mm, thickness 3.2 mm at seppa-dai and 2.7 mm at the rim. Weight: 97.7 g.
NBTHK Certificate №4004241: '
Hozon' attestation.
As for the motif: the concentric circles is a widespread and generic design. It is described by John W. Dower [The Elements of Japanese Design, 1985, p. 132, #2201-30] as follows: Circle: Enclosure (wa). As a crest by itself, the cirlce carries obvious connotations of perfection, harmony, completeness, integrity, even peace. [...] Ordinary circles are labeled according to their thickness, with terminology ranging from hairline to "snake's eye". The motif that is described by both Compton Collection and R.E. Haynes as "scrolls", presented by John W. Dower as "Handle (
kan): Although probably a purely ornamental and nonrepresentational design in origin, over the centuries this motif acquired the label
kan, denoting its resemblance to the metal handles traditionally used on chests of drawers. [...] Very possibly the "handle" motif represents an early abstract version of the popular
mokko, or melon pattern." Early Chinese Taoists claimed that special melon was associated with the Eastern Paradise of Mount
Horai just as life-giving peaches were associated with the Western Paradise of the
Kunlun Mountains. [...] A design motif called mokko (also translated as "melon" in accordance with the two ideographs with which it is written) may have nothing to do with the fruit.
Mokko designs... are widely used as crests of both private families and Shinto shrines and are repeated as background designs that evoke a sense of classicism" [Symbols of Japan. Merrily Baird, 2001].
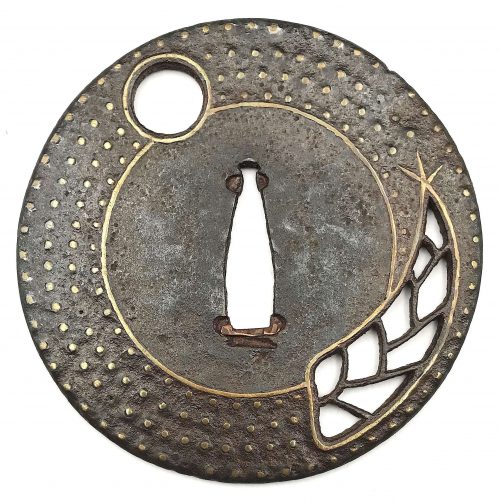
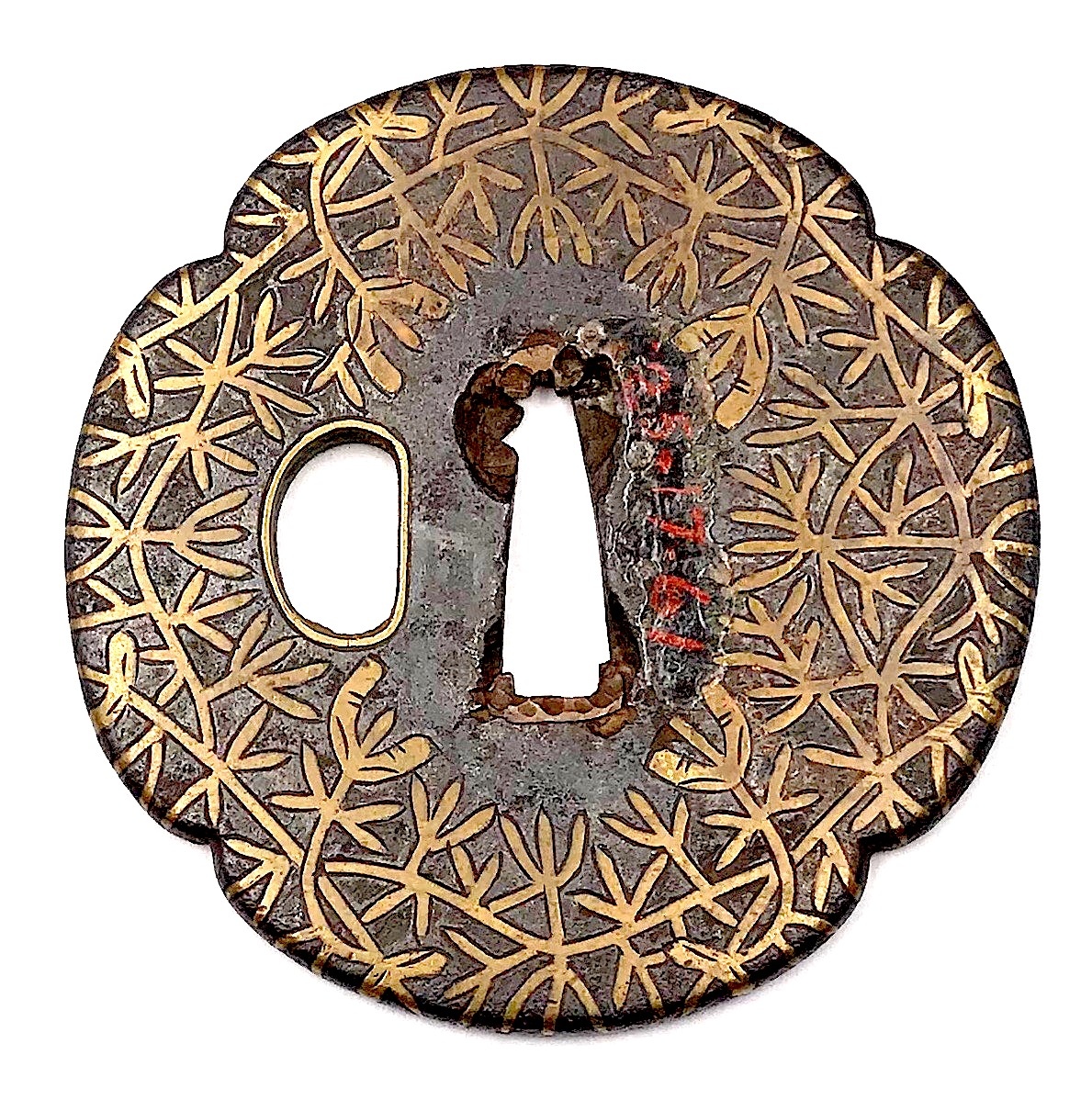
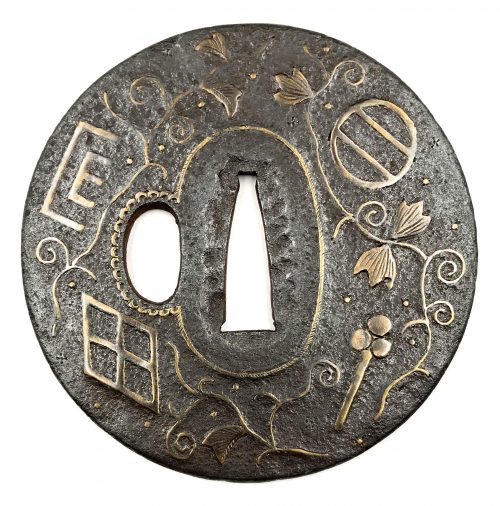
There is a look alike tsuba at Dr. Walter A. Compton Collection, 1992, Christie’s auction, Part II, pp. 14-15, №16:

The description goes: “A
kamakurabori type tsuba,
Muromachi period, circa 1400. The thin, six-lobed iron plate is carved on each side with a wide groove that follows the shape of the rim, and with six scroll lines and a single thin circular groove. […] The
hitsu-ana was added at a later date, circa 1500-1550. Height 8.3 cm, width 8.6 cm, thickness 2.5 mm. The tsuba was initially intended to be mounted on a
tachi of the battle type in use from
Nambokucho to early
Muromachi period (1333-1400)”. Sold at $935.
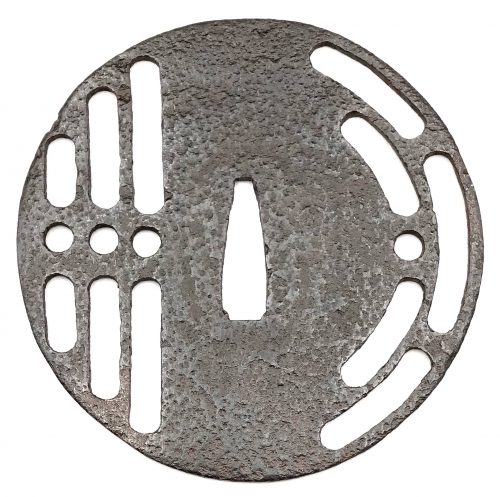
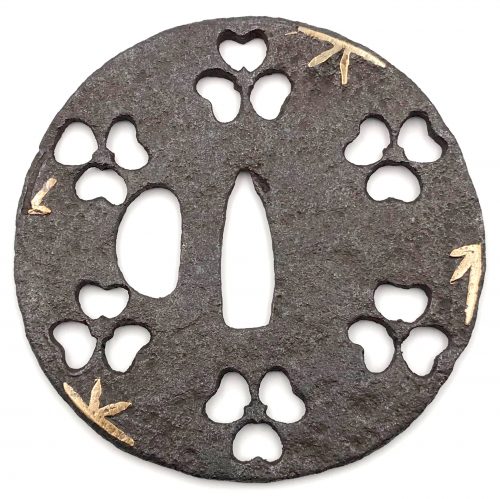
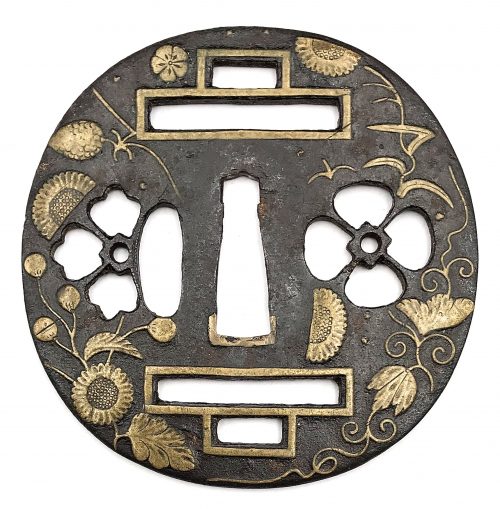
And another one in Robert E. Haynes Catalog #9 on page 24-25 under №23:

R.E. Haynes description: “Typical later
Kamakura-bori style work. This type of plate and carving show the uniform work produced by several schools in the
Muromachi period. Some had brass inlay and others were just carved as this one is. The
hitsu are later. Ca. 1550. Ht. 8.8 cm, Th. 3.25 mm”. Sold for $175.





















 The description goes: “A kamakurabori type tsuba, Muromachi period, circa 1400. The thin, six-lobed iron plate is carved on each side with a wide groove that follows the shape of the rim, and with six scroll lines and a single thin circular groove. […] The hitsu-ana was added at a later date, circa 1500-1550. Height 8.3 cm, width 8.6 cm, thickness 2.5 mm. The tsuba was initially intended to be mounted on a tachi of the battle type in use from Nambokucho to early Muromachi period (1333-1400)”. Sold at $935.
And another one in Robert E. Haynes Catalog #9 on page 24-25 under №23:
The description goes: “A kamakurabori type tsuba, Muromachi period, circa 1400. The thin, six-lobed iron plate is carved on each side with a wide groove that follows the shape of the rim, and with six scroll lines and a single thin circular groove. […] The hitsu-ana was added at a later date, circa 1500-1550. Height 8.3 cm, width 8.6 cm, thickness 2.5 mm. The tsuba was initially intended to be mounted on a tachi of the battle type in use from Nambokucho to early Muromachi period (1333-1400)”. Sold at $935.
And another one in Robert E. Haynes Catalog #9 on page 24-25 under №23:
 R.E. Haynes description: “Typical later Kamakura-bori style work. This type of plate and carving show the uniform work produced by several schools in the Muromachi period. Some had brass inlay and others were just carved as this one is. The hitsu are later. Ca. 1550. Ht. 8.8 cm, Th. 3.25 mm”. Sold for $175.
R.E. Haynes description: “Typical later Kamakura-bori style work. This type of plate and carving show the uniform work produced by several schools in the Muromachi period. Some had brass inlay and others were just carved as this one is. The hitsu are later. Ca. 1550. Ht. 8.8 cm, Th. 3.25 mm”. Sold for $175.