-
 An uncut fan print uchiwa-e, size 22.7 x 28.7cm, by an unknown artist.
An uncut fan print uchiwa-e, size 22.7 x 28.7cm, by an unknown artist. -
 Woodblock print album of thirteen prints, ōban, nishiki-e. Artist: Chōkyōsai Eiri [鳥橋斎 栄里] (Japanese, fl. c. 1789 ~ 1801 ). Models of calligraphy (Fumi no kiyogaki), New Year 1801. This title is taken from Chris Uhlenbeck's Japanese Erotic Fantasies Sexual Imagery of the Edo Period. — Hotei Publishing, 2005, ISBN 90-74822-66-5):. A detailed description of the album can be found at The Complete Ukiyo-e Shunga №9 Eiri, 1996, ISBN 4-309-91019. Most of the edition is in Japanese, though Richard Lane writes a section in English: Eiri: Love-letters, Love Consummated: Fumi-no-kiyogaki. The article starts with the following statement: "Why all the fuss about Sharaku? Because he is so "mysterious"? No, not at all: because he is such a good artist. But Sharaku is not the only great yet enigmatic ukiyo-e artist and I propose to resurrect here one of his important contemporaries who has been all too long neglected: Chōkyōsai Eiri. As with many of the notable ukiyo-e masters, nothing is known of Eiri's biography. All we can say is what we learn from his extant prints and paintings: that he flourished during the second half of the Kansei Period [1789-1801]; and that he was a direct pupil of the great Eishi - who, being of eminent samurai stock, may well have attracted pupils of similar background." Another citation from Japanese Erotic Fantasies: "This album is one of the boldest sets of ōban-size shunga known, The first edition contains thirteen instead of the customary twelve designs". Here I present all thirteen prints, though the edition I bought in Kyoto in 2014 contained only twelve. The thirteenth print was purchased later in the United States (sheet №12).
Woodblock print album of thirteen prints, ōban, nishiki-e. Artist: Chōkyōsai Eiri [鳥橋斎 栄里] (Japanese, fl. c. 1789 ~ 1801 ). Models of calligraphy (Fumi no kiyogaki), New Year 1801. This title is taken from Chris Uhlenbeck's Japanese Erotic Fantasies Sexual Imagery of the Edo Period. — Hotei Publishing, 2005, ISBN 90-74822-66-5):. A detailed description of the album can be found at The Complete Ukiyo-e Shunga №9 Eiri, 1996, ISBN 4-309-91019. Most of the edition is in Japanese, though Richard Lane writes a section in English: Eiri: Love-letters, Love Consummated: Fumi-no-kiyogaki. The article starts with the following statement: "Why all the fuss about Sharaku? Because he is so "mysterious"? No, not at all: because he is such a good artist. But Sharaku is not the only great yet enigmatic ukiyo-e artist and I propose to resurrect here one of his important contemporaries who has been all too long neglected: Chōkyōsai Eiri. As with many of the notable ukiyo-e masters, nothing is known of Eiri's biography. All we can say is what we learn from his extant prints and paintings: that he flourished during the second half of the Kansei Period [1789-1801]; and that he was a direct pupil of the great Eishi - who, being of eminent samurai stock, may well have attracted pupils of similar background." Another citation from Japanese Erotic Fantasies: "This album is one of the boldest sets of ōban-size shunga known, The first edition contains thirteen instead of the customary twelve designs". Here I present all thirteen prints, though the edition I bought in Kyoto in 2014 contained only twelve. The thirteenth print was purchased later in the United States (sheet №12). №1: "...one of the most exotic scenes in all shunga. A Dutch kapitan is discovered coupling with a lovely Japanese courtesan, beside a large window opening upon a garden...".
№1: "...one of the most exotic scenes in all shunga. A Dutch kapitan is discovered coupling with a lovely Japanese courtesan, beside a large window opening upon a garden...".

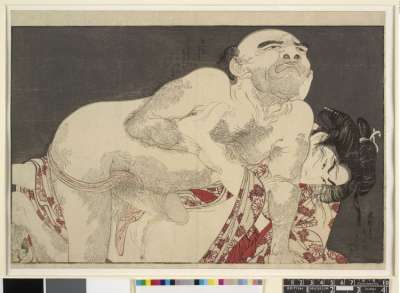
 №2: "...a fair young harlot is seen masturbating with a grinding-pestle - a man watches intently from under bedding." [I have two specimens of this design; the one from album is more soiled but less faded].
№2: "...a fair young harlot is seen masturbating with a grinding-pestle - a man watches intently from under bedding." [I have two specimens of this design; the one from album is more soiled but less faded].
 №3: "...the artist has effectively contrasted the lovers by depicting the man's face as seen through the geisha's gauze skirt. [...] we are impressed more by strikingly elegant composition, the dramatic coloring, rather than feeling any great urge to participate in the energetic proceedings..."
№3: "...the artist has effectively contrasted the lovers by depicting the man's face as seen through the geisha's gauze skirt. [...] we are impressed more by strikingly elegant composition, the dramatic coloring, rather than feeling any great urge to participate in the energetic proceedings..."
 №4: "This scene is a most straightforward one, featuring the standard Missionary Position [capitalization by R. Lane].; but withal, the contrast of the young and naked, secret lover and the richly-clothed courtesan amid luxurious bedding..."
№4: "This scene is a most straightforward one, featuring the standard Missionary Position [capitalization by R. Lane].; but withal, the contrast of the young and naked, secret lover and the richly-clothed courtesan amid luxurious bedding..."
 №5: "In a striking lesbian scene (which has no equivalent in Utamaro, and is, incidentally, often omitted in later editions of this album), the girl at left prepares to receive the harikata (dildo) worn by the older girl at right (who holds a seashell containing lubricant)."
№5: "In a striking lesbian scene (which has no equivalent in Utamaro, and is, incidentally, often omitted in later editions of this album), the girl at left prepares to receive the harikata (dildo) worn by the older girl at right (who holds a seashell containing lubricant)."
 №6: "In the first appearance of a matronly heroine in this series, we find a widow - with shaven eyebrows and clipped hair - sporting with a handsome yound shop-clerk, mounting him with all her might."
№6: "In the first appearance of a matronly heroine in this series, we find a widow - with shaven eyebrows and clipped hair - sporting with a handsome yound shop-clerk, mounting him with all her might."

 №7: "... lady of samurai court: here, shown taking advantage of an official outing to temple and theatre, to rendezvous with a secret lover on a teahouse balcony." R. Lane considers this design the least successful in the series, especially in comparison with the same theme by Utamaro: "Utamaro female is almost ferocious in her lust for sexual gratification", which does not sound true to me. See Utamaro's sheet №5 from the album Utamakura (歌まくら, Poem of the Pillow) [courtesy The British Museum without permission]:
№7: "... lady of samurai court: here, shown taking advantage of an official outing to temple and theatre, to rendezvous with a secret lover on a teahouse balcony." R. Lane considers this design the least successful in the series, especially in comparison with the same theme by Utamaro: "Utamaro female is almost ferocious in her lust for sexual gratification", which does not sound true to me. See Utamaro's sheet №5 from the album Utamakura (歌まくら, Poem of the Pillow) [courtesy The British Museum without permission]:
 Then, as Richard Lane states, "we are flung suddenly to the bottom rung of Edo society":
Then, as Richard Lane states, "we are flung suddenly to the bottom rung of Edo society":
 №8: "Here we find a fair yotaka ('night-hawk', e.i. streetwalker) accommodating a lusty client in a lumberyard by the bank of the Sumida River".
№8: "Here we find a fair yotaka ('night-hawk', e.i. streetwalker) accommodating a lusty client in a lumberyard by the bank of the Sumida River".
 №9: '... a slightly plump harlot of the lower class receives a night visit from her lover, whose naked form she tries to cover with a cloak."
№9: '... a slightly plump harlot of the lower class receives a night visit from her lover, whose naked form she tries to cover with a cloak."
 №10: "...likely maidservant and lackey - are depicted in bath-room, their passions are all too obviously fired by steaming water."
№10: "...likely maidservant and lackey - are depicted in bath-room, their passions are all too obviously fired by steaming water."
 №11: "...this scene of courtesan and secret lover ranks high not only in Eiri's œuvre but also in the annals of the ukiyo-e genre itself. Both design and colouring are impeccable and, for this period, there is nothing even in the work of great Utamaro that really surpasses it." Again, a doubtful statement, however, this is Utamaro's design for the reader to judge:
№11: "...this scene of courtesan and secret lover ranks high not only in Eiri's œuvre but also in the annals of the ukiyo-e genre itself. Both design and colouring are impeccable and, for this period, there is nothing even in the work of great Utamaro that really surpasses it." Again, a doubtful statement, however, this is Utamaro's design for the reader to judge:
 The last design in my album is this:
The last design in my album is this:
 #13: In most reference books it goes under number 13, and we will assign this number to the sheet. "The final scene of the album features naked participants, probably samurai man and wife. The print is rather subdued in tone and colour, if not in the degree of the passion displayed..."
An additional sheet, acquired separately from a reputable dealer in New York, is usually listed as №12:
#13: In most reference books it goes under number 13, and we will assign this number to the sheet. "The final scene of the album features naked participants, probably samurai man and wife. The print is rather subdued in tone and colour, if not in the degree of the passion displayed..."
An additional sheet, acquired separately from a reputable dealer in New York, is usually listed as №12:
 №12: "One might think that Eiri has reached his peak with the preceding plate 11 - and indeed he has, in both esthetic and erotic terms. But the album is not yet finished, and the next scene lends a needed variety to the series, a slightly comic tableau featuring a middle-aged lackey attempting to forcibly seduce a servant girl of the same domicile". Utamaro's design, that inspired Eiri is here:
№12: "One might think that Eiri has reached his peak with the preceding plate 11 - and indeed he has, in both esthetic and erotic terms. But the album is not yet finished, and the next scene lends a needed variety to the series, a slightly comic tableau featuring a middle-aged lackey attempting to forcibly seduce a servant girl of the same domicile". Utamaro's design, that inspired Eiri is here:
 All descriptions are taken from Richard Lane's article at The Complete Ukiyo-e Shunga №9 Eiri, 1996. He concluded: "...Eiri's erotic series represents a major contribution to shunga art towards the close of ukiyo-e "Golden Age". In part inspired by Utamaro's classic album, this series withal constitutes a unified and original achievement, providing a cumulative effect of gracefully elegant yet glowing eroticism, which remains in the mind's eye long after the pictures themselves are far away."
I only would like to mention here that in several reference sources this album goes under name of Eisho; unfortunately, this mistake is reproduced at www.ukiyo-e.org, which miraculously shows exactly my print, but under the wrong name of the artist. The same mistake can be found at Shunga. The art of love in Japan. Tom and Mary Anne Evans. Paddington Press Ltd., 1975. ISBN 0-8467-0066-2; plates 6.74-6.77: Chōkyōsai Eishō, c. 1800. Even the British Museum edition of 2010 gives the same erroneous attribution: Chōkyōsai Eishō (1793-1801); they provide the following translation of title: "Clean Draft of a Letter" [see: Shunga. Erotic art in Japan. Rosina Buckland. The British Museum Press, 2010; pp. 110-112]. To the honour of the British Museum, I must admit that they have corrected themselves in Shunga. Sex and pleasure in Japanese art. Edited by Timothy Clark, et al. Hotei Publishing, 2013. Now, they say Chōkyōsai Eiri (worked c. 1790s-1801); they also provide a new title: "Neat Version of the Love Letter, or Pure Drawings of Female Beauty". I have already mentioned Richard Lane's version of title: "Love-letters, Love Consummated", and Chris Uhlenbeck's "Models of calligraphy". In poorly designed and printed Shunga. Erotic figures in Japanese art. Presented by Gabriele Mandel. Translated by Alison L'Eplattenier. Crescent Books, New York, 1983, the artist is named Shokyosai Eisho (beginning of the 19th century); title provided: "Models of Calligraphy". Correct attribution to Chōkyōsai Eiri also can be found at Poem of the pillow and other stories by Utamaro, Hokusai, Kuniyoshi and other artists of the floating world. Gian Carlo Calza in collaboration with Stefania Piotti. Phaidon Press, 2010; though the title is translated as "Clean Copy of Female Beauty".
All descriptions are taken from Richard Lane's article at The Complete Ukiyo-e Shunga №9 Eiri, 1996. He concluded: "...Eiri's erotic series represents a major contribution to shunga art towards the close of ukiyo-e "Golden Age". In part inspired by Utamaro's classic album, this series withal constitutes a unified and original achievement, providing a cumulative effect of gracefully elegant yet glowing eroticism, which remains in the mind's eye long after the pictures themselves are far away."
I only would like to mention here that in several reference sources this album goes under name of Eisho; unfortunately, this mistake is reproduced at www.ukiyo-e.org, which miraculously shows exactly my print, but under the wrong name of the artist. The same mistake can be found at Shunga. The art of love in Japan. Tom and Mary Anne Evans. Paddington Press Ltd., 1975. ISBN 0-8467-0066-2; plates 6.74-6.77: Chōkyōsai Eishō, c. 1800. Even the British Museum edition of 2010 gives the same erroneous attribution: Chōkyōsai Eishō (1793-1801); they provide the following translation of title: "Clean Draft of a Letter" [see: Shunga. Erotic art in Japan. Rosina Buckland. The British Museum Press, 2010; pp. 110-112]. To the honour of the British Museum, I must admit that they have corrected themselves in Shunga. Sex and pleasure in Japanese art. Edited by Timothy Clark, et al. Hotei Publishing, 2013. Now, they say Chōkyōsai Eiri (worked c. 1790s-1801); they also provide a new title: "Neat Version of the Love Letter, or Pure Drawings of Female Beauty". I have already mentioned Richard Lane's version of title: "Love-letters, Love Consummated", and Chris Uhlenbeck's "Models of calligraphy". In poorly designed and printed Shunga. Erotic figures in Japanese art. Presented by Gabriele Mandel. Translated by Alison L'Eplattenier. Crescent Books, New York, 1983, the artist is named Shokyosai Eisho (beginning of the 19th century); title provided: "Models of Calligraphy". Correct attribution to Chōkyōsai Eiri also can be found at Poem of the pillow and other stories by Utamaro, Hokusai, Kuniyoshi and other artists of the floating world. Gian Carlo Calza in collaboration with Stefania Piotti. Phaidon Press, 2010; though the title is translated as "Clean Copy of Female Beauty".
-
 This print was sold to me with the following description: "Ikkansai EISHO (Fl. early 19th c.). A portrait of the wrestler Kuroyanagi Matsujiro, ring name Kumagatake Inosuke. Eisho was a pupil of Eishi. Published c. 1820s by Uoya Eikichi. Signed Shunsai Eisho ga." As a result of our joint effort with my beloved sister, we have so far found the following: The artis is mentioned in The Hotei Encyclopedia of Japanese Woodblock Prints, 2005, Vol 2; p. 438 under the name of Harukawa Eichō. From this source we learned that the artist was active from about 1818 till 1844, and was a print designer in Kyoto. He was a student first of Harukawa Goshichi and later studied in Edo (Tokyo) with Keisai Eisen, when he assumed the art name 'Eichō'. Other names: Shunsai. The Japanese web page dedicated to Harukawa Eichō provides more details: The artist lived from the 4th year of Tenmei ( 1784 ) to the first year of Kaei ( 1848 ). He was a student of Harukawa Goshichi, Kikukawa Eizan as well as of Keisai Eisen. His popular name was Kamenosuke. He was from Kyoto. He took "gagō" (artistic names) of Eishō when he was a student of Harukawa Goshichi; later, when he became a student of Kikukawa Eizan and Keisai Eisen he took the name of Kikukawa Eichō. The artist was mostly known for his bijinga (beautiful women) prints as well as kanazōshi illustrations. Nothing is said anywhere about his sumo prints, though the reference to another Kyushu sumo wrestler portrait has been found. The sumo wrestler Kuroyanagi Matsujiro is also a somewhat obscure figure: information about his life and career is quite inconsistent. It may so happened that two different persons were combined together. Wikipedia page about Aoi Aso Jinja, a Shinto shrine in Hitoyoshi in Kumamoto prefecture, tells us the following:This information has some inconsistencies already. If our hero was born in 1807 and promoted to ōzeki at the age of 32, it should have been the year 1839, not 1847. I found Kumagatake Isuke at "Sumo Reference" website:
This print was sold to me with the following description: "Ikkansai EISHO (Fl. early 19th c.). A portrait of the wrestler Kuroyanagi Matsujiro, ring name Kumagatake Inosuke. Eisho was a pupil of Eishi. Published c. 1820s by Uoya Eikichi. Signed Shunsai Eisho ga." As a result of our joint effort with my beloved sister, we have so far found the following: The artis is mentioned in The Hotei Encyclopedia of Japanese Woodblock Prints, 2005, Vol 2; p. 438 under the name of Harukawa Eichō. From this source we learned that the artist was active from about 1818 till 1844, and was a print designer in Kyoto. He was a student first of Harukawa Goshichi and later studied in Edo (Tokyo) with Keisai Eisen, when he assumed the art name 'Eichō'. Other names: Shunsai. The Japanese web page dedicated to Harukawa Eichō provides more details: The artist lived from the 4th year of Tenmei ( 1784 ) to the first year of Kaei ( 1848 ). He was a student of Harukawa Goshichi, Kikukawa Eizan as well as of Keisai Eisen. His popular name was Kamenosuke. He was from Kyoto. He took "gagō" (artistic names) of Eishō when he was a student of Harukawa Goshichi; later, when he became a student of Kikukawa Eizan and Keisai Eisen he took the name of Kikukawa Eichō. The artist was mostly known for his bijinga (beautiful women) prints as well as kanazōshi illustrations. Nothing is said anywhere about his sumo prints, though the reference to another Kyushu sumo wrestler portrait has been found. The sumo wrestler Kuroyanagi Matsujiro is also a somewhat obscure figure: information about his life and career is quite inconsistent. It may so happened that two different persons were combined together. Wikipedia page about Aoi Aso Jinja, a Shinto shrine in Hitoyoshi in Kumamoto prefecture, tells us the following:This information has some inconsistencies already. If our hero was born in 1807 and promoted to ōzeki at the age of 32, it should have been the year 1839, not 1847. I found Kumagatake Isuke at "Sumo Reference" website:Kuroki Matsujiro (黒木松次郎) was born in the village of Itsuki in Kuma district, Kumamoto prefecture, island of Kyushu in Bunka era, 4th year (1807). Since from his childhood he was blessed by great physique and tough strength. He had affection for sumo. At the age of 18 he became a sumo student of Kumamoto Shimakawa Ikuhei and took the name of Toyama Hidekichi (遠山日出吉). At the age of 23 (1830), he entered sumo stables in Kyoto, mastered the art of taming of young horses, and his talents improved. At the age of 31 he went to Edo, and became a disciple of the ōzeki Oitekaze Kitaro of Hirado domain in Hizen province, also from Kyushu island. After that, he changed his name and became Kuroyanagi Matsujiro (黒柳松次郎 – as on the print). In 1847 (Bunka era, 4th year) he distinguished himself by advancing to the first grade, and at the age of 32 he was promoted to ozeki level, becoming sekitori. After changing his name to Kuma-ga-take Inosuke (熊ヶ嶽猪之介 / くまがたけいのすけ) he displayed further efforts, and became one of the strongmen that fermented sumo wrestling in Edo. In 1853 (Kaei era, 6th year) he retired and returned to his village, becoming an employee as a strongman of Sagara domain (相良藩), and worked hard as instructor of the sumo training hall to train successors until 1855 (Ansei era, 2nd year) when he passed away at the age of 48. Even today Kuma-ga-take's home exists in Itsukimura (his native village). Also, on those grounds a descendant of Kuma-ga-take runs minshuku (guest house) that bears the name of "The Kuroki Pension (lodging) ", and tourists come to visit from various parts of Japan. In 2015, tenth month, within the borders of Aoi Aso Shrine there was built a gravestone publicly honoring Kuma-ga-take Inosuke, sumo wrestler from Edo / of Edo period.
The real name is the same, the ring name Kuroyanagi Matsujiro is the same, however, the date of birth here is 1815. He fought from 1836 till 1853 - which is quite similar to "At the age of 31 he went to Edo, and became a disciple of the ōzeki Oitekaze Kitaro". Though, in 1836 he might be 29 years old. His bouts are listed from spring 1841 to spring 1848 under the name of Kuroyanagi and from winter 1848 till spring 1853 he listed under the name of Kumagatake Isuke [Inosuke].Highest Rank Maegashira 4 Real Name Kuroki Birth Date 1815 Shusshin Kumamoto-ken, Kuma-gun Death Date March 6, 1855 (40 years) Heya Oitekaze Shikona Kuroyanagi Matsujiro - Kumagatake Isuke Hatsu Dohyo 1836.02 (Sandanme) Intai 1853.02 On another important sumo history website, I found that Kuroyanagi first appeared at ring in the spring of 1823 (he might have been 16 years old then, which does not seem right). Then, in the winter tournament of 1848 Kuroyanagi took the name Kumagatake. At the spring tournament of 1853 Kumagatake (Kuroyanagi) retired. This is quite consistent so far.
Then, I found Oitekaze Kitaro, allegedly the teacher of Kuroyanagi.
Everything look good with an exception of ring names (shikona): Kuroyanagi Matsujiro (1823-1828) - Kuroyanagi Sumiemon (1829-30) - Oitekaze Kitaro (1831-1839). May it be that Sato Matsutaro fought under the name of Kuroyanagi Matsujiro until Kuroki Matsujiro took this name from his master? I don't have another explanation of the enigma. What we know is that we have a portrait of a sumo wrestler called Kuroyanagi Matsujiro from Kyushu, but we don't know whether this was the one from Kumamoto (Kumagatake Inosuke, 1807/1815-1855) or the other from Kanagawa (Oitekaze Kitaro, 1799-1865). Subsequently, we may declare that the artist is Shunsai Eishō, a.k.a.Harukawa Eichō from Eishi school (The Hotei Encyclodepdia, p. 524), we can date the print from 1818 to 1844, and only tell that the wrestler is Kuroyanagi Matsujiro from Kyushu (either Kumagatake Inosuke or Oitekaze Kitaro). The publisher of the print is Moriya Jihei (Marks №353, p. 243-5). That's it.Highest Rank Ozeki Real Name SATO Matsujiro (Matsutaro#) Birth Date 1799 Shusshin Kanagawa-ken, Tsukui-gun Death Date May 4, 1865 (66 years) Heya Oitekaze Shikona Kuroyanagi Matsujiro - Kuroyanagi Sumiemon - Oitekaze Kitaro Hatsu Dohyo 1817.10 (Jonokuchi) Intai 1839.03 -
 Ippitsusai Bunchō [一筆斎文調] (Japanese, 1725 – 1794). Size: Vertical Hosoban. As the Library of Congress put it: "Print shows the actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II, full-length portrait, facing left, standing on the snow-covered veranda". Actor: Ichikawa Monnosuke II [市川門之助] (Japanese, 1743/56 – 1794); other names: Ichikawa Benzō I, Takinaka Hidematsu II, Takinaka Tsuruzō. According to Heroes of the Kabuki Stage [LIB-1197.2016] Ichikawa Monnosuke II was active from 11/1770 to 10/1794. Play: Chūshingura [忠臣蔵] (The Treasury of Loyal Retainers), played at Nakamuraza in the 4the month of Meiwa 8 (1771). The actor played in a variety of roles and performances and was the subject of multiple woodblock prints by many famous ukiyo-e artists, including Bunchō, Katukawa Shunkō, Katukawa Shunshō, Katsukawa Shun'ei, Tōshūsai Sharaku, and many others. Ref: Vever (1976), vol. 1, № 242, p. 227.
Ippitsusai Bunchō [一筆斎文調] (Japanese, 1725 – 1794). Size: Vertical Hosoban. As the Library of Congress put it: "Print shows the actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II, full-length portrait, facing left, standing on the snow-covered veranda". Actor: Ichikawa Monnosuke II [市川門之助] (Japanese, 1743/56 – 1794); other names: Ichikawa Benzō I, Takinaka Hidematsu II, Takinaka Tsuruzō. According to Heroes of the Kabuki Stage [LIB-1197.2016] Ichikawa Monnosuke II was active from 11/1770 to 10/1794. Play: Chūshingura [忠臣蔵] (The Treasury of Loyal Retainers), played at Nakamuraza in the 4the month of Meiwa 8 (1771). The actor played in a variety of roles and performances and was the subject of multiple woodblock prints by many famous ukiyo-e artists, including Bunchō, Katukawa Shunkō, Katukawa Shunshō, Katsukawa Shun'ei, Tōshūsai Sharaku, and many others. Ref: Vever (1976), vol. 1, № 242, p. 227.
Katsukawa Shun'ei. The Actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II in an Aragoto Role. LACME.

Actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II as Date no Yosaku Artist Tôshûsai Sharaku (Japanese, active 1794–1795), Publisher Tsutaya Jûzaburô (Kôshodô) (Japanese) 1794 (Kansei 6), 5th month. MFA.

Ippitsusai Bunchô. Actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II as Tsunewakamaru. Play: Iro Moyô Aoyagi Soga Theater: Nakamura. MFA.
-
 Ippitsusai Bunchō (一筆斎文調); lived 1725-1794; flourished 1755–1790. Size: Chuban; 26 x 20 cm The design presents a young woman reading a scroll while arranging her hear, and a young man with a rowing rod watching over her shoulder; the pair is standing on a giant shrimp that ferries them over a stream. The third passenger is a literate octopus, who's is attentively exploring the text of a scroll. This allusion comes to mind promptly: “Bodhidharma crossing the Yangzi River on a reed” (Royō Daruma).
Ippitsusai Bunchō (一筆斎文調); lived 1725-1794; flourished 1755–1790. Size: Chuban; 26 x 20 cm The design presents a young woman reading a scroll while arranging her hear, and a young man with a rowing rod watching over her shoulder; the pair is standing on a giant shrimp that ferries them over a stream. The third passenger is a literate octopus, who's is attentively exploring the text of a scroll. This allusion comes to mind promptly: “Bodhidharma crossing the Yangzi River on a reed” (Royō Daruma). Image from Asian Art Museum in San Francisco:
Image from Asian Art Museum in San Francisco:
Masanobu’s mitate wittily evokes an episode known as “Bodhidharma crossing the Yangzi River on a reed” (Royō Daruma). According to legend, the river crossing occurred en route to the Shaolin monastery, where Bodhidharma sat facing a wall for nine years without speaking. While serious interpretations abound in Chinese and Japanese paintings, popular prints of the Edo period often playfully substituted a beautiful woman for the monk. This parodic version was reportedly invented in response to a courtesan’s comment that she was more enlightened than Bodhidharma because she had spent ten years sitting, on display in a brothel.
An interesting article about this particular design is published at UKIYO-E.ORG BLOG. Though, the design is erroneously attributed to Harunobu. We see that Bunchō was quite fascinated by the idea of crossing a water obstacle with the help of an unsuitable means of transportation:
Female Daruma Riding a Mushroom. MFA # 21.4758.
-
 Evening Snow on Mount Hira (Hira no bosetsu), from the series Eight Views of Ōmi in Modern Guise (Ryaku Ōmi hakkei, (略近江八景). About 1773–75 (An'ei 2–4). Artist: Isoda Koryūsai (Japanese, 1735–1790) CATALOGUE RAISONNÉ: Hockley 2003, p. 202, #F-21-1 DIMENSIONS: Vertical chûban; 26 x 19.3 cm (10 1/4 x 7 5/8 in.)Signed: Koryû ga [湖竜画]
Evening Snow on Mount Hira (Hira no bosetsu), from the series Eight Views of Ōmi in Modern Guise (Ryaku Ōmi hakkei, (略近江八景). About 1773–75 (An'ei 2–4). Artist: Isoda Koryūsai (Japanese, 1735–1790) CATALOGUE RAISONNÉ: Hockley 2003, p. 202, #F-21-1 DIMENSIONS: Vertical chûban; 26 x 19.3 cm (10 1/4 x 7 5/8 in.)Signed: Koryû ga [湖竜画] -
 Isoda Koryūsai (礒田 湖龍斎, 1735–1790), flourished: 1769 to 1790. The print lacks signature (signature erased).
Isoda Koryūsai (礒田 湖龍斎, 1735–1790), flourished: 1769 to 1790. The print lacks signature (signature erased).Attributed definitely to Koryūsai: Jacob Pins, #491 [p.202] - Saigyo Hoshi admiring Mount Fuji. Signature erased but convincingly attributed to Koryusai. Tikotin Museum, Haifa. Catalogue raisonné: Allen Hockley: A3-J-5 (p. 261).
Saigyō Hōshi (西行 法師, 1118 – March 23, 1190) was a famous Japanese poet of the late Heian and early Kamakura period. -
 An unsigned print, presumably by Katsukawa Shunshō that presumably depicts a kabuki actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II. I was not able to find any reference of the image. Size: Hosoban. According to The actor's image. Print makers of the Katsukawa School. Timothy T. Clark and Osamu Ueda with Donald Jenkins. Naomi Noble Richard, editor The Art Institute of Chicago in association with Princeton University Press, 1994, Ichikawa Monnosuke II was born in 1743, in Ōji Takinogawa, Edo. He died on October 19, 1974. His specialities were young male roles (wakashu) and male leads (tachi yaku). He was considered to be one of the four best young actors of his day.
An unsigned print, presumably by Katsukawa Shunshō that presumably depicts a kabuki actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II. I was not able to find any reference of the image. Size: Hosoban. According to The actor's image. Print makers of the Katsukawa School. Timothy T. Clark and Osamu Ueda with Donald Jenkins. Naomi Noble Richard, editor The Art Institute of Chicago in association with Princeton University Press, 1994, Ichikawa Monnosuke II was born in 1743, in Ōji Takinogawa, Edo. He died on October 19, 1974. His specialities were young male roles (wakashu) and male leads (tachi yaku). He was considered to be one of the four best young actors of his day. -
 Katsukawa Shun'ei. Signed: Shun'ei ga (春英画). Vertical Ōban. No reference whatsoever. Unidentified play, actors, roles, year, theatre. SOLD
Katsukawa Shun'ei. Signed: Shun'ei ga (春英画). Vertical Ōban. No reference whatsoever. Unidentified play, actors, roles, year, theatre. SOLD -
 Print by Katsukawa Shun'ei that presumably depicts a kabuki actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II. I was not able to find any reference of the image. Size: Hosoban. SOLD
Print by Katsukawa Shun'ei that presumably depicts a kabuki actor Ichikawa Monnosuke II. I was not able to find any reference of the image. Size: Hosoban. SOLD -
 Katsukawa Shun'ei (勝川 春英; 1762 – 1819).TITLE: Sawamura Sôjûrô III as Kakogawa Honzô.SERIES: Kanadehon Chūshingura (Kana practice book: Treasury of the loyal retainers").DATE: 1795Signed: Shun'ei ga (春英画). Publisher: Iwatoya Kisaburō, Marks 173/p.169. Vertical Ōban: 14.75 x 9.625 inchOn 4th lunar month of 1795 Sôjûrô plays the roles of En'ya Hangan and Kakogawa Honzô in the drama "Kanadehon Chûshingura" at Miyakoza theater in Edo.
Katsukawa Shun'ei (勝川 春英; 1762 – 1819).TITLE: Sawamura Sôjûrô III as Kakogawa Honzô.SERIES: Kanadehon Chūshingura (Kana practice book: Treasury of the loyal retainers").DATE: 1795Signed: Shun'ei ga (春英画). Publisher: Iwatoya Kisaburō, Marks 173/p.169. Vertical Ōban: 14.75 x 9.625 inchOn 4th lunar month of 1795 Sôjûrô plays the roles of En'ya Hangan and Kakogawa Honzô in the drama "Kanadehon Chûshingura" at Miyakoza theater in Edo. -
 Katsukawa Shun'ei. The Sumo Bout between Yotsuguruma (right) and Yamaoroshi (left). Date: 1800 or 1805/06. Similar sheet can be found at Edo Tokyo Museum. Size: Vertical Ōban. Sumo wrestler Yotsuguruma Daihachi (1772 - 1809) first appeared in the records of national tournaments in winter of 1794. Then he lost 3 matches and won zero. He first won in the spring tournament of 1797 in a match against maegashira (the fifth-highest rank of sumo wrestlers) named Kougamine. Yamaoroshi Gengo (born 1762) came in at the winter tournament of 1799 . He was much more successful in his career than Yotsuguruma, but he had never won a tournament. It was the time of great Raiden, who won most of them. In the spring tournament of 1800 Yotsuguruma and Yamaoroshi fought against each other for the first time. Yotsuguruma lost. The next time they met on the ring was at the winter tournament of 1805, and again in 1806. Both matches were won by Yamaoroshi. Yamaoroshi retired in 1809; Yotsuguruma died in 1809.
Katsukawa Shun'ei. The Sumo Bout between Yotsuguruma (right) and Yamaoroshi (left). Date: 1800 or 1805/06. Similar sheet can be found at Edo Tokyo Museum. Size: Vertical Ōban. Sumo wrestler Yotsuguruma Daihachi (1772 - 1809) first appeared in the records of national tournaments in winter of 1794. Then he lost 3 matches and won zero. He first won in the spring tournament of 1797 in a match against maegashira (the fifth-highest rank of sumo wrestlers) named Kougamine. Yamaoroshi Gengo (born 1762) came in at the winter tournament of 1799 . He was much more successful in his career than Yotsuguruma, but he had never won a tournament. It was the time of great Raiden, who won most of them. In the spring tournament of 1800 Yotsuguruma and Yamaoroshi fought against each other for the first time. Yotsuguruma lost. The next time they met on the ring was at the winter tournament of 1805, and again in 1806. Both matches were won by Yamaoroshi. Yamaoroshi retired in 1809; Yotsuguruma died in 1809. -
 Artist: Katsukawa Shunkō [勝川 春好] (Japanese, 1743 – 1812).
Artist: Katsukawa Shunkō [勝川 春好] (Japanese, 1743 – 1812).Actor: Matsumoto Kōshirō IV [[松本幸四郎]; other names: Omegawa Kyōjūrō, Ichikawa Komazō II, Ichikawa Somegorô I, Ichikawa Takejūrō, Segawa Kinji, Segawa Kingo] (Japanese, 1737 – 1802).
Signed: Shunkō ga. Size: Hosoban; 14 x 33 cm. SOLD -
 Ichikawa Ebizō III (Matsumoto Kōshirō II, Ichikawa Danjūrō IV, 1711-1778) probably shown as Shinozuka Gorō in the Shibaraku scene of the play Ōyoroi Ebidō Shinozuka, performed at the Nakamura Theater in the 11th month of 1772 (Meiwa 9). This was the occasion when he celebrated his name change, from Matsumoto Kōshirō II to Ichikawa Ebizō III. The lobster or giant shrimp (ebi) upon the Ichikawa family crest (three concentric squares - three measures of rice) on his garment underscores the fact of the name change (ebizō).
Ichikawa Ebizō III (Matsumoto Kōshirō II, Ichikawa Danjūrō IV, 1711-1778) probably shown as Shinozuka Gorō in the Shibaraku scene of the play Ōyoroi Ebidō Shinozuka, performed at the Nakamura Theater in the 11th month of 1772 (Meiwa 9). This was the occasion when he celebrated his name change, from Matsumoto Kōshirō II to Ichikawa Ebizō III. The lobster or giant shrimp (ebi) upon the Ichikawa family crest (three concentric squares - three measures of rice) on his garment underscores the fact of the name change (ebizō). -
 Katsukawa Shunshō ( 勝川 春章; 1726 – 19 January 1793).
Katsukawa Shunshō ( 勝川 春章; 1726 – 19 January 1793).SIZE: 12.5 x 5.75 in.
-
 Katsukawa Shunshō ( 勝川 春章; 1726 – 19 January 1793).
Katsukawa Shunshō ( 勝川 春章; 1726 – 19 January 1793).Signed: Shunchô ga (春潮画); Censor's seal: kiwame (改印:極)
Publisher: Iwatoya Kisaburō (Eirindō); c. 1760s – 1832. Marks #173/p.169.
Reference: MFA ACCESSION NUMBER 11.21263. Not in Pins.
Act VII, Gion Ichiriki no ba ("The Ichiriki Teahouse at Gion") This act gives a taste of the bustling atmosphere of the Gion pleasure quarter in Kyoto. Yuranosuke is feigning a life of debauchery at the same teahouse to which Okaru has been indentured. Kudayū, the father of Sadakurō, arrives. He is now working for Moronō and his purpose is to discover whether Yuranosuke still plans revenge or not. He tests Yuranosuke's resolve by offering him food on the anniversary of their lord's death when he should be fasting. Yuranosuke is forced to accept. Yuranosuke's sword – the revered symbol of a samurai – is also found to be covered in rust. It would appear that Yuranosuke has no thoughts of revenge. But still unsure, Kudayū hides under the veranda. Now believing himself alone, Yuranosuke begins to read a secret letter scroll about preparations for the vendetta. On a higher balcony Okaru comes out to cool herself in the evening breeze and, noticing Yuranosuke close by, she also reads the letter reflected in her mirror. As Yuranosuke unrolls the scroll, Kudayū, too, examines the end which trails below the veranda. Suddenly, one of Okaru's hairpins drops to the floor and a shocked Yuranosuke quickly rolls up the scroll. Finding the end of the letter torn off, he realises that yet another person knows his secret and he must silence them both. Feigning merriment, he calls Okaru to come down and offers to buy out her contract. He goes off supposedly to fix the deal. Then Okaru's brother Heiemon enters and, hearing what has just happened, realises that Yuranosuke actually intends to keep her quiet by killing her. He persuades Okaru to let him kill her instead so as to save their honour and she agrees. Overhearing everything, Yuranosuke is now convinced of the pair's loyalty and stops them. He gives Okaru a sword and, guiding her hand, thrusts it through the floorboards to kill Kudayū. The main actor has to convey a wide variety of emotions between a fallen, drunkard rōnin and someone who in reality is quite different since he is only faking his weakness. This is called hara-gei or "belly acting", which means he has to perform from within to change characters. It is technically difficult to perform and takes a long time to learn, but once mastered the audience takes up on the actor's emotion. Emotions are also expressed through the colours of the costumes, a key element in kabuki. Gaudy and strong colours can convey foolish or joyful emotions, whereas severe or muted colours convey seriousness and focus. -
 Katsukawa Shunshō ( 勝川 春章; 1726 – 19 January 1793).
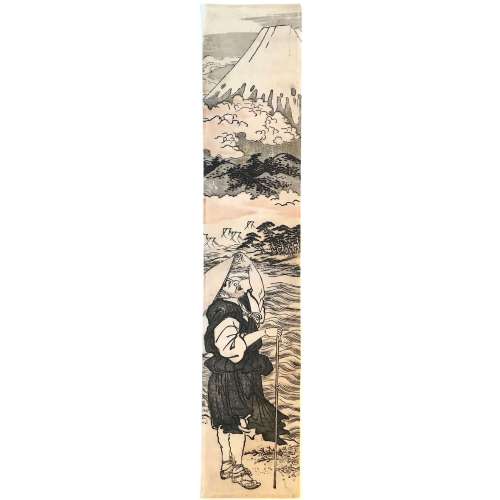
Katsukawa Shunshō ( 勝川 春章; 1726 – 19 January 1793).Signed: Katsukawa Shunshô ga (勝川春章画).
The size is somewhat larger than the standard pillar print (hashira-e): 16.3 x 67.7 cm.
No references found so far.
-
 The Seven Gods of Good Luck in the Takarabune (ship of fortune) with a crane (the phoenix) above them.
The Seven Gods of Good Luck in the Takarabune (ship of fortune) with a crane (the phoenix) above them.Attributed to Katsukawa Shunshō, fl. 1726–92. Publisher: Uemura from Shiba (Edo). Marks "Publishers": U361|25-300: Uemura han (1793-1813). Marks "Artists, publishers...": Emiya Kichiemon (1688-1835). Artist signature absent. Looks very much like Pins #565 [p.223], but NOT the same. This exact design has not been found anywhere.



